Showing 85 items matching "grassland"
-
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, "Pindarri" - John Serle, 1968, 1971
Pindarri was the name of the property on which artist John Serle lived on Pindari Road, St. Andrews. Colour painting reproduced on page 11 of "Pioneers & Painters: One hundred years of Eltham and its Shire" by Alan Marshall (1971). This chapter 1 "In the beginning" gives a physical description of the area: "Thick forest covered all the higher mountain ranges .. These areas were all heavily timbered, associated grasslands and eucalyptus extending from the thick forest country across undulating hills to the Yarra... The timber in general is gum, oak and Banksia, the two later are small, the gum two to four feet of diameter and from then to thirty feet high; on some of the low ground somewhat larger. The forest was open with little scrub..." The artist John Serle (born 1928) was the first local artist to become a councilor for the Shire of Eltham. He also worked for the Shire of Eltham grading roads. The Shire of Nillumbik hold a similiar painting in their collection (access via Victorian Collections) titled: Untitled (bush) Donor details on file. Location of original painting unknown. Most probably held in Serle family collection. Painting produced in 1968. Reproduced in "Pioneers and Painters", 1971 This photo forms part of a collection of photographs gathered by the Shire of Eltham for their centenary project book,"Pioneers and Painters: 100 years of the Shire of Eltham" by Alan Marshall (1971). The collection of over 500 images is held in partnership between Eltham District Historical Society and Yarra Plenty Regional Library (Eltham Library) and is now formally known as the 'The Shire of Eltham Pioneers Photograph Collection.' It is significant in being the first community sourced collection representing the places and people of the Shire's first one hundred years.4 x 5 inch colour reversal film (1) Condition: May not be true to colour of original work. Scanned from a 4 x 5 inch colour transparency which was taken c.1970 (approx. 50 years old) and which has undergone significant colour degradation towards the red spectrum. Allowances made for colour cast correction in scan with best guess for white balance. Significant light flare is reflected off glossy surface of original work at camera lens at lower left and right sides causing quality issues.pioneers and painters, sepp, shire of eltham pioneers photograph collection, john serle, pindarrri, bush -
 Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)
Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA)Driptorch - Firebug (hand held), c 1985
The origins of the humble handheld driptorch have been lost in time. They are widely used for ignition in controlled burning operations in forest and grasslands. The “Pacific Forester“ with its short central wand and somewhat leaky ball-valve was made by the American Wajax company in the 1940s. The Pacific Forester is slightly different in design from the more robust and common “Panama” driptorch first manufactured in 1933 and used extensively by Queensland cane farmers. The Panama is closely related to the current “Firebug” used in Victoria which is manufactured by Rodney Industries in Brisbane and has an offset wand design which gives it good balance. The fuel is a mixture of petrol and diesel and every FCV District had their own closely-guarded secret formula ... 2:1, 3:1, 1:1, 4:1 or 3:2 ratio. There was also the choice of 91, 95 or 98 octane petrol mixed with summer or winter diesel. Occasionally some of the old Avgas or Jet-A1 lying around the depot was added with a splash of engine oil to make the mixture stick to the fuel to be ignited. The fuel mixed also varied between autumn or spring, heathland, mixed forest, or high-intensity slash burnsCommon driptorch used throughout AustraliaDrip torch with handle Wand has loop and valve. The loop is designed to assist with even flow of fuel which flows out onto the burning head of the wand. Pressure equalising value in top of aluminum fuel container which holds 4 litres of burner mix. Gravitational feed of the driptorch allows the unit to drip fire, making it simple and quick to operate. Instructions for use. CF+L written with texta pen.bushfire -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPacific firelighter
The origins of the humble handheld driptorch have been lost in time. They are widely used for ignition in controlled burning operations in forest and grasslands. The “Pacific Forester“ with its short central wand and somewhat leaky ball-valve was made by the American Wajax company in the 1940s. The Pacific Forester is slightly different in design from the more robust and common “Panama” driptorch first manufactured in 1933 and used extensively by Queensland cane farmers. The Panama is closely related to the current “Firebug” used in Victoria which is manufactured by Rodney Industries in Brisbane and has an offset wand design which gives it good balance. The fuel is a mixture of petrol and diesel and every FCV District had their own closely-guarded secret formula ... 2:1, 3:1, 1:1, 4:1 or 3:2 ratio. There was also the choice of 91, 95 or 98 octane petrol mixed with summer or winter diesel. Occasionally some of the old Avgas or Jet-A1 lying around the depot was added with a splash of engine oil to make the mixture stick to the fuel to be ignited. The fuel mixed also varied between autumn or spring, heathland, mixed forest, or high-intensity slash burnsKerosene drip torch Short wand no valveBCR Holdingsforests commission victoria (fcv), planned burning, bushfire -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionBell Backburner Lighting Torch
The origins of the humble handheld driptorch have been lost in time. They are widely used for ignition in controlled burning operations in forest and grasslands. The “Pacific Forester“ with its short central wand and somewhat leaky ball-valve was made by the American Wajax company in the 1940s. The Pacific Forester is slightly different in design from the more robust and common “Panama” driptorch first manufactured in 1933 and used extensively by Queensland cane farmers. The Panama is closely related to the current “Firebug” used in Victoria which is manufactured by Rodney Industries in Brisbane and has an offset wand design which gives it good balance. The fuel is a mixture of petrol and diesel and every FCV District had their own closely-guarded secret formula ... 2:1, 3:1, 1:1, 4:1 or 3:2 ratio. There was also the choice of 91, 95 or 98 octane petrol mixed with summer or winter diesel. Occasionally some of the old Avgas or Jet-A1 lying around the depot was added with a splash of engine oil to make the mixture stick to the fuel to be ignited. The fuel mixed also varied between autumn or spring, heathland, mixed forest, or high-intensity slash burnsKerosene drip torch Long straight wand with control valveBell Backburnerforests commission victoria (fcv), planned burning, bushfire -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFirebug
The origins of the humble handheld driptorch have been lost in time. They are widely used for ignition in controlled burning operations in forest and grasslands. The “Pacific Forester“ with its short central wand and somewhat leaky ball-valve was made by the American Wajax company in the 1940s. The Pacific Forester is slightly different in design from the more robust and common “Panama” driptorch first manufactured in 1933 and used extensively by Queensland cane farmers. The Panama is closely related to the current “Firebug” used in Victoria which is manufactured by Rodney Industries in Brisbane and has an offset wand design which gives it good balance. The fuel is a mixture of petrol and diesel and every FCV District had their own closely-guarded secret formula ... 2:1, 3:1, 1:1, 4:1 or 3:2 ratio. There was also the choice of 91, 95 or 98 octane petrol mixed with summer or winter diesel. Occasionally some of the old Avgas or Jet-A1 lying around the depot was added with a splash of engine oil to make the mixture stick to the fuel to be ignited. The fuel mixed also varied between autumn or spring, heathland, mixed forest, or high-intensity slash burnsKerosene drip torch Long straight wand with control valveBell Backburnerforests commission victoria (fcv), planned burning, bushfire -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesAlbum - Colour prints, negatives and 35mm slides, Staff, Collection of Photographs Used by Staff, 1994-2000
Collection of photographs in envelopes which had belonged to staff members. Some are photographs from excursions, others are teaching material, plants. Some labelled: 1. Ruth Upper Merri Creek - negatives and prints; Merri Creek - negatives and prints; Merri Creek Panorama - prints; Merri Creek Posters 1995 - negatives and prints; Plants - negatives. 2. Western District Exhibition, labelled - negatives and prints of paintings; Mt Ridley (Excursion?) - negatives and prints; Energy Education Centre 15 November 1995; Gardens - Spring 1995 negatives (mostly James Hitchmough, Native Grasslands and Luffmann Ponds) Scanned; Student Party June 1994 - negatives; 3. Pot Trial - negatives and prints; Miscellaneous plant trials, Centenial Centre Shop, Arborists, Plants, Excursions - negatives; Excursions , 1 year 2000 - negatives and prints; Orchard (older) - black and white negatives and prints; Arborists - negatives and prints; 4. Staff, Graduate students - negatives and prints; Miscellaneous: Plants, - negatives, slides and prints. 7. Native Garden and other garden views - prints and negativesstaff, excursions, teaching material, merri creek, mt ridley, energy education centre, student party, pot trial, centenial centre shop, arborists, plants, graduates, students, plant database, jill kellow, orchard, james hitchmough grasslands, horticulture shop, ruth beilin, upper merri creek, merri creek panorama, merri creek posters -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Brown Falcon, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Brown Falcon is a small to medium bird of prey which can be found all throughout Australia. These birds are raptors and typically feed on mammals, birds, snakes, insects and rabbits. The Brown Falcon are located in all but the densest forests. They typically prefer to reside in locations of open grassland and agricultural areas which have scattered trees or telephone poles which the bird can perch on. When frequenting towns located in the Australian Outback, these birds are reportedly quite tame and can be approached by humans. They may stay in the same location throughout the year or chose to move around locally in response to any changes in weather conditions. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th centuryThis specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Brown Falcon specimen has plumage which is mostly brown and intermixed with white. This provides the appearance of having spotted colouring on the birds back. The head is also mostly brown with white under the beak area and a characteristic brown streak under the eye area. The eye is made from dark coloured glass.3 / Brown Hawk / See Catalogue, page 2 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, brown falcon, falconidae -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Eastern Rosella, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
Eastern Rosellas are multi-coloured medium-sized Australian parrots with distinctive white cheek patches. The Eastern Rosella is found throughout south-eastern Australia, from Queensland to Victoria, south-eastern South Australia, and eastern Tasmania. Despite their vibrant colours, Rosellas camouflage well into their surroundings when perching or when on the ground. The Eastern Rosella is found in open woodlands, grasslands, farmlands and remnant bushland. These birds are often found in urban habitats such as parks, gardens and golf courses. Early European settlers encountered the Eastern Rosella at Rose Hill, New South Wales, now Parramatta, and so they called it the Rosehill parakeet which became "Rosehiller", and eventually shortened to "rosella". This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century. This mature Eastern Rosella has a red head and breast, with a light green belly and distinctive white cheeks. The back is yellow-green with black mottling, the yellow-green turning green then to blue across the wings. The tail feathers are blue/black, with a red base on the underside. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg.Label: 79/ Rose-hill Parakeet / See catalogue, page 22 taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, australian birds, rosella, eastern rosella, rosehill parakeet, rose-hill parakeet -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Nankeen Kestrel, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Nankeen Kestrel, also known as the Australian Kestrel, is a common native to the open country's grasslands and farmlands, preferring agricultural areas. They are drawn to animal pests like mice, insects, small animals, reptiles, and birds. Due to the shape and ability of their tail feathers, which allows them to hoover over their prey, they do not rely on speed to catch their meal like most falcons in their family group. These birds are among the smallest raptors in the Falcon family, having well-known face characteristics and body shapes. The females of the species are distinguished by their darker patterns and red-brown (rufous) tones, as well as their larger size, whilst the males are more greyish. The yellow markings around the eyes and top of the beak, as well as the noticeable black dipped wings, distinguish each species. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Nankeen Kestrel is a small raptor in the Falcon family. It has a stockier appearance, with the upper parts of its body, such as the head and the tops of its wings, being a light red-brown (rufous) colour and the tips of its wings appearing dipped in black. The top of the beak and the eye rings are both yellow, and this bird's falcon appearance shows its inherent dark streak markings visible near the eyes and on the chest. The underparts are pale, with a tail feather that spreads out to help it hover and is ornamented with fine black decorations.20. / Unnamed / Catalogue page 5 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, nankeen kestrel -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Nankeen Kestrel, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Nankeen Kestrel, a small type of falcon, can be found all over Australia, usually in grassland or farmland areas. This falcon is carnivorous and hunts all manner of small prey including mice, lizards, insects, and other birds. When hunting, Nankeen Kestrels can be seen hovering in the air searching for prey. Nankeen Kestrels are generally monogamous, staying with the same breeding partner for multiple seasons. The Nankeen Kestrel is known for its reddish-brown feathers, spotted with a distinctive black pattern on its back, and have black-tipped wings and tail band, a stark contrast to its white chest. Females tend to be larger, and males will have a grey head and neck area. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This female Nankeen Kestrel is relatively small and slender. It is mostly reddish-brown, streaked with darker coloured areas. The tips of the wings and tail feathers are tipped in black. The chest is white with streaks of reddish-brown. The areas around its eyes, beak, and feet are a bright yellow. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg.Swing-tag: 19. / Unnamed / Catalogue page, 5 /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, nankeen kestrel, falcon -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Magpie-Lark, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Magpie-Lark, also commonly known as a Mudlark, is a carnivorous bird found in many regions of Australia, Indonesia, Timor, and Southern New Guinea. They are a non-migratory species and are extremely adaptable to a variety of environments. These environments include dry forest, savannah, grassland, and even urban areas. Magpie-Larks are typically monogamous and are often found in pairs. They are black and white, with a white underbelly, long legs, and a long, thin beak. The females of this species have a white throat, while the males have a white eyebrow and a black throat. While juveniles have dark eyes, mature adults have light irises. This information helps identify this specimen as an adult male. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Magpie-Lark is a small to medium-sized bird which has distinctive black and white colouring. The bill is long and thin and is a whitish colour which differentiates it to other Magpie species. When mature, like this particular specimen, the Magpie-Lark have distinctive light irises. The glass eyes provided for this specimen are accurate in colour. This male specimen has a white 'eyebrow' marking and a black chest or bib. This Magpie-Lark stands on a wooden mount with a swing tag attached to its leg.Swing-tag: 20a. / Reed Grallina / See catalogue page 10 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, mudlark, magpie-lark -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Northern Hawk Owl, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Northern Hawk-owl is a nomadic and generally solitary bird, although they can occasionally be seen in pairs. While these birds resemble owls, their behaviour is more similar to that of a hawk, hence their name. Normally active during the day (similar to the hunting habits of a hawk), they prefer to reside in boreal forest, grasslands, shrublands and temperate, cold and polar zones. Located in North America, Europe and Asia, these owls can also occasionally be found during migration, in the northern United States. There are three subspecies in North America, Central Asia and Siberia. At the present time (2021), its numbers are stable and so it is therefore considered of ‘least concern’ on the IUCN Red List, indicating it is not yet endangered. This particular specimen has been correctly mounted and presented as a relatively accurate representation of the actual bird. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.The Northern hawk-owl's face features white and brown soft feathery plumage and a dark brown border around its face/chin area, with a dark cream curving beak soft yellowy brown coloured eyes. Its front breast feathers are generally off white in colour with some flecks of brown. It has a long brown tail with off white banding, with creamy white claws. The owl has speckled brown and white plumage over the back of its body and wings and some areas of more solid brown are present around the back of its neck and top of wings. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and two identifying tags hang from its right leg, while a metal numbered tag hangs from its left.Swing-tag: 38 / Rayed Swin Owl –/ See Catalogue, Page 53. Tag with faded script: No 33 Strix[?] / misarea[?] / Sweden[?] Metal tag - digits on metal tag appear to read, either ‘5028’ or ‘6028’taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, surnia ulula, strigidae, northern hawk-owl, hawk-owl, canadian owl, hudsonian hawk-owl, owl, canada, asia, europe, north america -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesAlbum - Digitised, Sandra Pullman, Sandi Pullman Album, 1998-2000
93 photographs from Sandi Pullman's album. Scanned March 2013. Some have descriptions on reverse. Originals remain with Sandi Pullman (Student, FOBG). (13-19) John Delpratt's Grassland Project FOBG 30.05.98. (20-30) FOBG Working Bee 10.10.98 Ground Cover Trial Plots. (1-12) First Friends of Burnley Gardens Working Bee, "Planting the Back Car Park along the trainline 2nd May, 1998. (First Stage of the car park sited on Richmond City Council land at the rear of the College completed 1980.) (31-45) Back Car Park 11.09.99. (46-51) Native Garden 27.11.99. (52-53,72-75) 150th Celebration of What? Oct 2000, Ellis Stones Rockery Oct 2000. (54-58, 71, 76, 84, 86, 88-91, 93) Harvesting Grasses. (59-62) Nicki Rose from the Australian Plant Society presenting Dr Greg Moore with $1,500 cheque at an afternoon tea on the Citriodora Lawn 31.03.2000. (63-70) Melbourne International Flower & Garden Show (M.I.F.G.S.) 2000. (77-83) First Pruning Day 1999.sandi pullman, sandra pullman, fobg, john delpratt's grassland, working bee, native garden, ellis stones rockery, harvesting grasses, nicki rose, australian plant society, dr greg moore, melbourne international flower & garden show, m.i.f.g.s., back car park, wrong 150th celebrations, ground cover trials -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Black Shouldered Kite, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
The Black Shouldered Kite is commonly found throughout mainland Australia in grasslands and other open habitats. It is a raptor (bird of prey) that will eat mice and other small rodents. The species is monogamous and will find a mate by the male giving food to the female while both are in flight. It is sometimes confused with the letter-winged kite though there undercarriages when in flight are very different with the letter-winged showing the letter W or M and the black shouldered kite showing black wing tips with white towards its belly area. The feathers of this species when alive and in the wild are more white than this specimen. The iris is usually red in mature birds so this specimen may not have been a mature bird as its eyes are brown. However, this is difficult to ascertain because it is also possible that the taxidermist who replaced the original eyes with the current glass ones provided a colour which was not accurate to the age/species of the bird. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This Black Shouldered Kite has a white face and front of body with a grey posterior from the top of its head to its tail. It has black on its wings/shoulders. Its face is white with its eyes delineated by small black apostrophe like shapes from the inner eye to the top of the eye. The specimen stands on a wooden perch and has a swing tag tied around its right leg. Its eye colour is brown rather than red, indicating it is not a mature specimen.9. / Black Shouldered Kite / See Catalogue, page 3 / taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, black shouldered kite -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesAlbum, Jan Chamberlain, Friends of Burnley Gardens Achievement Book, 2000
camellia planting ceremony, kay hirst, a w jessep, dorothy jessep, tom kneen, andrew smith, camellia japonica 'a w jessep', camellia japonica' dorothy jessep', friends of burnley gardens, fobg, sir rupert hamer, open gardens scheme, ellis stones rock garden, ellis stones, australian plants society, grasslands project, 150th birthday celebration, pruning day 2000, planting ellis stones rockery 2000, summer house, shelter shed, native garden, herb garden, grey garden, orchard, field station, bulb bed, working bee, twilight working bee, ikebana exhibition -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Hawthorn hedges, Eltham-Yarra Glen Road, Kangaroo Ground, 3 October 2006
Hawthorn hedges are important reminders of Kangaroo Ground's Scottish heritage. They are Registered on the Victorian Heritage Register. They are "historically significant because the planting of hawthorn hedges reflects the adoption of Eurorpean farming techniques by the Kangaroo Ground population in the period following settlement and because the grid pattern of paddocks that the Hawthorn hedges define is very different to today's farm landscapes." Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p21 Hawthorn hedges bordering Kangaroo Ground’s gently rolling farmlands are important reminders of its Scottish heritage and are rare so close to Melbourne.1 As early as the 1840s newly arrived farmers from Scotland planted hawthorn hedges around their properties, to protect crops from the numerous kangaroos and wallabies. Many of these hedges survive today. These farmers had the good fortune to settle some of the most fertile land available for cropping in the Colony of Victoria. At that time the black volcanic soil could sustain an amazing two crops a year. By the mid 1850s, 500 acres (202ha) of wheat were growing in Kangaroo Ground. But the crops were threatened by kangaroos, which were so plentiful, that Surveyor-General, Robert Hoddle, named the district Kangaroo Ground in 1838. As post-and-rail fences proved inadequate barriers for the bounding kangaroos, the Scots planted hawthorn hedgerows as they had done in Scotland. Some also used the hedges to net birds, presumably for the table. Interestingly the farmers in the bordering townships of Panton Hill and Christmas Hills, did not plant hawthorn hedges around their properties. Perhaps it was because by the time they settled in the 1860s and 1870s most of the wildlife had been gunned down by residents.2 The canny Scots planted the hedges on public land outside their own farms, as the hedgerows could spread to about five yards (five m) in width. With this impenetrable barrier Kangaroo Ground’s industrious farmers flourished to gain the economic power that saw the Shire of Eltham governed from Kangaroo Ground for 79 years (1858-1937). The Scots jealously guarded their land, so hard to get in Scotland. That is why they refused to release any of it ‘for local roads to follow easier grades as was the case in surrounding districts where roads generally followed ridgelines or streams’.3 Instead the roads were built in accordance with the magnetic bearings of their first survey in 1847 whether that suited the steep topography or not. This could force traffic to diverge when wet through Greensborough and Diamond Creek. Until 1921, the Eltham-Yarra Glen Road beside Wellers Restaurant, ‘dipped down into the upper reaches of Stony Creek’.4 Later some corners were compulsorily cut for the increasing motor traffic. As late as the 1960s, corners were cut to form sweeping curves above and alongside the Kangaroo Ground Cemetery and opposite the Emergency Operations Centre. In the latter case, the farmers – understanding their hedgerows as important heritage – insisted upon their reinstatement to conform to the altered road alignment. Kangaroo Ground’s ancient manna gums also point to the district’s history and to that of the hedgerows. The Aboriginal people had transformed the original forests into grasslands with the fires they lit to attract kangaroos, (which the Scots were to exclude by planting hedgerows). But the Wurundjeri hunters left the gums (Eucalyptus vimminalis cygnetensis), on the grasslands as ‘stalking trees’ to hunt kangaroos. The hawthorn hedges in Kangaroo Ground were neglected for around 60 years from about the middle of the 20th century. Bushfires had created gaps and the hedgerows were not trimmed. Then in late 2005, local historian Mick Woiwod, formed a group to lobby the Nillumbik Shire to restore the hedges, which could last for many centuries. Some hedges in parts of Britain date back to AD 800.5 Although the original Scottish farmers have gone, the hedges are a reminder of when they flourished in the district, which has changed little in 150 years.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, eltham-yarra glen road, hawthorn hedgerow, kangaroo ground -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesAlbum - Digitised, Joanne Morris, Visit to Burnley April 2014, 2014
Collection of digitised photographs taken in preparation for the Class of 1973 Reunion in 2014. Garden views and buildings. Donated by Joanne Morris, former student, in June 2014. See Digitised photos- Garden Views folder- Visit to Burnley April 2014. (1) Luffmann Ponds. (2) Administration Building. (3) Emily Gibson Beds and Ginkgo biloba. (4) Looking towards Native Garden. (5) Oak tree. (6) Looking towards Rose Garden. (7) Looking towards Stream Garden and Fern Garden. (8) Looking towards Rose Garden. (9) Plaque at entrance to Field Station. (10) New gates at entrance to Field Station donated by the Friends of Burnley Gardens. (11, 12) Field Station. (13) Plaque in Herb Garden commemorating Enid Carberry. (14) Fountain in Herb Garden commemorating Enid Carberry. (15) Forestry Building. (16-18) Inside Forestry Building. (19) Sugar Gum Table Setting donated by the Friends of Burnley Gardens. (20) Plaque on Sugar Gum Table commemorating Geoff Olive. (21, 22) View of Luffmann Ponds and Summer House. (23) Plaque at Luffmann Ponds. (24) Luffmann Ponds. (25) View of former Egg-Curator's Residence from Nursery. (26) Back of Nursery. (27,28) The Burnley entry for the Melbourne International Flower and Garden Show 2014. (29) Back of Administration Building. (30) Plant Science Laboratories. (31) Student Amenities Building. (32-34) Plant Science Laboratories. (35) Citriodora Court. (36) Eucalyptus maculata at entrance to Native Garden. (37) Native Garden, James Hitchmough Grasslands. (38) Garden view. (39) Inside the Hall. (40,41) Roof Garden. (42,43) Library. (44-50) Views of the Quad and classrooms. (51) Dairy. (52) Building 904,(Centre for Urban Horticulture) now Waterway Ecosystem Research Group. (53) Yarra Boulevard entrance.class 1973, class reunion, garden views, buildings, joanne morris, students, luffmann ponds, administration building, emily gibson beds, ginkgo biloba, native garden, oak tree, rose garden, stream garden, fern garden, field station, friends of burnley gardens, plaques, herb garden, enid carberry, fountain, forestry building, sugar gum table, geoff olive, summer house, egg-curator, residence, nursery, melbourne international flower and garden show, 2014, plant science laboratories, student amenities building, citriodora court, eucalyptus, james hitchmough grasslands, roof garden, library, quad, classrooms, dairy, centre for urban horticulture, waterway ecosystem research group, yarra boulevard entrance -
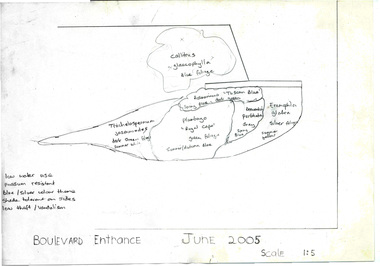 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesDocument - Personal files, Andrew Smith's Files, 1981-2022
cactus, cacti, clematis, orchard redevelopment, r. hall, geoff olive, pruning garden, field station, vcah, university of melbourne, burnley, jill kellow, field station redevelopment, field nursery, student gardens, turfgrass, grassy woodland, chris findlay, phil tulk, grasslands, herbaceous border, car park, native garden, restoration native garden, john rayner, hilda kirkhope rockery, herb garden, rainforest garden redevelopment, plant lists, shady walk, salvia, trees, tai-haku cherry, tree management, tree lists, david aldous, grey border -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Ian Lunt et al, Plains wandering : exploring the grassy plains of south-eastern Australia, 1998
An exploration of the flora and fauna of South-Eastern Australia.Colour photographs, b&w illustrationsvictorian southern tablelands, riverina, wimmera, gippsland plains, south australia, tasmania, grasslands, flora, fauna, ecology -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photograph, Dorothy Wickham, Winter's Swamp, Ballarat, January to April 2014
Study of Winter's Swamp commissioned by BEN and completed by BHS. The swamp was named after one of the first European settlers in the district. Winter Swamp LAT -37 32 LONG 143 47, Parish of Dowling Forest, County of Grenville Winter Swamp, on the southwest corner of Ballarat West Town Common, was not included in the original proclamation of the Common in 1861. However, being marshland, it was not considered suitable for grazing, so was added to the Common soon after 1861. Winter Swamp is a large wetland with native and exotic pasture significant for wildlife. John Winter (Jock) was born in Berwickshire, Scotland. He married Janet Margaret Irving the daughter of Robert Irving, advocate, Bonshaw, Dumfries, Scotland. Winter died in Ballarat in 1875 and was buried at the Ballaarat Old Cemetery. He took up the run Bonshaw from 1841; Leigh River Buninyong 1842-46; Junction, Delatite, March 1851 to September 1862; with sons: Carag Carag and Corop, April 1857 to September 1872; Colbinabbin and Stewart’s Plains, April 1857 to December 1872; St Germains February 1867 to March 1871. (The name became Winter-Irving in 1890). Mr John Winter, who died on August 22 at the age of 72, was a man of some note it the mining community of Ballarat. He was a self-made man, and one of our oldest colonists, it being over a quarter of a century age since he took up county about Ballarat and settled at Bonshaw. He died very rich. It is calculated that if he had retained an interest in all his runs, his income must have been not less than £10,000 or £50,000 a year. Some eight or ten years ago he sold his Bonshaw pre-emption to the Bonshaw Gold mining Company for £20,000, and a few years later the ground belonging now to Winter's Freehold Company brought him £50,000 more, the payment being made at the requisition of the deceased in sovereigns. In these relations Mr. Winter has been closely identified with the mining industry at Ballarat. The deceased was a native of Lauder, in Berwickshire, and landed in Victoria several years before the gold discovery.The principle task of this project was the delivery of a report outlining the history of European settlement in the Skipton and Cardigan/Ballarat districts as pertinent to the use of and impact on the natural environment of the two reserves Skipton Common and Winter Swamp. The report was delivered in digital form only. The report, upon completion, was presented to the Network’s Committee in order to discuss the project. The report identified and described the uses of Skipton Common and Winter Swamp, and their impacts. In particular, this report examined farming/grazing (official and informal), mining, vegetation removal (including the removal of woodlands for timber, grasslands for pasture improvement) & use of riparian areas for access to water and timber removal. Recording the more benign and environmentally friendly uses such as picnicking, community activities, nature walks and the roles of organisations such as Field Naturalists’ and Bird Observers’ clubs, school and scout/guide groups will be relevant in helping to depict overall community attitudes towards the reserves; e.g.: has the Common generally been viewed as little more than a grazing paddock and fire hazard; has Winter Swamp always been the unknown natural asset that seems to have been its lot for at least the past 40 years? In this regard, the more contemporary history of actions surrounding the use and management of the reserves is of particular interest, in view of the extant evidence at both reserves; e.g. the actions of the Shire of Ballarat in the 1980s in establishing Winter Swamp as something of a competitor to Lake Wendouree but with a more environmental bent (although almost none of the plants used are indigenous species, but that is part of the story); the trotting track constructed on Skipton Common in the 1960s following representations to Premier Henry Bolte and the cropping of the western section of the Common to raise funds for the town’s new swimming pool, the fertilizing of the land putting an end to the native grassland vegetation. There are obviously multiple sources of information to source in preparing the report, however sources that the contractor is specifically requested to consult are the Skipton Historical Society, the former Skipton Common managers (specifically Graeme Pett), the Cardigan Windermere Landcare Group and the Learmonth Historical Society (believed to hold many of the former Shire of Ballarat’s records pertaining to the Council’s role as the Committee of Management for both Winter Swamp and the Ballarat West Town Common – Winter Swamp was split between 2 separate Crown Land tenures). The contractor is also encouraged but not required to utilise community newsletters, such as the Skipton Community Newsletter, to publicise and seek information about the project. Skipton Historical Society (Mary Bradshaw) contacted on Thursday 12 June 2.30pm. Mary lived on a farm out of Skipton but is currently living in the township. She remembers walking along the creek of the Common especially in spring and autumn in bare feet and that it was a very pretty place. There were a few snakes around the waterway in summer. People put cows and a couple of horses on the commonage to graze. Graeme Pett has always lived close to the Common and would know a lot about it. Other possible contacts would be Nicole Petress, Secretary of the Progress Association, and the Corangamite Council, Camperdown. Digital images of Winter's Swampwinter's swamp, ballarat, john winter, ballarat environmental network, mullawullah -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photograph, Winter's Swamp surrounds, April 2014
The swamp was named after John (Jock) Winter. John Winter (Jock) was born in Berwickshire, Scotland. He married Janet Margaret Irving the daughter of Robert Irving, advocate, Bonshaw, Dumfries, Scotland. Winter died in Ballarat in 1875 and was buried at the Ballaarat Old Cemetery. He took up the run Bonshaw from 1841; Leigh River Buninyong 1842-46; Junction, Delatite, March 1851 to September 1862; with sons: Carag Carag and Corop, April 1857 to September 1872; Colbinabbin and Stewart’s Plains, April 1857 to December 1872; St Germains February 1867 to March 1871. (The name became Winter-Irving in 1890). Mr John Winter, who died on August 22 at the age of 72, was a man of some note it the mining community of Ballarat. He was a self-made man, and one of our oldest colonists, it being over a quarter of a century age since he took up county about Ballarat and settled at Bonshaw. He died very rich. It is calculated that if he had retained an interest in all his runs, his income must have been not less than £10,000 or £50,000 a year. Some eight or ten years ago he sold his Bonshaw pre-emption to the Bonshaw Gold mining Company for £20,000, and a few years later the ground belonging now to Winter's Freehold Company brought him £50,000 more, the payment being made at the requisition of the deceased in sovereigns. In these relations Mr. Winter has been closely identified with the mining industry at Ballarat. The deceased was a native of Lauder, in Berwickshire, and landed in Victoria several years before the gold discovery. BHS were commissioned by Ballarat Environment Network for a project on Winter's Swamp and Skipton Common. Winter's Swamp was part of Ballarat West Common. The principle task of this project was the delivery of a report outlining the history of European settlement in the Skipton and Cardigan/Ballarat districts as pertinent to the use of and impact on the natural environment of the two reserves Skipton Common and Winter Swamp. The report was delivered in digital form only. The report, upon completion, was presented to the Network’s Committee in order to discuss the project. The report identified and described the uses of Skipton Common and Winter Swamp, and their impacts. In particular, this report examined farming/grazing (official and informal), mining, vegetation removal (including the removal of woodlands for timber, grasslands for pasture improvement) & use of riparian areas for access to water and timber removal. Recording the more benign and environmentally friendly uses such as picnicking, community activities, nature walks and the roles of organisations such as Field Naturalists’ and Bird Observers’ clubs, school and scout/guide groups will be relevant in helping to depict overall community attitudes towards the reserves; e.g.: has the Common generally been viewed as little more than a grazing paddock and fire hazard; has Winter Swamp always been the unknown natural asset that seems to have been its lot for at least the past 40 years? In this regard, the more contemporary history of actions surrounding the use and management of the reserves is of particular interest, in view of the extant evidence at both reserves; e.g. the actions of the Shire of Ballarat in the 1980s in establishing Winter Swamp as something of a competitor to Lake Wendouree but with a more environmental bent (although almost none of the plants used are indigenous species, but that is part of the story); the trotting track constructed on Skipton Common in the 1960s following representations to Premier Henry Bolte and the cropping of the western section of the Common to raise funds for the town’s new swimming pool, the fertilizing of the land putting an end to the native grassland vegetation. There are obviously multiple sources of information to source in preparing the report, however sources that the contractor is specifically requested to consult are the Skipton Historical Society, the former Skipton Common managers (specifically Graeme Pett), the Cardigan Windermere Landcare Group and the Learmonth Historical Society (believed to hold many of the former Shire of Ballarat’s records pertaining to the Council’s role as the Committee of Management for both Winter Swamp and the Ballarat West Town Common – Winter Swamp was split between 2 separate Crown Land tenures). The contractor is also encouraged but not required to utilise community newsletters, such as the Skipton Community Newsletter, to publicise and seek information about the project. Skipton Historical Society (Mary Bradshaw) contacted on Thursday 12 June 2.30pm. Mary lived on a farm out of Skipton but is currently living in the township. She remembers walking along the creek of the Common especially in spring and autumn in bare feet and that it was a very pretty place. There were a few snakes around the waterway in summer. People put cows and a couple of horses on the commonage to graze. Graeme Pett has always lived close to the Common and would know a lot about it. Other possible contacts would be Nicole Petress, Secretary of the Progress Association, and the Corangamite Council, Camperdown. Mary can’t remember any photos in the Skipton Historical Society that pertain to the Common. Digital photos of Winter's swamp surrounds, later known as Mullawullah.winter, winter's swamp surrounds, winter's swap, john winter, ballarat environmental network, ballarat, mullawullah -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPamphlet, Native Grasslands and Indigenous Flora Gardens
native gardens, australian native plants -
 Friends of Ballarat Botanical Gardens History Group
Friends of Ballarat Botanical Gardens History GroupWork on paper - Victoria Park Precinct, City of Ballarat, Victorian Heritage Database place details -19/9/2017, 19/9/2017
Victoria Park is associated with gold mining in the 1860's, military manoevres in the late 19th century; as an army base during World War 2 and a recreation area.Victoria Park is a "landmark cultural landscape" in the city of Ballarat. This parkland established 1890-1910, was modelled on English country estates and London Parks. It demonstrates the civic pride of Ballarat citizens and is an important parkland for the local community. There is a collection of exotic and early planted native trees and areas of native grasslands.6 pages of print. p.1. is a front page with a map and Victoria Park marked in purple with a bibliography on p.4 and footnotes on p.6.None.john garner, victoria park, friends of ballarat botanical gardens, heritage overlay, gold mining, parkland, late nineteenth century, native grasslands, exotic and native trees, royal park, mullock heap, mount holled-smith, arbor day, messrs clegg&nicholls, william guilfoyle, w.o.allen, significant tree register, john garner collection, gardens, ballarat -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour Photograph, Clare Gervasoni, Mount Greenock, 2025, 28/06/2025
Mt Greenock is an extinct volcano with lava flows associated with a deep lead. It is a tall scoria cone with a broad shallow crater open to the northwest. In the crater are blocks and bombs of scoriaceous basalt. Long lava flows extend both north and south from the cone. It is considered a significant geological site, and part of the Major Mitchell Trail, with a 1936 ‘Centenary of Major Mitchell ‘monument on the summit. The flow to the north has been eroded by McCallum Creek which is a lateral stream. On the eastern base of the cone, the stream valley exposes a lava flow and underlying sedimentary rocks. The lava flow and the scoria cone overlie the Greenock lead (a buried valley with auriferous gravels). A line of mine tailing and abandoned mining relics associated with the former Union Mine occur on the margins of the lava flow. Mount Greenock is a 120 hectare ‘Geological Reserve’, is one of the few large scoria cones on public land and contains abundant outcrop and morphological evidence of its volcanic origin. Colour Photographs of Mt Greenock, near Talbot, Victoria. The photographs were taken in winter not long after the first post drought rains. mt greenock, mount greenock, mining, mullock heap, mt greenock geological reserve, union mine, volcanic grasslands, dunach -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour Photograph, Clare Gervasoni, Built Remains near Mount Greenock, 2025, 28/06/2025
Mt Greenock is an extinct volcano with lava flows associated with a deep lead. It is a tall scoria cone with a broad shallow crater open to the northwest. In the crater are blocks and bombs of scoriaceous basalt. Long lava flows extend both north and south from the cone. It is considered a significant geological site, and part of the Major Mitchell Trail, with a 1936 ‘Centenary of Major Mitchell ‘monument on the summit. The flow to the north has been eroded by McCallum Creek which is a lateral stream. On the eastern base of the cone, the stream valley exposes a lava flow and underlying sedimentary rocks. The lava flow and the scoria cone overlie the Greenock lead (a buried valley with auriferous gravels). A line of mine tailing and abandoned mining relics associated with the former Union Mine occur on the margins of the lava flow. Mount Greenock is a 120 hectare ‘Geological Reserve’, is one of the few large scoria cones on public land and contains abundant outcrop and morphological evidence of its volcanic origin. Colour Photographs of bluestone and brick buildings at Mt Greenock, near Talbot, Victoria. The photographs were taken in winter not long after the first post drought rains. mt greenock, mount greenock, mining, mullock heap, mt greenock geological reserve, union mine, volcanic grasslands, dunach
