Showing 1190 items
matching site development
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Camp Street Precinct Ballarat Conservation Management Plan (Draft), 1999, 10/1999
The conservation management plan was commissioned by the City of Ballarat to assist in the process of planning for the future management and development of the Camp Street precinct, having particular regard for the Camp Street Arts and Education Precinct.White, soft covered, spiral bound book relating to Ballarat's Camp Street Precinct. Contents include: Methodology, buildings and site layout. ballarat, camp street, clare gervasoni, ballarat fine art gallery, art gallery of ballarat, old colonists' hall, former ballarat mining exchange, former state offices, former police court, former police station, former police barracks, old police station, arts academy, archaeology, conservation management plan -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionReport, Concept Study for the Further Development of the Eureka Stockade Reserve Conservation Plan, Vol 3, c1992
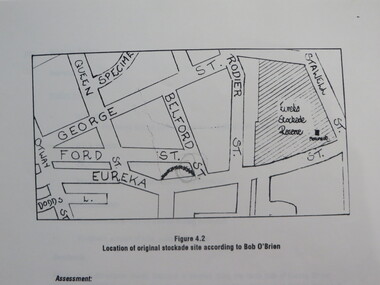
The objectives of the study were to * gather historical data and confirm the cultural significance of the site and reserve. * review existing site conditions including ownership together with current and proposed land uses. * Eureka Stockade location Copy of a 38 page report called "Concept Study for the Further Development of the Eureka Stockade Reserve Conservation Plan Vol 3", published by Ballarat University College. Authors are not stated. eureka, eureka stockade, ballarat university college, bert strange, bob o'brien, weston bate, alec barnett, jack chisholm, lloyd jenkins, eureka stockade location, cultural significance, eureka stockade site -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Mount Helen Campus Development Plan, 1970, 1970
The Ballarat School of Mines is the oldest site of technical education in Australia, and is a predecessor institution of Federation University Australia. The Mount Helen campus was originally the tertiary division of the Ballarat School of Mines until 1976. Green covered printed book.mount helen, ballarat institute of advanced education, mount helen campus, harrison, h.j. harrison, vernon, l.h. vernon, j.b. vernon, architecture, campus plan, ballarat school of mines and industries -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument, Graeme Tyrrell, Overview for the Development of Gardens Lydiard Street Campus, 1988, 01/12/1988
The report was prepared by Graeme Tyrrell, headgroundsman/Gardener at the Ballarat School of Mines (SMB) for Bob Feary, Manager of Facilities at SMB. The report was designed to present a broad cover of current plans for specific sites at the Lydiard Street campus.Seven page report on the development of the Ballarat School of Mines Gardens, including the Motor Mechanics Portable, Hickman Street (now demolished); Recreation Building (now demolished), E.P.U.Y Building, Hickman Street, vacant block behind creche (now site of UBTec building); Creche, Grant Street (now demolished); Former Courthouse building, Grant Street terrace, Brick Court yard, conifer beds lining Lydiard Street, Herb Garden above M.B. John Building, Terrraced area above Ballarat School of Mines Botanical Garden (referred to as Von Mueller garden). The report includes a campus plan. The report is copied onto white paper and is stapled at the top left corner. ballarat school of mines botanical gardens, ballarat school of mines, bob feary, graeme tyrrell, gardens, ballarat school of mines campus, smb campus -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet, Ballarat School of Mines, Ballarat School Of Mines Agenda for meeting with Chairman of the TAFE Board, 07/1985
Yellow covered A$ booklet bound with plastic. The book as in agenda for a meeting with I. Predl, acting Chairman of the TAFE Board. Items for discussion were: * L.F.J. Hillman Recreation Building * Maintenance of Buildings * Campus titles and future development * Quality Improvements * College Management Study * Uncertainties Re Blackburn The booklet also includes an aerial photograph of the Ballarat School of Mines campus, including dates each building was erected. The image shows the site of the newly demolished Ballarat Gao, and still has a tennis court and Mining laboratory onsite. The book also show allotment plans of the Ballarat School of Mines site. -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Planning Greenhill Enterprise Centre, 1996, 1996
At the Ballarat Technology Park (BTP) the spirit of innovation and entrepreneurship enables techno-driven businesses to thrive and prosper, in a dynamic and supportive environment. This fast evolving precinct encourages and supports the development of emerging and existing technology-oriented enterprises. Currently, more than 30 enterprises are located at the Park, including IBM, State Revenue Office, Emergency Services Telecommunications Authority, Primary Health Care and others. The Park's ideal location on the outskirts of Ballarat provides great lifestyle opportunities as well as having the convenience of being close to Melbourne, Geelong, Bendigo and Western Victoria. The BTP is a prestigious 29 hectare site set in a park-like environment, 7km from the thriving regional city of Ballarat. It is easily accessible from Melbourne, Geelong and Bendigo. Adjacent to Federation University's Mt Helen Campus, the BTP is ideally situated to support innovative technology-based enterprises grow and prosper. Enterprises can access skilled graduates through the University, as well as take advantage of the applied, academic and research knowledge available. BTP has been successfully supporting and fostering industry, innovation and job creation since 1995.Colour photograph of four men are seated at a low round table viewing design development drawings of the Greenhill Enterprise Centre prior to commencing documentation for tender purposes. They are Alan Webb (University of Ballarat Director, Buildings and Grounds), Professor David James (University of Ballarat Vice Chancellor), Michael Vincent (architect) and James Crisp (architect).ballarat technology park, university of ballarat., greenhill enterprise centre -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument, History of the Ballarat Technology Park, Oakbank
... was Buninyong's representative on the then Ballarat Development Committee... of the Ballarat Technology Research and Development Park in 1989. ballarat ...The Ballarat Technology Park is associated with Federation University Australia. The first stage commenced on 03 August 1989 when the first sod was turned by Hon, David White, Minister for Industry, Technology and Resources. John Beaumont was the Director of the Ballarat Technology Research and Development Park in 1989.Twenty items relating to the History of the Ballarat Technology Park as collected by John Parkin. .1) Handwritten notes by John Parkin on the history of the Ballarat Technology Park .2) Letter from A.E. Helyar (Shire of Buninyong Secretary), 08 March 1988 .3) Shire of Buninyong Minutes 07 June 1988 .4) Development of High Technology Activity by Jack Barker .5) Definition of a Technology Park by Derek Woolley .6) Shire of Buninyong minutes 28 June 1988 .7) Shire of Buninyong minutes 19 July 1988 .8) Invitation to a reception to commemorate the inauguration of the Ballarat Technology Park (John Parkin) by Shire of Buninyong President Cr Judith Coull to be held on 03 August 1989. .9) Invitation to a reception to the Ballarat Technology Park (John Beaumont) .10) Ballarat Courier article 04 August 1989 .11) Draft letter to Professor Geoffrey Blainey from John Parkin .12) Letter to the Editor from John Parkin, 18 December 2000 .13) University of Ballarat Development Appeal, 04 November 1994 .14 & .15) Invitation to installment dinner to celebrate the installation of Professor Geoffrey Blainey as Chancellor of the University of Ballarat to be held in the Union Building (now Albert Coates Building), Mt Helen campus .16) Letter to the editor from John Parkin .17) Letter from John Beaumont, 25 November 1994 .18) Invitation to the opening of the ISSC Southern Region Data Centre to be held on 24 November 1995. .19) Letter from Barry Traynor, 13 December 1995 .20) Planning Scheme information relating to the LaTrobe Research and Development Zone. .1) 2nd May 2005 History of Technology Park (I.T. centre) The history of the Technology Park started back in the mid-1980s. At the time I was a Buninyong Shire Councilor and as such I was Buninyong's representative on the then Ballarat Development Committee. At one of our meetings we received a request for information on a suitable site for a technology park. The requirements were for a site adjacent to a tertiary institution, secluded for security purposes and large enough to contain such a development. The next morning I contacted our Shire Engineer at the time, Newell Barrett and we drove around the area we both agreed that the current site was the most suitable we saw to meet the requirements. At the time it was owned by George Morrison. however the original enquiry to the B.D.C. came to nothing but the Shire Council and the B.D.C. decided to investigate the possibility of the site becoming a technology Park and information was collected. At about this time Mr Morrison put the property on the market and it was bought by a Ballarat builder, Mr John Beaumont, with the idea of developing it as a residential area. Council then arranged a meeting with Messrs Morrison and Beaumont to discuss the matter. I remember Mr Morrison saying he did not care what was done with it he just wanted to sell it and move down to the coast. Mr Beaumont, on the other hand, said he wasn't ready to retire yet and the idea interested him. As a result a committee consisting of the B.C.A.E., B.D.C. and Buninyong Shire Council (and Mr Beaumont) was formed to plan the development and rezone the area to technology park. It was previously zoned residential land and would seem to have been suitable for sub-division and residential development - its close proximity to the College being a major factor in its favour. The point of this is if Mr Beaumont had insisted on pursuing his original plan and had opposed the rezoning, I am quite confident he would have won an appeal at the A.A.T . (Administrative Appeals Tribunal - forerunner of V.C.A.T.) and the I.T. centre would not have got off the ground and the area would be covered with houses. But Mr Beaumont did go into the project with enthusiasm and the first stage was commenced on the 3rd August 1989 when the first sod was turned by Hon. David White, the Minister for Industry, Technology and resources (See the Courier 4th August 1989) Mr Beaumont went overseas to study similar parks and look for tenants. Unfortunately government did not support the project as they have now and apparently Mr Beaumont was ahead of his time for the private sector so Mr Beaumont could not continue the development and the site eventually passed to the College. I personally think more could have been done ... The work done by the Buninyong Shire Council and Ballarat Development Committee seems to have been forgotten as according to the Courier December 21, 2000 we are told the Park opened in 1995 as a joint venture between the City and the University. As a former Councillor said to me on the day "What happened to the plaque David White unveiled in 1989!" If there is any other information you want, please contact me. You may use my file for reference. Kind regards John Parkin PS I always felt a bit guilty that I encouraged John Beaumont and he was left in the lurch. ballarat technology park, parkin, john parkin, helyar, barker, woolley, shire of buninyong, beaumont, blainey, geoffrey blainey, southern region data centre, greenhill enterprise centre, stan jeffrey, jeffrey, john beaumont, david white -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionProgramme, Release of Technology Park Plans and Laying of Foundation Stone, 1995, 02/1995
The Ballarat Technology Park site consists of 28.8 hectares of freehold land zoned for technology Purposes. The development plan for the Park was prepared by the City of Ballarat. The construction of the ISSC Southern Regional Data Centre was the first stage of the project. ISSC Southern Regional Data centre is a $12.5 million building development at the corner of Geelong Road and gear Avenue. The building was constructed by H. Troon Pty Ltd. White card program for the Release of Technology Park Plans and Laying of Foundation Stone. ballarat technology park, issc southern region data centre, troon, david james, geoffrey blainey, bruce clark, john bligh, roger hallam, campus plan -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet, GIAE Official Opening, 1976, 11/1976
The Gippsland Institute of Advanced Education was established by an Order-in-Council in September 1968. On its establishment, the Institute assumed responsibility for the diploma coursed previously offered at Yallourn Technical College. In 1972 the Institute transferred part of its operations to the first of its permanent buildings on a large campus in rural surrounding near the township of Churchill, ten kilometres south of Morwell, and 160 kilometres east of Melbourne. The campus site plan report prepared in 1970 by the Institute's campus planners, Yuncken Freeman Architects Pty Ltd, provided the conceptual base for the development of a new campus at Churchill. All facilities were planned to converge on a central space; all having the ability to expand outwards. Central to the campus plan was the concept of an internal pedestrian street connecting all academic divisions to the central facilities. The first building was completed in 1972. The Administration Building, Visual Art & Maintenance Workshops, Multi-Purpose Building, and Student residences were designed by Yuncken Freeman Architects. The central Facilities Building (cafeteria and Union) were designed by Chancellor and Patrick, the Education Building and Applied Science Building is designed by Eggleston, McDonald and Secomb.Grey and yellow soft covered booklet prepared for the official opening of Gippsland Institute of Advanced Education.gippsland institute of advanced education, gippsland campus, churchill, m.w. hopper, c.h. ford, lindsay thompson, j.l. carrick, r.w. muncey -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Black and White, Former Ballarat Library, c1960
... First known development on this site was the establishment... known development on this site was the establishment ...First known development on this site was the establishment of the Government Camp from the early 1850s. It was established to accommodate officials, troopers and police who were needed to administer the goldfields. Some permanent buildings were constructed. Lack of materials and bad weather prolonged the building of more permanent buildings and most men were still living in tents. Area was known as Camp Reserve. In 1864 a subdivision map shows the reserve be used for Public Buildings. Library applied for land on corner of Sturt and Camp Streets in 1878. 1880s plans show section of the reserve be used for a Free Library and Reading Room. Lease was granted and the old mining boardroom was initially used. Land for additional building to house a Museum and Art Gallery sought and agreement reached in 1882-3. Compensation paid to owners and library granted the land. Plans for a new library building with tower and lantern roof abandoned due to lack of funds. It wasn't until 1895 that a solution to funding was found and the library was able to begin constructing the complex of buildings on the Free Library Reserve. A number of changes have occurred since 1910s - the Classical Revival facade replaced with an angled facade in a stripped Classical style with Art Deco features and high parapet. Building is now part of Federation UniversityPhotograph of former library. Shows a two-storey rendered brick building in a Classical style. Some Art Deco features. Central pair of double windows with single window either side. High parapet above.government camp, goldfields, camp reserve, free library, reading room, sturt street, camp street, museum, art gallery, troopers, police, barracks, camp street -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMachine - Treadle Lathe, 1920-1923
The lathe-making business incorporated in 1902 as Drummond Bros Ltd originated in the fertile mind of Mr Arthur Drummond, said to have been living at that time at Pinks Hill, on the southern edge of Broad Street Common, west of Guildford. Mr Drummond, whose accomplishments included several pictures hung in the Royal Academy, was unable to find a lathe suitable for use in model engineering. In 1896 he designed for himself a ‘small centre lathe … which had a compound slide rest with feed-screws and adjustable slides’. He also designed and built ‘lathes of 4.5 inch and 5 inch centre height, which had beds of a special form whereby the use of a gap piece was eliminated but the advantages of a gap-bed lathe were retained’. Assisted by his brother, Mr Frank Drummond, who had served an apprenticeship to an engineering firm at Tunbridge Wells, the first lathes were made in a workshop adjoining Arthur Drummond’s house. The demand that speedily built up led to the decision to form a company and manufacture the lathes for sale commercially. Land was acquired nearby, at Rydes Hill, and the first factory built. The enterprise was a success, and the company quickly established ‘a high reputation in this country and abroad for multi-tool and copying lathes, and gear-cutting machines’. Other lathes were added to the range, including the first of the ’round bed’ machines for which the firm became widely known. A Drummond 3.5 inch lathe was among the equipment of Captain Scott’s 1912 expedition to the South Pole, and large numbers of 3.5 inch and 4 inch designs were exported to Australia, Canada and India. By the outbreak of war in 1914, 5 inch, 6 inch and 7 inch screw cutting lathes, arranged for power drive, were on sale. Large orders were received from the government for 3.5 inch lathes, for use in destroyers and submarines, and 5 inch lathes for the mechanised section of the Army Service Corps. The latter were used in mobile workshops. The factory worked night and day to supply the forces’ needs, until production was disrupted by a fire which destroyed a large part of the works in May 1915. As soon as rebuilding was complete work restarted. At the end of the war the entire production was being taken by the Government departments, a special feature being a precision screw lathe, bought by the Ministry of Munitions in 1918. Between the wars Drummond Bros Ltd introduced new machines for the motor vehicle, and later the aircraft industry, and the works were extended on many occasions to fulfill the increasing orders. The Maxicut multi-tool lathe (1925), designed for high-production turning operations, was one of the first machines of this type to be built in England. It was followed (1928) by an hydraulic version for turning gear blanks, and similar work. Further developments provided machines which, during the Second World War, turned all the crankshafts and propeller shafts for Bristol engines. Others, ordered by the Ministry of Supply were employed in turning shells, and many other specific needs of vehicle and aircraft manufacture were catered for by new types of Drummond lathes. Production of the small centre lathes ceased during the war when the company needed to concentrate on building multi-tool lathes and gear shapers. After the war a completely new Maxicut range was introduced, replacing the older versions, and fully automatic. The types were continually developed, and new versions manufactured until the end of the company’s life in 1980. The disappearance from the scene of Mr Arthur Drummond in 1946, and the end of the company’s autonomous existence in 1953 when the company was acquired by William Asquith Ltd, which was in turn bought by Staveley in 1966, meant that the factory at Rydes Hill became one – albeit very effective – part of a large national engineering company. Achievements at the Guildford works during its last years included the development of automated Maxicut gear-shapers in what was ‘probably the most fully automated gear shop in the country’, while a machine from Guildford was sent to the Osaka Fair in 1962. In 1963 an agreement was signed with Hindustan Machine Tools for the manufacture of Maxicut gear-shapers in state owned factories in Bangalore and Chandigarh. During 1963 the two largest multi-tool lathes ever made in the UK were installed in Ambrose Shardlow’s works in Sheffield for handling cranks up to 14 foot long. In 1976 Drummond lathes were included in Staveley’s £14,000,000 installation in Moscow of an automated production line for Zil motor cars. Up to the end invention continued at Guildford: a new Drummond Multi-turn memory-controlled machine was shown at the International Machine Tool Exhibition in 1977. This could not save the works from the pressures of the late 1970s, and Staveley Industries closed its Guildford site in 1980.An early example of a lathe that was designed primarily for the hobbyist model maker. It is in good condition and sought today by collectors as many of it's attributes were innovative at the time and lead to further development and incorporation of some of its features into more industrial models of production machinery. Lathe, round bed, treadle powered lathe, Drummond Type A, Serial number and maker's inscription. 1920-1923, Made by Drummond Brothers in Guildford, Surrey, England. Lathe is complete with Chuck, Tool post and Tail Stock in situ (30 extra parts)"MADE BY DRUMMOND BROTHERS LIMITED - PATENT TEES - RYDE'S HILL n GUILDFORD SURREY", "Serial Number 01470," "L44" or "L45 " flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, lathe 1920-1923, round bed lathe, treadle lathe, drummond type a, guildford surrey, drummond brothers guildford surrey england, tread'e -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Hand operated embossing document press, 1910
The woollen mill was a vital part of Warrnambool for all but 22 years of the town’s history since it's the establishment in 1847 when the first land sales were held and white settlement began. In 1869 the Warrnambool Meat Preserving Company began operations on the mill site, in 1875, shareholders of the then defunct Warrnambool Meat Preserving Company happily sold the land and buildings on the Merri river to Warrnambool Woollen Mill Company Ltd for £5,000. The site was sold again in 1876 to grazer Robert Hood of Sherwood, who was chairman of directors of the failed company, which couldn’t raise sufficient capital to keep the works operating. The entrepreneurial Hood then used the existing plant to turn his own wool into tweed cloth. But just as the mill was starting to show a profit, a fire destroyed the building and plant on the night of 25 March 1882. So again, the mill was operational for six short years. Insurers only paid a fraction over 10% of the damage, Hood couldn't raise sufficient capital to rebuild on his own, and so the site lay unused until 1910. In 1908 Marcus Saltau and Peter John McGennan convinced the Warrnambool Chamber of Commerce to invest in a secondary industry with local capital. A public meeting in September 1908 agreed to raise £40,000, electing Saltau chairman of directors, a post he held for 34 years. A year later, using mostly local money, the Warrnambool Woollen Mill Company dispatched its first manager, John E. Bennett, to buy a plant and recruit 20 experienced staff from the Yorkshire woollen industry in December 1909. Another year more, the new mill was officially opened on 14 November 1910 by Marcus Saltau as company chairman and town mayor. Eighteen months on, in May 1912, the mill paid its first half-yearly dividend of 2 ½%. It was now working two shifts, with a year's orders to fill. In 1914 the mill ordered its own generator, providing the town with electricity and effectively doubling its plant size by October 1915, six months after Gallipoli. Thereafter, government orders for cloth and military supplies assured the mill’s success right through the First World War and on until 1923. A plant upgrade in 1922 for machinery to make worsted fabric drained profits, which, with a fall in demand, led to a loss in 1925. Profits were restored by the 1930s, despite the Depression, mostly due to tight management and robust marketing. Production boomed again during the Second World War, but soon foreign competition bit into profits, forcing the company to consolidate operations. The ‘50s and ‘60s were golden years for the mill. Security and growth gave the company confidence to trial Australia’s first electric blanket in 1958 and to install Swiss Sulzer looms in 1965. Over time, the building facades took on the modern look that the mill presented until it closed. The Dunlop company bought the mill in 1968, fending off a challenge from Onkaparinga in South Australia, and continued to expand by adding Wendouree Woollen Mill in the same year and Dream-spun Textiles a decade later, in 1979. Soon after that purchase, however, the mill began its slippery slide into decline. Dunlop sold to its former rival bidder Onkaparinga Woollen Co. Ltd in 1982, which in turn was taken over by Macquarie Worsted's only a year later, in 1983. Operations remained stable for a decade until 1994 when the Macquarie Group signaled that its newly rationalised operations left no room for the Warrnambool investment. The final operator of the mill was The Smith Family charity group, which ran the site by agreement with the Warrnambool City Council and a state government grant in that same year, 1994. The mill became more of a fabric recycler than a manufacturer. The site was sold to private operators in February 2003 and rezoned four months later to allow for the mixed housing development. The embossing press is significant for its association with the Warrnambool Woollen Mills 1910-1968, a major employer in the Warrnambool district. The press is also significant as an example of commercial office equipment used in the 19th and 20th century.Press, metal, for Company seal of Warrnambool Woollen Mill, stamping their brand as Western District Worsted Mills Pty Ltd. Metal is black with red and gold floral markings. Inscription of stamp reads "WESTERN DISTRICT WORSTED MILLS PROPRIETRY LIMITED" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, warrnambool woollen mills, western district worsted mills proprietry limited, worsted fabric, printing press, logo printing press, stamp printing press, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Ship's Fitting, circa 1825
This attractively patinated artefact was raised from the wreck site of the CHILDREN (wrecked January 1839, recovered February 1974) and was quite reasonably catalogued as a portion of a ships porthole. This identification is unlikely however, because the CHILDREN was built at Liverpool in 1824, and round portholes were not in common use until the 1850s. The catalogue identification has since been changed to "Ship's Fitting" Prior to the appearance of round portholes in the middle of the nineteenth century, the function of introducing light to lower decks was performed by square half-glassed ‘ports’ in the side of the hull (known as a port-sash) , or ground-glass ‘bullseyes’ inserted in the deck (scuttles). In historical terms, ports were always square, cut into the timber originally to allow the firing of a ships guns, and were closed in weather by a tight fitting square hatch. Flagstaff Hill Shipwreck Museum has three portholes on display that illustrate the gradual development and adoption of circular brass portholes. First in sequence is a small 12.5cm diameter window (with a deep frame for thick wooden hulls) from the 1855 wreck of SCHOMBERG. The second and third are larger 25cm diameter windows (with a shallower frame for thinner iron hulls) from the 1892 wreck of the NEWFIELD and the 1908 wreck of the FALLS OF HALLADALE . Once the apparently obvious use of the brass object is discounted, an accurate and reliable alternative classification is difficult to specify. One artefact register notes it was ‘found in about the centre of the wreck site’. This would mitigate against the possibilities of (1) ‘horseshoe frame’ joining pieces of the keel and hull at the bow of the vessel, or (2) ‘deckseat’ for a binnacle at the stern. It may support the idea of a ‘head frame’ on a cooped companionway or a ‘deckseat’ for a mainmast pump. But this is only speculation. The actual identification is not known. The wreck of the CHILDREN is of State significance - Victorian Heritage Register S116Ship's fitting, of heavy gauge brass circle, previously classified as section of ship's fitting, which was raised from the wreck of the Children. One end is broken off at an original bolt hole and the other is severed or cut at an acute angle from the inner rim. The artefact is 6cm across and 1cm deep, indicating strength and function as a substantial and finished item of moulded metal. The upper face bears sedimentary accretion stained red/brown. The rear face has been gouged by hard or corrosive materials and bears brilliant blue/green oxidisation.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, the children, brass flange, brass rim, shop fitting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Bed Pan, R. Fowler, 1927-1935
The company R. Fowler Limited was established in Ultimo, Sydney, in 1837 when Enoch Fowler (1807-1879) came to Australia from Ireland and is known today as the oldest pottery still in operation in Australia. They were mostly known for producing bottles, jars, and pipes. The pottery was originally located at Abercrombie Place on Parramatta Street, Chippendale, NSW before they relocated to Glebe in 1847. Later the pottery manufactured building materials such as tiles, pipes, and chimney pots. As the business grew, they moved to Parramatta in the 1850s. Enoch's son Robert (1839-1906) had joined the company, and took over its management in 1873, changing the name to “R Fowler Sydney” in 1880. Robert, introduced the black under glaze trademark with the archer as shown on the subject item. He went on to opened further sites at Marrickville and Bankstown, with the company becoming R. Fowler Limited in 1919. The factory at Thomastown, Melbourne was opened in 1927. Fowler also owned a Pottery somewhere near Lithgow, where they produced clay pipes that look like salt-glazed Earthenware pipes. There have been numerous developments to the company over subsequent decades, and the company was still operating in 2002 but is now owned by Caroma Industries Ltd, manufacturing only sanitary fixtures. An item made by an Australian company during the first half of the 20th century and quite rare today. The item is significant as it gives a snapshot of the early development of manufacturing companies in Australia. This informs our social history in Australia marking Australia's evolution into an independent country and no longer a colony of England. Bed pan ceramic white glaze handle at one end.Marked R Fowler Ltd and trademark a person sitting with a bow and arrow "00"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Alex Sideratos et al, Anderson's Mill Smeaton - Main Report. Student Project, 1992
Anderson's Mill Smeaton - Main Report. Student Project.White bound book of 80 pages and includes five appendices.anderson's mill, smeaton, alex sideratos, ozlem soyogul, michael pearlman, jane lennon, chris smith, simon nelly, barry golding, russel dawe, margaret giles, ross squires, executive summary, introduction, methodology, swot analysis, site analysis, concept/product analysis, summary of market research, other development options to consider, community involvement, preferred option & cost analysis, marketing recommendations, management issues, conclusion, the courier ballarat, department of conservation and natural resources, creswick business promotions committee, creswick, daylesford, kingston, allendale, flour mill, anderson brothers, convent gallery daylesford, mill restaurant malmsbury, oat mill -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Scene of foreshore development, 1950s
Port of Portland Authority archivesFront: (no inscriptions) Back: fd009 (pencil, upper left) P.G. 5. (blue pen, upper right)port of portland archives, bulldozer, excavation site, all saints, cliffs -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Main Breakwater construction, Portland, n.d
Port of Portland Authority ArchivesFront: 'Wharf piles, the Hat platform ones are ready for the decking. 'Tall ones await pile driver.' - Pencilport of portland archives, harbour construction, portland, battery point, harbour development -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Main Breakwater construction, Portland, Jan-60
Port of Portland Authority ArchivesFront: MAIN BREAKWATER PARAPET - View North at round head showing roundhead base completed and first two "bridge pier" Key blocks cast for straight parapet Jan '60 typed Back: Main Breakwater Parapet View N at roundhead, showing roundhead box completed and first two "bridge pier" key boxes cast for straight parapet. Written in blue biroport of portland archives, main breakwater, construction, portland, harbour, harbour development -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Main Breakwater construction, Portland, n.d
Port of Portland Authortity Achivesport of portland archives, main breakwater, construction, portland harbour, harbour development -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Main Breakwater construction, Portland, n.d
Port of Portland Authority Archivesport of portland archives, main breakwater, construction, portland harbour, harbour development, battery point -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Main Breakwater construction, Portland, n.d
Port of Portland Authority Archivesport of portland archives, main breakwater, construction, harbour development -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Main Breakwater construction, Portland, n.d
Port Of Portland Authority Archivesport of portland archives, main breakwater, construction, harbour development -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Main Breakwater construction, Portland, n.d
Port of Portland Authority ArchivesBack: Wharf piles, the flat platform one's are ready for the decking. Tall ones await pile driver. - Pencilport of portland archives, main breakwater, construction, harbour development -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Main Breakwater construction, Portland, n.d
Port of Portland Authority archivesport of portland archives, main breakwater, construction, harbour development -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Main Breakwater construction, Portland, n.d
Port of Portland Authority Archivesport of portland archives, main breakwater, construction, harbour development -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Main Breakwater construction, Portland, n.d
Port of Portland Authority Archivesport of portland archives, main breakwater, construction, harbour development -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Portland Harbour Development, n.d
Port of Portland Authority Archives -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
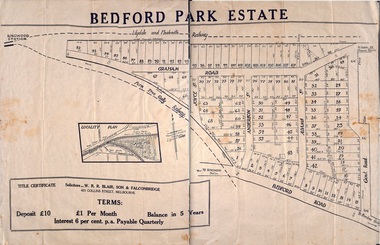
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPlan - Sub-division, Bedford Park Estate, Ringwood, Victoria - 1924
Bedford Park subdivisional development did not eventuate. The land adjoining the railway line became parkland with provision for sporting facilities and the remainder was purchased by the Education Department as the site for Ringwood High School/Secondary College. Poster size land sale advertisement.Subdivision plan includes Bedford Road, Graham Road, Joyce Street, Anderson Street, and Adams Street. Solicitors - W.R.R. Blair, Son & Falconbridge, 405 Collins Street, Melbourne. -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyMixed media - Video, RDHS Guest Speaker Presentation - "Heathmont 2020 Highlights" - Gerry Robinson and Peter Le Get
Digitised video (1.11GB). Duration: 20 minutes. Recorded March, 2021. (Video is available for viewing at Ringwood & District Historical Society Archives by appointment)Presenters: Gerry Robinson and Peter Le Get of Heathmont History Group (HHG) look back over developments in the area over the previous year. HEATHMONT HIGHLIGHTS FOR 2020 Summary - "Of course for 2020 the Covid 19 virus dominated. Other finalists included roadworks on Bedford Road corner, new Wards for MCC and their elections, 100th birthday and death of Rita James, opening of Milk & Wine Co. café replacing Barclays, election of Kylie Spears as Mayor, closure of Heathmont Medical Centre, demolition of Miller homestead in Coven Avenue, final edition of Maroondah Leader local newspaper, opening of HE Parker Sports pavilion, 50 more bollard arts, and the ugliness of the former Anglican Church and other local sites." -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Photographs, x3 Colour,, Highett Gasworks c1974, 1974
3 of 5 photographs of the Highett Gasworks c 1974 The Brighton Gas Company was established 1877 by local residents including Thomas Bent. Initially all went well for residents as gas light replaced kerosene lamps and street lights were installed. However disruption to supply, poor quality and failure to reach all house lead to dissatisfaction. Thomas Bent therefore began the Central Brighton and Moorabbin Gas Company 1885 and a price war ensued. This was unsustainable and the two companies amalgamated in 1877 supplying gas from the New Street Works site. 1930 this Company expanded to Highett where it had purchased 45 acres adjacent to the train line. 1927 a gas holder was built connected to the Brighton works 1936 construction began on a complete gas-making unit and the Highett Gasworks, Nepean Highway, began supply 1939. 1950 an extension program was completed. However by 1965 , with the discovery of Natural Gas offshore in Bass Strait, changes to Gas distribution were apparent. At first some of the facilities at Highett were used to distribute the gas piped from Sale, Gippsland. However after conversion of 450,000 homes to Natural Gas the Highett site was redundant. The gasometers were removed 1978. Moorabbin Council obtained part of the land for public recreation purposes. ( Dr. G Whitehead KCC Historian ) c2012 the Moorabbin Justice Centre / Magistrates Court of Victoria was built and further development of the area for apartments proceeds. The establishment of the Brighton Gas Company 1877 and the Highett Gasworks 1885 brought bright lighting to houses, businesses and streets in Moorabbin Shire and cooking ovens and heating improved the living conditions of residents. 3 x Colour photographs of the Highett Gasworks c1970bass strait gas, highett gasworks, brighton gasworks 1877, central brighton and moorabbin gas company 1885, whitehead dr. graham, magistrates court of victoria, horse drawn carts, toll gates brighton, motor cars 1900, steam engines, early settlers, bentleigh, parish of moorabbin, city of moorabbin, county of bourke, moorabbin roads board, shire of moorabbin, henry dendy's special survey 1841, were j.b.; bent thomas, o'shannassy john, king richard, charman stephen, highett william, ormond francis, maynard dennis, market gardeners, vineyards, orchards
