Showing 992 items
matching women at work
-
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, Portrait black and white, c.1930
This portrait photograph of Dame Mary Herring is a visual record of her taken during the time she was offering advice to Melbourne District Nursing Society After-Care Home (later Hospital)' as a member of their Committee from 1931. She was a Vice-president from 1943-1957 and acted as President in 1953. As a Medical practitioner she was involved with the formation of the MDNS After-Care Ante-Natal clinic in 1930 and the establishment of the Women's Welfare Clinic at the MDNS After-Care in 1934. Dame Mary Herring was born in Carlton on the 31st of March 1895. She graduated as a Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery (MB. BS) at the University of Melbourne in March 1921. During her training she went out with the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS), where she visited many in poor circumstances and through this decided she wanted to improve the lives of women and children. She married Edmund Herring on the 6th of April 1922 and he supported her to continue her Medical career. She established an Ante-Natal Clinic at the Prahran Health Centre in 1926 and assisted MDNS After-Care Home in the establishment of its Ante-Natal clinic in September 1930. In 1931, as Dr. Mary Herring she became a member of the Committee of the now named ‘Melbourne District Nursing Society After-Care Home’ (later Hospital), and as Lady Herring became a Vice-president from 1943 until 1957 and acted as President in 1953. In 1934, along with Dr. George Simpson and Dr. Victor Wallace, she established the Women’s Welfare Clinic at the MDNS After-Care Hospital for patients of the Society; the first of its kind in Melbourne. After its opening in October 1934 she was the Hon Secretary of the Welfare Clinic, which operated from a room in the Ante-Natal Clinic of the After-Care. Dr. Herring pioneered family planning services. The clinic ran until 1940 when women could now obtain this advice from other establishments. In 1953, as Acting President, Lady Herring was involved with the discussions of the District Division of MDNS relocating to ‘Airlie’, 452 St. Kilda Road, Melbourne and the separation of Melbourne District Nursing Society and After Care Hospital, with the District Division now a separate entity, known as Melbourne District Nursing Service with its Headquarters at 452 St. Kilda Road, Melbourne. In 1966 with Royal patronage, this became the Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS). Though asked to be President of the Hospital division of the MDNS Society, she declined due to her many activities. In 1940 Dr. Mary Herring was a founder of the A.I.F Women’s Association and served on the Women’s Welfare Subcommittee to assist the families of soldiers and now as Lady Herring, she became President from 1943-1946. She was a a founding member and first president of the Victorian Council of Social Service 1946, chairman of the Vera Scantlebury Brown Memorial Trust 1946-1979, Deputy-president of Victorian division of the Australian Red Cross 1944-1963, and of the Victoria League 1945-1972 and the Australian council of the Save the Children Fund from 1962-1967. Lady Herring was a tireless worker for many charities particularly charities for children. On the 10th of July 1953 she was made Commander of the Order of St. John in recognition of her charity work and on the 11th of June 1960 was made Dame Commander of the Order of the British Empire for “services to nursing in Victoria” In 1949 the Argus Newspaper (https://trove.nla.gov.au/newspaper/article/22776603) described her as “one of the finest examples of Australian women in our State, with a record of selfless devotion to the service of others. Calm, kindly, clear-minded, and intensely logical”,..... “she has taken all this in her stride without once stopping out of her aura of cool, unruffled efficiency, an efficiency which is tempered by her warmth and understanding, her approachability, and her human sympathy.” Dame Mary Ranken Herring died in Camberwell on the 26th of October 1981. This black and white photograph is a portrait view of Dame Mary Herring. She has curled light coloured hair. Only a portion of her scooped neck dark coloured frock which falls in soft folds can be seen. There is a light colour brooch attached on the left hand side of her frock near the shoulder. She is wearing a string of pearls around her neck. A curtain can be seen in the background of the photograph.Stuart Tompkin Studiomelbourne district nursing society, ante-natal clinic, women's welfare clinic, rdns, royal district nursing service, dame mary herring -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, Portrait black and white, 02.1970
This black and white photograph of Sister Pat McPherson was taken at the 1st International Congress on Domiciliary Nursing held in Melbourne. The congress was hosted by the Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) and ran from the 1st - 8th of February 1970. Following this Congress, Sister Patricia McPherson was employed by RDNS from 1970 - 2003, mainly in the area of Administration.Sister Patricia McPherson, State Registered Nurse, Midwife, and Infant Welfare trained nurse, B.A. was awarded an M.B.E. for her community health work among the Aboriginal communities during the time she worked as a Sister for the Australian Inland Mission (AIM). This was just prior to her joining Royal District Nursing Service. Patricia McPherson is listed on page 210 in the 'Women Shaping the Nation - Victorian Honour Roll of Women Vol 1 - 2001' - Centenary of Federation 1901 - 2001.This black and white photograph is a portrait head and shoulders view of Sister Patricia McPherson, who is smiling and has short straight dark hair. She is wearing a black and white patterned frock; on its upper right is attached a plastic name badge with two lines in white capital letters on black background stating: "Miss P. MCPHERSON / WESTERN AUSTRALIA' . Seen in the background is black and white vertical striped wallpaper.The Herald & Weekly Times Ltd, Melbourne, Australiardns, royal district nursing service, 1st internation congress on domisiciary nursing, sister patricia mcpherson -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, Portrait black and white, c.1950
Dame Ivy Evelyn Annie Wedgwood, as Senator in the Federal Government, presented the Senate with Statistics of visits done by Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) Trained nurses (Sisters) showing their visits increased threefold in the four years from 1952-1956. She was Honorary Treasurer of the now named Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) for many years. Dame Ivy Evelyn Annie Wedgwood trained as an Accountant and worked as a Secretary before joining the Australian Women's National League which led her to be a founding member of the Liberal Party, and the Victorian Liberal Party's women's section. She became the first Victorian woman Senator in the Federal Government in December 1949 and served until mid 1971. She presented the Senate with Statistics of visits done by Melbourne District Nursing Society Sisters showing their visits increased threefold in the four years from 1952-1956, and stating that many patients would have been hospitalized without the visits from the Society. She strongly supported the Home Nursing Subsidy Bill in Parliament which was passed in 1956, and continued to work for health, welfare and disability issues as well as being an advocate for women's interests, including equal pay for equal work, during her time in Parliament. Over the years she was a specialist magistrate to the Children's Court of Victoria, a Justice of the Peace, served on the National Council of Women, and was president of the Women's Justice Association, as well as Honorary Treasurer of the now named Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) for many years and the first President of the Australian Council of Domiciliary Nursing. In June 1967 she was appointed Dame Commander of the Order of the British Empire for 'distinguished services to Parliament and the community' and RDNS holds this award in its Archives. Following her retirement from Parliament she became President of the After-Care Hospital in 1972, and on the 24th of July 1975 after chairing a Board meeting she felt unwell and returned to her home in Toorak where she died, aged 78 years, later that evening.Black and white photograph showing Dame Ivy Wedgwood, who has short wavy dark hair; is wearing glasses and has a single string of pearls around her neck. She and is sitting in a light coloured covered chair and part of a cushion is seen. She is wearing a floral dress with mid length sleeves and is sitting in front of a filled bookcase. A smaller filled bookcase is seen to her left as well as some stacked books.melbourne district nursing society, mdns, after- care hospital, royal district nursing service, rdns, dame evelyn annie wedgwood -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, Portrait black and white, c.1940
Jessie Isabel Henderson was President of the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) form 1924 until 1947. She was made a Commander of the British Empire (CBE) for her welfare work. Jessie Isabel Henderson was a leader in all the welfare organizations in which she was involved, including the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) where she was elected as a Committee member in 1912. She was regarded as being "clear-sighted, level-headed, being able to see the right perspective when troubles arose" and having an exceptional memory. She was a representative on the newly formed Charities Board in 1923 and was elected President of the MDNS in 1924 and continued in this role until 1947. During this time she was involved with the formation of the Society's first Auxiliary; the founding, and later extensions, of the After-Care Home, the Society now being called 'Melbourne District Nursing Society and After-Care Home'. This involved many fund raising efforts for the purchase of property of the Nurses Home at No. 39 Victoria Parade, Collingwood and the building of the After-Care Home at No. 45. During her time as President the After-Care opened an Ante-Natal Clinic and a Women's Welfare Clinic, as well as the Society creating a 'Committee of Almoners' who assisted discharged patients from the After-Care to receive assistance from other organizations if required. The name changed to 'Ward Visitors' when an 'Institute of Almoners' was formed with newly trained Almoners. During the depression 1929-1933 she led the Society in extending its Midwifery and District services, including supplying milk for expectant mothers. Through the depression her philanthropy extended to, with the help of another, in assisting young ladies out of work. She sought sewing machines and material from businesses and set up a factory where the ladies were employed producing salable products. In 1933 Mrs. Henderson suggested the name of the After-Care Home be changed to the 'After-Care Hospital'; she felt using the word 'hospital' would aid with receiving grants and money from the public through appeals - this came into effect in 1934. In 1936 Jessie Isabel Henderson was made Commander of the British Empire (C.B.E) for her welfare work. Mrs. Henderson was unable to carry out her Presidential duties in 1947 due to ill health, and she resigned in 1948. She died on the 11th of January 1951. The After-Care Hospital dedicated wards 4, 5 and 6 in the Jessie Henderson wing in her memory. She is listed on page 180 in ‘Women Shaping the Nation - Victorian Honour Roll of Women, Vol 1, 2001’ Centenary of Federation 1901 - 2001 Black and white photograph of the head and shoulder view of Mrs. G.G. (Jessie Isabel) Henderson who has her wavy dark hair drawn back and is wearing a short necklace and a longer single string of pearls, She is wearing a black frock which has a square neckline.mdns, after-care hospital, melbourne district nursing society, rdns, royal district nursing service, mrs g.g. (jessie isabel) henderson -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, Portrait black and white, c.1890
Rev. Dr. Charles Strong arranged a meeting of some imminent citizens of Melbourne on the 17th of February 1885 when the decision was made to form the Melbourne District Nursing Society. Rev. Strong chaired the meeting, on 4th of March 1885, which accepted the Rules of the Society prepared by the Sub-committee. He chaired the first Annual meeting of the Society the following year and remained a Committee member for several years.Rev. Dr. Charles Strong had significant involvement in the establishment of the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS), the first District Nursing Society in Australia. He was born in Scotland and came to Melbourne with his family in 1875, initially being Minister of Scots Church in Collin Street. He left the Presbyterian church and became the first Minister of the newly formed, free religious, Australian Church in 1885. Rev. Strong cared passionately about social welfare issues and was a member of the Australian Health Society from 1880 and also president of the Convalescent Aid Society. He was involved with improving lodging houses in the slums of Melbourne and recognized the need for nursing care of the sick poor in their own homes. Many eminent citizens of Melbourne supported this idea and he arranged a meeting of these citizens, fifteen women and four men, at Mrs. William McCulloch's home on the 17th of February 1885, when the decision was made to form the Melbourne District Nursing Society. Dr. Strong, along with Dr. Caffyn, had experience of social welfare work in Scotland and were able to explain the object and scope of a District Nursing Society. A Sub-committee was formed, with Mrs. Charles Strong among the members, to draw up a Constitution and for suggestions to carrying on the Society's work. Rev. Strong chaired the meeting, on 4th of March 1885, which accepted the Rules of the Society prepared by the Sub-committee. A Special General Meeting was held on the 9th of April and the first Officers and Committee members, were elected with the Rev. and Mrs. Charles Strong being elected as members. Rev. Strong chaired the first Annual meeting of the Society the following year and remained a Committee member for several year. Reverend Dr. Charles Strong died on the 12th of February 1942 aged 97 years.This black and white portrait photograph shows an elderly Reverend Dr Charles Strong who has receding and thinning white hair and is sporting a white trimmed moustache and beard. His face shows the lines of an aging gentleman. He is wearing a winged collar on his white shirt and is wearing a black tie. He is also wearing a black jacket.melbourne district nursing society, mdns, rdns, royal district nursing service, rev. dr. charles strong -
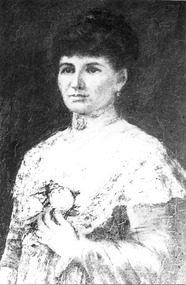 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, Portrait black and white, c.1900
This is a photograph taken from the painting by McCubbin of Lady Janet Clarke, a prominent Melbourne philanthropist who worked for social welfare issues and was a driving force in the early days of the Melbourne District Nursing Society. At the end of 1885 for her work with MDNS she was given a Testimonial Dinner where she was presented with a letter signed by 429 people expressing their thanks for her visits, kindness, sympathy and charity shown toward the sick poor. In 1887, at her home, she held the first function to raise money for the Society. Lady Janet Clarke was a generous and hospitable prominent socialite of Melbourne; a kind and sympathetic philanthropist who worked tirelessly for social welfare issues. The Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) was founded on the 17th of February 1885 and on the 9th of April a Special General Meeting was held to elect the committee for the following twelve months. Lady Clarke was elected a Vice-president; a position she held until being appointed President, when Mrs. Simon resigned on the 7th of June 1887, a role Lady Clarke held until she became ill in 1908; except during her trips overseas, when the role was held by another until her return. Her management and organizational skills enabled MDNS to flourish in its earliest days. She was actively involved taking her turn on the Superintendent sub-committee where she accompanied a Trained nurse when she visited patients; checking that high quality nursing care was maintained, as well as observing the patient's social condition; even giving a personal donation to a special case in need. The patients of the Society were so grateful for her sympathy, kindness and love that when she and her husband, Sir William Clarke, were going overseas at the end of 1885, a Testimonial was given for her at Scots Church District-hall where 200 attended to show their appreciation of her work carried out with MDNS. She was presented with a Bible from them, and their letter signed by 429 working persons expressing their thanks. In a time of great financial need of the Society, Lady Clarke offered the ballroom at her home, 'Cliveden', for a monster Cake, Flower, and Dairy produce Fair which raised a substantial amount saving the Society from closure. She promoted the Society and led it in further fund-raising events, such as the annual Ball, and Fairs where she often manned cake stalls. Near Christmas each year she made a special appeal to the public for 'comfort and good cheer' which could be given to poor families visited by the Society. During the depression of 1890 she had thick soup prepared in the Cliveden kitchens and this was distributed, with bread, from her home, and from a school room, to hundreds of the poor. In 1892 Lady Clarke agreed to represent the Society during her visit to England. During her years of leadership MDNS expanded; Nurses uniforms were introduced; lectures - for example, on hygiene and on the prevention of sickness and the treatment of children, were given by doctors for the patients; further Trained nursing staff were employed; Midwifery was introduced to the poor, the Society extended beyond the city centre and bicycles were introduced for transport; a system for regular annual subscriptions was introduced and sufficient funds were raised for the Society to rent its own premises, with Lady Clarke paying for a subscription to Mullen's bookstore each year for the use of the Nurses in the Nurses Home. As well as her work for MDNS she held roles in many other organizations . She donated a substantial amount of money to build a Hostel for Women University Students attending Trinity College, later named the Janet Clarke Hall. Lady Janet Marion Clarke died at Cliveden, aged 57 years, on the 28th of April 1909; a lady held in high esteem and affection by all she knew.This is a black and white photograph of a painting of Lady Janet Clarke. She is looking forward and has a serious visage; she is wearing her long dark hair drawn up and back and in her left ear a small dropped ear ring can be seen. She is wearing a light coloured, long sleeved, floral frock with a material short cape section seen over the top of her left sleeve. Her left arm is crooked with her hand resting just under a flower brooch fastened in the centre of her frock. She has a choker around her neck with a brooch in the centre..Janet Lady Clarke, president 1889-1908.From the painting by McCubbin.melbourne district nursing society, mdns, rdns, royal district nursing service, lady janet clarke -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Digital image, c.1930
The Melbourne District Nursing Society After-Care Home was built in 1926 to give short term care to MDNS patients who were too ill to remain in their home, but not ill enough to go to hospital. Melbourne hospitals also sent patients there who required further care after discharge from hospital. After convalescence they returned to their homes. Many children were nursed there, particularly during the Polio epidemic.The Society were pioneers in recognizing the need for premises where patients too ill to be in their own home, but not ill enough to go to hospital, was needed, and the Society built, then opened, the After-Care Home in 1926, (from 1934 called After-Care Hospital), for these patients, and patients from Hospitals. Many children were nursed there, some long term, during the Polio epidemic and the Society employed two School Teachers. The Society now ran two divisions, the After-Care with its own Trained nurses and the District division. The Society were the first in Melbourne, in early 1928, to recognize some patients leaving the After-Care, and many at home, needed further social care and they set up ‘Almoners’ from their Committee to visit these patients and be intermediaries in getting them social assistance. It was late the following year before the first training of Almoners took place in Melbourne. In 1930 the Society employed a full time kindergarten teacher to visit poor children in their homes. That year the Society were pioneers in opening an Ante-Natal Clinic at the After-Care, setting a high standard with equipment, keeping records and providing leaflets with instructions in how to keep healthy during pregnancy, what complications to look for, and what to do when labour commenced. In 1934 the Society were pioneers again when they opened the first Women’s Welfare Clinic in Melbourne giving advice on birth-control, at first attended by their own patients, but then accepting patients from public hospitals until their own clinics were opened. A trained Almoner was employed, but left after twelve months due to the amount of work required. Trained Almoners were in short supply so a Social Service Officer was employed at the After-Care who successfully gained better housing from the Housing Commission for families living under unsuitable conditions. In the 1950s the Hospital and Charities Commission decided to take over the After-Care Hospital, so the Melbourne District Nursing Society and After-Care Hospital separated and the Melbourne District Nursing Service was formed, setting up Headquarters at 452 St. Kilda Road. In 1966 Royal patronage was given and the name changed to Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS).Digital image of the rear of the extended Melbourne District Nursing Society After-Care Home 45 Victoria Parade, Collingwood. It shows a three story brick building with a tiled hip roof and open verandas running along each story with windows seen behind. A zigzag stair case runs down the left hand side of the building and on the right hand side of the image you can see a section set back with one window on each floor. Behind this section, part of another multi story building is seen. A wooden paling fence is seen in the foreground of the photograph. On the far right, part of another brick building with hip roof can be seen melbourne district nursing society, mdns, melbourne district nursing society and after-care home, rdns, royal district nursing service -
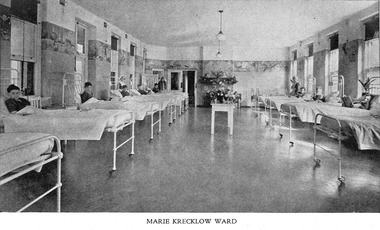 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Digital image, c.1934
In 1934 the Trustees of the Marie Krecklow Estate donated 500 pounds to furnish and equip an empty Ward in the Melbourne District Nursing Society After-Care Hospital in the memory of Mrs. Marie Krecklow. This image shows the furnishings in the Ward of the Hospital at 45 Victoria Parade, Collingwood. The boys in this image are receiving nursing care before returning home following their recuperation. Many children were nursed at the hospital, some long term during the Polio epidemic. The Society were pioneers in recognizing the need for premises where patients too ill to be in their own home, but not ill enough to go to hospital, was needed, and the Society built, then opened, the Melbourne District Nursing Society After-Care Home in 1926, (from 1934 called After-Care Hospital), for these patients, and patients from Melbourne Hospitals who required recuperation before returning home. Many children were nursed there, some long term during the Polio epidemic and the Society employed two School Teachers. The Society now ran two divisions, the After-Care with its own Trained nurses and the District division. The Society were the first in Melbourne, in early 1928, to recognize some patients leaving the After-Care, and many at home, needed further social care and they set up ‘Almoners’ from their committee to visit these patients and be intermediaries in getting them social assistance. It was late the following year before the first training of Almoners took place in Melbourne. In 1930 the Society employed a full time kindergarten teacher to visit poor children in their homes. That year the Society were pioneers in opening an Ante-Natal Clinic at the After-Care, setting a high standard with equipment, keeping records and providing leaflets with instructions in how to keep healthy during pregnancy, what complications to look for and what to do when labour commenced. In 1934 the Society were pioneers again when they opened the first Women’s Welfare Clinic in Melbourne giving advice on birth-control, at first attended by their own patients, but then accepting patients from public hospitals until their own clinics were opened.A trained Almoner was employed at the hospital but left after twelve months due to the volume of work. Unable to employ another trained Almoner due to a shortage of them, a Social Service Officer was employed at the After-Care who successfully gained better housing from the Housing Commission for families living under unsuitable conditions. In the 1950s the Hospital and Charities Commission decided to take over the After-Care Hospital, so the Melbourne District Nursing Society and After-Care Hospital separated and the Melbourne District Nursing Service was formed, setting up Headquarters at 452 St. Kilda Road. In 1966, following Royal patronage the name was changed to Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS).Digital mage showing the 'Marie Krecklow Ward' in the Melbourne District Nursing Society After-Care Hospital. The image shows five iron hospital beds along the left hand side and five iron hospital beds along the right hand side of the ward. Eight young boys, most with short dark hair and one with short blonde hair, are leaning against pillows sitting up in the beds. Some pillows are propped against an iron support which slopes from the headrest. Three sets of windows can be seen on either side of the ward which is painted grey and a wide floral border to the picture rails, then white paint above the picture rail which continues over the ceiling. A white table with vases of flowers is in the centre rear of the image. A Sister, wearing a white uniform and veil and a dark cape stands at the rear left hand side of the image, and two nurses wearing white aprons over dark uniforms and white caps stand half way down the ward, one on either side. mdns, melbourne district nursing society, after- care hospital, after-care home, rdns, royal district nursing service, mrs marie krecklow -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Digital image, c.1930
This image shows two of the 'Melbourne District Nursing Society After Care Home' Sisters who worked in the After Care section of the Society during the 1930s. The image was taken on the balcony of the After Care Home at 39 Victoria Parade, Collingwood. It depicts the style of uniforms worn by trained nurses (Sisters) in that era. The Society were pioneers in recognizing the need for premises where patients too ill to be in their own home, but not ill enough to go to hospital, was needed, and the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) built, then opened, the After-Care Home in 1926, (from 1934 called After-Care Hospital), for these patients, and patients from Melbourne Hospitals who required recuperation before returning to their home. Many children were nursed there, some long term during the Polio epidemic, and the Society employed two School Teachers. The Society now ran two divisions, the After-Care with its own nursing staff and the District division. The Society were the first in Melbourne, in early 1928, to recognize some patients leaving the After-Care, and many at home, needed further social care and they set up ‘Almoners’ from their committee to visit these patients and be intermediaries in getting them social assistance. It was late the following year before the first training of Almoners took place in Melbourne. In 1930 the Society employed a full time kindergarten teacher to visit poor children in their homes. That year the Society were pioneers in opening an Ante-Natal Clinic at the After-Care, setting a high standard with equipment, keeping records and providing leaflets with instructions in how to keep healthy during pregnancy, what complications to look for and what to do when labour commenced. In 1934 the Society were pioneers again when they opened the first Women’s Welfare Clinic in Melbourne giving advice on birth-control, at first attended by their own patients, but then accepting patients from public hospitals until their own clinics were opened. A trained Almoner was employed in 1934 but only stayed twelve months due to the amount of work required. Due to shortage of trained Almoners, a Social Service Officer was employed at the After-Care who successfully gained better housing from the Housing Commission for families living under unsuitable conditions. In the 1950s the Hospital and Charities Commission decided to take over the After-Care Hospital, so the Melbourne District Nursing Society and After-Care Hospital separated and the Melbourne District Nursing Service was formed, setting up Headquarters at 452 St. Kilda Road. With Royal patronage the name changed in 1966 to Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS).Digital image of two Sisters from the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) After-Care Home standing on the balcony of their building. The Sister on the left hand side is wearing a dark cape over her white uniform; she wears a white veil over her dark hair. The Sister on the right hand side is wearing a long white apron over her grey uniform which has white cuffs on the sleeves. She is wearing a white veil over her dark hair. They are leaning on the scrolled metal rail of the balcony which runs along the grey building; part of which can be seen behind them.mdns, melbourne district nursing society, after- care hospital, after-care home, rdns, royal district nursing service, nurses uniforms -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, c.1980
... . The Midwife worked in conjunction with the Doctors at the Women’s ...This photograph is taken in the home of the Mother and babe and shows a RDNS Sister who is visiting to give the mother and babe Post-natal care. Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) had a Domiciliary Infant and Maternal Care (DIMC) service which gave Post-natal care to new born mothers and babes in their homes following their early discharge from hospital, or if required for other reasons. In August 1893 Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS), commenced a Midwifery Service with Nurse Fowler, who was trained in General nursing and Midwifery nursing, being the first Midwife employed. Mothers were assessed for suitability of a home birth or if they required delivery at the Women’s Hospital. The Midwife worked in conjunction with the Doctors at the Women’s Hospital and if a complication arose before or after birth the patient was transferred to their care. Following birth, the Midwife gave Post-Natal care to both the mother and babe commencing with visits twice a day. In 1898 the service ceased due to lack of funds but recommenced in 1906, and in the August 1925 Annual Report the number of MDNS home births was recorded at 478. MDNS built the After-Care Home and a pioneering Anti-Natal Clinic was opened in 1930. The last Ante-Natal clinic was held there in December 1951 and the MDNS Midwifery service ceased in February 1952. In 1964 MDNS commenced a Post-Natal service with General and Midwifery trained MDNS Sisters working from a room on the ground floor at the Footscray Hospital Nurses quarters, and visiting early discharged Footscray Hospital maternity cases at home. Later, as Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), this service was extended and renamed as Domiciliary Infant and Maternal Care, (DIMC) service operating from most Centres and visiting early discharged, often 24 hours after birth, maternity cases from hospitals to give Post-natal care to the mother and babe. Many of the RDNS Sisters who worked in DIMC also had their Infant Welfare Certificate, though Midwifery trained nurses also visited. Black and white photograph showing, to the left, a Royal District Nursing (RDNS) Domiciliary Postnatal Sister, with long hair drawn up, and wearing a white gown. She is attending to a new born baby in her wicker bassinet at the baby's home. The Sister is smiling and has her left hand by the shoulder of the wrapped babe, and her right hand is resting lower on the baby. The baby's mother, who has curly short dark hair, is dressed in a floral blouse and dark cardigan. She is standing to the right of the Sister and behind the bassinet, and is looking down at her babe and smiling. Her left hand is resting on the bassinet. The baby has dark hair and has her hand partly covering her mouth. Part of a picture is seen on the wall behind the mother.rdns, royal district nursing service, rdns domiciliary post natal service, rdns domiciary infant and maternal care, rdns dimc -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, c.1980
... at the Women’s Hospital. The Midwife worked in conjunction ...This photograph depicts a Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) Sister (Sr.) visiting Mrs. Hodginson and babe in their home. Sr. Wan is weighing baby Tamara as part of the Post-Natal care she is giving. A nurse who is doing her Hospital training is visiting with the Sister and observing. RDNS had a Domiciliary Infant and Maternal Care, (DIMC) service operating from most Centres which visited early discharged, often 24 hours after birth, maternity cases from hospitals to give Post-natal care to the mother and babe. Sr. Wan is wearing her RDNS summer uniform of a short sleeve white blouse under a royal blue V neck tunic style frock and a dark blue cardigan. In August 1893 Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS), commenced a Midwifery Service with Nurse Fowler, who was trained in a hospital in General nursing and Midwifery nursing, being the first Midwife employed. Mothers were assessed for suitability of a home birth or if they required delivery at the Women’s Hospital. The Midwife worked in conjunction with the Doctors at the Women’s Hospital and if a complication arose before or after birth the patient was transferred to their care. Following birth, the Midwife gave Post-Natal care to both the mother and babe commencing with visits twice a day. In 1898 the service ceased due to lack of funds but recommenced in 1906, and in the August 1925 Annual Report the number of MDNS home births was recorded at 478. MDNS built the After-Care Home and a pioneering Anti-Natal Clinic was opened in 1930. The last Ante-Natal clinic was held there in December 1951 and the MDNS Midwifery service ceased in February 1952. In 1964 MDNS commenced a Post-Natal service with General and Midwifery trained MDNS Sisters working from a room on the ground floor at the Footscray Hospital Nurses quarters, and visiting early discharged Footscray Hospital maternity cases at home. Later, as Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), this service was extended and renamed as Domiciliary Infant and Maternal Care, (DIMC) service operating from most Centres and visiting early discharged, often 24 hours after birth, maternity cases from hospitals to give Post-natal care to the mother and babe. Many of the RDNS Sisters who worked in DIMC also had their Infant Welfare Certificate, though Midwifery trained nurses also visited. On the right of the black and white photograph is Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) DIMC Sister J. Wan, who has short dark curly hair and is wearing a white gown over her uniform, with the white collar and sleeves of her dark cardigan seen. She is laughing as she holds the top ring of hand held baby scales in her right hand; the bottom of the scale has a metal hook which has a sling attached to it with four cotton 'ropes'. Baby Tamara is supported in the sling which is just resting on a sheep skin and bunny rug covered metal framed change table. Sr. Wan has her left hand on the sling. To the left of the photograph is Tamara's smiling mother, Mrs. Lynda Hodginson, and in the centre of the photograph is observer Nurse Sheehan. Mrs. Hodginson is wearing a striped dress with a V neck, and has dark shoulder length hair. Nurse Sheehan has short dark hair and is wearing a white uniform and dark cardigan. A nursing watch is attached to the right hand side of her uniform. Part of a landscape picture can be seen on the wall behind her. A small white fluffy rabbit sits on the left hand side of the change table. Baby Tamara has sparse dark hair and is sucking on a dummy.Photographer's stampmdns, melbourne district nursing society, melbourne district nursing service, royal district nursing service, rdns, mdns midwifery, rdns domiciliary postnatal service, dimc, tamara hodginson, nurse sheehan, sister j. wan, mrs lynda hodginson -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, c. 1967
... , or if they required delivery at the Women’s Hospital. The Midwife worked ...This photograph depicts Post-Natal care being given by a Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), Sister who is working in the RDNS Domiciliary Infant and Maternal Care (DIMC) section of the Service. The photograph is taken in the home of the mother and baby and the Sister is in the process of putting the baby onto the Baby scales to ascertain the babe's weight. Sisters employed in the DIMC section of RDNS gave Post-natal care to both the mother and her newly born babe when they were discharged early from hospital. This photograph was taken in the year following Melbourne District Nursing Service (MDNS) being granted Royal patronage in 1966 and becoming Royal District Nursing Service. The Sister is wearing the the same grey uniform frock used by MDNS but the badge on her peaked cap has changed from a red Maltese cross to a metal round silver badge with a royal blue circle around the edge with the words 'Royal District Nursing Service' in white capital letters running inside the blue circle.The centre of the badge is divided into three sections; a silver rising sun top and bottom, and a thick royal blue horizontal central strip with 'RDNS' written in large white capital letters. This uniform continued to be worn until 1971 when it changed colour and style. In August 1893 Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS), commenced a Midwifery Service with Nurse Fowler, who trained in a Hospital and was qualified in General nursing and Midwifery nursing, being the first Midwife employed. Mothers were assessed for suitability of a home birth, or if they required delivery at the Women’s Hospital. The Midwife worked in conjunction with the Doctors at the Women’s Hospital and if a complication arose the patient was transferred to their care. Following birth they gave Post-Natal care to both the mother and babe. In 1898 the service ceased due to lack of funds but recommenced in 1906, and in the August 1925 Annual Report the number of MDNS home births was recorded at 478. MDNS built the After-Care Home and an Anti-Natal Clinic was opened in 1930. The last Ante-Natal clinic was held there in December 1951 and the MDNS Midwifery service ceased in February 1952. In 1964 MDNS commenced a Post-Natal service with General and Midwifery trained MDNS Sisters working from a room at Footscray Hospital, and visiting early discharged Footscray Hospital maternity cases at home. Now as Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), this service was extended to a Domiciliary Infant and Maternal Care, (DIMC) service operating from most Centres and visiting early discharged, often 24 hours after birth, maternity cases from hospitals to give post-natal care to the mother and babe. Many Sisters working in this area had a Certificate in Infant Welfare as well as their General and Midwifery Certificates.In the right rear of this black and white photograph is a Royal District Nursing Service, (RDNS), Sister who is wearing a white gown over her uniform, and wearing her grey peaked hat with the RDNS badge visible, looking down at a baby she is about to weigh. The baby has sparse dark hair, is wearing a white singlet and is crying. The Baby scales, which are sitting on a table in front of the Sister, are white with a rectangular base and curved sided tray on the top. The Sister is standing behind the scales, and is supporting the babe's body with her right hand and holding baby's legs with her left hand as she lowers babe fully onto the scales. On the left of the photograph, the mother, who has long dark hair with a hair scarf holding it back, and is wearing a striped frock, is siting on a chair with her arms crossed at her waist, and is smiling at her babe as she observes proceedings.. Photographers Stampmdns, melbourne district nursing society, melbourne district nursing service, rdns, royal district nursing service, rdns domiciliary postnatal service, dimc -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, 09 05 1967
... , or if they required delivery at the Women’s Hospital. The Midwife worked ...In 1964 Melbourne District Nursing Service (MDNS) commenced a Domiciliary Postnatal Service, later called Domiciliary Infant and Maternal.Care (DIMC), when Royal patronage was granted in 1966 (RDNS). The Sisters gave Post-natal care to the mother and babes and visited for support and advice as long as needed. The central RDNS badges on the Sisters hats is made of metal and has 'Royal District Nursing Service' written in the outside royal blue circle. The inner area is divided in three parts, the top and bottom sections are a silver rising sun and the central royal blue horizontal band has the letters 'RDNS' written white capital letters.In August 1893 Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS), commenced a Midwifery Service with Nurse Fowler, who was Hospital trained in General nursing and Midwifery nursing, being the first Midwife employed. Mothers were assessed for suitability of a home birth, or if they required delivery at the Women’s Hospital. The Midwife worked in conjunction with the Doctors at the Women’s Hospital and if a complication arose the patient was transferred to their care. Following birth they gave Post-Natal care to both the mother and babe. In 1898 the service ceased due to lack of funds but recommenced in 1906, and in the August 1925 Annual Report the number of MDNS home births was recorded at 478. MDNS built the After-Care Home and an Anti-Natal Clinic was opened in 1930. The last Ante-Natal clinic was held there in December 1951 and the MDNS Midwifery service ceased in February 1952. In 1964 MDNS commenced a Post-Natal service with General and Midwifery trained MDNS Sisters working from a room at Footscray Hospital, and visiting early discharged Footscray Hospital maternity cases at home. Later, as Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), this service was extended to a Domiciliary Infant and Maternal Care (DIMC), service operating from most Centres and visiting early discharged, often 24 hours after birth, maternity cases from hospitals to give post-natal care to the mother and babe. Many of the RDNS Sisters who did DIMC had their Triple Certificate (Infant Welfare), though Midwifery trained nurses also visited. Black and white photograph showing two Royal District Nursing Service, (RDNS), Postnatal Service Sisters visiting a mother and her triplets in their home. Both Sisters and the mother are smiling and sitting on a dark coloured couch with each holding one of the babes who are wrapped in light coloured bunny rugs. The Sister on the left is wearing a white gown, with the grey peaks of her uniform showing; her nursing badge is attached to the right hand peak of her uniform. She is wearing her grey peaked hat, with central attached RDNS badge, over her short dark curled hair. To her right is the mother, who has short straight dark hair, and is wearing a white blouse and dark tartan skirt. On the far right is Sister Barbara Weisart, wearing a white gown; with the grey peaks of her uniform showing, and wearing her grey peaked hat with central RDNS badge over her short dark straight hair. A set of white baby scales are seen to her rightPhotographers Stamp. Quote No. GE 13mdns, melbourne district nursing society, melbourne district nursing service, royal district nursing service, rdns, rdns domiciliary postnatal service, dimc, sister barbara weisart -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, 30 08 1967
... migrant women and families. This work was extended when she ...The rock and attached plaque to Caroline Chisholm stand in front of the Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) Essendon Centre. It was unveiled at the opening of the Centre on the 30 August 1967.The plaque has a deep silver colour background, light silver colour writing with gold coloured edging.Caroline Chisholm visited the goldfields of Victoria in 1854 and was horrified by the conditions en-route. The Memorial plaque to Caroline Chisholm, in front of the RDNS Essendon Centre which is situated on Crown Land, is in recognition for her work in establishing, with Government assistance, shelter sheds about a days walk apart, to enable the prospectors and their families heading for the goldfields shelter on their way. Caroline Chisholm, a Philanthropist, began her work in Madras in 1834 founding a Female School of Industry for the daughters of European soldiers. They were taught to read, write, cook, keep house and were given instructions in nursing. After coming to Sydney in 1838, she set up accommodation for poor young unemployed migrant women and families. This work was extended when she arranged employment for assisted immigrant women and families into the countryside, many times travelling with groups of young women to check their employment conditions. In seven years she placed 11,000 people in homes and employment. On her return to England she fought for, and won, free passage to Australia for wives and children of former convicts, and for children left behind in England by circumstances, when the family migrated. She established the Family Colonisation Loan Society in 1849, which set up a saving scheme for emigrants, and later loaned them half of their passage to Australia. The Society's Agents found them employment on arrival, and the loan was paid back within two years by a humane payment scheme. At first they used emigrant ships, but then the Society provided ships with much improved conditions, and this led to the upgrading of the passenger Act.. The Chisholm's lived in Kyneton for several years, returning to Sydney for health reasons, before going back to England where Caroline died, aged 68 years, on the 25th of March 1877.Black and white photograph of the Memorial plaque to Caroline Chisholm. The rectangular plaque sits on a rough light grey rock, and has light colour writing and edging, on a dark grey background. The inscription on the plaque is in five lines and reads: "On this site in the year 1855"/, "Mrs Caroline Chisholm"/, "Established a Shelter for"/, "Diggers and their families"/ "Travelling to the Goldfields"/.Photographers stamp. Quote No. GJ 56rdns, royal district nursing service, rdns centre, caroline chisholm, memorial plaque -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, 30 08 1967
... migrant women and families. This work was extended when she ...Mrs. R. Gordon is the President of the Victorian branch of the National Council of Women. The Memorial plaque to Caroline Chisholm stands on a rock in front of the Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) Essendon Centre, and was unveiled at the time of the opening of the Centre on the 30th of August 1967.Caroline Chisholm visited the goldfields of Victoria in 1854 and was horrified by the conditions en-route. The Memorial plaque to Caroline Chisholm, in front of the RDNS Essendon Centre, is in recognition for her work in establishing, with Government assistance, shelter sheds about a days walk apart, to enable the prospectors and their families shelter whilst heading to the goldfields. Caroline Chisholm, a Philanthropist, began her work in Madras in 1834, founding a Female School of Industry for the daughters of European soldiers. They were taught to read, write, cook, keep house and were given instructions in nursing. After coming to Sydney in 1838, she set up accommodation for poor young unemployed migrant women and families. This work was extended when she arranged employment in the countryside for assisted immigrant women and families, many times travelling with groups of young women to check their employment conditions. In seven years she placed 11,000 people in homes and employment. On her return to England she fought for, and won, free passage to Australia for wives and children of former convicts, and for children left behind in England by circumstances, when the family migrated. She established the Family Colonisation Loan Society in 1849, which set up a saving scheme for emigrants, and later loaned them half of their passage to Australia. The Society's Agents found them employment on arrival, and the loan was paid back within two years by a humane payment scheme. At first they used emigrant ships for passage, but then the Society provided ships with much improved conditions, and this led to the upgrading of the passenger Act.. The Chisholm's lived in Kyneton for several years, returning to Sydney for health reasons, before going back to England where Caroline died, aged 68 years, on the 25th of March 1877.Black and white photograph of Mrs. R, Gordon, wearing a dark coloured coat, black shoes, and a beret style white and black hat, pointing with her left hand to the unveiled Memorial plaque to Caroline Chisholm. The dark oblong plaque is adhered to a large rock.The British Flag can be seen in the foreground. Part of a building can be seen in the background; short glass windows can be seen above the brickwork on the left, with dark fascia above, and part of a large glass window to the right.Photographers stamp. Quote No. GJ 58rdns, royal district nursing service, rdns centre, essendon centre, memorial plaque, mrs r. gordon, caroline chisholm -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, 30 08 1967
... migrant women and families. This work was extended when she ...Mrs. R. Gordon is the President of the Victorian branch of the National Council of Women and is unveiling the Memorial plaque to Caroline Chisholm. The plaque stands on a rock in front of the Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) Essendon Centre, and was unveiled on the same day the Centre opened on the 30th of August 1967. Mrs. E.G. Wilson is President of the Royal District Nursing Service. Miss Mary Evans is the Director of Nursing of the Royal District Nursing Service and is wearing her dark grey Director's uniform.Caroline Chisholm visited the goldfields of Victoria in 1854 and was horrified by the conditions en-route. The Memorial plaque to Caroline Chisholm, in front of the RDNS Essendon Centre, is in recognition for her work in establishing, with Government assistance, shelter sheds about a days walk apart, to enable the prospectors and their families shelter whilst heading for the goldfields. Caroline Chisholm, a Philanthropist, began her work in Madras in 1834 founding a Female School of Industry for the daughters of European soldiers. They were taught to read, write, cook, keep house and were given instructions in nursing. After coming to Sydney in 1838, she set up accommodation for poor young unemployed migrant women and families. This work was extended when she arranged employment in the countryside for assisted immigrant women and families, many times travelling with groups of young women to check their employment conditions. In seven years she placed 11,000 people in homes and employment. On her return to England she fought for, and won, free passage to Australia for wives and children of former convicts, and for children left behind in England by circumstances, when the family migrated. She established the Family Colonisation Loan Society in 1849, which set up a saving scheme for emigrants, and later loaned them half of their passage to Australia. The Society's Agents found them employment on arrival, and the loan was paid back within two years by a humane payment scheme. At first they used emigrant ships for passage, but then the Society provided ships with much improved conditions, and this led to the upgrading of the passenger Act.. The Chisholm's lived in Kyneton for several years, returning to Sydney for health reasons, before going back to England where Caroline died, aged 68 years, on the 25th of March 1877.Black and white photograph showing Mrs. R. Gordon, wearing a black coat and black and white beret style hat, with her left hand on a rock and her right hand on the British Flag, whilst unveiling the Memorial plaque to Caroline Chisholm. Mrs. R. Gordon stands between Mrs. E.G. Wilson, who is to her left, and is wearing glasses and a black coat, hat and shoes. Miss Mary Evans, who is wearing her RDNS uniform of a dark grey skirt and jacket and brimmed hat, and with a handbag looped over her left arm, is to the right.. Part of a building is seen in the background; short glass windows can be seen above the brickwork to the left and a large glass window to the right.Photographers stamp and 'Quote No. GJ 60'rdns, royal district nursing service, essendon centre, caroline chisholm, memorial plaque, mrs r. gordon, miss mary evans, mrs e.g. (hazel janet) wilson -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, Barry Sutton, 23.02.1978
... at the Women’s Hospital. The Midwife worked in conjunction ...The RDNS Sister is giving Post Natal care to the Mother and babe. She is wearing her RDNS summer uniform which is a white short sleeve blouse under a royal blue V necked tunic dress with the RDNS insignia emblazoned on the upper left.In August 1893 Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS), commenced a Midwifery Service with Nurse Fowler, who was trained in General nursing and Midwifery nursing, being the first Midwife employed. Mothers were assessed for suitability of a home birth or if they required delivery at the Women’s Hospital. The Midwife worked in conjunction with the Doctors at the Women’s Hospital and if a complication arose the patient was transferred to their care. Following birth they gave Post-Natal care to both the mother and babe. In 1898 the service ceased due to lack of funds but recommenced in 1906, and in the August 1925 Annual Report the number of MDNS home births was recorded at 478. MDNS built the After-Care Home and an Anti-Natal Clinic was opened in 1930. The last Ante-Natal clinic was held there in December 1951 and the MDNS Midwifery service ceased in February 1952. In 1964 MDNS commenced a Post-Natal Service with general and midwifery trained MDNS nurses working from a room at Footscray Hospital, and visiting early discharged Footscray Hospital maternity cases at home. Now as Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), this service was extended to a Domiciliary Infant and Maternal Care, (DIMC) service operating from most Centres and visiting early discharged, often 24 hours after birth, maternity cases from hospitals to give post-natal care to the mother and babe.Black and white photograph of a Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), Sister visiting a family in their home. The family are sitting on a dark coloured couch. From left to right:- The father, who has short dark hair and is wearing a light coloured patterned shirt and dark pants, is looking at his young blond haired daughter who is sitting on his right knee. She is wearing a light coloured top and darker coloured bib and brace pants. The mother, who has long dark hair and wears glasses,.is next to him and is smiling and looking towards the RDNS Sister. She is wearing a long sleeve buttoned grey top and darker coloured slacks, and is holding her babe in her lap with both hands supporting the baby's head. The babe has sparse dark hair and is wrapped in a white bunny rug. Next is a young girl, who has short dark hair and is wearing a light coloured top, darker coloured slacks and has her hands on the top of her left striped sock. Seated on the far right is the RDNS Sister, who has short straight dark hair, and has her face turned towards the child and mother. She is wearing her RDNS uniform of a short sleeve white blouse under a dark V neck tunic style dress which has the RDNS insignia on its upper left. The Sister has a pen attached to the V neck of the tunic and is holding a note book in her hands. She has a watch with a dark band attached to her left wrist. In the background part of a wooden and glass door can be seen and a patterned wallpapered adorns the wall behind the couch.Photographer stamp. Quote No EA 28melbourne district nursing society, mdns, royal district nursing service, rdns, dimc, mdns midwifery, rdns domiciliary infant and maternal care -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, Barry Sutton, 23.02.1978
... delivery at the Women’s Hospital. The Midwife worked in conjunction ...General and Midwifery trained RDNS Sister Kaye Pilmore is supervising a Mother feeding her new born infant in their home. Sister Pilmore is wearing her RDNS summer uniform, which was a royal blue V neck tunic style dress, with the RDNS badge emblazoned on the upper left, worn over a short sleeve white blouse. In August 1893 Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS), commenced a Midwifery Service with Nurse Fowler, who was trained in General nursing and Midwifery nursing, being the first Midwife employed. Mothers were assessed for suitability of a home birth or if they required delivery at the Women’s Hospital. The Midwife worked in conjunction with the Doctors at the Women’s Hospital and if a complication arose before or after birth the patient was transferred to their care. Following birth, the Midwife gave Post-Natal care to both the mother and babe commencing with visits twice a days. In 1898 the service ceased due to lack of funds but recommenced in 1906, and in the August 1925 Annual Report the number of MDNS home births was recorded at 478. MDNS built the After-Care Home and an Anti-Natal Clinic was opened in 1930. The last Ante-Natal clinic was held there in December 1951 and the MDNS Midwifery service ceased in February 1952. In 1964 MDNS commenced a Post-Natal service with general and midwifery trained MDNS Sisters working from a room on the ground floor in the Footscray Hospital Nurses quarters, and visiting early discharged Footscray Hospital maternity cases at home. Later, as Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), this service was extended and renamed as the Domiciliary Infant and Maternal Care, (DIMC) service operating from most Centres and visiting early discharged, often 24 hours after birth, maternity cases from hospitals to give Post-natal care to the mother and babe. Many of the RDNS Sisters who worked in the DIMC section also had their Triple Certificate in Infant Welfare, though double certificate Midwifery trained nurses also made DIMC visits. Black and white photograph showing a Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), Sister sitting to the left of a mother who is holding her babe whilst she feeds her with a bottle. The Sister has short straight dark hair and is wearing her RDNS uniform of a dark V neck tunic style dress, with the RDNS badge emblazoned on the upper left, over a short sleeve white blouse. She is turned towards the babe and mother and is holding a sheet of white paper in her right hand and her left hand is supporting the end of the glass feeding bottle. The mother, who has long dark hair and is wearing glasses, and a grey long sleeve top and darker coloured slacks, has her baby across her knees with her left arm bent at the elbow and her arm and hand supporting her baby's head and neck. She is holding the feeding bottle with her right hand and the teat of the bottle is in the baby's mouth. The babe has sparse dark hair and is wrapped in a white bunny rug. They are sitting on a dark coloured couch with check cushions on the seat. A small low table is to the right of the couch against the wall. Patterned wallpaper can be seen on the wall behind the couch and table.Photographer stamp.Quote No. EA 35melbourne district nursing society, mdns, royal district nursing service, rdns, mdns midwifery, dimc, mdns post-natal care, rdns dimc, sister kaye pilmore -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, c.1930
The Matron and Sisters in this photograph worked in the Melbourne District Nursing Society After Care Home, (later called Hospital) full time and administered nursing care to patients who ranged in age from babes to adults. The Society also had a District Nursing division and these Sisters only worked in the community giving nursing care to patients in their homes.The Melbourne District Nursing Society were pioneers in recognizing the need for premises where patients too ill to be in their own home, but not ill enough to go to hospital, was needed, and the Society built, then opened, the After-Care Home in 1926, (from 1934 called After-Care Hospital), for these patients, and patients from Hospitals. Many children were nursed there, some long term during the Polio epidemic and the Society employed two School Teachers. The Society now ran two divisions, the After-Care with its own Sisters and nurses, and the District division. The Society were the first in Melbourne, in early 1928, to recognize some patients leaving the After-Care, and many at home, needed further social care and they set up ‘Almoners’ from their committee to visit these patients and be intermediaries in getting them social assistance. It was late the following year before the first training of Almoners took place in Melbourne. In 1930 the Society employed a full time kindergarten teacher to visit poor children in their homes. That year the Society were pioneers in opening an Ante-Natal Clinic at the After-Care, setting a high standard with equipment, keeping records, and providing leaflets with instructions in how to keep healthy during pregnancy, what complications to look for and what to do when labour commenced. In 1934 the Society were pioneers again when they opened the first Women’s Welfare Clinic in Melbourne giving advice on birth-control, at first attended by their own patients, but then accepting patients from public hospitals until their own clinics were opened. A trained Almoner was employed by the Society in 1934, doing a great deal of work with Midwifery patients, but she resigned after twelve months due to the amount of work. Due to a lack of trained Almoners, the Society employed a Social Service Officer at the After-Care who successfully gained better housing from the Housing Commission for families living under unsuitable conditions.A black and white photograph of Matron and twelve Trained nurses (Sisters) standing at the front entrance of the Melbourne District Nursing Society After Care Home, In the front of the portico is the Matron and four Sisters. Matron is dressed in a white long uniform dress and white veil over her short dark hair, and is wearing white stockings and white shores. To her right are four Sisters. Behind them are five Sisters, one standing between the left pair of round columns of the portico and the others to her right finishing just before the second set of columns. Two Sisters are to the left of the left hand column in front of the brick wall of the building. A short brick wall runs from the column to the building and hides the lower half of these Sisters. All the Sisters are dressed with white long aprons with white belts, which are covering their uniforms, only their dark grey sleeves and white collars can be seen. They are wearing white veils covering most of their short dark hair, grey stockings and black shoes. At the top of the portico can be seen the words 'District Nursing Society'. Part of the two story brick building can be seen behind the group; two long windows are visible on the upper and lower sections. To the right of the building some shrubs and a tree can be seen.nurses, after care hospital, uniforms, after-care home, melbourne district nursing society, mdns, rdns, royal district nursing service -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, Barry Sutton, 02.08.1973
... at the Women’s Hospital. The Midwife worked in conjunction ...This photograph shows an RDNS Sister doing Liaison work at a Hospital. She will pass the information given about the babe to the RDNS Domiciliary Infant and Maternal Care (DIMC) Sister who will be visiting the baby and her family in their home. Sr. Schofield is wearing the RDNS winter uniform of a blue/grey skivvie under a V neck tunic style frock made of herringbone winter material.Liaison had occurred between Doctors and the Trained nurses (Nurses) of the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS), from its inception in 1885. This increased when Midwifery was introduced in August 1893 with close liaising with the Women’s Hospital. As District nursing grew it was recognized that closer liaising between many Public Hospitals would be beneficial, for not only the MDNS, later called Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) Trained nurses (Sisters), but also for the patients and the hospitals. In August 1964 a Liaison Officer commenced at the Alfred Hospital. This soon increased to Liaison Officers working full time at several Public Hospitals. They facilitated the smooth transition from hospital to home for many patients who required ongoing nursing care. Liaison Sisters regularly attended discharge planning meetings, interviewed prospective patients, co-ordinated discharge, and booked the first visit by the visiting RDNS Sister. At the time of a patient’s discharge, the Liaison Sister forwarded information on their diagnosis and instructions regarding the care required at home to the appropriate RDNS Centre, and in turn the attending District Sister wrote a report of progress and any queries to the Hospital Doctor, via the Liaison Sister, at the time the patient was attending outpatients. Any new instructions were then sent back to the District Sister. Liaising also occurred between District Sisters and Doctors when patients were referred by General Practitioners and did not attend a hospital. In August 1893 Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS), commenced a Midwifery Service with Nurse Fowler, who was trained in General nursing and Midwifery nursing, being the first Midwife employed. Mothers were assessed for suitability of a home birth or if they required delivery at the Women’s Hospital. The Midwife worked in conjunction with the Doctors at the Women’s Hospital and if a complication arose before or after birth the patient was transferred to their care. Following birth, the Midwife gave Post-Natal care to both the mother and babe commencing with visits twice a day. In 1898 the service ceased due to lack of funds but recommenced in 1906, and in the August 1925 Annual Report the number of MDNS home births was recorded at 478. MDNS built the After-Care Home and a pioneering Anti-Natal Clinic was opened in 1930. The last Ante-Natal clinic was held there in December 1951 and the MDNS Midwifery service ceased in February 1952. In 1964 MDNS commenced a Post-Natal service with General and Midwifery trained MDNS Sisters working from a room on the ground floor in the Footscray Hospital Nurses quarters, and visiting early discharged Footscray Hospital maternity cases at home. Later, as Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), this service was extended and renamed as Domiciliary Infant and Maternal Care, (DIMC) service operating from most Centres and visiting early discharged, often 24 hours after birth, maternity cases from hospitals to give Post-natal care to the mother and babe. Many of the RDNS Sisters who worked in DIMC also had their triple Infant Welfare Certificate, though double certificate Midwifery trained Sisters also visited. On the left of this black and white photograph is Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) Sister Margaret Schofield, who has her long dark hair drawn back, and is smiling as she looks down at a baby being held in the arms of a Hospital Sister. Sr. Schofield is wearing a light grey skivvie under a V neck dark tunic style frock. She has a pen in the V of her tunic, and has a watch hanging under the RDNS logo on its left hand side. Her left hand is resting on a white table which has baby scales with a wicker basket on it. To the right, is the Hospital Sister, who is side-on and facing Sr. Schofield. She is wearing dark rimmed glasses; has her long dark hair drawn back and is wearing a dark cardigan over her white uniform. She has her right arm under the baby with her hand on babe's right leg; her left hand is holding the baby's feet. The baby has sparse dark hair and is wearing a white patterned jacket. Part of a dark filing cabinet is on the right of the photograph and behind the Sisters is a large window, then grass, small shrubs and part of a corrugated clad building can be seen beyond.Barry Sutton LP 43royal district nursing service, rdns, rdns dimc, rdns uniform, sister margaret schofield -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, Barry Sutton, 17.10.1973
... or if they required delivery at the Women’s Hospital. The Midwife worked ...Sister Snyders is based at RDNS Essendon Centre. She is a trained midwife working in the RDNS Domiciliary Infant and Maternal Care (DIMC), section and is attending a recently born baby in her home to give Post-Natal care. Often mothers and babes came home early from hospital, many after 24 hours of birth, and RDNS Sisters attended for several days to check babies progress, including - colour, feeding regime, weight, take a PKU test and give any advise needed to the mother. They also gave Post-Natal care to the mother. In August 1893 Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS), commenced a Midwifery Service with Nurse Fowler, who was trained in General nursing and Midwifery nursing, being the first Midwife employed. Mothers were assessed for suitability of a home birth or if they required delivery at the Women’s Hospital. The Midwife worked in conjunction with the Doctors at the Women’s Hospital and if a complication arose before or after birth the patient was transferred to their care. Following birth, the Midwife gave Post-Natal care to both the mother and babe commencing with visits twice a day. In 1898 the service ceased due to lack of funds but recommenced in 1906, and in the August 1925 Annual Report the number of MDNS home births was recorded at 478. MDNS built the After-Care Home and a pioneering Anti-Natal Clinic was opened in 1930. The last Ante-Natal clinic was held there in December 1951 and the MDNS Midwifery service ceased in February 1952. MDNS established Melbourne's first Family Planning Clinic in 1934. In 1964 MDNS commenced a Post-Natal service with General and Midwifery trained MDNS Sisters working from a room on the ground floor at the Footscray Hospital Nurses quarters, and visiting early discharged Footscray Hospital maternity cases at home. Later, as Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), this service was extended and renamed as Domiciliary Infant and Maternal Care, (DIMC) service operating from most Centres and visiting early discharged, often 24 hours after birth, maternity cases from hospitals to give Post-natal care to the mother and babe. Many of the RDNS Sisters who carried out DIMC visits also had their Triple i.e. Infant and Child Welfare Certificate, though Midwifery trained nurses also made visits. This black and white photograph shows a close up view of Sister (Sr.) Mary-Ann Snyders from Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), who is standing and cradling a recently born baby in the crook of her left arm; her supporting arm extends along the babe and her right arm is under babe. Sr. Snyders has short dark hair and is wearing a white gown over her uniform. She is smiling down at the babe, who has dark hair and is wearing a check bib over a white nightdress. To the left, voile curtains are seen over a window and in the background, part of an open patterned curtain is seen.Barry Sutton LW 4royal district nursing service, rdns, rdns dimc, sister mary-ann snyders -
 Bacchus Marsh & District Historical Society
Bacchus Marsh & District Historical SocietyBook, Pioneer Women of Bacchus Marsh: An Introduction to the Women of Bacchus Marsh Pioneer Women's Avenue
This book explores the lives of 274 pioneer women of Bacchus Marsh and district. In this work the pioneer period is defined as women who were either born in the Bacchus Marsh area before 1869 or arrived there prior to 1869. The women's stories in the book are derived from the list of women pioneers of the district compiled in 1936 to commemorate the centenary of European settlement in Bacchus Marsh.Importantly this 2015 publication identifies a number of First Nations women known to have lived in the district prior to 1869 and acknowledges the fact that many thousands of women have lived in the district prior to the European colonial era. Citation: Pioneer Women of Bacchus Marsh: An Introduction to the Women of the Bacchus Marsh Pioneer Women's Avenue. [Written and compiled by the Country Women's Association Branch, Bacchus Marsh]. Published by Country Women's Association of Victoria Inc., Bacchus Marsh Branch, 2015.An A4 sized printed book published in paperback edition. 228 pages, with black white photographs and portraits and illustrations. Includes a\subject and name indexes. BMDHS Location: AR/SU4non-fictionThis book explores the lives of 274 pioneer women of Bacchus Marsh and district. In this work the pioneer period is defined as women who were either born in the Bacchus Marsh area before 1869 or arrived there prior to 1869. The women's stories in the book are derived from the list of women pioneers of the district compiled in 1936 to commemorate the centenary of European settlement in Bacchus Marsh.Importantly this 2015 publication identifies a number of First Nations women known to have lived in the district prior to 1869 and acknowledges the fact that many thousands of women have lived in the district prior to the European colonial era. Citation: Pioneer Women of Bacchus Marsh: An Introduction to the Women of the Bacchus Marsh Pioneer Women's Avenue. [Written and compiled by the Country Women's Association Branch, Bacchus Marsh]. Published by Country Women's Association of Victoria Inc., Bacchus Marsh Branch, 2015.bacchus marsh vic. history, pioneers biographies, women pioneers bacchus marsh -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacySign, The 'Fighting Widow' dies
A newspaper article about the death of Jessie Vasey on 22 September 1966. Mrs J M Vasey was the wife of Major-General Vasey. During the second world war she became secretary of the AIF Women's Association, a body which sought to help soldiers' wives. Her work with this body drew her attention to the plight of war widows. After Major-General George Alan Vasey died in an aircraft accident on 5 March 1945 she became a widow herself. At the end of the war Mrs Vasey founded the War Widows Guild. This reproduction on display board may have been for an exhibition of Guild memorabilia at some time. The Victorian War Widows Guild closed in 2021. Some items, including this board, were donated to the Legacy archive for preservation. It was possible for a widow to be members of both Legacy and the War Widows Guild. Both organisations helped war widows in various ways.A record of the work done by Jessie Vasey and the War Widows Guild.Newspaper article 'The Fighting Widow dies' reproduced on a display board for signage of an exhibit.war widows guild, jessie vasey, wwg -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacySign, War Widows Creche Needs Toys
A newspaper article about the War Widows Creche in Collins St Melbourne from 29 July 1947. An article about the creche set up by the War Widows Guild to help its members to work or retrain. The War Widows Guild was established by Mrs J M Vasey. She was the wife of Major-General Vasey, during the second world war she became secretary of the AIF Women's Association, a body which sought to help soldiers' wives. Her work with this body drew her attention to the plight of war widows. After Major-General George Alan Vasey died in an aircraft accident on 5 March 1945 she became a widow herself. At the end of the war Mrs Vasey founded the War Widows Guild. This reproduction on display board may have been for an exhibition of Guild memorabilia at some time. The Victorian War Widows Guild closed in 2021. Some items, including this board, were donated to the Legacy archive for preservation. It was possible for a widow to be members of both Legacy and the War Widows Guild. Both organisations helped war widows in various ways.A record of the work done by Jessie Vasey and the War Widows Guild.Newspaper article 'War Widows Creche needs toys' reproduced on a display board for signage of an exhibit.war widows guild, jessie vasey, wwg -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacySign, Widows of War Protest - City Rally
A newspaper article about a protest by War Widows published 3 July 1947. An article showing more than 1500 people met to demand higher compensation for the loss of their husbands who had died for their country. Mrs J M Vasey received an ovation for her address to the meeting. She was the wife of Major-General Vasey, during the second world war she became secretary of the AIF Women's Association, a body which sought to help soldiers' wives. Her work with this body drew her attention to the plight of war widows. After Major-General George Alan Vasey died in an aircraft accident on 5 March 1945 she became a widow herself. At the end of the war Mrs Vasey founded the War Widows Guild. This reproduction on display board may have been for an exhibition of Guild memorabilia at some time. The Victorian War Widows Guild closed in 2021. Some items, including this board, were donated to the Legacy archive for preservation. It was possible for a widow to be members of both Legacy and the War Widows Guild. Both organisations helped war widows in various ways.A record of the work done by Jessie Vasey and the War Widows Guild.Newspaper article 'Widows of War Protest - City Rally' reproduced on a display board for signage of an exhibit.war widows guild, jessie vasey, wwg -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacySign, Women CAN get along!
A newspaper article about the 10th Anniversary of the War Widows Guild published on 23 November 1955. The War Widows Guild was founded by Mrs Jessie Vasey. She was the wife of Major-General Vasey and during the second world war she became secretary of the AIF Women's Association, a body which sought to help soldiers' wives. Her work with this body drew her attention to the plight of war widows. After Major-General George Alan Vasey died in an aircraft accident on 5 March 1945 she became a widow herself. At the end of the war Mrs Vasey founded the War Widows Guild. This reproduction on display board may have been for an exhibition of Guild memorabilia at some time. The Victorian War Widows Guild closed in 2021. Some items, including this board, were donated to the Legacy archive for preservation. It was possible for a widow to be members of both Legacy and the War Widows Guild. Both organisations helped war widows in various ways.A record of the work done by Jessie Vasey and the War Widows Guild.Newspaper article 'Women can get along' reproduced on a display board for signage of an exhibit.war widows guild, jessie vasey, wwg -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacySign - Photo, Mrs Jessie Vasey
A photograph of Jessie Vasey reproduced on display board. Mrs J M Vasey was the founder and president of the War Widows Guild. During the second world war she became secretary of the AIF Women's Association, a body which sought to help soldiers' wives. Her work with this body drew her attention to the plight of war widows. After her husband Major-General George Alan Vasey died in an aircraft accident on 5 March 1945 she became a widow herself. At the end of the war Mrs Vasey founded the War Widows Guild. This reproduction on display board may have been for an exhibition of Guild memorabilia at some time. The Victorian War Widows Guild closed in 2021. Some items, including this board, were donated to the Legacy archive for preservation. It was possible for a widow to be members of both Legacy and the War Widows Guild. Both organisations helped war widows in various ways.A record of the work done by Jessie Vasey and the War Widows Guild.Photograph of Mrs Vasey reproduced on a display board for signage of an exhibit.war widows guild, jessie vasey, wwg -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyDomestic object - Bookmark, Mrs Jessie Vasey
A bookmark made to honour the founder of the War Widows Guild, Mrs Jessie Vasey. It has a photo of her and the Guild Motto on the front and a brief summary of the guild on the reverse. The Guild Motto: "We all belong to each other. We all need each other. It is serving each other and in sacrificing for our common good that we are finding our true life", which was taken from the Christmas speech of King George VI in 1941. Mrs J M Vasey was the founder and president of the War Widows Guild. During the second world war she became secretary of the AIF Women's Association, a body which sought to help soldiers' wives. Her work with this body drew her attention to the plight of war widows. After her husband Major-General George Alan Vasey died in an aircraft accident on 5 March 1945 she became a widow herself. At the end of the war Mrs Vasey founded the War Widows Guild, established on 22 November 1945. The Victorian War Widows Guild closed in 2021. Some items, including this bookmark, were donated to the Legacy archive for preservation. It was possible for a widow to be members of both Legacy and the War Widows Guild. Both organisations helped war widows in various ways.A record of the work done by Jessie Vasey and the War Widows Guild.Bookmark honouring the founder of the War Widows Guild.war widows guild, jessie vasey, wwg -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyNewspaper - Article, Widows "Unaware" of Fund
A newspaper article the work of the War Widows Guild, there is a mention of Legacy sending widows to the Guild. The War Widows Guild was founded by Mrs J M Vasey, the wife of Major-General Vasey. During the second world war she became secretary of the AIF Women's Association, a body which sought to help soldiers' wives. Her work with this body drew her attention to the plight of war widows. After Major-General George Alan Vasey died in an aircraft accident on 5 March 1945 she became a widow herself. At the end of the war Mrs Vasey founded the War Widows Guild. The Victorian War Widows Guild closed in 2021. Some items, including this board, were donated to the Legacy archive for preservation. It was possible for a widow to be members of both Legacy and the War Widows Guild. Both organisations helped war widows in various ways.A record of the work done by Jessie Vasey and the War Widows Guild.Newspaper article 'Widows Unaware of Fund'.war widows guild, jessie vasey, wwg -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyNewspaper - Article, Pilgrimage to the Shrine 2004, 2004
A newspaper article saved by the War Widows Guild, of a pilgrimage to the Shrine of Remembrance in 2004. It is an annual Legacy event. The War Widows Guild was founded by Mrs J M Vasey, the wife of Major-General Vasey. During the second world war she became secretary of the AIF Women's Association, a body which sought to help soldiers' wives. Her work with this body drew her attention to the plight of war widows. After Major-General George Alan Vasey died in an aircraft accident on 5 March 1945 she became a widow herself. At the end of the war Mrs Vasey founded the War Widows Guild. The Victorian War Widows Guild closed in 2021. Some items, including this article, were donated to the Legacy archive for preservation. It was possible for a widow to be members of both Legacy and the War Widows Guild. Both organisations helped war widows in various ways.A record of the work done by Jessie Vasey and the War Widows Guild and of a close link to Legacy.Newspaper article with a photo of the pilgrimage to the Shrine in 2004.war widows guild, wwg, pilgrimage
