Showing 694 items
matching politicians
-
 Brighton Historical Society
Brighton Historical SocietyAccessory - Parasol, circa 1900
This parasol belonged to Clara Johnstone Miller (nee Bell, 1866-1910). Clara was the only daughter of Mr James Bell, a councillor of the Shire of Leigh (today a part of Golden Plains Shire) and owner of Woolbrook Homestead in Teesdale, near Geelong. In 1888, Clara married prominent businessman, racehorse owner, racing identity and pastoralist Septimus Miller (1854-1925). Septimus was the sixth of seven children born to Henry 'Money' Miller and Eliza Miller (nee Mattinson). 'Money' Miller was a well known financier and politician and reputedly one of Australia's wealthiest people in his time. In 1889, Clara and Septimus moved into the house 'Cantala' in Dandenong Road, Caulfield. They had one child, Gwendoline Stewart Miller, who died in 1902 at the age of thirteen of diabetes - a largely untreatable condition at the time (insulin would not be discovered until 1921). Clara died in 1910, aged only 44. Septimus subsequently married Helen (nee Henderson), with whom he had a son, Ronald (1915-1990). The Millers were buried in the Brighton General Cemetery in a large Gothic-style vault. Upon Clara's death, Septimus sent much of her clothing and Gwendoline's to her mother Mary Bell. Some of these items were passed down to two of Clara's nieces, Miss Mary Bell and Mrs Lois Lillies, who donated them to BHS around 1973.A black silk, wood and ivory handled parasol from circa 1900. The black silk of the parasol body has been treated with a decorative hemstitch towards the lower edge. The handle and frame are made of wood, metal and either ivory or an early plastic designed to mimic ivory. The ivory section is carved with a design reminiscent of a palm tree trunk and finished with a ball. The handle also features a leather looped strap that the hand would pass through to aid holding the parasol.The handle bears an engraved inscription that appears to be 'VML' in a highly florid script. The frame bears the name 'Hartnells'.clara miller, woolbrook, septimus miller, henry 'money' miller, gwendoline miller, cantala, parasols, caulfield, brighton general cemetery -
 Brighton Historical Society
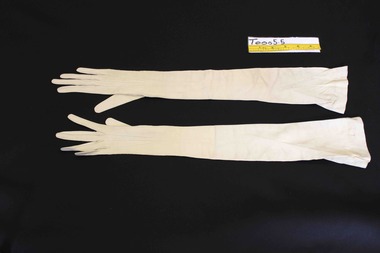
Brighton Historical SocietyAccessory - Gloves, 1900
These gloves belonged to Clara Johnstone Miller (nee Bell, 1866-1910). Clara was the only daughter of Mr James Bell, a councillor of the Shire of Leigh (today a part of Golden Plains Shire) and owner of Woolbrook Homestead in Teesdale, near Geelong. In 1888, Clara married prominent businessman, racehorse owner, racing identity and pastoralist Septimus Miller (1854-1925). Septimus was the sixth of seven children born to Henry 'Money' Miller and Eliza Miller (nee Mattinson). 'Money' Miller was a well known financier and politician and reputedly one of Australia's wealthiest people in his time. In 1889, Clara and Septimus moved into the house 'Cantala' in Dandenong Road, Caulfield. They had one child, Gwendoline Stewart Miller, who died in 1902 at the age of thirteen of diabetes - a largely untreatable condition at the time (insulin would not be discovered until 1921). Clara died in 1910, aged only 44. Septimus subsequently married Helen (nee Henderson), with whom he had a son, Ronald (1915-1990). The Millers were buried in the Brighton General Cemetery in a large Gothic-style vault. Upon Clara's death, Septimus sent much of her clothing and Gwendoline's to her mother Mary Bell. Some of these items were passed down to two of Clara's nieces, Miss Mary Bell and Mrs Lois Lillies, who donated them to BHS around 1973.A pair of very fine ivory doeskin evening gloves. The gloves feature full pique insert seams around the fingers and thumb with a slit on the inside arm from mid thumb to mid fore arm and three white shell buttons. The gloves extend high to high on the upper arms and feature a ribbon covered elastic to aid hold on the upper arm. A black ink stamp on the inside of the right glove over the wrist: 5 3/4, Made in France, Buckley and Nunn Limited, Melbourne. A black ink stamp on the inside of the left glove over the wrist: Grand Prix Exposition, 1900, Medallere D'or, Merlier, Depose (? Very faint), Made in France. A blue ink stamp on the inside of the left glove over the top side of the wrist: 797, 221'65, C51Cwoolbrook, septimus miller, henry 'money' miller, gwendoline miller, cantala, clara miller, gloves, caulfield, brighton general cemetery, 1900s fashion, buckley and nunn -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Dr. W. H. Embling - Public Vaccinator
William Henry Embling was born in London on September 25, 1840, and came to Victoria with his parents when he was about 9 years old. When still in his teens, William was sent to Germany, and afterwards to England, to study for the medical profession. Whilst in London he became involved with the British Legion which sailed for Italy and fought in the Garibaldian campaign. He rose to the rank of Lieutenant. After moving to Glasgow to study for the Licentiate of the Royal College of Surgeons, William returned to Australia in 1863 and set up practice in St. Kilda, Victoria. Embling was appointed resident surgeon at Melbourne Hospital, practiced in Ballarat from 1866-1873 and was an honorary physician at the Alfred Hospital in 1877 In 1878 he was appointed to the Central Board of Health, and in this role travelled to many rural areas including Wodonga as the Public Vaccinator. For some time, he was regularly in Wodonga on Fridays. He was also Chairman of the Police Medical Board and President of the Working Men's College in Melbourne. In 1892 William Embling was elected as a member of the Legislative Council. One of the many roles he filled as a politician was as a member of the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Railways. In this role he also visited Wodonga when consultations were in progress for development of the new railways throughout Victoria. Dr. Embling died from pneumonia in St. Kilda, Victoria on 24 May 1912.This item is significant because it depicts a doctor who provided an important service to Wodonga and to the wider Victorian community.A black and white photograph of Dr. Embling standing in front of his consulting room in a house in Wodonga.Signs to left of door: Below Crown and Letters C. R. Dr Embling Public Vaccinator Vaccinations Every Friday Free Service To Right of Door: Dr Embling Surgeon dr. w. h. embling, wodonga medical services, public vaccinator wodonga -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyPhotograph - Portrait, Legatee Harold E Cohen, 194
A portrait of Legatee Harold Edward Cohen CMG, CBE, DSO, VD, MLC, he served in both World Wars, attained the rank of Brigadier. He was the first president of Legacy in 1923 to 1924. The portrait was in an album of photos taken in the 1940s (mostly 1945). Harold Edward Cohen (1881-1946), soldier, lawyer, politician and businessman, was born on 25 November 1881. His early interest in soldiering led to him being first commissioned in the Australian Military Forces in 1901 in the Field Artillery. On the outbreak of the First World War he took overseas the 6th Australian Field Artillery Brigade, seeing service in France and Egypt, and being awarded the CMG and DSO, and being twice mentioned in despatches. He was twice wounded in action. He was awarded the Volunteer Decoration in 1921 and the CBE in 1934. In 1929 Brigadier Cohen entered Parliament as the member for Melbourne South in the Legislative Council, and in 1935 transferred to the Assembly as member for Caulfield, which seat he held until 1943. During the Second World War Brigadier Cohen served in the Middle East as honorary Red Cross Commissioner overseas. Returning to Australia in 1942 he was appointed director of amenities, and subsequently Deputy Adjutant-General to the AMF, which post he held until his retirement in 1944. A different photo of Legatee Cohen is framed and hung in the Level 2 function room (see 03991).A record of a prominent legatee who was President of Legacy.Black and white portrait of Harold E Cohen, who was the first president of Legacy in 1923. Part of a photo album with blue leather look back and front cover. From one of 20 pages with black and white photos.legatee, portrait, past president, harold cohen -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncArchive (series) - Subject File, Authors (Kew), 1958
Various PartiesReference, Research, InformationKHS OrderReference file containing Sundry information about authors (poets, novelists, playwrights, historians, politicians, journalists) who were born, educated, lived or died in Kew, initially compiled by Society member Elizabeth Mackie who had previously researched the artists of Kew. Since the file was created, various items including correspondence and newspaper articles/cuttings have been added. Some information relates to organisations rather than individuals, such as that Kew was once the headquarters of the Fellowship of Australian Writers (1/317 Barkers Road). Within the file there is correspondence and curriculum vitae supplied by: Allan Aldous, Lillian Wood, Michele Nayman (1981), Yetta Rothberg (1981), Judith Rodriguez (1981), Rev Dr Arthur de Quetteville Robin (1982). The File also includes a photocopy of a letter supplied by Prof A D Hope (1981) relating to his memories of Kew. Authors mentioned in the file include: Allan Aldous, F G A Barnard, James Bonwick, Martin Boyd, Vincent Buckley, Sir Macfarlane Burnet, Anne M Carson, John Clements, Rita Erlich, Barbara Giles, Alison Goding, A D Hope, Wendy Jacobs, Lally Katz, Jill Manton, Philip Martin, James McAuley, Pauline McKinnon, Philip Mendez, Marrion Miller, Michele Nayman, Brenda Niall, Mark O’Connor, Nettie Palmer, Vance Palmer, Rev Dr Arthur de Quetteville Robin, Judith Rodriguez, Myra Roper, Dorothy Rogers, Yetta Rothberg, Frederick Sinnett, John Stanley, Peter Steele, W D Vaughan, Gwen Walker, J M Walsh, Lillian Wood.authors - kew (vic)authors - kew (vic) -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotographs - Demolition of the old Tawonga District General Hospital. Set of 8 colour photographs
In the early stages of the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme the State Electricity Commission took over the financial and construction responsibility of the Tawonga District General Hospital building at a cost of 27,000 pounds. This included the removal and re-erection of the ex-military Bonegilla ward from Wodonga while in addition they carried out all the necessary building works that allowed the hospital to operate as a functional unit. The work was completed and handed over to the Hospital Committee of Management on September 1, 1949. Local residents raised 3,400 pounds through fund raising. The balance was met by the SEC and the Hospital and Charities Commission. The initial project was to provide for a basic temporary hospital which was later to include an Operating Theatre, Offices, Store, Mortuary and a Nurse’s Home, until the establishment of a permanent medical premises. Following the opening, 455 patients were admitted to the Tawonga District General Hospital and 254 operations were performed in the first year. The hospital relocated to Mount Beauty in the former SEC administration offices located in the town centre. Official opening of the 18 bed Tawonga District General Hospital on April 29 in 1961. The old weatherboard building was demolished around the late 1900’s to early 2000’s and replaced with a new modern brick building. Alpine Health CEO Mr Lyndon Seys oversaw the opening of the new Mount Beauty Hospital in November 2001 alongside Board of Management President Mr Andrew Randell, other board members and politicians. The Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme the State Electricity Commission played a pivotal part in the planning and initial funding of the Tawonga District General Hospital, with a view to providing medical support for its many workers on the Hydro scheme. Later, spouse and family members of workers were also able to access medical assistance The hospital was originally located in Tawonga away from the majority of the patients as the Hospital and Charities Board was not prepared to have it within the SEC controlled area and it was not until the gate at Tawonga South was taken down that the hospital was moved to the main centre of population at Mount Beauty.8 Colour photographs of the demolition of the original Tawonga and District Hospital situated in Mt Beauty circa 20001. No inscriptions 2. Side view of Tawonga District General Hospital, 1990’s 3. Demolition of the weatherboard hospital: Nurses station, ward and corridor 4. Demolition of the weatherboard hospital: kitchen & utility rooms 5. Demolition of the weatherboard hospital” front entrance & gardens 7. Demolition of the weatherboard hospital: Matrons House 8. No inscriptions tawonga & district general hospital; kiewa hydro electric scheme; mt beauty; -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotographs – Old Tawonga District General Hospital Mt Beauty. Set of 19 colour photographs
In the early stages of the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme the State Electricity Commission took over the financial and construction responsibility of the Tawonga District General Hospital building at a cost of 27,000 pounds. This included the removal and re-erection of the ex-military Bonegilla ward from Wodonga while in addition they carried out all the necessary building works that allowed the hospital to operate as a functional unit. The work was completed and handed over to the Hospital Committee of Management on September 1, 1949. Local residents raised 3,400 pounds through fund raising. The balance was met by the SEC and the Hospital and Charities Commission. The initial project was to provide for a basic temporary hospital which was later to include an Operating Theatre, Offices, Store, Mortuary and a Nurse’s Home, until the establishment of a permanent medical premises. Following the opening, 455 patients were admitted to the Tawonga District General Hospital and 254 operations were performed in the first year. The hospital relocated to Mount Beauty in the former SEC administration offices located in the town centre. Official opening of the 18 bed Tawonga District General Hospital was on April 29 in 1961. The old weatherboard building was demolished around the late 1900’s to early 2000’s and replaced with a new modern brick building. Alpine Health CEO Mr Lyndon Seys oversaw the opening of the new Mount Beauty Hospital in November 2001 alongside Board of Management President Mr Andrew Randell, other board members and politicians. The Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme the State Electricity Commission played a pivotal part in the planning and initial funding of the Tawonga District General Hospital, with a view to providing medical support for its many workers on the Hydro scheme. Later, spouse and family members of workers were also able to access medical assistance The hospital was originally located in Tawonga away from the majority of the patients as the Hospital and Charities. Many SEC workers and their families have received medical care at Tawonga District General Hospital and Alpine Health over the years. A number of family members of SECV workers as well as other dedicated staff have provided high quality medical attention and support in all the facilities as nursing staff, support staff and volunteers. Many past staff members and their families still remain living in the Kiewa Valley area 19 Colour photographs of the Tawonga and District Hospital situated in Mt Beauty circa 2000. Including photographs of interior and of some staff members1. No markings 2. G Ryder at front entrance 3. Sister G Ryder in the Resuscitation Room 4. Nurse D Hateley in the Kitchen 5. Nurse D Hateley in the Casualty Room 6. Sister W McClelland in new nurse’s station 7. R Forrest, G Ryder, ?, M Ranton 8. Nurse D Hateley in the Pan Room 9. Tawonga District General Hospital: Resuscitation Room 10. Hospital Hallway 11. Empty Nurses Station 12. Tawonga District General Hospital: Nursery 13. Patient Tea Room 14, 15, 16, 17, & 18. No marking mt beauty district hospital, tawonga district hospital, bonegilla ward, ryder family -
 Waverley RSL Sub Branch
Waverley RSL Sub BranchPlaque Vietnam Vererans Parade Sydney 1987, Vietnam Vererans Parade Sydney 1987
Anecdotal evidence holds that most men returned from Vietnam in the dead of night, hidden from the public. In fact, large numbers actually returned on HMAS Sydney, to a welcome by dignitaries and a parade. The manner of their homecoming affected the way in which veterans recovered from the war, those who did arrive late at night to no fanfare and the seeming indifference of the military had more trouble adjusting to life at home than did those whose return was more public and who had had the benefit of a couple of weeks unwinding on board Sydney before reaching Australia. But the return home was only the beginning of a long period of readjustment. For a long time after the war large numbers of Vietnam veterans felt that many in Australia blamed them, rather than politicians, for the war and the way it had been conducted. Images of the war, many still familiar, of children burned by napalm, of the dead of My Lai, of a South Vietnamese general summarily executing a member of the Viet Cong in the streets of Saigon, had an effect on public opinion and public understanding. The fact that these images related more to the American/Vietnamese experience in Vietnam was less remarked upon. People associated the role of Australians in the war with that of the Americans in a way that failed to recognise the two countries’ different approaches to fighting in Vietnam. see https://www.google.com.au/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=3&cad=rja&ved=0CDwQtwIwAg&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.youtube.com%2Fwatch%3Fv%3DYL06ddRmiJE&ei=O9OJUYnxC5GaiQeey4HQCA&usg=AFQjCNEjq876qAoYu0WnWslDSNRUJlmuBw&bvm=bv.46226182,d.aGc Wooden Plaque 15cm x 13cmVietnam Vererans Parade Sydney 1987 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Biography, Arthur D. Elliot, The Life of George Joachim Goschen First Viscount Goschen 1831-1907 Vol 1, 1911
This book is one of two volumes, ‘The Life of George Joachim Goschen First Viscount Goschen 1831-1907’, written by Arthur D. Elliot in 1911. George Joachim Goschen, 1st Viscount Goschen (1831-1907) was a late 19th-century British administrator and economist. He became prominent in financial affairs and at the age of 27 was appointed as a Director of the Bank of England. He was famous for his book, ‘Theory of the Foreign Exchanges’. The book is part of Flagstaff Hill’s Pattison Collection of books which originated from the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute. Arthur D. Elliot (1846-1923) wrote ‘in 1911. He was born and educated in England and worked as a politician, a journal editor and an author. His leg was amputated at the age of four after a fall but he was still able to climb, ride and swim. The publisher firm, Longmans, Green & Co, was originally founded in 1724 in London by Thomas Longman under the name Longman. In August of that year, he bought the two shops and goods of William Taylor and set up his publishing house there at 39 Paternoster Row. The shops were called Black Swan and Ship, and it is said that the 'ship' sign was the inspiration for Longman's Logo. After many changes of name and management, the firm was incorporated in 1926 as Longmans, Green & Co. Pty Ltd. The firm was acquired by Pearson in 1968 and was known as Pearson Longman or Pearson PLC. Interestingly, the logo in some books, such as “Steam Turbines 2nd edition, published in 1922” has the year “1724” but the logo in books such as “Advanced Agriculture, published in 1894” has the year “1726” in the logo.The book provides information on the social and political background in England in the late- 19th and early-20th centuries, Which influenced Australia’s history. The book is significant for its connection to the publisher Longmans, Green and Co., of London, a firm that has been established for over two centuries, renowned for publishing encyclopedias, dictionaries, books on English grammar, textbooks, poetry, reference books, novels, magazines and more. The book has additional importance for its connection to the Pattison Collection, which, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institutes’ Collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and its important role in people's intellectual, cultural and social development throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance.The Life of George Joachim Goschen First Viscount Goschen 1831-1907 Vol 1 Author: Arthur D Elliot Publisher: Longmans Green & Co Date: 1911 Volume 1 of two volumes with illustrations and portraits. The book is part of the Pattison Collection. Green-blue hardcover book with embossed gold text and symbol on the cover and spine. Inscriptions on a label, stickers, stamp and handwriting.Label: "PAT 920 GOS" Sticker: "Warrnambool Mechanics Institute and Free Library" Sticker: "Corangamite Regional Library Service" Stamp: "Corangamite Regional Library Service" Handwriting: "5493/923.2"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, pattison collection, ralph eric pattison, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, mechanics’ institute library, warrnambool library, free library, corangamite regional library service, longmans green and co., thomas longman, paternoster row london, arthur d. elliot, the life of george joachim goschen first viscount goschen, 1831-1907, george joachim goschen, first viscount goschen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Biography, Arthur D. Elliot, The Life of George Joachim Goschen First Viscount Goschen 1831-1907 Vol 2, 1911
This book is one of two volumes, ‘The Life of George Joachim Goschen First Viscount Goschen 1831-1907’, written by Arthur D. Elliot in 1911. George Joachim Goschen, 1st Viscount Goschen (1831-1907) was a late 19th-century British administrator and economist. He became prominent in financial affairs and at the age of 27 was appointed as a Director of the Bank of England. He was famous for his book, ‘Theory of the Foreign Exchanges’. The book is part of Flagstaff Hill’s Pattison Collection of books which originated from the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute. Arthur D. Elliot (1846-1923) wrote ‘in 1911. He was born and educated in England and worked as a politician, a journal editor and an author. His leg was amputated at the age of four after a fall but he was still able to climb, ride and swim. The publisher firm, Longmans, Green & Co, was originally founded in 1724 in London by Thomas Longman under the name Longman. In August of that year, he bought the two shops and goods of William Taylor and set up his publishing house there at 39 Paternoster Row. The shops were called Black Swan and Ship, and it is said that the 'ship' sign was the inspiration for Longman's Logo. After many changes of name and management, the firm was incorporated in 1926 as Longmans, Green & Co. Pty Ltd. The firm was acquired by Pearson in 1968 and was known as Pearson Longman or Pearson PLC. Interestingly, the logo in some books, such as “Steam Turbines 2nd edition, published in 1922” has the year “1724” but the logo in books such as “Advanced Agriculture, published in 1894” has the year “1726” in the logo.The book provides information on the social and political background in England in the late- 19th and early-20th centuries, which influenced Australia’s history. The book is significant for its connection to the publisher Longmans, Green and Co., of London, a firm that has been established for over two centuries, renowned for publishing encyclopedias, dictionaries, books on English grammar, textbooks, poetry, reference books, novels, magazines and more. The book has additional importance for its connection to the Pattison Collection, which, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institutes’ Collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and its important role in people's intellectual, cultural and social development throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance.The Life of George Joachim Goschen First Viscount Goschen 1831-1907 Vol 2 Author: Arthur D Elliot Publisher: Longmans Green & Co Date: 1911 Volume two of two volumes with illustrations and portraits. The book is part of the Pattison Collection. Green-blue hardcover book with embossed gold text and symbol on the cover and spine. Inscriptions on a label, stickers, stamp and handwriting.Label: "PAT 920 GOS" Sticker "Warrnambool Mechanics Institute and Free Library" Sticker "Corangamite Regional Library Service" Stamp: "Corangamite Regional Library Service" Handwritten "8494 / 923.2"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, pattison collection, ralph eric pattison, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, mechanics’ institute library, warrnambool library, free library, corangamite regional library service, longmans green and co., thomas longman, paternoster row london, arthur d. elliot, the life of george joachim goschen first viscount goschen, 1831-1907, george joachim goschen, first viscount goschen -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationImage, Joseph Chamberlain, 1864
Joseph Chamberlain was was an important businessman and a politician. He worked to improve education, and cities. He was a Member of Parliament from 1876 to 1914, and Colonial Secretary (controlling British colonies) from 1895 to 1903. His son Austen won the Nobel Peace Prize and another son Neville was Prime Minister from 1937 to 1940. (Wikipedia) Chamberlain was a Unitarian, a Christian who believes Christ was an example of the way to live life, but was not divine (not a part of God). Unitarians try to work to help society. There were many problems in Birmingham after the industrial revolution, and many men were not allowed to vote. In 1868 Chamberlain helped a liberal man to become the Member of Parliament for Birmingham. In 1869, he started a group working for free primary education for all children. In November 1869, he became a member of Birmingham City Council. There he worked for cheaper land prices for rural (countryside) workers, and became very popular. In 1873 he became the Mayor of Birmingham. He bought the gas companies and water companies for the city, so people were able to have clean and safe water. He made parks, roads, schools museums and built new houses for poor people. In June 1876 he became the Member of Parliament (MP) for Birmingham. In parliament he worked to unite radical M.P.s (MPs that wanted change) against the Whig party who were in power. His work helped William Ewart Gladstone to become Prime Minister in 1880. Chamberlain often spoke about education in parliament. (Wikipedia)Image of a man called Joseph Chamberlain.ballarat irish, chamberlain, joseph chamberlain -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotographs – Photographs of staff from Tawonga District General Hospital & Alpine Health – Set of 13 colour photographs
In the early stages of the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme the State Electricity Commission took over the financial and construction responsibility of the Tawonga District General Hospital building at a cost of 27,000 pounds. This included the removal and re-erection of the ex-military Bonegilla ward from Wodonga while in addition they carried out all the necessary building works that allowed the hospital to operate as a functional unit. The work was completed and handed over to the Hospital Committee of Management on September 1, 1949. Local residents raised 3,400 pounds through fund raising. The balance was met by the SEC and the Hospital and Charities Commission. The initial project was to provide for a basic temporary hospital which was later to include an Operating Theatre, Offices, Store, Mortuary and a Nurse’s Home, until the establishment of a permanent medical premises. Following the opening, 455 patients were admitted to the Tawonga District General Hospital and 254 operations were performed in the first year. The hospital relocated to Mount Beauty in the former SEC administration offices located in the town centre. Official opening of the 18 bed Tawonga District General Hospital on April 29 in 1961. Kiewa Valley House nursing home was officially opened on March 6th, 1985, with a new lounge extension opening in May, 1993. Prior to this, residents had to travel to Beechworth, Wangaratta or Wodonga for care. The old weatherboard building was demolished around the late 1900’s to early 2000’s and replaced with a new modern brick building. Alpine Health CEO Mr Lyndon Seys oversaw the opening of the new Mount Beauty Hospital in November 2001 alongside Board of Management President Mr Andrew Randell, other board members and politicians.The Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme the State Electricity Commission played a pivotal part in the planning and initial funding of the Tawonga District General Hospital, with a view to providing medical support for its many workers on the Hydro scheme. Later, spouse and family members of workers were also able to access medical assistance. Many SEC workers and their families have received high medical care at Tawonga District General Hospital and Alpine Health and/or as residents of Kiewa Valley House over the years. A number of family members of SECV workers as well as other dedicated staff have provided high quality medical attention and support in all three facilities as nursing staff, support staff and volunteers. Many past staff members and their families still remain living in the Kiewa Valley area Set of 13 colour photographs of past nursing staff and support staff from Tawonga District General Hospital, Kiewa Valley House & Alpine Health 1. Marg Hickey, Barbara Clark & Margaret Ranton 2. Cheryl Clutterbuck & Rosemary Forrest 3. Margaret Ranton 4. Margaret Ranton holding unknown infant 5. Gwen Goss 6. Barbara Clark & Margaret Ranton 7. Margaret Ranton, Sue Zeinert & Jenny Piera 8. Margaret Ranton, Gloria Ryder & Jenny Piera 9. Sue Wesley, Ruth Barton, Margaret Ranton, Rosemary Forrest & Nola Henry 10. F Bogaski & H Sigmund 11. Maintenance Supervisor H Sigmund 12. Gardener Fred Keat & Handyman Joe Trezise (1977) 13. Nursing staff in new hospital 1-9 No markings 10 F Bogaski & H Sigmund 11. Maintenance Supervisor H Sigmund 12. Gardener Fred Keat & Handyman Joe Trezise (1977) 13. Nursing staff in new hospital tawonga district general hospital, kiewa valley house, alpine health -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph (black & White), Right Honorable Cecil John Rhodes - South Africa
Cecil Rhodes was a British businessman, mining magnate and politician in South Africa. He was Prime Minister of the Cape Colony from 1890 to 1896. He believed in British Imperialism and he and his British South Africa Company formed the territory of Rhodesia in the early 1890s. He was forced to resign as Prime Minister in 1896 after the disastrous Jameson Raid, an unauthorised attack on Paul Kruger's South African Republic (Transvaal), which sent his brother to prison convicted of high treason and nearly sentenced to death. This event contributed to the outbreak of the Second Boer War. Rhodes went to Kimberley in a political move. During the war the military felt he was more of a liability than an asset and found him intolerable. The officer commanding the garrison of Kimberley, Lieutenant Colonel Robert Kekewich, experienced serious personal difficulties with Rhodes because of the latter's inability to co-operate. However, he still remained a leading figure in the politics of southern Africa. Rhodes was dogged by ill health his whole life. He died in 1902, aged 48, at his seaside cottage in Muizenberg. He was cared for by Leander Starr Jameson during his illness, becoming a trustee of his estate and residuary beneficiary of his will, which allowed him to continue living in Rhode's mansion after his death. His final will left a large area of land on the slopes of Table Mountain. Part of the estate became the upper campus of the University of Cape Town, another part became the Kirstenbosch National Botanical Garden. The rest was spared development and is now an important conservation area. His will also provided for the establishment of the Rhodes Scholarship. Individual image from photographed poster of tobacco and cigarette cards.cecil rhodes, mining magnate south africa, politician south africa, prime minister cape colony, british south africa company, rhodesia, jameson raid, paul kruger, south africa republic, transvaal, second boer war, kimberley, robert kekewich, leander starr jameson, muizenberg, table mountain, university of cape town, kirstenbosch national garden -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Statue of Sir Rupert James Hamer, AC, KCMG, ED, 2016, 21/02/2016
Sir Albert Arthur Dunstan, KCMG was an Australian politician. A member of the Country Party (now National Party of Australia), Dunstan was the 33rd Premier of Victoria. His term as Premier was the second-longest in the state's history, behind Sir Henry Bolte. Dunstan, who was Premier from 2 April 1935 to 14 September 1943 and again from 18 September 1943 to 2 October 1945, was the first Premier of Victoria to hold that office as a position in its own right, and not just an additional duty taken up by the Treasurer, Attorney General, or Chief Secretary. Sir Henry BoltePrint Page Print this page 15-November-2018[Diane Watson] 15-November-2018[Diane Watson] 15-November-2018[Diane Watson] 21-November-201615-November-2018 [Diane Watson]21-November-201615-November-2018[Diane Watson]15-November-2018[Diane Watson]21-November-2016 Photographs supplied by Sandra Brown / Diane Watson A statue commemorates the former Premier of Victoria, Sir Henry Bolte for his services to Victoria and Ballarat. In the 1955 elections an almost unknown sheep farmer from the bush, Henry Bolte, became premier. His long, uninterrupted Liberal rule was a seminal period in Victoria`s history, not least for the unprecedented development of the hitherto languishing state and the political stability that his election in 1955 delivered. There was a chaotic political culture in Victoria before Bolte was elected. It was effectively a national joke with one minority government in 1943 lasting just five days and another in 1952 lasting only four.Statue of Henry Bolte and Sir Allbert Dunstantreasury gardens, statue, henry bolte, albert dunstan, premier -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Brian Dixon, Undated
Brian James Dixon (born 20/05/1936) is a former Australian rules footballer and Victorian politician. Dixon played 252 VFL games for Melbourne between 1954 and 1968, playing mostly on the wing. He had a stellar football career, playing in five premierships, winning Melbourne's best and fairest in 1960, while in 1961 he was selected in the All-Australian team and he also won the Tassie Medal for his performances at the 1961 Brisbane Carnival. In 2000 he was named in Melbourne's Team of the Century. Despite still playing football for Melbourne, he entered parliament in 1964, as the member for the now abolished seat of St Kilda, representing the Liberal Party. Being from the moderate wing of the party he clashed with then Premier Henry Bolte, especially over the hanging of Ronald Ryan which Dixon strongly opposed.[1] After Rupert Hamer took over as Liberal Party leader and Premier, Dixon was promoted to the ministry. He variously served in several portfolios including youth, sport and recreation, housing and Aboriginal affairs. His most remembered achievement was introducing the iconic Life. Be in it. program.[2] In 1979 Dixon won St Kilda by an extremely narrow margin, which crucially gave the Hamer Liberal government a majority of one seat in the Legislative Assembly and meant that the Liberal Party did not need to form a Coalition with the National Party with whom relations were traditionally poor in Victoria. However, in 1982 Dixon was defeated as the Liberals lost government after 27 years in office. After his defeat, Dixon has worked predominantly in sports administration and he currently runs public speaking seminars. Brian currently travels the world representing TAFISA and ASFAA. He is also president of AFL South Africa and takes a keen interest in other countries playing Australian rules football.[3]B & W photograph of Brian Dixon in profile.dixon, brian, football, victorian parliament -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationImage, James Ryan, c1864, 1864
Ryan was an Irish politician. He was elected to the First Dáil at the 1918 general election and, apart from the Third Dáil (1922–1923), held his seat for Wexford until his retirement at the 1965 general election. During his long career he served as Minister for Agriculture (1932–1947), Minister for Health and Social Welfare (1947–1948 and 1951–1954) and Minister for Finance (1957–1965). (Wikipedia) While studying at university in 1913 Ryan became a founder-member of the Irish Volunteers and was sworn into the Irish Republican Brotherhood the following year. During the Easter Rising in 1916 Ryan was the medical officer in the General Post Office (GPO). He was, along with James Connolly, one of the last people to leave the GPO when the evacuation took place. Following the surrender of the patriots Ryan was deported to Stafford Jail in England and subsequently at Frongoch. He was released in August 1916. Ryan rejoined the Volunteers immediately after his release from prison, and in June 1917 he was elected Commandant of the Wexford Battalion. His political career began the following year when he was elected as a Sinn Féin candidate for the constituency of Wexford South in the 1918 general election. Like his fellow Sinn Féin MPs Ryan refused to attend the Westminster Parliament. Instead he attended the proceedings of the First Dáil on 21 January 1919. As the War of Independence went on Ryan became Brigade Commandant of South Wexford and was also elected to Wexford County Council, serving as chairman on one occasion. In September 1919 he was arrested by the British and interned on Spike Island and later Beare Island until he was released after the truce with the other TDs to attend the deliberations of the Dáil concerning the Anglo-Irish Treaty which he voted against. Ryan was later imprisoned again during the subsequent Civil War, however, while interned he won back his Dáil seat as an abstentionist Sinn Féin TD at the 1923 general election. (Wikipedia)Image of a bearded man known as James Ryan. -
 Brighton Historical Society
Brighton Historical SocietyClothing - Dressing gown, circa 1894
This dressing gown belonged to Clara Johnstone Miller (nee Bell, 1866-1910). Clara was the only daughter of Mr James Bell, a councillor of the Shire of Leigh (today a part of Golden Plains Shire) and owner of Woolbrook Homestead in Teesdale, near Geelong. In 1888, Clara married prominent businessman, racehorse owner, racing identity and pastoralist Septimus Miller (1854-1925). Septimus was the sixth of seven children born to Henry 'Money' Miller and Eliza Miller (nee Mattinson). 'Money' Miller was a well known financier and politician and reputedly one of Australia's wealthiest people in his time. In 1889, Clara and Septimus moved into the house 'Cantala' in Dandenong Road, Caulfield, where they hosted lavish receptions for Melbourne's elite. Clara was known as a stylish hostess who wore elegant imported fashions. This dressing gown is believed to have been manufactured by Japanese silk merchant Shiino Shōbei. Following the opening of the port of Yokohama to foreign trade in 1859, Shōbei began producing western-style silk garments, initially selling them to foreigners living in Japan and later exporting them around the world, even exhibiting at the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. His popular exports included quilted 'at-home' gowns or dressing gowns similar to this one. They had one child, Gwendoline Stewart Miller, who died in 1902 at the age of thirteen of diabetes - a largely untreatable condition at the time (insulin would not be discovered until 1921). Clara died in 1910, aged only 44. Septimus subsequently married Helen (nee Henderson), with whom he had a son, Ronald (1915-1990). The Millers were buried in the Brighton General Cemetery in a large Gothic-style vault. Upon Clara's death, Septimus sent much of her clothing and Gwendoline's to her mother Mary Bell. Some of these items were passed down to two of Clara's nieces, Miss Mary Bell and Mrs Lois Lillies, who donated them to BHS around 1973.A hand stitched purple pink silk quilted dressing gown with pale pink embroidery from circa 1894. The dressing gown is embroidered from the collar and shoulders though the centre front body to just above the hemline, on the cuffs and remaining pocket in a pale pink Perle thread embroidery featuring leaves and flowers. The entire gown is hand quilted with vertical parallel lines. The gown's neckline features a flat collar and the sleeve head fits on the neat shoulder line. The sleeve head is gathered and full tapering to a loose flat cuff at the wrist. The front of the garment is currently secured by fourteen decorative frogs of two different styles, none of which appear to be original. There is also evidence of a fifteenth toggle that has been removed from the base. The gown's original left hand pocket has been removed and attached to an area around the right breast presumably to patch a hole or obscure some damage. It is unknown when these modifications have been made. The back of the gown features a gathered pink and black concertina pleated silk insert panel from the neck through to the base of the garment. The garment is lined with a very fine pale pink silk over the woollen batting.clara miller, woolbrook, septimus miller, cantala, gwendoline miller, caulfield, brighton general cemetery, shiino shobei, s. shobey -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratAustralian Prime Ministers, Grattan, Michelle, 2000
... Politicians ...A biography of Australian prime ministers (Barton-Howard) and political analysis. Essays by a variety of authors.Relevance to the history of politics in Australia, particularly the federal government and prime ministers. Biographical interest.Paperback book. Front cover: black background; sepia portrait photographs of all prime ministers up to John Howard; gold and white lettering.Front cover: editor's name and book title. Back cover: description; editor's biography; list of contributors.btlc, ballarat regional trades and labour council, ballarat trades hall, prime ministers - australia - edmund barton, prime ministers - australia - alfred deakin, prime ministers - australia - chris watson, prime ministers - australia - george reid, prime ministers - australia - andrew fisher, prime ministers - australia - joseph cook, prime ministers - australia - william morris hughes, prime ministers - australia - stanley melbourne bruce, prime ministers - australia - james scullin, prime ministers - australia - joseph lyons, prime ministers - australia - earle page, prime ministers - australia - robert menzies, prime ministers - australia - arthur fadden, prime ministers - australia - john curtin, prime ministers - australia - francis forde, prime ministers - australia - ben chifley, prime ministers - australia - harold holt, prime ministers - australia - john mcewan, prime ministers - australia - john gorton, prime ministers - australia - william mcmahon, prime ministers - australia - gough whitlam, prime ministers - australia - malcolm fraser, prime ministers - australia - robert hawke, prime ministers - australia - paul keating, prime ministers - australia - john howard, politics, politicians, house of representatives, parliament, biography -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationImage, Isaac Butt, c1864, 1864
An Irish barrister, politician, Member of Parliament (M.P.), and the founder and first leader of a number of Irish nationalist parties and organisations, including the Irish Metropolitan Conservative Society in 1836, the Home Government Association in 1870 and in 1873 the Home Rule League. (Wikipedia) After being called to the bar in 1838, Butt quickly established a name for himself as a brilliant barrister. He was known for his opposition to the Irish nationalist leader Daniel O'Connell's campaign for the repeal of the Act of Union.[4] He also lectured at Trinity College, Dublin, in political economy. His experiences during the Great Famine led him to move from being an Irish unionist and an Orangeman[5] to supporting a federal political system for the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland that would give Ireland a greater degree of self-rule. This led to his involvement in Irish nationalist politics and the foundation of the Home Rule League. Butt was instrumental in fostering links between Constitutional and Revolutionary nationalism through his representation of members of the Fenians Society in court. (Wikipedia) He began his career as a Tory politician on Dublin Corporation. He was Member of Parliament for Youghal from 1852 to 1865, and for Limerick from 1871 to 1879 (at the 1852 general election he had also been elected for the English constituency of Harwich, but chose to sit for Youghal). The failed Fenian Rising in 1867 strengthened Butt's belief that a federal system was the only way to break the dreary cycle of inefficient administration punctuated by incompetent uprisings.[6] In 1870 he founded the Irish Home Government Association. This was in no sense a revolutionary organisation. It was designed to mobilise public opinion behind the demand for an Irish parliament, with, as he put it, "full control over our domestic affairs."[6] He believed that Home Rule would promote friendship between Ireland and her neighbour to the east. In November 1873 Butt replaced the Association with a new body, the Home Rule League, which he regarded as a pressure-group, rather than a political party. In the General Election the following year, 59 of its members were elected. However, most of those elected were men of property who were closer to the Liberal cause.[7] In the meantime Charles Stewart Parnell had joined the League, with more radical ideas than most of the incumbent Home Rulers, and was elected to Parliament in a by-election in County Meath in 1875.[8] Butt had failed to win substantial concessions at Westminster on the things that mattered to most Irish people: an amnesty for the Fenians of '67, fixity of tenure for tenant-farmers and Home Rule. Although they worked to get Home Rulers elected, many Fenians along with tenant farmers were dissatisfied with Butt's gentlemanly approach to have bills enacted, although they did not openly attack him, as his defence of the Fenian prisoners in '67 still stood in his favour.[9] However, soon a Belfast Home Ruler, Joseph Gillis Biggar (then a senior member of the IRB), began making extensive use of the ungentlemanly tactic of "obstructionism" to prevent bills being passed by the house. When Parnell entered Parliament he took his cue from John O'Connor Power and Joseph Biggar and allied himself with those Irish members who would support him in his obstructionist campaign. MPs at that time could stand up and talk for as long as they wished on any subject. This caused havoc in Parliament. In one case they talked for 45 hours non-stop, stopping any important bills from being passed. Butt, ageing, and in failing health, could not keep up with this tactic and considered it counter-productive. In July 1877 Butt threatened to resign from the party if obstruction continued, and a gulf developed between himself and Parnell, who was growing steadily in the estimation of both the Fenians and the Home Rulers.[10] The climax came in December 1878, when Parliament was recalled to discuss the war in Afghanistan. Butt considered this discussion too important to the British Empire to be interrupted by obstructionism and publicly warned the Irish members to refrain from this tactic. He was fiercely denounced by the young Nationalist John Dillon, who continued his attacks with considerable support from other Home Rulers at a meeting of the Home Rule League in February 1879. Although he defended himself with dignity, Butt, and all and sundry, knew that his role in the party was at an end.[11] Butt, who had been suffering from bronchitis, had a stroke the following May and died within a week. He was replaced by William Shaw, who in turn was replaced by Charles Stewart Parnell in 1880. (Wikipedia)Image of a man known as Isaac Butt. -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomUniform, Service Dress WW1, c 1914
Sir Murray William James Bourchier (1881-1937), grazier, soldier and politician, was born on 4 April 1881 at Pootilla, Bungaree, Victoria, eldest son of Edward Bourchier, Geelong-born farmer, and his wife Francis (Fanny), née Cope. In 1878 Edward and his three brothers had taken up four adjoining selections on the Murray River near Tocumwal. Within a few years their properties had expanded considerably: Edward's, near Strathmerton, was called Woodland Park; the other three were known collectively as Boomagong. After a private education in Melbourne, Murray returned to Woodland Park. From 1909 until the outbreak of World War I he commanded a troop of light horse at Numurkah, attending annual camps and courses. Bourchier's military service was distinguished. He enlisted in the Australian Imperial Force in August 1914 and sailed as a lieutenant in the 4th Light Horse Regiment, serving seven months on Gallipoli. After the Sinai campaign in 1916-17, during which he was promoted lieutenant-colonel commanding his regiment, he made the crucial final assault on Beersheba. On 31 October 1917 he led his men, many of them from his own district, at full gallop over two miles into Turkish entrenchments and on for a further two miles (3.2 km) into Beersheba to capture vital wells before the Turks could destroy them. Lacking sabres, the regiment used bayonets held in their hands as shock weapons. For this exploit he was awarded the Distinguished Service Order and earned the sobriquet 'Bourchier of Beersheba'. Eleven months later, after fighting north through Palestine, he commanded a joint force of the 4th and 12th Light Horse regiments (Bourchier Force) in the final advance on Damascus; on entering the city the 4th captured 12,000 Turks and set about relieving their sufferings. Bourchier was three times mentioned in dispatches. He was appointed C.M.G. in June 1919 and his A.I.F. appointment ended in October. In 1921 he was promoted colonel, commanding the 5th Cavalry Brigade, and in 1931 brigadier, in charge of the 2nd Cavalry Division. He returned to Strathmerton but later farmed a property at Katandra, which he named Kuneitra. - Source: Australian Dictionary of BiographyService dress of General Sir Murray Bourchier, complete with jacket, trousers, shirt, tie, boots (high rise),Sam Browne belt, peaked cap, medal ribbons, badges of rank, medal ribbons -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomUniform, Mess Kit, c 1914
Sir Murray William James Bourchier (1881-1937), grazier, soldier and politician, was born on 4 April 1881 at Pootilla, Bungaree, Victoria, eldest son of Edward Bourchier, Geelong-born farmer, and his wife Francis (Fanny), née Cope. In 1878 Edward and his three brothers had taken up four adjoining selections on the Murray River near Tocumwal. Within a few years their properties had expanded considerably: Edward's, near Strathmerton, was called Woodland Park; the other three were known collectively as Boomagong. After a private education in Melbourne, Murray returned to Woodland Park. From 1909 until the outbreak of World War I he commanded a troop of light horse at Numurkah, attending annual camps and courses. Bourchier's military service was distinguished. He enlisted in the Australian Imperial Force in August 1914 and sailed as a lieutenant in the 4th Light Horse Regiment, serving seven months on Gallipoli. After the Sinai campaign in 1916-17, during which he was promoted lieutenant-colonel commanding his regiment, he made the crucial final assault on Beersheba. On 31 October 1917 he led his men, many of them from his own district, at full gallop over two miles into Turkish entrenchments and on for a further two miles (3.2 km) into Beersheba to capture vital wells before the Turks could destroy them. Lacking sabres, the regiment used bayonets held in their hands as shock weapons. For this exploit he was awarded the Distinguished Service Order and earned the sobriquet 'Bourchier of Beersheba'. Eleven months later, after fighting north through Palestine, he commanded a joint force of the 4th and 12th Light Horse regiments (Bourchier Force) in the final advance on Damascus; on entering the city the 4th captured 12,000 Turks and set about relieving their sufferings. Bourchier was three times mentioned in dispatches. He was appointed C.M.G. in June 1919 and his A.I.F. appointment ended in October. In 1921 he was promoted colonel, commanding the 5th Cavalry Brigade, and in 1931 brigadier, in charge of the 2nd Cavalry Division. He returned to Strathmerton but later farmed a property at Katandra, which he named Kuneitra. Source: Australian Dictionary of BiographyMess kit of General Sir Murray Bourchier complete with peaked cap, jacket, cummerbund, shirt, tie, waistcoat, trousers, shoes, AMF lapel badges & badges of rank -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Rev. Brian Howe MP, 1986
Brian Leslie Howe, AO (born 23 January 1936), is an Australian former politician who served as the Deputy Prime Minister of Australia in the Labor government under prime ministers Bob Hawke and Paul Keating from 1991 to 1995. Howe was born in Melbourne. He spent his early childhood in the suburb of Malvern and was educated at Melbourne High School and the University of Melbourne. He later studied theology in Chicago (1967–69) and then returned to Australia. He served as a minister with the Methodist Church and the Uniting Church in various parts of Victoria – Morwell, Eltham and Fitzroy. Howe was elected to the House of Representatives in 1977 representing the northern Melbourne metropolitan electoral Division of Batman. He defeated the incumbent Horrie Garrick for Labor preselection in a hard-fought contest.[1] A member of the Socialist Left faction of the Labor Party, he was Minister for Defence Support in the government of Bob Hawke from 1983. In 1984 he became Minister for Social Security and carried out various radical reforms to Australia's welfare system.[2] Howe appeared to face significant opposition within his electorate in 1988, when up to 60 members of the Greek Westgarth branch of the ALP defected to join the Australian Democrats. One of the defectors, tram-conductor George Gogas, contested Batman as a Democrat candidate in 1990, but polled only 12.9 per cent of the vote.[3] After the 1990 election Howe was appointed to the post of Minister for Community Services and Health. When Paul Keating resigned from Cabinet in 1991, Howe succeeded him as Deputy Prime Minister. He became Minister for Health, Housing and Community Services in the Keating government in December 1991, dropping the health part of the portfolio in 1993. In June 1995 he resigned as Deputy Prime Minister and was succeeded by Kim Beazley. He did not stand for re-election at the 1996 election. Following his parliamentary career, Howe has been appointed as an Associate Professor for Melbourne University and continues to work with social policy and related fields. He is a member of the Church of All Nations in Carlton, and active in the Uniting Church. A full biography in his own words can be found in the Proceedings of the Uniting Church Historical Society, Synod of Victoria and Tasmania, Vol. 21, No. 1 for June 2014.Howe standing by a window in his office 1986.Identification of Howe. -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Rev. Brian Howe MP, 1984
Brian Leslie Howe, AO (born 23 January 1936), is an Australian former politician who served as the Deputy Prime Minister of Australia in the Labor government under prime ministers Bob Hawke and Paul Keating from 1991 to 1995. Howe was born in Melbourne. He spent his early childhood in the suburb of Malvern and was educated at Melbourne High School and the University of Melbourne. He later studied theology in Chicago (1967–69) and then returned to Australia. He served as a minister with the Methodist Church and the Uniting Church in various parts of Victoria – Morwell, Eltham and Fitzroy. Howe was elected to the House of Representatives in 1977 representing the northern Melbourne metropolitan electoral Division of Batman. He defeated the incumbent Horrie Garrick for Labor preselection in a hard-fought contest.[1] A member of the Socialist Left faction of the Labor Party, he was Minister for Defence Support in the government of Bob Hawke from 1983. In 1984 he became Minister for Social Security and carried out various radical reforms to Australia's welfare system.[2] Howe appeared to face significant opposition within his electorate in 1988, when up to 60 members of the Greek Westgarth branch of the ALP defected to join the Australian Democrats. One of the defectors, tram-conductor George Gogas, contested Batman as a Democrat candidate in 1990, but polled only 12.9 per cent of the vote.[3] After the 1990 election Howe was appointed to the post of Minister for Community Services and Health. When Paul Keating resigned from Cabinet in 1991, Howe succeeded him as Deputy Prime Minister. He became Minister for Health, Housing and Community Services in the Keating government in December 1991, dropping the health part of the portfolio in 1993. In June 1995 he resigned as Deputy Prime Minister and was succeeded by Kim Beazley. He did not stand for re-election at the 1996 election. Following his parliamentary career, Howe has been appointed as an Associate Professor for Melbourne University and continues to work with social policy and related fields. He is a member of the Church of All Nations in Carlton, and active in the Uniting Church. A full biography in his own words can be found in the Proceedings of the Uniting Church Historical Society, Synod of Victoria and Tasmania, Vol. 21, No. 1 for June 2014.Full-face, looking into the camera 1984 - part of an advertisement for Wesley Church's 126th anniversary 9/9/1984.Identification of Howe -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Rev. Brian Howe MP, 1985
Brian Leslie Howe, AO (born 23 January 1936), is an Australian former politician who served as the Deputy Prime Minister of Australia in the Labor government under prime ministers Bob Hawke and Paul Keating from 1991 to 1995. Howe was born in Melbourne. He spent his early childhood in the suburb of Malvern and was educated at Melbourne High School and the University of Melbourne. He later studied theology in Chicago (1967–69) and then returned to Australia. He served as a minister with the Methodist Church and the Uniting Church in various parts of Victoria – Morwell, Eltham and Fitzroy. Howe was elected to the House of Representatives in 1977 representing the northern Melbourne metropolitan electoral Division of Batman. He defeated the incumbent Horrie Garrick for Labor preselection in a hard-fought contest.[1] A member of the Socialist Left faction of the Labor Party, he was Minister for Defence Support in the government of Bob Hawke from 1983. In 1984 he became Minister for Social Security and carried out various radical reforms to Australia's welfare system.[2] Howe appeared to face significant opposition within his electorate in 1988, when up to 60 members of the Greek Westgarth branch of the ALP defected to join the Australian Democrats. One of the defectors, tram-conductor George Gogas, contested Batman as a Democrat candidate in 1990, but polled only 12.9 per cent of the vote.[3] After the 1990 election Howe was appointed to the post of Minister for Community Services and Health. When Paul Keating resigned from Cabinet in 1991, Howe succeeded him as Deputy Prime Minister. He became Minister for Health, Housing and Community Services in the Keating government in December 1991, dropping the health part of the portfolio in 1993. In June 1995 he resigned as Deputy Prime Minister and was succeeded by Kim Beazley. He did not stand for re-election at the 1996 election. Following his parliamentary career, Howe has been appointed as an Associate Professor for Melbourne University and continues to work with social policy and related fields. He is a member of the Church of All Nations in Carlton, and active in the Uniting Church. A full biography in his own words can be found in the Proceedings of the Uniting Church Historical Society, Synod of Victoria and Tasmania, Vol. 21, No. 1 for June 2014.Howe alighting from a car at Williamstown dockyards March 1985.Identification of Howe. -
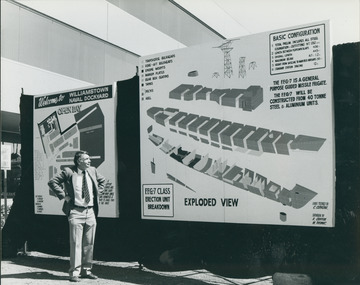 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Rev. Brian Howe MP, 1984
Brian Leslie Howe, AO (born 23 January 1936), is an Australian former politician who served as the Deputy Prime Minister of Australia in the Labor government under prime ministers Bob Hawke and Paul Keating from 1991 to 1995. Howe was born in Melbourne. He spent his early childhood in the suburb of Malvern and was educated at Melbourne High School and the University of Melbourne. He later studied theology in Chicago (1967–69) and then returned to Australia. He served as a minister with the Methodist Church and the Uniting Church in various parts of Victoria – Morwell, Eltham and Fitzroy. Howe was elected to the House of Representatives in 1977 representing the northern Melbourne metropolitan electoral Division of Batman. He defeated the incumbent Horrie Garrick for Labor preselection in a hard-fought contest.[1] A member of the Socialist Left faction of the Labor Party, he was Minister for Defence Support in the government of Bob Hawke from 1983. In 1984 he became Minister for Social Security and carried out various radical reforms to Australia's welfare system.[2] Howe appeared to face significant opposition within his electorate in 1988, when up to 60 members of the Greek Westgarth branch of the ALP defected to join the Australian Democrats. One of the defectors, tram-conductor George Gogas, contested Batman as a Democrat candidate in 1990, but polled only 12.9 per cent of the vote.[3] After the 1990 election Howe was appointed to the post of Minister for Community Services and Health. When Paul Keating resigned from Cabinet in 1991, Howe succeeded him as Deputy Prime Minister. He became Minister for Health, Housing and Community Services in the Keating government in December 1991, dropping the health part of the portfolio in 1993. In June 1995 he resigned as Deputy Prime Minister and was succeeded by Kim Beazley. He did not stand for re-election at the 1996 election. Following his parliamentary career, Howe has been appointed as an Associate Professor for Melbourne University and continues to work with social policy and related fields. He is a member of the Church of All Nations in Carlton, and active in the Uniting Church. A full biography in his own words can be found in the Proceedings of the Uniting Church Historical Society, Synod of Victoria and Tasmania, Vol. 21, No. 1 for June 2014.Howe at Williamstown dockyard with an exploded view of a frigate September 1984.Identification of Howe.rev brian leslie howe, deputy prime minister of australia -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - HANRO COLLECTION: PROMOTIONAL PHOTOGRAPHS, 1940's
Sir George Victor Lansell (1883-1959), businessman, politician and philanthropist, was born on 3 October 1883 in London, elder son of George Lansell, the Bendigo 'Quartz King', and his second wife Harriet Edith, née Bassford. George was educated at St Andrew's College, Bendigo, and Melbourne Church of England Grammar School. On 20 January 1910 at All Saints Pro-Cathedral, Bendigo, he married a skiing champion, Edith Florence Gwendoline Frew; they had three daughters. As a young man Lansell excelled in revolver shooting, boxing and swimming but his militia interests endured longest. First commissioned in the 8th Australian Infantry Regiment in 1904, he was a captain in 1909. In May 1916 he was commissioned captain in Bendigo's 38th Battalion, Australian Imperial Force. Entering the front line in France on 1 December he was wounded two days later and invalided back to Australia next March for discharge in August. After the war he rose in 1923 to major commanding the 38th Battalion, Australian Military Forces. Lieutenant-Colonel in 1927, he retired as honorary colonel in 1942 after having organized the north-west Victorian group of the Volunteer Defence Corps early in World War II. Lansell's major contribution was his service to returned soldiers. He was president of the Bendigo sub-branch of the Returned Sailors' and Soldiers' Imperial League of Australia for nearly thirty years. His work extended beyond grand gesture and he is remembered affectionately for his personal generosity to ex-servicemen and their dependants. Lansell was director of the powerful Sandhurst Trustees' Co., the Bendigo Mutual Permanent Land & Building Society and many other local companies. In 1926 he brought to Bendigo the overseas-based Hanro Knitting Mills (Hanro comes from the Swiss firm Handschin and Ronus which made high quality underwear and knitwear at Liestal, Switzerland) and the Australian Swiss Watch Co. Early in his business career he acquired the Bendigo Independent and amalgamated it with the Bendigo Advertiser in 1918. He had interests in the Riverine Herald, the Rochester Irrigator, the Stock and Station Journal and Central Victorian Broadcasters Ltd, and was a delegate to Empire press conferences in Canada (1920), England (1923) and Australia (1925).Lever arch folder containing Hanro black and white promotional photographs. 53 studio photographs of women's knitwear and lingerie 20.5cm x 25.2cm. 1 studio photograph of men's knitwear 19cm x 23.5cm. 2 x photo's 19cm x 23.3cm Photographer Reg Brock. 27 black and white photo's 15cm x 21cm of men's knitwear, womenswear and lingerie, were donated by Ann Peters.Reg Brock Studios Bendigo. Labels or stamps on back of photographs.business, retail, hanro promotional photographs, george victor lansell, bendigo hanro, ralph birrell collections -
 University of Melbourne, School of Chemistry
University of Melbourne, School of ChemistryCombustion Demonstration
John Macadam was a Scottish born analytical chemist, medical practitioner and politician. As a student he soon showed a flair for analytical chemistry, and later also studied medicine. He arrived in Melbourne in 1855 to take up an appointment as lecturer in chemistry and natural science at Scotch College, a position he held until 1865. In 1857 Ferdinand von Mueller named the Macadamia nut after him. He officiated as one of two umpires at one of the earliest recorded games of Australian rules football, between Scotch College and Melbourne Grammar in 1858. Macadam was appointed government analytical chemist in 1858 and health officer to the City of Melbourne in 1860. He represented Castlemaine in the Legislative Assembly between 1859 and 1864. Appointed secretary of the Royal Society of Victoria in 1860 and vice-president in 1863, he was also the secretary of the exploration committee of the Burke and Wills expedition. When the Medical School of the University of Melbourne opened in 1862 Macadam was appointed lecturer in chemistry. He was a skilled, popular and eloquent lecturer, learned and generous with his knowledge. Sadly, just three years later, and aged only 38, he died at sea on the way to give evidence at a murder trial in New Zealand, leaving his widow Elizabeth (n�e Clark), and a son. He was accompanied on that voyage by his assistant, the medical student John Drummond Kirkland, who later became the University?s first Professor of Chemistry. Born in Ireland, John Drummond Kirkland trained as a chemical analyst through apprenticeship in a medical laboratory in Dublin, before migrating to Australia in 1852 and moving to Melbourne in 1855. While still an undergraduate medical student at the University of Melbourne, he was appointed lecturer in chemistry following the sudden death of John Macadam in 1865. Due to the enthusiastic support of his fellow students this temporary role became a permanent appointment the following year. Kirkland continued his studies, graduating in medicine in 1873 and surgery in 1880. His son, John Booth Kirkland, was appointed as his assistant in 1878, later leading to accusations of nepotism. In 1882 John Drummond Kirkland became the University?s first professor of chemistry and metallurgy, continuing until his death in 1885. Today?s researchers use a high performance computing facility named ?Kirkland? after the first Professor of Chemistry at the University of Melbourne. Chemistry was still controlled by the medical school during Kirkland?s career, but became part of the science degree from 1886, along with the appointment of David Orme Masson as professor. Kirkland struggled for University funding to buy new apparatus. To compensate, he bought much from his own personal funds, including analytical chemistry equipment. Chemistry was first taught at Melbourne in the medical school, located in the area now occupied by Physics and the Ian Potter Museum of Art.Demonstration of combustion Mid 19th century, used by McCoy, MacAdam,and Kirkland -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMemorabilia - Horseshoe Case, 1906 – 1907
The horseshoes in this purpose-built display case were made by Thomas Alfred Chapman in 1906-1907. Chapman operated a blacksmith’s shop in Mortlake Rd, Purnim, about 15 mins drive from Warrnambool. Chapman made this horseshoe case especially for the 3rd Exhibition of Australian Manufacturers and Products, held in the Exhibition Building in Melbourne, which was organised and promoted by the Australian Natives Association (ANA). Reference is made to the horseshoe case in the Exhibition’s Souvenir Catalogue of 1907 on page 85, under the heading 'In the Machinery Section the following exhibits are also shown … 'CHAPMAN, T.A. , Woolsthorpe, via Warrnambool, Case of Horseshoes'. The Australian Natives’ Association (ANA) were a non-partisan and non-sectarian, friendly society founded in Melbourne, Australia in April 1871. It was set-up for the benefit of Australian-born white men, and membership was restricted exclusively to that group. Men of other races including the Chinese and Indigenous people were not allowed to join. The ANA had relatively progressive views on women (for the time) and attracted suffragists seeking support for their cause, and in 1894, the ANA advocated for women’s enfranchisement. Although, white women were only admitted as members from 1964. The organisation was most prominent in Victoria and sought to shape Australia’s national identity and was a training ground for businessmen, trade unionists and politicians including many of Australia’s early prime ministers such as Edmund Barton, Alfred Deakin, James Scullin and Francis Forde, and the first Australian-born governor-general, Isaac Isaacs, was a member. By 1910 it had developed into a nationwide association with real political and social influence, and members would participate in many activities. The ANA lobbied strongly for anti-Chinese legislation and were an ardent believer of colonial unification. Its mission and efforts are largely credited for the successful referendums that resulted in Federation of the six Australian colonies into a new nation, the association’s most important legacy. The ANA was also a supporter of trade protection, and were a staunch advocate of the first act of Australia's new parliament, the Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (cth) or commonly known as the White Australia Policy, which became one of the central pillars of Australian nationalism in the 20th-century. The ANA campaigned against the Australian Federal Government's new immigration policy after the Second World War (non-British immigration from southern and central Europe) in order to maintain a 'white Australia', and resisted changes when the Labor government during the 1970s fully dismantled and abandoned the White Australia Policy. The ANA merged with Manchester Unity Independent Order of Oddfellows, in 1993 to become Australian Unity Ltd. The display case of horseshoes changed hands several times, going from its maker Thomas Chapman to his mother then various other members of his family. The case was also displayed at the Lee Family’s butcher shop at 188 Liebig St Warrnambool, and in the Purnim Hotel during the Warrnambool May Races. In the late 1950s the horseshoe case went to Thomas’s son, Brian. He was a Master Farrier and completed his apprenticeship at Flemington Racecourse, and in Warrnambool he owned a blacksmith business at the Warrnambool Racecourse Grounds. Brian later operated a blacksmith’s at Flagstaff Hill, where his customers would bring their horses to be shod. Brian passed away in August 2017. The horseshoe case is significant as an example of trades in the early 20th century in Western Victoria, Australia. It is also significant as an example of horseshoes from the early 20th century. The horseshoe display case is also significant for its association with the Australian Exhibition of 1907, showcasing Australian produce and manufacturing to the world. The horseshoe display case is locally significant for its association with local families, essential businesses and community events. Display case of homemade horseshoes. Wooden case with glass front containing 16 horse shoes grouped in sets, each set with a label: Made 1906-1907 for Australian Exhibition of 1907 by Thomas Alfred Chapman of Warrnambool. The case contains (a) complete chrome set each of Trotting Shoes, Hunting Shoes and Racing Plates, and (b) one pair of Hind Polo Shoes and one pair of Front Aluminium Shoes. The wooden frame has gold lettering on each side proclaiming “Australian Natives Association, T.A. Chapman, horse shoer, Warrnambool” and is topped by a painted Australian coat of arms. Gold lettering on frame, in the order of top/bottom/ left/right “AUSTRALIAN.NATIVES.ASSOCIATION / T.A. CHAPMAN / Horse Shoer / Warrnambool”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, horseshoe display case 1906-1907, chromed set of trotting shoes 1906-1907, chrome set of hunting shoes 1906-1907, chrome set of racing plates 1906-1907, pair of hind polo shoes 1906-1907, pair of front aluminium shoes 1906-1907, australian exhibition 1907, australian natives association (ana), t.a. chapman horse shoer warrnambool, thomas alfred chapman, brian chapman, brian “snacks” chapman, blacksmith warrnambool, warrnambool may races, warrnambool racecourse, purnim hotel, lee family’s butcher shop warrnambool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Portrait, David Charles McArthur, Superintendent, Bank of Australasia 1867-1876, 1970s
The subject of this photograph, David Charteris McArthur was the founding manager of the Bank of Australasia in Port Phillip (Melbourne). McArthur was born in 1808 in Gloucester, England, and educated in Scotland. He worked for an insurance firm in Edinburgh where in 1835 he married Caroline nee Wright. McArthur and his family party sailed from the U.K. to arrive in Sydney in October 1835, where he joined the Bank of Australasia when it opened in Sydney in December. McArthur sailed to Melbourne in August 1838 with 3000 pounds in coins, protected by armed guards and two bulldogs, to open the Melbourne branch of the Bank of Australasia. The branch grew quickly, servicing both private and government customers. He opened many branches in the goldfields during the1850’s. In 1862 he was appointed as general inspector of branches. He spent time with the bank in New Zealand. On his return to Melbourne, at age 57, he was put in charge of the entire bank. McArthur lived in the hills of Heidelburg, Melbourne. He was the first chairman of Associated Banks and was advisor to politicians and merchants. He was retired in October 1876 by the London directors and given a free trip to London, an annuity and a seat on the bank’s Advisory Board. McArthur was active in the community, being a member of the Mechanics’ Institute, on the committee that advised Governor Hotham on the Colony’s finances, chairman of the Heidelburg Road Board, one of the original trustees of the Library of Victoria in 1853 and president of trustees of the Public Library, Museums and National Gallery of Victoria in 1880-83. He was also on many other community organisations. He died in his home “Charterisville” in East Ivanhoe in 1887. He and Caroline had no children. The Melbourne branch of Australia and New Zealand Bank has a portrait of McArthur in its boardroom. St John's Church, Heidelberg, commemorates him with a stained-glass window entitled 'King David'. The McArthur Gallery in the National Gallery of Victoria is also named after him. (David's brother, Donald, moved from Sydney to Melbourne in 1836 with the first government survey team.) ABOUT THE BANK OF AUSTRALASIA In 1836 the Bank of Australasia was established in London by Royal Charter. In 1951 the bank merged with the Union Bank of Australia, to form ANZ Bank Limited. In 1970 it merged with the English, Scottish and Australian Bank to become Australia and New Zealand Banking Group Limited. Since that time the ANZ has acquired other banks and introduced Internet banking and mobile banking. BANK OF AUSTRALASIA IN WARRNAMBOOL The Bank of Australasia first opened in Warrnambool in July 1854 in a building on Merri Street. The manager was Mr Samuel Hannaford. The bank then purchased and moved to a stone building on the corner of Timor and Gibson Streets, previously owned by Cramond and Dickson and almost opposite the Examiner’s office. In January 1957 Mr W.H. Palmer became the new manager and was there until November 1869. The bank then built its own building on the corner of Timor and Kepler Streets in 1859. Mr Basil Spence, the teller, was appointed acting manager in 1869 and Mr H.B. Chomley was the next appointed manager, in April 1873 and was still manager in 1886. The municipality of Warrnambool first banked with the Bank of Australasia from 1856 to April 1857. David Charteris McArthur was the founding manager of the Bank of Australasia. This photograph of him represents the beginnings of Warrnambool's commercial history, with the municipality using the Bank of Australasia as its bank from 1856-April 1857.Photograph; portrait of David Charteris McArthur. Heavily retouched black and white print in plain brown varnished frame, behind glass, with plaque on lower edge and inscription lower left corner.Lower left corner "A-H 1-9". Engraved on plaque "DAVID CHARTERS MCARTHUR \ SUPERINTENDENT \ BANK OF AUSTRALASIA \ 1867-1876"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, bank of australasia, david charteris mcarthur, superintendent bank of australasia, colonial commerce, manager bank of australasia melbourne, colonial bank, warrnambool bank of australasia, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, boa, union bank, australia & new zealand bank, anz bank, david charters mcarthur, d c mcarthur -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationImage, Justin McCarthy M.P., 1864
McCarthy, JUSTIN, Irish politician, journalist, novelist, and historian, b. at Cork, November 22, 1830; d. at Folkestone, England, June 24, 1912. He was the son of Michael McCarthy, and was educated at a private school in his native city. At the age of eighteen he obtained a position on the literary staff of the "Cork Examiner". In 1853 he went to Liverpool as a journalist; in 1860 became Parliamentary reporter of the London "Morning Star", which he edited later (1864-68). From 1868 till 1871 he lectured with great success throughout the United States of America and was one of the assistant editors of the New York "Independent". On his return to England he contributed frequently to the "Nineteenth Century", the "Fortnightly Review", and the "Contemporary Review", and for many years was leader writer for the London "Daily News". From 1879 till 1896 he was a member of the British Parliament, representing the Irish constituencies of County Longford, Derry City, and North Longford. In November, 1880, he joined the Irish Land League, which won so many victories for the Catholic peasantry; two years later he became chairman of the National Land and Labor League of Great Britain. In 1886 he revisited the United States. From 1890 till 1896 he was chairman of the Irish Parliamentary party in succession to Parnell, having previously been vice-chairman for many years. His courtesy and moderation won him the respect of all parties in Parliament. Though participating so actively in the political life of Ireland, McCarthy took more interest in letters than in politics. His first novel, "The Waterdale Neighbors", appeared in 1867, and was followed by about twenty others, many of which are still popular. Of these the chief are: "Dear Lady Disdain" (1875); "A Fair Saxon" (1873); "Miss Misanthrope" (1877) and "The Dictator" (1893). Other publications were: "Con Amore", a volume of essays (1868), and biographies of Sir Robert Peel (1891), Leo XIII (1896), and Gladstone (1897). McCarthy's popularity as a writer depends rather on his historical writings, which are always lucid, forceful, and wonderfully free from party spirit. Of these works the most important are: "History of our own Times" (7 vols., London, 1879-1905), dealing with the events from the year 1830 to the death of Queen Victoria and supplemented by "Reminiscences of an Irishman" (1899); "A short History of our own Times" (1888); "The Epoch of Reform, 1830-1850" (London, 1874); "History of the Four Georges" (4 vols., 1884-1901), of which vols. 3 and 4 were written in collaboration with his son, Justin Huntly McCarthy well-known as a novelist and play-writer; "Ireland and her Story" (1903); "Modern England" (1899); "Rome in Ireland" (1904). Failing health and old age could not induce McCarthy to lay down his pen, and even as late as November, 1911, he published his "Irish Recollections", describing with his wonted charm the events of his earlier life. He was an ardent advocate of Catholic rights, and, though he had been indifferent for many years, in his old age he returned to the practices of his religion. A.A. MACERLEAN [http://oce.catholic.com/index.php?title=Justin_McCarthy, accessed 3/12/2013]Image of a bearded man wearing glasses. He is Justin McCarthy, M.P.ballarat irish, justin mccarthy, cork
