Showing 1019 items matching "shilling"
-
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Programme - 1956 Olympic Games Official Programme - Basketball, A. H. Massino & Co. Pty. Ltd (text), C 1956
Official programme - Basketball- November 27th to 1st December 1956.XVI th Olympiad - Melbourne Exhibition Building Annexe. Booklet - purple & green Olympic Games - Melbourne 1956 Basketball - Official programme One shillinginternational olympic committee, 56th olympiad, melbourne 1956 -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumAdministrative record - IMMUNISATION NOTICE, 1908
MR. LACHLAN McLENNAN OF GEORGE STREET CLUNES - GENTLEMAN TO ATTEND DOCTORS RESIDENCE FOR HIS CHILD WINIFRED MAUD MCLENNAN TO RECEIVE VACCINATION 21ST JULY 1908.DOCUMENT OF NOTICE FOR CHILD TO BE VACCINATED BY MEDICAL PRACTIONER OR PARENT WILL BE LIABLE TO A PENALTY OF TEN TO FORTY SHILLINGS.local history, certificate, health -
 Nhill Aviation Heritage Centre
Nhill Aviation Heritage CentreBook - Text book for trainee navigators, Edgar H. Ballie, Aircraft Recognition, Photographs, silhouettes & details of 100 military aircraft, c1940s
Black and tan cover with off colour pages, black print and photos and front side and elevation view. 98 pagesaircraft recognition, book, -
 Waverley RSL Sub Branch
Waverley RSL Sub BranchKorean Currency and N.A.T.O. Forces Notes
Used during Korean War Won (1947-) Main article: North Korean won After the division of Korea, North Korea continued using the Korean yen for 2 years until the Central Bank of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea was established on December 6, 1947 and a new currency was issued. It was at the time pegged at par to the Soviet ruble. It was revalued at a rate of one hundred to one in February 1959 and new won were issued. In the following years the won faced some devaluation, caused by the subsequent devaluation and redenomination of the Soviet ruble. From 1978 to 2001, the North Korean government maintained an iconic rate of 2.16 won to the US dollar; since then banks in the country exchange at rates closer to the black market rate. However, rampant inflation has been eroding the North Korean wŏn's value to such an extent that currently it is believed to be worth about the same as the South Korean wŏn. In any case, the U.S. dollar and other currencies are still worth more in North Korean wŏn on the black market than officially. South Korean currencies[edit] Won (1945-1953)[edit] Main article: South Korean won (1945) Following the end of the division of Korea, the won was introduced to replace the Korean yen. The won was subdivided in 100 jeon. The first banknotes were issued by the Bank of Joseon in denominations ranging from 5 jeon to 100 won. In 1950 the currency management switched to the Bank of Korea and new notes were then issued, mostly with higher denominations. The first note put in circulation by the Bank of Korea in 1950 was printed in Japan by the National Printing Bureau (国立印刷局). The next year the Korea Minting and Security Printing Corporation was created and took over as printer of South Korean currency. At the time of the introduction in 1945 the won was pegged to the Japanese yen at a rate of 1 won = 1 yen. In October of the same year the anchor currency got change to the US dollar at a rate of 15 won = 1 dollar. Toward the end of the Korean War the won was devaluated at 6000 won = 1 dollar. Following that the hwan was introduced as the new currency at a rate of 1 hwan = 100 won. Hwan (1953-1962)[edit] Main article: South Korean hwan Due to devaluation of the won the hwan was introduced on February 15, 1953 at the rate of 1 hwan = 100 won. It was subdivided in 100 jeon, but they were never used. New banknotes in denominations between 10 and 1000 hwan were issued. Starting in 1959, 10 and 50 hwan coins were also issued to replace the lower denomination notes. Those were the first circulating coins in South Korea. Due to the short notice of the change in currency, the first series of the new notes was commissioned from the United States Government Printing Office. The notes were released in five denominations, all with an identical design. Some replacement notes with a more suited Korean theme were later issued, starting with the 100 hwan just a month later. The hwan suffered from inflation as well. At its introduction, it was pegged to the United States dollar at 1 dollar = 60 hwan, but toward the end of its life it was devaluated at 1 dollar = 1250 hwan. In 1962, the won was reintroduced at the rate of 1 won = 10 hwan. The 10 and 50 hwan coins were kept in circulation until March 22, 1975.5 Currency notes issued by Korean Government and R.A.A.F. denominations of 100, 100 Won and 1 shilling国立印刷局, currency korea, money korea, money korean war -
 Tarnagulla History Archive
Tarnagulla History ArchiveDocument - Postal Order: Latimer to Burgess, 18th October 1867
Williams Family Collection. Probably filled out at Tarnagulla Post Office. George Latimer was a Tarnagulla miner. A postal money order for funds (one shilling) sent from George Latimer to Martin Burgess, Noarlunga. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - H.A & S.R. WILKINSON COLLECTION: APPLEBY SIGNS INVOICE
Appleby Signs Invoice 823 dated 31/10/1956 for auction board 15 shillings. The invoice is stapled to statement 280 dated November 1956. A receipt is attached acknowledging receipt of the 15 shillings, the receipt is dated December 1956 No. 210. The document is in a manilla folder.organization, business, h.a. & s.r wilkinson real estate, yellow label 595. -
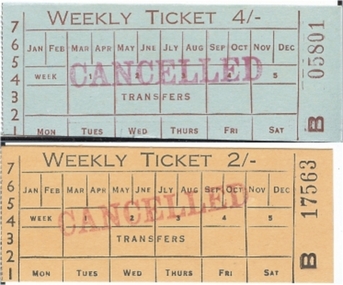 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - BASIL MILLER COLLECTION: TRAMS TICKETS
Two (2) weekly tickets. Yellow 2/-(two shillings) No. B17563 and Blue 4/-(four shillings) No. B05801. Other printing on these is too much to list, see scan.The yellow ticket has been cancelled with a red stamp, and the blue ticket cancelled with mauve stamp.person, individual, basil miller -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - L. PROUT COLLECTION: SANDHURST MUTUAL PERMANENT INVESTMENT & BUILDING SOCIETY DEPOSIT ACCOUNT
Pass book, deposit account in the name of Miss Lillian Prout issued by The Sandhurst Mutual Permanent Investment & Building Society. It covers period from 1937 to 1959. Opening balance of 102 pounds 8 shillings, closing balance 530 pounds 18 shillings 7 pence.organization, business, sandhurst mutual investment society -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyreceipt docket, May 5th 1908
This receipt was found inside a book that came from Orbost House. Orbost House, believed to have been established by the Macalister family around the turn of the 20th century was a boarding house in Lochiel Street, Orbost. James Bugg was an early settler at Murrangower.A paper receipt from the Shire of Orbost made out to Jas Bugg Year 1908 for seven shillings and sixpence.receipt bugg-james docket -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - COLONY OF VICTORIA FIVE SHILLING MINER'S RIGHT CENTRAL DEBORAH GOLD MINE BENDIGO, 1851-1901
Blank buff and Sepia Five Shilling Miner's Rights License No. 22330 Central Deborah Gold Mine Bendigo.australia, gold mining, bendigo central deborah -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Flyer - Christmas Gifts at the Beehive
Early 1950s items and costs (in pounds shillings and pence) pre-decimal charges for itemised gifts. Beehive buildings. This was originally the Sandhust Mining Exchange and as such was the oldest purpose built exchange in Australia and was one of only two in regional Australia. It was initially established in the 1850's to service the miners of the area. It's first double story incarnation as the Bendigo Stock Exchange, contained up to 2000 stockbrokers and 5000 shareholders. In 1871 the building burnt to the ground and the new and current building was completed in 1872. The modern building was designed by Charles Webb, who was also responsible for the Royal Arcade in Melbourne. and features a pitched glass roof similar to the Royal Arcade, Melbourne.Christmas Gifts at the Beehive - a shopping flyer for the Beehive department store, circa early 1950s. the flyer covers Christmas gifts across the various departments of the Beehive Store in Pall mall and Hargreaves Street Bendigo. Two-page folded flyer, black printed on cream paper. Printed by Cambridge Press, Bendigo. Early 1950s items and costs (in pounds shillings and pence) pre-decimal charges for itemised gifts.the beehive, christmas gifts -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - BASIL MILLER COLLECTION: TRAMS TICKETS
Five(5) State Electricity Commission of Victoria Provincial Tramways Scholars Monthly tickets. No.B02369 5/-(Five shillings), Red stamped across the front with the word Cancelled in red ink. No.A03910 11/-(eleven shillings) Unused. No.A24951 8/6(eight shillings and sixpence) Unused No.A000250 12/6(Twelve shillings and sixpence)Has the word Cancelled and two diagonal lines,one long and one short with an initial in green biro.No.A000250 17/6(seventeen shillings and sixpence) with the word Cancelled and two diagonal lines,one long and one short with an initial in green ink. Three of the tickets are printed in black ink on the lighter side and two on the yellow side. Reverse: One, 5/-, is red. Two 11/- and 8/6 are yellow, Two 12/6 and 17/6 are light coloured.person, individual, basil miller -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Booklet - Booklet - Guide to Fruit & Vegetable preserving, Preserving fruits & vegetables, C 1940's
Marked 'D M Smith 1944'A booklet from the Victorian Dept of Agriculture detailing 'Preserving fruits & vegetables'.Dept of Agriculture, Victoria Bulletin No 43. 'Preserving fruits and vegetables'. Price 1 shilling.instructional preserving cookbook -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEphemera - Miner's Right - Collins, 1888
This Miner’s Right was issued post the rush of the 1850s-60s but is testament to the ongoing interest in gold although the great rush had dwindled. Local papers continued to report on findings and hopes of success, including syndicates and explorations across the south-west district of Victoria and Otways. The Warrnambool correspondent of the “Hamilton Spectator”, 31/1/1878, p4 attest to the price of a good season of potatoes comparing “favourably with the unsteady returns of any precarious gold-bearing quartz reefs in the colony.” A James Collins (1842-1918) is listed in the Pioneers’ Register, Warrnambool, Township and Shire 1839-1900, Volume One, A.I.G.S Warrnambool Branch, 2004, p137. As are numerous other Collins pioneer families of the district. This item is significant in that it illustrates that people associated with the region were interested in taking their chances in prospecting for gold similar to many others. A lure that is still present for some today. Although the southwest region found it's source of wealth in other industries from whaling and fishing, wool and other agricultural pursuits. This is a top to bottom upright image of a Miner’s Right. It is a buff coloured document printed in black ink. It was issued in “BALLARAT” and rubber stamped twice in red ink. The issue to “James Collins”, is dated “23rd August 1889” to “22nd August 1890”. The signature of the authority could be Bennet. All handwriting is script style in black ink. Looking from the front the lefthand side has a serrated edge. The back is printed in black ink and there are no “particulars of registration”. The Miner’s Right is from “Series J, Book No. 3, ticket “No. 15”. A “Colony of Victoria” coat of arms is displayed at the top of the document. An insignia runs along the lefthand side of the license featuring coat of arms with a kangaroo and emu, then a miner’s pick and shovel, two crossed Union Jack flags sit behind a monogram “VR” with a hanging set of scales supported by a sword. "By Authority Robt. S. Brain, Government Printer.""Series J. Book No. 3 Five Shillings. No. 15. Colony of Victoria. Miner's Right"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, james collins, australian goldfields, miner's rights, the history of ballarat, gold rush -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1819
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1819, the year before King George III died. There were over 7 million of these coins minted. King George III succeeded his grandfather, King George II, on the throne in 1760. He reigned until his death on 29th January 1820. The shield in the centre of the reverse of the coin is the Hanoverian Shield, showing that the House of Hanover was elected to the crown rather than taking the crown as a victory. This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - The 6 pence coin is 19mm - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) - The Half Crown is 32mm British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George III by the Grace of God, King of the British territories, Defender of the Faith”. The engraver of the obverse image was Benedetto Pistrucci. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated "Evil to him who evil thinks” The engraver of the reverse image was Thomas Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time Australia became a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation, the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling, 1819. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George III head, looking right. Reverse; crown on top of quartered shield, 2 diagonally opposite quarters both show 3 lions, another quarter has a rampant lion, another quarter has a harp; in the centre of the shield is a small crowned shield with 3 symbols that appear to be lions. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEOR . III D . G . BRITT . REX F . D .” and “1819” Reverse “HONI . SOIT . Q [UI obscured] . MAL . Y . PENSE” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1819, king george iii currency, colonial australia currency, benedetto pistrucci, thomas wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1819
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1819, the year before King George III died. There were over 7 million of these coins minted. King George III succeeded his grandfather, King George II, on the throne in 1760. He reigned until his death on 29th January 1820. The shield in the centre of the reverse of the coin is the Hanoverian Shield, showing that the House of Hanover was elected to the crown rather than taking the crown as a victory. This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - The 6 pence coin is 19mm - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) - The Half Crown is 32mm British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George III by the Grace of God, King of the British territories, Defender of the Faith”. The engraver of the obverse image was Benedetto Pistrucci. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated "Evil to him who evil thinks” The engraver of the reverse image was Thomas Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling, 1819. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George III head, looking right. Reverse; crown on top of quartered shield, 2 diagonally opposite quarters each show 3 lions, another quarter has a rampant lion, another quarter has a harp; in the centre of the shield is a small crowned shield with 3 symbols that appear to be lions. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEOR . III D . G . BRITT . REX F . D .” and “1819” Reverse “HONI . SOIT . Q [UI obscured] . MAL . Y . PENSE” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1819, king george iii currency, colonial australia currency, benedetto pistrucci, thomas wyon, numismatics -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Coin, English Penny Victoria Det Gratia 1854, 1854
English currency before decimalisation in the 1970's consisted of pounds, shillings and pence with twelve pennies to the shilling and twenty shillings to the pound.Coins ranged from farthings which were one quarter of a penny through to pennies, threepence, sixpence, shillings ,half crowns and crowns. Most coins had a variety of common names such as a " bob" for a shilling a "quid for a pound and a tanner for a sixpence. This coin is the equivalent of five shillings and is known as a crown. The text around the obverse, "Victoria Dei Gratia 1844". On the reverse the text of Reg Fid Def"Britanniar translates as Queen of Britain and defender of the faith. This coin is one of the smaller denominations.A common currency coin which has social and historical significance.Round copper coin with flat edge. The The obverse has an image of the young Victoria with text around the edge.The reverse has an image of Brittania in a chariot.Dotted edge around the inside rim of both sides.BRITTANNIAR REG FID DEFon the reverse and Victoria Dei gratia on the obverse.english penny, 1854 penny -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument - Ports and Harbours, Ports and Harbours, Tender for Warrnambool Light, 24-06-1907
The document confirms that the Tender for the supply of maintenance to the Warrnambool Light, also known as the Lighthouse, by the Warrnambool Gasworks was successful. The Tender was issued by the Engineer in Charge, C. Maclean, Ports and Harbours, Melbourne, for a the period ending 30th June 1908, at the offered rate of 10/- (ten shillings) per 100.0 c/f (cubic feet). The Manager of the Warrnambool Gasworks expected to follow this acceptance with a visit to the Collector of Customs to sign the Conditions of Contract and Bond. The light of Warrnambool's Lady Bay Lighthouse was originally powered by oil. Later it was converted to gas, followed by electricity, then solar power, and finally to battery power. The Warrnambool Gas Company operated the gas works from the 1870's to the late 1920's.This document connects Warrnambool's Lady Bay Lighthouse to the Warrnambool Gas Works during the first decade of the 20th century. It documents to process of a Government department requesting Tenders for the supply of goods to operate a service, the the formal documentation required at that time.Pale cream rectangular paper with template text printed in black and completed in black ink script. Letterhead of the Department of Ports and Harbours, Melbourne, and addressed to the Gas Works, Warrnambool, dated 25th June 1907, for the supply of maintenance to the Warrnambool Light until 30th June 1908 at the cost of Ten Shillings per 100 cubic feet. A purple stamped signature is also added and initialled in red pen."25th [June] 1907" Warrnambool [Light]" "Manager W'bool Gasworks" "supply of gas to" "1908" "10/- per 100.0 c/f" "Collector of Customs" " The Manager / Warrnambool Gasworks" [Signature] "for" [Engineer in Charge, Ports and Harbours] Stamped " C. -. Maclean"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, department of ports and harbours, ports and harbours, ports and harbours melbourne, warrnambool light, warrnambool lighthouse, warrnambool gas works, w'bool gas works, gas works, gas supply, early 1900s, early 20th century, shillings, cubic feet, collector of customs, customs, warrnambool customs, engineer in charge, lady bay lighthouse, warrnambool gas company, gasworks, warrnambool gasworks, maintenance, c. - maclean -
 Queen Victoria Women's Centre
Queen Victoria Women's CentreEnvelope, E.S. Wigg & Son Pty. Ltd, c.1996
1996 Queen Vic. Shilling Fund donation Reply Paid envelope. Cream paper. Green and navy blue ink. envelopes, charitable organisations -
 Tarnagulla History Archive
Tarnagulla History ArchiveDocument - Postal Order: Knight to Bull (?), 17th September 1867
Williams Family Collection. Probably filled out at Tarnagulla Post Office. A postal money order for funds (two pound, 10 shillings) sent from Edward Knight to W.S. Bull in Dunolly. tarnagulla -
 Tarnagulla History Archive
Tarnagulla History ArchiveDocument - Postal Order: Burstall to Ingham, 1st October 1867
Williams Family Collection. Probably filled out at Tarnagulla Post Office. Newman & Burstall were Tarnagulla butchers. A postal money order for funds (one pound, ten shillings) sent from Newman Burstall to Alfred Ingham, Melbourne. tarnagulla -
 Ringwood RSL Sub-Branch
Ringwood RSL Sub-BranchDocument Canteen Order, Australian Defence Canteens Service, C 1940
Sent to an Australian soldier serving in the Middle East in WW2WW2 Canteen Order - Australian Defence Canteens Service Value Five Shillings Issued at Healesville Post Office V108878Sent to VX5414 C. L. Cowley 22nd May 1941. Sent by Mrs E. A. Humphries C/O N. L. Taylor. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - H.A. & S.R. WILKINSON COLLECTION: RECEIPT
A copy of a receipt dated 31st July 1954. under the date the words: rs. E. Plant, 83 Sternberg Street Bendigo. Possibly for rent due by McKerlie, L. I. period 24/06/1954 to 29/07/1954 6 pounds 5 shillings and Walkerdon, R. A. period 28/06/1954 to 26/07/1954 6 pounds. A deduction of 12 shillings 3 penny is applied to bring the total to 11 pounds 12 shillings 9 penny. The document is in a manilla folder.organization, business, h.a. & s.r wilkinson real estate, yellow label 594. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - ANNALS OF BENDIGO 1910 - 1920 VOLUME 4, 1910-1920
Annals of Bendigo, 1910 - 1920 91 pages. Paper cover, with print 'The business side of Pall Mall, Bendigo, Vic. ' on front cover. Price One shilling overwritten on original price of Two Shillings and Sixpence. Printed by Cambridge Press, Bendigo. Complete. Metal clip binding. Silver duct tape on spine.G. Mackaybendigo, history, annals of bendigo, annals of bendigo -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCoin, 1948
Coin, One Shilling, dated 1948. Obverse shows George V1, Reverse shows a loin with sword and sceptre sitting on a crown.. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, one shilling, coin, british currency -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - BADHAM COLLECTION: LONDON STORES RECEIPT DATED 10.9.1928, 10/09/1928
Receipt for seven pounds nine shillings dated 10.9.1928. Paper receipt. with 2d duty stamp. London Stores Ltd. Melbournecostume, male uniform, civilian, london stores melbourne. receipt. -
 Beechworth RSL Sub-Branch
Beechworth RSL Sub-BranchArtwork, other - Trench Art - Silver ring, C: 1939 - 45
Item made Cpl W C Clark VX34546 whilst on active duty for his wife Ellen ClarkSoldiers in their down time often took to making thing (trench art). This piece was made as gift for his wifeA hand made ring made from a two shilling coin in WWII; it originally had an insert made from a plastic toothbrushtrench art -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyCoin - Coins, Royal Australian Mint, Pre-Decimal coins, 1949-1959
5 pre-decimal coins: half penny (1949), penny (1952), sixpence (1958), one shilling, damaged (1959) and florin (2 shillings) (1952).In 1966, Australian currency changed from sterling (pounds, shillings and pence) to decimal (dollars and cents). 5 coins, in black folder with contents listed on cover.currency, coins, pre-decimal coins, australian coins -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumBook, Accounts, 1924, 1928
A book of receipts dated 1925-1928 for payment of subscriptions to Presbyterian Tennis Club. Men 7/6 . Ladies 5/-shillings, Children 2/- shillingsbooks, accounts, presbyterian tennis club, receipt book, tennis club subscriptions -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Trunk
This metal travelling trunk belonged to David and Alice Ellis, a young couple married in Dublin in 1855. They left for Australia on the Schomberg clipper ship on October 6 that same year, joining the other passengers for the luxury sailing ship’s first voyage, bound for Melbourne, Australia. The Schomberg was grounded on a sand spit near Peterborough. All passengers and crew were safely rescued. They had been allowed to take something small with them when leaving the sinking vessel, and as such, Alice took a small cane basket and coin purse. The metal trunk was also amongst the couple’s possessions, along with a pair of candlesticks and a Bible. Their trunk was later retrieved from the ship’s deck by the crew of a steamer sent from Melbourne. At that time, David was 23 years old (born in Wales, in 1832) and Alice was 26 (born in Ireland, 1829). The couple lived in Tasmania for a short period before settling in the Western Districts of Victoria. David worked as a gardener and, when land in the area was available to purchase, David and Alice claimed a selection on Noorat Road near Terang. They settled there for the remainder of their lives, expanding the property that they named, ‘Allambah’, and had six children. David died in 1911, aged 79, and Alice passed away the following year, aged 83. B, B & B. Brand: - The company was renowned for its strongly constructed and high-quality travel goods. In 1906 the company was sold and renamed Buffalo Trunk Manufacturing Co. Interestingly, the trunk maker’s promise on its printed label is certainly fulfilled: - "B B BRAND. These Goods are manufactured of the best steel sheets, and are guaranteed to give every satisfaction, and will last for years."David and Alice Ellis’s donated possessions have great significance as a group of personal belongings saved from the sinking luxury clipper ship, the Schomberg, in 1855. The strong, well-crafted metal trunk is an example of high-quality travel luggage owned by newlyweds on their journey to a new life across the world. The well-made trunk is a rare shape. It joins Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg shipwreck, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612). The ship has historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, built to carry emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. The ship’s design included the technical advances needed to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. The relationship of the objects in Flagstaff Hill’s Schomberg collection allows has potential interpretation of the story of the Schomberg. The collection of objects is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger ship, as it represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history, in addition to its association with the shipwreck and the ship.Traveller's metal trunk; small brown woodgrain patterned trunk with dark red features and brass lock. This well-made strong and sturdy piece of secure hand luggage has rounded corners and sides, with the ends of the lid slightly bulbous. The lid is reinforced inside across the centre. The lid and sides have dark red metal D-shaped handles that fold down. The two hinges on the lid have their fittings inside the trunk which is hinged across the back. Two dark red painted latches secure the front along with a brass rod and lockable latch in the centre front. The metal is shaped with a group of corrugated ribs on each side of the centre, around the trunk. A white printed and lacquered label is inside the lid and has additional handwritten text. The truck was the luggage of David and Alice Ellis on the sailing ship SCHOMBERG in 1855. Printed on the label: "B B BRAND./ These Goods are manufactured of the best / steel sheets, and are guaranteed to give every / satisfaction, and will last for years." Handwritten on the label: "8/3- 7/-" (possibly meaning Eight shillings and three pence, Seven shillings)flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, schomberg, sailing ship, 1855, david and alice ellis, schomberg passengers, b b brand, american made, traveller's trunk, hand luggage, metal trunk, schomberg ship, 1855 shipwreck, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, david ellis, alice ellis, allambah terang, dublin emigrants, terang presbyterian church, western district victoria, antique trunk, vintage trunk, travel goods, travelling trunk, steel trunk, tin trunk, schomberg trunk, newlyweds, b b & b, boyd boyd & boyd, pittsburgh, rare shape, luggage, vintage luggage, victorian era, travel trunk, three locks, steamer trunk
