Showing 597 items matching "1834-1838"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageClock, 1867-1870
Chauncey Jerome (1793–1868) was an American clock maker in the early to mid 19th century. He made a fortune selling his clocks, and his business grew quickly. Jerome was born in Canaan USA in 1793 son of a blacksmith and nail-maker. He began his career in Plymouth, making dials for long-case clocks where he learned all he could about clocks, particularly clock cases, and then went to New Jersey to make seven-foot cases for clocks mechanisms. In 1816 he went to work for Eli Terry making "Patent Shelf Clocks," learning how to make previously handmade cases using machinery. Deciding to go into business for himself, Jerome began to make cases, trading them to Terry for wooden movements. In 1822 Jerome moved his business to Bristol New Haven, opening a small shop with his brother Noble and began to produce a 30-hour and eight-day wooden clocks. By 1837 Jerome's company was selling more clocks than any of his competitors. A one-day wood-cased clock, which sold for six dollars had helped put the company on the map. A year later his company was selling that same clock for four dollars. The company also sold one line of clocks at a wholesale price of 75 cents and by 1841 the company was showing an annual profit of a whopping $35,000, primarily from the sale of its brass movements. In 1842 Jerome moved his clock-case manufacturing operation to St. John Street in New Haven. Three years later, following a fire that destroyed the Bristol plant, Jerome relocated the entire operation to Elm City factory. Enlarging the plant, the company soon became the largest industrial employer in the city, producing 150,000 clocks annually. In 1850 Jerome formed the Jerome Manufacturing Co. as a joint-stock company with Benedict & Burnham, brass manufacturers of Waterbury. In 1853 the company then became known as the New Haven Clock Co, producing 444,000 clocks and timepieces annually, then the largest clock maker in the world. Jerome's future should have been secure but in 1855 he bought out a failed Bridgeport clock company controlled by P.T. Barnum, which wiped him out financially, leaving the Jerome Manufacturing Co. bankrupt. Jerome never recovered from the loss. By his admission, he was a better inventor than a businessman. When Jerome went bankrupt in 1856 the New Haven Clock Company purchased the company. One of the primary benefits of Jerome purchasing New Haven in the first place was the good reputation of the Jerome brand and the network of companies that remained interested in selling its clocks. In England, Jerome & Co. Ltd. sold Jerome clocks for the New Haven company until 1904, when New Haven purchased the English firm outright. After his involvement with the New Haven Company in 1856, Jerome traveled from town to town, taking jobs where he could, often working for clock companies that had learned the business of clock making using Jerome's inventions. On returning to New Haven near the end of his life, he died, penniless, in 1868 at the age of 74. The company struggled on after Jerome's bankruptcy until after World War II, when the company endeavored to continue through disruptions caused by a takeover along with poor sales, finally having to fold its operations in 1960 a little more than 100 years after it had been founded. The item is significant as it is associated with Chauncey Jerome who had made a historic contribution to the clock making industry during the 19th century when he began to substitute brass mechanisms for wooden mechanisms in his clocks. This was said to be the greatest and most far-reaching contribution to the clock industry. Because of his discovery of stamping out clockwork gears rather than using castings, Jerome was producing the lowest-priced clocks in the world. That can only add to his significance as the major clock manufacture of the 19th century. Jerome may have made and lost, a fortune selling his clocks but was perhaps the most influential and creative person associated with the American clock business during the mid-19th century. Also, he had served his community as a legislator in 1834, a Presidential elector in 1852 and mayor of New Haven, Connecticut from 1854 to 1855.Eight day movement wall clock with Roman numerals, octagonal shaped rosewood veneered casing, hinged face with locking clip. Wound from front. Face has adjustment for Fast-to-Slow.Part paper label on back of case can just make out "Jerome" and "ight and One" probable meaning is "Eight and One Day" describing the movements operational time between winding the mechanism.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, clock maker, jerome & co, new haven, chauncey jerome, canaan -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, "Ripponlea", Hotham Street, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages.From Victorian Heritage Database citation for Rippon Lea H0614 https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/427(as at 23/10/2020) Rippon Lea was commenced in 1868 by Frederick Sargood, a most successful politician and merchant. He was born in England in 1834 and arrived in Melbourne in 1850. He soon joined his father's wholesale soft goods firm, spending some time as its manager on the goldfields. Sargood entered the Legislative Council in 1874. He was Victoria?s first Minister for Defence in 1883. Sir Frederick Sargood was created CMG. In 1885 and KCMG in 1890 as a reward for his contribution to public life. He died suddenly in 1903. Rippon Lea was designed by the leading firm of architects, Reed and Barnes. Joseph Reed had travelled in Europe in 1863, including northern Italy. When he returned he introduced the use of polychromy. While not the first examples, Rippon Lea and the Independent Church in Collins Street were the best and set a fashion which became a distinctly Melbourne style, particularly used for houses and churches. Its popularity was possible because of the new availability of different coloured bricks. Reed's fine Lombardic Romanesque details soon became debased by others. As Sargood's family grew and his fortunes prospered, Rippon Lea was extended to include 33 rooms - a complete mansion. The cast iron porte cochere and the northern conservatory were added in 1897. The architects were Taylor and Fitts. The ballroom was added in 1882 and remodelled in 1889. Many alterations have changed the interior and exterior during the ownerships of Benjamin Nathan and later his daughter Mrs Louisa Jones in the 1930s and are in their own right of significance. Sir Thomas Bent owned the property from 1903 until 1911 but never lived there. He subdivided much of the land. The original garden dates from about 1868, and it seems that William Guilfoyle of the Botanic Gardens was involved. It was redesigned in a more natural style in the 1880s by Sargood and his head gardener, Adam Anderson. The lake, waterfalls, fernery, hill and grotto are balanced by mighty deciduous trees and conifers. These are interspersed with, but never dominated by Australian species such as eucalyptus and other exotics. The sinuous drive with its carefully prepared approach to the house is notable. The original vegetable gardens, orchard and outer paddocks no longer survive. The shade house is important as the largest known in Australia and possibly the world. Its curved plan and form of construction are particularly notable. It was built about 1884.Page 94 of Photograph Album with four photographs (three landscape and one portrait) of Ripponlea - stables, lookout and neighbouring cottages.Handwritten: "Ripponlea" Hotham Street [top right] / Neg 256 Dec 1972 STABLES [under top left photo] / Neg 248 Dec 1972 LOOKOUT [under top right photo] / Neg 254 Dec 1972 / COTTAGES WILLOW STREET [under bottom left photo] / Neg 259 Dec 1972 STABLES [under bottom right photo] / 94 [bottom right]trevor hart, elsternwick, mansion, hotham street, frederick sargood, reed and barnes, 1860's, 1890's, 1880's, benjamin nathan, nathan, louisa jones, thomas bent, sir thomas bent, william guilfoyle, guilfoyle, adam anderson, ripponlea, victorian, sir frederick sargood, architects, bricks, polychrome bricks, taylor and fitts, stables, lookouts, cottages, outbuildings, rippon lea -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Ripponlea, 192 Hotham Street, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages.From Victorian Heritage Database citation for Rippon Lea H0614 https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/427(as at 23/10/2020) Rippon Lea was commenced in 1868 by Frederick Sargood, a most successful politician and merchant. He was born in England in 1834 and arrived in Melbourne in 1850. He soon joined his father's wholesale soft goods firm, spending some time as its manager on the goldfields. Sargood entered the Legislative Council in 1874. He was Victoria's first Minister for Defence in 1883. Sir Frederick Sargood was created CMG. In 1885 and KCMG in 1890 as a reward for his contribution to public life. He died suddenly in 1903. Rippon Lea was designed by the leading firm of architects, Reed and Barnes. Joseph Reed had travelled in Europe in 1863, including northern Italy. When he returned he introduced the use of polychromy. While not the first examples, Rippon Lea and the Independent Church in Collins Street were the best and set a fashion which became a distinctly Melbourne style, particularly used for houses and churches. Its popularity was possible because of the new availability of different coloured bricks. Reed's fine Lombardic Romanesque details soon became debased by others. As Sargood's family grew and his fortunes prospered, Rippon Lea was extended to include 33 rooms - a complete mansion. The cast iron porte cochere and the northern conservatory were added in 1897. The architects were Taylor and Fitts. The ballroom was added in 1882 and remodelled in 1889. Many alterations have changed the interior and exterior during the ownerships of Benjamin Nathan and later his daughter Mrs Louisa Jones in the 1930s and are in their own right of significance. Sir Thomas Bent owned the property from 1903 until 1911 but never lived there. He subdivided much of the land. The original garden dates from about 1868, and it seems that William Guilfoyle of the Botanic Gardens was involved. It was redesigned in a more natural style in the 1880s by Sargood and his head gardener, Adam Anderson. The lake, waterfalls, fernery, hill and grotto are balanced by mighty deciduous trees and conifers. These are interspersed with, but never dominated by Australian species such as eucalyptus and other exotics. The sinuous drive with its carefully prepared approach to the house is notable. The original vegetable gardens, orchard and outer paddocks no longer survive. The shade house is important as the largest known in Australia and possibly the world. Its curved plan and form of construction are particularly notable. It was built about 1884.Page 90 of Photograph Album with five photographs (one landscape and 4 portrait) of Ripponlea - two different views of the front entrance to the mansion, one of the front gates and two different views of the main residence.Handwritten: "Ripponlea" 192 Hotham Street [top right] / North [under top left photo] / Neg 255 Dec 1972 MAIN DRIVE [under bottom left photo] / Neg 238 8 OCT 1966 [under middle right photo] / 88 [bottom right]trevor hart, elsternwick, mansion, hotham street, frederick sargood, reed and barnes, cast iron porte cochere, conservatory, 1860's, 1890's, ballroom, 1880's, benjamin nathan, louisa jones, thomas bent, sir thomas bent, william guilfoyle, adam anderson, lake, grotto, shade house, portico, ripponlea, victorian, sir frederick sargood, architects, polychrome bricks, lombardic romanesque architectural style, rippon lea, taylor and fitts, land subdivisions, gardens, drives, vegetable gardens, orchards -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Ripponlea, 192 Hotham Street, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages.From Victorian Heritage Database citation for Rippon Lea H0614 https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/427(as at 23/10/2020) Rippon Lea was commenced in 1868 by Frederick Sargood, a most successful politician and merchant. He was born in England in 1834 and arrived in Melbourne in 1850. He soon joined his father's wholesale soft goods firm, spending some time as its manager on the goldfields. Sargood entered the Legislative Council in 1874. He was Victoria?s first Minister for Defence in 1883. Sir Frederick Sargood was created CMG. In 1885 and KCMG in 1890 as a reward for his contribution to public life. He died suddenly in 1903. Rippon Lea was designed by the leading firm of architects, Reed and Barnes. Joseph Reed had travelled in Europe in 1863, including northern Italy. When he returned he introduced the use of polychromy. While not the first examples, Rippon Lea and the Independent Church in Collins Street were the best and set a fashion which became a distinctly Melbourne style, particularly used for houses and churches. Its popularity was possible because of the new availability of different coloured bricks. Reed's fine Lombardic Romanesque details soon became debased by others. As Sargood's family grew and his fortunes prospered, Rippon Lea was extended to include 33 rooms - a complete mansion. The cast iron porte cochere and the northern conservatory were added in 1897. The architects were Taylor and Fitts. The ballroom was added in 1882 and remodelled in 1889. Many alterations have changed the interior and exterior during the ownerships of Benjamin Nathan and later his daughter Mrs Louisa Jones in the 1930s and are in their own right of significance. Sir Thomas Bent owned the property from 1903 until 1911 but never lived there. He subdivided much of the land. The original garden dates from about 1868, and it seems that William Guilfoyle of the Botanic Gardens was involved. It was redesigned in a more natural style in the 1880s by Sargood and his head gardener, Adam Anderson. The lake, waterfalls, fernery, hill and grotto are balanced by mighty deciduous trees and conifers. These are interspersed with, but never dominated by Australian species such as eucalyptus and other exotics. The sinuous drive with its carefully prepared approach to the house is notable. The original vegetable gardens, orchard and outer paddocks no longer survive. The shade house is important as the largest known in Australia and possibly the world. Its curved plan and form of construction are particularly notable. It was built about 1884.Page 91 of Photograph Album with four photographs (two portrait and two landscape) of various external views of Ripponlea.Handwritten: SOUTH [under top left photo] / SOUTH [under top right photo] / WEST [under bottom left photo] / 91 [bottom left]trevor hart, elsternwick, mansion, hotham street, frederick sargood, reed and barnes, cast iron porte cochere, conservatory, 1860's, 1890's, ballroom, 1880's, benjamin nathan, louisa jones, thomas bent, sir thomas bent, william guilfoyle, adam anderson, lake, grotto, shade house, portico, ripponlea, victorian, sir frederick sargood, architects, taylor and fitts, rippon lea, polychrome bricks, lombardic romanesque style -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Ripponlea, Hotham Street, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages.From Victorian Heritage Database citation for Rippon Lea H0614 https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/427(as at 23/10/2020) Rippon Lea was commenced in 1868 by Frederick Sargood, a most successful politician and merchant. He was born in England in 1834 and arrived in Melbourne in 1850. He soon joined his father's wholesale soft goods firm, spending some time as its manager on the goldfields. Sargood entered the Legislative Council in 1874. He was Victoria?s first Minister for Defence in 1883. Sir Frederick Sargood was created CMG. In 1885 and KCMG in 1890 as a reward for his contribution to public life. He died suddenly in 1903. Rippon Lea was designed by the leading firm of architects, Reed and Barnes. Joseph Reed had travelled in Europe in 1863, including northern Italy. When he returned he introduced the use of polychromy. While not the first examples, Rippon Lea and the Independent Church in Collins Street were the best and set a fashion which became a distinctly Melbourne style, particularly used for houses and churches. Its popularity was possible because of the new availability of different coloured bricks. Reed's fine Lombardic Romanesque details soon became debased by others. As Sargood's family grew and his fortunes prospered, Rippon Lea was extended to include 33 rooms - a complete mansion. The cast iron porte cochere and the northern conservatory were added in 1897. The architects were Taylor and Fitts. The ballroom was added in 1882 and remodelled in 1889. Many alterations have changed the interior and exterior during the ownerships of Benjamin Nathan and later his daughter Mrs Louisa Jones in the 1930s and are in their own right of significance. Sir Thomas Bent owned the property from 1903 until 1911 but never lived there. He subdivided much of the land. The original garden dates from about 1868, and it seems that William Guilfoyle of the Botanic Gardens was involved. It was redesigned in a more natural style in the 1880s by Sargood and his head gardener, Adam Anderson. The lake, waterfalls, fernery, hill and grotto are balanced by mighty deciduous trees and conifers. These are interspersed with, but never dominated by Australian species such as eucalyptus and other exotics. The sinuous drive with its carefully prepared approach to the house is notable. The original vegetable gardens, orchard and outer paddocks no longer survive. The shade house is important as the largest known in Australia and possibly the world. Its curved plan and form of construction are particularly notable. It was built about 1884.Page 92 of Photograph Album with four photographs (three landscape and one portrait) of Ripponlea - views of entrance and left front of mansion.Handwritten: "Ripponlea" Hotham Street [top right] / Neg 245 Dec 1972 [under top left photo] / Neg 246 Dec 1972 [under bottom left photo] / Neg 247 Dec 1972 [under bottom right photo] / 92 [bottom right]trevor hart, elsternwick, mansion, hotham street, frederick sargood, reed and barnes, lombardic, romanesque, cast iron porte cochere, conservatory, 1860's, 1890's, ballroom, 1880's, benjamin nathan, louisa jones, thomas bent, sir thomas bent, william guilfoyle, adam anderson, lake, grotto, shade house, portico, ripponlea, victorian, sir frederick sargood, architects, polychrome bricks, lombardic romanesque style, rippon lea, entrances -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Ripponlea, Hotham Street, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages.From Victorian Heritage Database citation for Rippon Lea H0614 https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/427(as at 23/10/2020) Rippon Lea was commenced in 1868 by Frederick Sargood, a most successful politician and merchant. He was born in England in 1834 and arrived in Melbourne in 1850. He soon joined his father's wholesale soft goods firm, spending some time as its manager on the goldfields. Sargood entered the Legislative Council in 1874. He was Victoria?s first Minister for Defence in 1883. Sir Frederick Sargood was created CMG. In 1885 and KCMG in 1890 as a reward for his contribution to public life. He died suddenly in 1903. Rippon Lea was designed by the leading firm of architects, Reed and Barnes. Joseph Reed had travelled in Europe in 1863, including northern Italy. When he returned he introduced the use of polychromy. While not the first examples, Rippon Lea and the Independent Church in Collins Street were the best and set a fashion which became a distinctly Melbourne style, particularly used for houses and churches. Its popularity was possible because of the new availability of different coloured bricks. Reed's fine Lombardic Romanesque details soon became debased by others. As Sargood's family grew and his fortunes prospered, Rippon Lea was extended to include 33 rooms - a complete mansion. The cast iron porte cochere and the northern conservatory were added in 1897. The architects were Taylor and Fitts. The ballroom was added in 1882 and remodelled in 1889. Many alterations have changed the interior and exterior during the ownerships of Benjamin Nathan and later his daughter Mrs Louisa Jones in the 1930s and are in their own right of significance. Sir Thomas Bent owned the property from 1903 until 1911 but never lived there. He subdivided much of the land. The original garden dates from about 1868, and it seems that William Guilfoyle of the Botanic Gardens was involved. It was redesigned in a more natural style in the 1880s by Sargood and his head gardener, Adam Anderson. The lake, waterfalls, fernery, hill and grotto are balanced by mighty deciduous trees and conifers. These are interspersed with, but never dominated by Australian species such as eucalyptus and other exotics. The sinuous drive with its carefully prepared approach to the house is notable. The original vegetable gardens, orchard and outer paddocks no longer survive. The shade house is important as the largest known in Australia and possibly the world. Its curved plan and form of construction are particularly notable. It was built about 1884.Page 93 of Photograph Album with four photographs (two landscape and two portrait) of Ripponlea - lake and gardens.Handwritten: Neg 239 Dec 1973 LAKE [under top left photo] / Neg 242 Dec 1973 FERN HOUSE [under top right photo] / Neg 243 Dec 1972 FERN HOUSE [under bottom left photo] / Neg 241 Dec 1972 LAKE [under bottom right photo] / 93 [bottom left]trevor hart, elsternwick, mansion, hotham street, frederick sargood, sargood, reed and barnes, 1860's, 1890's, 1880's, benjamin nathan, nathan, louisa jones, thomas bent, sir thomas bent, william guilfoyle, adam anderson, lake, grotto, shade house, portico, ripponlea, victorian, sir frederick sargood, architects, taylor and fitts, rippon lea, gardens, ferns, bridges, walking trails -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageClock, 1867-1870
Chauncey Jerome (1793–1868) was an American clock maker in the early to mid 19th century. He made a fortune selling his clocks, and his business grew quickly. Jerome was born in Canaan USA in 1793 son of a blacksmith and nail-maker. He began his career in Plymouth, making dials for long-case clocks where he learned all he could about clocks, particularly clock cases, and then went to New Jersey to make seven-foot cases for clocks mechanisms. In 1816 he went to work for Eli Terry making "Patent Shelf Clocks," learning how to make previously handmade cases using machinery. Deciding to go into business for himself, Jerome began to make cases, trading them to Terry for wooden movements. In 1822 Jerome moved his business to Bristol New Haven, opening a small shop with his brother Noble and began to produce a 30-hour and eight-day wooden clocks. By 1837 Jerome's company was selling more clocks than any of his competitors. A one-day wood-cased clock, which sold for six dollars had helped put the company on the map. A year later his company was selling that same clock for four dollars. The company also sold one line of clocks at a wholesale price of 75 cents and by 1841 the company was showing an annual profit of a whopping $35,000, primarily from the sale of its brass movements. In 1842 Jerome moved his clock-case manufacturing operation to St. John Street in New Haven. Three years later, following a fire that destroyed the Bristol plant, Jerome relocated the entire operation to Elm City factory. Enlarging the plant, the company soon became the largest industrial employer in the city, producing 150,000 clocks annually. In 1850 Jerome formed the Jerome Manufacturing Co. as a joint-stock company with Benedict & Burnham, brass manufacturers of Waterbury. In 1853 the company then became known as the New Haven Clock Co, producing 444,000 clocks and timepieces annually, then the largest clock maker in the world. Jerome's future should have been secure but in 1855 he bought out a failed Bridgeport clock company controlled by P.T. Barnum, which wiped him out financially, leaving the Jerome Manufacturing Co. bankrupt. Jerome never recovered from the loss. By his admission, he was a better inventor than a businessman. When Jerome went bankrupt in 1856 the New Haven Clock Company purchased the company. One of the primary benefits of Jerome purchasing New Haven in the first place was the good reputation of the Jerome brand and the network of companies that remained interested in selling its clocks. In England, Jerome & Co. Ltd. sold Jerome clocks for the New Haven company until 1904, when New Haven purchased the English firm outright. After his involvement with the New Haven Company in 1856, Jerome traveled from town to town, taking jobs where he could, often working for clock companies that had learned the business of clock making using Jerome's inventions. On returning to New Haven near the end of his life, he died, penniless, in 1868 at the age of 74. The company struggled on after Jerome's bankruptcy until after World War II, when the company endeavored to continue through disruptions caused by a takeover along with poor sales, finally having to fold its operations in 1960 a little more than 100 years after it had been founded. The item is significant as it is associated with Chauncey Jerome who had made a historic contribution to the clock making industry during the 19th century when he began to substitute brass mechanisms for wooden mechanisms in his clocks. This was said to be the greatest and most far-reaching contribution to the clock industry. Because of his discovery of stamping out clockwork gears rather than using castings, Jerome was producing the lowest-priced clocks in the world. That can only add to his significance as the major clock manufacture of the 19th century. Jerome may have made and lost, a fortune selling his clocks but was perhaps the most influential and creative person associated with the American clock business during the mid-19th century. Also, he had served his community as a legislator in 1834, a Presidential elector in 1852 and mayor of New Haven, Connecticut from 1854 to 1855.Clock, marine, in octagonal rosewood veneer case. Roman numerals to dial, has a seconds dial. 2 key-winding holes slow-to-Fast adjustment pin through dial. Small lever in lower edge of case activates a chime. "8 day, 8 inch, Lever Striking escarpment " Paper label on the back of the clock "Jerome & Co, New Haven, Conn" "Manufacturers of every variety of Office and Home Clocks and Time Pieces".flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, clock, jerome & co, new haven, clock maker, chauncey jerome -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionNewspaper, Ballarat Courier, Ballarat 150 years: Supplement to the Ballarat Courier, 1988, 17 March 1988
Collection of photographs and articles telling the history of Ballarat from the 1800sNewspaper - tabloid1838 pastoral period, first settlers, anderson family, ballarat pioneers, aborigines, goldfields, eureka, school of mines, technical school, ballarat clubs, victorian city -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Book, Henry Field Gurner, Chronicle of Port Phillip, now the colony of Victoria, from 1770 to 1840, 1876
52ppnon-fictionport phillip bay region vic, victoria history 1834-1851 -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumBooklet, Debutantes, 1938
List of names of debutantes presented to Miss Pearl Maskell, Military ball 4 July 1938.Pale blue cover, black lettering, wood threaded at spine.debutants, military ball, miss pearl maskell, 1838 debutant ball -
 Nillumbik Shire Council
Nillumbik Shire CouncilSculpture: Anthony PRYOR (b.1951- d.1991 Melb, AUS), Paretaio, 1985
In the early 1970s, Arthur Boyd bought and restored a large, two-storey traditional farmhouse called Il Paretaio. Situated on the crest of a hill and surrounded by fields and olive groves, it is five kilometres from the village of Palaia in the province of Pisa, Tuscany. Boyd established this farmhouse as a residency programme, (which was later managed by the Australia Council). The residency program ended in 1990. Anthony Pryor undertook an Australia Council residency at Paretaio in 1984. This work is one in a series made during his time there. This work was entered into the Shire of Eltham Art Award in 1985.Pryor is an artist of national significance. This work is an example of his series of 'boxes' made principally for his own pleasure and often swapped with artists and other friends as soon as they were finished. The 'box' series was part inspired by Japanese techniques of wooden construction. Pryor first visited Japan in 1975 and was immediately drawn to Japanese methods of working with stone and wood. Many of these boxes are based upon the principles of the Japanese Zen Buddhist monk Sengai Gibon (1750-1838). This work relates to Sengai's famous hanging scroll Circle, Triangle and Square in which the circle can be read to stand for the cosmos, the square for the individual, and the triangle for aspiration. A heavy, box-like (cube) structure created from huon pine, with bronze, brass and stone elements. Within the cube is an eastern inspired, rear lattice wall in combination with bronze domestic fittings, and symbols (cube, pyramid and circle). Metal lightning, clouds and wooden rainbow hover over an asymmetrical bronze bed floating within the cube. A chair leans and a tilting ladder reaches towards the sky. Stamped into wood: lower right 'ANTHONY PRYOR PARETAIO'huon pine, pryor, brass, bronze, stone, cube, paretaio, italy, eastern, japan, sengai gibon, symbols, zen buddhism, sculpture, personal -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBooklet, Boys, Robert Douglass, Australian History : Summary of historical events from 1768
Contents: James Cook; Arthur Phillip; John Pascoe Fawkner; The Sydney Cove; George Bass; Tobias Furneaux; John Hunter; Matthew Flinders and George Bass; John Batman; James Grant; John Murray; Discovery of Port Phillip Bay; Proposed Settlement at Port Phillip; Matthew Flinders; Nicolas Baudin and Emmanuel Hamelin; Charles Robbins; Charles Grimes; The Settlement at Sullivan Bay, Sorrento; General Orders; Garrison Orders; Some Events at Sullivan Bay; Western Port; Edward Henty; Sealing; The Geordy; John Oxley; Hamilton Hume and William Hilton Hovell; The Settlement at Western Port; Port Fairy and Portland Bay; Charles Sturt; The Lively; Portland Bay and the Hentys;36 p. ; footnotes; 24 cm.Contents: James Cook; Arthur Phillip; John Pascoe Fawkner; The Sydney Cove; George Bass; Tobias Furneaux; John Hunter; Matthew Flinders and George Bass; John Batman; James Grant; John Murray; Discovery of Port Phillip Bay; Proposed Settlement at Port Phillip; Matthew Flinders; Nicolas Baudin and Emmanuel Hamelin; Charles Robbins; Charles Grimes; The Settlement at Sullivan Bay, Sorrento; General Orders; Garrison Orders; Some Events at Sullivan Bay; Western Port; Edward Henty; Sealing; The Geordy; John Oxley; Hamilton Hume and William Hilton Hovell; The Settlement at Western Port; Port Fairy and Portland Bay; Charles Sturt; The Lively; Portland Bay and the Hentys; australia-history-summary 1768-1834, australia-discovery and exploration-summary, port phillip-settlement p.17-35 -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBook, Batman, John (See Victoriana series), The Settlement at Port Phillip, 1835, 1983
John Batman was born in New South Wales in 1801. With his brother, Henry, he moved to Van Diemen's Land in 1821. In 1824, John received a grant of 600 acres near Ben Lomond and in 1828 he married Eliza Thompson. Batman, with his friend J.H. Wedge and J.T. Gellibrand, determined on an expedition into New Holland. Motivated by Hume and Hovell's discoveries they applied for a grant of land at Western Port. This was refused, but in 1834 the ideas of the Port Phillip Association was discussed...56 p. : 1 folded map. ; 21 cm.John Batman was born in New South Wales in 1801. With his brother, Henry, he moved to Van Diemen's Land in 1821. In 1824, John received a grant of 600 acres near Ben Lomond and in 1828 he married Eliza Thompson. Batman, with his friend J.H. Wedge and J.T. Gellibrand, determined on an expedition into New Holland. Motivated by Hume and Hovell's discoveries they applied for a grant of land at Western Port. This was refused, but in 1834 the ideas of the Port Phillip Association was discussed...batman, john, 1801-1839. | victoria. settlement, 1835. batman, john, 1801-1839. correspondence, diaries, etc.. | pioneers -- victoria -- correspondence. | victoria -- history -- 1834-1851 -- sources. -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBook, Bassett, Marnie, The Hentys : an Australian colonial tapestry, 1962
This book tells the remarkable story of a family who left England to settle in Australia in 1829 and 1831. The Henty family is well known in all ?ustralianStates, particularly in Victoria, Western Australia and Tasmania.pp.578; bibliography; Table; index; plates; maps; This book tells the remarkable story of a family who left England to settle in Australia in 1829 and 1831. The Henty family is well known in all ?ustralianStates, particularly in Victoria, Western Australia and Tasmania.henty family. | pioneers -- australia -- biography. | frontier and pioneer life -- australia. | western australia -- history -- to 1829. | victoria -- history -- 1834-1851. -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBook, Bride, Thomas Francis, Letters from Victorian pioneers : being a series of papers on the early occupation of the colony, the Aborigines, etc., addressed by Victorian pioneers to His Excellency Charles Joseph La Trobe, Esq., Lieutenant-Governor of the colony of Victoria, 1899
The letters record events which will recall to many persons still living old Vctorian memories, and will have a great value for the future historian of Victoria, as narrating the experiences of actual movers in the early scenes of our colonization, while they will also possess interest as incidental contributions to the biographies of the men who half a century ago beagan to encounter the hardships and perils which beset the pioneer in every part of this continent. These papers also contain interesting contributions to our knowldge of the aborigines-their languages, customs , and conflicts with the white men; and although some of the incdents narrated have found their way into print before, they are now for the first time given in their entirety to the public.xiii, 325 p. : figs., map. index; Barabool dialect list; names of the tribe, about 1841-43; ; 22 cThe letters record events which will recall to many persons still living old Vctorian memories, and will have a great value for the future historian of Victoria, as narrating the experiences of actual movers in the early scenes of our colonization, while they will also possess interest as incidental contributions to the biographies of the men who half a century ago beagan to encounter the hardships and perils which beset the pioneer in every part of this continent. These papers also contain interesting contributions to our knowldge of the aborigines-their languages, customs , and conflicts with the white men; and although some of the incdents narrated have found their way into print before, they are now for the first time given in their entirety to the public. frontier and pioneer life -- victoria. | victoria -- history -- 1834-1900 -- sources. -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBook, C. E. Sayers (Original edition edited by Bride, Thomas Francis), Letters from Victorian pioneers : a series of papers on the early occupation of the colony, the Aborigines, etc. addressed by Victorian pioneers to His Excellency Charles Joseph La Trobe, Esq., Lieutenant-Governor of the Colony of Victoria, 1983
Brief notes on the contributors and incidents have been included in this edition although the above-mentioned items have been left out, some marginal notes made by Governor La Trobe have been dealt with in the footnotes. "From the original edition edited for the Trustees of the Public Library by Thomas Francis Bride'. Previously published: Melbourne : Heinemann, 1969. Originally published: Melbourne : Government Printer for the Trustees of the Public Library, Museums and National Gallery of Victoria, 1898.xiv, 455 p., 31 p. of plates : map ; 26 cm.Brief notes on the contributors and incidents have been included in this edition although the above-mentioned items have been left out, some marginal notes made by Governor La Trobe have been dealt with in the footnotes. "From the original edition edited for the Trustees of the Public Library by Thomas Francis Bride'. Previously published: Melbourne : Heinemann, 1969. Originally published: Melbourne : Government Printer for the Trustees of the Public Library, Museums and National Gallery of Victoria, 1898.pioneering, 1836-1854. victoria. correspondence, diaries, etc. | victoria. description & travel, 1836-1854. correspondence, diaries, etc. | frontier and pioneer life -- victoria. | victoria -- history -- 1834-1900 -- sources. | victoria -- description and travel -- 1851-1900. -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBook, Barrett, Charles, White blackfellows : the strange adventures of Europeans who lived among savages, 1948
Stories of William Buckley (1835) - Victoria; Sammy Cox or Samuel Emanuel Jervis (1789) - Tasmania; James Murrells or Jemmy Morrill (1846) - Qld.; James Davis called Duramboi &? Wandi Bracefield or Bracefell (1826) - Wide Bay, Qld.; Mrs. Fraser (1835) - Qld. on the Stirling Castle; wreck of the Charles Eaton, survivors were John Ireland and William Doyley (1834) - Murray Is.; Thomas Pamphlet, Richard Parsons, John Finnegan (1823) Moreton Bay; William Jackman (1836) - Great Australian Bight; Barbara Thomson (1848) - Cape York; Chapter on Aborigines and bushrangers.xvi, 261 p., [23] p. of plates : ill., maps, ports. ; 22 cm.Stories of William Buckley (1835) - Victoria; Sammy Cox or Samuel Emanuel Jervis (1789) - Tasmania; James Murrells or Jemmy Morrill (1846) - Qld.; James Davis called Duramboi &? Wandi Bracefield or Bracefell (1826) - Wide Bay, Qld.; Mrs. Fraser (1835) - Qld. on the Stirling Castle; wreck of the Charles Eaton, survivors were John Ireland and William Doyley (1834) - Murray Is.; Thomas Pamphlet, Richard Parsons, John Finnegan (1823) Moreton Bay; William Jackman (1836) - Great Australian Bight; Barbara Thomson (1848) - Cape York; Chapter on Aborigines and bushrangers.wilderness survival -- australia. | aboriginal australians -- social life and customs. | australia -- history -- 1788-1851. -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBook, Bonwick, James, Port Phillip settlement, 1883
Contents: Discovery; Mr. Grimes round the Bay, 1803; Settlement of 1803; The settlement of 1826; Hume and Hovell's overland journey; The Western Port settlement; Captain Sturt on the Murray; Portland Bay settlement in 1834; Major Mitchell's discoveries in Australia Felix; Life of John Batman; Batman's journal and report; The wild white man; The surveyor's note-book and report; Life of Mr. Fawkner before 1835; Fawkner on the Yarra Yarra; Official correspondence; The Port Phillip Association; Official recognition of trespassers; First Government of Port Phillip; Mr Gellibrand lost in the bush; The Governor's visit to the Yarra; Melbourne and its land sale; The stock question; Mr Mackillop's narrative; Progress of the settlement; The early Melbourne press; Discovery of Gipps Land; The Black Question; Narratives of Old Hands; Causes of emigration in 1835; An Overland journeyx, 537 pages, [36] leaves of plates (some folded.) illustrations (1 colour), facsimiles, portraits ; 23 cm.Contents: Discovery; Mr. Grimes round the Bay, 1803; Settlement of 1803; The settlement of 1826; Hume and Hovell's overland journey; The Western Port settlement; Captain Sturt on the Murray; Portland Bay settlement in 1834; Major Mitchell's discoveries in Australia Felix; Life of John Batman; Batman's journal and report; The wild white man; The surveyor's note-book and report; Life of Mr. Fawkner before 1835; Fawkner on the Yarra Yarra; Official correspondence; The Port Phillip Association; Official recognition of trespassers; First Government of Port Phillip; Mr Gellibrand lost in the bush; The Governor's visit to the Yarra; Melbourne and its land sale; The stock question; Mr Mackillop's narrative; Progress of the settlement; The early Melbourne press; Discovery of Gipps Land; The Black Question; Narratives of Old Hands; Causes of emigration in 1835; An Overland journeymelbourne (vic.) -- history -- to 1834. | melbourne (vic.) -- history -- 1834-1851. | port phillip bay region (vic.) -- history. -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustDocument - Printed Sheets, Batey, Isaac, The Aboriginals - transcript of the handwritten memoirs of Isaac Batey
This memoir contains observations of the Aboriginal people in the Sunbury area mainly. From 1844 onwards this young boy has recounted memories of his life, this section deals with Aboriginals. Although the language and observations may offend some people they are also a reflection of the attitudes of his times, and give an indication of the settlers' reactions to the inhabitants of a new land. Recorded in 1909.17 P.;This memoir contains observations of the Aboriginal people in the Sunbury area mainly. From 1844 onwards this young boy has recounted memories of his life, this section deals with Aboriginals. Although the language and observations may offend some people they are also a reflection of the attitudes of his times, and give an indication of the settlers' reactions to the inhabitants of a new land. Recorded in 1909.batey, isaac b. 1838., sunbury - red stone hill - ?boriginals, history., aboriginals - woiworong - hunting; possum skin rug making; baskets; cooking ovens; death-customs; myrnong. -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBook, Bonwick, James, Discovery and Settlement of Port Phillip; being a history of the country now called Victoria, up to the arrival of Mr. Superintendent Latrobe, in October, 1839 by James Bonwick; revised, at request, by W. Westgarth, 1856
Contents: Discovery of Port Phillip; First Settlement of Port Phillip; Abandonment of the Colony of Port Phillip; Further discoveries in the Country; Hume and Hovell's Overland Trip; Settlement of Western Port; Captain Sturt on the Murray; Major Mitchell's Australia Felix; The Successful Settlement of Port Phillip; Batman and Gellibrand's Application; Settlement of Portland Bay; Life of Batman; Batman's visit to Port Phillip; Fawkner's Yarra Settlement; Mr. Wedge's Narrative; William Buckley; The Association and Government; Progress of the Settlement; Flocks and Flock-masters; Government; Stewart, Simpson, Lonsdale, Latrobe; The Land and Land Sales; Law, Police and Port; Commerce, Trade and Shipping; Melbourne and Geelong; Hotels and Licences; Amusements; Rise and Progress of the Port Phillip Press; Religion in Port Phillip.142 p. : 1 fold-out map. ; 21 cm.Contents: Discovery of Port Phillip; First Settlement of Port Phillip; Abandonment of the Colony of Port Phillip; Further discoveries in the Country; Hume and Hovell's Overland Trip; Settlement of Western Port; Captain Sturt on the Murray; Major Mitchell's Australia Felix; The Successful Settlement of Port Phillip; Batman and Gellibrand's Application; Settlement of Portland Bay; Life of Batman; Batman's visit to Port Phillip; Fawkner's Yarra Settlement; Mr. Wedge's Narrative; William Buckley; The Association and Government; Progress of the Settlement; Flocks and Flock-masters; Government; Stewart, Simpson, Lonsdale, Latrobe; The Land and Land Sales; Law, Police and Port; Commerce, Trade and Shipping; Melbourne and Geelong; Hotels and Licences; Amusements; Rise and Progress of the Port Phillip Press; Religion in Port Phillip.victoria -- history -- to 1834. | victoria -- history -- 1834-1851. | melbourne (vic.) -- history -- to 1834. | melbourne (vic.) -- history -- 1834-1851. -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBook, Byrt, Pauline, The Thomas papers in the Mitchell Library : a comprehensive index, 2004
The CD-ROM contains the Index and also selected transcriptions by Pauline Byrt Centre for Australian Indigenous Strudies Monash University, and transcriptions of Linguistic Data relating to the language of the Melbourne area by Stephen D. Morey Research Centre for Linguistic Typology, La Trobe University.251 p. ; 30 cm. + 1 CD-ROM.The CD-ROM contains the Index and also selected transcriptions by Pauline Byrt Centre for Australian Indigenous Strudies Monash University, and transcriptions of Linguistic Data relating to the language of the Melbourne area by Stephen D. Morey Research Centre for Linguistic Typology, La Trobe University.thomas, william 1793-1867 - assistant protector of aborigines, indexes - thomas william-papers-mitchell library collection |, victoria-history-aboriginals-1838-1867. -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBook, Roberts, Janine P, Jack of Cape Grim : a Victorian adventure, 1986
Contents: The Tasmanians; Move the Tasmanians to Port Phillip; The Squatters; Melbourne Protected; Melbourne Aborigines Take Up the Gun; The Tasmanians Fight; The Trial; The Execution; The Sequel. Blurb: Jack of Cape Grim is a true story, set in Tasmania and Victoria in the mid1800s. Jack, an Aboriginal, and his friends, the famous Truganini (said, incorrectly, to be the 'last' Tasmanian Aborigine), Bob, Matilda and Fanny brought to Victoria from Tasmania to help'tame' the Victorian Aborigines. The group breaks away from Robinson, the Aboriginal Protector, to seek revenge for their fate, stranded far from homeland. The early white settlers of the Port Phillip District get more than they expected as the Aborigines rampage on the Peninsula, chased by trooper. The outcome is the horrific first public execution in the bustling town of Melbourne.123 p., [24] p. of plates : ill., facsims., maps, ports. ; 22 cm.Contents: The Tasmanians; Move the Tasmanians to Port Phillip; The Squatters; Melbourne Protected; Melbourne Aborigines Take Up the Gun; The Tasmanians Fight; The Trial; The Execution; The Sequel. Blurb: Jack of Cape Grim is a true story, set in Tasmania and Victoria in the mid1800s. Jack, an Aboriginal, and his friends, the famous Truganini (said, incorrectly, to be the 'last' Tasmanian Aborigine), Bob, Matilda and Fanny brought to Victoria from Tasmania to help'tame' the Victorian Aborigines. The group breaks away from Robinson, the Aboriginal Protector, to seek revenge for their fate, stranded far from homeland. The early white settlers of the Port Phillip District get more than they expected as the Aborigines rampage on the Peninsula, chased by trooper. The outcome is the horrific first public execution in the bustling town of Melbourne.truganini, 1812-1876. | aboriginal tasmanians -- treatment. | aboriginal tasmanians -- victoria -- treatment. | aboriginal tasmanians -- government relations. | aboriginal australians -- victoria -- government relations. | victoria -- history -- 1834-1851. -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustDocument - Report, Board for Protection of Aborigines, Report of the Board Appointed to Enquire into, and Report upon, the Present Condition and Management of the Coranderrk Aboriginal Station, together with the minutes of evidence. 1882, 1882
Report of the board appointed to enquire into, and report upon, the present condition and management of the Coranderrk Aboriginal Station, together with the minutes of evidence.141 p. ; 36 cm.Report of the board appointed to enquire into, and report upon, the present condition and management of the Coranderrk Aboriginal Station, together with the minutes of evidence.coranderrk aboriginal station -- history -- sources. | aboriginal australians -- victoria -- history -- sources. | victoria -- history -- 1834-1900 -- sources. -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBook, Boys, Robert Douglass, First years at Port Phillip : preceded by a summary of historical events from 1768, 1935
Foreword: This Chronology extends from the first permanent settlement of "Port Phillip" or "Australia Felix," at Portland Bay, by Edward Henty, until the beginning of the proceedings of the first Town Council of Melbourne. In order to provide the necessary historical perspective, the Chronology has been preceded by a Summary of Historical Events. Many matters are here noted for the first time, and, through the courtesy of the Trustees of the Public Library of Victoria, the compiler was allowed to publish in full the diary kept by Sir Richard Bourke during his visit to Port Phillip in March, 1837. In addition to the authorities quoted in the text, recourse has been had to the large collection of official documents in the Public Library of Victoria (including the collection of La Trobe papers), the Historical Records of Australia, and the books and pamphlets dealing with the first decade of this State.159 p., [4] leaves of plates : ill. ; index; 22 cm.Foreword: This Chronology extends from the first permanent settlement of "Port Phillip" or "Australia Felix," at Portland Bay, by Edward Henty, until the beginning of the proceedings of the first Town Council of Melbourne. In order to provide the necessary historical perspective, the Chronology has been preceded by a Summary of Historical Events. Many matters are here noted for the first time, and, through the courtesy of the Trustees of the Public Library of Victoria, the compiler was allowed to publish in full the diary kept by Sir Richard Bourke during his visit to Port Phillip in March, 1837. In addition to the authorities quoted in the text, recourse has been had to the large collection of official documents in the Public Library of Victoria (including the collection of La Trobe papers), the Historical Records of Australia, and the books and pamphlets dealing with the first decade of this State.victoria -- history -- 1834-1851. | victoria -- history -- to 1834. -
 Parliament of Victoria
Parliament of VictoriaVictoria the Golden, Strutt, William 1825-1915, Victoria the golden : scenes, sketches, and jottings from nature, 1850-1862, 1850-1862, c.1895
"Victoria the Golden" documents life in Victoria between 1850 and 1862 as viewed by artist William Strutt. Momentous events in the Colony’s history such as Separation Day (1 July 1851), the sitting of the first Legislative Council (13 November 1851), the death of Burke (June 1861) and the Black Thursday bushfires (6 February 1851) are depicted. In 1907 the Premier of Victoria Thomas Bent purchased "Victoria the Golden" from Strutt for £120 and presented it to the Library. The album depicts events in chronological order with what Strutt considered “fidelity to nature and accuracy”, so that present day Victorians may view the sketches “as records of what we may now look upon as the dim past in the rapidly progressive history of Victoria”. Victoria the Golden is celebrated as one of the Parliament’s great treasures. It is a testament to William Strutt’s skill as a draughtsman and contains over 100 assorted images which were executed between the years of 1850-1862. Strutt’s particular talent was to be able to step back and record each event with particular care to detail. Many of the pieces contained within this album are littered with notes, such as the correct resting position of a corporal’s sword or details about the cloth and cut of a subject’s jacket. Strutt also notes in one of his many sketches of the new Legislative Council chamber at Spring Street that the President, Sir James Palmer, is seated ‘a little too high’ (page 30). Throughout the album, Strutt’s illustrations bring to life the diverse nature and peoples of the new colony. His range of subjects is comprehensive and includes parliamentarians, lawyers, wives and daughters, merchants, labourers, police and military officers, indigenous communities, farmers, miners, prisoners and explorers. The everyday and the extraordinary are depicted with each turn of the page. 44 leaves heavy card, approximately 1mm thick. Sketches, watercolours and prints of varying sizes and papers are glued onto the pages. Full leather binding in blue leather with title and decorative border in gold. There are four raised bands on the spine, with gold decoration on the bands and at the head and tail of the spine. Marbled end papers and flyleaves. Gold on the edges of the book block. Card pages have a sheet of mottled blue paper on recto. Album leaf connection is a guarded system with stiff stubs and cloth hinges. Each page has a sheet of glassine paper attached at the binding edge to protect the images. Many pages stamped with "Parliament of Victoria" verso. Printed in gold, recto: "VICTORIA THE GOLDEN/ SCENES,/ SKETCHES,/ AND JOTTINGS FROM NATURE./ BY/ Wm. STRUTT/ MELBOURNE, VICTORIA./ 1850-1862" First pages include handwritten 'introductory remarks' and index of plates.parliament of victoria, colony of victoria, separation day, victorian legislative council, burke and wills expedition, wills, william john, 1834-1861, burke, robert o'hara, 1821-1861, strutt, william, 1825-1915, bent, thomas sir, 1838-1909, native police corps, fawkner, john pascoe, 1792-1869, black thursday bushfires, gold rush, princes bridge, melbourne -
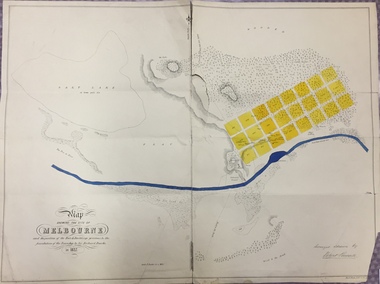 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncMap, Robert Russell, Map Shewing the Site of Melbourne and the Position of the Huts & Buildings Previous to the Foundation of the Township by Sir Richard Bourke in 1837
Map shows the first layout of Melbourne by Government surveyor Robert Russell, who accompanied Governor Richard Bourke in 1837. The surveyed blocks extend from present-day Flinders Street to Lonsdale Street, and Spring Street to Spencer Street, with extensive vacant land west to a salt lake (afterwards Batman's Swamp, later drained), north beyond Flagstaff Hill and south towards South Melbourne. Vegetation coverage is indicated, and tracks and existing buildings and cultivated land are shown.Printed map was created by Day & Haghe, Lithographers to the Queen, sometime after 1838, when the company received its Royal appointment. Copies of the 1837 map exist in several major map collections in Australia; most are uncoloured. This particular map is the earliest in the Kew Historical Society's map collection. It is a nationally significant artefact. Black and white lithographed map hand-coloured in blue and yellow gouache of the town of Melbourne in 1837. In contrast to the original lithograph, the river and the township blocks are coloured blue and yellow. A similar, partly coloured copy is in the collection of the University of Melbourne.maps - melbourne - 1830s, governor sir richard bourke, robert russell - surveyor, cartography -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncSouvenir, Lapel Pin, Melbourne 150, 1985, 1985
Melbourne 150A lapel pin in the shape of the coat of arms of the City of Melbourne with Melbourne 150 belowMelbourne 150 (front) Pinstop 869 9390 (reverse)melbourne 1834-1984, melbourne - 150th anniversary, souvenirs - lapel pins -
![Glimpses of Life in Victoria / [by] a 'Resident'](/media/collectors/550653872162f11fb04854aa/items/5ed05546dcf9cd08346c11f9/item-media/5ed055fedcf9cd08346c1974/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncBook, Melbourne University Press, Glimpses of Life in Victoria, 1996
An account of pioneering, bushrangers, gold-digging, land sales and swindles, the aborigines, and colonial society.xxxii, 322 p. : illus. (some col.)An account of pioneering, bushrangers, gold-digging, land sales and swindles, the aborigines, and colonial society.melbourne (vic.) -- description and travel., victoria -- social life and customs -- 1834-1900. -
![Victoria's Colonial Governors 1839-1900 / [by] McCaughey, Perkins & Trumble](/media/collectors/550653872162f11fb04854aa/items/5ed05921dcf9cd08346c3084/item-media/5ed05a20dcf9cd08346c3c12/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncBook, Victoria's Colonial Governors 1839-1900 / [by] McCaughey, Perkins & Trumble, 1993
The stories of the acheivements, friends and adversaries, changing roles and expectations, imagery and daily life of each of the Colonial Governors of Victoria starting with La Trobe in 1839 to 1854 and ending up with Lord Brassey who held the position from 1895 to 1900.xix, 453 p., 1 folded leaf, [8] p. of plates : ill. (some col.), ports. (some col.) ; 25 cm.non-fictionThe stories of the acheivements, friends and adversaries, changing roles and expectations, imagery and daily life of each of the Colonial Governors of Victoria starting with La Trobe in 1839 to 1854 and ending up with Lord Brassey who held the position from 1895 to 1900.governors -- victoria -- biography, victoria -- politics and government -- 1834-1900 -
![Colonial Consorts: The wives of Victoria's Governors 1839-1900 / [by] Marguerite Hancock](/media/collectors/550653872162f11fb04854aa/items/5ed05c0fdcf9cd08346c4ced/item-media/5ed05cbddcf9cd08346c5235/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncBook, Colonial Consorts: The wives of Victoria's Governors 1839-1900 / [by] Marguerite Hancock, 2001
xxii, 324 p., [10] p. of plates : ill. (some col.), ports., photos. ; 25 cm.non-fictiongovernors' spouses -- victoria -- history -- 19th century., victoria -- politics and government -- 1834-1900.
