Showing 12790 items
matching weller
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Watch, ca 1878
HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Ladies fob watch, gold, covered in encrustation (small section has broken off to reveal the engraved surface). Face and hands are missing, revealing the workings. Found in the Loch Ard gorge and said to have been from the Loch Ard.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, ladies fob watch, gold watch, fob watch, pocket watch, horology, accessory, time keeping, scientific instrument -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePainting - Vessel, Sailing Ship, C Smith, artist, Loch Ard, late 20th century
HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Painting of 1873 sailing ship the "Loch Ard". Oil painting on board behind glass, framed in white painted timber. Artist is C Smith. Inscription on back. "Loch Ard launched 1873, sunk near Pt Campbell, with loss of 52 lives 1878" "C. Smith" "Loch Ard" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, loch ard gorge, maritime oil painting, c. smith, sailing vessel -
 National Communication Museum
National Communication MuseumVehicle - Mobile Telephone Exchange, c. 1965
Manufactured in the 1960s, this mobile emergency telephone exchange was fitted into a caravan. Part of the Shepparton Division State Disaster Plan, the caravan could be towed to areas affected by disasters to enable communications to recommence. The caravan remained in service until approximately 1974.Mobile infrastructure plays an important role in Australian communications, owing to the often remote and hostile environments in which Australians live and work. Exchanges such as this facilitated phone calls in the aftermath of an emergency, particularly for hospitals, police and other emergency services. Today, Mobile Exchange on Wheels (MEOWs), Cell on Wheels (CoW) and Satellite Cell on Wheels (SatCOW) - which provide temporary landline and broadband services, mobile phone coverage and service in areas without communications infrastructure respectively - are a critical part of emergency response procedures for natural disasters such as fire and flood. Though technology has progressed, the need for rapid service in remote areas remains a present concern of the communications service providers in Australia. This mobile service infrastructure is historically significant as an early example of a service which has evolved over decades, yet is still needed today. The exchange, as a representative example of a vehicle which would provide early-response in a disaster, is socially significant as a facilitator of critical communications needs in devastated communities: access to emergency services and contact with family and friends. The exchange itself, intact from its period of use, provides an insight into technology of the 1970s.Mobile emergency exchange housed in a caravan trailer on 2 wheel base, duralin body, steel tow bar, Caravan divided into 3 sections; the exchange room; the relay room and the main frame room. The exchange room contains 3 switchboards, a folding table, cupboards, benches and switch rack (.1). table (.2), steel bar for attaching the table (.3), back boards of switchboards (.4-.6), switches (.7-.16), box of switches (.17). There is a wall phone magneto, 300 type handset on wall and 2 skylights with wire screens. .11? hat pegs and shelf; there are 2 fluorescent tubes for lighting, all in exchange section. The floor is covered with 2 tone grey tiles and there are wire mesh on outside of windows and a geometric curtain inside behind switch rack. There is a flywire screen door as well as exterior door. The relay room has a sectioned door so half can open at a time. Room contains a cupboard with folding bench top beneath a curtained window. The opposite wall has a bank of batteries and transmission condensers; there is a shelf above window, one fluorescent tube and fuse boxes. Tiles on floor also. The main frame room contains many metres of coiled black covered cable, a black covered magneto wall telephone with 300 type handset; grey plastic jumper cords, a rack of termination points and wire with wasp nests attached. There is a small iron step under door, a fluorescent tube on wall and 3 hat hooks. Roll of Paper Handtowels (.18), cord and handle (.19), red exchange cords and plugs (.20-.22), plastic aluminium runners (.23,.24), headset (.25,.26), logbook (.27), battery readings (.28), box containing papers circuit drawings etc (.29-.93), paper lists off wall (.94,.95). Books, record books etc (.96-.103). Manila folder (.104) containing circuit drawings (105-.124). Wooden drawer (.125), metal drawer containing subscribers master cards, record of faults cards, particular switchboards connected, Junction line cards (.126). Box of valves (.127), box of clamps (.128). Box of 2000 type rack fuses, red 1 1/2 AMPS, black 3 AMP, blue 1/2 AMP (.129). Box of sleeves for covering wire joints (.130), plastic beakers (.131,.132), soap (.133), box of white plastic squares (.134), time switch "Venner BF/43 time switch" Made in England (.135), box of bolts, knobs etc (.136), box of switchboard number indicators (.137), fuse (.138), fuse wire (.139), football card (.140). Box of cartridge fuse 6 AMP (.141). Envelope of drawing pins, rubber bands (.142), black plastic, paper tape centres (.143-.152), metal plug (.153), 2 signs "Beware of vehicles" (.154-.155). Paper listing Naringal East automatic conversion (.156). Green Commonwealth of Australia note pad (.157). Wiring plug for tail lights (.158). Black fuse plugs (.159,.160). Box of bolts (.161). 2 sections of blue plastic coated wires (.162,.163). Gloves used for working on batteries (.164-.167). Wasp nests (.168,.169). White fuse (.170). Photographs of van in use (.171,.172)..1 on front: "ANOTHER / MOBILETRAIL / PRODUCT" "MAX SPEED / 25MPH" "TRAILER BRAKES / --- / " On sides: "EMERGENCY TELEPHONE EXCHANGE" "NO 1" "PMG" "TCQ / GROSS 250 / TARE 182 / LOAD 162" "6" "COUNTRY BRANCH / NORTH REGION / [SHEPPARTON DIVISION]" "LAW'S SIGNS" "Telecom Australia" On back: "DANGER / LONG LOAD" "MQA 3787" .133: "FIR OIL" "AUSTRALIA"mobile telephone exchanges, mobile telecommunications trailers, trailers, transport, natural disaster, black saturday, bushfires, floods, emergency communications -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionWork on paper - Vertical file, City of Camberwell
A vertical file of clippings and general information relating to the City of Camberwell including: 1. Election notice, The Argus, 28.8.1937 (1 page). 2. “City news”: Council announces conservation position. Undated. (8 pages). 3. “Council to introduce new waste collection”. Undated Council publication. (4 pages). 4. Camberwell newsletter (incomplete, undated). (4 pages). 5. Camberwell City News, December 1983. (8 pages). 6. Camberwell City News, October, 1984. (8 pages). 7. City of Camberwell 1984/5 budget. (8 pages). 8. ‘’Recycling – It’s up to you’’ (source uncertain, like Council publication undated). (1 page). 9. ‘’Big bins arrive’’, Free Press, 1.2.1984. (1 page). 10. New bins photo and article – no heading; Free Press, 11 April 1884 with note re role of Cr Jim Rumpf. 11. Booklet: Camberwell Your City 82, 31 pages includes business ads as well as municipal information; published 1982. 12. Article re Richard Pearse, newly elected councillor re his philosophy; SHNN No 9, April / May 1984. 13. Article re Mary Drost, newly elected councillor re her philosophy; SHNN No 4, June / July, 1983. 14. Article re Irene Wegner, newly elected councillor re his philosophy; SHNN No 18, October / November 1985. 15. Article asking questions of ward candidates Patrick Trost and Alex Briggs, SHNN No 11, August / September 1984. 16. Articles re new councillors Jennie Carey and Sally Brentnall, SHNN No 39, April /May 1989. 17. Articles re views of ward candidates Wendy Nettle, David McCloskey and Alan Black, SHNN No 23, August / September 1986. 18. Article re CEO Brian Jones, SHNN No 39, April / may 1989. 19. Article questioning Council's conservation strategy in the light of proposed Red rooster development and forthcoming sale of then post office in Canterbury Road, SHHN No 64, June / July 1993. 20. Article urging voting at August 1992 local government elections; candidates mentioned: Bryan Steele, Joe Stanley, Ted Dugdale, Ilias Gouletas, Dennis Whelan, Phillip Barresi, SHNN No 59, August / September 1992. 21. Article re Phillip Barresi and Ilias Gouletsas - with photos, SHNN No 59, August / September 1992. 22. Article re Dennis Whelan and Ted Dugdale - with photos, SHNN No 59, August / September 1992. 23. Exhibition pamphlet: 'Camberwell - As we were' produced for Victoria's 150th anniversary, 3-21 June 1985. (REF: SH2023/1/2) 24. Pamphlet re Centenary of proclamation of Boroondara Shire, 17 November 1871; includes photos. (REF: SH2023/1/5) 25. Letter from John Paech to Miss V White of Barton Street re opposition to proposed transfer of part of Surrey Hills from City of Camberwell to City of Box Hill, dated 25 July 1986. NB/ Correspondant is Miss Val White. 26. City of Camberwell By-Law No 214 - Incinerator, BBQ & Open Air Burning By-Law, dated 20 April 1988. 27. City of Camberwell By-Law No 207 - Prevention & extinguishing fires, suppressing nuisances, and regulating times incinerators may be used; dated 16 July 1984. city of camberwell, cr jim rumpf, waste collection, recycling, local government -
 Old Castlemaine Schoolboys Association Inc.
Old Castlemaine Schoolboys Association Inc.Poem, The Castlemaine Old Schoolboys' Annual Reunion
Written by George E Scott who was born in Creswick March 1900. Moved to Vaughan in 1904. Attended Yapeen State School utill 1913 then to Castlemaine high school and technical schools. Poem written in 1950s.There is a lift to the old boys step tonight, and is feeling young and gay his eyes are bright and his heart is light, and his thoughts are far away. Back in his dear old Castlemaine, or out in the hills around living the days of his youth again feeling his pulses bound. For he's just answered the call that comes to the loyal hearts every year insistent, clear as the beating of drums it falls on the listening ear so the old boy went and his mates went to back home in their hundreds strong and years were bridged in at long day through in story and speech and song. At at the Bush school love so well he gathered with his comrades gay, old Lads and Lassie's with tales to tell of memories tucked away. And bright eyed children had joined them in there happy young faces shone, as they showed old scholars are pride and care in the school that was handed on. Around them the bushland was bright with flowers, and the dear little orchid blue Bloom there with bright, in the sunlit bowers- for it is our emblem true. So the old boy drained through that day again, and it lifted his heart like a song, then Knight came down on the old home town and the hall, with its happy throng. In long brave lines they had mustered there as they had on the days of yore, and as they answered the roll - but the years take toll- there were mates who would come no more. The toast called, and the speeches made, when, trooping into the hall, with faces bright, and their eyes alight, came the girls- the toast of them all. So they broke up and wandered and formed into groups, while many have time for a song, But bashing the ear was permissible here, and they kept at it- steady and long. So the hours flitted by happiest notes of memories sweet old refrain, old friendships renewed - past doing's reviewed, the old boy was feeling strain. For his ears had been punished, his hand had been wrung, his voice was hoarse as a crow, with an ache in his jaw- "I can't take any more, while I'm all in one piece, mates, I'll go." With Auld lang syne is singing a broke up and parted, "next year we will see you again" when the message goes ringing, their thoughts will go winging and calling them back to 'Mainepoem, yapeen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, From The Earth to The Moon
This item is from the ‘Pattison Collection’, a collection of books and records that was originally owned by the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute, which was founded in Warrnambool in 1853. By 1886 the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) had grown to have a Library, Museum and Fine Arts Gallery, with a collection of “… choice productions of art, and valuable specimens in almost every branch and many wonderful national curiosities are now to be seen there, including historic relics of the town and district.” It later included a School of Design. Although it was very well patronised, the lack of financial support led the WMI in 1911 to ask the City Council to take it over. In 1935 Ralph Pattison was appointed as City Librarian to establish and organise the Warrnambool Library as it was then called. When the WMI building was pulled down in 1963 a new civic building was erected on the site and the new Warrnambool Library, on behalf of the City Council, took over all the holdings of the WMI. At this time some of the items were separated and identified as the ‘Pattison Collection’, named after Ralph Pattison. Eventually the components of the WMI were distributed from the Warrnambool Library to various places, including the Art Gallery, Historical Society and Flagstaff Hill. Later some were even distributed to other regional branches of Corangamite Regional Library and passed to and fro. It is difficult now to trace just where all of the items have ended up. The books at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village generally display stamps and markings from Pattison as well as a variety of other institutions including the Mechanics’ Institute itself. RALPH ERIC PATTISON Ralph Eric Pattison was born in Rockhampton, Queensland, in 1891. He married Maude Swan from Warrnambool in 1920 and they set up home in Warrnambool. In 1935 Pattison accepted a position as City Librarian for the Warrnambool City Council. His huge challenge was to make a functional library within two rooms of the Mechanics’ Institute. He tirelessly cleaned, cleared and sorted a disarrayed collection of old books, jars of preserved specimens and other items reserved for exhibition in the city’s museum. He developed and updated the library with a wide variety of books for all tastes, including reference books for students; a difficult task to fulfil during the years following the Depression. He converted all of the lower area of the building into a library, reference room and reading room for members and the public. The books were sorted and stored using a cataloguing and card index system that he had developed himself. He also prepared the upper floor of the building and established the Art Gallery and later the Museum, a place to exhibit the many old relics that had been stored for years for this purpose. One of the treasures he found was a beautiful ancient clock, which he repaired, restored and enjoyed using in his office during the years of his service there. Ralph Pattison was described as “a meticulous gentleman whose punctuality, floorless courtesy and distinctive neat dress were hallmarks of his character, and ‘his’ clock controlled his daily routine, and his opening and closing of the library’s large heavy doors to the minute.” Pattison took leave during 1942 to 1945 to serve in the Royal Australian Navy, Volunteer Reserve as Lieutenant. A few years later he converted one of the Museum’s rooms into a Children’s Library, stocking it with suitable books for the younger generation. This was an instant success. In the 1950’s he had the honour of being appointed to the Victorian Library Board and received more inspiration from the monthly conferences in Melbourne. He was sadly retired in 1959 after over 23 years of service, due to the fact that he had gone over the working age of council officers. However he continued to take a very keen interest in the continual development of the Library until his death in 1969. WARRNAMBOOL PUBLIC LIBRARY The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison. Jules Verne (1828–1905) Jules Verne pursued his writing career after finishing law school in 1849, during this time he was writing poetry and short stories. He began to hit his stride after meeting publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel in1862, who nurtured many of the works that would later comprise the author's 54 novels the (Voyages Extraordinaires). Often referred to as the "Father of Science Fiction," Verne wrote books about a variety of innovations and technological advancements years before they were practical realities. In 1856, Verne met and fell in love with Honorine de Viane, a young widow with two daughters. They married in 1857, and in 1861, the couple's only child, Michel Jean Pierre Verne, was born. Realizing he needed a stronger financial foundation, Verne began working as a stockbroker. However, he refused to abandon his writing career, and that year he published his first book, The 1857 Salon (Le Salon de 1857). In all Verne authored more than 60 books as well as dozens of plays, short stories and librettos. He conjured hundreds of memorable characters and imagined countless innovations years before their time, including stories about submarine and space travel, terrestrial flight and deep-sea exploration. Jules Verne died in 1905, at his residence in the French city of Amiens, stricken with diabetes, on March 24, 1905. Verne had many memorable novels, his most famous being Five Weeks in a Balloon, Journey to the Centre of the Earth, From the Earth to the Moon, Around the World in Eighty Days, In Search of the Castaways and Twenty Thousand Leagues under the Sea Additional works surfaced decades later. Backwards to Britain based on his many trips to the United Kingdom was finally printed in 1989, 130 years after it was written. Also Paris in the Twentieth Century, originally considered too far-fetched with its depictions of skyscrapers, gas-fuelled cars and mass transit systems, followed in 1994. Citation Information Biography.com Editors Jules Verne Biography: https://www.biography.com/writer/jules-verne The Pattison Collection, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. The Warrnambool Mechanics Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and the important role it played in the intellectual, cultural and social development of people throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance. From The Earth to The Moon Author: Jules Verne Label on spine cover with typed text PAT 843 VER Front loose endpaper has sticker from Warrnambool Public Library covered by a sticker from Corangamite Regional Library Service Front loose endpaper has a stamp from Corangamite Regional Library Servicewarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, pattison collection, warrnambool library, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, ralph eric pattison, corangamite regional library service, warrnambool city librarian, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, warrnambool children’s library, great ocean road, from the earth to the moon, jules verne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, The Steam House Part 1 The Demon of Cawnpore
This item is from the ‘Pattison Collection’, a collection of books and records that was originally owned by the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute, which was founded in Warrnambool in 1853. By 1886 the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) had grown to have a Library, Museum and Fine Arts Gallery, with a collection of “… choice productions of art, and valuable specimens in almost every branch and many wonderful national curiosities are now to be seen there, including historic relics of the town and district.” It later included a School of Design. Although it was very well patronised, the lack of financial support led the WMI in 1911 to ask the City Council to take it over. In 1935 Ralph Pattison was appointed as City Librarian to establish and organise the Warrnambool Library as it was then called. When the WMI building was pulled down in 1963 a new civic building was erected on the site and the new Warrnambool Library, on behalf of the City Council, took over all the holdings of the WMI. At this time some of the items were separated and identified as the ‘Pattison Collection’, named after Ralph Pattison. Eventually the components of the WMI were distributed from the Warrnambool Library to various places, including the Art Gallery, Historical Society and Flagstaff Hill. Later some were even distributed to other regional branches of Corangamite Regional Library and passed to and fro. It is difficult now to trace just where all of the items have ended up. The books at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village generally display stamps and markings from Pattison as well as a variety of other institutions including the Mechanics’ Institute itself. RALPH ERIC PATTISON Ralph Eric Pattison was born in Rockhampton, Queensland, in 1891. He married Maude Swan from Warrnambool in 1920 and they set up home in Warrnambool. In 1935 Pattison accepted a position as City Librarian for the Warrnambool City Council. His huge challenge was to make a functional library within two rooms of the Mechanics’ Institute. He tirelessly cleaned, cleared and sorted a disarrayed collection of old books, jars of preserved specimens and other items reserved for exhibition in the city’s museum. He developed and updated the library with a wide variety of books for all tastes, including reference books for students; a difficult task to fulfil during the years following the Depression. He converted all of the lower area of the building into a library, reference room and reading room for members and the public. The books were sorted and stored using a cataloguing and card index system that he had developed himself. He also prepared the upper floor of the building and established the Art Gallery and later the Museum, a place to exhibit the many old relics that had been stored for years for this purpose. One of the treasures he found was a beautiful ancient clock, which he repaired, restored and enjoyed using in his office during the years of his service there. Ralph Pattison was described as “a meticulous gentleman whose punctuality, floorless courtesy and distinctive neat dress were hallmarks of his character, and ‘his’ clock controlled his daily routine, and his opening and closing of the library’s large heavy doors to the minute.” Pattison took leave during 1942 to 1945 to serve in the Royal Australian Navy, Volunteer Reserve as Lieutenant. A few years later he converted one of the Museum’s rooms into a Children’s Library, stocking it with suitable books for the younger generation. This was an instant success. In the 1950’s he had the honour of being appointed to the Victorian Library Board and received more inspiration from the monthly conferences in Melbourne. He was sadly retired in 1959 after over 23 years of service, due to the fact that he had gone over the working age of council officers. However he continued to take a very keen interest in the continual development of the Library until his death in 1969. WARRNAMBOOL PUBLIC LIBRARY The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison. Jules Verne (1828–1905) Jules Verne pursued his writing career after finishing law school in 1849, during this time he was writing poetry and short stories. He began to hit his stride after meeting publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel in1862, who nurtured many of the works that would later comprise the author's 54 novels the (Voyages Extraordinaires). Often referred to as the "Father of Science Fiction," Verne wrote books about a variety of innovations and technological advancements years before they were practical realities. In 1856, Verne met and fell in love with Honorine de Viane, a young widow with two daughters. They married in 1857, and in 1861, the couple's only child, Michel Jean Pierre Verne, was born. Realizing he needed a stronger financial foundation, Verne began working as a stockbroker. However, he refused to abandon his writing career, and that year he published his first book, The 1857 Salon (Le Salon de 1857). In all Verne authored more than 60 books as well as dozens of plays, short stories and librettos. He conjured hundreds of memorable characters and imagined countless innovations years before their time, including stories about submarine and space travel, terrestrial flight and deep-sea exploration. Jules Verne died in 1905, at his residence in the French city of Amiens, stricken with diabetes, on March 24, 1905. Verne had many memorable novels, his most famous being Five Weeks in a Balloon, Journey to the Centre of the Earth, From the Earth to the Moon, Around the World in Eighty Days, In Search of the Castaways and Twenty Thousand Leagues under the Sea Additional works surfaced decades later. Backwards to Britain based on his many trips to the United Kingdom was finally printed in 1989, 130 years after it was written. Also Paris in the Twentieth Century, originally considered too far-fetched with its depictions of skyscrapers, gas-fuelled cars and mass transit systems, followed in 1994. Citation Information Biography.com Editors Jules Verne Biography: https://www.biography.com/writer/jules-verne The Pattison Collection, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. The Warrnambool Mechanics Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and the important role it played in the intellectual, cultural and social development of people throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance. The Steam House Part 1 The Demon of Cawnpore Author: Jules Verne Publisher: Samson Low, Marston, Searle & Rivington Label on spine cover with typed text PAT 843 VER Front loose endpaper has sticker from Warrnambool Public Library covered by a sticker from Corangamite Regional Library Service Front loose endpaper has a stamp from Corangamite Regional Library Servicewarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, pattison collection, warrnambool library, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, ralph eric pattison, corangamite regional library service, warrnambool city librarian, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, warrnambool children’s library, great ocean road, the steam house part 1 the demon of cawnpore, the demon of cawnpore, jules verne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, The Tribulations of A Chinaman
This item is from the ‘Pattison Collection’, a collection of books and records that was originally owned by the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute, which was founded in Warrnambool in 1853. By 1886 the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) had grown to have a Library, Museum and Fine Arts Gallery, with a collection of “… choice productions of art, and valuable specimens in almost every branch and many wonderful national curiosities are now to be seen there, including historic relics of the town and district.” It later included a School of Design. Although it was very well patronised, the lack of financial support led the WMI in 1911 to ask the City Council to take it over. In 1935 Ralph Pattison was appointed as City Librarian to establish and organise the Warrnambool Library as it was then called. When the WMI building was pulled down in 1963 a new civic building was erected on the site and the new Warrnambool Library, on behalf of the City Council, took over all the holdings of the WMI. At this time some of the items were separated and identified as the ‘Pattison Collection’, named after Ralph Pattison. Eventually the components of the WMI were distributed from the Warrnambool Library to various places, including the Art Gallery, Historical Society and Flagstaff Hill. Later some were even distributed to other regional branches of Corangamite Regional Library and passed to and fro. It is difficult now to trace just where all of the items have ended up. The books at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village generally display stamps and markings from Pattison as well as a variety of other institutions including the Mechanics’ Institute itself. RALPH ERIC PATTISON Ralph Eric Pattison was born in Rockhampton, Queensland, in 1891. He married Maude Swan from Warrnambool in 1920 and they set up home in Warrnambool. In 1935 Pattison accepted a position as City Librarian for the Warrnambool City Council. His huge challenge was to make a functional library within two rooms of the Mechanics’ Institute. He tirelessly cleaned, cleared and sorted a disarrayed collection of old books, jars of preserved specimens and other items reserved for exhibition in the city’s museum. He developed and updated the library with a wide variety of books for all tastes, including reference books for students; a difficult task to fulfil during the years following the Depression. He converted all of the lower area of the building into a library, reference room and reading room for members and the public. The books were sorted and stored using a cataloguing and card index system that he had developed himself. He also prepared the upper floor of the building and established the Art Gallery and later the Museum, a place to exhibit the many old relics that had been stored for years for this purpose. One of the treasures he found was a beautiful ancient clock, which he repaired, restored and enjoyed using in his office during the years of his service there. Ralph Pattison was described as “a meticulous gentleman whose punctuality, floorless courtesy and distinctive neat dress were hallmarks of his character, and ‘his’ clock controlled his daily routine, and his opening and closing of the library’s large heavy doors to the minute.” Pattison took leave during 1942 to 1945 to serve in the Royal Australian Navy, Volunteer Reserve as Lieutenant. A few years later he converted one of the Museum’s rooms into a Children’s Library, stocking it with suitable books for the younger generation. This was an instant success. In the 1950’s he had the honour of being appointed to the Victorian Library Board and received more inspiration from the monthly conferences in Melbourne. He was sadly retired in 1959 after over 23 years of service, due to the fact that he had gone over the working age of council officers. However he continued to take a very keen interest in the continual development of the Library until his death in 1969. WARRNAMBOOL PUBLIC LIBRARY The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison. Jules Verne (1828–1905) Jules Verne pursued his writing career after finishing law school in 1849, during this time he was writing poetry and short stories. He began to hit his stride after meeting publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel in1862, who nurtured many of the works that would later comprise the author's 54 novels the (Voyages Extraordinaires). Often referred to as the "Father of Science Fiction," Verne wrote books about a variety of innovations and technological advancements years before they were practical realities. In 1856, Verne met and fell in love with Honorine de Viane, a young widow with two daughters. They married in 1857, and in 1861, the couple's only child, Michel Jean Pierre Verne, was born. Realizing he needed a stronger financial foundation, Verne began working as a stockbroker. However, he refused to abandon his writing career, and that year he published his first book, The 1857 Salon (Le Salon de 1857). In all Verne authored more than 60 books as well as dozens of plays, short stories and librettos. He conjured hundreds of memorable characters and imagined countless innovations years before their time, including stories about submarine and space travel, terrestrial flight and deep-sea exploration. Jules Verne died in 1905, at his residence in the French city of Amiens, stricken with diabetes, on March 24, 1905. Verne had many memorable novels, his most famous being Five Weeks in a Balloon, Journey to the Centre of the Earth, From the Earth to the Moon, Around the World in Eighty Days, In Search of the Castaways and Twenty Thousand Leagues under the Sea Additional works surfaced decades later. Backwards to Britain based on his many trips to the United Kingdom was finally printed in 1989, 130 years after it was written. Also Paris in the Twentieth Century, originally considered too far-fetched with its depictions of skyscrapers, gas-fuelled cars and mass transit systems, followed in 1994. Citation Information Biography.com Editors Jules Verne Biography: https://www.biography.com/writer/jules-verne The Pattison Collection, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. The Warrnambool Mechanics Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and the important role it played in the intellectual, cultural and social development of people throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance. The Tribulations of A Chinaman Author: Jules Verne Publisher: Samson Low, Marston, Searle & Rivington Date: 1885Label on spine cover with typed text PAT 843 VER Fron loose endpaper has sticker from Warrnambool Public Library covered by a sticker from Corangamite Regional Library Service Front loose endpaper has a stamp from Corangamite Regional Library Servicewarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, pattison collection, warrnambool library, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, ralph eric pattison, corangamite regional library service, warrnambool city librarian, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, warrnambool children’s library, great ocean road, the tribulations of a chinaman, jules verne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, The Steam House Part 2 Tigers and Traitors
This item is from the ‘Pattison Collection’, a collection of books and records that was originally owned by the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute, which was founded in Warrnambool in 1853. By 1886 the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) had grown to have a Library, Museum and Fine Arts Gallery, with a collection of “… choice productions of art, and valuable specimens in almost every branch and many wonderful national curiosities are now to be seen there, including historic relics of the town and district.” It later included a School of Design. Although it was very well patronised, the lack of financial support led the WMI in 1911 to ask the City Council to take it over. In 1935 Ralph Pattison was appointed as City Librarian to establish and organise the Warrnambool Library as it was then called. When the WMI building was pulled down in 1963 a new civic building was erected on the site and the new Warrnambool Library, on behalf of the City Council, took over all the holdings of the WMI. At this time some of the items were separated and identified as the ‘Pattison Collection’, named after Ralph Pattison. Eventually the components of the WMI were distributed from the Warrnambool Library to various places, including the Art Gallery, Historical Society and Flagstaff Hill. Later some were even distributed to other regional branches of Corangamite Regional Library and passed to and fro. It is difficult now to trace just where all of the items have ended up. The books at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village generally display stamps and markings from Pattison as well as a variety of other institutions including the Mechanics’ Institute itself. RALPH ERIC PATTISON Ralph Eric Pattison was born in Rockhampton, Queensland, in 1891. He married Maude Swan from Warrnambool in 1920 and they set up home in Warrnambool. In 1935 Pattison accepted a position as City Librarian for the Warrnambool City Council. His huge challenge was to make a functional library within two rooms of the Mechanics’ Institute. He tirelessly cleaned, cleared and sorted a disarrayed collection of old books, jars of preserved specimens and other items reserved for exhibition in the city’s museum. He developed and updated the library with a wide variety of books for all tastes, including reference books for students; a difficult task to fulfil during the years following the Depression. He converted all of the lower area of the building into a library, reference room and reading room for members and the public. The books were sorted and stored using a cataloguing and card index system that he had developed himself. He also prepared the upper floor of the building and established the Art Gallery and later the Museum, a place to exhibit the many old relics that had been stored for years for this purpose. One of the treasures he found was a beautiful ancient clock, which he repaired, restored and enjoyed using in his office during the years of his service there. Ralph Pattison was described as “a meticulous gentleman whose punctuality, floorless courtesy and distinctive neat dress were hallmarks of his character, and ‘his’ clock controlled his daily routine, and his opening and closing of the library’s large heavy doors to the minute.” Pattison took leave during 1942 to 1945 to serve in the Royal Australian Navy, Volunteer Reserve as Lieutenant. A few years later he converted one of the Museum’s rooms into a Children’s Library, stocking it with suitable books for the younger generation. This was an instant success. In the 1950’s he had the honour of being appointed to the Victorian Library Board and received more inspiration from the monthly conferences in Melbourne. He was sadly retired in 1959 after over 23 years of service, due to the fact that he had gone over the working age of council officers. However he continued to take a very keen interest in the continual development of the Library until his death in 1969. WARRNAMBOOL PUBLIC LIBRARY The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison. Jules Verne (1828–1905) Jules Verne pursued his writing career after finishing law school in 1849, during this time he was writing poetry and short stories. He began to hit his stride after meeting publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel in1862, who nurtured many of the works that would later comprise the author's 54 novels the (Voyages Extraordinaires). Often referred to as the "Father of Science Fiction," Verne wrote books about a variety of innovations and technological advancements years before they were practical realities. In 1856, Verne met and fell in love with Honorine de Viane, a young widow with two daughters. They married in 1857, and in 1861, the couple's only child, Michel Jean Pierre Verne, was born. Realizing he needed a stronger financial foundation, Verne began working as a stockbroker. However, he refused to abandon his writing career, and that year he published his first book, The 1857 Salon (Le Salon de 1857). In all Verne authored more than 60 books as well as dozens of plays, short stories and librettos. He conjured hundreds of memorable characters and imagined countless innovations years before their time, including stories about submarine and space travel, terrestrial flight and deep-sea exploration. Jules Verne died in 1905, at his residence in the French city of Amiens, stricken with diabetes, on March 24, 1905. Verne had many memorable novels, his most famous being Five Weeks in a Balloon, Journey to the Centre of the Earth, From the Earth to the Moon, Around the World in Eighty Days, In Search of the Castaways and Twenty Thousand Leagues under the Sea Additional works surfaced decades later. Backwards to Britain based on his many trips to the United Kingdom was finally printed in 1989, 130 years after it was written. Also Paris in the Twentieth Century, originally considered too far-fetched with its depictions of skyscrapers, gas-fuelled cars and mass transit systems, followed in 1994. Citation Information Biography.com Editors Jules Verne Biography: https://www.biography.com/writer/jules-verne The Pattison Collection, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. The Warrnambool Mechanics Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and the important role it played in the intellectual, cultural and social development of people throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance. The Steam House Part 2 Tigers and Traitors Author: Jules Verne Publisher: Sampson Low, Marston, Searle & Rivington Date: 1887Label on spine cover with typed text PAT 843 VER Front endpaper has sticker from Warrnambool Public Library covered by a sticker from Corangamite Regional Library Service Front loose endpaper has a stamp from Corangamite Regional Library Service warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, pattison collection, warrnambool library, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, ralph eric pattison, corangamite regional library service, warrnambool city librarian, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, warrnambool children’s library, great ocean road, the steam house part 2 tigers and traitors, jules verne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Fiction, Jules Verne, The Giant Raft Part 2 The Cryptogram, 1885
This book is one of several books in Flagstaff Hill's historic book collection by the author Jules Verne, who was a popular mid-to-late 19th-century fiction author. Some of his works included Journey to the Center of the Earth, Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea, and Around the World in Eighty Days. The book is part of the Pattison Collection. This item is from the ‘Pattison Collection’, a collection of books and records that was originally owned by the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute, which was founded in Warrnambool in 1853. By 1886 the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) had grown to have a Library, Museum and Fine Arts Gallery, with a collection of “… choice productions of art, and valuable specimens in almost every branch and many wonderful national curiosities are now to be seen there, including historic relics of the town and district.” It later included a School of Design. Although it was very well patronised, the lack of financial support led the WMI in 1911 to ask the City Council to take it over. In 1935 Ralph Pattison was appointed as City Librarian to establish and organise the Warrnambool Library as it was then called. When the WMI building was pulled down in 1963 a new civic building was erected on the site and the new Warrnambool Library, on behalf of the City Council, took over all the holdings of the WMI. At this time some of the items were separated and identified as the ‘Pattison Collection’, named after Ralph Pattison. Eventually the components of the WMI were distributed from the Warrnambool Library to various places, including the Art Gallery, Historical Society and Flagstaff Hill. Later some were even distributed to other regional branches of Corangamite Regional Library and passed to and fro. It is difficult now to trace just where all of the items have ended up. The books at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village generally display stamps and markings from Pattison as well as a variety of other institutions including the Mechanics’ Institute itself. RALPH ERIC PATTISON Ralph Eric Pattison was born in Rockhampton, Queensland, in 1891. He married Maude Swan from Warrnambool in 1920 and they set up home in Warrnambool. In 1935 Pattison accepted a position as City Librarian for the Warrnambool City Council. His huge challenge was to make a functional library within two rooms of the Mechanics’ Institute. He tirelessly cleaned, cleared and sorted a disarrayed collection of old books, jars of preserved specimens and other items reserved for exhibition in the city’s museum. He developed and updated the library with a wide variety of books for all tastes, including reference books for students; a difficult task to fulfil during the years following the Depression. He converted all of the lower area of the building into a library, reference room and reading room for members and the public. The books were sorted and stored using a cataloguing and card index system that he had developed himself. He also prepared the upper floor of the building and established the Art Gallery and later the Museum, a place to exhibit the many old relics that had been stored for years for this purpose. One of the treasures he found was a beautiful ancient clock, which he repaired, restored and enjoyed using in his office during the years of his service there. Ralph Pattison was described as “a meticulous gentleman whose punctuality, floorless courtesy and distinctive neat dress were hallmarks of his character, and ‘his’ clock controlled his daily routine, and his opening and closing of the library’s large heavy doors to the minute.” Pattison took leave during 1942 to 1945 to serve in the Royal Australian Navy, Volunteer Reserve as Lieutenant. A few years later he converted one of the Museum’s rooms into a Children’s Library, stocking it with suitable books for the younger generation. This was an instant success. In the 1950’s he had the honour of being appointed to the Victorian Library Board and received more inspiration from the monthly conferences in Melbourne. He was sadly retired in 1959 after over 23 years of service, due to the fact that he had gone over the working age of council officers. However he continued to take a very keen interest in the continual development of the Library until his death in 1969. WARRNAMBOOL PUBLIC LIBRARY The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison. Jules Verne (1828–1905) Jules Verne pursued his writing career after finishing law school in 1849, during this time he was writing poetry and short stories. He began to hit his stride after meeting publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel in1862, who nurtured many of the works that would later comprise the author's 54 novels the (Voyages Extraordinaires). Often referred to as the "Father of Science Fiction," Verne wrote books about a variety of innovations and technological advancements years before they were practical realities. In 1856, Verne met and fell in love with Honorine de Viane, a young widow with two daughters. They married in 1857, and in 1861, the couple's only child, Michel Jean Pierre Verne, was born. Realizing he needed a stronger financial foundation, Verne began working as a stockbroker. However, he refused to abandon his writing career, and that year he published his first book, The 1857 Salon (Le Salon de 1857). In all Verne authored more than 60 books as well as dozens of plays, short stories and librettos. He conjured hundreds of memorable characters and imagined countless innovations years before their time, including stories about submarine and space travel, terrestrial flight and deep-sea exploration. Jules Verne died in 1905, at his residence in the French city of Amiens, stricken with diabetes, on March 24, 1905. Verne had many memorable novels, his most famous being Five Weeks in a Balloon, Journey to the Centre of the Earth, From the Earth to the Moon, Around the World in Eighty Days, In Search of the Castaways and Twenty Thousand Leagues under the Sea Additional works surfaced decades later. Backwards to Britain based on his many trips to the United Kingdom was finally printed in 1989, 130 years after it was written. Also Paris in the Twentieth Century, originally considered too far-fetched with its depictions of skyscrapers, gas-fuelled cars and mass transit systems, followed in 1994. Citation Information Biography.com Editors Jules Verne Biography: https://www.biography.com/writer/jules-verne The Pattison Collection, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. The Warrnambool Mechanics Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and the important role it played in the intellectual, cultural and social development of people throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance. Book; The Giant Raft (Part II) The Cryptogram Author: Jules Verne Publisher: Sampson Low, Marston, Searle & Rivington Date: 1885 Blue hardcover book with fabric on cover. The title and original library shelf location are printed on the spine. A line drawing on the fly page is within a circle bordered by a vine plant. Within the circle is a man dressed in a suit, wearing a cravat, holding an unravelled scroll with marks like a crossword, and tugging at a vine wrapped around his neck. This illustrated fiction book has a handwritten paper label taped to the spine. The fly page has a handwritten inscription. The book is part of the Pattison Collection. Label "PAT 843 VER" Front loose endpaper sticker: "Warrnambool Public Library" covered by a sticker from "Corangamite Regional Library Service" Front loose endpaper Stamped "Corangamite Regional Library Service" Handwritten script inscription on Fly "C. L F. (or could be T.) 2/4/. (could be 2 pounds 4 shillings)" On Fly page "ILLUSTRATED" "1885"warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, pattison collection, warrnambool library, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, ralph eric pattison, corangamite regional library service, warrnambool city librarian, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, warrnambool children’s library, great ocean road, the giant raft part 2 the cryptogram, jules verne, the cryptogram, the giant raft, science fiction, 1885 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, Keraban The Inflexible (part 1) The Captain of The Guidara
This item is from the ‘Pattison Collection’, a collection of books and records that was originally owned by the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute, which was founded in Warrnambool in 1853. By 1886 the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) had grown to have a Library, Museum and Fine Arts Gallery, with a collection of “… choice productions of art, and valuable specimens in almost every branch and many wonderful national curiosities are now to be seen there, including historic relics of the town and district.” It later included a School of Design. Although it was very well patronised, the lack of financial support led the WMI in 1911 to ask the City Council to take it over. In 1935 Ralph Pattison was appointed as City Librarian to establish and organise the Warrnambool Library as it was then called. When the WMI building was pulled down in 1963 a new civic building was erected on the site and the new Warrnambool Library, on behalf of the City Council, took over all the holdings of the WMI. At this time some of the items were separated and identified as the ‘Pattison Collection’, named after Ralph Pattison. Eventually the components of the WMI were distributed from the Warrnambool Library to various places, including the Art Gallery, Historical Society and Flagstaff Hill. Later some were even distributed to other regional branches of Corangamite Regional Library and passed to and fro. It is difficult now to trace just where all of the items have ended up. The books at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village generally display stamps and markings from Pattison as well as a variety of other institutions including the Mechanics’ Institute itself. RALPH ERIC PATTISON Ralph Eric Pattison was born in Rockhampton, Queensland, in 1891. He married Maude Swan from Warrnambool in 1920 and they set up home in Warrnambool. In 1935 Pattison accepted a position as City Librarian for the Warrnambool City Council. His huge challenge was to make a functional library within two rooms of the Mechanics’ Institute. He tirelessly cleaned, cleared and sorted a disarrayed collection of old books, jars of preserved specimens and other items reserved for exhibition in the city’s museum. He developed and updated the library with a wide variety of books for all tastes, including reference books for students; a difficult task to fulfil during the years following the Depression. He converted all of the lower area of the building into a library, reference room and reading room for members and the public. The books were sorted and stored using a cataloguing and card index system that he had developed himself. He also prepared the upper floor of the building and established the Art Gallery and later the Museum, a place to exhibit the many old relics that had been stored for years for this purpose. One of the treasures he found was a beautiful ancient clock, which he repaired, restored and enjoyed using in his office during the years of his service there. Ralph Pattison was described as “a meticulous gentleman whose punctuality, floorless courtesy and distinctive neat dress were hallmarks of his character, and ‘his’ clock controlled his daily routine, and his opening and closing of the library’s large heavy doors to the minute.” Pattison took leave during 1942 to 1945 to serve in the Royal Australian Navy, Volunteer Reserve as Lieutenant. A few years later he converted one of the Museum’s rooms into a Children’s Library, stocking it with suitable books for the younger generation. This was an instant success. In the 1950’s he had the honour of being appointed to the Victorian Library Board and received more inspiration from the monthly conferences in Melbourne. He was sadly retired in 1959 after over 23 years of service, due to the fact that he had gone over the working age of council officers. However he continued to take a very keen interest in the continual development of the Library until his death in 1969. WARRNAMBOOL PUBLIC LIBRARY The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) was formed by a voluntary community group in 1863, within six years of Warrnambool’s beginnings, and its Reading Room opened in 1854. The WMI operated until 1963, at which time it was one of the oldest Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes offered important services to the public including libraries, reading rooms and places to display and store collections of all sorts such as curiosities and local historical relics. In 1886 a Museum and Fine Arts Gallery were added to the WMI and by the beginning of the 20th century there was also a billiards room and a School of Art. By this time all Mechanics’ Institutes in country Victoria had museums attached. Over the years the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Library was also known as the Warrnambool Public Library the Warrnambool Library and the Free Library. Early funding from the government was for the “Free Library”. The inscription in a book “Science of Man” was for the “Warrnambool Public Library”, donated by Joseph Archibald in 1899. Another inscription in the book “Catalogue of Plants Under Cultivation in the Melbourne Botanic Gardens 1 & 2, 1883” was presented to the “Warrnambool Library” and signed by the author W.R. Guilfoyle. In 1903 the Warrnambool Public Library decided to add a Juvenile Department to library and stock it with hundreds of books suitable for youth. In 1905 the Public Library committee decided to update the collection of books and added 100 new novels plus arrangements for the latest novels to be included as soon as they were available in Victoria. In July 1911 the Warrnambool Council took over the management of the Public Library, Art Gallery, Museum and Mechanics’ Institute and planned to double the size of the then-current building. In 1953, when Mr. R. Pattison was Public Librarian, the Warrnambool Public Library’s senior section 10,000 of the 13,000 books were fiction. The children’s section offered an additional 3,400 books. The library had the equivalent of one book per head of population and served around 33 percent of the reading population. The collection of books was made up of around 60 percent reference and 40 percent fiction. The library was lending 400 books per day. In 1963 the Warrnambool City Council allocated the site of the Mechanics’ Institute building, which included the Public Library, Museum and Art Gallery, for the new Municipal Offices and the Collections were dispersed until 1971. The Warrnambool Library took over the Mechanics’ Institute Library’s holdings on behalf of the Warrnambool City Council. Since the closure of the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute the exact location and composition of the original WMI books and items has become unclear. Other materials have been added to the collection, including items from Terang MI, Warrnambool Court House and Customs House. Many of the books have been identified as the Pattison Collection, named after the Librarian who catalogued and numbered the books during his time as Warrnambool Public Librarian in the time before the Mechanics’ Institute closed. It seems that when Warrnambool became part of the Corangamite Regional Library some of the books and materials went to its head office in Colac and then back to Warrnambool where they were stored at the Art Gallery for quite some time. Some then went to the Warrnambool Historical Society, some stayed at the Art Gallery and some were moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The various stamps and labels on the books held at Flagstaff Hill show the variety of the collection’s distribution and origin. The books in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village date from the 1850’s to the late 1950’s and include rare and valuable volumes. Many of the books are part of the “Pattison Collection” after the Warrnambool’s Public Librarian, Mr. R. Pattison. Jules Verne (1828–1905) Jules Verne pursued his writing career after finishing law school in 1849, during this time he was writing poetry and short stories. He began to hit his stride after meeting publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel in1862, who nurtured many of the works that would later comprise the author's 54 novels the (Voyages Extraordinaires). Often referred to as the "Father of Science Fiction," Verne wrote books about a variety of innovations and technological advancements years before they were practical realities. In 1856, Verne met and fell in love with Honorine de Viane, a young widow with two daughters. They married in 1857, and in 1861, the couple's only child, Michel Jean Pierre Verne, was born. Realizing he needed a stronger financial foundation, Verne began working as a stockbroker. However, he refused to abandon his writing career, and that year he published his first book, The 1857 Salon (Le Salon de 1857). In all Verne authored more than 60 books as well as dozens of plays, short stories and librettos. He conjured hundreds of memorable characters and imagined countless innovations years before their time, including stories about submarine and space travel, terrestrial flight and deep-sea exploration. Jules Verne died in 1905, at his residence in the French city of Amiens, stricken with diabetes, on March 24, 1905. Verne had many memorable novels, his most famous being Five Weeks in a Balloon, Journey to the Centre of the Earth, From the Earth to the Moon, Around the World in Eighty Days, In Search of the Castaways and Twenty Thousand Leagues under the Sea Additional works surfaced decades later. Backwards to Britain based on his many trips to the United Kingdom was finally printed in 1989, 130 years after it was written. Also Paris in the Twentieth Century, originally considered too far-fetched with its depictions of skyscrapers, gas-fuelled cars and mass transit systems, followed in 1994. Citation Information Biography.com Editors Jules Verne Biography: https://www.biography.com/writer/jules-verne The Pattison Collection, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. The Warrnambool Mechanics Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and the important role it played in the intellectual, cultural and social development of people throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance. Keraban The Inflexible (part 1) The Captain of The Guidara Author: Jules Verne Publisher: Sampson Low, Marston, Searle & Rivington Date: 1887Label on spine cover with typed text PAT 843 VER Front loose endpaper has sticker from Warrnambool Public Library covered by a sticker from Corangamite Regional Library Service Front loose endpaper has a stamp from Corangamite Regional Library Servicewarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, pattison collection, warrnambool library, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, ralph eric pattison, corangamite regional library service, warrnambool city librarian, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, warrnambool children’s library, great ocean road, keraban the inflexible (part 1) the captain of the guidara, jules verne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Date Stamp, Mid 20th century
This hand held, mechanical date stamp, made in mid-20th century by English Numbering Machines Ltd (ENM) in Enfield, England and is part of the stationary items once used by Dr. W.R. Angus in his medical service. ENM was a well know manufacturer of mechanical counters and hand numbering machines, both printing and non-printing, for the stationery industry, offices, sales control and the legal profession. The company was amongst the exhibitors at the Birmingham section of the British Industries Fair, (stand number D 539). This Fair operated annually from the 1920 – 1960 and was attended by royalty and dignitaries as well as the general public. At its peak there were over 1000 exhibitors. This date stamp was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) According to Berry, her mother Gladys made a lot of their clothes. She was very talented and did some lovely embroidery including lingerie for her trousseau and beautifully handmade baby clothes. Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . Its first station was in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital (a 2 bed ward at the Nelson Street Practice) from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what previously once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr Tom and his brother had worked as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He had been House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan had gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. When Dr Angus took up practice in the Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan’s old premises he obtained their extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926. A large part of this collection is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. and an ALDI sore is on the land that was once their tennis court). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served with the Australian Department of Defence as a Surgeon Captain during WWII 1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. He had an interest in people and the community They were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Metal date stamp with Bakelite handle, made in Britain by English Numbering Machines. Model No. 4531; part of the W.R. Angus Collection. Stamped on metal: “ENM / British made / Model 4531” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, date stamp, office stationery, mechanical date stamp, enm date stamp, english numbering machines, enm model 4531 -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Black and White, St Peter's Daylesford Communion Breakfast, 1930, 09/11/1930
"ST. PETER'S DAYLESFORD. General Communion and Breakfast. On Sunday November 9, a general Communion of the men; of the parish will be held in St Peter's Church, Daylesford. A communion breakfast will subsequently take place." Melbourne Advocate, 30 October 1930. "General Communion and Breakfast, Daylesford War Memorial Protest by Rev. Dr. Collins Rights of Catholics Ignored THE splendid Catholicity of the Daylesford parish was demonstrated on Sunday morning last when a general Communion of the men of the parish took place at the 8 o'clock Mass at St. Peter's Church. This proud and edifying demonstration of faith concluded a very successful mission in the parish, conducted by the Rev. Fr. O'Flynn, C.SS.R., and Rev. Fr. Frean, C.SS.R., Daylesford parish is fairly scattered, and from every corner of it came men to take their part in the general Communion. The missioners and the Rev. W. M. Collins. D.D., P.P.. have reason to be deeply gratified at the result of the mission. His Grace the Archbishop of Melbourne (Most Rev. Dr. Mannix) was the celebrant of the Mass. He was assisted in administering the Sacrament by Rev. Dr. Collins. At the close of the Mass the hymn, "Faith of Our Fathers." was sung. The breakfast was served in the Daylesford Town Hall, the men marching there from the church. More than 250 partook of breakfast. In the balcony were lady parishioners who wished to listen to the speeches. His Grace the Archbishop was at the head table, and with him were Rev. W. M. Collins, P.P.; Crs. Bolton and Gleeson (Shire of Glenlyon), and Courtney (Shire of Davlesford); Messrs. Cleary and Egan (Blampied). Mr. J. T. Murphy. Mr. Considine, and Mr. O'Donnell (BuIIarto). Several selections were played by the Holy Cross Convent orchestra, Daylesford, and the catering was admirably carried out by Mrs. Mann. It was a well-organised and successful function, and the general arrangements reflected the highest credit on the Rev. Dr. Collins and those associated with him. Much favourable comment was made upon the great success achieved. A WAR MEMORIAL SERVICE. Strong Protest by Rev. Dr. Collins. The Rev. Dr. Collins said it was no exaggeration for him to say that he was a proud pastor that day. He had reason to be proud of the magnificent demonstration of faith made by the Catholic men of the parish at St. Peter's Church. It was promoted by a supernatural motive, and the men were sure to get their reward. He knew that many men had attended at great sacrifice, and that numbers had to grope about in the early hours to get everything in readiness at their farms and dairies. He was deeply thankful for the fine response made by the men to his invitation, and no greater encouragement could be given to him in his work in the parish. They had made a creditable demonstration before the people of Daylesford, whose good opinion they valued and wanted to retain. Catholics were part of the community, and the community's troubles were their troubles. Generally they had a few of their own troubles, but they were not wanting in helping the community to bear its troubles. Just now they were passing through a difficult time. The surrounding shires seemed to be better off than Daylesford, but the municipal fathers at Daylesford had spent a lot of money wisely in attracting tourists to the beautiful district. The money spent, he was certain, would come back a hundredfold. They appreciated the good work done by the municipal authorities, and were prepared to do their part in shoulder-ing their civic obligations. A Frankly Protestant Memorial Service. He could not let the occasion pass without calling the attention of the Daylesford people to an injustice that was being done the Catholic body, unwittingly he believed. Hie referred to the ceremony for the unveiling of the Soldiers' Memorial. It had been decided to adopt a frankly Protestant service. Catholics could not take part in a non-Catholic service, and that was not due in any way to any recent whim or caprice. Catholics had made common sacrifices, and the war memorial should stand for the Catholic boys who had fallen as well as non-Catholic soldiers. Catholics had contributed towards the cost of the memorial, and yet a programme had been adopted on the occasion of the public unveiling that excluded Catholics from taking part. They had a right to be at the ceremony, but it was asking them too much to shed their principles in order to be present. Their forefathers did not shed their principles when there was much more at stake, and they did not intend to shed theirs. They took that stand for Faith, and were still loyal citizens of Australia. The great majority, he was certain, did not realise the difficulties of Catholics, and that the stand taken was a matter of principle. There was always a minority, however, who were ever ready to score a victory over Rome at any price. Thanks to Non-Catholics. Having made his protest, he would not be honest if he did not express his gratitude to many non-Catholics in Daylesford for their help. In the Boxing Day carnival, which was their principal effort on behalf of the schools, non-Catholics gave splendid support, which he very much appreciated. The success of the carnival was dependent to a large extent on the generous help of Protestants. He trusted that the Catholic men generally would take note of what he said, and turn over a new leaf, as so many new leaves had been turned over since the mission. Missioners and Nuns Thanked. The work of the Redemptorist Fathers had been fruitful of results in the parish, and what they had done had paved the way for the magnificent men's demonstration. He wished heartily to thank the Fathers, and his thanks were also due to the Holy Cross Convent. If the Faith were strong in Daylesford, it was largely due to the Catholic schools in the district. They should never forget the Presentation nuns, and should be prepared to help them in every possible way. He was very thankful to the Rev. Mother for her kindness in entertaining many at the convent, and also for providing the orchestra at the Communion breakfast. A Splendid Success. He was greatly delighted at the presence of his Grace the Archbishop. When he started to talk about the breakfast, many told him it would not be a success. First of all, it was intended to hold the breakfast in the schoolroom, but the response was so good that it was considered they should get the Rex Theatre. Finally, they were compelled to take the Town Hall in order to accommodate the large number who purchased tickets. The presence of his Grace gave additional lustre to the successful demonstration. He was proud of the men of the parish, and hoped God would bless them and their families. (Applause.) The first toast honoured was that of "The Pope and the King." WELCOME TO HIS GRACE Proposing the toast of "His Grace the Archbishop," Cr. J. Bolton said he wished to congratulate the Rev. Dr. Collins on the wonderful success of the two functions. All parts of the parish were represented at the general Communion in St. Peter's Church, and it was an inspiring spectacle. It showed that the Faith was deep and strong in Daylesford. A great privilege had been given to them, and they owed grateful thanks to the Rev. Dr. Collins. He wished to welcome his Grace the Archbishop, and he trusted that he would enjoy his visit to the district. The country was passing through a difficult time at present, and it required plenty of clear thinking and acting to put things right again. He hoped his Grace would touch on the situation, and give them the benefit of his thoughtful and wellreasoned views. Whatever his Grace said would be worth listening to. (Applause.) THE ARCHBISHOP CONGRATULATES PASTOR AND PEOPLE. DAYLESFORD A MODEL PARISH. His Grace the Archbishop said he need not assure them that he came to Daylesford with great pleasure. His visits to Daylesford were always pleasant, but the present visit was additionally pleasant and memorable because he had the opportunity of assisting at one of the most inspiring functions that it had ever been his good fortune to attend. He was really touched to the heart when he stood on the altar and saw the beautiful St. Peter's Church—there were few churches to compare with it in the country—filled with the men of Daylesford and of the surrounding districts. Practically all the Catholic men in the parish were present at the general Communion, and it gave him very deep satisfaction and genuine pleasure to be amongst them. As the Rev. Dr. Collins and Cr. Bolton had said, it was a proof of the depth and soundness of the Faith of the Catholic people of the parish. He wished to congratulate the Rev. Dr. Collins upon the magnificent success that had attended his efforts since he came to Daylesford. He thought the Rev. Dr. Collins had been a very happy man since he took up work in the parish. He came to Daylesford more or less broken in health, and his best friends were doubtful whether his health would stand the strain of parochial duty. However, he had never looked back. He doubted if Dr. Collins would care to leave Daylesford, unless he were appointed Prefect of Propaganda, Rome, or some very high distinction was conferred on him. At all events, things had gone on well with Dr. Collins since he came to Daylesford, and he could see some of the reason for it in looking at the fine gathering before him. The Rev. Dr. Collins was a very zealous and spiritual man, and his lot had been cast amongst people who had responded to his labours. ... (Melbourne Advocate, 13 November 1930) Black and white photograph taken in Daylesford Town Hall depicting numerous men standing, and sitting at tables during the St Peter's Catholic Church Communion Breakfast. Arch Bishop Daniel Mannix stands centre back.st peter's catholic church, daylesford, communion breakfast, daylesford town hall, daniel mannix, george gervasoni, gus gervasoni -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesPhotograph, Charles Ernest and Jessie Barrie with family, Unknown
This document is has been compiled by Wendy Barrie daughter of Ernest (Bon) and Edna Barrie and granddaughter of Charles E and Jessie M Barrie. I was born in during WW 11 and the first child of my generation to live on the ‘ Darlingsford’ property at Melton. My grandfather was well known in the district and was mostly referred to as Ernie. He shared the same initials as his second son Edgar. His three eldest sons lived and farmed in Melton for their entire lives. His descendants are still associated with farming, engineering and earthmoving in Melton. Ernie Barrie operated a travelling Chaff Cutter in the St Arnaud area where his parents William and Mary Ann had taken up land at Coonooer West in 1873. Ernie commenced his working life with a team of bullocks and a chaff cutter. The earliest connection he had with Melton was in 1887. By the beginning of the 20th century Ernie and his father William and brothers, William, Samuel, James Edwin,[Ted] Robert, Arthur and Albert have been associated with farming and milling in the Melton district. In the early 1900’s Ernie and his brother Ted were in partnership in a Chaff cutting and Hay processing Mill on the corner of Station and Brooklyn road Melton South. The mill was managed by William for a time. By 1906 Charles Ernest and James Edwin were in partnership in the Station Road mill when a connecting rail line across Brooklyn Road for a siding was constructed to the Melton Railway Station. In 1911 the Mill’s letterhead shows C.E. BARRIE Hay Pressing and Chaff Cutting Mills. Melton Railway Station. Telephone No 1 Melton. This Mill as sold to H S K Ward in 1916 and stood until 1977 when it burnt down in a spectacular fire. Ernie built a house at Melton South beside the Chaff Mill at Station Road in 1906 and married Jessie May Lang in August at the Methodist Church. Jessie’s father was Thomas Lang. He came to Melton in 1896 and was the Head Teacher at Melton State School No 430 until he retired in 1917. They had 9 children with 8 surviving to adulthood. Jessie and Ernie had 6 sons and 3 daughters. All the children lived at Darlingsford. In April 1910 the family left Melton for a brief period and moved to a farm in Trundle in NSW. They returned to Melton and purchased Darlingsford in May 1911. For a time during WW1 they lived at Moonee Ponds near the Lang grandparents at Ascot Vale. Mary and Bon attended Bank St State School. The children developed diphtheria in 1916 and their youngest boy, Cecil died of complications. Mary and Bon were taken to Fairfield Hospital and both recovered. At the end of the war influenza broke out the family returned to Darlingsford and shared the home for a short while with the Pearcey family who had been working the farm. By 1922 the family had and grown and Edgar, Tom, Horace, Jessie, Joyce and Jim were living a Darlingsford. Ernie continued during the 1920’s working the farm and attend his many civic and community commitments. Two 8 clydesdale horse teams were used to work the land which meant early rising for the horses to be fed and harnessed to commence the days work. In 1916 Ernie also became involved in a Chaff Mill on the corner of Sunshine and Geelong Road West Footscray, which at the time was being run by John Ralph Schutt. It was known an Schutt Barrie. A flour mill was added at a later stage. Other Schutt and Barrie mills were situated at Parwan and Diggers Rest. Another mill was situated beside the railway line at Rockbank. The Footscray mill ceased operation in 1968 Ernie spent a lot of time and energy at the Parwan Mill and travelling around Parwan and Balliang farms, where he came to know many of the families in the district. Ernies commitment to the civic development to the Melton and district was extensive, he was involved with a number of large events during the 1920’s such as the Melton Exhibitions and the 1929 Back to Melton Celebrations. He was a member of the Australian Natives Association at the turn of the century. He was Chairman of the School Committee at Melton State School 430 and the Melton South State School in thw1920s. He donated the land for a Hall for Melton South in 1909, known as Exford Hall and later in 1919 renamed Victoria Hall. The Hall was demolished in 1992. He was a Councillor, JP, and Vice President and President of the Melton Mechanics Institute Hall Committee in 1915- 1916. He was a member of the Methodist Church and later the Scots Presbyterian Church. He was Superintendent of the Sunday School of the Methodist Church to 1910 and later Scots Presbyterian Church until 1931. This is reflected in the theme of children in the stained glass window which was dedicated in his memory by his wife Jessie as a gift to the Scots Church. Charles Ernest Barrie made many generous donations to many charities who supported young people and children. In 1918 Jessie and Ernie made the first donation to a very prominent Victorian charity whose work still continues. Yooralla. In July 1931 Ernie’s untimely death was a major blow to the family and the Melton community. To this day people still vividly recall the day they lined the streets for his funeral. The day of the funeral is recalled as the day Melton stood as two of their prominent citizens who tragically died on the same day. Their eldest daughter Mary had married Keith Robinson in 1930 and had just moved to Heatherdale Toolern Vale with their year old baby son. Bon the eldest son was 22, Edgar 18, Tom 16, Horace 15, Jessie and Joyce 10 and Jim 8 years old. A heavy burden of responsibility fell on the shoulders of the two eldest children, Mary particularly for her mother and Bon stepped in assuming head of the family for his mother, brothers and sisters living at the Darlingsford homestead. In the early 1930’s the three eldest sons took on many of the Civic and Church commitments which their father had held. This community involvement extended well into the 1980s. In 1941 Bon married Edna Myers and they moved into a house shifted from Harkness Lane to Harkness Lane on the eastern section of the Darlingford property. Edgar married Margaret Hodgkinson a Primary school teacher at Melton in 1949 and they lived in the Darlingsford house. Earlier Tom married May Ferris and lived on the eastern side of Ferris Lane in the Ferris home. Bon , Edgar and Tom often operated as a team effort, in particular at harvest time when a larger team of workers was needed. The three farms cultivated wheat, barley and oats and supplied the Mill with sheafed hay. They continued using horse teams until mechanisation in the 1940’s made the horses redundant. By the 1960s their five sons continued with farming. Many loads of hay were transported to the Mill in Footscray. Well into the 1960s hired harvest hands along with agricultural university students were involved in bringing in he harvest. Stacking was an art form in itself and Tom held the expertise for building and shaping the sides and roof. The stacks built in the district each had their own unique shape and could be recognized by their builders. The Barrie brothers developed a mechanical fork lift for picking up complete stooks and moving them to be loaded to the elevator to build the haystack. The prototype built by Bill Gillespie was attached to a Bedford truck. Later refinements in a collaborative effort with the Gillespie brothers a multi pronged fork was attached to the front of tractor which was hydraulically operated to raise each stook onto trucks to be transported to the site of the haystacks. This method of handling sheaves significantly reduced laborious pitchforking individual sheaves. This invention was soon taken up by farmers far and wide and was a common sight in the district at harvest time in the stacking season. I recall visiting farmers calling in at the house at Ferris Road farm to inspect this break through invention. The Clydesdale horse teams were used into the 1940s but by the 1950s the Barries’ farms were fully mechanised. When the demand for sheafed hay declined other crops were introduced these included barley, lucerne, wheat and peas. Sheep were added to the mix in the 1950s in an attempt to keep the farms more viable. In the 1970s part of the Barrie’s farms were facing a major disruption with the impending compulsorily acquisition of a strip of land for the construction the freeway bypass, which divided access between the Darlingsford homestead with those on Ferris Lane. Charles Ernest Barrie and Jessie May Lang's children: 1. Mary Ena BARRIE was born on 07 October 1907. She died on 29 April 1999. 2. Ernest Wesley BARRIE was born on 29 April 1909 in Ascot Vale, Victoria, Australia.He died on 25 December 1985 in Melton, Victoria, Australia. 3. Cecil William BARRIE was born on 23 February 1911.He died on 25 May 1916. 4. Charles Edgar BARRIE was born on 01 June 1913.He died on 06 October 1975. 5. Thomas Lindsay BARRIE was born on 25 November 1914.He died on 14 September 1990 in Melton, Victoria, Australia. 6. William Horace BARRIE was born on 11 October 1915.He died on 19 December 1950. 7. Jessie Maud BARRIE was born on 06 November 1920 in Bacchus Marsh, Victoria, Australia.She died on 26 February 1994. 8. Dorothy Joyce BARRIE was born on 06 November 1920 in Bacchus Marsh, Victoria, Australia.She died on 18 March 2003.. 9. James Edward BARRIE was born on 17 January 1922 in Bacchus Marsh, Victoria, Australia.He died on 23 August 2004Family Photo with Edgar, Tom, Mary, Ernest (Bon), Horace, Jim, Charles Ernest, Jessie and Joycelocal identities -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyLetter, Property for sale - Ringwood Shop and Dwelling Estate, Ringwood, Victoria - circa 1925
ID 5225 note: Further information relating to allotments marked on the hand-drawn plan are included in ID 5224 - Ringwood Station Estate.Typewritten letter from A.V. Greenwood with hand drawn plan of Ringwood Shop and Dwelling Estate, detailed description of property for sale, and top and side elevation views of house. (7 pages)(Transcript of first page - to unknown recipient) Phone 988 Central, 331 Canty Greenwood Pty. Ltd. 5 Flinders Street Melbourne. Dear Sir, 1. Attached please find drawings of my house at Ringwood. 2. It is for sale at £4,865 or to let at £5 per week to an approved tenant. 3. I sold it to Mr. De Garis and vacated it, but it is now back on my hands. 4. I leased another place instead of living in my own. I may be able to cancel same; in the meantime, however, I propose to sell or let my own. The painters are now going through the place; re-varnishing, re-oiling and re-polishing so that in about five days it will look "spick and span". 5. The house was specially built under my own supervision. 6. It is very suitable for a high class Guest House, Doctor's residence, Hospital or Convalescent Home. If you know of anyone whom it might suit, please communicate with them. DESCRIPTION 7. It stands on 305 feet of land facing Greenwood Avenue. It is cement, roughcast and hardwood, well oiled, and is now being redone so that the house is as good as new; red tile roof; verandahs three sides; two sleep-outs; five bedrooms; large dining room; very large music room with nooks, upstairs lounge, study; sewing room; built-in wardrobes and cupboards throughout; handsome kitchen with handsome pantry cupboard with drawers and glass front; one bath room; one shower room; wash house with patent copper and laundry. Every modern convenience, hot water system (through copper pipes with large copper cylinder) electric lights everywhere, outside and in, Yan Yean water laid on everwhere throughout house and gardens. Floors throughout are the very best, close set, stained and polished; dainty lead light windows etc. 8. There is a big garage, with tiled roof and two rooms with all conveniences for a married couple. Property is well drained with a system of its own. The house stands upon the top of a hill close to Railway Station, say 500 feet from the Footbridge. 9. The garden has expansive shrubs; sheds; fernery; tennis court. 10. A handsome piece of furniture goes with the house; a combination pantry and storeroom for groceries, milk, bread etc., consisting of drawers, glass and wire doors, as mentioned above. 11. It is within easy distance of Melbourne as it is only two minutes from Ringwood Station, which is a frequent electric train service bringing it within 39 minutes of the City. It is thought better by some to go further out into the country atmosphere and walk a short distance at the end than to go by train 20 minutes then walk 15 to 20 minutes. 12. The price quoted of £4,865 is made up as follows - 305 feet of land @ £5 ... £1,515 Garage and dwelling ... £300 House hot water system, American cupboard ... £2,600 Water, fencing, sheds & drain ... £250 For the lot ... £4,865 Should you require copies of the enclosed drawings I shall be pleased to supply same. 13. Mr. J.B. McAlpin is the local agent, Phone Ring. 7 (after hours Ring. 44) or you may phone me Central 988. 14. The house is south of the line, facing Greenwood Avenue and immediately at the back of Ringwood House, which is also my property. Yours sincerely, A.V. Greenwood (illegible) ..... (Transcript of second page) RINGWOOD SHOP AND DWELLING ESTATE See these letters on plan attached (H.) Ringwood House and Shops on 100 by 150 feet of land fronting Bedford Road 100 feet @ £10 per foot - £1,000 House and shops - £2,400 ... £3,400 Ringwood House consists of Boarding House, (Phone 101) and two shops, mainly brick; 9 inch walls. Will carry another story. Has music room, dining room, entrance halls, 10 bedrooms, large verandahs, all conveniences, hot and cold water, and stands on what will become a most valuable business corner. (F.)(G.) Mr. Greenwood's house, garage and sheds, stands on 307 feet of land fronting Greenwood Avenue. See detailed description attached ... £4,865 (J.) Cottage on Block 81 in William Street ... £750 (K.) Cottage in Pitt Street ... £650 (Total) £9,665 ..... (Description of third page - Subdivision Plan) Drawn by Edyth Greenwood, phone 988 Central. Subdivision includes Station Street, Pitt Street, Bedford Road, Wantirna Road, James Street, William Street (later Kendall Street), Greenwood Avenue, Ellison Street, and Haig Street. Circles denote blocks for sale. Squares denote house properties for sale. Other features marked include location of businesses along Main Street (Maroondah Highway), cool store, railway station, shop and police station on Bedford Road, church on Station Street, site of schoolmaster's residence and State School, and location of proposed public baths -
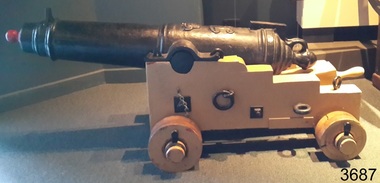 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Carronade, 1840
The carronade was designed as a short-range naval weapon with a low muzzle velocity for merchant ships, but it also found a niche role on warships. It was produced by the Carron Iron Works and was at first sold as a complete system with the gun, mounting, and shot altogether. Carronades initially became popular on British merchant ships during the American Revolutionary War. A lightweight gun that needed only a small gun crew and was devastating at short range was well suited to defending merchant ships against French and American privateers. The invention of the cannon is variously attributed to Lieutenant General Robert Melville in 1759, or to Charles Gascoigne, manager of the Carron Company from 1769 to 1779. In its early years, the weapon was sometimes called a "mellvinade" or a "gasconade". The carronade can be seen as the culmination of a development of naval guns reducing the barrel length and thereby the gunpowder charge. The Carron Company was already selling a "new light-constructed" gun, two-thirds of the weight of the standard naval gun and charged with one-sixth of the weight of the ball in powder before it introduced the carronade, which further halved the gunpowder charge. The theory of its design was to use less powder and had other advantages that were advertised in the company's sales pamphlet of the time, state. The smaller gunpowder charge reduced the barrel heating in action, also reduced the recoil. The mounting, attached to the side of the ship on a pivot, took the recoil on a slider, without altering the alignment of the gun. The pamphlet advocated the use of woollen cartridges, which eliminated the need for wadding and worming, although they were more expensive. Carronades also simplified gunnery for comparatively untrained merchant seamen in both aiming and reloading that was part of the rationale for adopting the gun. Other advantages promoted by the company were. The replacement of trunnions by a bolt underneath, to connect the gun to the mounting, reduced the width of the carriage that enhanced the wide angle of fire. A merchant ship would almost always be running away from an enemy, so a wide-angle of fire was much more important than on a warship. A carronade weighed a quarter as much as a standard cannon and used a quarter to a third of the gunpowder charge. This reduced charge allowed Carronades to have a shorter length and much lighter weight than long guns. Increasing the size of the bore and ball reduces the required length of the barrel. The force acting on the ball is proportional to the square of the diameter, while the mass of the ball rises by the cube, so acceleration is slower; thus, the barrel can be shorter and therefore lighter. Long guns were also much heavier than Carronades because they were over-specified to be capable of being double-shotted, (to load cannons with twice the shot, for increased damage at the expense of range), whereas it was dangerous to do this in a carronade. A ship could carry more carronades, or carronades of a larger calibre, than long guns, and carronades could be mounted on the upper decks, where heavy long guns could cause the ship to be top-heavy and unstable. Carronades also required a smaller gun crew, which was very important for merchant ships, and they were faster to reload. The small bore carronade and carriage is part of a collection of nineteenth Century Flagstaff Hill Guns and Cannon, which is classified as being of significance and was made a few years after the beginning of Queen Victoria's reign in 1837 and fires a 6 lb pound cannon ball. This nineteenth century artillery piece is a rare and representative item of artillery of this era, used predominately on ships, both military and merchant. The artillery piece, individually and as part of the collection, is highly significant for its historical, scientific and aesthetic reasons at the state, national and world level. This carronade represents the methods of artillery technology, its advancement and its modifications to suit dangerous situations that sailors encountered from attacks from free booters (pirates, living from plunder) or others at the time. Carronade firing a 6 lb cast iron ball, with a smooth bore barrel 6.5 cm in dia the item is mounted on stepped wooden carriage with wooden wheels. Cannon barrel can have its elevation adjusted via a wooden wedge. Gun carriage has loops for locating and holding in position to a deck by ropes. Carriage is a replica made 1982Cast into the barrel is the royal emblem of Queen Victoria (VR "Victoria Regina") indicating the carronade was cast during Queen Victoria's reign / 1840 & 4-2-0 denoting the weight of the barrel. Right hand trunnion has a serial number “8708”. Also on top of the barrel is the British "Board of Ordinance" identifying mark a broad arrow indicating the carronade was in military use. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, colonial defences, victoria’s coastal defences, warrnambool fortification, warrnambool garrison battery, warrnambool volunteer corps, ordinance, armaments, garrison gun, smooth bore cannon, carronade, black powder, 12 pounder, 1840, artillery, lieutenant general robert melville, charles gascoigne, carron company, mellvinade, gasconade -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Post Office Receiving Pillar, 1885
Post Office Receiving Pillar was Collected from Warrnambool City Council’s Scott Street Depot and transported to Flagstaff Hill, stored in the Barracks area Friends of Flagstaff Hill began the project of restoring the Post Office Receiving Pillar in early 2011. The replacement dome required a pattern to be made from paper, then timber, then someone to manufacture it. The cast iron body required sand blasting and undercoating. The pillar was installed in Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in March 2014. A specialist visited the Village and painted the pillar with 7 coats of ‘post office red’ then completed the job with gold paint on the details. In 2015 an information plate of brass was fitted to the Pillar in the position that would have originally announced the clearing times. It was originally manufactured by G Couch, Engineer, Alliance Iron Works, Melbourne. Gordon Couch passed away in June 1896 and his Works were offered for auction in November 1897. HISTORY OF POST OFFICE RECEIVING PILLARS In 1851 ‘pillar boxes’ were installed at roadside locations in the island of Jersey, England; they had already been successful in several European countries. The use of new prepaid, adhesive postage stamps as well as the roadside pillar boxes meant there was no need for the public to take a trip to the Post Office just to post a letter. By 1855 London had installed its first six Pillar Boxes. In 1856 the pillar boxes were first introduced in Sydney. These were circular with a crown on the dome, supported by leaves. Early Victoria Mail was originally collected by ‘letter carriers’, first appointed in Melbourne in 1841, equipped with leather bag and hand bell. He wore a red coat with brass buttons and a black top hat! In 1844 two wooden receiving boxes were erected in Melbourne. The first cast iron boxes were installed in South Melbourne (Emerald Hill) and were still in service until 1967. They were a fluted circular design and made in England. In the early 1860’s the ‘low door round’ design posting box was introduced, being circular and surrounded by a crown, with two broad embossed bands around its circumference. The clearance door was in front of the box and low down. These were made in Australia. In the early 1870’s square boxes with a tapering top were being used. These too were made in Australia by different manufacturers with slight variations on style such as the orientation and number of slots. Next came the circular boxes again, similar to the ‘low door round’ but with the clearance door extending to just below the posting slot, often referred to as ‘high door round’. These boxes did not have embossed bands. In 1887 small cast iron boxes were introduced, attached to posts and poles and called ‘lamp post receivers’. Around 1930 a ‘London’ model was used in Victoria. It was copied from the flat-domed type in London but made in Tasmania. … [References: Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village records, The Argus, 11th April, 1890, The Argus, 2nd July, 1896, The Argus, 30th Nov. 1897, “Stamps.Au” http://www.stampsau.com, 4th April 2011 (Extracted from “Australian Street Posting Boxes” by Ken Sparks – out of print)] Post Office Receiving Pillar, or letterbox.1885 "High Door Round" design, restored 2014 Tall cast iron sylinder with decorative dome cap, slot in side, hinged door with handle shaped as a fist. Painted red with gold trip..Reconditioned barrel, reconstructed dome. Restored by Friends of Flagstaff Hill, 2014. Now a working letterbox. Made in Melbourne.Oval maker's plate “ - G. COUCH - / ENGINEER / ALLIANCE IRON / WORKS / MELBOURNE”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, post office receiving pillar, letterbox, mailbox, australia post -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Fay Bridge, Former Glynn's Dairy Farm, Glynns Road, North Warrandyte, 31 August 2018
Glynn’s farm Originally Section 7, Parish of Nillumbik marked Aborigine Reserve in 1866 Crown Allotment 8, Section 7, Parish of Nillumbik, County of Evelyn, Certificate of Title Volume 4095, Folio 818.835, approx. 93 acres purchased by Joseph Panton in 1881 for £1/acre and known as Panton’s Point. By 1924 owned by S.S. Sergeant and called Riverswood. Sergeant commissioned Edna Walling to design the garden. In September 1929 the property was sold at auction by Mortgagee’s sale. Described as well built, brick, tile roof, Attic Villa containing downstairs 7 good rooms, bath, scullery, inside lavatory, etc. Upstairs 2 bedrooms and sleep out. Outbuildings compromising of brick and weatherboard wash house, stables, workshop, feed room, cow bails, large G.I. Hay shed, etc In January 1931 Riverswood property was proclaimed a sanctuary for native game for the entire year. A private swing bridge crossed the river at Pound Bend was known as Pearson’s bridge after C.W.K. Pearson who bought Riverswood in the early 1930s. The bridge was swept away in the December 1934 floods. Riverswood was sold by C.W.K. Pearson at auction on 25 November 1936. Described as a beautiful farm home of 93 acres and over one mile of River Yarra frontage, modern brick residence, lovely garden, rich river flat pastures, model poultry farm. The fine brick home was destroyed on Black Friday (13 Jan.) 1939. It was still a ruin when the Evelyn Evans purchased Waikowhane above Riverswood in 1940. The Glynn family purchased the Riverswood property in 1941 from Robert and Emily Hannon. Their son Kenneth Patrick Glynn inherited the property and he set about clearing the land during WW2 selling wood. Prior to marriage, Kenneth was living alone on the farm in a house he had built from whatever was available. He used the bluestone foundations from the original fine brick home. He met and married Honora Elizabeth Drew in early 1945 and their daughter Anna grew up on the farm. It was compulsorily acquired by the Board of Works in 1976 who then rented the house out in the 1980s. The property was transferred to Melbourne Parks and Waterways in 1996. Waikowhane was a pretty timber house built on top of the hill on 50 acres above Riverswood by retired nurse Jessie MacBeth. (This would be at the intersection of Glynns Road and Overbank Road where the big water tank is now situated on what was once James Orford’s property.) It was also destroyed Black Friday and she rebuilt it from the plans living in a caravan on site supervising the build. It was almost complete when she died May 1939. The property was bought by Evelyn Evans (a city girl) and her estranged husband in 1940. She had two sons, one only 9 months old at the time. It was a timber house with no power or water connected. The Ewen Cameron family bought Waikowhane in 1957. They had to evacuate when the 1961 bushfires swept through. The house was saved by Matcham Skipper. It was demolished by Melbourne Water in the 1990s when they acquired it.fay bridge collection, 2018-08-31, glynn's, glynn's dairy farm, glynns road, north warrandyte, parks victoria, ruins, riverswood, kenneth patrick glynn -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPostcard - Photograph postcard, Panorama at Eltham, Vic, c.1923
The Rose Series P. 4284 post card Taken from near what would be present day CLC car park looking southwest across Diamond Street, present-day Andrew Park to the railway station and developing Eltham shopping precinct. Arthur Street visible, Pryor and Luck Street not evident. Sunnybrook, the Taylor home is visible at the top of the hill in Bible Street. Only three residences visible in Arthur Street on the southern side, two of these are the David Harbison Rest Home at 10 and 12 Arthur Street (built and opened in November 1919), present day site of Eltham Mall. There are none on the north side of the street. Based on 1945 aerial view there are 8 buildings on the northern side between Main Road and Bible Street which and given the extent of commercial development on Main Road, it is estimated this image is circa 1925. Luther Haley was the first to build an open a baker and General Store in this location next to the railway station in 1902. However, it took nearly twenty years until the early to mid-1920s when a period of significant growth in the Eltham shopping centre happened with many businesses relocating their operations from the original town centre of Maria Street in Little Eltham as well as new businesses opening. Other stores/buildings noted (L-R) are: Stationmaster's House built circa 1910 Eltham Hardware Store opposite the railway station first opened on Main Road opposite the Railway Station around late 1922. An advertisement placed in the Hurstbridge Advertiser advised that the Hardware Store had just opened with a varied stock of Saws, Hammers, Nails, Shovels, Screw Drivers, and every article required in a house or on a farm. People were also encouraged to try their Jams, Pickles, Sauces, Cups and Saucers, etc. Newsagency with 'Leader' advertising on awning - E. J. Andrew opened his newsagency shop opposite the station in March 1923, advertising for sale stationery, school requisites and periodicals. Bird Brothers Cash Grocer & Fruiterer opposite the railway station offering summer drinks and confectionery a specialty with a full Stock of groceries of the best quality always on hand at city prices opened December 1921 William Capewell's Butcher shop at the corner of Dudley Street. Capewell previously had a small shop in front of the station opposite Luck Street. He enlisted in the AIF during WW1 and returned home in 1919. He re-applied for a slaughtering license in February 1920 and was advertising by October 1922 supplying all districts. Not visible (or not yet identified) but in business by October 1922 were: J.H. Fraser, Carpenter and Builder at Luck Street opposite the station George A. Danslow, Hairdresser and Tobacconist opposite the railway station Miss Barber's 'Blue Gum' Soda Fountain opened October 1922 opposite the railway station (hidden behind Stationmaster's House). It was so named due to its proximity to a tall Blue Gum tree G.H. McDonald Boot Repairer opposite the railway station In December 1923 the first portion of the main street to be formed from Dudley to Arthur streets was almost completed. This is the section in front of Capewell's Butcher shop though it is difficult to fully make out from the photoDigital file only Postcards scanned from the collection of Michael Aitken on loan to EDHS, 2 Sep. 2022michael aitken collection, eltham, postcards, arthur street, david harbison rest home, electrine candles, eltham railway station, eltham shopping centre, lloyd's general store, red rattler, rose series postcard, rose stereograph company, tait train, velvet soap, andrew park, bible street, bird brothers cash grocer & fruiterer, bird brothers cash grocer and fruiterer, butcher, diamond street, dudley street, eltham hardware and timber, eltham hardware store, eltham mall, main road, station masters house, stationmaster's house, sunnybrook, w.j. capewell, w.j. capewell butcher shop -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Postcard, The Great Tokyo Earthquake on September 1st, 1923: Asakusa 12-Story Tower with its Upper Floors Destroyed, 1923
The Great Kantō Earthquake of 1 September 1923 devastated the major cities of Tokyo and Yokohama, as well as five other surrounding prefectures and was one of the world’s worst natural disasters of the early twentieth century. In terms of loss of life and material damage, with an estimated 140,000 deaths and countless homeless, it is still Japan’s worst national disaster. Nearly 90% of the newspaper printers were destroyed in the earthquake. These postcards were not produced for aesthetics but as a major tool for the spread of information. Seeing how newspaper companies were left with their offices in shambles, postcard publishers tried to fill the gap hence some were in three languages. A very small number of publishing companies were fortunate enough to survive, one of them being Mitsumura Printing, which took advantage of its remaining resources to churn out postcards. When the Ōsaka Mainichi Shinbunsha published its bilingual three-volume photographic pictorial of the Great Kantō Earthquake just two weeks after the event, the calamity had already been captured in thousands of images that circulated on a national and international media highway. Commercial photographers and photojournalists produced the most abundant and immediate images of the quake, which were transmitted in newspapers, special-issue newspaper pictorials, commemorative photography collections, illustrated survivors’ accounts, and sets of commemorative postcards. These photographic images functioned as both news and souvenirs, rendering their consumers/viewers, inside and outside the devastated locale, into both witnesses and voyeurs. Images in the news media and those issued by respected publishing houses carried the visual authority of supposed facticity. As such they both produced and became the historical record of the event. Since the vast majority of 1923 disaster postcards that survive have no writing on them, they were likely treated more as collectibles than as a form of postal communication. Many were put into albums, creating new ways to combine images and create visual cultures of disaster for home viewing. Accordion-style albums allowed for personalized, serial organization of images that produced unique, imagistic narratives of the event. The album pages were also two-sided and could be stretched out to view a series of images on recto and verso. References: Imaging Disaster: Tokyo and the Visual Culture of Japan’s Great Earthquake of 1923 震災をイメージ化する 東京と1923年関東大震災のヴィジュアルカルチャー - The Asia. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://apjjf.org/2015/13/6/gennifer-weisenfeld/4270 The Great Kanto Earthquake: Postcards of Tragedy. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://www.tokyoweekender.com/art_and_culture/japanese-culture/the-great-kanto-earthquake-postcards/ See also: Postcards from Hell – Glimpses of the Great Kantō Earthquake; M. William STEELE (International Christian University, Japan) 14th Conference of the European Association of Japanese Studies: Visual Culture and Postcard Research Papers – East Asia Image Collection Blog. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://sites.lafayette.edu/eastasia/2014/09/01/14th-conference-of-the-european-association-of-japanese-studies-visual-culture-and-postcard-research-papers/] And https://icu.repo.nii.ac.jp/record/4503/files/ACS44_01Steele.pdfThis item, a souvenir from Japan from between the wars (circa 1923) was brought home to Research, Victoria by Bill Teagle who was serving in the Royal Australian Navy (1919-1945). Bill Teagle's sister Violet Amelda Teagle had married Theodore (Curly) Feldbauer in 1933. Bill's brother-in-law Curly was taken as a Prisoner of War by the Japanese and died at Sandakan in March 1945. The family did not learn of Curly’s death till months later and Bill's sister, Violet, herself could never forgive the Japanese for what happened to Curly. Curly is remembered on the Eltham Roll of Honour Board and his son, Albert Feldbauer (Bill’s nephew and youngest child of the children of the soldier fathers attending a school in the district), was given the honour of turning the first sod for the Eltham War Memorial Infant Welfare Centre Building. Despite this, the family maintained this cherished souvenir from a time of previous foreign friendship with Japan. The item was possibly given by Bill Teagle to his sister Margaret Rose (formerly Ingram) who later married Richard Edward (Eddie) Fielding in early 1948. (Eddie had been engaged to someone else before he went to war, but his fiancée broke it off before his return to Australia.) It was cared for by the Teagle/Fielding family for approximately one hundred years. It is of particular significance given the family's connection to the Eltham War Memorial and the significance of that memorial to the local community and represents that despite the horrors of war, former friends then foes can become friends again.tom fielding collection, japanese postcard, postcard, 1923, great kanto earthquake, japan, tokyo, yokohama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Postcard, The Great Tokyo Earthquake on September 1st, 1923: burnt remains of Asakusa Kannon Temple, 1923
The Great Kantō Earthquake of 1 September 1923 devastated the major cities of Tokyo and Yokohama, as well as five other surrounding prefectures and was one of the world’s worst natural disasters of the early twentieth century. In terms of loss of life and material damage, with an estimated 140,000 deaths and countless homeless, it is still Japan’s worst national disaster. Nearly 90% of the newspaper printers were destroyed in the earthquake. These postcards were not produced for aesthetics but as a major tool for the spread of information. Seeing how newspaper companies were left with their offices in shambles, postcard publishers tried to fill the gap hence some were in three languages. A very small number of publishing companies were fortunate enough to survive, one of them being Mitsumura Printing, which took advantage of its remaining resources to churn out postcards. When the Ōsaka Mainichi Shinbunsha published its bilingual three-volume photographic pictorial of the Great Kantō Earthquake just two weeks after the event, the calamity had already been captured in thousands of images that circulated on a national and international media highway. Commercial photographers and photojournalists produced the most abundant and immediate images of the quake, which were transmitted in newspapers, special-issue newspaper pictorials, commemorative photography collections, illustrated survivors’ accounts, and sets of commemorative postcards. These photographic images functioned as both news and souvenirs, rendering their consumers/viewers, inside and outside the devastated locale, into both witnesses and voyeurs. Images in the news media and those issued by respected publishing houses carried the visual authority of supposed facticity. As such they both produced and became the historical record of the event. Since the vast majority of 1923 disaster postcards that survive have no writing on them, they were likely treated more as collectibles than as a form of postal communication. Many were put into albums, creating new ways to combine images and create visual cultures of disaster for home viewing. Accordion-style albums allowed for personalized, serial organization of images that produced unique, imagistic narratives of the event. The album pages were also two-sided and could be stretched out to view a series of images on recto and verso. References: Imaging Disaster: Tokyo and the Visual Culture of Japan’s Great Earthquake of 1923 震災をイメージ化する 東京と1923年関東大震災のヴィジュアルカルチャー - The Asia. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://apjjf.org/2015/13/6/gennifer-weisenfeld/4270 The Great Kanto Earthquake: Postcards of Tragedy. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://www.tokyoweekender.com/art_and_culture/japanese-culture/the-great-kanto-earthquake-postcards/ See also: Postcards from Hell – Glimpses of the Great Kantō Earthquake; M. William STEELE (International Christian University, Japan) 14th Conference of the European Association of Japanese Studies: Visual Culture and Postcard Research Papers – East Asia Image Collection Blog. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://sites.lafayette.edu/eastasia/2014/09/01/14th-conference-of-the-european-association-of-japanese-studies-visual-culture-and-postcard-research-papers/] And https://icu.repo.nii.ac.jp/record/4503/files/ACS44_01Steele.pdfThis item, a souvenir from Japan from between the wars (circa 1923) was brought home to Research, Victoria by Bill Teagle who was serving in the Royal Australian Navy (1919-1945). Bill Teagle's sister Violet Amelda Teagle had married Theodore (Curly) Feldbauer in 1933. Bill's brother-in-law Curly was taken as a Prisoner of War by the Japanese and died at Sandakan in March 1945. The family did not learn of Curly’s death till months later and Bill's sister, Violet, herself could never forgive the Japanese for what happened to Curly. Curly is remembered on the Eltham Roll of Honour Board and his son, Albert Feldbauer (Bill’s nephew and youngest child of the children of the soldier fathers attending a school in the district), was given the honour of turning the first sod for the Eltham War Memorial Infant Welfare Centre Building. Despite this, the family maintained this cherished souvenir from a time of previous foreign friendship with Japan. The item was possibly given by Bill Teagle to his sister Margaret Rose (formerly Ingram) who later married Richard Edward (Eddie) Fielding in early 1948. (Eddie had been engaged to someone else before he went to war, but his fiancée broke it off before his return to Australia.) It was cared for by the Teagle/Fielding family for approximately one hundred years. It is of particular significance given the family's connection to the Eltham War Memorial and the significance of that memorial to the local community and represents that despite the horrors of war, former friends then foes can become friends again.tom fielding collection, japanese postcard, postcard, 1923, great kanto earthquake, japan, tokyo, yokohama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Postcard, The Great Tokyo Earthquake on September 1st, 1923: Fire in the middle of rain - National Sumo Stadium on fire, 1923
The Great Kantō Earthquake of 1 September 1923 devastated the major cities of Tokyo and Yokohama, as well as five other surrounding prefectures and was one of the world’s worst natural disasters of the early twentieth century. In terms of loss of life and material damage, with an estimated 140,000 deaths and countless homeless, it is still Japan’s worst national disaster. Nearly 90% of the newspaper printers were destroyed in the earthquake. These postcards were not produced for aesthetics but as a major tool for the spread of information. Seeing how newspaper companies were left with their offices in shambles, postcard publishers tried to fill the gap hence some were in three languages. A very small number of publishing companies were fortunate enough to survive, one of them being Mitsumura Printing, which took advantage of its remaining resources to churn out postcards. When the Ōsaka Mainichi Shinbunsha published its bilingual three-volume photographic pictorial of the Great Kantō Earthquake just two weeks after the event, the calamity had already been captured in thousands of images that circulated on a national and international media highway. Commercial photographers and photojournalists produced the most abundant and immediate images of the quake, which were transmitted in newspapers, special-issue newspaper pictorials, commemorative photography collections, illustrated survivors’ accounts, and sets of commemorative postcards. These photographic images functioned as both news and souvenirs, rendering their consumers/viewers, inside and outside the devastated locale, into both witnesses and voyeurs. Images in the news media and those issued by respected publishing houses carried the visual authority of supposed facticity. As such they both produced and became the historical record of the event. Since the vast majority of 1923 disaster postcards that survive have no writing on them, they were likely treated more as collectibles than as a form of postal communication. Many were put into albums, creating new ways to combine images and create visual cultures of disaster for home viewing. Accordion-style albums allowed for personalized, serial organization of images that produced unique, imagistic narratives of the event. The album pages were also two-sided and could be stretched out to view a series of images on recto and verso. References: Imaging Disaster: Tokyo and the Visual Culture of Japan’s Great Earthquake of 1923 震災をイメージ化する 東京と1923年関東大震災のヴィジュアルカルチャー - The Asia. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://apjjf.org/2015/13/6/gennifer-weisenfeld/4270 The Great Kanto Earthquake: Postcards of Tragedy. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://www.tokyoweekender.com/art_and_culture/japanese-culture/the-great-kanto-earthquake-postcards/ See also: Postcards from Hell – Glimpses of the Great Kantō Earthquake; M. William STEELE (International Christian University, Japan) 14th Conference of the European Association of Japanese Studies: Visual Culture and Postcard Research Papers – East Asia Image Collection Blog. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://sites.lafayette.edu/eastasia/2014/09/01/14th-conference-of-the-european-association-of-japanese-studies-visual-culture-and-postcard-research-papers/] And https://icu.repo.nii.ac.jp/record/4503/files/ACS44_01Steele.pdfThis item, a souvenir from Japan from between the wars (circa 1923) was brought home to Research, Victoria by Bill Teagle who was serving in the Royal Australian Navy (1919-1945). Bill Teagle's sister Violet Amelda Teagle had married Theodore (Curly) Feldbauer in 1933. Bill's brother-in-law Curly was taken as a Prisoner of War by the Japanese and died at Sandakan in March 1945. The family did not learn of Curly’s death till months later and Bill's sister, Violet, herself could never forgive the Japanese for what happened to Curly. Curly is remembered on the Eltham Roll of Honour Board and his son, Albert Feldbauer (Bill’s nephew and youngest child of the children of the soldier fathers attending a school in the district), was given the honour of turning the first sod for the Eltham War Memorial Infant Welfare Centre Building. Despite this, the family maintained this cherished souvenir from a time of previous foreign friendship with Japan. The item was possibly given by Bill Teagle to his sister Margaret Rose (formerly Ingram) who later married Richard Edward (Eddie) Fielding in early 1948. (Eddie had been engaged to someone else before he went to war, but his fiancée broke it off before his return to Australia.) It was cared for by the Teagle/Fielding family for approximately one hundred years. It is of particular significance given the family's connection to the Eltham War Memorial and the significance of that memorial to the local community and represents that despite the horrors of war, former friends then foes can become friends again.tom fielding collection, japanese postcard, postcard, 1923, great kanto earthquake, japan, tokyo, yokohama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Postcard, The Great Tokyo Earthquake on September 1st, 1923: The situation is miserable, 1923
The Great Kantō Earthquake of 1 September 1923 devastated the major cities of Tokyo and Yokohama, as well as five other surrounding prefectures and was one of the world’s worst natural disasters of the early twentieth century. In terms of loss of life and material damage, with an estimated 140,000 deaths and countless homeless, it is still Japan’s worst national disaster. Nearly 90% of the newspaper printers were destroyed in the earthquake. These postcards were not produced for aesthetics but as a major tool for the spread of information. Seeing how newspaper companies were left with their offices in shambles, postcard publishers tried to fill the gap hence some were in three languages. A very small number of publishing companies were fortunate enough to survive, one of them being Mitsumura Printing, which took advantage of its remaining resources to churn out postcards. When the Ōsaka Mainichi Shinbunsha published its bilingual three-volume photographic pictorial of the Great Kantō Earthquake just two weeks after the event, the calamity had already been captured in thousands of images that circulated on a national and international media highway. Commercial photographers and photojournalists produced the most abundant and immediate images of the quake, which were transmitted in newspapers, special-issue newspaper pictorials, commemorative photography collections, illustrated survivors’ accounts, and sets of commemorative postcards. These photographic images functioned as both news and souvenirs, rendering their consumers/viewers, inside and outside the devastated locale, into both witnesses and voyeurs. Images in the news media and those issued by respected publishing houses carried the visual authority of supposed facticity. As such they both produced and became the historical record of the event. Since the vast majority of 1923 disaster postcards that survive have no writing on them, they were likely treated more as collectibles than as a form of postal communication. Many were put into albums, creating new ways to combine images and create visual cultures of disaster for home viewing. Accordion-style albums allowed for personalized, serial organization of images that produced unique, imagistic narratives of the event. The album pages were also two-sided and could be stretched out to view a series of images on recto and verso. References: Imaging Disaster: Tokyo and the Visual Culture of Japan’s Great Earthquake of 1923 震災をイメージ化する 東京と1923年関東大震災のヴィジュアルカルチャー - The Asia. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://apjjf.org/2015/13/6/gennifer-weisenfeld/4270 The Great Kanto Earthquake: Postcards of Tragedy. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://www.tokyoweekender.com/art_and_culture/japanese-culture/the-great-kanto-earthquake-postcards/ See also: Postcards from Hell – Glimpses of the Great Kantō Earthquake; M. William STEELE (International Christian University, Japan) 14th Conference of the European Association of Japanese Studies: Visual Culture and Postcard Research Papers – East Asia Image Collection Blog. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://sites.lafayette.edu/eastasia/2014/09/01/14th-conference-of-the-european-association-of-japanese-studies-visual-culture-and-postcard-research-papers/] And https://icu.repo.nii.ac.jp/record/4503/files/ACS44_01Steele.pdfThis item, a souvenir from Japan from between the wars (circa 1923) was brought home to Research, Victoria by Bill Teagle who was serving in the Royal Australian Navy (1919-1945). Bill Teagle's sister Violet Amelda Teagle had married Theodore (Curly) Feldbauer in 1933. Bill's brother-in-law Curly was taken as a Prisoner of War by the Japanese and died at Sandakan in March 1945. The family did not learn of Curly’s death till months later and Bill's sister, Violet, herself could never forgive the Japanese for what happened to Curly. Curly is remembered on the Eltham Roll of Honour Board and his son, Albert Feldbauer (Bill’s nephew and youngest child of the children of the soldier fathers attending a school in the district), was given the honour of turning the first sod for the Eltham War Memorial Infant Welfare Centre Building. Despite this, the family maintained this cherished souvenir from a time of previous foreign friendship with Japan. The item was possibly given by Bill Teagle to his sister Margaret Rose (formerly Ingram) who later married Richard Edward (Eddie) Fielding in early 1948. (Eddie had been engaged to someone else before he went to war, but his fiancée broke it off before his return to Australia.) It was cared for by the Teagle/Fielding family for approximately one hundred years. It is of particular significance given the family's connection to the Eltham War Memorial and the significance of that memorial to the local community and represents that despite the horrors of war, former friends then foes can become friends again.tom fielding collection, japanese postcard, postcard, 1923, great kanto earthquake, japan, tokyo, yokohama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Postcard, The Great Tokyo Earthquake on September 1st, 1923: Keizen's after-disaster earthquake Daiichi Hamaki - overall view of Yokohama City, 1923
The Great Kantō Earthquake of 1 September 1923 devastated the major cities of Tokyo and Yokohama, as well as five other surrounding prefectures and was one of the world’s worst natural disasters of the early twentieth century. In terms of loss of life and material damage, with an estimated 140,000 deaths and countless homeless, it is still Japan’s worst national disaster. Nearly 90% of the newspaper printers were destroyed in the earthquake. These postcards were not produced for aesthetics but as a major tool for the spread of information. Seeing how newspaper companies were left with their offices in shambles, postcard publishers tried to fill the gap hence some were in three languages. A very small number of publishing companies were fortunate enough to survive, one of them being Mitsumura Printing, which took advantage of its remaining resources to churn out postcards. When the Ōsaka Mainichi Shinbunsha published its bilingual three-volume photographic pictorial of the Great Kantō Earthquake just two weeks after the event, the calamity had already been captured in thousands of images that circulated on a national and international media highway. Commercial photographers and photojournalists produced the most abundant and immediate images of the quake, which were transmitted in newspapers, special-issue newspaper pictorials, commemorative photography collections, illustrated survivors’ accounts, and sets of commemorative postcards. These photographic images functioned as both news and souvenirs, rendering their consumers/viewers, inside and outside the devastated locale, into both witnesses and voyeurs. Images in the news media and those issued by respected publishing houses carried the visual authority of supposed facticity. As such they both produced and became the historical record of the event. Since the vast majority of 1923 disaster postcards that survive have no writing on them, they were likely treated more as collectibles than as a form of postal communication. Many were put into albums, creating new ways to combine images and create visual cultures of disaster for home viewing. Accordion-style albums allowed for personalized, serial organization of images that produced unique, imagistic narratives of the event. The album pages were also two-sided and could be stretched out to view a series of images on recto and verso. References: Imaging Disaster: Tokyo and the Visual Culture of Japan’s Great Earthquake of 1923 震災をイメージ化する 東京と1923年関東大震災のヴィジュアルカルチャー - The Asia. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://apjjf.org/2015/13/6/gennifer-weisenfeld/4270 The Great Kanto Earthquake: Postcards of Tragedy. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://www.tokyoweekender.com/art_and_culture/japanese-culture/the-great-kanto-earthquake-postcards/ See also: Postcards from Hell – Glimpses of the Great Kantō Earthquake; M. William STEELE (International Christian University, Japan) 14th Conference of the European Association of Japanese Studies: Visual Culture and Postcard Research Papers – East Asia Image Collection Blog. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://sites.lafayette.edu/eastasia/2014/09/01/14th-conference-of-the-european-association-of-japanese-studies-visual-culture-and-postcard-research-papers/] And https://icu.repo.nii.ac.jp/record/4503/files/ACS44_01Steele.pdfThis item, a souvenir from Japan from between the wars (circa 1923) was brought home to Research, Victoria by Bill Teagle who was serving in the Royal Australian Navy (1919-1945). Bill Teagle's sister Violet Amelda Teagle had married Theodore (Curly) Feldbauer in 1933. Bill's brother-in-law Curly was taken as a Prisoner of War by the Japanese and died at Sandakan in March 1945. The family did not learn of Curly’s death till months later and Bill's sister, Violet, herself could never forgive the Japanese for what happened to Curly. Curly is remembered on the Eltham Roll of Honour Board and his son, Albert Feldbauer (Bill’s nephew and youngest child of the children of the soldier fathers attending a school in the district), was given the honour of turning the first sod for the Eltham War Memorial Infant Welfare Centre Building. Despite this, the family maintained this cherished souvenir from a time of previous foreign friendship with Japan. The item was possibly given by Bill Teagle to his sister Margaret Rose (formerly Ingram) who later married Richard Edward (Eddie) Fielding in early 1948. (Eddie had been engaged to someone else before he went to war, but his fiancée broke it off before his return to Australia.) It was cared for by the Teagle/Fielding family for approximately one hundred years. It is of particular significance given the family's connection to the Eltham War Memorial and the significance of that memorial to the local community and represents that despite the horrors of war, former friends then foes can become friends again.tom fielding collection, japanese postcard, postcard, 1923, great kanto earthquake, japan, tokyo, yokohama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Postcard, The Great Tokyo Earthquake on September 1st, 1923: Bank in Chidoricho Hungama - Disastrous scene of Yokohama Honmachi Town. No. 1 Bank Building, 1923
The Great Kantō Earthquake of 1 September 1923 devastated the major cities of Tokyo and Yokohama, as well as five other surrounding prefectures and was one of the world’s worst natural disasters of the early twentieth century. In terms of loss of life and material damage, with an estimated 140,000 deaths and countless homeless, it is still Japan’s worst national disaster. Nearly 90% of the newspaper printers were destroyed in the earthquake. These postcards were not produced for aesthetics but as a major tool for the spread of information. Seeing how newspaper companies were left with their offices in shambles, postcard publishers tried to fill the gap hence some were in three languages. A very small number of publishing companies were fortunate enough to survive, one of them being Mitsumura Printing, which took advantage of its remaining resources to churn out postcards. When the Ōsaka Mainichi Shinbunsha published its bilingual three-volume photographic pictorial of the Great Kantō Earthquake just two weeks after the event, the calamity had already been captured in thousands of images that circulated on a national and international media highway. Commercial photographers and photojournalists produced the most abundant and immediate images of the quake, which were transmitted in newspapers, special-issue newspaper pictorials, commemorative photography collections, illustrated survivors’ accounts, and sets of commemorative postcards. These photographic images functioned as both news and souvenirs, rendering their consumers/viewers, inside and outside the devastated locale, into both witnesses and voyeurs. Images in the news media and those issued by respected publishing houses carried the visual authority of supposed facticity. As such they both produced and became the historical record of the event. Since the vast majority of 1923 disaster postcards that survive have no writing on them, they were likely treated more as collectibles than as a form of postal communication. Many were put into albums, creating new ways to combine images and create visual cultures of disaster for home viewing. Accordion-style albums allowed for personalized, serial organization of images that produced unique, imagistic narratives of the event. The album pages were also two-sided and could be stretched out to view a series of images on recto and verso. References: Imaging Disaster: Tokyo and the Visual Culture of Japan’s Great Earthquake of 1923 震災をイメージ化する 東京と1923年関東大震災のヴィジュアルカルチャー - The Asia. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://apjjf.org/2015/13/6/gennifer-weisenfeld/4270 The Great Kanto Earthquake: Postcards of Tragedy. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://www.tokyoweekender.com/art_and_culture/japanese-culture/the-great-kanto-earthquake-postcards/ See also: Postcards from Hell – Glimpses of the Great Kantō Earthquake; M. William STEELE (International Christian University, Japan) 14th Conference of the European Association of Japanese Studies: Visual Culture and Postcard Research Papers – East Asia Image Collection Blog. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://sites.lafayette.edu/eastasia/2014/09/01/14th-conference-of-the-european-association-of-japanese-studies-visual-culture-and-postcard-research-papers/] And https://icu.repo.nii.ac.jp/record/4503/files/ACS44_01Steele.pdfThis item, a souvenir from Japan from between the wars (circa 1923) was brought home to Research, Victoria by Bill Teagle who was serving in the Royal Australian Navy (1919-1945). Bill Teagle's sister Violet Amelda Teagle had married Theodore (Curly) Feldbauer in 1933. Bill's brother-in-law Curly was taken as a Prisoner of War by the Japanese and died at Sandakan in March 1945. The family did not learn of Curly’s death till months later and Bill's sister, Violet, herself could never forgive the Japanese for what happened to Curly. Curly is remembered on the Eltham Roll of Honour Board and his son, Albert Feldbauer (Bill’s nephew and youngest child of the children of the soldier fathers attending a school in the district), was given the honour of turning the first sod for the Eltham War Memorial Infant Welfare Centre Building. Despite this, the family maintained this cherished souvenir from a time of previous foreign friendship with Japan. The item was possibly given by Bill Teagle to his sister Margaret Rose (formerly Ingram) who later married Richard Edward (Eddie) Fielding in early 1948. (Eddie had been engaged to someone else before he went to war, but his fiancée broke it off before his return to Australia.) It was cared for by the Teagle/Fielding family for approximately one hundred years. It is of particular significance given the family's connection to the Eltham War Memorial and the significance of that memorial to the local community and represents that despite the horrors of war, former friends then foes can become friends again.tom fielding collection, japanese postcard, postcard, 1923, great kanto earthquake, japan, tokyo, yokohama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Postcard, The Great Tokyo Earthquake on September 1st, 1923: Refugee evacuation, 1923
The Great Kantō Earthquake of 1 September 1923 devastated the major cities of Tokyo and Yokohama, as well as five other surrounding prefectures and was one of the world’s worst natural disasters of the early twentieth century. In terms of loss of life and material damage, with an estimated 140,000 deaths and countless homeless, it is still Japan’s worst national disaster. Nearly 90% of the newspaper printers were destroyed in the earthquake. These postcards were not produced for aesthetics but as a major tool for the spread of information. Seeing how newspaper companies were left with their offices in shambles, postcard publishers tried to fill the gap hence some were in three languages. A very small number of publishing companies were fortunate enough to survive, one of them being Mitsumura Printing, which took advantage of its remaining resources to churn out postcards. When the Ōsaka Mainichi Shinbunsha published its bilingual three-volume photographic pictorial of the Great Kantō Earthquake just two weeks after the event, the calamity had already been captured in thousands of images that circulated on a national and international media highway. Commercial photographers and photojournalists produced the most abundant and immediate images of the quake, which were transmitted in newspapers, special-issue newspaper pictorials, commemorative photography collections, illustrated survivors’ accounts, and sets of commemorative postcards. These photographic images functioned as both news and souvenirs, rendering their consumers/viewers, inside and outside the devastated locale, into both witnesses and voyeurs. Images in the news media and those issued by respected publishing houses carried the visual authority of supposed facticity. As such they both produced and became the historical record of the event. Since the vast majority of 1923 disaster postcards that survive have no writing on them, they were likely treated more as collectibles than as a form of postal communication. Many were put into albums, creating new ways to combine images and create visual cultures of disaster for home viewing. Accordion-style albums allowed for personalized, serial organization of images that produced unique, imagistic narratives of the event. The album pages were also two-sided and could be stretched out to view a series of images on recto and verso. References: Imaging Disaster: Tokyo and the Visual Culture of Japan’s Great Earthquake of 1923 震災をイメージ化する 東京と1923年関東大震災のヴィジュアルカルチャー - The Asia. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://apjjf.org/2015/13/6/gennifer-weisenfeld/4270 The Great Kanto Earthquake: Postcards of Tragedy. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://www.tokyoweekender.com/art_and_culture/japanese-culture/the-great-kanto-earthquake-postcards/ See also: Postcards from Hell – Glimpses of the Great Kantō Earthquake; M. William STEELE (International Christian University, Japan) 14th Conference of the European Association of Japanese Studies: Visual Culture and Postcard Research Papers – East Asia Image Collection Blog. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://sites.lafayette.edu/eastasia/2014/09/01/14th-conference-of-the-european-association-of-japanese-studies-visual-culture-and-postcard-research-papers/] And https://icu.repo.nii.ac.jp/record/4503/files/ACS44_01Steele.pdfThis item, a souvenir from Japan from between the wars (circa 1923) was brought home to Research, Victoria by Bill Teagle who was serving in the Royal Australian Navy (1919-1945). Bill Teagle's sister Violet Amelda Teagle had married Theodore (Curly) Feldbauer in 1933. Bill's brother-in-law Curly was taken as a Prisoner of War by the Japanese and died at Sandakan in March 1945. The family did not learn of Curly’s death till months later and Bill's sister, Violet, herself could never forgive the Japanese for what happened to Curly. Curly is remembered on the Eltham Roll of Honour Board and his son, Albert Feldbauer (Bill’s nephew and youngest child of the children of the soldier fathers attending a school in the district), was given the honour of turning the first sod for the Eltham War Memorial Infant Welfare Centre Building. Despite this, the family maintained this cherished souvenir from a time of previous foreign friendship with Japan. The item was possibly given by Bill Teagle to his sister Margaret Rose (formerly Ingram) who later married Richard Edward (Eddie) Fielding in early 1948. (Eddie had been engaged to someone else before he went to war, but his fiancée broke it off before his return to Australia.) It was cared for by the Teagle/Fielding family for approximately one hundred years. It is of particular significance given the family's connection to the Eltham War Memorial and the significance of that memorial to the local community and represents that despite the horrors of war, former friends then foes can become friends again.tom fielding collection, japanese postcard, postcard, 1923, great kanto earthquake, japan, tokyo, yokohama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Postcard, The Great Tokyo Earthquake on September 1st, 1923: Azuma Bridge, Tokyo, 1923
The Great Kantō Earthquake of 1 September 1923 devastated the major cities of Tokyo and Yokohama, as well as five other surrounding prefectures and was one of the world’s worst natural disasters of the early twentieth century. In terms of loss of life and material damage, with an estimated 140,000 deaths and countless homeless, it is still Japan’s worst national disaster. Nearly 90% of the newspaper printers were destroyed in the earthquake. These postcards were not produced for aesthetics but as a major tool for the spread of information. Seeing how newspaper companies were left with their offices in shambles, postcard publishers tried to fill the gap hence some were in three languages. A very small number of publishing companies were fortunate enough to survive, one of them being Mitsumura Printing, which took advantage of its remaining resources to churn out postcards. When the Ōsaka Mainichi Shinbunsha published its bilingual three-volume photographic pictorial of the Great Kantō Earthquake just two weeks after the event, the calamity had already been captured in thousands of images that circulated on a national and international media highway. Commercial photographers and photojournalists produced the most abundant and immediate images of the quake, which were transmitted in newspapers, special-issue newspaper pictorials, commemorative photography collections, illustrated survivors’ accounts, and sets of commemorative postcards. These photographic images functioned as both news and souvenirs, rendering their consumers/viewers, inside and outside the devastated locale, into both witnesses and voyeurs. Images in the news media and those issued by respected publishing houses carried the visual authority of supposed facticity. As such they both produced and became the historical record of the event. Since the vast majority of 1923 disaster postcards that survive have no writing on them, they were likely treated more as collectibles than as a form of postal communication. Many were put into albums, creating new ways to combine images and create visual cultures of disaster for home viewing. Accordion-style albums allowed for personalized, serial organization of images that produced unique, imagistic narratives of the event. The album pages were also two-sided and could be stretched out to view a series of images on recto and verso. References: Imaging Disaster: Tokyo and the Visual Culture of Japan’s Great Earthquake of 1923 震災をイメージ化する 東京と1923年関東大震災のヴィジュアルカルチャー - The Asia. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://apjjf.org/2015/13/6/gennifer-weisenfeld/4270 The Great Kanto Earthquake: Postcards of Tragedy. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://www.tokyoweekender.com/art_and_culture/japanese-culture/the-great-kanto-earthquake-postcards/ See also: Postcards from Hell – Glimpses of the Great Kantō Earthquake; M. William STEELE (International Christian University, Japan) 14th Conference of the European Association of Japanese Studies: Visual Culture and Postcard Research Papers – East Asia Image Collection Blog. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://sites.lafayette.edu/eastasia/2014/09/01/14th-conference-of-the-european-association-of-japanese-studies-visual-culture-and-postcard-research-papers/] And https://icu.repo.nii.ac.jp/record/4503/files/ACS44_01Steele.pdfThis item, a souvenir from Japan from between the wars (circa 1923) was brought home to Research, Victoria by Bill Teagle who was serving in the Royal Australian Navy (1919-1945). Bill Teagle's sister Violet Amelda Teagle had married Theodore (Curly) Feldbauer in 1933. Bill's brother-in-law Curly was taken as a Prisoner of War by the Japanese and died at Sandakan in March 1945. The family did not learn of Curly’s death till months later and Bill's sister, Violet, herself could never forgive the Japanese for what happened to Curly. Curly is remembered on the Eltham Roll of Honour Board and his son, Albert Feldbauer (Bill’s nephew and youngest child of the children of the soldier fathers attending a school in the district), was given the honour of turning the first sod for the Eltham War Memorial Infant Welfare Centre Building. Despite this, the family maintained this cherished souvenir from a time of previous foreign friendship with Japan. The item was possibly given by Bill Teagle to his sister Margaret Rose (formerly Ingram) who later married Richard Edward (Eddie) Fielding in early 1948. (Eddie had been engaged to someone else before he went to war, but his fiancée broke it off before his return to Australia.) It was cared for by the Teagle/Fielding family for approximately one hundred years. It is of particular significance given the family's connection to the Eltham War Memorial and the significance of that memorial to the local community and represents that despite the horrors of war, former friends then foes can become friends again.tom fielding collection, japanese postcard, postcard, 1923, great kanto earthquake, japan, tokyo, yokohama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Postcard, The Great Tokyo Earthquake on September 1st, 1923: Mitsukoshi Department Store, Tokyo, 1923
The Great Kantō Earthquake of 1 September 1923 devastated the major cities of Tokyo and Yokohama, as well as five other surrounding prefectures and was one of the world’s worst natural disasters of the early twentieth century. In terms of loss of life and material damage, with an estimated 140,000 deaths and countless homeless, it is still Japan’s worst national disaster. Nearly 90% of the newspaper printers were destroyed in the earthquake. These postcards were not produced for aesthetics but as a major tool for the spread of information. Seeing how newspaper companies were left with their offices in shambles, postcard publishers tried to fill the gap hence some were in three languages. A very small number of publishing companies were fortunate enough to survive, one of them being Mitsumura Printing, which took advantage of its remaining resources to churn out postcards. When the Ōsaka Mainichi Shinbunsha published its bilingual three-volume photographic pictorial of the Great Kantō Earthquake just two weeks after the event, the calamity had already been captured in thousands of images that circulated on a national and international media highway. Commercial photographers and photojournalists produced the most abundant and immediate images of the quake, which were transmitted in newspapers, special-issue newspaper pictorials, commemorative photography collections, illustrated survivors’ accounts, and sets of commemorative postcards. These photographic images functioned as both news and souvenirs, rendering their consumers/viewers, inside and outside the devastated locale, into both witnesses and voyeurs. Images in the news media and those issued by respected publishing houses carried the visual authority of supposed facticity. As such they both produced and became the historical record of the event. Since the vast majority of 1923 disaster postcards that survive have no writing on them, they were likely treated more as collectibles than as a form of postal communication. Many were put into albums, creating new ways to combine images and create visual cultures of disaster for home viewing. Accordion-style albums allowed for personalized, serial organization of images that produced unique, imagistic narratives of the event. The album pages were also two-sided and could be stretched out to view a series of images on recto and verso. References: Imaging Disaster: Tokyo and the Visual Culture of Japan’s Great Earthquake of 1923 震災をイメージ化する 東京と1923年関東大震災のヴィジュアルカルチャー - The Asia. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://apjjf.org/2015/13/6/gennifer-weisenfeld/4270 The Great Kanto Earthquake: Postcards of Tragedy. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://www.tokyoweekender.com/art_and_culture/japanese-culture/the-great-kanto-earthquake-postcards/ See also: Postcards from Hell – Glimpses of the Great Kantō Earthquake; M. William STEELE (International Christian University, Japan) 14th Conference of the European Association of Japanese Studies: Visual Culture and Postcard Research Papers – East Asia Image Collection Blog. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://sites.lafayette.edu/eastasia/2014/09/01/14th-conference-of-the-european-association-of-japanese-studies-visual-culture-and-postcard-research-papers/] And https://icu.repo.nii.ac.jp/record/4503/files/ACS44_01Steele.pdfThis item, a souvenir from Japan from between the wars (circa 1923) was brought home to Research, Victoria by Bill Teagle who was serving in the Royal Australian Navy (1919-1945). Bill Teagle's sister Violet Amelda Teagle had married Theodore (Curly) Feldbauer in 1933. Bill's brother-in-law Curly was taken as a Prisoner of War by the Japanese and died at Sandakan in March 1945. The family did not learn of Curly’s death till months later and Bill's sister, Violet, herself could never forgive the Japanese for what happened to Curly. Curly is remembered on the Eltham Roll of Honour Board and his son, Albert Feldbauer (Bill’s nephew and youngest child of the children of the soldier fathers attending a school in the district), was given the honour of turning the first sod for the Eltham War Memorial Infant Welfare Centre Building. Despite this, the family maintained this cherished souvenir from a time of previous foreign friendship with Japan. The item was possibly given by Bill Teagle to his sister Margaret Rose (formerly Ingram) who later married Richard Edward (Eddie) Fielding in early 1948. (Eddie had been engaged to someone else before he went to war, but his fiancée broke it off before his return to Australia.) It was cared for by the Teagle/Fielding family for approximately one hundred years. It is of particular significance given the family's connection to the Eltham War Memorial and the significance of that memorial to the local community and represents that despite the horrors of war, former friends then foes can become friends again.tom fielding collection, japanese postcard, postcard, 1923, great kanto earthquake, japan, tokyo, yokohama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Postcard, The Great Tokyo Earthquake on September 1st, 1923: Shirokiya Department Store, Tokyo, 1923
The Great Kantō Earthquake of 1 September 1923 devastated the major cities of Tokyo and Yokohama, as well as five other surrounding prefectures and was one of the world’s worst natural disasters of the early twentieth century. In terms of loss of life and material damage, with an estimated 140,000 deaths and countless homeless, it is still Japan’s worst national disaster. Nearly 90% of the newspaper printers were destroyed in the earthquake. These postcards were not produced for aesthetics but as a major tool for the spread of information. Seeing how newspaper companies were left with their offices in shambles, postcard publishers tried to fill the gap hence some were in three languages. A very small number of publishing companies were fortunate enough to survive, one of them being Mitsumura Printing, which took advantage of its remaining resources to churn out postcards. When the Ōsaka Mainichi Shinbunsha published its bilingual three-volume photographic pictorial of the Great Kantō Earthquake just two weeks after the event, the calamity had already been captured in thousands of images that circulated on a national and international media highway. Commercial photographers and photojournalists produced the most abundant and immediate images of the quake, which were transmitted in newspapers, special-issue newspaper pictorials, commemorative photography collections, illustrated survivors’ accounts, and sets of commemorative postcards. These photographic images functioned as both news and souvenirs, rendering their consumers/viewers, inside and outside the devastated locale, into both witnesses and voyeurs. Images in the news media and those issued by respected publishing houses carried the visual authority of supposed facticity. As such they both produced and became the historical record of the event. Since the vast majority of 1923 disaster postcards that survive have no writing on them, they were likely treated more as collectibles than as a form of postal communication. Many were put into albums, creating new ways to combine images and create visual cultures of disaster for home viewing. Accordion-style albums allowed for personalized, serial organization of images that produced unique, imagistic narratives of the event. The album pages were also two-sided and could be stretched out to view a series of images on recto and verso. References: Imaging Disaster: Tokyo and the Visual Culture of Japan’s Great Earthquake of 1923 震災をイメージ化する 東京と1923年関東大震災のヴィジュアルカルチャー - The Asia. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://apjjf.org/2015/13/6/gennifer-weisenfeld/4270 The Great Kanto Earthquake: Postcards of Tragedy. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://www.tokyoweekender.com/art_and_culture/japanese-culture/the-great-kanto-earthquake-postcards/ See also: Postcards from Hell – Glimpses of the Great Kantō Earthquake; M. William STEELE (International Christian University, Japan) 14th Conference of the European Association of Japanese Studies: Visual Culture and Postcard Research Papers – East Asia Image Collection Blog. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://sites.lafayette.edu/eastasia/2014/09/01/14th-conference-of-the-european-association-of-japanese-studies-visual-culture-and-postcard-research-papers/] And https://icu.repo.nii.ac.jp/record/4503/files/ACS44_01Steele.pdfThis item, a souvenir from Japan from between the wars (circa 1923) was brought home to Research, Victoria by Bill Teagle who was serving in the Royal Australian Navy (1919-1945). Bill Teagle's sister Violet Amelda Teagle had married Theodore (Curly) Feldbauer in 1933. Bill's brother-in-law Curly was taken as a Prisoner of War by the Japanese and died at Sandakan in March 1945. The family did not learn of Curly’s death till months later and Bill's sister, Violet, herself could never forgive the Japanese for what happened to Curly. Curly is remembered on the Eltham Roll of Honour Board and his son, Albert Feldbauer (Bill’s nephew and youngest child of the children of the soldier fathers attending a school in the district), was given the honour of turning the first sod for the Eltham War Memorial Infant Welfare Centre Building. Despite this, the family maintained this cherished souvenir from a time of previous foreign friendship with Japan. The item was possibly given by Bill Teagle to his sister Margaret Rose (formerly Ingram) who later married Richard Edward (Eddie) Fielding in early 1948. (Eddie had been engaged to someone else before he went to war, but his fiancée broke it off before his return to Australia.) It was cared for by the Teagle/Fielding family for approximately one hundred years. It is of particular significance given the family's connection to the Eltham War Memorial and the significance of that memorial to the local community and represents that despite the horrors of war, former friends then foes can become friends again.tom fielding collection, japanese postcard, postcard, 1923, great kanto earthquake, japan, tokyo, yokohama -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Postcard, The Great Tokyo Earthquake on September 1st, 1923: Ueno Hakuhinkan, Tokyo - Scene around Ueno Museum, 1923
The Great Kantō Earthquake of 1 September 1923 devastated the major cities of Tokyo and Yokohama, as well as five other surrounding prefectures and was one of the world’s worst natural disasters of the early twentieth century. In terms of loss of life and material damage, with an estimated 140,000 deaths and countless homeless, it is still Japan’s worst national disaster. Nearly 90% of the newspaper printers were destroyed in the earthquake. These postcards were not produced for aesthetics but as a major tool for the spread of information. Seeing how newspaper companies were left with their offices in shambles, postcard publishers tried to fill the gap hence some were in three languages. A very small number of publishing companies were fortunate enough to survive, one of them being Mitsumura Printing, which took advantage of its remaining resources to churn out postcards. When the Ōsaka Mainichi Shinbunsha published its bilingual three-volume photographic pictorial of the Great Kantō Earthquake just two weeks after the event, the calamity had already been captured in thousands of images that circulated on a national and international media highway. Commercial photographers and photojournalists produced the most abundant and immediate images of the quake, which were transmitted in newspapers, special-issue newspaper pictorials, commemorative photography collections, illustrated survivors’ accounts, and sets of commemorative postcards. These photographic images functioned as both news and souvenirs, rendering their consumers/viewers, inside and outside the devastated locale, into both witnesses and voyeurs. Images in the news media and those issued by respected publishing houses carried the visual authority of supposed facticity. As such they both produced and became the historical record of the event. Since the vast majority of 1923 disaster postcards that survive have no writing on them, they were likely treated more as collectibles than as a form of postal communication. Many were put into albums, creating new ways to combine images and create visual cultures of disaster for home viewing. Accordion-style albums allowed for personalized, serial organization of images that produced unique, imagistic narratives of the event. The album pages were also two-sided and could be stretched out to view a series of images on recto and verso. References: Imaging Disaster: Tokyo and the Visual Culture of Japan’s Great Earthquake of 1923 震災をイメージ化する 東京と1923年関東大震災のヴィジュアルカルチャー - The Asia. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://apjjf.org/2015/13/6/gennifer-weisenfeld/4270 The Great Kanto Earthquake: Postcards of Tragedy. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://www.tokyoweekender.com/art_and_culture/japanese-culture/the-great-kanto-earthquake-postcards/ See also: Postcards from Hell – Glimpses of the Great Kantō Earthquake; M. William STEELE (International Christian University, Japan) 14th Conference of the European Association of Japanese Studies: Visual Culture and Postcard Research Papers – East Asia Image Collection Blog. (2024, March 31). Retrieved from https://sites.lafayette.edu/eastasia/2014/09/01/14th-conference-of-the-european-association-of-japanese-studies-visual-culture-and-postcard-research-papers/] And https://icu.repo.nii.ac.jp/record/4503/files/ACS44_01Steele.pdfThis item, a souvenir from Japan from between the wars (circa 1923) was brought home to Research, Victoria by Bill Teagle who was serving in the Royal Australian Navy (1919-1945). Bill Teagle's sister Violet Amelda Teagle had married Theodore (Curly) Feldbauer in 1933. Bill's brother-in-law Curly was taken as a Prisoner of War by the Japanese and died at Sandakan in March 1945. The family did not learn of Curly’s death till months later and Bill's sister, Violet, herself could never forgive the Japanese for what happened to Curly. Curly is remembered on the Eltham Roll of Honour Board and his son, Albert Feldbauer (Bill’s nephew and youngest child of the children of the soldier fathers attending a school in the district), was given the honour of turning the first sod for the Eltham War Memorial Infant Welfare Centre Building. Despite this, the family maintained this cherished souvenir from a time of previous foreign friendship with Japan. The item was possibly given by Bill Teagle to his sister Margaret Rose (formerly Ingram) who later married Richard Edward (Eddie) Fielding in early 1948. (Eddie had been engaged to someone else before he went to war, but his fiancée broke it off before his return to Australia.) It was cared for by the Teagle/Fielding family for approximately one hundred years. It is of particular significance given the family's connection to the Eltham War Memorial and the significance of that memorial to the local community and represents that despite the horrors of war, former friends then foes can become friends again.tom fielding collection, japanese postcard, postcard, 1923, great kanto earthquake, japan, tokyo, yokohama
