Showing 1571 items
matching prior street
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph, Ballarat Teachers' College Class Photo, 1951-1952, 1951
Copy of the 1951 Ballarat Teachers' College Class photo. MOst students wear the blue Ballarat Teachers' College blazer. The photograph is taken in the grounds of the Dana Street Primary School, where the Teachers' College was located.frank nolan, ballarat teachers' college, dana street primary school, keith pyers, a. williams, p. quinlan, m. constable, a. dunn, r. watson, g. prior, . spinks, p. readman, b. voight, k. coles, max martin, l/ mcarthur, j. o'connor, l. whelehan, d. mayne, r. colbourne, b. pohlner, p. nolan, alan sonsee, mavis canty, tom turner, edward doney, howard pattendon, j. walters -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMagazine, J.A. Hoskin & Son, Ballarat Teachers' College Magazine "Extra Muros', 1951
Blue soft covered magazine of 28 pages. Includes a drawing of the bluestone building at Dana Street Primary School by J. DawsonFront Cover "Frank Nolan"frank nolan, ballarat teachers' college, dana street primary school, keith pyers, a. williams, p. quinlan, m. constable, a. dunn, r. watson, g. prior, p. readman, b. voight, k. coles, max martin, j. o'connor, l. whelehan, d. mayne, r. colbourne, b. pohlner, p. nolan, alan sonsee, mavis canty, tom turner, edward doney, howard pattendon, j. walters, ros menadue, j.m. hill, g.a. jenkins, j. dudley, r.r. reed, a.o. puls, m.g. crooke, j. dawson, j. klein, t.w.h. turner, monica miller, betty walpole, patricia smith, grampians, student representative council, f. holcombe, s. rowe, m. crooke, c. sheehy, m. robinson, p. smith, crooke, dana street state school -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionAdministrative record - Ledger, General Ledger Transfer No.2, 1914-1947
Donated by abattoir staff during cleanup prior to demolition in 1996. Company at that time owned by Australian Meat Holdings.borthwicks, thomas borthwick and sons, abattoir, portland, accounts -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Early Shipping: Ocean / Railway Pier, n.d
Port of Portland Authority ArchivesBack: Lighter used for transporting cargo. Prior to construction of the Deep Water Pier' in pencil, Also stamp 'A.G. Baker Box 21 Portland 3305port of portland archives -
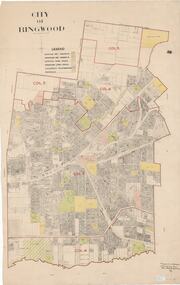 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyMap, City of Ringwood - Rateable Properties Layout - c.1966. Overlay showing Reserves, Open Space, Playgrounds, and Schools
A0-size (approx) map of named streets, lot-numbered properties and locality features within City of Ringwood boundary. Colour-coded legend identifying Existing Rec Reserves, Proposed Rec Reserves, Existing Open Space, Children's Playgrounds, and Schools.Scale: 8 chains to 1 inch. Map picked up in Engineer's office at old town hall prior to demolition 1971. -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Manufactured Glass, baby feeding bottle, c1950
A baby bottle is a bottle with a rubber or latex teat attached so that baby can drink directly from it by sucking on the teat. It is typically used by infants and young children ,when a mother does not breastfeed, to feed infant formula, expressed breast milk or paediatric electrolyte solution. Australian Glass Manufacturers produced glass bottles for pharmacy, brewery, dairy and domestic use 1913 – 1970 . Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co Pty Ltd Registered in Victoria in 1903 amalgamated with the Waterloo Glass Bottle Works Ltd in 1915 to form Australian Glass Manufacturers Company, Limited. .Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Spotswood 1872- 1970 comprising a complex of buildings constructed between 1880 and 1940, (at Booker Street, Douglas Parade, 2-38 Hudson Road, Raleigh Street and Simcock Avenue, Spotswood ) originally made bottles for druggists Felton Grimwade before it was sold to the State Government by US multinational, OI glass manufacturers. . The Baby feeding bottle has graduated markings in 1- 6 ounces which shows that it was made prior to the introduction of Decimal Currency in Australia 14/2/1966. A clear glass feeding bottle. It is 'banana shaped' and open both ends with graduated measurements - 1-6 ouncesAGEE/ THE PERFECT FEEDING BOTTLE / OUNCES 1-6* bottles, feeding bottles, infants, breastfeeding, moorabbin, bentleigh, ormond cheltenham, glass, australian glass manufacturing company ltd, decimal currency, imperial measurements, ounces, milk, dairy, baby formulae, -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Fork, c. 1878
This fork was recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard. It is the Old English design that has been very popular since the 19th century. It has been restored to resemble its original state prior to the disaster in 1878. The for was originally plated with silver, which is when a base metal such as nickel or nickel alloy with copper and/or zinc has been plated or coated with a thin layer of silver. Wear on the metal will cause the base metals to appear through the silver plating. Some manufacturers gave a warranty that the cutlery was ‘white throughout’ but didn’t necessarily say it was solid silver. LOCH ARD 1873-1878 – The Scottish-built clipper ship Loch Ard was bound for Melbourne in 1878 with 54 people on board. The mixed cargo it carried included items for the 1880 International Exhibition in Melbourne, one of which was the now famous Majorca ware Minton ‘Peacock’ statue. The Loch Ard was wrecked on June 1st when the ship crashed into Mutton Bird Island, east of Port Campbell. The only survivors were Tom Pearce, a crew member, and Eva Carmichael, a young passenger who was rescued by Pearce. The Gibsons, owners of nearby Glenample Homestead, cared for Tom, and for Eva who stayed longer before returning to Ireland. The wreck of the Loch Ard was discovered in 1967, before the introduction of the Victorian historic shipwreck legislation. In 1969 it was decided that all recovered material should be lodged with the Receiver of Wrecks. In 1980 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum Divers received a permit to recover artefacts from the wreck to safeguard them from looters. In 1982 the site was listed as a Historic Shipwreck, and the Maritime Archaeology Unit recovered loose artefact material. The fork is recognised as being historically significant as an example of cutlery either as part of the flatware service of the ship ‘Loch Ard’ or part of the ship’s cargo, imported for use in Colonial Victoria in the 19th to early 20th century. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Fork; silver plated. The fork is the Old English design and is embossed with several marks. it has recently been restored. Shipwreck artefact from the Loch Ard. 3 letters within an oval (- - S) 4 letters within circles (E) (P) (N) (S) 1 letter within a shield appears to be a [B] flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, victoria, eva carmichael, tom pearce, cutlery, silver flatware, silver plate, antique, old english flatware pattern, eating utensil, fork, silverware, dining utensil -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Water standpipe, Langlands Bros. & Co, 1880-1893
This water standpipe is believed to be the only one of its kind in working order. It was originally located in Warrnambool, on the hillside at the corner of Mickle Crescent and Banyan Street, providing water for the Chinese Market Gardens below, on the flats. It was removed from this location on May 2nd, 1979, with the intention to relocate it at the new Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum & Village. The standpipe lay in storage for years until the Warrnambool Company, Chemblast, offered to restore it for use as a working display. The display was officially opened on March 31, 2014. The water from the adjacent lake is drawn out with a hand operated water pump, and goes up into the standpipe, where flows through the canvas hose and into the top of the Furphy Farm Water Cart. The display is a visual acknowledgement of the years served by Flagstaff Hill volunteer and Friends of Flagstaff Hill Chairperson, Bob Crossman. Warrnambool’s early settlers had no water supply prior to the mid-1850s. They relied on rain water tanks, domestic wells and springs. The town experienced a huge, destructive fire in William Bateman Jnr. & Co.’s large produce store in November 1856, which highlighted the need for both a fire brigade and a good supply of water. In 1863 a volunteer fire brigade was established. In August 1880 the town celebrated the installation of its first water standpipe on the corner of Liebig and Timor streets. The water was pumped from springs at Cannon Hill through the connected pipeline to the standpipe, then distributed to households via horse and cart. Each of the licenced cart drivers were compelled by Council regulations to keep their carts full from sunset to sunrise, ready to cart water to outbreaks of fire. They received a fee for this service. In 1893 the town installed a water supply, sourced from the Merri River, stored in a reservoir basin and tower in north Liebig Street, and distributed throughout the town in a system of pipes. By late 1939 a reticulated supply was installed, with the water piped in under the Otway Scheme. Standpipes are still used in modern times in rural and remote areas for homes, farms, stock, agriculture and firefighting. Many commercial or government owned standpipes are metered, charging a fee for the quantities of water supplied. This water standpipe was made by Langlands Foundry Co. Limited, Melbourne, which was establish in 1842. It was Melbourne’s first foundry and iron shipbuilder, and one of the largest employers in Victoria at the time. Langlands was known for its high quality workmanship and wide range of goods for mining, engineering, marine, railway and other industrial uses. The company made the first cast bell, the first lamp posts in the colony, and the boiler for the first Australian train. In the 1860s it produced cast iron pipes for the Board of Works, which laid the pipes for Melbourne’s first reticulated water supply. The firm was bought by Austral Otis Co. in 1897.This water standpipe is significant historically as it is believed to be the only one of its type in working condition. The standpipe is significant for being manufactured by early colonial firm Langlands Foundry of Melbourne, which was known for high quality, cast iron products. The firm made the boiler for the first Australian train, assembled the first Australian paddle steamer and made the first Australian cast bell and lamp posts. Langlands was one of the largest employers in Victoria at the time. The standpipe is significant historically as it represents the evolution of water supply services in Australia. Standpipe; vertical cast iron water pipe, painted crimson, fixed in position, tapering inward from the round base to the rectangular joint near the finial on top. A hexagonal pipe extends at right angles from the joint, with an outlet fitting and flow-controlling wheel on the end. A length of canvas hose hangs from the outlet fitting. Inscriptions are on one face of the joint. The standpipe was made by Langlands Foundry Company of Melbourne. Embossed “LANGLANDS FOUNDRY CO. / LIMITED / ENGINEERS / MELBOURNE”warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, flagstaff hill, standpipe, stand-pipe, water standpipe, fire standpipe, firefighting equipment, water supply equipment, chinese market gardens, banyan street, liebig street, water tower, bateman’s fire, working display, water supply, town water, rural water, reticulated water, cannon hill spring, merri river, otway water, water carters, horse and cart water supply, volunteer fire brigade, langlands foundry, early melbourne, iron works, bob crossman, late 19th century water supply -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAnimal specimen - Whale bone, Undetermined
Prior to carrying out a detailed condition report of the cetacean skeletons, it is useful to have an understanding of the materials we are likely to encounter, in terms of structure and chemistry. This entry invites you to join in learning about the composition of whale bone and oil. Whale bone (Cetacean) bone is comprised of a composite structure of both an inorganic matrix of mainly hydroxylapatite (a calcium phosphate mineral), providing strength and rigidity, as well as an organic protein ‘scaffolding’ of mainly collagen, facilitating growth and repair (O’Connor 2008, CCI 2010). Collagen is also the structural protein component in cartilage between the whale vertebrae and attached to the fins of both the Killer Whale and the Dolphin. Relative proportions in the bone composition (affecting density), are linked with the feeding habits and mechanical stresses typically endured by bones of particular whale types. A Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus Linnaeus, 1758) skeleton (toothed) thus has a higher mineral value (~67%) than a Fin Whale (Balaenoptera physalus Linnaeus, 1758) (baleen) (~60%) (Turner Walker 2012). The internal structure of bone can be divided into compact and cancellous bone. In whales, load-bearing structures such as mandibles and upper limb bones (e.g. humerus, sternum) are largely composed of compact bone (Turner Walker 2012). This consists of lamella concentrically deposited around the longitudinal axis and is permeated by fluid carrying channels (O’Connor 2008). Cancellous (spongy) bone, with a highly porous angular network of trabeculae, is less stiff and thus found in whale ribs and vertebrae (Turner Walker 2012). Whale oil Whales not only carry a thick layer of fat (blubber) in the soft tissue of their body for heat insulation and as a food store while they are alive, but also hold large oil (lipid) reserves in their porous bones. Following maceration of the whale skeleton after death to remove the soft tissue, the bones retain a high lipid content (Higgs et. al 2010). Particularly bones with a spongy (porous) structure have a high capacity to hold oil-rich marrow. Comparative data of various whale species suggests the skull, particularly the cranium and mandible bones are particularly oil rich. Along the vertebral column, the lipid content is reduced, particularly in the thoracic vertebrae (~10-25%), yet greatly increases from the lumbar to the caudal vertebrae (~40-55%). The chest area (scapula, sternum and ribs) show a mid-range lipid content (~15-30%), with vertically orientated ribs being more heavily soaked lower down (Turner Walker 2012, Higgs et. al 2010). Whale oil is largely composed of triglycerides (molecules of fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule). In Arctic whales a higher proportion of unsaturated, versus saturated fatty acids make up the lipid. Unsaturated fatty acids (with double or triple carbon bonds causing chain kinks, preventing close packing (solidifying) of molecules), are more likely to be liquid (oil), versus solid (fat) at room temperature (Smith and March 2007). Objects Made From the Whaling Industry We all know that men set forth in sailing ships and risked their lives to harpoon whales on the open seas throughout the 1800s. And while Moby Dick and other tales have made whaling stories immortal, people today generally don't appreciate that the whalers were part of a well-organized industry. The ships that set out from ports in New England roamed as far as the Pacific in hunt of specific species of whales. Adventure may have been the draw for some whalers, but for the captains who owned whaling ships, and the investors which financed voyages, there was a considerable monetary payoff. The gigantic carcasses of whales were chopped and boiled down and turned into products such as the fine oil needed to lubricate increasing advanced machine tools. And beyond the oil derived from whales, even their bones, in an era before the invention of plastic, was used to make a wide variety of consumer goods. In short, whales were a valuable natural resource the same as wood, minerals, or petroleum we now pump from the ground. Oil From Whale’s Blubber Oil was the main product sought from whales, and it was used to lubricate machinery and to provide illumination by burning it in lamps. When a whale was killed, it was towed to the ship and its blubber, the thick insulating fat under its skin, would be peeled and cut from its carcass in a process known as “flensing.” The blubber was minced into chunks and boiled in large vats on board the whaling ship, producing oil. The oil taken from whale blubber was packaged in casks and transported back to the whaling ship’s home port (such as New Bedford, Massachusetts, the busiest American whaling port in the mid-1800s). From the ports it would be sold and transported across the country and would find its way into a huge variety of products. Whale oil, in addition to be used for lubrication and illumination, was also used to manufacture soaps, paint, and varnish. Whale oil was also utilized in some processes used to manufacture textiles and rope. Spermaceti, a Highly Regarded Oil A peculiar oil found in the head of the sperm whale, spermaceti, was highly prized. The oil was waxy, and was commonly used in making candles. In fact, candles made of spermaceti were considered the best in the world, producing a bright clear flame without an excess of smoke. Spermaceti was also used, distilled in liquid form, as an oil to fuel lamps. The main American whaling port, New Bedford, Massachusetts, was thus known as "The City That Lit the World." When John Adams was the ambassador to Great Britain before serving as president he recorded in his diary a conversation about spermaceti he had with the British Prime Minister William Pitt. Adams, keen to promote the New England whaling industry, was trying to convince the British to import spermaceti sold by American whalers, which the British could use to fuel street lamps. The British were not interested. In his diary, Adams wrote that he told Pitt, “the fat of the spermaceti whale gives the clearest and most beautiful flame of any substance that is known in nature, and we are surprised you prefer darkness, and consequent robberies, burglaries, and murders in your streets to receiving as a remittance our spermaceti oil.” Despite the failed sales pitch John Adams made in the late 1700s, the American whaling industry boomed in the early to mid-1800s. And spermaceti was a major component of that success. Spermaceti could be refined into a lubricant that was ideal for precision machinery. The machine tools that made the growth of industry possible in the United States were lubricated, and essentially made possible, by oil derived from spermaceti. Baleen, or "Whalebone" The bones and teeth of various species of whales were used in a number of products, many of them common implements in a 19th century household. Whales are said to have produced “the plastic of the 1800s.” The "bone" of the whale which was most commonly used wasn’t technically a bone, it was baleen, a hard material arrayed in large plates, like gigantic combs, in the mouths of some species of whales. The purpose of the baleen is to act as a sieve, catching tiny organisms in sea water, which the whale consumes as food. As baleen was tough yet flexible, it could be used in a number of practical applications. And it became commonly known as "whalebone." Perhaps the most common use of whalebone was in the manufacture of corsets, which fashionable ladies in the 1800s wore to compress their waistlines. One typical corset advertisement from the 1800s proudly proclaims, “Real Whalebone Only Used.” Whalebone was also used for collar stays, buggy whips, and toys. Its remarkable flexibility even caused it to be used as the springs in early typewriters. The comparison to plastic is apt. Think of common items which today might be made of plastic, and it's likely that similar items in the 1800s would have been made of whalebone. Baleen whales do not have teeth. But the teeth of other whales, such as the sperm whale, would be used as ivory in such products as chess pieces, piano keys, or the handles of walking sticks. Pieces of scrimshaw, or carved whale's teeth, would probably be the best remembered use of whale's teeth. However, the carved teeth were created to pass the time on whaling voyages and were never a mass production item. Their relative rarity, of course, is why genuine pieces of 19th century scrimshaw are considered to be valuable collectibles today. Reference: McNamara, Robert. "Objects Made From the Whaling Industry." ThoughtCo, Jul. 31, 2021, thoughtco.com/products-produced-from-whales-1774070.Whale bone was an important commodity, used in corsets, collar stays, buggy whips, and toys.Whale bone piece. Advanced stage of calcification as indicated by deep pitting. Off white to grey.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, whales, whale bone, corsets, toys, whips -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAnimal specimen - Whale bone, Undetermined
Prior to carrying out a detailed condition report of the cetacean skeletons, it is useful to have an understanding of the materials we are likely to encounter, in terms of structure and chemistry. This entry invites you to join in learning about the composition of whale bone and oil. Whale bone (Cetacean) bone is comprised of a composite structure of both an inorganic matrix of mainly hydroxylapatite (a calcium phosphate mineral), providing strength and rigidity, as well as an organic protein ‘scaffolding’ of mainly collagen, facilitating growth and repair (O’Connor 2008, CCI 2010). Collagen is also the structural protein component in cartilage between the whale vertebrae and attached to the fins of both the Killer Whale and the Dolphin. Relative proportions in the bone composition (affecting density), are linked with the feeding habits and mechanical stresses typically endured by bones of particular whale types. A Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus Linnaeus, 1758) skeleton (toothed) thus has a higher mineral value (~67%) than a Fin Whale (Balaenoptera physalus Linnaeus, 1758) (baleen) (~60%) (Turner Walker 2012). The internal structure of bone can be divided into compact and cancellous bone. In whales, load-bearing structures such as mandibles and upper limb bones (e.g. humerus, sternum) are largely composed of compact bone (Turner Walker 2012). This consists of lamella concentrically deposited around the longitudinal axis and is permeated by fluid carrying channels (O’Connor 2008). Cancellous (spongy) bone, with a highly porous angular network of trabeculae, is less stiff and thus found in whale ribs and vertebrae (Turner Walker 2012). Whale oil Whales not only carry a thick layer of fat (blubber) in the soft tissue of their body for heat insulation and as a food store while they are alive, but also hold large oil (lipid) reserves in their porous bones. Following maceration of the whale skeleton after death to remove the soft tissue, the bones retain a high lipid content (Higgs et. al 2010). Particularly bones with a spongy (porous) structure have a high capacity to hold oil-rich marrow. Comparative data of various whale species suggests the skull, particularly the cranium and mandible bones are particularly oil rich. Along the vertebral column, the lipid content is reduced, particularly in the thoracic vertebrae (~10-25%), yet greatly increases from the lumbar to the caudal vertebrae (~40-55%). The chest area (scapula, sternum and ribs) show a mid-range lipid content (~15-30%), with vertically orientated ribs being more heavily soaked lower down (Turner Walker 2012, Higgs et. al 2010). Whale oil is largely composed of triglycerides (molecules of fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule). In Arctic whales a higher proportion of unsaturated, versus saturated fatty acids make up the lipid. Unsaturated fatty acids (with double or triple carbon bonds causing chain kinks, preventing close packing (solidifying) of molecules), are more likely to be liquid (oil), versus solid (fat) at room temperature (Smith and March 2007). Objects Made From the Whaling Industry We all know that men set forth in sailing ships and risked their lives to harpoon whales on the open seas throughout the 1800s. And while Moby Dick and other tales have made whaling stories immortal, people today generally don't appreciate that the whalers were part of a well-organized industry. The ships that set out from ports in New England roamed as far as the Pacific in hunt of specific species of whales. Adventure may have been the draw for some whalers, but for the captains who owned whaling ships, and the investors which financed voyages, there was a considerable monetary payoff. The gigantic carcasses of whales were chopped and boiled down and turned into products such as the fine oil needed to lubricate increasing advanced machine tools. And beyond the oil derived from whales, even their bones, in an era before the invention of plastic, was used to make a wide variety of consumer goods. In short, whales were a valuable natural resource the same as wood, minerals, or petroleum we now pump from the ground. Oil From Whale’s Blubber Oil was the main product sought from whales, and it was used to lubricate machinery and to provide illumination by burning it in lamps. When a whale was killed, it was towed to the ship and its blubber, the thick insulating fat under its skin, would be peeled and cut from its carcass in a process known as “flensing.” The blubber was minced into chunks and boiled in large vats on board the whaling ship, producing oil. The oil taken from whale blubber was packaged in casks and transported back to the whaling ship’s home port (such as New Bedford, Massachusetts, the busiest American whaling port in the mid-1800s). From the ports it would be sold and transported across the country and would find its way into a huge variety of products. Whale oil, in addition to be used for lubrication and illumination, was also used to manufacture soaps, paint, and varnish. Whale oil was also utilized in some processes used to manufacture textiles and rope. Spermaceti, a Highly Regarded Oil A peculiar oil found in the head of the sperm whale, spermaceti, was highly prized. The oil was waxy, and was commonly used in making candles. In fact, candles made of spermaceti were considered the best in the world, producing a bright clear flame without an excess of smoke. Spermaceti was also used, distilled in liquid form, as an oil to fuel lamps. The main American whaling port, New Bedford, Massachusetts, was thus known as "The City That Lit the World." When John Adams was the ambassador to Great Britain before serving as president he recorded in his diary a conversation about spermaceti he had with the British Prime Minister William Pitt. Adams, keen to promote the New England whaling industry, was trying to convince the British to import spermaceti sold by American whalers, which the British could use to fuel street lamps. The British were not interested. In his diary, Adams wrote that he told Pitt, “the fat of the spermaceti whale gives the clearest and most beautiful flame of any substance that is known in nature, and we are surprised you prefer darkness, and consequent robberies, burglaries, and murders in your streets to receiving as a remittance our spermaceti oil.” Despite the failed sales pitch John Adams made in the late 1700s, the American whaling industry boomed in the early to mid-1800s. And spermaceti was a major component of that success. Spermaceti could be refined into a lubricant that was ideal for precision machinery. The machine tools that made the growth of industry possible in the United States were lubricated, and essentially made possible, by oil derived from spermaceti. Baleen, or "Whalebone" The bones and teeth of various species of whales were used in a number of products, many of them common implements in a 19th century household. Whales are said to have produced “the plastic of the 1800s.” The "bone" of the whale which was most commonly used wasn’t technically a bone, it was baleen, a hard material arrayed in large plates, like gigantic combs, in the mouths of some species of whales. The purpose of the baleen is to act as a sieve, catching tiny organisms in sea water, which the whale consumes as food. As baleen was tough yet flexible, it could be used in a number of practical applications. And it became commonly known as "whalebone." Perhaps the most common use of whalebone was in the manufacture of corsets, which fashionable ladies in the 1800s wore to compress their waistlines. One typical corset advertisement from the 1800s proudly proclaims, “Real Whalebone Only Used.” Whalebone was also used for collar stays, buggy whips, and toys. Its remarkable flexibility even caused it to be used as the springs in early typewriters. The comparison to plastic is apt. Think of common items which today might be made of plastic, and it's likely that similar items in the 1800s would have been made of whalebone. Baleen whales do not have teeth. But the teeth of other whales, such as the sperm whale, would be used as ivory in such products as chess pieces, piano keys, or the handles of walking sticks. Pieces of scrimshaw, or carved whale's teeth, would probably be the best remembered use of whale's teeth. However, the carved teeth were created to pass the time on whaling voyages and were never a mass production item. Their relative rarity, of course, is why genuine pieces of 19th century scrimshaw are considered to be valuable collectibles today. Reference: McNamara, Robert. "Objects Made From the Whaling Industry." ThoughtCo, Jul. 31, 2021, thoughtco.com/products-produced-from-whales-1774070.Whale bone was an important commodity, used in corsets, collar stays, buggy whips, and toys.Whale bone piece. Advanced stage of calcification as indicated by deep pitting. Off white to grey.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, whales, whale bone, corsets, toys, whips -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageArtwork, other - Diorama with seaweed specimens, Richard Foster Norton, 1860
The diorama of mounted specimens of seaweed was framed by Richard Foster Norton for Thomas Watson and is dated 1860. Watson was the Warrnambool District Surveyor at the time (1860). The inscription on the back of the frame links the artwork to the Pigeon Hill property, which was located on Allansford Road (corner of Staffords Road – north side of the Princes Highway-A1). In the 1860s, the property known as Pigeon Hill was owned by William Wall who was a publican who ran several hotels in Warrnambool and district. In 1860 Wall, was running a hotel in Wangoom, near Pigeon Hill. Further research is required to determine the exact location, but Pigeon Hill could also have been the name for that area and may have had other people living there. Thomas Watson was a member of the local horticultural society. Another possible creator of the artwork is Samuel Hannaford, a biologist with a particular interest in collecting marine flora. Hannaford left Warrnambool in 1857 and went to Geelong, so it is possible he collected the specimens had them framed in Geelong, and then arranged for their return to Watson. The other known seaweed collector was Henry Watts, who lived in Warrnambool in the mid-19th century. The seaweed collection in this box was possibly one of Watts' and could have been prepared for the Victorian Exhibition of 1861, Richard Foster Norton, also known as R.F Norton, was one of only a handful of picture framers in 1850s Melbourne. Norton was born on the 24th of July 1822 in Yelvertoft, Northamptonshire and prior to his arrival in Australia, Norton is listed in England as having the occupation of a painter. It appears that he established his business in Melbourne in 1854 or 1855. Between 1855 and 1865 he operated from 87, then 83, and later 80 Collins Street. In the Argus newspaper, Norton advertised his business as a Print seller, Carver, Gilder and Picture Frame manufacturer, supplying the growing demand for artworks and decorative furnishings in the colony during the Gold Rush. Norton also had a Geelong branch in Market Square, where this work was produced. This framed work is highly significant. Previous research has found that only six frames are in existence that can be attributed to be made Norton, dating from the late 1850’s to the mid 1860’s. Moreover, Thomas Watson the owner of the artwork, is one of the government surveyors of the region during the mid-19th century.Diorama in deep wooden frame, behind glass. Seaweed specimens have been mounted within the frame. The back of the frame has handwritten inscriptions including the framer's label (portions missing). The diorama was framed by Richard Fraser Norton. Printed label; "RICHARD FOS --- Picture Framer and -- MANUF -- CARVER, GILDER, ---- PAINTINGS CLEANED, LINED AND --- GLASSES RESILVERED, FRAMES --- Architectual Decorations created to any design in Paper Mache, Carlton Pierre, or Composition, Country Orders promptly attended to, The Order Suppl ---, BRANCH ESTABLISHMENT, MARKET SQUARE, GEELONG" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, richard foster norton, r.f norton, picture framers, melbourne, geelong, artwork and decorative furnishings, gold rush, seaweed, botanical specimens, 1860, pigeon hill, district surveyor, thomas watson, william wall, wangoom, samuel hannaford, henry watts, victorian exhibition, 1861, yelvertoft, northamptonshire, market square -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - LONG GULLY HISTORY GROUP COLLECTION:THE LONG GULLY CRICKET TEAM
Black and white photocopy of the Long Gully cricket Team. Photo by W H Robinson. The names are R Kerr (umpire), C Prior, J Pabst, J Gibson, Joe Harry, J Vinnard, R Lanyon (umpire), T Hickey, W E Sutton, C Loader, J Trewartha, Pellow, J Lindsay, J Truscott and E Magee. Written at the bottom is 1899.bendigo, history, long gully history group, the long gully history group - the long gully cricket team, w h robinson, r kerr, c prior, j pabst, j gibson, joe harry, j vinnard, r lanyon, t hickey, w e sutton, c loader, j trewartha, pellow, j lindsay, j truscott, e magee -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - H.A. & S.R. WILKINSON COLLECTION: CONDITION OF SALE
Conditions of sale of freehold land & dwelling by private contract dated 2nd April, 1930, issued by T.C. Watts 7 Son licensed Real Estate Agents between R. Fletcher and T.G. Fletcher executors of the will of R.H Fletcher deceased (sellers) and J. Prior (buyer) for land being Crown allotment 5 section 24 at Eaglehawk having frontage to Campbell Street of 85 links by a depth along Church Street of 223.5 links, land described in certificate of title volume 1541 folio 308073, together with all buildings and erection thereon. Price 415 pounds.organization, business, h.a. & s.r wilkinson real estate -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - H.A. & S.R. WILKINSON COLLECTION: CONDITION OF SALE
Conditions of sale by private contract dated 25th August, 1939 between J. Prior (seller) and H.V. Toma (buyer) for land situate corner Campbell and Church Streets, Eaglehawk, being Crown allotment 5 section 24 described in certificate of title volume 1541 folio 308073, together with 6-roomed weatherboard dwelling and all sundry. Price 225 pounds.organization, business, h.a. & s.r wilkinson real estate -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - H.A. & S.R. WILKINSON COLLECTION: CONDITION OF SALE
Conditions of sale by private contract dated 25th August, 1939 between J. Prior (seller) and H.V. Toma (buyer) for land situate corner Campbell and Church Streets, Eaglehawk, being Crown allotment 5 section 24 described in certificate of title volume 1541 folio 308073, together with 6-roomed weatherboard dwelling and all sundry. Price 225 pounds.organization, business, h.a. & s.r wilkinson real estate -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Slide - DIGGERS & MINING. THE GOLD ERA, c1850s
Diggers & mining. The gold era. Of the foreigners who arrived in Victoria during the gold rush, by far the largest group were the Chinese. There had been a few Chinese in the Port Phillip District prior to the gold rush. Markings 23 994.031 GOL:5. Used as a teaching aid.hanimounteducation, tertiary, goldfields -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - H.A. & S.R. WILKINSON COLLECTION: CONTRACT OF SALE
Conditions of sale by private contract dated 1st April, 1933 between H.M.I. Prior (seller) and A.E. Ramsay (buyer) for land situate Brown Street, Eaglehawk, being land described in certificate of registration as residence area No. 3916, together with 4-roomed weatherboard dwelling and all sundry. Price 150 pounds.organization, business, h.a. & s.r wilkinson real estate -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - JENNY FOLET COLLECTION: WATCH AND CLOCK
Bendigo Advertiser ''The way we were'' from 2000. Watch and clock: James Pickens established his business prior to 1872. In 1901 he was listed as ''watch and clock'' maker. He made and repaired English and colonial jewellery to order. The premises were on the High Street and Sailors Gully Road junction. The clip is in a folder.newspaper, bendigo advertiser, the way we were -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - JENNY FOLEY COLLECTION: AWASH
Bendigo Advertiser ''The way we were'' from 2000. Awash: the Golden Square swimming pool is swamped in this photo of the flooded Bendigo Creek about 1949. The picture was taken on Maple St. looking towards Howard's Bridge, and the diving tower and springboard at the pool can be seen in the centre foreground. The date of the photo is unknown, but is believed to have been taken prior to the floods of late 1949. The clip is in a folder.newspaper, bendigo advertiser, the way we were -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - JENNY FOLEY COLLECTION: BENDIGO ADVERTISER
Bendigo Advertiser ''The way we were'' from 2000. July 29,1962: the premises and plant of the Bendigo Advertiser were almost totally destroyed by fire. Damage to the premises, which were opened only six month prior was 250,000 pounds. One of the unfortunate losses was the newspaper's files dating back to 1853. Luckily, copies were kept in duplicate by the Bendigo City Council of the time. With the help of a number of regional print shops, the Advertiser still managed to produce a newspaper the next day. In 147 years of production The Advertiser has never missed an issue. The clip is in a folder.newspaper, bendigo advertiser, the way we were -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - THE MANHOOD OF THE MASTER
... Student Movement Press, 225 Collins Street, Melbourne. Brown,Prior... Student Movement Press, 225 Collins Street, Melbourne. Brown,Prior ...Book, The Manhood of the Master, Les Gillies Collection. A green hard covered book by Harry Emerson Fosdick,D.D.. Melbourne Student Movement Press, 225 Collins Street, Melbourne. Brown,Prior & Co. 167-171 Queen St., Melbourne. 186 pages.Harry Emerson Fosdick, D.D.religions, christian, christian religion -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - JENNY FOLEY COLLECTION: ROLL CALL
Bendigo Advertiser ''The way we were'' from 2001. Roll call: grade two pupils of Camp Hill Primary School in 1946. Back row: Austin Lamgely, Stanly Beer, Russel Brown, John Cook, Freddy Addicoat, Stewart Schodde, Geoff Whylie, Colin Parke, Russel Bradley, Lance Prior, Graham Dupuy, Don Craig, John Wilson, Chard Iverson and John Partridge. Second row: Lois Gaskell, Beverly Coombs, Lynnette Raphael, Josephine ? , Lynnette Reed, Ann Jones, Hellen Jallard, Barbara Fulton, Margaret McRorie, Maree Holt and Helen Wilson. Third row: Alma Rogers, Margaret Galbraith, Elizabeth Richards, Alma O'Brien, Pat Belchambers, Mavis Clee, ??, Beth McClure, Noeline Lapsley, ??, and Mary Baxter. Fourth row: June McGowan, Christine ? , Lorraine Dunstan, Janice Taylor, Waverly Lee, Margaret Marshall, Enid Cartright, ??, Joan Clee, Kay Lyons, Hilda Sinfield, Dorothy Kimpton and Anita Hinton. Front row: Dennis McOrmond, Ray Kingsley, Ted Barkmeyer, Jimmy Glen, Alex Sandner, Ross Anderson, Val Tippett, Kevin North, Max Kuhn, Billy (Harry) Judd, Lyle Kilby, Kevin Luzza and Bobby Watson. The clip is in a folder.newspaper, bendigo advertiser, the way we were -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - JENNY FOLEY COLLECTION: AT THE BENDIGO CLUB
Bendigo Advertiser ''The way we were'' from 2001. At the Bendigo golf club: Len Prior, John Hoken, Newton Turner, Ken Giovanetti, Ricky Wines, Ian Stanley and John Evans. The player on the extreme right is unknown. The clip is in a folder.newspaper, bendigo advertiser, the way we were -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - FOREST STREET BUILDING SITE, ARCHAEOLOGICAL STUDY 2009
Copy of three colour images of demolition of building site in Forest Street in 2009/. Images show cleared site, workmen and women on site inspecting surface area prior to archaeological study being undertaken.buildings, commercial, forest street, forest street, archaeology -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - LYDIA CHANCELLOR COLLECTION; INVITATION
... , Barkly Street, is requested prior to the 16th inst.' Macdonald..., addressed to the Town Clerk, Barkly Street, is requested prior ...A cream card invitation from 'The Mayor of Ballaarat East and Mrs. J. M. Kline requesting ' the pleasure of His Worship the Mayor of Bendigo & Mrs. Curnow Company at a Musical Evening to be held in the Alfred Hall. On Thursday, 23rd. July, 1903, at 8 o'clock, p.m. The favor of a reply, addressed to the Town Clerk, Barkly Street, is requested prior to the 16th inst.' Macdonald, Printer Ballarat.event, official, music, lydia chancellor, collection, invitation, ballarat, civic mementoes, entertainment, music -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - LYDIA CHANCELLOR COLLECTION; INVITATION TO VIEWING OF TOM ROBERT'S PAINTING OF PARLIAMENTARY OPENING
An invitation in the form of a card with black print. ' The Opening of the First Parliament of the Commonwealth.' 'By Tom Roberts. The honor of your presence is requested at the Queen's Hall, Parliament House, on Friday next (13th inst.) at Three o'clock, to view the progress of the Picture prior to its departure for London. John Rowe for Australian Art Association Pty. Ltd.' Handwritten in black ink are the words 'His Worship the Mayor of Bendigo & Lady.'event, official, painting, lydia chancellor, collection, australian art, art work, australian history, history, painting, tom roberts, politics, australian politics, australian parliament, event -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - POLICE STATION, THORPE STREET, CALIFORNIA GULLY
... Street California Gully, Bendigo, prior to demolition. Timber... Inc. History House 11 Mackenzie Street Bendigo goldfields ...colour photo : image shows former police station Thorpe Street California Gully, Bendigo, prior to demolition. Timber house, verandah surrounding, iron roof. Building is surrounded by security fencing.organisation, government, california gully police station, bendigo, sandhurst, police station, thorpe street, california gully, demolition -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - ALEC H CHISHOLM COLLECTION: BOOK ''NEW SONG IN AN OLD LAND''
Book. ALEC H CHISHOLM COLLECTION. 105 page hardcover book of Australian verse by various poets chosen by Rex Ingamells. Published in 1943 by Longmans, Green & Co. for the Jindyworobak Club. Printed by Brown, Prior, Anderson Pty Ltd, Melbourne. Catalogue sticker ''2057 ING'' on spine. Poets featured include - Mary Gilmore, Dorothea MacKellar, A. B. Paterson, Henry Lawson, Adam Lindsay Gordon.Variousbooks, collections, poetry, alec h chisholm collection, australian poets, poetry -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - NORMAN OLIVER COLLECTION: ADDRESS TO BENDIGO TEACHERS' COLLEGE 24 MAR 1965
The Norman Oliver collection. Norman Oliver was three times Mayor of Bendigo - 1950-51, 1964-65, 1970-71.Four typed pages with 'Address to Bendigo Teachers College 24 Mar 65' written in green pen across the top of the first page. In the speech Oliver mentions past principals of the College: George Mills and Len Prior (instrumental the establishment of tertiary degree institutions to the country). In black pen at the end of the typed address is written - 'Commonwealth Youth Sunday meeting next Monday at B.T.H. at 8 P.M.'bendigo, council, speech notes, norman joseph oliver , councillor norman oliver. mayor of bendigo. bendigo teachers' college. len prior. george mills -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - SIR HARRY LAWSON PREMIER AND SENATOR, 1976
Sir Harry Lawson, Premier and Senator, 93 pages in hard cover with dustcover showing photograph of Sir Harry Lawson, printed by Brown Prior Anderson Melbourne, published by Mullaya publications with black and white photographs.Robert S Lawsonperson, individual, sir harry lawson
