Showing 192 items matching "oxygen"
-
 Queenscliffe Maritime Museum
Queenscliffe Maritime MuseumEquipment - Gauge, Oxygen, deep sea diving
Oxygen Gauge used for deep sea divingNo. G21271. Siere, Gormann and Co. Ltd. London -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Mirage Inspection Instructions
-
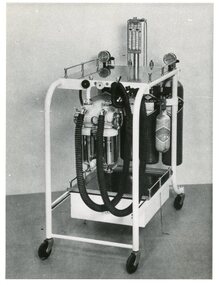 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryPhotograph
Black and white photograph of a Boyle's anaesthetic machine. The light-coloured metal frame on castors has a metal top with a flowmeter attached to the top, and there is one drawer at the bottom of the trolley. One side of the trolley has two vaporisers connected to two corrugated tubes with a facemask. An oxygen cylinder and two nitrous oxide cylinders are on the other side of the machine along with a small cyclopropane cylinder.anaesthetic equipment, boyle's machine, anaesthetic machine, nitrous oxide, oxygen, flowmeter -
 Ambulance Victoria Museum
Ambulance Victoria MuseumResuscitator, Komesaroff, Medical Developments Australia, Circa 1980
One each carried in an ambulance and used to resuscitate patients. Developed by a Dr Komesaroff this equipment replaced earlier resuscitators. These units took some time to get used to using but were deemed effective in operation. Source Chas Martin AHSV curator 4 April 2016.Oxygen bottle, gauges and carry handle mounted on an aluminium carry board.KOMESAROFF RESUSCITATOR -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Inhaler, Bruck, 1908
The Bruck Inhaler is a modification of the Clover Inhaler, designed by Lambert Bruck. Bruck added a glass dome which enabled the level of ether to be monitored during administration. This was a revolutionary change as it removed guess work from the process.The Bruck Inhaler is a historically, aesthetically and scientifically significant piece. The basic design is based on the Clover Inhaler, but with a rounded bottom. The idea of a glass viewing window was possibly inspired by Wilson-Smith Inhaler. The Bruck Inhaler is historically significant as it is the first inhaler to be made with a completely clear lower glass section. This improved the usability for the ether administrator, and eliminated much of the guesswork associated with dosage and ether levels, which in turn improved the patient experience. This piece provides a strong local link to both anaesthetic and general medical practice at the turn of the century. The design is credited to Ludwig Bruck of Sydney, and was presumably manufactured in the same area. Bruck, as the attributed designer, holds much relevance to the significance of the object, as connected with him is much historical information about the social context of medical practice. Ludwig Bruck was a prominent figure in the medical industry. He started his medical career in Sydney as a Medical Transfer Agent, and later owned a shop at 16 Castlereagh Street, Sydney. This business is listed in the 1903 Register of Firms as a Medical Agent and Importer of Medical Instruments and Books. Bruck was vocal as a journalist and published analyses of medical statistics, as well as the well known Australasian Medical Dictionary and Handbook, which included the “List of Unregistered Medical Practitioners”. Ludwig Bruck was an immigrant. He was of German descent, which placed him in a precarious position within Sydney society during the turn of century. Bruck conducted several public conversations with prominent members of the Australian Natives Association through the Sunday News in regards to his disagreement of the employment of medical practitioners by the ANA specifically to corroborate their health insurance policies. He was also a stalwart supporter of the Australian arm of the British Medical Association, being the publisher of the first and subsequent editions of The Australian Medical Gazette. Bruck chose to end his life with a combination of poison and chloroform on 14 August 1915, after being accused of trading with the enemy during World War One. His suicide note stated his horror at leaving his business partner to deal with the tarring of his reputation as the reason for his decision. The Bruck Inhaler has aesthetic significance as it is a beautiful example of turn of the century surgical design and craftsmanship. Aseptic methods of surgery were well known by 1909, and the aesthetic design of the Bruck Inhaler conformed to these principles. The ability for the surgeon to unscrew, clean and sterilize each part of the Inhaler contributes to the streamlined design of the piece. The Buck Inhaler holds scientific significance. There is the capacity for further research to be undertaken on the object. Geoffrey Kaye often collected multiple examples of equipment, usually one for reverse engineering and another for teaching. There are currently two examples of the Bruck Inhaler in the collection, presenting an opportunity for further technical research on the object. The inhaler is oval shaped with one half made of glass to allow observation of the ether level. A vertical cross tube, 22mm in diameter passes between the face-piece and the bag [missing]. There is a stopcock for admission of oxygen or nitrous oxide opposite the bag attachment. There is a central tube, 28mm in diameter, with controllable ports on either side. There is also a tear-drop shaped fask mask.Hand engraved on side of base: L. Bruck / Sydneyclover, joseph, bruck, lambert, inhaler, rebreather, nitrous oxide, oxygen, williams, probyn -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Stopcock, Hewitt, George Barth & Co. Ltd, c. 1895
When Hewitt introduced his regulating stopcock in 1887, attempts were made to dilute the nitrous oxide with air and so obviate the element of asphyxiation. The method was to be seen in London, mainly in dentistry and minor surgery, so late as 1930. It was not very successful. To give even 10% of oxygen (which is not enough) the gas-mixture must contain 55% of air and 45% of nitrous oxide. The latter is thus so diluted by atmospheric nitrogen as to be incapable of producing anaesthesia except by asphyxiation. "Gas-air" was confined to analgesia, for example in midwifery. (Source: Penn catalogue)Brown leather facemask attached to metal inhaler and stopcock device that has been sectioned to reveal its inner workings. The various exposed channels have been painted either green, red, blue or purple.Engraved into side of stopcock: HEWITT'S / N20-02 / 1895 / G. Kaye sect. 1952. •Stamped into other side of stopcock: [indecipherable] BARTH & CO. / SOLE MAKERS / 54. POLAND STREET LONDON.W.frederic hewitt, stopcock, nitrous oxide, oxygen, gas-air -
 University of Melbourne, School of Chemistry
University of Melbourne, School of ChemistryTorches
Glass blower's torches. For age, see Gall Cat.No 1020 for "Oxygen" type. -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Inhaler, Bruck
The Bruck Inhaler is a modification of the Clover Inhaler, designed by Lambert Bruck. Bruck added a glass dome which enabled the level of ether to be monitored during administration. This was a revolutionary change as it removed guess work from the process.The inhaler is oval shaped with two halves. One half should be made of glass [missing] to allow observation of the ether level. A vertical cross tube, 22mm in diameter passes between the face-piece and the bag [broken]. There is a stopcock for admission of oxygen or nitrous oxide opposite the bag attachment. There is a central tube, 28mm in diameter, with controllable ports on either side.The Bruck Inhaler is a modification of the Clover Inhaler, designed by Ludwig Bruck. Bruck added a glass dome which enabled the level of ether to be monitored during administration. This was a revolutionary change as it removed guess work from the process.joseph clover, lambert bruck, inhaler, rebreather, nitrous oxide, oxygen, probyn williams, hewitt -
 Ringwood RSL Sub-Branch
Ringwood RSL Sub-BranchEquipment - LIF-O-GEN
white cylinderLIF-O-GEN OXYGEN UNIT Made in USA -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Calcite crystals
Calcite is a common mineral and is found worldwide due to it being a primary component of many other rocks such as limestone and marble. It is a softer mineral that scratches easily and is often found colourless or with a cream/white shade but may show up in colours such as red, yellow, green, and violet. In sedimentary rocks calcite is often found in the form of invertebrate shells, making it an important biomineral. Calcite is used in many industries such as farming, building, and medicine. This particular specimen was found at Broken Hill mine in Broken Hill, New South Wales, Australia. Broken Hill mine is one of the largest mines working silver and lead in Australia and at its peak employed 6500 staff across 7.5km long of land. The site was founded in 1883 by Charles Rasp, where Rasp and 6 other men from various backgrounds came together to form the first BHP mine. It has become one of the most popular mining sites due to its abundance and longevity. The ore body was created 1685 million years ago due to volcanic activity causing heated seawater to flow up through the seafloor where it mixed with the cold water creating black sulphide precipitates. These then settled back onto the seafloor forming sediment layers rich in minerals. Over time the land eroded until it was discoverable by humans.Historically this specimen is significant due to the origin of its location. Broken Hill mine has a long history in both its location and its findings and has resulted in a variety of minerals being discovered at its site. It is beneficial in the understanding of the Australian landscape over millions of years. Due to its properties, calcite today is used in a multitude of different industries such as agriculture, construction, medicine, and farming.A small sized calcium, carbon and oxygen made mineral specimen in shades cream and greycalcite, mineral, limestone, marble, sedimentary, invertebrate shells, biomineral, farming, medicine, broken hill, broken hill mine, new south wales, charles rasp, syndicate of seven, volcanic activity, black sulphide precipitates, calcite crystals, beechworth museum, indigo shire, beechworth -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - C.I.G. Water depression flowmeter
A sectioned water depression flowmeter apparatus on a tall metal stand with castors. There are three knobs on the camera-facing side of the apparatus: one black, one yellow, and one blue, which correspond to oxygen, propylene, and nitrous oxide respectively. Two gas canister lids attached to the apparatus with long metal ball chains read "AUSTOX/OPEN SLOWLY". Above the knobs is a set of glass tubes, that have had a metal panel between them cut out. Part of the valve on the left below the knobs has been sectioned away to show the spring mechanism inside.nitrous oxide, oxygen, propylene, hospital, anaesthesia -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionScientific Instrument, Orsat Apparatus
The Orsat was returned to the Historical Collection by Len Taylor, former staff member of SMB. For a period of time it was with Gary Price who rebuilt the Orsat to working order. Gary used a similar apparatus at Sidchrome and Ballarat Heat Treatment Pty. The Orsat apparatus is used to measure volumes of Carbon Dioxide, Oxygen, and Carbon Monoxide within a fixed volume of a sample of gas.Timber box with lift up front revealing a number of valves, pressure measure and glass container of red liquid attached to hose. Gas analysis apparatusorsat, len taylor, gary price, carbon dioxide, oxygen, carbon monoxide, gas, measure, apparatus -
 Anglesea and District Historical Society
Anglesea and District Historical SocietyCandle Snuffer - Antique
Small box on a scissor-like contraption which extinguished candle flame by denying the flame oxygen.candle snuffer -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumEquipment (item) - US Military Pilot Carry Case For Helmet And Oxygen Mask
Specification MIL-C-19666A(WEP) Contract No. DSA-100-1203 Sock No. 8415-753-2901 -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEphemera - Label, Cylinder, Commonwealth Industrial Gases Ltd
Large unused hexagonal shaped CIG label made for use on carbogen cylinders. Beige and green background with black lettering.Information printed on label: CIG MEDICAL SECTION [logo] / OXYGEN 90% CARBON DIOXIDE 10% / (These Percentages are subject to a tolerance) / Contents..........Imp. Gallons / COMPRESSED / CARBOGEN / C.I.G. (Victoria) Pty. Ltd. / 550 Latrobe Street, Melbourne, C.3 / Telephone: FJ6681 / USE NO OIL / OR GREASElabel, cylinder, cig, carbogen, compressed carbogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, cig victoria -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMachine - Portable dental and midwifery anaesthetic machine, Commonwealth Industrial Gases Ltd, circa 1950
This gas anaesthesia machine comprises a four yolk manifold, two circular metal components for nitrous oxide and two for oxygen. It is mounted atop a four pointed stand on casters for portability. In addition to reducing valves and regulators, the main stand also supports a cream-coloured, cylindrical Austox fractional rebreather and an ether vaporiser with variable bypass control within a circular glass container. portable, anaesthesia, midwifery, dentistry, obstetrics, oxygen, nitrous oxide, commonwealth industrial gases ltd, cig, austox fractional rebreather, ether vaporiser, variable bypass control, 1950 -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Article, Unit meeds need, 1993
An urgently needed oxygen unit has been donated to the Mid-Eastern Palliative Care Association by St John's Parish, MitchamAn urgently needed oxygen unit has been donated to the Mid-Eastern Palliative Care Association by St John's Parish, MitchamAn urgently needed oxygen unit has been donated to the Mid-Eastern Palliative Care Association by St John's Parish, Mitchamhealth services, mid-eastern palliative care association, parker, mary, bergman, doug, dillon, kevin joseph, fr. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumHeadwear (item) - Flying Helmet MK 3B With Oxygen Mask
Stores Ref. 22C/1301773 S/N 11121 -
 Ambulance Victoria Museum
Ambulance Victoria MuseumResuscitator, Oxy Viva, Mk II, circa 1975
Used in Victorian and New South wales Ambulances during the 1970s to resuscitate patients. The equipment was effective but replaced by newer versions then a different brand after a few years service (source Chas Martin AHSV curator 16 Mar 2016). These items were also kept for use at swimming pools and other public places.Stainless steel metal box on white carry frame with black oxygen bottle fitted beneath. Metal box filled with resuscitation equiomentresuscitation, ambulance equipment -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Cylinder, Medical Compressed Air
Early cylinders were coloured as their maker saw fit, usually black, perhaps with a white top for oxygen. The Americans first achieved standardisation, but other countries do not follow American Standards. Australia follows the colour-scheme of the British Oxygen Corporation. The body is coloured individually for each gas, viz: compressed air, grey; carbon dioxide, brown; oxygen, black; nitrous oxygen, blue’ cyclopropane, primrose-yellow’ ethylene, mauve. Panels of other colours may appear on the body, but indicate technical points of cylinder-design and do not concern the anaesthetist. (Penn catalogue entry)Empty small pale green painted cylinder with rounded base and attached outflow valve with circular 'On-Off' knob.Handwritten in red paint across the main body of the cylinder: ST. VINCENTS 32510 Printed on manufacturer's label: 'KEEP CYLINDER COOL / CIG [logo] / MADE IN AUSTRALIA / MEDICAL AIR COMPRESSED / DO NOT ALLOW OIL OR GREASE ON VALVE / OPEN VALVE SLOWLY CLOSE AFTER USEcompressed air, cylinder, colour standardisation -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Mask, Spectacle frame, c. 1930
The use of a catheter for oxygen therapy was introduced by Arbuthnot Lane in 1907. However, its true value can be seen in its use during WWI. Masks were cumbersome and uncomfortable for the wounded and nasal delivery of oxygen was received more easily. The Tudor Edwards' Spectacle-frame was manufactured in London during the 1930s. Dr Penn recorded that it was an inefficient means of oxygen therapy because of the smallness of the nasal tubes.Metal mask resembling spectacles with round frames and rounded ends of the arms to secure around the ear. There is a tube coming from each round eye frame to end in a curve that sits in the nostril. The other end of this tube has a rubber tube attached which meets in the middle via a metal connector.oxygen therapy, intra-nasal -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Piper Manuals Various see "Description"
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Illustrated Parts Breakdown Aircraft: Emb-110 Bandeirante T.O. 1Emb110 P1-4-5
Description: Fuel AirCondition or completenessing Oxygen Systems Level of Importance: World. F.G. Brown -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Headwear - Flying helmet, Downing
Air Force flying helmet. white and green markings, oxygen mask attached, mounted on a wooden base. A replacement for one lost in jungle after ejection. Air force cloth badgeCertificate Of Martin Baker Clubhelmet, downing, pilot, flying helmet, raaf, john downing -
 Nhill Aviation Heritage Centre
Nhill Aviation Heritage CentreMemorabilia - Headphones and throat microphone
Used by Air crew, allowed operator to use without hands also fits under oxygen maskHeadphones with white leather pads held by metal supports and attached cotton braided wire lead and plug. Attached is a throat microphone with elastic straps and metal closer hookA & M with a crown between, 10A/12401headphone, microphone, throat mic, headset, radio, -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Tube, Endotracheal, de Caux
Francis Percival de Caux invented this endotracheal tube which was devised for use during nitrous oxide/oxygen anaesthesia. Though he wasn't the first to use a two-tube method of anaesthesia, de Caux's invention was particularly effective; in 1930 he reported having given 20,868 nitrous oxide/oxygen anaesthetics in a four year period without a fatality. A long flexible metal tube formed from tightly wound metal with a small bulbous introducer at the distal end. The tube is mostly encased in a metal and rubber sheath. The proximal end has a finger ring and screw clamp.endotracheal, de caux, airway, nitrous oxide, anaesthesia -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionEquipment - Equipment - Scientific, VIOSH: Equipment for creating Dust Explosions which are the result of high concentrations of combustible dust particles
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. Dust explosions are the result of high concentrations of combustible dust particles rapidly combusting inside an enclosed space. When mixed with oxygen these fine particles can ignite when in contact with a spark, metal ember, cigarette butt or other source.Wooden box with metal edges on top. Chrome handle and indicator buttons for Power, Air, Compression, Spark. Hinged front section that opens to show contents. Electrical Engineering lecturer Graeme Hood remembers Paul Brass demonstrating this unit to show how dangerous a combination of dust and electricity it. The demonstration would take about 1 minute, and would culminate with a loud bang which would make everyone jump. This item was probably last used by Paul Brass.viosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, dust explosion, combustible dust particles, enclosed space, spark, ember, cigarette, oxygen -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryMachine - Vapouriser, Endotracheal, Ether, Australian Army Endotracheal Ether Apparatus, 1939
Dr Geoffrey Kaye worked as an adviser to the Director-General of Medical Services, Australian Infantry Forces during the inter-war years. During this time he developed an ether vapouriser specifically for the Army. This is the prototype designed and made by Dr Kaye during 1939.Round metal tray with round ether apparatus inside consisting of an ether sight glass indicator, oxygen bypass, control tap and trap bottle. There are three rubber hoses, two red and one black. geoffrey kaye, vapouriser, royal army medical corps, ether, endotracheal, prototype, blowover, world war ii, wwii, ww2 -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Armstrong-Whitworth Argosy 650 Series Illustrated Parts Catalogue Volume 5, AW. 650 Aircraft Manual
Topics include flight controls, fuel, hydraulics, ice and rain protection, instruments, landing gear, lights, navigation, oxygen, and water/waste. -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Equipment - Equipment, RAAF, Ejection Seat
Mk. 3 Martin Baker ejection seat. Canberra bomber pilot reat. Consists of oxygen hose, safety harness, leg restraints, face blind, seat harness, head cushion, parachute back support padejection seat, canberra bomber
