Showing 835 items
matching mid-19th century
-
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyfood cover, late 19th - early 20th century
... used in the late 19th-mid 20th century. food-storage domestic ...Food covers were used to cover food and protect it from insects. This food cover is a simple shape and would be a domestic utensil.This food cover is an example of a simple kitchen item used in the late 19th-mid 20th century.Small black metal meat cover with small handle.food-storage domestic kitchen -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical SocietyMembership Certificate, 1960's
... in the mid-19th Century by immigrants from England who had been ...From Grand United Order of Oddfellows. MU100F - membership and competition. 1966-67 winners in "B" Class - Loyal Orbost Lodge.Friendly Societies were founded in the Australian Colonies in the mid-19th Century by immigrants from England who had been members in Societies which dated back to the 18th Century. Like all working people these immigrants experienced sickness, accidents, unemployment, death and burial. They needed help of like fellows to tide their families over these times. So they formed a branch of one of the Friendly Societies back in the mother country. The idea was to make fixed contributions to a fund and when they were off work they would receive a payment. When they died funeral benefits would be paid and the widow and children would be cared for. It was a form of local insurance for hard times. This was a time of 'look after yourself' as the Colonial Governments did not provide pensions or benefits. This item reflects those times.Membership and competition certificate from Bairnsdale district. Large certificate with large painting of Collins Street Melbourne in wood and glass frame.document oddfellows certificate lodge muioof -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societydoily, Woodward, Ruth (daughter of Alan Richardson), 1910-1930
... of Australian women of the late 19th to mid 20th century. Women's focus ...Doily was hand made by Riuth Woodward who was the daughter of Alan Richardson, a sawmiller at Tabbara. He held ticket for the paddlesteamer Curlip.This item represents an important pastime of Australian women of the late 19th to mid 20th century. Women's focus was the home and its decoration was important. Embroidery and crochet work was an affordable way to personalise and add aesthetic value, and examples of embroidered and crocheted pieces could be found in most Australian homes, decorating or protecting furniture, floors and walls, and keeping off flies and insects from food.Small square needlepoint doily with kangaroo pattern and beaded triangular fringe. Centre is white with pink clear beading.doily handcrafts needlework beading richardson-alan -
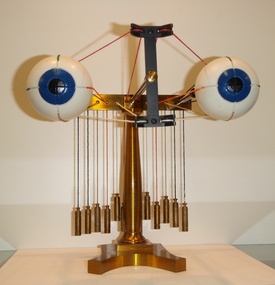 The Cyril Kett Optometry Museum
The Cyril Kett Optometry MuseumOphthalmotrope, unknown, (estimated); mid 20th century
This model was used in lectures in the College from the mid 20th century. An ophthalmotrope is a mechanical model constructed to demonstrate the movements of the eyes and the actions of the various muscles which produce them. The first ophthalmotrope was made by Theodore Reute in 1845 and it was he who gave it the name 'ophthalmotrope'. Frans Donders (1818-1889) became interested in eye movements on reading Reute's work, and his subsequent studies were of physiological interest and also provided the basis for principles underlying the correction of squint. Because of the complexity of the actions and counter actions of the eye muscles, ophthalmologists of the 19th century sought a practical solution with the construction of mechanical models. Reute's second model of 1857 was more sophisticated. Its eyeballs contained lenses and the optical system could be moved backwards and forwards to simulate accommodation. Later ophthalmotropes are known by Landolt, Knapp and Snellen.This ophthalmotrope is the one that was used as a teaching aid in the College from the mid 20th century.Brass framed model to illustrate actions of extra-ocular muscles. Two painted wooden globes mounted in brass frame with coloured strings attached to brass weights positioned to show actions of various extra-ocular muscles. Also wooden storage box. Materials: brass, metal, wood, string.optometry, ophthalmology, ophthalmotrope, eye, eye movements, extra ocular muscles, eye muscles, eye teaching -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyperfume, 1960's
These perfumes were owned by Marjorie Burton. Marjorie Burton ( nee Whiteman), born 12 June, in Birmingham, England came to Orbost in 1995. In England she did office work – typing, shorthand and secretarial work - in accountants’ offices and also trained as a comptometrist with Burroughs in London. She came from a middle-class, working, church-going family. Her mother was a milliner who made many of Marjorie’s clothes, hats and outfits. Marjorie was married in 1938 to a salesman who later became a mechanic in the R.A.F Perfume is a mixture of fragrant essential oils used to give the human body a pleasant scent. Modern perfumery began in the late 19th century but it was only in the 20th century that scents and designer perfumes were really mass produced. These items are evocative of the mid 20th century.One bottle of 4711 Eau de Cologne. It has round shoulders, a gold cap and a green and gold label. 2483.58 is a box containing three bottles : Carven Ma Griffe; Robe d'un Soir and Vert et Blanc. The box is pale green with darker green diagonal stripes. 2483.59 is a packet of two sachets of cologne tissues.2483.57 has 4711 embossed on the back of the bottle. 2483.58 has a sticker on the back - sold on board of KLM aircraft. 2483.59 - Boots perfumes burton-marjorie cosmetics -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyjug cover, 1953
... for Australian women of the late 19th to mid 20th century. Women's focus ...this item was made to commemorate the coronation of Queen Elizabeth !! in 1953. In June 1953 , Elizabeth II was crowned Queen of the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Ceylon (now Sri Lanka), and Pakistan, and became the Head of the Commonwealth. Many souvenirs were made to mark this occasion. Some were unique and hand-made. The main sources for crochet and other needlework designs available to women were in journals, magazines and pattern books.This milk jug cover reflects an important pastime for Australian women of the late 19th to mid 20th century. Women's focus was the home and its decoration was important. Embroidery and crochet work was an affordable way to personalise and add aesthetic value, and examples of embroidered and crocheted pieces could be found in most Australian homes, decorating or protecting furniture, floors and walls, and keeping flies and insects away from food. It is also a tangible souvenir of the coronation of Queen Elizabeth 11.A rectangular jug cover hand crocheted in white thread. It has blue and red beads sewn into the edges. the design is "JUNE" above a crown with "E 11 R 1953" below the crown. -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybook / colection, early 19th century
... to mid 19th century. on front : "V BROOME with CANN RIVER crossed ...George Cruikshank (27 September 1792 – 1 February 1878) was a British caricaturist and book illustrator.. His book illustrations for his friend Charles Dickens, and many other authors, reached an international audience. George Cruikshank was inventive. In the 1800's, puns and other forms of word-play were loved by all. Some of these illustrations come from his 'Scraps and Sketches' album, published for adults in 1832, though the drawings were done between 1828 and 1832. Volumes of George Cruikshank's Scraps and Sketches were intended to be cut and pasted in home-made albums and scrapbooks; George Cruikshank was a well-known British caricaturist and book illustrator. This item represents this popular art form of the early to mid 19th century.A collection of artworks (copies of etchings) of George Cruikshank. They are bound together with masking tape. The pages are dated 1828-1823. They are satirical cartoons printed in black ink.on front : "V BROOME with CANN RIVER crossed through ORBOST 78 PERRY ST 5154 2855" -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeremonial object - Ciborium and Lid, Before 1855
... as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century ...Ciborium is the ancient Greek word for the cup-shaped seed vessel of the Egyptian water lily "nelumbium speciosum" and came to describe a drinking cup made from that seed casing. These vessels were particularly common in ancient Egypt and the Greek East. The word "'ciborium'" was also used in classical Latin to describe such cups. In medieval Latin, and in English, "Ciborium" more commonly refers to a covered container used in Roman Catholic, Anglican, Lutheran and related churches to store the consecrated hosts of the sacrament of Holy Communion. It resembles the shape of a chalice but its bowl is more round than conical and takes its name from its cover, surmounted by a cross or other sacred design. This ciborium is part of a Communion Set that was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg in 1975 after 120 years in the sea. Five years later during the cleaning of the ciborium, a diamond ring was found secreted in the underside of the ciborium's lid. This ring has since come to be called the Schomberg Diamond and is also on display as part of the Flagstaff Hill Museums Schomberg collection. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill (Peter Ronald, former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Colin Goodall and Gary Hayden), found an ornate communion set at the Schomberg wreck site. The set comprised a jug, the ciborium, a chalice and a plate. The ciborium remained untouched for a number of years before restoration began and the marine growth was removed. In 1980 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery at Flagstaff Hill. The collection also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets as well as photographs from the Schomberg. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked.This ciborium is significant as an example of an item in common use in the mid-19th century that is still in use today. It is also important for it relationship with the famous Schomberg Diamond that was discovered by accident, hidden inside it. The ciborium is particularly significant in that along with other items from the wreck helped in part to have the legislation changed to protect shipwrecks, with far tighter controls being employed to oversee the salvaging of wreck sites around our coast. This salvaged item forms part of the Schomberg collection at Flagstaff Hill maritime museum. The collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered Schomberg shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of additional significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes from society at the time of the wreck.Silver engraved Ciborium or chalice with lid, part of the five-piece Communion Set. The chalice is a round cup with a long stem and a floral-shaped base with embossed decoration. It has a matching round lid that comes to a rounded apex on top. Engravings on chalice feature flowers and a Fleur-de-lis pattern.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, schomberg, 1855, clipper ship, james baines & co, black ball line, luxury ship, emigrant ship, captain forbes, bully forbes, ss queen, peterborough shipwreck, communion set, religious service, communion service, ceremonial service, mass, ciborium, chalice, schomberg diamond -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Bullet Mould, From 1600s to early 19th century
... or pistols from the early part of the 18th to mid 19th century. After ...Musket balls are the ammunition used in muskets the weapons used during the English and American Civil Wars. The balls could be made from any metal alloy, but many were made from lead. Lead can be melted at reasonably low temperatures and so lead musket balls could be made over a camp fire. Lead could be readily sourced from such places like church roofs or even coffins, and recast from old musket balls, so it was an easy material to work with while preparing for battle. The soldier would carry a crucible in which to melt the lead, he would put the material into it and place it over the fire until it had formed into a liquid. Musket ball moulds like the subject item, had a small hole above one of the domes where the liquid could be poured into once the two domes were closed together. The soldier would wait until it cooled then opened the mould to reveal a solid lead ball inside. Because these were cast in halves even though pressed together, there would always be a small amount of liquid lead leakage which would form a thin crust around the ball. These needed to be filed off before being used inside a musket, so some soldiers would pop a few in their mouths and roll them around, chewing off the excess until the ball was smooth. The obvious downside to this method is that lead is poisonous. A tool used to make ammunition for black powder firearms either muskets or pistols from the early part of the 18th to mid 19th century. After this time enclosed brass cartridges that held the propellent powder and bullet were starting to come into wide spread use, negating the need for a firearm to first have black powder placed in a barrel then the ball rammed on top and finally the firearm primed with powder or a percussion cap.Musket rifle/ pistol bullet mold. Makes .50 -caliber- round balls with a sprew cutter to cut off excess lead.Marked 50flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shot pliers, lead shot, shot, armoury, firearms, bullet, cast bullet, lead ball, lead shot, scissor mould -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Router Plane, A Mathieson & Son, Mid 19th to early 20th centuries
... enterprise. A significant item from the mid to late 19th century ...The subject router is commonly referred to disparagingly as the ‘old woman’s tooth’ or ‘hag’s tooth.’ It is a router that houses a plough plane iron instead of a purpose made shoe-type cutting iron. They work fine but rarely give the type of clean surface required for veneer inlays. These types of tools are adjusted by the same hammer-tap tapping method used generally on wooden-bodied planes on the iron or plane body. These tools are effective and practical when used in general carpentry and joinery. Company History: The firm of Alexander Mathieson & Sons was one of the leading makers of hand tools in Scotland. Its success went hand in hand with the growth of the shipbuilding industries on the Firth of Clyde in the nineteenth century and the emergence of Glasgow regarded as the "second city of the Empire". It also reflected the firm's skill in responding to an unprecedented demand for quality tools by shipyards, cooperage's and other industries, both locally and far and wide. The year 1792 was deemed by the firm to be that of its foundation it was in all likelihood the year in which John Manners had set up his plane-making workshop on Saracen Lane off the Gallowgate in the heart of Glasgow, not far from the Saracen's Head Inn, where Dr Johnson and James Boswell had stayed on their tour of Scotland in 1773. Alexander Mathieson (1797–1851) is recorded in 1822 as a plane-maker at 25 Gallowgate, but in the following year at 14 Saracen's Lane, presumably having taken over the premises of John Manners. The 1841 national census described Alexander Mathieson as a master plane-maker at 38 Saracen Lane with his son Thomas Adam working as a journeyman plane-maker. In 1849 the firm of James & William Stewart at 65 Nicolson Street, Edinburgh was taken over and Thomas was put in charge of the business, trading under the name Thomas A. Mathieson & Co. as plane and edge-tool makers. Thomas's company acquired the Edinburgh edge-tool makers Charles & Hugh McPherson and took over their premises in Gilmore Street. The Edinburgh directory of 1856/7 the business is recorded as being Alexander Mathieson & Son, plane and edge-tool makers at 48 Nicolson Street and Paul's Work, Gilmore Street. The 1851 census records indicate that Alexander was working as a tool and plane-maker employing eight men. Later that year Alexander died and his son Thomas took over the business. Under the heading of an edge-tool maker in the 1852/3 (Post-Office Glasgow Annual Directory) the firm is now listed as Alexander Mathieson & Son. By the early 1850s, the business had moved to 24 Saracen Lane. The directory for 1857/8 records that the firm had moved again only a few years later to East Campbell Street, also off the Gallowgate, and that through further diversification was also manufacturing coopers' and tinmen's tools. The ten-yearly censuses log the firm's growth and in 1861 Thomas was a tool manufacturer employing 95 men and 30 boys; in 1871 he had 200 men working for him and in 1881 300 men. By 1899 the firm had been incorporated as Alexander Mathieson & Sons Ltd, even though only Alexander's son Thomas appears ever to have joined the firm. A vintage tool made by a well-known firm made for other firms and individuals that worked in wood. The tool was used for making timber veneers or smoothing a trench in a piece of timber that was then used in some form of cabinet manufacture or wood working enterprise. A significant item from the mid to late 19th century that today is sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture was made predominately by hand and with tools that were themselves hand made and required considerable skill in their use. Old Woman's Tooth Router Mathieson. Single iron cut down from a larger plane iron. Has Marked A Mathieson & Son also stamped inscription on side G Hill. (owner)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, plane, old woman's tooth, router, hag's tooth router, cabinet making, woodworking tools, a mathieson & sons, cabinet tool makers -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Moulding Plane, Routledge, 1869-1910
... to late 19th century by a known maker that today is quite rare ...A moulding plane is a specialised plane used for making the complex shapes found in wooden mouldings that are used to decorate furniture or other wooden object. Traditionally, moulding planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding planes for the full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about Richard Routledge is that he was a tool maker and retailer that operated a business at either 23 or 64 Bull St Birmingham between 1869 to sometime in the early 20th century. There are many of his tools including decorative moulding planes of all sizes and designs for sale around the world and that his tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools. A vintage tool made by an early tool manufacturer Richard Routledge, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce an ornamental finish to timber. The tool was used before routers and spindle moulders came into use after World War ll, a time when to produce a decorative moulding for a piece of furniture, door trims etc. or other items had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. These profiled planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a decorative finish. A significant tool from the mid to late 19th century by a known maker that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves handmade shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item. Moulding Plane Side Bead 5/8 type with a single Box 5/8" "Routledge Birmingham " also inscribed "J.A.S. Burden" (owner of the plane)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, plane, moulding, routledge, side bead, single box, moulding plane, richard routledge, jas burten -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Joiner or Jack Plane, Late 19th to first quarter of the 20th century
... planes and improvements in the late 19th century. A jack plane ...A jack plane (or fore plane) is a general-purpose woodworking bench plane, used for dressing timber down to the correct size in preparation for truing and/or edge jointing. It is usually the first plane used on rough stock, but in exceptional cases can be preceded by the scrub plane. Jack planes are 300–460 mm long and 64–76 mm wide, with wooden-stocked planes sometimes being slightly wider. The blade is 44–57 mm wide that is often slightly convex (or ground with rounded corners) to prevent digging in to or marking the work. The cut is generally set deeper than on most other planes as the plane's purpose is to remove stock rather than to gain a good finish (smoothing planes are used for that). In preparing stock, the jack plane is used after the scrub plane and before the jointer plane and smoothing plane. The carpenters' name for the plane is related to the saying "jack of all trades" as jack planes can be made to perform some of the work of both smoothing and jointer planes, especially on smaller pieces of work. Its other name of the fore plane is more generally used by joiners and may come from the fact that it "is used before you come to work either with the Smooth Plane or with the Jointer". Early planes were all wood, except for the cutter, or combined a wood base with a metal blade holder and adjustment system on top. Although there were earlier all-metal planes, Leonard Bailey patented many all-metal planes and improvements in the late 19th century. A jack plane came to be referred to as a "No. 5" plane or a "Bailey pattern No. 5" at the end of the 19th century. A vintage tool made by an unknown company, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could remove large amounts of timber. These jack or dressing planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a flat and even finish to timber surfaces before the use of smoothing planes and came in many sizes. A significant tool from the mid to late 19th century that is still in use today with early models sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other finishes were created on timber by the use of cutting edged hand tools. Tools that were themselves handmade shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative or even finish that was needed for the finishing of timber items. Jack or Fore plane with blade and wedge. Marked "D Morris" (owner)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, plane, fore plane, d morris, jack plane, wood working tools -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Chain Drill Attachment, Millers Falls Co, 1900-1931
... that were produced during the mid-19th and early 20th centuries ...An auxiliary tool for use with a breast drill or bit brace, when extra power is needed, or where pressure cannot be easily applied. The drill is automatically fed into the work by an adjustable friction feed which is automatically regulated by the resistance the drill encounters. These were made to fit on breast drills, and used for drilling metal, particularly round sections like a pipe. The chain is run around the object being drilled and gradually tightens as the hole is drilled, maintaining pressure while being a bit easier on the operator. Millers Falls Co. is a tool manufacturing company originally based in Millers Falls, Massachusetts, USA. It was established in Greenfield, Massachusetts in 1868 as Gunn & Amidon by Levi J. Gunn and Charles H. Amidon. Gunn and Amidon, along with a third partner, Henry L. Pratt built a factory in the north of Greenfield. After the Greenfield factory burned down, the company was reorganized as the Millers Falls Manufacturing Co. It merged with Backus Vise Co. in 1872 to form Millers Falls Co. In 1931 Millers Falls tools purchased the majority of the shares of Goodell-Pratt tools and merged with that manufacturer in 1932. In 1962 the company was acquired by Ingersoll Rand. In 1982, Ingersoll Rand sold the Millers Falls business to the newly created Millers Falls Tool Co. The company was head quartered in Alpha, New Jersey. Since 2002 the company trademark has belonged to Hangzhou Great Star Industrial, of Hangzhou, China. The item is associated with a tool manufacturing company established in the mid-19th century that pioneered the development of many types of tools used in many differing trades. The company grew to become a major supplier of tools around the world and today its tools that were produced during the mid-19th and early 20th centuries are now collectable items. Drill attachment with chain No 717 from 1925 catalogue 1/2 socket hole Millers Falls, Massachusettsflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, chain drill, mast drill, millers falls, drilling attachment, drilling tools -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Smoothing Wood Plane, John Welsh & Co, 1845-1850
... to late 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after ...A vintage tool made by a obscure early 19th century woodworking Scottish tool maker. This item would have been made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could produce a flat smooth finish to timber. These tools were used before routers and spindle moulders came into use in the late 19th and early 20th centuries before this time to produce a decorative moulding or to smooth a piece of furniture timber, door trims etc. had to be accomplished using hand tools and in particular one of these types of planes. The subject item is a smoothing plane Known as a Coffin Plane due to its shape. Traditionally wood planes were blocks of wear resistant hardwood, often beech or maple, which were worked to the shape of the intended moulding or had a flat blade use for achieving a flat and smooth finish to timber. The blade, or iron was likewise formed to the intended moulding profile or for smoothing and secured in the body of the plane with a wooden wedge. A traditional cabinetmakers shop might have many, perhaps hundreds, of moulding and flat bladed planes for a full range of work to be performed. Large crown mouldings required planes of six or more inches in width, which demanded great strength to push and often had additional peg handles on the sides, allowing the craftsman's apprentice or other worker to pull the plane ahead of the master who guided it. All we known about John Welsh is that he was a tool maker and possibly a retailer that operated a business in Dundee Scotland between 1845-1850. This is the only record we have to date that he existed and is from the Master Catalogue of Scottish woodworking tool makers. His tools in particular moulding planes are well sought after by collectors of vintage tools due to their rarity. A significant tool from the mid to late 19th century that today is quite rare and sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other decorative finishes were created on timber by the use of hand tools. Tools that were themselves handmade shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative finish that was needed to be made for any timber item. Wood Plane Rounded base, blade attached. Owner J Huband Marked J Welsh, Dundee maker and "J Huband" (Owner)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, plane, compass plane, j welsh, j huband -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Caulking mallet, Mid 19th to early 20th centuries
... by an unknown maker from the mid to late 19th century and is significant ...The subject item is a vintage Nautical Shipwrights Ship Boat Caulking Hammer Mallet, Unusual Small Size. These mallets were routinely used in the 1800s when ships were made of wood. This mallet was used with caulking irons to drive the oakum (caulk) between the ship's bottom planking to seal them up. The mallet has slots to dampen the vibration of the mallet blows on the user's elbows. The head is made of a very hard wood, possibly Lignum Vitae or another dark tropical wood. The item seems to be of a very early design with the two preened-over metal rods for reinforcing the head. Item appears to be of early manufacture by an unknown maker from the mid to late 19th century and is significant as tools of this era are quite rare. This tool is also significant as it gives an insight into how ships made of wooden planks were made sea-worthy by inserting caulking material between the boards thereby making the vessel watertight. Caulking Mallet Wooden with iron ferrules on each end. Wooden head with two large bolts passing through body. Stamped W Milne. James S Steele tool box.Stamped W Milne & James S Steele tool box.mallet, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, caulking mallet, caulking, james steele, shipwrights tools -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLeisure object - Stereoscope, H C White, Late 19th century
... today, stereography during the second half of the 19th century ...The development of stereoscopic photography views or stereographs was immensely popular in the United States and Europe from about the mid-1850s through the early years of the 20th century. First described in 1832 by English physicist Sir Charles Wheatstone, stereoscopy was improved by Sir David Brewster in 1849. The production of the stereograph entailed making two images of the same subject, usually with a camera with two lenses placed 6 cm apart to simulate the position of the human eyes, and then mounting the positive prints side by side laterally on a stiff backing. Brewster devised a stereoscope through which the finished stereograph could be viewed; the stereoscope had two eyepieces through which the laterally mounted images, placed in a holder in front of the lenses, were viewed. The two images were brought together by the effort of the human brain to create an illusion of three-dimensionality. Stereographs were made of a wide range of subjects, the most popular being views of landscapes and monuments and composing narrative scenes of a humorous or slightly suggestive nature. Stereoscopes were manufactured for various price ranges and tastes, from the simple hand-held device introduced by Oliver Wendell Holmes who promoted stereography through articles to elaborate floor models containing large numbers of images that could be flipped into place. The stereograph became especially popular after Queen Victoria expressed interest in it when it was exhibited at the 1851 Crystal Palace Exposition. Like television today, stereography during the second half of the 19th century was both an educational and a recreational device with a considerable impact on public knowledge and taste. The Fine-art Photographers' Publishing Co. published many stereoscopic pictures from many different photographers from around the world under license. They also not only sold these images of various scenes and of famous people of the time but also were retail sellers of the viewers with the subject item having been made in the USA probably by H C White who held the patent for the subject items design from 1895 to 1902.An item that was very popular from the mid 19th century through to the beginning of the Edwardian period. Used for entertainment and also educational purposes and significant as it gives us a snapshot into the Victorian era and its social and domestic societal norms. Stereoscope viewer with adjustable view-finder that has a padded nose rest. The slide holder can move along the channel to suit the viewer. Made in London by the Fine-art Photographers' Publishing Co. Printed on metal plate "THE FINE-ART PHOTOGRAPHERS' PUBLISHING CO. 48 Rydevale Rd, LONDON, S.W." Embossed on viewing cup "U.S.A. PATENT OCT.15.1895" "CANADA / FRANCE / GERMANY / D'R''G'M' NO. 53803" "JUNE 3.1902 / FEBY 1.1896 / B.S.G.D.B. / GREAT BRITAIN / AUSTRIA / BELGIUM"warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, stereoscope, stereographs, stereoscope viewers, home entertainment -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, Mid to late 19th century
... Mid to late 19th century...-to-late 19th century. At this time cannot be associated ...A mass produced hand made bottle made for containing sparkling wine no history or manufacturing provenance currently available.The bottle is a good example from the mid-to-late 19th century. At this time cannot be associated with an historical event, person or place, provenance is unknown.Bottle, dark green glass cork in neck flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, bottle, green glass bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ceramic Bottle (Chinese Style), Minton Potteries, Late 19th century
The subject item is believed to be a "Chinese style stoneware liquor bottle used to store "Tiger Whiskey" (rice wine). These Chinese liquor jugs are made of glazed pottery known as brown stoneware and have been made throughout the centuries by many makers until well after American Prohibition. Later varieties from the mid 20th century are commonly found in the USA with the raised lettering "Federal Law Forbids Sale Or Re-use of this bottle" a sure sign of post-1934 manufacture. This example is interesting as it has a British Minton mark of two triangles on the base indicating a date of 1879 and was likely exported to Australia by Minton. These ceramic bottles virtually always have irregularities and flaws which indicate a product has been hastily manufactured, in any event, this is a fine example of a relatively common item that may have been copied by Minton and sold as a decorative domestic item for display or mass produced for storing liquor. Giles Family: The pair of ceramic bottles were given to Vera Giles by Jim Thompson and are just many 19th century items of furniture, linen and crockery donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by, Vera and Aurelin Giles. The items are associated with Warrnambool and the Giles Family history. Items donated by the family have come to be known as the “Giles Collection”. Many items in the Lighthouse Keeper’s Cottage were donated by Vera and Aurelin Giles and mostly came from the home of Vera’s parents-in-law, Henry Giles and his wife Mary Jane (nee Freckleton) who married in 1880 and whose photos are on display in the parlour. Henry was born at Tower Hill in 1858, and was a labourer on the construction of the Warrnambool Breakwater before leaving in 1895 for around seven years to build bridges in NSW. Mary Jane was born in 1860 at Cooramook and she attended Mailor’s Flat State School and where she eventually was to become a student teacher. After which she became a governess at “Injemiara” where her grandfather, Francis Freckleton, had once owned land. Henry and Mary’s family consisted of six, some of the children were born at Mailor’s Flat and later some children at Wangoom. They lived with their parents at Wangoom and Purnim west, and this is where Henry died in 1933 and Mary Jane in 1940. A significant item of lead-glazed ceramic with the possibility it was made by the Minton potteries in England who were renowned for making quality pottery. The item style is in all probability a copy of a Chinese liquor bottle that was in common use throughout the British colonies and America up until the mid 20th Century. The Giles family collection has social significance at a local level, because it illustrates the level of material support the Warrnambool community gave to Flagstaff Hill when the Museum was established.Chinese liquor bottle one of a pair, lead glazed ceramic, dark brown and blue/black. Part of the Giles Collection.Mark of a double triangle, apex touching, on base, (Minton mark for 1879).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, vase, pottery, ceramic ornament, domestic ware, late 19th - early 20th centuy ornament, giles collection, henry giles, tower hill, cooramook, warrnambool breakwater, mailor’s flat, wangoom, 19th century household goods -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Syringe
... to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer ...In 1821 the French otologist Jean Marc Itard irrigated the ear canal to remove hard wax, by using a syringe prototype designed for enemas which was made from tin and brass. This glass and cork ear syringe was manufactured by the Ambson Company in the United Kingdom, about eighty years afterwards. Its lightweight properties would have been ideal for application to the sensitive regions of the ear canal. https://www.racgp.org.au/the-racgp/history/the-racgp-museum-collection/syringes/ambson-ear-syringe Otology is a branch of medicine which studies normal and pathological anatomy and physiology of the ear (hearing and vestibular sensory systems and related structures and functions) as well as their diseases, diagnosis and treatment. Otologic surgery generally refers to surgery of the middle ear and mastoid related to chronic otitis media, such as tympanoplasty, or ear drum surgery, ossiculoplasty, or surgery of the hearing bones, and mastoidectomy. Otology also includes surgical treatment of conductive hearing loss, such as stapedectomy surgery for otosclerosis. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Otology The ear syringe was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) According to Berry, her mother Gladys made a lot of their clothes. She was very talented and did some lovely embroidery including lingerie for her trousseau and beautifully handmade baby clothes. Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . Its first station was in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital (a 2 bed ward at the Nelson Street Practice) from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what previously once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr Tom and his brother had worked as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He had been House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan had gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. When Dr Angus took up practice in the Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan’s old premises he obtained their extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926. A large part of this collection is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. and an ALDI sore is on the land that was once their tennis court). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served with the Australian Department of Defence as a Surgeon Captain during WWII 1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. He had an interest in people and the community They were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”.The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery.Glass ear syringe. Has cork stopper at top and cotton wrapped at base of plunger. Has a curved end.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, otology, ears, ear syringe, deafness, ear wax -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Auger, Robert Sorby, First half of the 20th Century
A scotch eye auger is perfect for quickly making holes in dry or wet wood for making chairs, stools, and any number of woodworking projects. The scotch eye serves as a peg gauge and whatever peg you make to go into the hole should fit into the augers eye. Robert Sorby & Sons: The forbearer's of Robert Sorby had been cutlers in the Sheffield region of England, dating from the mid 17th century. Robert Sorby and Sons were registered in Sheffield in 1828 as a manufacturer of edge tools, saws, scythes and hay knives. In addition to manufacturing tools, they also diversified into the manufacture of crucible steel for tool manufacture. From circa 1860-1967, the Sorby factory in Sheffield was known as the “Kangaroo Works”. The Kangaroo Brand of tools was made by Robert Sorby & Sons. During the 19th century, they had a large trade in Australasia. By the early 20th century, they were manufacturing carving tools, planes and plane irons, circular saws, wood saws, butchers saws and cleavers, garden tools, pruning knives, coopers’ knives, bricklayers tools and joiners tools. In 1923 Robert Sorby & Sons was bought by Sheffield company Hattersley and Davidson. They are today one of the few remaining British tool manufacturers.The company has a long tradition of making edged tools for various uses and exporting them to Australia, however the subject item was probably made from the early 20th century up until 1967 when the company stopped exporting to Australia.Scotch Eye Auger, Double Twist with Lead Screw, square shaft, socket set at right angleRob Sorbey Sheffield stamped on shaft with Kangaroo trade markflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, ring auger, carpenders tools, hole drilling, rob sorby & sons -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Plane, David Malloch, Late 19th to early 20th Century
... maker's tool from the mid 19th to early 20th century giving ...David Malloch was born in 1818 in Dundee Scotland and died in January 1891, his father was James Malloch a weaver and his mother was Jane nee Watson. David Malloch had taken over a plane and tool-making business from John McGlashan a Perth plane maker in 1849 after McGlashan had died. David and later his son (John) ran the business at first from South Methven Street Perth, until early 1856 then the business moved to the center of town in Kirkside at 25 John's Street. He used these premises until 1870 when he moved again to 50 South Street Perth. It is believed his son John was involved at this time and the move was due to the business had outgrown the premises at John Street. It was noted in local publications that the firm by this time had nine employees and regarded as a manufacturer of edge tools of various kinds for cabinet makers, specifically wood planes. The firm continued under David Malloch's son John after David's death in 1891 but the company appears to have ceased trading in 1913.A vintage cabinet maker's tool from the mid 19th to early 20th century giving a snapshot into early cabinet and furniture making. Wood Plane with flat base curved sides single iron, 2 inch, size.D Malloch and Son Perth, Scotlandflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Stove, 1850-1890
... item is a mid to late 19th century settlers stove probably ...In the industrialized world, as stoves replaced open fires and braziers as a source of more efficient and reliable heating, models were developed that could also be used for cooking, and these came to be known as kitchen stoves. The first manufactured cast-iron stove was produced at Lynn, Mass., in 1642. This stove had no grates and was little more than a cast-iron box. About 1740 Benjamin Franklin invented the “Pennsylvania fireplace,” which incorporated the basic principles of the heating stove. The Franklin stove burned wood on a grate and had sliding doors that could be used to control the draft (flow of air) through it. Because the stove was relatively small, it could be installed in a large fireplace or used free-standing in the middle of a room by connecting it to a flue. The Franklin stove warmed farmhouses, city dwellings, and frontier cabins throughout North America. Its design influenced the development of the pot-bellied stove, which was a familiar feature in some homes well into the 20th century. The first round cast-iron stoves with grates for cooking food on them were manufactured by Isaac Orr at Philadelphia, Pa., in 1800. The base-burning stove for burning anthracite coal was invented in 1833 by Jordan A. Mott. The subject item is a mid to late 19th century settlers stove probably of Canadian manufacture imported into Australia around this time. The stove gives us a social snapshot into what life must have been like for our early colonialists using this device for heating and cooking in their meagre homes. Cast iron stove with four-legs, 2 plates on top and a hinged front door. The door has been cast with a maple leaf design and the sides have a pattern cast into them.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, stove, domestic heating, domestic cooking, heater, cooking unit, pot belly stove, wood fired stove, wood stove -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Printing Press, Harrild and Sons, 1866
... printer from the mid-19th century. The use of the printer ...This Albion printing press was manufactured by Harrild & Sons of London and exported in 1868 from London to the colonial Western Victoria town of Coleraine, population of 700 at that time. It was installed in the Colerain Albion printing office. It was used to print the first edition of the Coleraine Albion newspaper in 1868 and continued until publication ceased in 1974. The Albion Press is still being used today by a volunteer printer in the “Examiners Office” in the village at Flagstaff Hill. Amongst the items produced are printed paper bags for the Tea Rooms and posters for visitors. ALBION PRINTING PRESS The Albion press was invented and manufactured in London by Richard Whittaker Cope around 1820 and was still being produced in the 1930s. The Albion was manufactured under licence by several companies from the 1850s onwards, one of which was Harrild & Sons of Fleet Works, London. Harrild & Sons describes its business as “printing materials manufacturer”. The business was established in 1807 by Robert Harrild and named R. Harrild & Co. In 1813 he showed that rollers could be used to ink a printing plate instead of inking balls, the method in use at the time. He then established a company to make the rollers. Eventually his company would make other printing materials and equipment. Robert’s sons joined him in the 1830s, when the company was renamed Harrild & Sons, and they continued to run the company after his death in 1853 and up until the mid-1900s. COLERAINE ALBION PRINTING OFFICE The Coleraine Albion Printing Office was established by W.L. Ambler. The first issue of the Coleraine Albion was dated 4th January 1868. Arrangements had been made to receive news from Melbourne, nearby provinces, other colonies and England. The second issue on 18 January 1868 printed articles from many agencies, including the Melbourne Age and the Warrnambool Examiner. The Albion office was sold to William Hatherleigh, formerly of Portland, in October 1868. Thereafter the Albion office had many owners. The last was L. A. & E. Oliver, who took over in January 1972 and was the last to be stated as printers and publishers of the Coleraine Albion. The office was wound up in 1974. The Albion Press and other equipment was distributed to Star printing in Terang. Star Printing donated the Albion press to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village around 1980 and Stan Philp, owner of Philprint in Warrnambool, transported it to Warrnambool, brought it up to good working order and organised the supply of appropriate printer’s type. The Albion hand operated printing press is significant for producing the first newspaper in Coleraine, Western Victoria and continuing production for over 100 years. The Albion is technologically significant as a working example of a hand operated printer from the mid-19th century. The use of the printer is demonstrated by volunteers at Flagstaff Hill, printing items such as lolly and treat bays for use in the Village. The Albion is socially significant for its role in the isolated provincial colony, providing communication with the outside world, both in Australia and overseas. Newspaper printers were often amongst the first businesses of a small town. Printing press; hand operated Albion Press, Patent 2105. The machine has an upright iron frame at the back that supports the upper press that has a wooden handled metal bar is attached. The frame and legs support a thick metal flatbed. A metal leg supports the front of the press bed. The iron work is painted black with gold highlights. The decorative legs are finished with the golden feet of an animal. The frame above the metal bed includes a crown shaped finial symbol above the maker’s emblem. The maker’s details and the name of the printer are embossed on the upright frame. A plaque with the patent number is below a Lion and Unicorn emblem.Embossed maker’s emblem [A red cross - above a double ring – square inside ring – three banners below ring]. - Inside the double rings “PRINTING MATERIALS MANUFACTURE” - Inside the square, intertwined text “H & S” [representing Harrild & Sons] - Inside the three banners ““FLEET” “WORKS.” “LONDON.E.C.” Embossed across the shoulders “ALBION PRESS / HARRILD & SONS, / MAKERS LONDON.” Emblem above plaque [Lion and Unicorn] Embossed on the plaque “PATENT / 2105” Stamped into upright machine part above the printing bed “2105 / 1866” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, albion press, printing press, 1866 printing press, printing equipment, communications, coleraine albion printing office, coleraine newspaper, albion newspaper, south west victoria newspapers, harrild and sons london, richard whittaker cope, star printing terang, philprint, coleraine albion, hand operated press -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFurniture - Linen Chest, First half of the 19th Century
... when she migrated to Australia during the mid 19th century ...This chest came from County Cavan, North Ireland, with Jane Fleming, when she migrated to Australia arriving at Port Fairy in approximately 1863. Jane Flemming was about 6 or 7 years old at the time and later was to become the mother of Mary Jane Giles (nee Flemming). This chest is one of many 19th century items of furniture, linen and crockery donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by, Vera and Aurelin Giles. The items are associated with Warrnambool and the Giles Family history. Items donated by the family have come to be known as the “Giles Collection”. Many items in the Lighthouse Keeper’s Cottage were donated by Vera and Aurelin Giles and mostly came from the home of Vera’s parents-in-law, Henry Giles and his wife Mary Jane (nee Freckleton) who married in 1880 and whose photos are on display in the parlour. Henry was born at Tower Hill in 1858, and was a labourer on the construction of the Warrnambool Breakwater before leaving in 1895 for around seven years to build bridges in NSW. Mary Jane was born in 1860 at Cooramook and she attended Mailor’s Flat State School and where she eventually was to become a student teacher. After which she became a governess at “Injemiara” where her grandfather, Francis Freckleton, had once owned land. Henry and Mary’s family consisted of six, some of the children were born at Mailor’s Flat and later some children at Wangoom. They lived with their parents at Wangoom and Purnim west, and this is where Henry died in 1933 and Mary Jane in 1940.The chest is of historical significance as an example of an early piece of furniture brought to Australia by Jane Flemming when she migrated to Australia during the mid 19th century. The chest is associated with the Giles family as Jane later was to become the mother Of Mary Jane Giles (nee Flemming). The Giles family collection is of social and historical significance at a local level, because it not only illustrates the level of material support the Warrnambool community gave to Flagstaff Hill during it’s establishment. But the Giles collection also gives us today a snapshot into what domestic life was like in early colonial times prior to Federation. Linen chest wood construction with hinged lid and lock. Hinges are brass. Painted black. ( Giles Collection)Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, wooden chest, cabin trunk, giles collection, henry giles, tower hill, cooramook, mailor’s flat, wangoom, 19th century household goods, jane flemming, mary jane giles, linen chest -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Jug, 1881
... item. A mid to late 19th century ironstone jug with no makers ...Over 1500 pottery firms have operated in Stoke-on-Trent since the early 1700's - Some lasted only a few years and some for well over 200 years. Some potters built and owned their own works. Many others were tenants in works built by others and a succession of potters occupied the same works. It was also a common practice for a works to be split between two different pottery companies or for a larger manufacturer to let out a smaller section of his works to a potter who would make wares which were not of interest to the pot works owner. Some potters purchased 'blanks' from other manufacturers and put their own decoration on them some items have two back stamps some have no marks at all. This adds to the confusion and frustration of trying to trace details of a particular manufacturer such as the subject item.A mid to late 19th century ironstone jug with no makers markings only a date letter therefore at this time cannot be associated with an historical event, person or place, provenance regards maker is unknown, item assessed as a collection asset given it was produced before 1950.Jug, white Earthenware with leaf decoration around the base, handle and lip.Letter "E" date mark for 1881flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, ceramic jug, drink ware, kitchen ware, table ware, ceramic, pottery, milk jug, cream jug, ironstone jug -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, Physiological Principles in Treatment, 1930
... an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr ...This book was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969.The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Book Title- 'Physiological Principles in Treatment' by Brown and Hilton, 6th edition. Red hard cover book with title stamped into cover. Approximately 464 pages.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, physiological principles in treatment, medical book 1930 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Bowl, J & G Meakin, Late 19th or early 20th Century
The Process of Making Pottery Decorating, Firing, Glazing, Making, Technical There is a rhythm and flow to clay. It can’t be done all at once! Even the making process! It can take weeks to get everything done, especially if you can only work on your pottery once a week! Even though we have three hour classes, it’s often just not enough time! Here is an overview of some of the processes so you have a bit more grasp on some of the technical stuff! Step One – Design There are SO many ideas out there for making stuff in clay! From delicate porcelain jewellery, through to heavy sculptural work and everything in between. Deciding your direction is sometimes not that easy – when you first start, try everything, you will naturally gravitate to the style that you enjoy! The options and variations are endless and can get a wee bit overwhelming too! Check in with me before you start to ensure your ideas will work, what order you might do things, how you could achieve the look you are seeking and any other technical data required! Step Two – Making Clay is thixotropic. This means that as you work with it, the clay first gets sloppier and wetter, before is begins to dry in the atmosphere. For most things, you simply can’t do all parts of the project at once. An example of work order might look like: Get last weeks work out from the shelves Prepare clay for today’s work – roll your clay, prepare balls for throwing, make the first stage of a pinch pot) Clean up last week’s work and put it on the shelf for bisque firing Check that you have any glazing to do – and do enough of it that you will have time to finish your main project Do the next step of your next project – there might be a further step that can’t be complete immediately, in that case, wrap your work well and put onto the shelves. Letting your work rest for a while can really help keep your work clean and professional looking. Many things require bagging under plastic to keep it ready for work the next week – put your name on the outside of the bag so you can find your work easily. We have stickers and markers. Consider how you want to decorate your work – coloured slip can be applied at a fairly wet stage (remembering that it will make your work even wetter!). Trying to apply slip to dry clay won’t work! If you want to do sgraffito – you will need to keep the work leather hard (a state of dryness where you can still work the clay with a little effort and a little water and care). Step Three – Drying Most of the time your work can go into the rack uncovered to let it dry out for the following week. If you want to continue forming or shaping you will need to double bag your work – put your work on a suitable sized bat and put the bat in a bag so the base of the bag is under the bat, then put another bag over the top of the work and tuck the top of the bag under the bat. If you want to trim (or turn) your thrown work the following week, it should also be double bagged. If your work is large, delicate, or of uneven thicknesses, you should lightly cover your work for drying. When considering the drying process, bare in mind the weather, humidity and wind! The hotter and dryer, the faster things dry and work can dry unevenly in the shelves – this can lead to cracking – another time to lightly cover your work for drying. Step Four – Trimming and Cleaning Up Your work is dry! It is called greenware now and it is at it’s most fragile! Handle everything with two hands. I often refer to soft hands – keep everything gentle and with your fingers spread as much as possible. Try to not pick up things like plates too much, and always with both hands! Before your work can be bisque fired it should be “cleaned up”. You work won’t go into the kiln if it has sharp edges – when glazed, sharp edges turn into razor blades! Use a piece of fly wire to rub the work all over – this will scratch a little so be light handed. Use a knife or metal kidney to scrape any areas that require a bit more dynamic treatment than the fly wire offers! Finally, a very light wipe over with a slightly damp sponge can help soften and soothe all of your edges and dags! Trimming thrown work: If you are planning to trim (or turn) your thrown work (and you should be), make sure you bag it well – your work should be leather hard to almost dry for easiest trimming. Use this step to finish the work completely – use a metal kidney to polish the surface, or a slightly damp sponge to give a freshly thrown look. Wipe the sponge around the rim after trimming, and check the inside of the pot for dags! Trimming slip cast work: Usually I will trim the rims of your work on the wheel the following day to make that stage easier, however you will still need to check your work for lumps and bumps. Last but not least – check that your name is still clearly on the bottom of your work. Step Five – Bisque Firing When the work is completely dry it can go into the bisque kiln. The bisque kiln is fired to 1000°C. This process burns off the water in the clay as well as some of the chemically bound water. The structure of the clay is not altered that much at this temperature. Inside the bisque kiln, the work is stacked a little, small bowl inside a larger bowl and onto a heavy plate. Smaller items like decorations or drink coasters might get stacked several high. Consideration is paid to the weight of the stack and shape of the work. A bisque kiln can fire about one and a half times the amount of work that the glaze kiln can fire. The firing takes about 10 hours to complete the cycle and about two days to cool down. Once it has been emptied the work is placed in the glaze room ready for you to decorate! Step Six – Glazing Decorating your work with colour can be a lot of fun – and time consuming! There are three main options for surface treatment at this stage: Oxide Washes Underglazes Glazes Washes and underglazes do not “glaze” the work – It will still need a layer of glaze to fully seal the clay (washes don’t need glaze on surfaces not designed for food or liquid as they can gloss up a little on their own). Underglazes are stable colourants that turn out pretty much how they look in the jar. They can be mixed with each other to form other colours and can be used like water colours to paint onto your work. Mostly they should have a clear glaze on top to seal them. Oxides are a different species – the pink oxide (cobalt) wash turns out bright blue for instance. They don’t always need a glaze on top, and some glazes can change the colour of the wash! The glazes need no other “glaze” on top! Be careful of unknown glaze interactions – you can put any combination of glaze in a bowl or on a plate, but only a single glaze on the outside of any vertical surface! Glazes are a chemical reaction under heat. We don’t know the exact chemicals in the Mayco glazes we use. I can guess by the way they interact with each other, however, on the whole, you need to test every idea you have, and not run the test on a vertical surface! Simply put, glaze is a layer of glass like substance that bonds with the clay underneath. Clay is made of silica, alumina and water. Glaze is made of mostly silica. Silica has a melting point of 1700°C and we fire to 1240°C. The silica requires a “flux” to help it melt at the lower temperature. Fluxes can be all sorts of chemicals – a common one is calcium – calcium has a melting point of 2500°C, however, together they both melt at a much lower temperature! Colourants are metal oxides like cobalt (blue), chrome (green through black), copper (green, blue, even red!), manganese (black, purple and pink) iron (red brown), etc. Different chemicals in the glaze can have dramatic effects. for example, barium carbonate (which we don’t use) turns manganese bright pink! Other elements can turn manganese dioxide brown, blue, purple and reddish brown. Manganese dioxide is a flux in and of itself as well. So, glazes that get their black and purple colours, often interact with other glazes and RUN! Our mirror black is a good example – it mixes really well with many glazes because it fluxes them – causes them to melt faster. It will also bring out many beautiful colours in the glazes because it’s black colouring most definitely comes from manganese dioxide! Glaze chemistry is a whole subject on it’s own! We use commercial Mayco glazes on purpose – for their huge range of colour possibilities, stability, cool interactions, artistic freedom with the ability to easily brush the glazes on and ease of use. We currently have almost 50 glazes on hand! A major project is to test the interactions of all glazes with each other. That is 2,500 test tiles!!!! I’m going to make the wall behind the wheels the feature wall of pretty colours! Step Seven – Glaze (Gloss or sometimes called “Glost”) Firing Most of the time this is the final stage of making your creation (but not always!) The glaze kiln goes to 1240°C. This is called cone 6, or midrange. It is the low end of stoneware temperatures. Stoneware clays and glazes are typically fired at cone 8 – 10, that is 1260 – 1290°C. The energy requirement to go from 1240°C to 1280°C is almost a 30% more! Our clay is formulated to vitrify (mature, turn “glass-like”) at 1240°, as are our glazes. A glaze kiln take around 12 hours to reach temperature and two to three days to cool down. Sometimes a third firing process is required – this is for decoration that is added to work after the glaze firing. For example – adding precious metals and lustres. this firing temperature is usually around 600 – 800°C depending upon the techniques being used. There are many students interested in gold and silver trims – we will be doing this third type of firing soon! After firing your work will be in the student finished work shelves. Remember to pay for it before you head out the door! There is a small extra charge for using porcelain clay (it’s more than twice the price of regular clay), and for any third firing process! Once your work has been fired it can not turn back into clay for millennia – so don’t fire it if you don’t like it! Put it in the bucket for recycling. https://firebirdstudios.com.au/the-process-of-making-pottery/This bowl was made by renowned pottery company J & G Meakin of England. The firm was established in the mid-1800's. The bowl is an example of kitchenware used in the 19th century and still in use today.Bowl; white ceramic, round and tapering inwards towards base. Made by J and G Meakin England.On base, 'Ironstone China Reg SOL 391413' with symbolflagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, mixing bowl, food preparation, j & g meakin, pottery, stoke-on-trent, kitchen equipment, ceramic -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Fork
Naturally, we tend to take commonplace objects for granted, because they have always been there. Yet how many of you actually have thought “hey, where do forks come from?” Well, it takes one trip to China and a 3-year-old laughing at your face because of your desperate attempt to eat with chopsticks to finally appreciate something so ordinary such as a fork. So, where do forks come from? The early history of the fork is obscure. As a kitchen and dining utensil, it is believed to have originated in the Roman Empire, as proved by archaeological evidence. The personal table fork most likely originated in the Eastern Roman (or Byzantine) Empire. Its use spread to what is now the Middle East during the first millennium AD and then spread into Southern Europe during the second millennium. It did not become common in northern Europe until the 18th century and was not common in North America until the 19th century. Carving fork from 1640. Source: Wikipedia/Public Domain Carving Fork from 1640. Source: Wikipedia/Public Domain Some of the earliest known uses of forks with food occurred in Ancient Egypt, where large forks were used as cooking utensils. Bone forks had been found on the burial site of the Bronze Age Qijia culture (2400–1900 BC) as well as later Chinese dynasties’ tombs.The Ancient Greeks used the fork as a serving utensil. Read also: Steven Spielberg to Remake the Classic Musical ‘West Side Story’ In the Roman Empire, bronze and silver forks were used. The use varied according to local customs, social class and the nature of food, but forks of the earlier periods were mostly used as cooking and serving utensils. The personal table fork was most likely invented in the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire, where they were in everyday use by the 4th century (its origin may even go back to Ancient Greece, before the Roman period). Records show that by the 9th century a similar utensil known as a barjyn was in limited use in Persia within some elite circles. By the 10th century, the table fork was in common use throughout the Middle East. Bronze forks made in Persia during the 8th or 9th century.Source: Wikipedia/Public Domain Bronze forks made in Persia during the 8th or 9th century.Source: Wikipedia/Public Domain The first recorded introduction of the fork to Western Europe, as recorded by the theologian and Cardinal Peter Damian, was by Theophano Sklereina the Byzantine wife of Holy Roman Emperor Otto II, who nonchalantly wielded one at an Imperial banquet in 972, astonishing her Western hosts.By the 11th century, the table fork had become increasingly prevalent in the Italian peninsula. It gained a following in Italy before any other Western European region because of historical ties with Byzantium and continued to get popularity due to the increasing presence of pasta in the Italian diet. At first, pasta was consumed using a long wooden spike, but this eventually evolved into three spikes, design better suited to gathering the noodles. In Italy, it became commonplace by the 14th century and was almost universally used by the merchant and upper classes by 1600. It was proper for a guest to arrive with his fork and spoon enclosed in a box called a cadena; this usage was introduced to the French court with Catherine de’ Medici’s entourage. In Portugal, forks were first used at the time of Infanta Beatrice, Duchess of Viseu, King Manuel I of Portugal’s mother around 1450. However, forks were not commonly used in Western Europe until the 16th century when they became part of Italian etiquette. The utensil had also gained some currency in Spain by this time, and its use gradually spread to France. Nevertheless, most of Europe did not adopt the use of the fork until the 18th century. Read also: The 8 Most Famous ‘Functioning Alcoholics’ in History Long after the personal table fork had become commonplace in France, at the supper celebrating the marriage of the Duc de Chartres to Louis XIV’s natural daughter in 1692, the seating was described in the court memoirs of Saint-Simon: “King James having his Queen on his right hand and the King on his left, and each with their cadenas.” In Perrault’s contemporaneous fairy tale of La Belle au bois dormant (1697), each of the fairies invited for the christening is presented with a splendid “fork holder”. The fork’s adoption in northern Europe was slower. Its use was first described in English by Thomas Coryat in a volume of writings on his Italian travels (1611), but for many years it was viewed as an unmanly Italian affectation. Some writers of the Roman Catholic Church expressly disapproved of its use, St. Peter Damian seeing it as “excessive delicacy.” It was not until the 18th century that the fork became commonly used in Great Britain, although some sources say that forks were common in France, England, and Sweden already by the early 17th century. Spaghetti fork By Lady alys - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=6414948 Spaghetti Fork By Lady alys – Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, The fork did not become popular in North America until near the time of the American Revolution. The curved fork used in most parts of the world today was developed in Germany in the mid 18th century while the standard four-tine design became current in the early 19th century. The fork was important in Germany because they believed that eating with the fingers was rude and disrespectful. The fork led to family dinners and sit-down meals, which are important features of German culture. https://www.thevintagenews.com/2016/08/31/priority-fork-came-italy-european-country-pasta/?chrome=1Serving fork, two prongs, with a shaped wooden handle. Badly rusted.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, food, meat, carving -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Piano, John Broadwood & Sons, circa 1862
... for entertainment and worship from the mid-19th to early-20th century ...The company that made this piano was founded in 1728 by Burkat Shudi, a Swiss harpsichord maker. John Broadwood, a joiner and cabinetmaker, worked for Shudi and eventually married his daughter and became a partner in the firm. Broadwood continued in this business after Shudi died in 1773. John's son James also worked for the firm and in 1795 they became John Broadwood & Son, then when a third son joined as partner in 1808 they become John Broadwood & Sons Ltd. and the name has continued on even now. Pianos manufactured by John Broadwood are of world renown.This piano is significant as a historical musical instrument. It is an example of the type of instruments used for entertainment and worship from the mid-19th to early-20th century. Piano, cottage upright, wooden casing in dark wood with a rich grain. Piano features a pair of brass candlestick holders, music holder and fitted lock on keyboard cover. Decorative design etched in panel between candlestick holders, Maker's name is in fancy lettering behind the keyboard. Made by John Broadwood and Sons, London. Painted in fancy text "John Broadwood & Sons/ / London"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, piano, upright, candlestick holder, john broadwood & sons london, musical instrument, upright cottage piano, antique piano, victorian entertainment -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Porthole Frame, Alexander Hall and Son, ca. 1855
... of an ship's fitting in common use in the mid-19th century ...The porthole was recovered from the wreck of the clipper ship Schomberg. ABOUT THE SCHOMBERG (October 6 to December 27, 1855)- When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Baines Black Ball Line had commissioned her for their fleet of passenger liners. The Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the clippers designed the three-masted wooden clipper ship to be fast. The timber used for the diagonal planking was British oak with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury emigrant vessel was designed for superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first-class passengers. The master for Schomberg’s maiden voyage was Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes. He drunkenly predicted at her launch that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons of cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The poor winds slowed Schomberg’s sail across the equator. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the coastal steamer SS Queen at dawn and sent a signal. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers safely disembarked. In 1975, 120 years after the Schomberg was wrecked, divers from Flagstaff Hill found an ornate communion set at the wreck site along with many other artefacts. In 1978 a diamond ring was discovered under the concretion in the lid of the communion set, which is currently on display. Former Director of Flagstaff Hill, Peter Ronald, had salvaged most of the artefacts from the wreck. This porthole is significant as an example of an ship's fitting in common use in the mid-19th century. The Schomberg collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of prime significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes.Porthole frame. Square thick metal plate with formed holes for fixing. Central round opening in the plate is fitted with a hinged round frame with a handle opposite the hinge. Bolts are embedded in the inner frame. The surface is encrusted and the plate is broken near one corner. The frame was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, schomberg, 1855, clipper ship, black ball line, luxury ship, emigrant ship, captain forbes, bully forbes, ss queen, james baines & co, porthole frame
