Showing 184 items
matching hook hand
-
 Shepparton RSL Sub Branch
Shepparton RSL Sub BranchSlouch Hat, 1972
Possible used by Cadets because of the several names inside the hatPossible use by CadetsKharki Slouch hat, no rising sun cap badge or hook to brim, 7 fold Pungaree with 2x small Australia buttons on right hand side, chin strap missing and replaced with leather bootlace, several names written on inside One of the names is Sgt J. Kelly. 351414Size 6 3/4. Made by Fayrefield. Melbourne. Circa. 970s -
 Shepparton RSL Sub Branch
Shepparton RSL Sub BranchGoggles
Goggles constructed of two oval lenses in metal frame which attaches to thin canvas which is stretched over wire frame which touches eye. Thin khaki elastic strap on left and right side attaches at back with thin hook and eye in metal. Two lenses attached via hand stitched brown leather strap with some fur attached. -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumUniform - SKIRT WW2, C. 1943
Item issued to Mavis Keillor, refer Cat No 3402 for her service records.Plain khaki skirt. Bottom hem resewn by hand. x 1 angled pocket at rear, x 1 angled pocket on front. Front held together with hook & eye fastener. Waist held by single strap & buckle of same material.Name inside tag: “KEILLOR”uniform, skirt, kahki -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageClothing - Jacket, before April 1874
THE JACKET This jacket has been tailored to flatter the wearer’s figure. It also has elements that keep it in good shape and condition, preserve it from soiling and give it a longer life: - the hooks and eyes that join the jacket to the skirt allow the outfit to be made in two pieces but fit close to the body without exposing undergarments - the seams for the metal stays have been cut and stitched to allow maximum movement of the wearer and still keep a trim figure - the discreet breast pocket allows the wearer to keep a handkerchief, coins or other small items close at hand - the lining includes removable padded shields to absorb underarm perspiration - the lining has two cotton loops attached for hanging up to air and freshen it - new cuffs have been attached over the original sleeves that have buttonholes but no buttons. The buttons may have been used to replace missing buttons on the front of the jacket or perhaps to repair worn cuffs The amber coloured satin jacket is fully lined, has turned-back cuffs, a band collar, and looped, coffee-coloured braid trim. A row of closely spaced, round bronze buttons with a floral motif form a decorative closure most of the way down the front of the jacket, below which are metal hooks and eyes that finish at the waist. Underneath the cuffs there is a closely fitted cuff with a row of three button holes but no buttons. The jacket lining has vertical metal stays spaced around the midriff, sides and back. There is an absorbent, removable pad hand-stitched to the underarm section of each sleeve opening. A small satin pocket is stitched discreetly onto the lining above the chest on the right-hand side. There are also two cotton loops sewn onto the lining. Several small metal rings are sewn at intervals around the inside of the waist A satin bow from the same fabric is attached at the centre back of the jacket at waist level. antique satin jacket, colonial evening jacket, ladies evening jacket, 19th century ladies satin jacket, evening outfit -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageUniform - Tunic, 1899-1903
This original tunic or jacket is part of the full dress uniform of the pre-Federation Victorian Permanent Artillery regiment. Its owner had the rank of Sergeant, as indicated by the three inverted chevrons. The Artillery design of the badges and buttons indicate the date of the tunic to be from 1893 to 1903. However the maker of the tunic, W. Moncton, began manufacture in Melbourne in 1899, so this the tunic can be dated between 1899 and 1903. The donor's grandfather was given this tunic but not the name of the original owner. It has since been suggested to the family that the tunic was worn by a local Western District Light Horse member. This could very well have been the case because mounted troops were officially referred to as the Light Horse in the late 19th to early 20th century. Several local men were involved in the Light Horse during the First World War. The donor's grandfather wore this tunic in the local district when riding a penny farthing bicycle. The donor's father also wore the tunic when dressed as a 'Captain' hosting a local disco dance. BRIEF MILITARY HISTORY- The Crimean War began In 1854 and many people in colonial Australia were afraid of a Russian attack. Volunteer forces were established to strengthen the British Imperial troops posted here. A battery of artillery was raised in Victoria as well as in other Australian states. In 1870 Australia became responsible for its own naval and military defence. The Volunteer Corps and Victorian Navy shared the responsibility of defending the existing forts, assisted by volunteer coastal and mobile field batteries. The Permanent Victorian Artillery force was established. It was disbanded in 1880 then re-formed in 1882 as the Victorian Garrison Artillery Corps. In 1895 the Geelong, Warrnambool, Port Fairy and Portland Batteries became part of the Western District Garrison Artillery. Many of the volunteers who served in the Artillery were from rural areas. They belonged to rifle clubs and were experience horsemen as well. Australia's defence at this time relied on these mounted troops, or Light Horse men. In 1899 the Victorian Garrison Artillery Corps amalgamated with the New South Wales and Queensland Permanent Artillery to become the Victorian Regiment of the Royal Australian Artillery (RAA). Then prior to Federation, the RAA and the Permanent Artillery of South Australia, Western Australia and Tasmania all combined, becoming the Royal Australian Artillery Regiment with two Batteries of Field Artillery; Battery A from Sydney and Battery B from Melbourne.This original uniform tunic of the pre-Federation Victorian Permanent Artillery is significant for its association with Australia's military defence and the fortifications of our district, state and country. The tunic is also significant, representing part of the history and evolution of uniforms in the Australian military forces. The tunic is also significant in its representation of Australia's independence in forming its own defences. The tunic has local significance in its connection with local social events.Tunic or jacket, part of the full dress uniform of the pre-Federation Victorian Permanent Artillery operating from 1893 to 1903. Original, single-breasted tunic of dark blue wool, red piping trim, black cotton lining in body. Sleeves lined with blue striped, white cotton. Front closure has eight brass buttons. Red band-style collar with hook-and-eye closure has gold bullion braid trim and a brass badge pinned each side at the front. Upper right sleeve has three inverted chevrons on red fabric with gold bullion braid trim (rank of Sergeant). Both sleeves have gold bullion braid 'Austrian knot' emblems stitched onto lower arm, with ends finishing on the inner sleeve. Shoulder epaulettes have red piping and smaller brass buttons. Closed back vent has vertical scalloped design with six brass buttons, in two columns of three, and red piping trim. Brass belt hook is attached to the left back waist, close to the seam (right side has a mark indicating a previous similar clip). Inside left breast is a concealed pocket. Tunic has both machine and hand stitching. All brass shank-style buttons have matching Artillery emblems with inscriptions on the back. The two brass collar badges have additional artillery emblems of exploding grenade and star as well as an inscription. Buttons were made for W. Moncton, of Melbourne and marked with his name. He traded from 1899, dating the tunic to between 1899 and 1903.Button front: Artillery emblem on front (field cannon facing left, in front of a muzzle-loading ram rod). Button back: engraved "W. MONCTON . MELBOURNE ." Collar badges: Artillery emblem (field cannon facing right | stars | exploding grenade | "AUSTRALIA")flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, uniform jacket, uniform tunic, garrison volunteer uniform, fortifications in victoria, victorian permanent artillery, pre-federation military uniform, sergeant's uniform, jacket, militia, victoria, victorian volunteer forces, victorian regiment, royal australian artillery, raa, field gun, sergeant, w. moncton, garrison, dress uniform, tunic, scarlet collar, red collar, scarlet piping, red piping, gold bullion, artillery emblem, light horse, artillery, mounted troops, victorian garrison artillery corps -
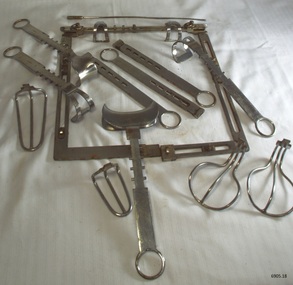 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSurgical Kit, c. 1920's
This H.B Devin’s operating frame and abdominal retractor kit is named after its designer, Sir Hugh Berchmans Devine, 1878-1959, son of a Werribee district grazier in Victoria, Australia, surgeon at the Royal Melbourne Hospital. A text book diagram of H.B. Devine’s Abdominal Retractor shows the frame and retractors set up for a pelvic operation. The accompanying text reads “Devine’s retractor is so designed that there are no screws, yet the retractors and “mechanical hands” by a jamming action remain firmly on the frame in whatever position they are placed. This is accomplished by a system of inclined planes incorporated in the frame and in the single and double hooks, retractor blades and handles of the “mechanical hands”. Set comprises 3 “mechanical hands” 5 retractor blades. (Pg 72, The 1948 Catalogue of Surgical Instruments, published by Felton, Grimwade & Duerdins Pty Ltd of Melbourne). Devine became a general surgeon who later gained an international reputation for his for his contribution in the advancement of abdominal surgery. Devine was educated in Ballarat and later became an Honourable Fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons. During his career he became Senior Surgeon and Dean of the Medical School at St Vincent’s Hospital in Melbourne. He served in the Australian Army Medical Corps in WWI and developed techniques in gastro-intestinal surgery. He was instrumental in the foundation of the Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, retiring from the council in 1948. A survey on needs for operating room equipment notes that “In the past some surgeons associated themselves with particular instrument makers… The Melbourne surgeon [Hugh Devine] had his special abdominal retractor made by a small firm in South Yarra…” Hugh Devine writes instructions for inserting the Operating Frame in his book “The Surgery of the Alimentary Tract”. He says “ … the author’s operating frame is inserted into the wound … for exposure of the stomach … and exploration of the abdomen” and adds a note that the frame is “obtainable from J. Ludbrooke & Son, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia”. He accompanies his text with a diagram of the frame set into the wound. This surgical kit was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) According to Berry, her mother Gladys made a lot of their clothes. She was very talented and did some lovely embroidery including lingerie for her trousseau and beautifully handmade baby clothes. Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . Its first station was in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital (a 2 bed ward at the Nelson Street Practice) from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what previously once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr Tom and his brother had worked as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He had been House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan had gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. When Dr Angus took up practice in the Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan’s old premises he obtained their extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926. A large part of this collection is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. and an ALDI sore is on the land that was once their tennis court). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served with the Australian Department of Defence as a Surgeon Captain during WWII 1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. He had an interest in people and the community They were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. [References: The 1948 Catalogue of Surgical Instruments; hospital supplies and guide to instruments for operatons, published by Felton, Grimwade & Duerdins Pty Ltd, 21 Alfred Place, Melbourne; Sir Hugh Berchmans Devine, Royal College of Surgeons, http://livesonline.rcseng.ac.uk/biogs/E004999b.htm; Equipment, What Surgeons Want in Operating Rooms, https://mpatkin.org/op_room_planning/what_surgeons_want.htm ]The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine, administration, household equipment and clothing from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Surgical Kit containing operating frame and abdominal retractors, part of the W.R. Angus Collection. Kit cover is brown kid leather lined with navy cotton, 6 leather pockets inside and cotton flaps to close. Contains Sir Hugh Devine operating frame and abdominal retractors, stainless steel, made by J. Ludbrooke and Sons, Melbourne. Note with instruments "Sir Hugh Devine, surgeon at Royal Melbourne Hospital” c. 1920’sImpressed into instruments “J. LUDBROOKE AND SONS”, “PATENT 12990/28”, “83”, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, medical history, surgical kit, j. ludbrooke and sons, operating frame, abdominal retractor set, abdominal surgery, alimentary surgery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCoat hanger, mid 1900's
This wooden and wire, folding coat hanger was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s SS Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Folding coat hanger owned by Dr Angus. Wooden centre piece and looped metal shoulder pieces and metal hook. Wood is stamped “UNION / Made in U.S.A.” and hand engraved “W.R.A.”. Folded measurements (W.R. Angus Collection) Wood is stamped “UNION / Made in U.S.A.” and hand engraved “W.R.A.”. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, dr w r angus, medical equipment, surgical instrument, dr ryan, ophthalmology, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, flying doctor, medical history, medical treatment, mira hospital, medical education, medical text book, t.s.s largs bay -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaArtwork, other - Crucifix, 1950-1970
The Lay Reader David Conolly was associated with the Mission for many years in particular working with trainee cadets and RAN Officers. Painted wood crucifix on a very thin backing support of hardboard. Style of the painting is that of icon artist of Russian/Greek/Byzantine style. An inscription on the reverse. Small steel hanging hook at top edge on reverse. The edges of the icon are painted red and the whole depiction is decorated with much gilding. The whole support is in the form of a t-shaped cross. The top section depicts a risen Christ at the centre surrounded by ten disciples or saints and the hand of God appears to be at the upper central edge. The Christ figure is flanked on the main cross piece by five archangels and Saint Peter. Flanking the torso of the crucified figure appear to be Maria and St Joan and on the right side Mary Magdalen, Mark (Saint?) and a centurion figure. Three small figures also featured in this section. At the lower right corner are two haloed male figures (unidentified).Front; above haloed head of the crucified figure U.C.; IHSNAZARE in gold on a red ground/ REXIVDEORV. Beneath the central panel again gold on red SEASIOANNES AND MARIA. On the other side of the central figure; MARIAMARK CENTURIU/ MAGDALEN...IACO/ BI. Hand-written inscription on reverse; "For/ all who enter/ this sacred space./ The gift of/ David Conolly/ sometime stipendiary Lay Reader/ in the Mission/ 1956-1958.david conolly, crucifix, icons, othodox, artwork -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionFunctional object - Fishing lure, n.d
Wooden hand made fishing lure for barracouta and salmon. Solid wood, round white plastic coating, two holes drilled into one end, wire threaded through and out two holes either side of lure, hook attached.fishing, travel, lure, recreation, sport -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionTool - Tool - Fishing Caff, n.d
Hand made fishing gaff. Wooden, bound with red twine at handle end, middle section of gaff and top section, where it is used to attach the hook to the pole -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionEquipment - Equipment - Fishing Lures, n.d
Two metal hand made fishing lures for barracouta and salmon. Each one is a metal cylinder filled with lead, encasing fish hook one end, metal loop the other -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionFunctional object - Box of Fish Hooks, Edgar Sealey & Sons, Redditch England, n.d
Cardboard box of fish hooks, Edgar Sealey & Sons brand, hand forged. Green and black label on top of box with details of hooks. -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyHook Button, late 1800's to mid 1900's
This item and its use and design spans the 1800's to early 1900's both in its fashion and application requirements. The genteel factor must be made when applying it to the Kiewa Valley. The evolution of general clothing and apparel has moved from solid(long lasting) and sometimes expensive material and fasteners to a cheaper and more "throw away" fashion of sometimes monthly change in the later 1900's to 2000's.The significance of this item to a rural setting such as the Kiewa Valley not only points to an integration of "modern" fashion in semi remote rural Australian environments but also the limited connections to "high" fashion through magazines and audible (radio) and visual (cinema) advertising. It also "spotlights" the differences between the European and British social networking and lack of interaction between towns and counties to the "Australian" levels of interactions between rural and city environments. Although physical distances in Australia, during this period (1800's to early 1900's) was a retarding factor in the diffusion of the latest fashion apparel it was not as noticeable as when the global communication and the physical travel abilities were "exploded" in the latter 1900's. This shift towards "the smaller" globe scenario has overcome the physical distances that were so apparent in the previous century.This silver button/glove hook was based on late 1800's designs when buttons became more integrated and fashionable than "tie up" laces. This was more so in genteel fashion. The main hook extension from the "pronged" hand piece has been constructed in a way that allows for easy replacement by either longer or shorter hooks.costume accessories, footwear, shoes and boots with buttons, gloves, costume -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyTimer Favag, Circa 1950
This Favag Timer apparatus was a part of the first electronic control system -(1960's), in Victoria), which worked using telephone stepping selectors to convey a change in voltage providing a regulated pulse from the control centre(Mount Beauty) to the remote Power Stations opening and closing (stop/start) of various devices at the Power Station and a return signal confirmed the action taken. Testing of this unit was carried out using a "dummy" device at the remote Power Station so as not to disrupt the power plant's operation. This timer was one of many electrical apparatus connected to the large SEC Victoria Hydro Scheme's electrical power producing generators. These generators are powered by the hydro force of "stored" water at a higher altitude. The establishment of both the NSW and Victorian Hydro Schemes was achieved from the early 1900's to the 1960's. At this point in time the need for additional power sources to quench both an industrial and domestic demand for electricity was purely an economic and not and environmental (carbon reduction) factor. This hydro scheme was instigated by "the Government of the day" as a bold move and was the major force of the World War II refugee and "technical" workforce,inclusion of skilled and unskilled, migration into the Australian environment. Although this mass "invasion" of workers with families was thought of in some circles as intrusive, the expansion of population post war years and its integration into the Australian rural sector, produced the multi- lingual multi-cultural diversity of later years.This Favag Timer was one of the crucial pieces of equipment that made it possible for the Mount Beauty Terminal Station to control the operations of these Power Stations; McKay, Clover, West Kiewa Power Stations and the Dederang Terminal Station.This aluminium and anodised "FAVAG" (pulse) timer is fastened to a base structure which comes with its own metal cover that is fastened by two metal hooks. From the top of these hooks runs a thick leather "carry" strap.The instrument, itself, a small "micro motor" at one end tape feeding spool on the other. Aluminium metal structures offer a preventative barrier against any electronic spikes from static electricity sources. There are two toggle switches to the bottom right hand side and twelve coloured "pin" connection points.There is a sliding access sleeve which exposes a circuit board.with various leads fastened on each side. In front of one of this slide are two "screw in" fuses, spare fuses are in a small envelope taped above. Circuit diagrams are etched white on black background on the top face of the main structure. At the base of the back section is a two pronged input terminal. There is a fine black rubber layer (cushioning) for the mian top cover.On the cover fastened with two rivets "FAVAG" underneath in small print "Fabrique d'appareils electriques S.A." underneathe "NEUCHATEL-SUISSE". on one end is a "STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA" metal label screwed on.The back label has manufacturers' type and model number.sec vic kiewa hydro scheme, alternate energy supplies, alpine population growth -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyNebulizer - Medical
This medical / hospital instrument was used in the Tawonga District General Hospital which was built in the 1950's specifically for the increase in population due to the Kiewa Hydro Scheme. Previous UKV 325Historical: Shows the development of scientific hospital equipment. Provenance: Used in the Tawonga District General Hospital which was remote and therefore required good equipment. Good condition and good interpretation capacity.Brown cardboard box containing 3 clear glass instruments. Two have a sphere in the middle with a long thin hollow cylinder at one end and a similar one at the other end except this one continues into the sphere and ends in a hook. The other instrument consists of a hollow cylinder that curves at the bottom and goes into a hollow ball. The ball has one small hollow appendage coming out at an angle and another short wide round hollow cylinder at its top. Label at end of box hand written: "Used for croupette"Box label: 'Nebulizer for Croupette"nebulizer, medical, hospital, croupette, tawonga district hospital -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyWedding Dress and Veil
Wedding dress and veil worn by Margaret Vyner at her wedding to Ian McKendrick on 11th January 1958The McKendrick family came to Mt Beauty very early in the Kiewa Hydro Electric Scheme (KHES) days. Their son, Ian, worked in the Mt Beauty Post Office for 40+ years. The Vyner family were long time employees of the SECV working on the KHES and were residents of Mt Beauty. Margaret was a nurse at the Tawonga District Hospital at the Tawonga site and at the Mt Beauty site.Long soft white taffeta under-skirt. The outer is cut on the cross, made of nylon and with a train and has appliqued lace of a flower and is beaded. The sleeves are long and shear. The taffeta bodice is fitted with a featured V waistline. The sleeves are pointed (to cover over the hand) with a flower applique. There are 5 pearl buttons down the back and are fastened with loops. The side zip is metal and on the right hand side and at the top there is a hook and eye. The bridal veil - A large tulle circle edged with lace and formed into a 2 tiered veil held together with a green covered wire circlet decorated with wax flowers.vyner family, mckendrick family, wedding dress with veil -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyDress, Hand made, c.1900
... on this dress. Back opens with 8 hooks. Dress Hand made ...This dress is hand made possibly by a mother for her daughters. It is hand and machine stitched. This style of dress would have been worn for special occasions, eg going to church or special outings.This item is very significant for the following reasons. Historic and social - it shows what little girls wore during the early 1900's of the Kiewa Valley. It also shows fashion of the times and how these styles of dresses were made. All of which is valuable for research on these topics. There are only two of these dresses in the collection of the KVSH, and therefore would be very rare. The condition is good enough to display, therefore it has good interpretive capacity.Brown Cotton Dress. Top and sleeves are lined in calico. Home made, with manual machine stitches and some hand sewing. The dress has a high round neck and long sleeves. There is a band around the waist to which a gathered skirt it attached with hand stitching. Two different shades of brown are used on this dress. Back opens with 8 hooks. Water stains on dresschild, homemade, dress, girl, kiewa-valley -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietySlate - School, early 1900
Historically this school writing slate pre-dates paper and electronic writing pads. This was used for non permanent written communication within or outside the classroom. It use was mainly as a quick temporary method and could be easily erased by cloth or fingers. As it could be used repeatedly without additional cost and was therefore a very cheap method of teaching and learning outdoors as well as indoors. This was especially relevant to country schools and outdoor excursions. It was fairly robust but could shatter if allowed to fall on the ground.This item evolved from a form of communication, that of primitive engravings on stone. This tablet was a refined writing/drawing pad that did not require any electronic/battery power input. This writing slate was so useful in an era where relative isolation (Kiewa Valley Schools) from electronic and cheap writing pads was the reality and the norm. This was a time when the hand writing and hand drawing was a basic form of non spoken communication. Students used this slate pad to reinforce their skills which would come in handy when they needed to produce temporary notices on slate information boards, e.g. rail/bus-time/route alterations.Writing slate used for Primary School classes. Wooden frame. Has hole in frame and string threaded through to allow it to be hung on a hook or nail.slate pads, chalk boards, school learning utensils -
 Warrnambool RSL Sub Branch
Warrnambool RSL Sub BranchTrousers, Australian Government Clothing Factory (A.G.C.F.), 1978
These trousers are part of a winter mess dress uniform belonging to Bernard Farley during service with the Australian Airforce. Worn in 1978, this trouser style was first developed in the 1950s and continues to be worn as mess uniform in the present day.This item has aesthetic significance and is a representative example of uniform design from the 1950s to present day. This item has clear provenance, having been donated by RSL member and Secretary (2019), Bernard Farley after its use during Bernard’s service in the Airforce. As a former member of the Australian Airforce and member of the Warrnambool ex-service community, Bernard’s uniform has great social significance, telling a broader story of life after service.Dark navy blue dress trousers with cream coloured lining on waistband and pockets; dark synthetic material rectangles are sewn on interior of pants hem on pressed edge. Seven buttons, coloured black, are present on the interior of the waistband and were likely used as attachments for suspenders; reverse of pants rise into two points either side of the spine. Pants are fastened with a black plastic zip and a hook and eye at the top of the fly. Two pockets are present on both left and right hips and one small pocket on the front right hand side near the pelvic bone. Fabric is pleated twice on the front and has two darts on the reverse. Label on interior collar reads “A.G.C.F./VIC. 1978/(arrow symbol)/NO./NAME” Inscription on interior left hand pocket lining reads “992”dress uniform, airforce, commonwealth government clothing factory, uniform -
 Warrnambool RSL Sub Branch
Warrnambool RSL Sub BranchTrousers, Australian Defence Apparel, 2015
These trousers are part of a General Purpose Uniform issued by the Australian Airforce to Bernard Farley during service. This uniform type was developed in 2014 and replaced camouflage as the uniform worn during general base duties and in non-warlike environments. Although a camouflage pattern, this design is not intended for use as camouflage. This item has social significance, as an item of uniform worn by Warrnambool RSL community member and Secretary (2019), Bernard Farley during service with the Australian Airforce. The item is a representative example of current Airforce General Purpose Uniform and is in excellent condition. As a set, the uniform has aesthetic significance in it’s design, incorporating GPU uniform design from the Army alongside the colours and motifs of the Australian Airforce. General Purpose Uniform (GPU) trousers in Airforce colours of blue and grey in camouflage pattern. Long pants with elasticised drawstring fastener at ankle and velcro adjustment fasteners at the waist. Pants take a straight leg style and bears several pockets: two thigh level pockets with zippered horizontal opening, two open hip pockets on the front, one open pocket on the reverse right hand side with blue plastic button fastener. Five large belt loops encircle the waist and there is a zippered fly, secured at the top with a blue plastic button.Label on interior front right of trousers reads: “A193/ADA/MADE IN AUSTRALIA/JUL 2015/ PO: CC2X91/NSN: 8415 66 161 4017/SIZE: 95 R/(broad arrow)/NAME:............/PM KEYS NO:............./75% COTTON 25% POLYESTER/WARM MACHINE WASH 40*C/RINSE WELL, WARM IRON/DO NOT IRON OVER HOOK AND PILE/DO NOT BLEACH/DO NOT STARCH/MAY BE TUMBLE DRY 40*C/DRYCLEANABLE (P)”camouflage, general purpose uniform, airforce, uniform, australian defence force -
 Warrnambool RSL Sub Branch
Warrnambool RSL Sub BranchTrousers, Australian Defence Apparel, 2015
These trousers are part of a Disruptive Pattern Combat Uniform issued by the Australian Airforce to Bernard Farley during service. This uniform type was used in base and field activities and was replaced in 2014 by the General Purpose Uniform as the uniform worn during general base duties and in non-warlike environments.This item has social significance, as an item of uniform worn by Warrnambool RSL community member and Secretary (2019), Bernard Farley during service with the Australian Airforce. The item is a representative example of previously standard issue Airforce uniform and is in excellent condition. As a set, the uniform has aesthetic significance in it’s design, incorporating the Disruptive Pattern style of camouflage which has its roots in the 1980s and continues to be adapted into uniform design by the Defence Force.Disruptive Pattern trousers in five colours of green and brown. Long pants with elasticised drawstring fastener at ankle and velcro adjustment fasteners at the waist. Pants take a straight leg style and bears several pockets: two thigh level pockets with zippered horizontal opening, two open hip pockets on the front, one open pocket on the reverse right hand side with blue plastic button fastener. Five large belt loops encircle the waist and there is a zippered fly, secured at the top with a blue plastic button.Label on interior front right of trousers reads: “A13/ADA/VICTORIA 2008/(broad arrow)/SPECIFICATION ARMY (AUST)6542/NSN: 8415 66 152 1059/SIZE: 95 S/NAME/SERVICE NO/75% COTTON 25% POLYESTER/WARM MACHINE WASH 40*C/RINSE WELL, WARM IRON/DO NOT IRON OVER HOOK AND PILE/DO NOT BLEACH/DO NOT STARCH/MAY BE TUMBLE DRY 40*C/MADE IN AUSTRALIA” The name “FARLEY” is also handwritten on the back interior waist band of the trousers. camouflage, general purpose uniform, airforce, uniform, australian defence force -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical SocietyBread maker, Landers Frary and Clark, Early 20th century
Bread machines were made for quite a long time from the 1890's on. They came in different heights and capacities. The advertisements at the time stated that making bread with their machine was superior to hand kneading, This item is good example of a domestic appliance used when most foods were home-made. Access to commercial bread was limited in rural areas and housewives became skilled at bread-making.Metal bucket with lid. Lid has hole in centre through which a handle for turning the dough hook comes. Grey rusty coloured.Put in all liquids first, then flour, turn 3 minutes, raise in pail. After raising, turn until dough forms a ball. Take off cross piece, lift out dough with kneader.bread domestic-appliance bread-maker food-technology bakery -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyrazor strop, first half 20th century
A razor strop is flexible strip of leather or canvas used to maintain a shaving edge on a thin blade such as a straight razor. Fine powdered jeweler's rouge or other pastes can be added as an abrasive to polish the blade. The strop may be a hanging strip or a hand-held paddle. This one is a hanging strop. Strops were quite commonly found in barber shops and homes before the invention of the safety razor, They are still used for sharpening tool blades. This one was owned and used by Mr Bill Weston, an early Orbost sleeper cutter.This item is an example of the self-reliance shown by rural families when household necessities were not readily available.A brown leather (probably horse hide) razor strop with a double hook at one end. It consists of two strips of leather with padded 'tongue' at bottom. This is a hanging strop which has a metal swivel on top so that the strop can be turned over while hanging from a hook/peg Front top in gold : MALWA Base in gold: 910razor-strop shaving personal-effects -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyfasteners, mid 20th century
These items belonged to Helena Warren (nee McKeown) of Newmerella. Helena warren was a self taught photographer who became a competent commercial photographer. She was married to William John Warren and lived in Newmerella. She was known for her soft toy making and these items were probably purchased for that activity.These items reflect the popularity of needlework and the making of hand crafted items by women in the mid 20th century.Two packets of metal fasteners. One packet, 2494.1, contains 13 unused snap fasteners - Sew'n Save. They are on a rectangular piece of yellow cardboard. It has black print. There is a pink sticker on the back - 3 different sizes 1/0;3/0;2/0. 2494.2 is a torn piece of cardboard with 5 hooks/eyes attached.needlework warren-helena fasteners newey-goodman -
 Cheese World Museum
Cheese World MuseumBucket Yoke
... yoke twine hooks metal [019] Hand carved wooden yoke shaped ...Part of the Uebergang CollectionHand carved wooden yoke shaped to sit around a persons neck and shoulders. The turned hand grips have lengths of binder twine tied on with metal hooks attached to the ends.[019] uebergang, allansford, yoke, twine, hooks metal -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Optical, Binoculars, 1878 (estimated)
This pair of brass binoculars was presented to Tom Pearce in recognition of his heroic efforts at the wrecking of the Loch Ard and saving Eva Carmichael. They were presented to him by the Lady Mayoress of Sydney on 27th July 1878 on behalf of the colonists of New South Wales "In recognition of his gallant conduct on the occasion of the wreck of the Loch Ard". Tom (Thomas) Pearce was born in Ireland in 1859 and arrived in Melbourne two years later; he considered himself as Australian. Before sailing on the Loch Ard he had been at sea for three years as an apprentice sailor and had already experienced one shipwreck. Tom was on the deck of the Loch Ard with Captain Gibb throughout the night of May 31st 1878. It was mistakenly thought they were 150 miles (240 km) southwest of Cape Otway. By 2:00 am on June 1st, the wind was blowing "pretty fresh" but a thick haze remained and, when it eventually cleared, the land was so close the unsuccessful battle to save the Loch Ard began. After the ship struck Mutton Bird Island Tom and five others were sent to the lifeboats. Conditions were very dangerous as waves broke over the decks and they were all washed away. Tom found himself in the stormy waters and under a lifeboat, which had also been washed into the sea. After being swept into the gorge Tom left the boat and swam into shore; he was alone. Eva Carmichael, a passenger on the ship, had been snatched from her bed just before dawn and into the chaos, confusion and terror of the shipwreck, with rigging and rocks raining down. Thrown into the sea, she afterwards said: "God taught me to swim in my distressful plight, for I never swam before". Clinging to a spar, she was swept into the gorge and saw Tom Pearce walking along the beach. Upon hearing the cries of Eva, Tom swam out and with great difficulty brought her to the shore and placed her safely in a cave where he made a bed of grass and shrubs and gave her brandy to revive her. She sank into exhausted unconsciousness. Tom then scrambled to the top of the high cliff and after walking for some time he stumbled upon workers from Glenample Homestead. They rode back to the homestead for help but Tom insisted on returning to Eva. When Eva awoke she found herself alone, "cold, weak and terrified with the wild waves before me, and caves and cliffs around me" and upon hearing strange noises, which she imagined to be made by the local indigenous people, she hid. The noises were made by the rescue party from Glenample Homestead. After eventually discovering Eva they hauled her up the cliff in the darkness of night, “a work of great difficulty and danger” and took her to Glenample. Sadly, Tom and Eva were the only survivors of the 54 people on board the Loch Ard. Tom’s rewards for his bravery included the Gold Medal of the Humane Society, a gold watch and £1000 from the Victorian Government, a set of nautical instruments, (which included the binoculars) from the people of Sydney and £60 from the people of Warrnambool. He was also presented with a Bible by a “Friend of the Loyal Orange Institution of Victoria, Protestant Hall Melbourne” in August 1878. Coleman Jacobs composed the music "The Young Hero Schottische" and dedicated it, by permission, to Mr Thomas R. (Tom) Pearce. The sheet music was published in 1878 by Mr Roberts, professor of dancing and was on sale for 3/- (3 shillings) in aid of the "Loch Ard" fund. Tom Pearce went on to join the Loch Sunart on her return to England, only to be wrecked again off the Irish coast in January 1879. Tom left the Loch Line in 1883 and the following year married Edith Gurney Strasenbergh, the sister of his friend Robert who had died on the Loch Ard. They had three children, unfortunately, two of the male children were to die at sea. In 1895 Tom obtained his first command as Master of The Larne, a vessel with the Royal Mail Steam Packet Company. He remained with the company until he died in Southampton, England, on 14th December 1908. Tom Pearce never saw Eva Carmichael after he had fare welled her some 30 years before. Eveline Victoria Berta Carmichael was born in 1859 in Mountrath, Queens County, Ireland. After recovering from her ordeal in August 1878 Eva returned to Ireland and in 1884 married Thomas Achilles Townshend, a Civil Engineer. They had three sons, all of whom had successful military careers, and when Eva’s death notice appeared in the Melbourne Argus It read. "Townshend on 8th April 1934 aged 74 at her residence in Bedford, England, Evaline Victoria, widow of the late Thomas Archilles Townshend, C.E. of Co. Cork, Ireland. Mrs Townshend was the Eva Carmichael who, with the late Tom Pearce, were the only two survivors of the ship Loch Ard, which was wrecked near Port Campbell on June 1st 1878." The binoculars are significant for their association with the wreck of the Loch Ard and the only two surviving members of that wreck Tom Pearce and Eva Carmichael. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from Loch Ard is significant for being one of the largest. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The assemblage of items from the wreck is of historical significance in that they are associated with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history. Pair of brass marine binoculars in a wooden box On the left hand eye piece, on the underside, is an engraved inscription and another engraved word. On the right hand eye piece there is another small inscription and on the underside there is a small green mark. The binoculars have a pattern of embossed tiny circles on the outside. Some of the patterning is very shiny due to wear and rubbing, there is a brass ring on the underside of the binoculars for the attachment of a lanyard. The wooden box has a hinged lid and on the front of the box in the centre is a lock, and at either end are two hooks and eyes. The box is split across the top for about 3/4 of the length. Marking on the left underside reads, 'Presented on behalf of the Colonists of New South Wales By the Mayoress of Sydney on 27th. July 1878 to Mr Thomas B Pearce. In recognition of his gallant conduct on the occasion of the wreck of the "Loch Ard"'. Underneath this inscription is engraved 'Sydney'. On the other eye piece is engraved what looks like 'Mac Donnell & Co' binoculars, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, loch ard shipwreck, tom pearce, thomas r pearce, eva carmichael, mutton bird island, loch ard survivor, loch ard hero, coleman jacobs, the young hero schottische, photograph of tom pearce, glenample homestead -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Accordion, International Accordion Company, 1930's
This MEZON brand button accordion was made specifically for Lyons, Musical Instrument Importer, 207 Bourke Street Melbourne, as can be seen on the embossed lettering on the top of the accordion. The hand inscribed nameplate indicates that the owner was T H Betts. On August 19th, 1903, Michael Edward Lyons applied to the Trade Mark’s Office of Sydney for registration of “The Invented word “MEZON” to be applied to musical instruments. In 1908 he was advertising himself as sole agents for MEZON accordions. He had been at that address for 15 years (since 1893) and was moving to larger premises at 256 Bourke Street, Melbourne. Still at this address in 1925, Lyons advertises MEZON accordions as “The ideal Xmas present, Maker your friends happy, This Xmas let the Present be a MEZON”. There was a choice of three styles: The Organ, The Wonder and The Grand Organ. They came with a Fibre Case with Lock and Key and a Leather Handle. The promise was “They Give Satisfaction”. They were obtainable at all stores or from Sole Distributors in Australia. In 1927 the MEZON was sold by Albert & Sons in Western Australia, Victoria, New South Wales and Queensland as well as by Lyons in Melbourne. The favoured German accordion brands were Monarch and Sterling, which were made by the International Accordion Company in Leipzig, Saxony, Germany. The company was founded in 1871 by Ernest Deines and made a variety of musical instruments. The company closed business in 1834. The International Accordion Company’s accordion range made the International brand and others such as MEZON, Globe, and Dienst. Australia imported the MEZON brand. American companies imported a range of the popular German branded accordions until World War II, when they were no longer available. In general, accordions produced after the war were not as high a quality and not loud enough to be heard over the electronic guitars and the drum kit of the bands. This accordion represents the type of musical instruments used in the late 19h and early 20th century, locally and Australia wide. In colonial Australia musical instruments like this one were imported from Germany as well as other countries. At that time, German made instruments represented good quality. This accordion is significant for being especially imported into Australia by a Melbourne retailer. Music was a part of family and social life, associated with dances, song and general fun.Button accordion with case. Accordion with steel reeds, three bass valves and ten treble valves. It is coloured black with very dark green trim, decorative silver metal reinforcing on main corners, gold reinforcing on corners of the bellows and delicate printed, gold printed patterned trims. Hand support for buttons is made of fabric. Folds of the bellows are light coloured with fine dark pattern. It has a nameplate on the front. Black wooden case has red lining, two brass hinges, two brass hook and eye catches and a swivel brass lock. The base of the case has a loose brass fitting. The top has a thin metal handle. Inscription on hand inscribed name on front, label inside case lid, silver reinforcing, leather on bellows top, and frame of accordion. Manufactured with the brand MEZON in Saxony, Germany, for Lyons of Melbourne. Once the property of T H Betts.Printed on label “MEZON ACCORDEONS.” Impressed in metal corners and reinforcing “MEZON” with logo [circle enclosing entwined capital D and E] “MADE IN SAXONY” Embossed in gold on frame “Made in Saxony”, “MEZON Accordion/ manufactured for LYONS / MELBOURNE, Bourke Street” Name inscribed by hand “T H Betts”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, mezon accordion, lyons, made in saxony, t h betts, betts, mezon, squeeze box, musical instrument, button accordion, germany, michael lyons, international accordion company, ernest deines, circle enclosing d e, d e, e d, german accordion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Stretching Hook
Hand forged metal tool, possibly a sailmaker's hook with the hook broken. It may be a fire iron. The twisted metal is a skill learned by a blacksmith.The item is a handmade tool, an example of the work of a blacksmith. Smiths were sought after in colonial Australia. Their trade allowed them to custom make work for the different industries necessary for survival in a new land.Sailmaker's stretching tool; long thin metal rod bent in half, with centre forming a handle or loop, and long ends twisted together to form a stem. The loose ends are formed together but appear broken.warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, tool, sailmaker's tool, fire iron, blacksmith, twisted rod, twisted wire, sailmaker's hook -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Sewing Machine, early 20th century
Sewing machine, portable, hand operated, with Premier logo. Has folding crank handle, body painted black with floral design, wooden base and separate wooden cover with lock. Base has compartment with accessories, covered by curved ended, sliding wooden panel. Decorative linework on side, carvings on each corner. Wooden handle on cover is carved in rings, folds down. Below handle is decorative inlaid pattern. Serial number on plate at back of machine. Accessories include 13 attachments, key (broken), screwdriver, sewing machine needle, razor blades (2) and buttons. Attached to inside of case is a square of paper with a number on it. Instruction book for Singer Sewing Machines is included. Also with machine are white tailor's chalk and a cut out, fabric pocket with tissue paper pattern pinned to it.Serial number "579200" is stamped into plate at back of machine. Brand on transfer on front of machine is "Premier". Paper inside case has hand written number "334A". Instruction book "Instructions for using Singer Sewing Machines No. 66 - Oscillating hook for family use" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, sewing machine, permier sewing machine, hand operated sewing machine, dressmaker, fasion, singer no. 66 manual, textile, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, sewing machine, permier sewing machine, hand operated sewing machine, dressmaker, fasion, singer no. 66 manual, textile -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageClothing - Mourning Outfit, jacket, Late 19th to early-20th centuries
This Edwardian era mourning outfit was worn by a wealthy woman from the rural area of Willaura, southeast of the Grampians. It was inherited by the donor from his mother, who had purchased it from a clearing sale in the 1960s. The jacket has a peplum or flounce below the waistline, a fashion that was seen in the 1860s and is still around in the 1900s. The outfit represents the female mourning fashion and wardrobe from the late 19th to early 20th centuries. Such garments were a necessary inclusion as death occurred often to the young, due to illness, accidents and hard work - it was a regular part of life in rural Victoria. Mourning outfits were a part of a person’s wardrobe and often passed from one generation to the next. This particular outfit appears to have been adjusted at some stage to allow for a wider waistline. The original skirt may have been replaced by the one that is now part of this outfit; the skirt is all machine-sewn, unlike the jacket and petticoat. The fabric of the skirt may be silk or it could be a synthetic fibre such as artificial silk or rayon; both were available in the 1800s,but nylon wasn’t invented until the 1930s. This skirt has sunray pleating, which was advertised on skirts for sale in the 1890s, and 1909, and was part of a fashionable bridal gown train in the 1930s. The mourning of death was part of both family and community life, particularly in rural and remote areas. People were bonded through work, religion, disasters, tragedy and social activities, supporting one another. They came together from near and far on such an occasion, giving each other the care that was needed and showing respect for the member who had passed away.This three-piece silk Edwardian mourning outfit is significant historically for its connection with rural Victoria and the social and religious customs surrounding the death of a family or community member. The high-quality outfit is also significant for representing the financial management of the times, being tailored by a dressmaker for a person of means and then adjusted to fit at least one different-sized person. The black silk tailor-made jacket is one of three pieces of a ladies’ Edwardian mourning outfit. It has long sleeves, a stand-up collar trimmed with appliqued black crochet lace, and pleated sashes on the left and right sides from front to back fastened at the shoulder and waist. The jacket has a peplum or flounce below the waistline. The front of the jacket has brass hooks and fabric eye fastenings. The back of the jacket has two tails. The jacket is lined and the shoulders are padded. It has been machine sewn and finished with hand stitching. A white card is tied with a ribbon inside and has an inscription. The poplin skirt on the jacket has been cut up to the waist at the side seams. There is an attached card with an inscription, handwritten in ballpoint pen.“Jenny” and “Mrs Sheila Handscombe, Wallaura, Jenny”flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, edwardian era, tailor-made, dressmaker, mourning outfit, handmade garment, mourning dress, death mourning, sunray pleats, sunburst pleats, western district victoria, mourning jacket
