Showing 9073 items
matching ship's-wheel
-
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyDocument - Article, Legatee Richard Wheeler, President 1986
A cutting from from a Melbourne Legacy President's report showing a photo of Legatee Richard Norman Wheeler (President of Melbourne Legacy in 1986). It was collected to be a record of a photo of past presidents. During World War 2 Dick served as a pilot with the RAAF and the RAF in North Africa, Italy and Yugoslavia. He joined Melbourne Legacy in 1976. The newspaper cuttings of his death notice from September 1989. The article was part of an album of past presidents from 1965 to 1989. The folder included biographical details and obituaries, eulogies and death notices of prominent Legatees. The items have been catalogued separately.A record of Legatee Dick Wheeler a past president of Legacy. The information was collected to record the lives of prominent legatees in a folder.An article with a black and white photo of Legatee Richard Wheeler - President 1986 and two newspaper cuttings of his death notice.past presidents, dick wheeler -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCraft - Ship model, Golden Hind
This is a ship model of the famous galleon the "Golden Hind". About the “Golden Hind” The English galleon “Golden Hind”, a mid-16th century Elizabethan warship, was launched in 1577. It was formerly known as the “Pelican”. The Golden Hind was the flagship of Captain Sir Frances Drake, in which he became the first Englishman to circumnavigate the world 1577-1580. Tonnage 100-150 tons Displacement 300 tons [fully loaded] Speed 8-15 knots Armament 22 guns Crew 80 sailors, 10 officers Built Aldeburgh, Suffolk, then moved to Plymouth, Devon in 1576 Type of ship Galleon; multi-decked ship (5 decks), square rigged, 3 masted sailing ship Estimated size Length - 70 feet (21.3m); Breadth – 19 feet (5.8m); Depth – 9 feet (2.7m) The Pelican set sail in 1577 on an expedition sponsored partly by Queen Elizabeth and Sir Christopher Hatten (whose family crest was a golden hind). His companion ships were the Swan, Marigold, Benedict and the Elizabeth. During this voyage, in 1578, Drake renamed the Pelican as the Golden Hind in honour of is patron. Sir Francis Drake [1544 – 1596] brought the Golden Hind home from his circumnavigation of the globe with looted gold, percelain, jewels and cash worth 35,000,000 million pounds in today’s money. It was the largest treasure every captured at that date. Only two ships returned – the “Golden Hind” and the “Elizabeth”. The ship model of the Golden Hind captained by Sir Frances Drake represents the first English circumnavigation of the globe.Ship model of the16th century galleon "The Golden Hind", Sir Francis Drake’s flagship (not in a glass case.) flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, ship model, model ship, galleon golden hind 1577, galleon golden hinde 1577, galleon pelican 1577, 16th century galleon, 16th century warship, sir frances drake, captain frances drake, first englishman to circumnavigate the globe -
 Queenscliffe Maritime Museum
Queenscliffe Maritime MuseumPainting - MV Surriento, Dacre Smyth, Surriento
Like so many ships that were used during WWII, she was laid up and remained idle for several years, until finally in 1948 the US Government sold her at auction and the highly decorated USS Barnett, ex MS Santa Maria was officially purchased by the well known Italian Multi Millionaire ship owner Mr. Achille Lauro on April 13, 1948. Soon she headed for a Baltimore shipyard where she received some work to ensure that her engines that had been shut down for a considerable time, were back in full working condition. When the work had been completed she was certified for her delivery voyage to Italy! The delightful all white MS Surriento was ready to depart Genoa on her very first voyage to Australia in her brand new passenger/migrant liner role. A framed oil painting of the migrant ship MV SurrientoSurrientoms surriento, migrant ships, emmigration -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePrint - Lithograph Picture, Madagascar Indiaman, Unknown
Madagascar was a large British merchant ship built for the trade to India and China in 1837 that disappeared on a voyage from Melbourne to London in 1853. The disappearance of Madagascar was one of the great maritime mysteries of the 19th century and has probably been the subject of more speculation than any other 19th-century maritime puzzle, except for the Mary Celeste. Madagascar, the second Blackwall Frigate, was built for George and Henry Green at the Blackwall Yard, London, a shipyard that they co-owned with the Wigram family. A one-eighth share in the vessel was held throughout her 16-year career by her first master Captain William Harrison Walker Walker. Madagascar carried freight, passengers, and troops between England and India until the end of 1852. In addition to her normal crew, she also carried many boys being trained as officers for the merchant marine. Known as midshipmen from naval practice, their parents or guardians paid for their training, and they only received a nominal wage of usually a shilling a month. Due to the Victorian Gold Rush, Madagascar, under the command of Captain Fortescue William Harris, was sent to Melbourne with emigrants. She left Plymouth on 11 March 1853 and, after an uneventful passage of 87 days, reached Melbourne on 10 June. Fourteen of her 60 crew jumped ship for the diggings, and it is believed only about three replacements were signed on. She then loaded a cargo that included wool, rice, and about two tonnes of gold valued at £240,000, and took on board about 110 passengers for London. On Wednesday 10 August, just as she was preparing to sail, police went on board and arrested a bushranger John Francis, who was later found to have been one of those responsible for robbing on 20th July the Melbourne Private Escort between the McIvor goldfield at Heathcote, Victoria and Kyneton. On the following day, the police arrested two others, one on board the ship and the other as he was preparing to board. As a result of these arrests, Madagascar did not leave Melbourne until Friday 12 August 1853. After she left Port Phillip Heads Madagascar was never seen again. When the ship became overdue many theories were floated, including spontaneous combustion of the wool cargo, hitting an iceberg and, most controversially, being seized by criminal elements of the passengers and/or crew and scuttled, with the gold being stolen and the remaining passengers and crew murdered. There have been many rumors as to what happened to Madagascar over the years but what really happened is still a mystery. The lithograph was made around 1950 from an original painting of Madagascar a Vessel with a notorious past and is interesting and a significant item for the ships part in early Victorian history. The picture is it’s self not valuable or can be associated with a significant person in history. The interest lies in the events that are linked to the ship in the mid 19th century.Lithograph of the ship Madagascar, in a wooden frameThe Madagascar East Indiaman 1000 tonsflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, lithograph, the madagascar, east indiaman -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Geelong tram body being fitted with a truck or wheelset
Provides information on how a tramcar body was fitted with a wheelset or truck (Brill Radiax EB1 type). Lifted on the jacks after delivery by a horse drawn jinker from the Railway Station (See Reg Item 8321) The wheel set is being pushed under the tramcar by another tramcar. Once fitted the tramcar would have been towed back into the depot and the motors etc connected. Has the Blakiston & Co. building in the background. Yields information about how tramcar bodies were lifted outside the Geelong tram depot in Brougham St in order to be made operational. Copy photograph on black plastic type backing with black edges of a Pengelley Adelaide built tramcar body on jacks being fitted with a truck or wheel set.geelong, tramways, pengelley, tram bodies, brill radiax truck, brougham st, trams -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumFunctional object - TIME CLOCK, INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MASHINES CORP, 1924
THIS TIME CLOCK WAS USED IN THE INTERKNIT HOSIERY CO. KNITTING MILL FROM 1946 - 1977 TO RECORD EMPLOYEES TIME SHEET WHICH IS PLACED IN THE GLASS FRONTED CUPBOARD BEHIND BEHIND AND WHEEL.BROWN VARNISHED CUPBOARD WITH TIME CLOCK ON FRONT. A LEVER WITH PUNCH LIKE DEVICE TO RECORD TIME OF ARRIVAL AND DEPARTURE OF EMPLOYEES. A DOUBLE ROW OF HOLES ROUND THE EDGE OF A WHEEL NUMBERED 1 - 100, BEING EMPLOYEES NUMBERS. INTERNATIONAL TIME RECORDING CLOCK.local history, horology, chronometers, knitting mill interknit hosiery co. -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaPhotograph - Photograph, Sepia, Caretaker SS Koolonga, 1928
The ship was originally requisitioned by the RAN as a collier and supply ship. It was decommissioned from RAN service in 1915 which may have required a caretaker. This image is one of several attached to loose album pages which include some images with miscellaneous undated and handwritten inscriptions. This ship served in WW1. As an Australian ship may well have visited Melbourne and the Mission staff may have made ship visits and made this image.A sepia image of an older gentleman with moustache in a long jacket and a flat cap stands on a ship deck near a cargo hatch. An inscription / title is drawn from an album page. (see image)hmas koolonga, caretaker, ss koolonga, fan album, ships -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Deadeye, Late 19th century to 1950s
A dead eye is a part of a vessel’s rig On board sailing ships, dead eyes were used in three different areas. Traditionally dead eyes are made of wood but they have different forms according to where they were used in the vessel rigging. The most common type of dead-eye is flat, with three holes and was used to tension the shrouds, the heavy lines which steadied the masts on each side. Each shroud had a dead eye at the lower end, which corresponded to a similar dead eye attached to the side of the ship. The two were connected with a rope called a lanyard, which was used to tighten the assembly. The stays, heavy lines running forward from the masts, were also tensioned with dead eyes. These are much larger and rectangular, with four or six holes. The third type of dead-eye was a two-holed version attached to an eye at the end of the parallel, which tied a yard to the mast. The loose ends of the parallel rope passed through the dead eye and then down to the deck, making it possible to tighten or slacken the parallel from the deck so that the yard could be more easily manoeuvred. It was especially important for the mizzen yard, which had to be shifted from one side of the mast to the other when tacking the ship.An item used on sailing ships rigging this item of ships equipment and its use has been used from the beginning of the invention of sailing ships going back to ancient times. Its use on sailing vessels had not changed in design or use until they went out of fashion and steamships took their place.Circular wooden ships rigging dead eye with three holes Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, sailing vessel rigging, dead eye, sailing equipment -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Deadeye, Late 19th century to 1950s
A dead eye is a part of a vessel’s rig On board sailing ships, dead eyes were used in three different areas. Traditionally dead eyes are made of wood but they have different forms according to where they were used in the vessel rigging. The most common type of dead-eye is flat, with three holes and was used to tension the shrouds, the heavy lines which steadied the masts on each side. Each shroud had a dead eye at the lower end, which corresponded to a similar dead eye attached to the side of the ship. The two were connected with a rope called a lanyard, which was used to tighten the assembly. The stays, heavy lines running forward from the masts, were also tensioned with dead eyes. These are much larger and rectangular, with four or six holes. The third type of dead-eye was a two-holed version attached to an eye at the end of the parallel, which tied a yard to the mast. The loose ends of the parallel rope passed through the dead eye and then down to the deck, making it possible to tighten or slacken the parallel from the deck so that the yard could be more easily manoeuvred. It was especially important for the mizzen yard, which had to be shifted from one side of the mast to the other when tacking the ship.An item used on sailing ships rigging this item of ships equipment and its use has been used from the beginning of the invention of sailing ships going back to ancient times. Its use on sailing vessels had not changed in design or use until they went out of fashion and steamships took their place.Circular wooden ships rigging dead eye with three holes Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, sailing vessel rigging, dead eye, sailing equipment -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPrint - PRINT, FRAMED
White information labels - black print ink. At top - HMAS Kanimbla crest with two lions. Printing: "HMS - HMAS/KANIMBLA/ Donated by the Kanimbla Association Inc/ Painted by Bob "Bluey" Paton ex crew member/and Ship's Artist "HMAS Kanimbla"HMAS Kanimbla, original painted by Bob "Bluey" Paton, ex crew member and ship's artist. Painting: colour oil painting of a ship at sea. Foreground - sea, background - sky and clouds, ship in camouflage colours. Signed bottom right corner by artist. Two white information labels - one front, one back. Handwriting on back.Artist signature, white paint "R. "BLUEY" PATON / EX KANIMBLA" Handwritten on back in black felt HP pen 'IAN S DIXON' Two white information labels - see context.framed painting, ships, navy -
 Queenscliffe Maritime Museum
Queenscliffe Maritime MuseumPainting - MV Fairsea, Dacre Smyth, MV Fairsea, Sitmar Line
History of the post World War II Migrant Ship Fairsea. The Fairsea made several journeys to Australia under the International Refugee Organisation (IRO) from 1949 to 1951, carrying displaced persons affected by World War II. She was later chartered by the Australian Government to transport assisted immigrants from Britain and also New Zealand between 1949 and 1969.MRs B SmythA framed oil painting of the migrant ship MV FairseaFairseamv fairsea, migrant ships -
 Great Stupa of Universal Compassion
Great Stupa of Universal CompassionCeremonial object - Prayer wheel, hand-held
A prayer wheel is used in Tibetan Buddhism for personal worship. Tibetans believe that spinning the prayer wheel which as thousands or millions of mantras inside is equal to saying that many mantras, while being done in a fraction of the time. This helps accumulate merits, purify negative karma and obstacles on the path to enlightenment. This wheel has a hollow metal cylinder attached to a rod handle, made of ivory (with carved elephants), inlaid with coral and turquoise. Inside the cylinder is a tightly wound scroll printed with numerous mantras and wrapped around a spindle. The cylinder is embossed and decorated with inlaid coral and turquoise. A chain with a small weight at the end (made out of copper alloy) is affixed to the cylinder, allowing it to be spun by a slight rotation of the wrist. tibetan buddhism, holy objects, worship devices -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Rigging
The shrouds or fore-rigging are a part of the standing rigging on a sailing ship. They are used in pairs on each side of a ship to help hold the masts in place and to aid the sailors who climb the rigging. They are part of the basic framework for the sails. Larger vessels may have two or three pairs, and some ships may have upper and lower shrouds. The upper shrouds would be fixed to a protruding structure on the top of the masts so that they hung from the right angle. The ropework skills of the sailmaker would be used to create the shrouds, choosing fibres with properties suitable for the job at hand and creating the triangular shape carefully. Deadeyes and ropes were then used to attach the shrouds to the ship's structure.This shroud is an example of a part of the standing rigging of a sailing ship. Shrouds were used in pairs on larger sailing vessels to help hold the masts in place and give access to adjustable rigging such as sails.Fore Rigging or Shrouds, made from rope fibres. This shroud includes the upper and lower wooden deadeyes. They are part of a ship's rigging. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, shroud, fore-rigging, ropework, sailing ship rigging, standing rigging, natural fibres, sailmakers, handmade, deadeye, knot making -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Rigging
The shrouds or fore-rigging are a part of the standing rigging on a sailing ship. They are used in pairs on each side of a ship to help hold the masts in place and to aid the sailors who climb the rigging. They are part of the basic framework for the sails. Larger vessels may have two or three pairs, and some ships may have upper and lower shrouds. The upper shrouds would be fixed to a protruding structure on the top of the masts so that they hung from the right angle. The ropework skills of the sailmaker would be used to create the shrouds, choosing fibres with properties suitable for the job at hand and creating the triangular shape carefully. Deadeyes and ropes were then used to attach the shrouds to the ship's structure.This shroud is an example of a part of the standing rigging of a sailing ship. Shrouds were used in pairs on larger sailing vessels to help hold the masts in place and give access to adjustable rigging such as sails.Fore Rigging or Shrouds, made from rope fibres. This shroud includes the upper and lower wooden deadeyes. They are part of a ship's rigging.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, shroud, fore-rigging, ropework, knot making, sailing ship rigging, standing rigging, natural fibres, sailmakers, handmade, deadeye -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumNewspaper, Bacchus Marsh Telegraph, "Loved Tram changes diet", Sep. 1995
Newspaper clipping from "Bachchus Marsh Telegraph", 9/1995? about the relocation of ex MMTB W2 340 from the Hungry Jacks Restaurant Melton to Greendale and Mr. Robert Lilburn who attended the loading of the tram. Has a photo of Bob, holding a trolley wheel ex Geelong as well and some details of Bob as a tram enthusiast. Date: - Assumed to be 25/9 by notation on cutting and that the tram arrived in Melton in 1989 and was being moved six years later. No date on the cutting and on the rear page is an advertisement from KFC Bacchus Marsh opening in November 1995 and seeking staff.On cutting "Trolley Wheel Geelong 19", "Tram 340 25/9 Mon 9am) and "Bacchus Marsh Telegraph".geelong, tramcars, melton -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Machine - Chaff Cutter, c1890
Large caste iron wheel on which two knife cutters are fitted - hand rotated - material to be cut is fed through a canter-levered wooden box - reduction gears are used to ease the effort for the person operating it. All of this is mounted on a caste iron frame. Capable of cutting 'I/2 . 1/2 Chaff'|Similar one sold by Welch, Perrin & Co P/L in 1929 for 8 pound .The 'Bentall' Chaff Cutter moulded on the reduction gear cover. 'Bentall Improved (or Patented?) Chaff Cutter 913 Heybridge, Maldon, England' - on the body and wheel.rural industry, livestock -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageRail
Part of rail of LeyLands Ship "Speke "ashore in Westernport 1906Rail wooden polished which is part of a ship's rail from vessel "Speke" on front of the object a photograph of some remains of the vessel.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, rail, speke -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHub Nut
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oat with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned.32 In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery.33 Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck. The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Wagon wheel Hub Nut with "S" hook in concretion. Artefact Reg No S/43. Recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, wagon wheel hub nut, hub nut, schomberg -
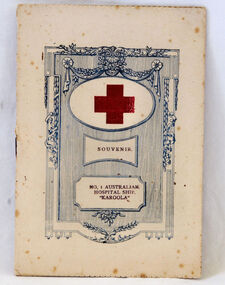 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societysouvenir card, 1916
His Majesty's Australian Hospital ship Karoola was converted in England to a fully equipped Hospital ship with beds for 463 patients. It spent 3 years transporting the sick and wounded between England and Australia.White card with blue decoration and red cross on front. A souvenir booklet for soldiers who returned home on the No.1 Australian Hospital Ship "Karoola".Inside cover -"Trooper James Drew 2563"souvenir karoola world-war-one drew-james hospital-ship -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionSculpture - Bas-relief, Ronald C. Skate, Untitled (Early Maritime Industries), n.d
Commissioned by State Bank to produce 5 copper bas-reliefs for 73 Percy Street, Portland. Spoke with Miss Betty Vivian (Member of the Portland Historical Society) re Portland's history. Commonwealth Bank stored objects in Melbourne (c.1991). Negotiations between Portland Historical Society and Commonwealth Bank of Australia led to gift of works to People of Portland. Stored at Council depot c.1998, retrieved for Maritime Discovery Centre display.Copper bas-relief. Depicting a man in raincoat and wide-brimmed rain hat at a ship's wheel. Behind him are flying birds and in front of him is the tail of a seal diving into waves on the left and the front of a seal on the right. -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaDecorative object - Vase, mid 20th Century
The caravel type ship with the cross represents the Santa Maria of Christopher Columbus. It is one of the symbols of the great sea explorers. A similar vase on sale on Ebay (April 2023) suggesting it was mass produced.One of the many decorative furnishings which date from the intense service periods of the Mission from the 1930s through to the 1960s. White painted ceramic vase on shallow circular foot with relief design of a stylised sailing ship (caravel) on one side. Original colour appears to have been green.The foremost sail of the ship bears a cross; small chip on rim.vase, ship, caravel, santa maria, sea exploration, great navigators -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Syd Cuffe, Portland Town Crier on Portland Harbour, n.d
Syd Cuffe in Town Crier regalia on a wharf, watching ship under sail coming into a harbour, place unknownColoured photo. Syd Cuffe in Town Crier regalia on a wharf, watching ship under sail coming into a harbour. -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumTextile - Textile fragment, c.1797
Woollen fabric fragment from the wreck of ship "Sydney Cove" found underwater after many years.Small fragment of woven woollen fabric, brown colour. with some white fibres through it. The fragment is frayed and coming apart. It is boxed in a circular clear plastic lidded container, taped and with a typed paper label on the lid.Wording: Fabric scrap from/wreck of ship "Sydney Cove"/ NWM 940112";Method: typed;Location: on label on lidwool - history textile history textile mills textile mills, wool - history, textile history, textile mills -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSouvenir - Wood Sample, Alexander Stephen and Sons, 1869
This teak wood sample was part of a handrail from the wreck of the ship Otago. The Otago 1869-1931 The iron-hulled 3-masted barque Otago was built in Glasgow by Alexander Stephen & Sons Ltd, Kelvinhaugh, as a merchant ship and launched in 1869. The vessel changed hands several times in the late 19th century after being sold to an Australian firm in 1871. During one of its voyages, the captain died while the ship was in port at Bangkok. Marine author Joseph Conrad was on board and, being a qualified captain, he took command and continued the journey to Sydney and Mauritius. It was the only ship he ever commanded. In 1903 the Melbourne shipping company Huddart, Parko & Co., purchased the Otago and converted it to serve as a coal hulk for use in Sydney. The Otago was later sent to Hobart, Tasmania, where it continued as a hulk until 1931. It was sold for scrap and eventually abandoned on the banks of the Derwent River at a place now known as Otago Bay, opposite Conrad Drive, Otago. The outline of the hull is still visible and a nearby plaque tells the story. There are other vessels also named Otago, one of them in the same year. Joseph Conrad (1857-1927): - Polish-born Joseph Conrad became a British subject in 1886. He was a renowned marine fiction writer and, for a short time, a mariner and Captain. As a 13-year-old boy, Joseph Conrad desired to be a sailor. At 19, he joined the British merchant marine, working in several roles. He eventually qualified as a captain but only served in this role once: from 1888 to 1889, when he commanded the barque Otago, taking over from the deceased captain and completing the ship’s journey from Sydney to Mauritius. In 1889 he began writing his first novel, Almayer’s Folly. He retired from life as a mariner in 1894, aged 36. Conrad’s affection for Australia and his visits to Australia from 1878 to 1982 were later commemorated by a plaque in Circular Quay, Sydney. Conrad continued as an author; some characters in his books were said to be inspired by his maritime experiences and the people he had met. By the end of his life, he had completed 19 novels, many stories, and essays, plus one incomplete novel, Suspense, which was finished and published posthumously. In 1924, Prime Minister Ramsay MacDonald offered Conrad a knighthood for his work but he declined. There is an 1882 sailing ship named the Joseph Conrad, after the author, that is now preserved at the Mystic Seaport Maritime Museum in the USA as part of the fleet of historic ships, used as an exhibit and a training ship. The Danish square-rigged training ship was originally named Georg Stage but was renamed by marine author Alan Villiers when he bought It in 1934. The wood sample from the Otago is significant for its association with renowned marine author Joseph Conrad, who had once commanded the vessel; it was his only command as Captain and was known as Joseph Conrad's Otago. The maritime connection with Conrad extends to items in the collection, including some of his maritime novels based on his first-hand knowledge, a wooden ship model of a ship named after him, and a navigation chart of Otago Harbour. The sample of teak is significant as an example of materials used in the construction of the 1869 iron-hulled sailing ship, built in Glasgow, Scotland, specifically for use to sail across the world with cargo to trade between the colonies including Australian ports. Wood sample; a rectangular section of a teak wood handrail that has a bead planed along one side. Two cards with the sample have inscriptions, one handwritten and one typed. The sample is from the wreck of the barque Otago, once under the command of Captain Joseph Conrad. Handwritten card: "PART OF TEAK HANDRAIL / from / Joseph CONRAD'S ship / OTAGO / (HULK at RISDON, DERWENT River, TASMANIA) Typed card: "PART OF THE TEAK HANDRAIL / FROM JOSEPH CONRAD'S SHIP / "OTAGO" / (HILK AT RISDON, DERWENT / RIVER, TASMANIA)"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, joseph conrad, joseph conrad's ship, captain joseph conrad, otago, barque otago, merchant ship, cargo ship, hulk, 1869 ship, iron hull, sailing ship, handrail, fitting, souvenir, wood sample, teak, new zealand, sydney, newcastle, tasmania, hobart, derwent river, otago harbour, otago bay, conrad drive, 19th century, mauritius, marine author, marine novel, alex villiers, georg stage -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today in the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Photograph of Falls of Halladale fully rigged wrecked sailing ship. Written on back. "Bill Kelson 75 Macquarie Ave Padbury 6025" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaBook (item) - Visitor log book, Melbourne Visitors log book, 2005-2006
This book reflects the changed nationalities of sailors on visiting ships with many being from the Asian subcontinent and South-East Asia.The logbook provides an insight into which ships and the origins of their crews were visiting Melbourne in 2005-2006 On a yellow post-it note stuck to the cover are the words: "Melbourne Visitors Log 29/10/05 to 08/05/06"logbook, visitor, sailors, seamen, seafarers, mission to seafarers, seamen mission, melbourne, flinders street, crew, nationality -
 Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.
Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Cowes Pier
From Jessie smith's collection. Foreshore at Cowes pier showing ship arriving.Black & White Photograph. Ship approaching Cowes pier from right. Heavy planting of tall and scrub trees on Cowes foreshorelocal history, photographs, cowes foreshore - cowes pier - phillip island, black & white photograph, transport movement, shipping, cowes, phillip island, jessie smith collection, stan mcfee -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Plaque, Wooden Naval plaques
Carved & painted wooden Naval plaques. HMAS Brisbane; HMAS Melbourne; HMAS Parramatta; HMAS Stuart; HMAS Swan; HMAS Sydney; HMAS Torrens & HMAS Yarra.Ships namednaval plaques -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumStencil
T/SHIPPEDwool sales export - wool wool - transportation, wool sales, export - wool, wool - transportation -
 Queenscliffe Maritime Museum
Queenscliffe Maritime MuseumNewspaper - '84 news article re the Rip 1 - a buoy & maintenance ship in Port Phillip, Port maintenance services, 18 April 1984
Port Phillip's Ports & Harbour maintenance ship RIP 1.Ports & Harbour maintenance ship RIP 1Full clipping ex The Sun Wed April 18, 1984, Pg 34 & 35, re Rip 1 ship, Ports & HarbourReverse " NIL "
