Showing 1250 items matching "measuring"
-
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionMetal Jug
Thought to be used for measuring liquids in retail premises by Council Inspectors of Weights & Measures Department of Shire of Bulla and donated by Hume Council when amalagmation of Councils took place.Tapered metal container with pouring spout and handle used for measuring liquids.on side "1 GALLON" on spout "crown/15 91/VIC"shire of bulla, george evans collection -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Craft - Craftwork, tape measure c 1880, c1880
c1880 This tiny tape measure, in Imperial measurements, was part of a Victorian era lady's sewing basket. The case is of polished timber, and the little winder, to retract the tape, is made of brass with a small ivory handleEarly settlers and market gardeners of Moorabbin Shire had to be self reliant producing their own food and making their farm equipment and clothing. The women of these families were skilful in all craftwork.c1880 this tiny, retractable, tape measure, in Imperial measure, is made of polished timber with a brass winder and ivory handle. Imperial ‘inch’ measurements on tape dressmaking, tape measure, sewing, craftwork, pioneers, early settlers, market gardeners, moorabbin, brighton, bentleigh cheltenham -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumFunctional object - METAL MEASURING JUGS
JUGS USED TO MEASURE PETROL IN COMMERCIAL GARAGEONE GALLON METAL MEASURING JUG AND TWO HALF-GALLON JUGS, WITH HANDLESlocal history, commerce, containers, commerce -
 City of Greater Bendigo - Civic Collection
City of Greater Bendigo - Civic CollectionInstrument - Weights and Measures, Potter, Standard Volume 28 lbs, c 1863
Victoria became a separate colony of the United Kingdom on 1 July 1851; however it took until 1864 for a workable system of weights and measures administration to be introduced. Standard of weights and measures were obtained and issued to local authorities to administer in their local areas. These standards were numbered, as were the Crown stamps used by inspectors to indicate that trade weights and measures had been checked and found to be legal to use in the day-to-day businesses of local traders. By the 1870's each local council had a set of standards that were used to test the scales, weights and measures of local merchants and businesses.Standard 28lb brass measure. Ball shaped weight with single handle on top. Front; Standard / lb / 28 AV / Potter / London / 25.8.1864 / 24.3.90 / 9.6.95 / 17.10.00 / 5.10.05 / 20.3.11 / 25.8.16 / 27.9.21 / 10.11.26 / 17.11.31 / 16.11.35 / 4.12.41 / 24.11.52city of greater bendigo commerce -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionAnemometer
Used to measure wind speed which is an important factor in fire behaviourHand held battery operated anemometer used to measure wind speedKestrel 3000forests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement -
 City of Greater Bendigo - Civic Collection
City of Greater Bendigo - Civic CollectionInstrument - Gunter Chain, not known
Gunter's chain (also known as Gunter’s measurement) is a distance measuring device used for surveying. It was designed and introduced in 1620 by English clergyman and mathematician Edmund Gunter (1581–1626). It enabled plots of land to be accurately surveyed and plotted, for legal and commercial purposes. The provenance of this particular Gunter Chain is unknown but it is believed to be used either by the City of Bendigo / Sandhurst or the Lands Department locally when measuring and laying out plots and streets locally. A 66-foot (20.1 m) chain divided into 100 links, marked off into groups of 10 by brass rings or tags. Each link is 7.92 inches (201 mm) long. A quarter chain, or 25 links, measures 16 feet 6 inches (5.03 m) also called a a rod (or pole) measure. Ten chains measure a furlong and 80 chains measure a statute mile. city of greater bendigo surveying -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Tool - Compass
... measuring ...Used by donor's husband in early 1940sSmall brass and steel compass for drawing circles/curves and measuring. Sharp steel point. School instrument, geometryinstruments, measuring, trades, drafting -
 Marysville & District Historical Society
Marysville & District Historical SocietyPhotograph (Item) - Black and white photograph, Nicholas John Caire, 1878-1904
Shows two men measuring around the base of a Cumberland Valley giant tree. An early black and white photograph of a Cumberland Valley giant tree. This photograph was taken by Nicholas John Caire between 1878 and 1904. Nicholas John Caire was born in 1837 in Guernsey. He arrived in Adelaide about 1860 along with his parents who encouraged his early interest in photography. He opened a studio in Adelaide in 1867 after traveling extensively throughout the Gippsland taking photographs. After marrying in 1870 he moved to Talbot in Victoria until 1876 when he opened a studio in the Royal Arcade in Melbourne. After 1885 Nicholas John Caire gave up his city work and made his home in South Yarra and devoted the rest of his life to outdoor photography, specializing in the bush, the gullies, and the mountains of south-eastern Victoria. big tree, mountain ash, cambarville, victoria, photograph, cumberland valley, nicholas john caire -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncBook, Shire of Stawell, A Brief History of Imperial Weights & Measures Equipment of Wimmera Weights and Measures Union – Previously Cat No 3631, 1991
History of the Weights and Measures in Stawell from 1863 to 1991. The Physical Weights are on display in the MuseumLight Yellow paper cover with Victorian coat of arms and black print. with yellow tape on the spine.Victoria Coat of Arms VICTORIA The rest is undelined: A Brief History of Imperial Weights and Measures Equipment of Wimmera weights and Measures Union Donated to Stawell Historical Society Inc. by Former Shire of Stawell 26 July 1991stawell -
 Otway Districts Historical Society
Otway Districts Historical SocietyBook, Hoppus's Practical Measurer
Manufactured by E. Hoppus the Hoppus's Practical Measurer, or measuring made easy by a new set of tables which show by looking the solid content of any piece of timber, stone, etc, either square, round or unequally sided, and the value at any price of cubic feet. The book also gives the superficial comtent of boards, glass, painting and plastering with explanations of the uses and applications of the tables. The contents are given in feet, inches, quarters and twelfth parts of an inch. It includes the measurment of timber by several dimensions together with tables showing the weight of iron by measure.Hoppus's Practical Measurer; or, Measuring made easy by a new set of tables, which show, at sight, the solid content of any piece of timber, stone, &c. W. Nicholson & Sons; London; nd. 238 p. Hard cover.e. hoppus; measurment; timber; stone; boards; glass; painting; plastering, iron; -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumEquipment - MAP MEASURER/OPISMETER, DEPOSE
Vintage opisometer used for measuring distances on maps. Part of the Kevin John Herdman, No. 397661, Collection. See Catalogue No. 5942P for details of his service record..1) Circular chromed metal instrument with handle. Calibrated dial with black markings and hand on a white background. Reverse face has unit conversion details in black text on white background. Each face is covered with a convex glass lens. On the opposite end to the handle is a small wheel with milled edge. As it turns, the hand on the front dial turns to measure distance. .2) Rigid plastic rectangular storage case in two parts. Base is yellow, top is clear..1) Printed on front dial: 'INCHES, MADE IN FRANCE'. Printed on back dial: 'Unit conversion details'. Stamped on metal near wheel: 'DEPOSE, H(logo)B'. .2) Stamped on clear cover: 'CURVIMETRE, MAP MEASURER, H(logo)B, MADE IN FRANCE'.map, map measure, equipment, opisometer, kevin john herdman -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyTape Measure 33ft, Early to mid 1900's
This flexible measuring tape was used by the SEC Victoria in the mid to late 1900's. It was in a period before digital measuring instruments were in use. This is a 33ft long tape measure and would have been used by the construction workers when building the Kiewa Valley Hydro System. The warning details (embossed into the leather covering) was to warn users to be careful not to use the tape near live electricity terminals or linkages. This tape was produced mainly for wooden structures and not electricity conductive material. This was during the 1950's to 1960's.This imperial tape measure is very significant to the Kiewa Valley as it was used in the construction of the Kiewa Valley Hydro Scheme of the 1950's-1960's. It provides evidence that small measuring equipment used in the construction and the continuing maintenance of the scheme was of the imperial measure and used by construction workers who remained and settled in the town of Mount Beauty and Kiewa Valley long after the construction period. This flexible metallic measuring tape (33 ft in length) is contained in a round circular leather bound container. It has brass fittings (winder and tape guide) and is stitched with heavy grade twine. The tape measure is graduated in feet and inches on one side and yards on the other. Embossed in the leather casing"MADE IN ENGLAND" and around the inner circle "HOCKLEY ABBEY" and "JOHN RABONE & SONS"imperial tape measure, distance measures, imperial tools -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFCV measuring band
Used for measuring distances in the forest. Steel bands (out of tradition were called the chain) were created around 1890. They replaced the traditional Gunter chain. The band could be repaired by soldering slip-on joiners and than and recalibrating.Steel measuring band (50m) on plastic reel with winding handleFCV 281forests commission victoria (fcv), assessment, forest measurement, surveying, mapping -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFCV measuring band
Used for measuring distances in the forest. Steel bands (out of tradition were called the chain) were created around 1890. They replaced the traditional Gunter chain. The band could be repaired by soldering slip-on joiners and than and recalibrating.Steel measuring band (50m) on plastic reel with winding handle missingFCV 188forests commission victoria (fcv), assessment, forest measurement, surveying, mapping -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionFCV measuring band
Used for measuring distances in the forest. Steel bands (out of tradition were called the chain) were created around 1890. They replaced the traditional Gunter chain. The band could be repaired by soldering slip-on joiners and than and recalibrating.Steel measuring band (1 chain - 66 feet) on metal reelFCV 075forests commission victoria (fcv), assessment, forest measurement, surveying, mapping -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaFunctional object - Object, Tactile tape measure, 200
This tape measure is designed to indicate measurements by feel. The 150cm tape is marked by small eyelets at every cm, medium eyelets at 5 cm and two eyelets at every 10cm. 1 white measuring tape with black markings and numbers including tactile raised eyeletsassistive devices, recreation -
 Blacksmith's Cottage and Forge
Blacksmith's Cottage and ForgeSpoon, early 20th century
... measuring ...Possibly used for food/liquid measuringDomestic itemOval shaped spoon with handleFive makers' marksdomestic, spoon, measuring, food preparation -
 Parks Victoria - Wilsons Promontory Lightstation
Parks Victoria - Wilsons Promontory LightstationContainer, Ventometer
The cylindrical cardboard container with lid formerly contained a ventometer, a small simple tool for measuring wind speed. It consisted of a clear tube containing a small diaphragm which had a hole in the bottom for wind to enter. Once the wind entered the tube it pushed up the diaphragm, indicating the rate of velocity. Ventometers were common devices that have since been replaced by more sophisticated measuring equipment, such as digital air speed meters. Further information on this particular example, including perhaps the name of the manufacturer, may survive on the container but this has not been recorded. The small simple tool for measuring wind speed pre-dates the electronic devices at Gabo Island.Tubed shaped cardboard container with lid to house instrument for measuring. (instrument is missing) Inscriptions and illustrations on exterior. -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Domestic object - Kitchen equipment, spirit-fuelled sad iron, c1920
Sad-irons or "solid" irons were made by blacksmiths and used to smooth out material by pressing the hot iron over it. A piece of sheet -iron was placed over the kitchen fire and the irons placed on it could be heated whilst remaining clean of ash.. The women used 2 irons - one heating while the other was used. Thick cloth or gloves protected their hands from the hot irons. The handle was removed from the cool iron and re- attached to remove the hot iron from the fire. The cool iron was replaced on the fire or stove to heat again. These irons were cleaned with steel wool to prevent them marking the material. If the iron was too hot the material would scorch. Most homes set aside one day for ironing and some large households had an ironing room with a special stove designed to heat irons. However, most women had to work with a heavy, hot iron close to the fireplace even in summer. Late in the 19thC designers experimented with heat retaining fillings for these irons. William Coleman began selling Kerosene lanterns in 1900 in Kingfisher, Oklahoma, USA. He moved to Wichita, Kansas in 1902 and the company became world wide. The company also produced a range of cooking stoves and domestic irons. This spirit- fuelled flat iron was very popular in 1920s - 30s These sad irons remind us of the difficult circumstances experienced in their daily routines by the pioneers and early settlers of Moorabbin Shire The family of Miss M Curtis were early settlers in Moorabbin ShireA) spirit- fuelled, sad iron with chrome plated sole c1920, and metal trivet The iron is blue enamel with a white speckled body, with a hemispherical tank for the Coleman 'Lighting Petrol' that provided the heat for smoothing the material B) Coleman Fuel measuring can and funnellMetal Trivet/stand " COLEMAN" ; Petrol can " COLEMAN" / MEASURING CAN / for INSTANT LIGHTING IRON/ with printed instructionssad iron, kitchen equipment, coleman william, kansas, oklahoma, pioneers, early settlers, market gardeners, sewing, craftwork, clothing, moorabbin, brighton, bentleigh, fireplaces, stoves, petrol fuelled irons, spirit flat irons, coleman lamp stove co. ltd. -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaPhotograph (item) - Image, Royal National Institute for the Blind, Liquid measure
Glass bottle with attached phallic shaped measuring device. Attached label to the bottle states that this was used by a physiotherapist and provides a reference for the bottle: RNIB 9448. The Royal National Institute for the Blind did sell materials around the world, and this item could have been ordered from them. royal victorian institute for the blind, equipment -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Jug, Between 1910 -1936
The beginning of standardised weights and measures began In Victoria when the Melbourne Observatory received sets of standard weights and measures, which had been tested in Britain against the then British Imperial standards. These included the primary standard yard and pound for the Colony of Victoria. Other standards of weights and measure held by shires and the administrative body's within the colony could then be compared to these primary standards. A Weights and Measures Act was passed in Victoria in 1862, establishing local inspectors throughout the colony. By the 1870s each local council and shire in Victoria held a set of standards that were used to test scales, weights and dry measures used by wholesalers, factories and shops. Every ten years the councils’ standards would themselves need to be rechecked against the Victorian Standards. The checking was done by the Victorian Customs Department in the 19th century, but with the transfer of responsibility for customs to the Federal Government in 1901, weights and measures function was retained by the Victorian Government and was shifted to the Melbourne Observatory. In 1904, a new building was erected at the south end of the Great Melbourne Telescope House, where the standard weights and measures and testing equipment was installed. This room had a large whirling apparatus for testing air meters and became known as the Whirling Room. When the Melbourne Observatory closed in 1944, the Weights and Measures Branch was formed to continue and this branch remained at the Observatory site unit until 1995.An example of a brass measuring jug made specifically to maintain government standard liquid measurements that were sold to the public. The probability is that this artefact was made sometime between George V reign (1910-1936) and gives us today a snapshot of how imperial weights and measures were checked by Government departments prior to decimalisation and how a standard for the various types of measurement was developed in Australian based on the Imperial British measurement system. The container has social significance as an item used in Victoria as a legal standard measure to ensure that goods sold in Victoria were correct. Jug brass haystack form with a deep lip and pouring spout, small neck and broad base. It displays a curved pistol handle. Inscription at base of handle top of jug stamped 61 GVR SM. These marks signify that the measure complied with the Victorian Government capacity liquid standard measurement. Item made during the reign of George V (1910-1936 (GVR).Other marks indicate model number (61) & SM possible could be either small measure, the maker, or Standards Melbourne.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Standard measure, Mid to Late 19th Century
The beginning of standardised weights and measures began In Victoria when the Melbourne Observatory received sets of standard weights and measures, which had been tested in Britain against the then British Imperial standards. These included the primary standard yard and pound for the Colony of Victoria. Other standards of weights and measure held by shires and the administrative body's within the colony could then be compared to these primary standards. A Weights and Measures Act was passed in Victoria in 1862, establishing local inspectors throughout the colony. By the 1870s each local council and shire in Victoria held a set of standards that were used to test scales, weights and dry measures used by wholesalers, factories and shops. Every ten years the councils’ standards would themselves need to be rechecked against the Victorian Standards. The checking was done by the Victorian Customs Department in the 19th century, but with the transfer of responsibility for customs to the Federal Government in 1901, weights and measures function was retained by the Victorian Government and was shifted to the Melbourne Observatory. In 1904, a new building was erected at the south end of the Great Melbourne Telescope House, where the standard weights and measures and testing equipment was installed. This room had a large whirling apparatus for testing air meters and became known as the Whirling Room. When the Melbourne Observatory closed in 1944, the Weights and Measures Branch was formed to continue and this branch remained at the Observatory site unit until 1995. J & M Ewan History: J&M Ewan was a Melbourne firm that began by selling retail furniture and wholesale ironmongery. They had substantial warehouses situated at the intersection of 81-83 Elizabeth and Little Collins Streets, the business was established by James M Ewan in 1852. Shortly afterwards he went into partnership with William Kerr Thomson and Samuel Renwick. When Ewan died in 1868 his partners carried on and expanded the business under his name J & M Ewan. The business was expanded to provide a retail shop, counting-house and private offices. Wholesale warehouses adjoined these premises at 4, 6 and 10 Little Collins Street, West. This company provided and sold a large and varied amount of imported goods into the colony that consisted of agriculture equipment, building materials, mining items as well as steam engines, tools of all types and marble fireplaces. They also supplied the Bronze measuring containers in the Flagstaff Hill collection and the probability is that these containers were obtained by the local Melbourne authority that monitored weights and measures in the mid to late 19th century. The company grew to employ over 150 people in Melbourne and opened offices at 27 Lombard St London as well as in New Zealand and Fiji. The company also serviced the Mauritius islands and the pacific area with their steamship the Suva and a brig the Shannon. Robert Bate History: Robert Brettell Bate (1782-1847) was born in Stourbridge, England, one of four sons of Overs Bate, a mercer (a dealer in textile fabrics, especially silks, velvet's, and other fine materials)and banker. Bate moved to London, and in 1813 was noticed for his scientific instrument making ability through the authority of the “Clockmakers Company”. Sometime in the year 1813 it was discovered that one Robert Brettell Bate, regarded as a foreigner in London had opened a premises in the Poultry selling area of London. He was a Mathematical Instrument maker selling sundials and other various instruments of the clock making. In 1824, Bate, in preparation for his work on standards and weights, leased larger premises at 20 and 21 Poultry, London, at a rental of four hundred pounds per annum. It was there that Bate produced quality metrological instruments, which afforded him the recognition as one of one of the finest and principal English metrological instrument-makers of the nineteenth century. English standards at this time were generally in a muddle, with local standards varying from shire to shire. On 17 June 1824, an Act of Parliament was passed making a universal range of weights, measures, and lengths for the United Kingdom, and Bate was given the job of crafting many of the metrological artifacts. He was under instruction from the renown physicist Henry Kater F.R.S. (1777-1835) to make standards and to have them deposited in the principal cities throughout the United Kingdom and colonies. Bate experimented with tin-copper alloys to find the best combination for these items and by October 1824, he had provided Kater with prototypes to test troy and avoirdupois pounds, and samples with which to divide the troy into grams. Bate also cast the standard for the bushel, and by February 1825, had provided all the standards required of him by the Exchequer, Guildhalls of Edinburgh, and Dublin. In 1824, he also made a troy pound standard weight for the United States, which was certified for its accuracy by Kater and deposited with the US Mint in 1827. Kater, in his address to the Royal Society of London, acknowledged Bate's outstanding experimentation and craftsmanship in producing standards of weights, measures, and lengths. An example of a dry Bronze measuring container made specifically for J & M Ewan by possibly the most important makers of measurement artefacts that gives us today a snapshot of how imperial weights and measures were used and how a standard of measurement for merchants was developed in the Australian colonies based on the Imperial British measurement system. The container has social significance as an item retailed by J & M Ewan and used in Victoria by the authorities who were given legal responsibility to ensure that wholesalers and retailers of dry goods sold in Victoria were correct. The container was a legal standard measure so was also used to test merchants containers to ensure that their distribution of dry goods to a customer was correct.Maker Possibly Robert Brettell Blake or De Grave, Short & Co Ltd both of LondonContainer brass round for measuring quantities- Has brass handles & is a 'Bushel' measurement. 'Imperial Standard Bushel Victoria' engraved around container. Container bronze round shape for measuring dry quantities has brass handles & is a 'Bushel' measurement"IMPERIAL STANDARD BUSHEL" engraved around the top of the container. VICTORIA engraved under "J & M Ewan & Co London and Melbourne" engraved around the bottom of the container.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, standard measure, bushel, bushel measurement, j & m ewan, dry measurement, victorian measurement standard, bronze container, melbourne observatory, robert brettell bate -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Book, Turner Australia Hand Tools, 1963
Printed Catalogue of hand tools.Catalogue of hand tools - screwdrivers, planes, hammers, knives, spirit levels, hacksaws, measuring tapes, gardening tools, lawn mowers, with price list.Printed Catalogue of hand tools.turner industries, lawnmowers, tools -
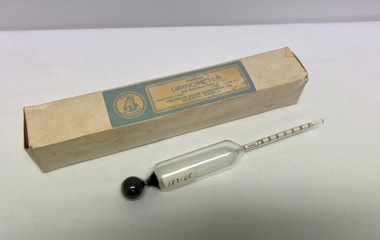 Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing Archive
Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing ArchiveInstrument - Specific gravity urinometer, Diabetes Urinometer
Glass urine specific gravity measure.Cream coloured manufacturers box labelled with a pale blue and cream label: "Diabetes Urinometer and Specimen Tube. Manufacturer Precision Glass Instrument Co, Melbourne". Blown glass urinometer used to measure the specific gravity of urine. It consists of 3 parts: I. The float: is the air containing part II. Weight: the lower end of urinometer (metal ball bearings) III. Stem- Has calibrations with numbers marked to measure the specific gravity Missing urine holding specimen tubeHospital type diabetes urinometer 60 degrees F Precision Glass Instrument Co. Melb. Measurements on stem from 000 to 030 urine specific gravity measure, urine testing -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyclinometer rule, mid 19th -earl 20th century
This clinometer, is a hand-held optical scientific instrument used in surveying to measure vertical angles. It is used to measure the angle of elevation from the ground in a right-angled triangle. It may have been used by a surveyor or a forester to measure the height of tall things where you couldn't possibly reach to the top of e.g. flag poles, buildings or trees.This item is an example of an early hand held measuring instrument.. Today the use of electronic sensors is an important component in the design and function of the clinometers.A rectangular wooden folding measuring instrument. the panels are brass framed. Inside is a brass semi-protractorgraduated 90-0-90' with index arm pointeran dwith a graduated edge in inches. Outside is a temperature conversion scale,Troughton & Simms, LONDONscientific-instrument measurement clinometer -
 Yarrawonga and Mulwala Pioneer Museum
Yarrawonga and Mulwala Pioneer MuseumFunctional object - Horse measuring stick
Measuring stick belonging to the late Kath Connell. Life member and past Ring Master of the Yarrawonga Show, also founder member of the Yarrawonga Mulwala pony Club. Donated to the A and P Association by M and B Gorman and family after Kath's death and loaned to the Historical Society for display. Long bamboo stick with hook end. Fitted with a sliding metal measure with inch and cm markingsnoneagricultural shows, pony club, horse measure -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Standard measure, Mid to late 19th Century
The beginning of standardised weights and measures began In Victoria when the Melbourne Observatory received sets of standard weights and measures, which had been tested in Britain against the then British Imperial standards. These included the primary standard yard and pound for the Colony of Victoria. Other standards of weights and measure held by shires and the administrative body's within the colony could then be compared to these primary standards. A Weights and Measures Act was passed in Victoria in 1862, establishing local inspectors throughout the colony. By the 1870s each local council and shire in Victoria held a set of standards that were used to test scales, weights and dry measures used by wholesalers, factories and shops. Every ten years the councils’ standards would themselves need to be rechecked against the Victorian Standards. The checking was done by the Victorian Customs Department in the 19th century, but with the transfer of responsibility for customs to the Federal Government in 1901, weights and measures function was retained by the Victorian Government and was shifted to the Melbourne Observatory. In 1904, a new building was erected at the south end of the Great Melbourne Telescope House, where the standard weights and measures and testing equipment was installed. This room had a large whirling apparatus for testing air meters and became known as the Whirling Room. When the Melbourne Observatory closed in 1944, the Weights and Measures Branch was formed to continue and this branch remained at the Observatory site unit until 1995. J & M Ewan History: J&M Ewan was a Melbourne firm that began by selling retail furniture and wholesale ironmongery. They had substantial warehouses situated at the intersection of 81-83 Elizabeth and Little Collins Streets, the business was established by James M Ewan in 1852. Shortly afterwards he went into partnership with William Kerr Thomson and Samuel Renwick. When Ewan died in 1868 his partners carried on and expanded the business under his name J & M Ewan. The business was expanded to provide a retail shop, counting-house and private offices. Wholesale warehouses adjoined these premises at 4, 6 and 10 Little Collins Street, West. This company provided and sold a large and varied amount of imported goods into the colony that consisted of agriculture equipment, building materials, mining items as well as steam engines, tools of all types and marble fireplaces. They also supplied the Bronze measuring containers in the Flagstaff Hill collection and the probability is that these containers were obtained by the local Melbourne authority that monitored weights and measures in the mid to late 19th century. The company grew to employ over 150 people in Melbourne and opened offices at 27 Lombard St London as well as in New Zealand and Fiji. The company also serviced the Mauritius islands and the pacific area with their steamship the Suva and a brig the Shannon, the company ceased trading in 1993. Robert Bate History: Robert Brettell Bate (1782-1847) was born in Stourbridge, England, one of four sons of Overs Bate, a mercer (a dealer in textile fabrics, especially silks, velvet's, and other fine materials)and banker. Bate moved to London, and in 1813 was noticed for his scientific instrument making ability through the authority of the “Clockmakers Company”. Sometime in the year 1813 it was discovered that one Robert Brettell Bate, regarded as a foreigner in London had opened a premises in the Poultry selling area of London. He was a Mathematical Instrument maker selling sundials and other various instruments of the clock making. In 1824, Bate, in preparation for his work on standards and weights, leased larger premises at 20 and 21 Poultry, London, at a rental of four hundred pounds per annum. It was there that Bate produced quality metrological instruments, which afforded him the recognition as one of one of the finest and principal English metrological instrument-makers of the nineteenth century. English standards at this time were generally in a muddle, with local standards varying from shire to shire. On 17 June 1824, an Act of Parliament was passed making a universal range of weights, measures, and lengths for the United Kingdom, and Bate was given the job of crafting many of the metrological artifacts. He was under instruction from the renown physicist Henry Kater F.R.S. (1777-1835) to make standards and to have them deposited in the principal cities throughout the United Kingdom and colonies. Bate experimented with tin-copper alloys to find the best combination for these items and by October 1824, he had provided Kater with prototypes to test troy and avoirdupois pounds, and samples with which to divide the troy into grams. Bate also cast the standard for the bushel, and by February 1825, had provided all the standards required of him by the Exchequer, Guildhalls of Edinburgh, and Dublin. In 1824, he also made a troy pound standard weight for the United States, which was certified for its accuracy by Kater and deposited with the US Mint in 1827. Kater, in his address to the Royal Society of London, acknowledged Bate's outstanding experimentation and craftsmanship in producing standards of weights, measures, and lengths. An example of a dry Bronze measuring container made specifically for J & M Ewan by possibly the most important makers of measurement artefacts that gives us today a snapshot of how imperial weights and measures were used and how a standard of measurement for merchants was developed in the Australian colonies based on the Imperial British measurement system. The container has social significance as an item retailed by J & M Ewan and used in Victoria by the authorities who were given legal responsibility to ensure that wholesalers and retailers of dry goods sold in Victoria were correct. The container was a legal standard measure so was also used to test merchants containers to ensure that their distribution of dry goods to a customer was correct.Maker Possibly Robert Brettell Blake or De Grave, Short & Co Ltd both of LondonContainer bronze round shape for measuring dry quantities has brass handles & is a 'half-bushel' measurement"IMPERIAL STANDARD HALF BUSHEL" engraved around the top of the container. VICTORIA engraved under "J & M Ewan & Co London and Melbourne" engraved around the bottom of the container.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, standard measure, bronze, peck measurement, j & m ewan, victorian standard dry measurement, bronze container, victorian standards, melbourne observatory, robert brettell bate -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyTape Measure, mid 1900s
This item predates the change of Imperial measure (England -1824) to decimal measure (Europe) in Australia (1970 to 1988). This item was manufactured in England as, was the majority of measuring tool and equipment. It was not until the late 1950s that other countries e.g. United States and Europe provided the same type of manufactured tools for the Australian market. World War II, when Australia had to defend its own boarders that the political push for self sufficiency of manufactured goods started local production. Workers in the Kiewa Valley had always relied on the high quality of tools and manufactured goods coming from England. From the middle to late 1950s migration by skilled workers from a war torn Europe provided the source of manpower for the expansion of the manufacturing industries in Australia.The requirement of an accurate measuring tool has always been critical. This item was used at the time when Australia was using the British Imperial measurements. Accurate measurements by carpenters and other trades people for both town and rural needs was just as critical as for the larger cities. The transition period from Imperial to metric was a period of over four years but it still presented those who had used the Imperial measurements for a longer period in their trades with a dual system of measurement for a longer time(usually up to their retirement) Other nations still using Imperial measurements kept the transition from Imperial to metric alive (the UK and USA still uses Imperial measurements in 2012)Retractable metallic wired tape measure within a leather casing. Length of tape is 66 feet. Brass fittings on casing(winder and back plate)Tape on one side marked in inches and feet and on the other in links. Winder lever marked "66ft No 401" on front and arrow with"wind this way". Leather cover marked "John R A Bone & Sons Birmingham England" on reverse side "Metallic wired tape R A Bone & Sons"wired tape measure, tool, mobile tool, construction tool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCalipers, Moore & Wright, 1925-1935
Established in 1906, Frank Moore soon became well known amongst discerning tradespeople for the quality & accuracy of his tools. The Company was acquired by John Shaw & Son in 1945 & James Neill & Co in 1970. Currently part of the Bower Meteorology UK Group, they still produce superb tools & measuring instruments in Sheffield. The subject item is made from high-grade carbon silver tool steel with the patented 'Firm Lock' joint, that identifies the maker as Moore & Wright.A tool used for external measurement of items made by a maker who patented the "firm lock" jointing system now used on many different types of tools in many different industries. These items are now collectible and quite rare as a result are sought by tool collectors in the USA and UK.‘Firm Joint’ external measuring calipers believed made by Moore & Wright. Impressed into the metal "L A J S" (Probably the owner and company that used the item nothing to do with manufacturing) flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, calipers, callipers, external calipers, outer caliper, pottery tools, masonry tools, glass making tools, external measurement -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPlanimeter (roller digital)
The rollers move over the map as the tracing arm is used to follow the boundary to be measured. The wheels allow unlimited horizontal travel and vertical travel within the limits of the arm movement. They measure in the X and Y directions Reading from the digital scale the area in square centimetres could be measured. Knowing the scale of the mapsheet the figure was converted to areas or hectares Generally at least three measurements were taken to ensure accuracy and precisionPlanimeter used to measure areas from scale maps. Includes box but no charger Plancom KP90forests commission victoria (fcv), forest measurement, surveying
