Showing 190 items
matching anaesthetic
-
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - SS White nitrous oxide/oxygen apparatus
With the introduction of nitrous oxide for patients undergoing dental treatment, 100% nitrous oxide was usually administered as an anaesthetic. This caused the patient to lose consciousness quickly and could also cause severe hypoxia. In the late 1890s, dentist Samuel Stockton White introduced this two cylinder apparatus, which could administer oxygen with N2O.Early model apparatus with cast iron stand, and two gas bottles. Comes with two canvas gas bags and a detached metal mask and fabric connecting tube.samuel stockton white, nitrous oxide, oxygen, hypoxia -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Oscillotonometer, von Recklinghausen
This oscillotonometer was owned by Dr. Herbert Claus Newman, an Anaesthetist who gained his diploma in Anaesthetics in 1956. Dr Newman served in the Vietnam War and was also one of over 50 of Australia's medical professionals who signed a joint statement in 2004 condemning the Federal Government for committing Australian troops to the Iraq war.Brown leather case with silver clasp and brown leather handle. Case contains Dr. von Recklinghausen Scala Alternans Oscillotonometer – a round silver pressure gauge with paper scale and needle point reader. The silver valve and lever at the bottom of the gauge connects black and orange rubber tubing to the grey linen arm cuff rolled closed with Velcro and a rubber inflation bulb.Yellow sticker on top of case in yellow type: H. NEWMAN Printed on face of gauge: Oscillotonometer / n. Dr. von Recklinghausen / "SCALA ALTERNANS" / 6585868 / S|K Printed on scale near zero reading: mmHg Printed on scale near highest reading: mm Hg = Torr Printed on scale is numbers 0 to 300 in increments of 20 Stamped on reverse of valve: 148blood pressure, oscillotonometer, dr. von recklinghausen, scala alternans, newman, h., newman, herbert claus, vietnam war -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Vaporiser, Tecota, Cyprane Ltd, c. 1970
Used by mothers during childbirth, the anaesthetic Trilene (trichloroethylene) was inhaled through a face mask [missing] attached to the rubber tubing [missing] and the vaporising chamber. The Trilene was poured into the chamber to be turned into a vapour. The machine was used in the obstetric wards at University College Hospital, London. Trilene was introduced in the 1940s. The machine was made by Cyprane Ltd.Khaki metal multi layered cylinder. Set on top of khaki metal plate with four (4) rubber feet.Stamped in red on top level of vaporiser: Cyprane Ltd •Stamped in red on serial plate: TECOTA MARK 6 / CHARGE WITH TRICHLOROETHYLENE B.P. / CYPRANE LTD. SERIAL No / KEIGHLEY / YORKS. / T1469 •Clear sticker with red printed text stuck on metal plate: PAT No 646680 / PATENTS PENDINGtrichlorethylene vaporiser, tecota mark 6 -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Atomiser, De Vilbiss, Circa 1910
Dr. Allen De Vilbiss (1841-1917) of Toledo, Ohio, developed his first atomiser around 1887. This device was designed to allow for dissolving cocaine, as a local anaesthetic agent, in oil, and spraying into the nose and throat. In the early to mid 20th Century, The DeVilbiss Company began making perfume atomisers instead of medical ones. Red, heavy cardboard box with manufacturer's label at one end, containing a glass bottle with metal spray attachment, and a khaki rubber bulb for pumping liquid through the atomiser.Stamped into top of metal atomiser: DE VILBISS TOLEDO USAatomiser, local anaesthetic -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMachine - Bird Anaesthesia Assistor/Controller Mark 4
The Bird Mark 4 is an anaesthesia assistor or controller with pressure and volume controller to be driven by a respirator. Combination of Mark 4 with respirator makes an automatic anaesthesia respirator eliminating manual bagging. The machine can work through Boyle anaesthetic system. It is designed for both paediatric and adult application. (Drugs and Equipment in Anaesthesia Practice, Aruna Parameswari, 2019)Green metal box atop a clear plastic unit with a black bellows inside, which forms one part of the overall unit. The unit is attached to a pole, enabling height adjustment. The pole is, in turn, attached to a set of four castors [not original].White text on black stick on strip on top of metal box: DO NOT PULL APART / FOR USE IN THEATRE ONLY A series of instructions are printed in white text over the unit.anaesthesia assistor, anaesthesia controller, pressure controller, volume controller, paediatric, adult -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
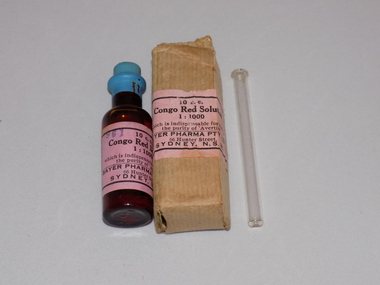
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryContainer - Congo Red Solution, Bayer Pharma Pty Ltd, pre 1932
Congo Red Solution was used to test the purity of Avertin before use. Avertin is a rectal anaesthetic that was used heated which could created dibromacetaldehyde and hydrobomic acid, the former being highly corrosive to rectal mucosa. Once this was known it was recommended that the solution should not be heated above body temperature and should be tested with Congo Red prior to use.Brown cardboard box with pink manufacturer's label adhered to front and text printed in black. The box contains an amber coloured bottle with blue wax seal and pink manufacturer's label with black printed text. There is also a clear glass dropper.avertin, dibromacetaldehyde, hydrobomic acid, rectal anaesthesia, rectal mucosa -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
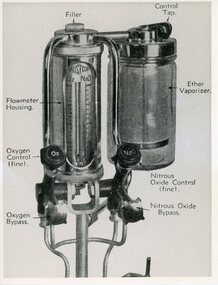
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryPhotograph
Black and white photograph of a drawing of anaesthetic equipment, a flowmeter and an ether vaporiser. On the right is the ether vaporiser inside a glass cylinder, with a control tap on top of it. It is attached to a metal cylinder which houses the flowmeter which is measuring the Oxygen and Nitrous Oxide. There is a round Oxygen control and a Nitrous Oxide control attached underneath the metal cylinder, as well as an Oxygen Bypass and a Nitrous Oxide Bypass. The diagram has each part of the apparatus named with an arrow pointing to the parts.ether vaporiser, anaesthetic equipment, flowmeter, nitrous oxide, oxygen -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryHeadwear - Academic Bonnet
This academic bonnet belonged to Dr Mary Burnell. Mary Taylor Burnell was born on 21 February 1907, in Norwood, South Australia. She graduated with her MBBS in 1931. In 1932, Burnell served as a resident medical officer at Adelaide Children’s Hospital. By 1934 she was their Honorary Anaesthetist. It was also during this period that Burnell became the first female member of the Australian Society of Anaesthetists. One year later, in 1935, she worked as Secretary for the South Australian Section of the Society. Although resigning from her position at the Children’s Hospital in 1937, Burnell returned in 1942. The outbreak of World War II meant hospital staff and resources were drained. During her work, Burnell lobbied for a Department of Anaesthetics in the Children’s Hospital. Through working at both hospitals, she became aware of the great differences between administering anaesthesia to children and administering it to adults. In 1953 she was elected President of the Australian Society of Anaesthetists. She was the first female to be elected to this position. Two years later in 1955, Burnell was elected as a member of the Board of Faculty of Anaesthetists, Royal Australasian College of Surgeons. In 1966 she was elected Dean of the Faculty of Anaesthetists. Again, she was the first female to be elected to this position. Burnell worked tirelessly to promote the importance of anaesthetics in Australia. Burnell’s contributions to anaesthetics were recognised with Honorary Fellowships to both the Australian Faculty of Anaesthetists and Royal College of Surgeons. Navy blue velvet cloth bonnet with stiffened brim covered in same fabric as bonnet. Around the hat is tied a gold cord with tassels.burnell, mary, academic bonnet, australian society of anaesthetists, faculty of anaesthetists, royal australasian college of surgeons, royal college of surgeons, fellowship -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Cannula, Tracheostomy
This was gifted to Robin William Smallwood on his retirement. Smallwood graduated from medicine in the mid-1950s and decided to make a career in anaesthetics, was granted Fellowship in 1965, became a member of the Board of the Faculty in 1976 and became Dean in 1986-1987. It has been made by Arnold & Sons of London who were medical instrument manufacturers and became Mayer & Meltzer.Silver tube in two pieces, which form an innner and outer tube. The inner tube is curved with a flat plate at the top and two squared hooks (handles) coming off the plate. The outer tube has been spliced, creating two separate curved sides with an oval, bowl-like plate at the end, with an oval shaped holed punched through either side. Attached to the square hook of the inner tube is a green cotton ribbon.Stamped into the bowl shaped plate: ARNOLD & SONS / SILVERsmallwood, robin, •faculty dean, faculty of anaesthetists, royal australasian college of surgeons, ffaracs, racs, fanzca -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryTool - Boyle-Davis gag tongue depressor, ANAX
Stainless steel tongue depressor with tightly curved distal end and slightly curved L-shaped proximal end. Includes a provision for an electronic light source to illuminate indside the patient's mouth.boyle-davis, gag, tongue depressor, oral apparatus, anaesthetic, anax, boyle gag, davis tongue depressor -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumEquipment - Ethyl Chloride
Chloroethane, commonly known by its old name ethyl chloride, is a chemical compound with chemical formula CH3CH2Cl, once widely used in producing tetraethyllead, a gasoline additive. It is a colorless, flammable gas or refrigerated liquid with a faintly sweet odor. Originally, it was proposed as a general anaesthetic, filling the gap between the weaker narcotic nitrous oxide and the more powerful drugs ether and chloroform. 8670.1 - Dark blue cardboard lid. 8670.2 - Dark Blue cardboard box. 8670.3 - Cotton ball padding. 8670.4 - Semi circle cardboard. 8670.5 - Small rectangular boxes (2) placed either side of the top of the cylinder. 8670.6 - Glass cylinder with metal fitting. 8670.7 - Paper label on cylinder.- 100 c.c./- MEDCO./- 3 1/2 fl. oz./- ETHYL CHLORIDE./- Pure./- This conforms to all the requirements of the BRITISH PHARMACOPOEIA. 1932./- LOCAL ANAESTHESIA/- MEDICINAL CHEMICALS CORPOATION LIMITED. SYDNEY. -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryContainer - Ampoule, Hypnotic 8064
Thiopentone was known as Hypnotic 8064 prior to its release onto the market. Thiopentone became popular during the inter-war years as a fast acting, short duration anaesthetic. It is used less frequently now as propofol is more popular. Also known as Pentothal sodium.Thiopentone has also been embroiled in controversy since being linked to deaths following the bombing of Pearl Harbor.Large clear glass ampoule containing powdered Hypnotic 8064. A small white label (now discoloured) with typed information is stuck on to the ampoule.Typed on label: HYPNOTIC 8064thiopentone, propofol, pearl harbor, short duraction, fast acting -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Tube, Endotracheal, de Caux
Francis Percival de Caux invented this endotracheal tube which was devised for use during nitrous oxide/oxygen anaesthesia. Though he wasn't the first to use a two-tube method of anaesthesia, de Caux's invention was particularly effective; in 1930 he reported having given 20,868 nitrous oxide/oxygen anaesthetics in a four year period without a fatality. A long flexible metal tube formed from tightly wound metal with a small bulbous introducer at the distal end. The tube is mostly encased in a metal and rubber sheath. The proximal end has a finger ring and screw clamp.endotracheal, de caux, airway, nitrous oxide, anaesthesia -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Equipment - Box of Astra Xylocaine 1% ampoules associated with Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, Astra, c. 1985
Lidocaine (or lignocaine) is a local anaesthetic (numbing medication) that is used to numb an area of your body to help reduce pain or discomfort caused by invasive medical procedures such as surgery, needle punctures, or insertion of a catheter or breathing tube. It is also sometimes used to treat irregular heart rhythms that may signal a possible heart attack, and can be given in an epidural (spinal block) to reduce the discomfort of contractions during labour.This is one of a collection of items received from the practice of Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, FRCOG, Launceston, Tasmania.Cardboard box containing 19 ampoules of Xylocaine 1%. The ampoules are in three strips of five, and one strip of four. Expiry date noted on the box for this medication is August 1985.surgery -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Inhaler, Probyn Williams (sectioned), Mayer & Co. London, c. 1900
Dr Geoffrey Kaye was a clinical anaesthetist at a time when very few full time anaesthetists existed. He was passionate about the training of future anaesthetists and would often section anaesthetic equipment to reveal its inner workings and show those to students. This Probyn Williams Inhaler is one apparatus which has been sectioned and the various elements of the inhaler have been painted to highlight the differences in function.Oval shaped metal inhaler with attached metal facemask. The inhaler has been sectioned to reveal its inner workings and the ether chamber has been painted black while the air-channel has been painted red. The manufacturer's logo, stamped into the inhaler, has been sectioned as well, leaving only half the information available.Engraved on dome side of inhaler: PROBYN WILLIAMS / G.K. sect. 1939 •Stamped into dome side of inhaler MAYER & / LONanaesthesia, anaesthetist, inhaler, ether, medical history -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Inhaler, Snow (replica), 1950
John Snow was England's first full-time anaesthetist. He noted that the common mode of administration of ether was liable to lead to anoxia, and invented this inhaler to overcome this. Later, he turned to chloroform anaesthetics without a death. He administered chloroform to Queen Victoria for the birth of Prince Leopold, this largely being responsibe for overcoming objections to the use of analgesia in childbirth. This replica was made in 1950 and gifted to the museum by A Charles King Esquire.The complete object is in six parts and made up of a brass metal box with swing latches in the middle section for secure closing. The lid is in two parts with one half that comes off entirely. Inside the box is the circular inhaler, detachable tube and dark yellow/green fabric covered tube. The mask made of brass and chamois leather with an exporatory valve does not fit into the box. A brown fabric case has been made to store the inhaler in.Etched onto the detachable lid, This replica of the Snow's Ether Inhaler of 1847 was made by John Henry Hawkes of A. Charles King Ltd. August 1950.john snow, chloroform, ether, queen victoria, prince leopold, john henry hawkes, a. charles king -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryPhotograph
Black and white photograph of anaesthetic apparatus inside a portable case which is standing upright and open. Inside the right half of the case is a flowmeter connected to several rubber tubes and a small Vinyl Ether vaporiser with a lever switched to ON. The left half of the case has four shelves with equipment on each shelf. The top shelf has an oropharyngeal airway tube. The second shelf has a metal facemask inhaler and a glass vaporiser. The third and fourth shelves hold metal cylindrical inhalers. In front of the case is a metal inhaler with face mask, attached to a rebreathing bag.Handwritten in grey pencil on reverse: Fig 17 new bookanaesthetic equipment, portable case, flowmeter, inhaler, vinyl ether -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryPhotograph
Black and white photograph of anaesthetic apparatus inside a portable case which is standing upright and open. Inside the right half of the case is a flowmeter connected to several rubber tubes and a small Vinyl Ether vaporiser with a lever switched to OFF. The left half of the case has four shelves with equipment on each shelf. The top shelf has an oropharyngeal airway tube. The second shelf has two metal facemask inhalers. The third and fourth shelves hold metal cylindrical inhalers. The photograph shows the letters A - J with arrows, pointing to the different parts of the equipment.anaesthetic equipment, portable case, flowmeter, inhaler -
 Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing Archive
Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing ArchiveBook - Illustrated book, Gary McKay et al, With healing hands: the untold stories of the Australian civilian nursing teams in Vietnam, 2009
From October 1964 until the end of 1972, over 450 surgeons, nurses and other medical specialists from Australian hospitals volunteered to work in South Vietnam. In the towns of Long Xuyen, Bien Hoa, Vung Tau and Ba Ria they brought expert medical and surgical care, comfort and support to a war-weary and traumatised civilian population. The extraordinary story of these Australian civilians at war is told here, based on interviews with many of those who served in the teams, The book includes two appendices: one lists the dates of service of the teams, the other lists the members of the teams.Illustrated book, Fronts cover has a photograph of two women in operating theatre dress with a young child (Vietnamese anaesthetic technician Tran Thi Dung, theatre nurse Cathy Blackmore and a young patient in an operating theatre at Bien Hoa Hospital, in early 1972). Below this on a background photo of bandages title and authors names are printed in shades of brown. Abbreviated title (light brown ink) and authors names (dark brown ink) are also printed on the spine along with the publisher's mark. A summary of the book, along with information about the authors, is [rinted on the back cover. non-fictionFrom October 1964 until the end of 1972, over 450 surgeons, nurses and other medical specialists from Australian hospitals volunteered to work in South Vietnam. In the towns of Long Xuyen, Bien Hoa, Vung Tau and Ba Ria they brought expert medical and surgical care, comfort and support to a war-weary and traumatised civilian population. The extraordinary story of these Australian civilians at war is told here, based on interviews with many of those who served in the teams, The book includes two appendices: one lists the dates of service of the teams, the other lists the members of the teams.vietnam war 1961-1975-medical care, vietnam war 1961-1975-participation-australia, vietnam war 1961-1975-personal narratives-australian, volunteer workers in medical car-vietnam-history, alfred hospital -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Magill's Endobroncheal Tube
This endobronchial tube was invented by Sir Ivan Magill. It can be identified as pre 1948, as from that time on the wire spiral was eliminated from the body of the tubes. Sir Ivan Magill is famous for his involvement in modern anaesthesia. He worked closely alongside plastic surgeon Harold Gillies in the treatment of facial injuries sustained in World War 1. He was responsible for many items of anaesthetic equipment, but most particularly the single-tube technique of endotracheal anaesthesia.Tightly wound wire spiral tube with metal 'T' nozzle at the opposite end.magill, endotracheal, tube -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Kimpton Brown flask, 1913
The Kimpton Brown flask was first described in 1913; the first successful citrated blood transfusion occurred in November 1914.Frosted, cylindrical glass flask with brown rubber stopper at top. A fluid outlet is located on the bottom of the flask and a narrow, horizontal and cylindrical valve is located below the flask rim. The flask contains a maximum volume of 600cc of fluid. The item was used in the collection and administration of blood transfusion procedures and the inside of the flask has a coating of paraffin wax to retard coagulation.flask, blood transfusion, anaesthetic, glass, parrafin wax, kimpton, 1914, coagulate, blood, frosted -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)'Atomist' atomiser associated with Dr Frank Forster
The all purpose 'Atomist' atomiser was used from the 1930s to the late 1960s. The atomiser had a detachable nasal mount, and a rubber bulb which was attached to a length of tubing. It also had an adjustable spray tip. It could be used as an anaesthetic cocaine or other spray. In the 1950s it was in extensive use as a laryngeal, nasal and throat spray. The spray nozzle could be turned upwards or downwards and was similar in appearance to the De Villiers Canadian spray. The atomiser could also be used as a vaginal douche with lotion for the treatment of vaginal infections. An atomizer spray consisting of a glass container with a hollow metal tube at front and long black rubber tubing attached to a rubber bulb at the rear. Glass container has residue of white liquid in it. WARNIING: dried white powdery substance may be arsenic. Contained in sealed bag. Handle wearing nitrile gloves and ensure examination is in open area, not enclosed space. -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryContainer - Phial, Ethyl Chloride, Bengue & Co. Ltd. Mfg. Chemists, Circa 1900
The glass phial contained liquid ethyl chloride, little pressure being required to liquefy the gas at room temperature. By directing the nozzle downwards at the skin or mucous membrane to be analgesed, a stream of liquid squirts out, vaporising on contact, thus producing transient local temperatures of approximately -10 qc. Ether's unpleasant smell agitated patients. Ethyl chloride's pleasant odour reduced agitation. It could be used for induction and worked quickly without irritating respiratory passages. Ethyl chloride spray could also be used as a local anaesthetic. Faded rectangular burgundy box containing a glass phial with metal and rubber lid that forms a spray nozzle. The lid of the box had a mustard coloured manufacturer's label wtih burgundy writing. The phial has a discoloured white label with red writing and a blue label with white writing.Printed in white ink on blue label: IMPORTANT / NOT DESTROY THIS TUBE, IT CAN / BE REFILLED FOR / 2/10bengue & co. ltd., london, ethyl chloride, 1900, local anaesthesia -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMachine - EMO (Epstein, Macintosh, Oxford) Ether Inhaler & Vaporiser
The Epstein, Macintosh, Oxford vaporizer (EMO) was designed in 1952 by Dr H. G. Epstein and Sir Robert Macintosh of the Nuffield Department of Anaesthetics at the University of Oxford, with the aid of their technician, Mr Richard Salt. It was essentially a refinement of their earlier Oxford vaporizer and designed specifically to deliver ether in known concentrations, irrespective of the temperature of the ether. Robert Macintosh was born at Timaru New Zealand in 1897. In December 1915 he travelled to Britain and was commissioned in the Royal Scots Fusiliers, soon transferring to the Royal Flying Corps. He was shot down behind enemy lines on 26 May 1917 and taken prisoner, escaping several times. When the war ended he returned to medical school and qualified in 1924 as MRCS LRCP. Macintosh's initial intention was to be a surgeon, but soon after qualifying he developed an interest in the field of anaesthesia. Macintosh became the first professor of anaesthetics at Oxford although the university was at first against the appointment. He recruited the scientists Dr Kurt Mendelssohn and Dr H G Epstein and together they designed and built the Oxford vaporiser, a simple, portable, and accurate means of delivering varying concentrations of ether which was to see service in the second world war. He was knighted in 1955 and died at Oxford in 1989.The apparatus is a round, barrel style object with three small rubber feet and a moulded handle over the top. It consists of a vaporising chamber, wick, ether level indicator, temperature compensating value, air bypass chamber and mixing chamber. Manufacturer's label on reverse: EMO, Longworth Scientific Inst. Co. Ltd. England. Serial No. 5878macintosh, epstein, oxford, vaporiser, nuffield, ether -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryTool - Tongue Depressor
J. Austen chrome plated tongue depressor blade only. Size 2 1/4, stainless steel material. The top arm of the instrument has a serrated grip below to facilitate tongue adherence, also has a middle space canal with semi circular welded rings to possibly introduce or attach an anaesthetic tube. This piece has in its internal lateral side engraved the possible owner's initial and last name. Minor scratches and dust marks are present over the piece as well as oxidation spots around engraved name. Weld spots in metallic semi circles edges on top of the piece.Engraved at the internal side of the handle, V. BRAND Stamped at the external side of the handle, J.AUSTEN / 2 1/4 / STAINLESStongue depressor, medical instruments, airway instruments, j. austen -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Mask, Julliard, 1877
This is a large metal framework covered in gauze, the whole mask completely enclosing the patient's face excluding any possibility of carbon dioxide being excreted. This object was found in the possession of the Italian Army in Libya in 1940, and donated to the museum by Dr Geoffrey Kaye. Gustave Julliard, of Geneva, after a death from chloroform had occurred in his practice, abandoned the use of that anaesthetic and adopted ether. He administered it from a large, wire frame, the outside of which was covered with waxed cloth to make it impermeable to air, the inside with surgical gauze on to which the ether was poured. Large metal wire frame mask, covered in waxed paper, with gauze wrapped around the rim to prevent ether leaking out, effectively forming a rebreathing apparatus.ether, carbon dioxide, italian army, libya, 1940 -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMachine - Boyle's Machine, British Oxygen Company, circa 1950
This Boyle’s machine was made by the British Oxygen Company (BOC) in the 1950’s. The original Boyle's machine was invented by the British anaesthetist, Henry Boyle in 1917. His machine was a modification of the American Gwathmey apparatus of 1912, and became the best known early continuous flow anaesthetic machine. The Boyle’s machine was first made by Coxeter and Sons, under the direction of Lord George Wellesly, which was later acquired by the British Oxygen Company (BOC). Though a lot of changes have been made to the original design of the Boyle’s machine, the basic structure remains the same today.Green trolley on casters with flowmeter and vaporiser bottles attached to a stainless steel cross bar. There is a glass shelf at top of the trolley and a second glass shelf at base of trolley, above a pull out drawer. The pull out drawer contains 4 x black rubber masks, 3 x black rubber tubing connectors, 4 x seals, 1 a black corrugated rubber hose with red rebreather bag, red tube and masonite support board.Tin plate attached to upper portion of trolley: THE / BOYLE / apparatus / BY THE BRITISH OXYGEN CO. LTD.henry boyle, anaesthetic machine, gas, oxygen, flowmeter, nitrous oxide, british oxygen company, boc, coxeter and sons -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Mask, Wire, Ether, 1910
Mask used for administering ether anaesthesia. This mask also has a carbon dioxide inlet tube. Carbon dioxide was found to promote deeper breather which assisted in attaining faster anaesthesia. The mask was designed by an American anaesthetist James Tayloe Gwathmey, (1863-1944). Gwathmey invented a range of anesthesia equipment. In 1904, he introduced this mask as one part of a resuscitation apparatus. Gwathmey modified an existing mask to more closely fit the contours of the face. The holes in the rim allow for oxygen to be delivered for resuscitation or for the delivery of a combination of oxygen and anaesthetic. Wire framed mask in tear shape. There is a hinged top bracket which allows for a piece of flannel or domette to secured to the mask, onto which the ether would be administered. There is an inlet tube near the hinged bracket to allow for the administration of CO2 or oxygen and the rim is pierced with holes.james tayloe gwathmey, ether, anaesthesia, anesthesiologist, carbon dioxide, oxygen -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMachine - Small ether inhaler
Dr Thomas Small designed this ether anaesthesia and analgesia machine while he was an Honorary Medical Officer at the Royal Women's Hospital in Sydney during the 1930s. The inhaler is compact and portable. Initially, Small experimented with other agents for the relief of labour pain but was not happy with any of them. He also tried various agents on himself, including nitrous oxide/oxygen, chloroform and ethyl chloride. Finally he settled on ether via a Clover inhaler as the best analgesic. This inhaler is only described in use in Australia and New Zealand, although it was used for almost 40 years. Black leather box with leather handle, lockable latches on either side and drop down front case panel containing a metal ether inhaler and length of black corrugated rubber hose with one end attached to the inhaler and the other end open for attaching a mask. The metal inhaler drum is circular and attached to the floor of the case with a small tap/lever to one side and a mixing valve on the top near the hose connection. The lever has incised gradings of quarter increments from 0 to 1. The box is designed for the ether inhaler to be portable.ether, small, thomas, analgesia, obstetrics, anaesthesia, anaesthetic, royal women's, sydney, queen victoria, melbourne -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
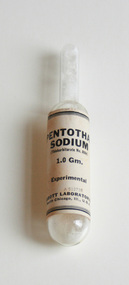
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryContainer - Pentothal Sodium, c 1935
Experiments with intravenous anaesthesia were undertaken in 1872 using chloral hydrate. The high mortality rates discouraged further experimentation until the early 20th Century. Thionembutal, or Pentothal Sodium, was one of these early developments. This ampoule has "Experimental" stamped on it. It has come directly from the manufacturing process. Pentothal Sodium is its trade name. It is now more commonly known as thiopentone.Glass ampoule of Pentothal Sodium (Thiobarbiturate No. 8064) 1.0 gm with large yellowed white label.Printed in black ink on label: Experimental / A 512738 / Abbott Laboratories / North Chicago. Ill., USA.pentothal, sodium, thionembutal, thiopentone, experimental, drugs, intravenous, anaesthesia, anaesthetic, john lundy, ralph waters
