Showing 1307 items
matching aboriginal australian. |
-
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, South Australia Department of Education and Children's Services, Languages : Australian Indigenous languages, 2003
wall chartslanguage teaching south australia, curriculum development, curriculum standards, secondary education -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, South Australia Department of Education and Children's Services, R-10 languages (Australian Indigenous) teaching resource, 2005
Looks at an outline of learning and teaching of Indigenous Languages across the primary and secondary school years.mapslanguage learning, primary school education, secondary school education -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Senior Secondary Assessment Board of South Australia, Australia's Indigenous languages in practice, 1996
Based on the Australian Indigenous Languages Framework.b&w illustrations, tables, word lists, sample programs and examination paperskaurna, pitjantjatjara, yankunytjatjara, antikirinya, yolgnu, pilbara, language and culture, bilingual education, linguistics, language and technology, teaching programs, -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Intechnics, Australian mammals : with Aboriginal perspectives and drawings
... Australian mammals : with Aboriginal perspectives and...Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages 33 Saxon ...B&w illustrations, maps, word listseducation, australian fauna, monotremes, marsupials, mammals, primary school education, environmental education -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Australian Indigenous Languages Framework Project, Australian Indigenous languages framework, 1994
diagrams, graphseducation, bilingual education, lote, languages other than english, language revival, aboriginal english, language ecology -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Australian Indigenous Languages Framework Project, Australian Indigenous languages framework support materials, 1994
maps, tableskaurna, education, bilingual education, lote, languages other than english, language revival, aboriginal english, language ecology -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Intechnics, Australian birds : with Aboriginal perspectives and language supplement
... Australian birds : with Aboriginal perspectives and..., word lists Australian birds : with Aboriginal perspectives ...B&w illustrations, maps, word listsaustralian birds, education, primary school education, environmental education -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Rosalind Berry et al, Making the jump : a resource book for teachers of Aboriginal students, 1997
The focus of Making the Jump is the acceptance of Aboriginal students' home language, and the use of that language as a jumping off point for teaching Standard Australian English. It is a valuable classroom resource for teachers working with students whose home language is Kriol or Aboriginal English. Ch. 1. First impressions Ch. 2. Cultures in the classroom Ch. 3. Understanding the languages Ch. 4. Separating the languages Ch. 5. SAE- Planning and practice Ch. 6. Discovering the differences Ch. 7. Games.B&w illustrations, diagrams, gamesbilingual education, catholic school education, linguistics and education -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Education Department of Western Australia, Deadly ideas: a collection of two-way bidialectal teaching strategies, 2004
This book contains a selection of teaching strategies that were collected from teachers involved in the Deadly Ways to Learn project conducted jointly by the Education Department of Western Australia, the Catholic Education Office of Western Australia and the Association of Independent Schools of Western Australia during 1998 and 1999. -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, St Philip's College Alice Springs - Principal Chris Tudor & Deputy Principal Chris Eldridge, 09/1986
In 1945 the Reverend Harry Griffiths, who worked for the Methodist Inland Mission in Alice Springs, saw the need for a boarding facility for children of families living in remote areas in Central Australia who needed access to schools. He and his wife established Griffiths House, on a site in the town centre, and for many years it became home for students from all over the Outback, including many young Aboriginal people. In the late 1950's the Rev Fred McKay, successor to the Rev John Flynn as Superintendent of the Australian Inland Mission, lobbied the United Church in the Northern Territory to build and expand on this important start. Together the Presbyterian, Methodist and Congregational churches embarked on a missionary venture to develop St Philip's College - a new, larger residential hostel which would one day become a full boarding school. An ideal site - 22 acres of bush at the junction of the Charles and Todd Rivers and backing on to the Telegraph Station National Park - was secured and after six years of planning, construction began in 1964. Fred McKay led the legendary work parties comprised of volunteers from all over Australia who travelled to Alice Springs, paying their own way and volunteering their expertise, time and labour, to turn a dream into a reality. This fantastic tradition continues today, with work parties arriving each mid-year holiday. On 13 February 1965 the first boarders moved in to St Philip's College. For the first 24 years, therefore, St Philip's College operated as a residential hostel only. The College’s ninth Headmaster, Mr Christopher Tudor, arrived in 1986. He and the Council Chairman, Mrs Jan Heaslip, judged that the time was right to complete the original plan to turn St Philip’s College into a fully fledged independent boarding/day school, serving not only “bush” families, but also the growing population of Alice Springs. The then College Council embraced the idea and three years of frantic, determined preparation and planning commenced, culminating in an extensive $2 million building program in 1988. To this day there continues to be further development with the new landscaping underway near The Minnamurra Hall, Reception and Rivergum Cafe, plus the recent completion of the Science & Food Technology building and the new Rivergum Cafe.Head & Shoulders of Chris Eldridgest. philip's college, tudor, chris, eldridge, chris -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, St Philip's College Alice Springs - Principal Chris Tudor & Deputy Principal Chris Eldridge, 09/1986
In 1945 the Reverend Harry Griffiths, who worked for the Methodist Inland Mission in Alice Springs, saw the need for a boarding facility for children of families living in remote areas in Central Australia who needed access to schools. He and his wife established Griffiths House, on a site in the town centre, and for many years it became home for students from all over the Outback, including many young Aboriginal people. In the late 1950's the Rev Fred McKay, successor to the Rev John Flynn as Superintendent of the Australian Inland Mission, lobbied the United Church in the Northern Territory to build and expand on this important start. Together the Presbyterian, Methodist and Congregational churches embarked on a missionary venture to develop St Philip's College - a new, larger residential hostel which would one day become a full boarding school. An ideal site - 22 acres of bush at the junction of the Charles and Todd Rivers and backing on to the Telegraph Station National Park - was secured and after six years of planning, construction began in 1964. Fred McKay led the legendary work parties comprised of volunteers from all over Australia who travelled to Alice Springs, paying their own way and volunteering their expertise, time and labour, to turn a dream into a reality. This fantastic tradition continues today, with work parties arriving each mid-year holiday. On 13 February 1965 the first boarders moved in to St Philip's College. For the first 24 years, therefore, St Philip's College operated as a residential hostel only. The College’s ninth Headmaster, Mr Christopher Tudor, arrived in 1986. He and the Council Chairman, Mrs Jan Heaslip, judged that the time was right to complete the original plan to turn St Philip’s College into a fully fledged independent boarding/day school, serving not only “bush” families, but also the growing population of Alice Springs. The then College Council embraced the idea and three years of frantic, determined preparation and planning commenced, culminating in an extensive $2 million building program in 1988. To this day there continues to be further development with the new landscaping underway near The Minnamurra Hall, Reception and Rivergum Cafe, plus the recent completion of the Science & Food Technology building and the new Rivergum Cafe.Head & Shoulders of Chris Tudor.st. philip's college, tudor, chris, eldridge, chris -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, St Philip's College Alice Springs - Principal Chris Tudor & Deputy Principal Chris Eldridge, 09/1986
In 1945 the Reverend Harry Griffiths, who worked for the Methodist Inland Mission in Alice Springs, saw the need for a boarding facility for children of families living in remote areas in Central Australia who needed access to schools. He and his wife established Griffiths House, on a site in the town centre, and for many years it became home for students from all over the Outback, including many young Aboriginal people. In the late 1950's the Rev Fred McKay, successor to the Rev John Flynn as Superintendent of the Australian Inland Mission, lobbied the United Church in the Northern Territory to build and expand on this important start. Together the Presbyterian, Methodist and Congregational churches embarked on a missionary venture to develop St Philip's College - a new, larger residential hostel which would one day become a full boarding school. An ideal site - 22 acres of bush at the junction of the Charles and Todd Rivers and backing on to the Telegraph Station National Park - was secured and after six years of planning, construction began in 1964. Fred McKay led the legendary work parties comprised of volunteers from all over Australia who travelled to Alice Springs, paying their own way and volunteering their expertise, time and labour, to turn a dream into a reality. This fantastic tradition continues today, with work parties arriving each mid-year holiday. On 13 February 1965 the first boarders moved in to St Philip's College. For the first 24 years, therefore, St Philip's College operated as a residential hostel only. The College’s ninth Headmaster, Mr Christopher Tudor, arrived in 1986. He and the Council Chairman, Mrs Jan Heaslip, judged that the time was right to complete the original plan to turn St Philip’s College into a fully fledged independent boarding/day school, serving not only “bush” families, but also the growing population of Alice Springs. The then College Council embraced the idea and three years of frantic, determined preparation and planning commenced, culminating in an extensive $2 million building program in 1988. To this day there continues to be further development with the new landscaping underway near The Minnamurra Hall, Reception and Rivergum Cafe, plus the recent completion of the Science & Food Technology building and the new Rivergum Cafe.Tudor and Eldridge in conversation with the College in the background.st. philip's college, tudor, chris, eldridge, chris -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Rev. Djiniyini Gondarra, 1986
Rev Dr Djiniyini Gondarra OAM, was born in Milingimbi, eastern Arnhemland in 1945. He was educated at Milingimbi Mission School and pursued his theological education as a youth leader and Sunday School teacher through the Methodist Church, before attending college in Brisbane. In 1969 he trained as a Minister in Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands under the Uniting Church, before returning to Arnhemland to minister his own people at the Galiwin’ku parish, firstly as a lay pastor (1971-1972) and then as a Minister from 1976-1982. In 1983-84, Rev Djiniyini worked as a Lecturer in Theology at Nungalinya College, Darwin. He was honoured with a Diploma of Theology (Honorary) from there in 1984, and in 1991 received a Cultural Doctorate in Literature (Honorary) from the World University, Roundtable, Arizona USA. Rev Djiniyini was awarded the Order of Australia Medal (OAM) in 1995. As well as being the Chairman of ALPA since 1993, Rev Djiniyini is currently the Director of Duduy’ngu Pty Ltd, which provides consultancy and cross-cultural services. He is also Director of Yirrkala Business Enterprises. Over the years, Rev Djiniyini has served on many committees and councils including: Member of the Steering Committee of the Australian Indigenous Cultural Network (1998-2001), CEO of Aboriginal Resource and Development Services Inc (1998-2001), CEO of the Northern Regional Council of the Uniting Aboriginal and Islander Christian Congress (1998-2001), Director of Reconciliation Australia Limited (2000-2001), Member of Council for Aboriginal Reconciliation (1998-2000), Chairman of Uniting Aboriginal and Islander Christian Congress (1995-2000 & 1990-1993), Member of Central Committee of the World Council of Churches (1991-1994), Moderator of Northern Synod, Uniting Church in Australia (1985-1987), Secretary of newly formed Aboriginal Presbytery, Northern Synod, Uniting Church in Australia (1985), and Vice-President of Uniting Aboriginal and Islander Christian Congress Uniting Church in Australia (1983-1987). Rev Dr Djiniyini Gondarra OAM has also been extensively published, and his works include: • Information Papers (co authored), Aboriginal Resource and Development Services: • Confusion Between Cultures (1998) • MHead & Shoulders of Djiniyini Gondarra facing right of picture."Rev. Djiniyini Gondarra 1986. Moderator Northern Synod and Vice President of Uniting Aboriginal and Islander Christian Conference."gondarra, djiniyini, uaicc, northern synod uca -
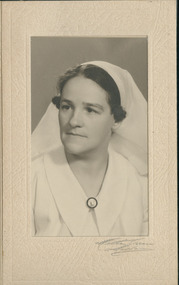 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, C1947
Hilda Charlotte Foster, 1902 - 1990, was a Double Certified Nurse when, at the age of 35, she successfully applied to the board of the Australian Inland Mission (AIM) to work at an outback field centre in South Australia. Born and raised in suburban Melbourne, she had been inspired by stories told to her by other missionaries about the fulfilment to be gained working amongst Aboriginal communities. Given her religious faith and nursing skills, she believed she could make a difference. She worked in Oodnadatta in South Australia for two years (1937-1939), followed by a stint in Innamincka in New South Wales in 1940 -1942. Before she became a nurse, Hilda Foster trained to be a Sunday School teacher and was a member of the Sunday School Council of Victoria. She completed first aid courses run through the Presbyterian Deaconesses Institute in Carlton, Victoria, and in 1930 successfully applied to become a trainee nurse at the Austin Hospital for Incurables, in Heidelberg. She commenced her training there in 1931, before moving to the Women's Hospital in 1933. In 1934 she had six months at the Fairfield Infectious Diseases Hospital, before returning to the Austin, where she was employed when she sat her final exams in November 1934. Her combined skills made her a most attractive option for the Australian Inland Mission. As well as being multi-skilled as a nurse, she provided religious instruction and spiritual ministry to members of the community. https://trove.nla.gov.au/people/762093?c=people Sister Foster nursed at Toora Bush Hospital prior to leaving for the Paton Memorial Hospital, Vila, New Hebrides in 1944. She left the New Hebrides in 1946.Matt, black and white, head and shoulders, studio portrait of Sister Hilda Charlotte Foster on card.australian inland mission, presbyterian deaconess, sister hilda charlotte foster, paton memorial hospital vila new hebrides -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, 19th century, but undated newspaper cutting
B: 1808 10 May in Cornwall England; D: 21 October 1865 Portland Vic. See "Cross at the Campfire" by Heather Le Griffon for the full history of Francis Tuckfield and his attempts to establish a mission near Birregurra, Vic. Also "Australian Dictionary of Biography, Vol. 2, 1967.Two photographs cut from a newspaper in one card frame of Rev. Francis Tuckfield - the first from 1837; the second from 1865, the year he died.The 1837 photo has "Preacher … Geelong, July 28th 1838"tuckfield, francis, buntingdale aboriginal mission, wesleyan methodist -
 The Adam Lindsay Gordon Commemorative Committee Inc.
The Adam Lindsay Gordon Commemorative Committee Inc.Book, Adam Lindsay Gordon and Other Australian Writers- Inscribed by Charles R Long to Isaac Selby- Pioneers Day 1937
Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 - 1954), Tuesday 26 October 1937, page 16 Pioneers' Day. Novemher 19 has been fixed as Pioneers' day The annual historical service organised by tho Pioneers' Association will be held in the Melbourne General Cemetery on Sunday. November 21. Addresses will be delivered by Messrs. W. A. Sanderson. J. Selby. E. Tozer. 13. W. Mylrea and C. R. Long. The memorial over the grave of William Pascoe Crook will be unveiled by Rev. W. Alblston. president of the Congregational Union. An aboriginal concert will be held in the Central Hall on November 10. -
 Duldig Studio museum + sculpture garden
Duldig Studio museum + sculpture gardenSculpture, Karl Duldig, Moses by Karl Duldig 1956 (Bronze Cast 1979), 1956 / 1979
... across a variety of disciplines, noted that Australia’s post war ...This sculpture is a bronze cast of Karl Duldig’s 1956 terracotta sculpture titled 'Moses'. The terracotta sculpture won the 1956 Victorian Sculptor of the Year award, an honor given by the Victorian Society of Sculptors. The National Gallery of Victoria purchased the original terracotta sculpture for the Gallery’s collection in 1956. In 1979 the NGV allowed Karl to cast the original terracotta sculpture in bronze (to a limited edition of 5). The National Gallery of Victoria holds one of these casts and one is in Duldig Studio collection. The original terracotta sculpture was exhibited in 1956 at the Olympic Arts Exhibition in Wilson Hall at the University of Melbourne. Two other works by Karl were also exhibited, a sandstone titled 'Adam and Eve' and a work titled 'Fountain'. The catalogue for the Olympic exhibition, which promoted modernism across a variety of disciplines, noted that Australia’s post war immigration program had given ‘further momentum to the modernist cause’. The identification of émigré artists, such as Karl Duldig, with the acceptance of modernism in Australia became a major theme in any discussion of art and design in the post war period. Ann Carew 2016The subject Moses and the tablets of law is an important theme in the history of art. For example the National Gallery of Victoria collection includes paintings on this topic by the Australian Aboriginal artist, Queenie McKenzie (1991), prints by the Russian-French modernist artist, Marc Chagall (1956), and a painting by 19th century British academic painter, John Rogers Herbert (1870s). Michelangelo’s sculpture of Moses is perhaps the most famous sculptural interpretation of the subject. In Karl’s hands we have a modern interpretation of the theme. His simplification and abstraction of form and attention to surface modeling is masterly. The figure has an emotional intensity and despite its relatively small scale, a ‘forceful monumentality’. The sculpture is aesthetically significant for its craftsmanship, expressive qualities and modernity. It is historically significant because of its associations with the 1956 Olympic Arts Festival. The Duldig Studio’s bronze cast of the sculpture was exhibited in the exhibition '1956: Melbourne, modernity and the XVI Olympiad, Museum of Modern Art at Heide.' Apart from the formal qualities of a work like Moses, its relevance as a motif in Judaism and Christian faiths ensures its place as a work of spiritual significance. Ann Carew 2016Bronze cast from terracotta sculpture. Depicts Moses as in Exodus 32 when he returns from Sinai with the tablets of the law to find his people worshipping the golden calf, in his fury he holds the tablets aloft above his head before crashing them down on the ground. -
 Warrnambool Art Gallery
Warrnambool Art GalleryPooneed-ke (child carrier), c. 1890-1920
This mat was donated to the Museum by the Rev. Andrew Rule Osborn. Reverend Osborn donated several artefacts including Aboriginal artefacts, Zulu and Pacific Islander objects. The Reverend came over from Tasmania to serve here in Warrnambool. His wife Annie was a fantastic author and wrote children's literature which was serialised in the newspapers. She was a supporter of women's suffrage and also the first woman editor of The Age.A flat circular mat made from native Australian grasses. Indigenous Australians would use this as a baby-carrier on the back. One band would be placed around the lower back and mat and two higher up. The child would be placed between the back and the mat. It was also sometimes used as a sun shade or something to sit on. It is a spiral form with grasses woven around to bind it together.aboriginal, indigenous, child carrier, mat, native grasses, reverend andrew rule osborn, annie osborn, women, mothers -
 Peterborough History Group
Peterborough History GroupBook, Australian Aborigines: the languages and customs of several tribes of aborigines in the Western District of Victoria, Published 1981, First published 1881
Information about local aboriginal tribesDoesn't specifically refer to Peterborough but explains early aboriginal culture and their relationship to the coastHardcover 111 page book with 104 page of annexures and index. Introduction by Jan Critchett, Warrnambool Institute of Advanced Education.Adhesive book plate with the name H W Grimwade.peterborough pre history, kirrie wurung, kaawirn kuunawarn, hissing swan aborigines, kirrae wurung, yarruun parpur tarneen -
 Peterborough History Group
Peterborough History GroupBook, My Heart is Breaking, 1993
... people in district. aboriginal australians aboriginal history ...Part 1 is an annoted listing of relevant archives and index of family names. Part 2 is an overview of the interaction between white australians and aboriginal peopleSoftcover 191page book with a general index and including an index of names.non-fictionPart 1 is an annoted listing of relevant archives and index of family names. Part 2 is an overview of the interaction between white australians and aboriginal peopleaboriginal australians, aboriginal history -
 Nillumbik Shire Council
Nillumbik Shire CouncilSculpture, Ghost, 2012
The (logging) truck carries a representation of John Glover’s painted landscapes, which Cox has painted on a solid block of wood. John Glover is one of Australia’s most celebrated colonial landscape painters. Born in England, he was a highly successful water-colourist and painter of landscapes in the tradition of French artist Claude Lorrain. Arriving in Australia in 1831, Glover adapted his picturesque style and luminous technique to his new surrounds, creating naturalistic and atmospheric paintings of Australian nature, settler life, and Aboriginal culture. Working out of doors, Glover developed an understanding of the unfamiliar Australian landscape, especially the twisting forms of native eucalyptus trees. His direct experience of nature, as both pioneer settler and painter, resulted in a new approach using a subtle palette of olive greens, ochres, misty greys and intense blues, and layered glazes of mauve, grey and gold, to portray Australian light and atmosphere. Dale Cox continues the ongoing preoccupation and tradition of landscape painting in the Nillumbik area and our impact on the environment in a contemporary way. The truck creates a playful nexus between painting (representational landscape) and sculpture, purposely bluring boundaries across these traditionally distinct disciplines. ‘Ghost’ seeks to convey the idea that when we remove something significant from a location, like the landscape itself, the remaining ‘place’ changes to become a new ‘place’. This may seem self-evident until we think more deeply about location and landscape. The white truck is a ghost, an ethereal, transient being that spirits away an entire place, forever removed from itself, and forever changed. Logging wild trees can never be like harvesting a ‘crop’. Logging removes a landscape, and changes a place forever. The ‘packaging’ of this painted landscape highlights the anomaly between commodity and our environment. Dale Cox was a local artist and this work was highly commended at the 2012 Nillumbik Prize. White plastic toy (logging) truck with a landscape painting on a wooden block. The landscape painting is reminiscent of paintings by colonial artist John Glover. N/Alandscape, truck, sculpture, environment, john glover, colonial, painting, ghost, nillumbik prize -
 Inglewood/Bridgewater RSL Sub Branch
Inglewood/Bridgewater RSL Sub BranchShield, 1942
This item presented by the indigenious community to their local police officer on the the occasion of his joining the Armed Services in 1942 which resulting in his interment in ChangiUnique personal gift to this ServicemanLacquered wood hand made. Hand grip to rear"CENTRAL AUSTRALIA / 1942" RISING SUN Emblem at centre ("AUSTRALIAN COMMONWEALTH MILITARY FORCES") Pinstriping in silver and red.ww2, shield, central australia, police officer, storey, indigenous gift -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumMap, Northern Territory of Australia - Pastoral map
Pastoral map of the Northern Territory, 1955. Includes pastoral leases, stations, aboriginal settlements,pastoral industry - history sheep stations - history, northern territory of australia, pastoral industry - history, sheep stations - history -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncBook - Educational, Indigenous Service, 2013
A Resource for Primary Schools, investigating the wartie experiences of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander People, from the First World War to the present.Photos of Service people overlaid with Aboriginal flag ColoursAustralian Government Department of Veterans Affairs, Shrine of Remembrance Melbourne -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBook, Beveridge, Peter, The Aborigines of Victoria and Riverina, 1889
... Federation Square, Melbourne melbourne Aboriginal Australians ...The author arrived in Victoria at the age of 10 years in 1839. His family gave their name to the Victorian town. He and his brother settled at 'Tyntynder' outside Swan Hill in 1845. His brother was killed by Aborigines. Brought into daily contact with the Aborigines of the area he gradually acquired their language and was permitted to learn much denied to other whites. By 1883 he had amassed a large amount of information which he put into the form of a Paper, read before the Royal Society of New South Wales. This paper may be regarded as the skeleton of the volume now publishjed. Victoria -- Riverina Aboriginals, Victoria -Swan Hill region. Lifestyle; customs and beliefs. Tyntynder(Vic) Aboriginals - Murray River tribes; language; magic; religion and practices.191p.; vocab. list; The author arrived in Victoria at the age of 10 years in 1839. His family gave their name to the Victorian town. He and his brother settled at 'Tyntynder' outside Swan Hill in 1845. His brother was killed by Aborigines. Brought into daily contact with the Aborigines of the area he gradually acquired their language and was permitted to learn much denied to other whites. By 1883 he had amassed a large amount of information which he put into the form of a Paper, read before the Royal Society of New South Wales. This paper may be regarded as the skeleton of the volume now publishjed. Victoria -- Riverina Aboriginals, Victoria -Swan Hill region. Lifestyle; customs and beliefs. Tyntynder(Vic) Aboriginals - Murray River tribes; language; magic; religion and practices.aboriginal australians -- victoria. | aboriginal australians -- murray river valley (n.s.w.-s.a.) -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBook, Roberts, Jan, Massacres to mining : the colonisation of Aboriginal Australia, 1981
... Massacres to mining : the colonisation of Aboriginal.... | Aboriginal Australians -- Treatment. | Australia -- Colonization.... Treatment by White Australians. | Aboriginal Australians ..."If you take a people from their land and homes they will die. The mining, pastoral, forestry and tourism bodies are doing this every day of the year in Australia. But, more importantly, as this land - and in fact all things - are a part of us as we are a part of them both physically and spiritually, then to destroy all that - the environment- is to destroy the people. Massacre!"198 p.; maps; figs; ill.; index; 24 cm."If you take a people from their land and homes they will die. The mining, pastoral, forestry and tourism bodies are doing this every day of the year in Australia. But, more importantly, as this land - and in fact all things - are a part of us as we are a part of them both physically and spiritually, then to destroy all that - the environment- is to destroy the people. Massacre!"australian aborigines. treatment by white australians. | aboriginal australians -- treatment. | australia -- colonization -- history.massacres-aborigines, australia, | weipa mine-land dispossession, | mining companies-australia, | land rights-history -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustDocument - Printed Sheets, Barwick, Diane E, This most resolute lady : a biographical puzzle, 1985
... . Festschriften. | Anthropology. | Aboriginal Australians. 199-254pp, 30cm ...199-254pp, 30cmlouisa briggs | stanner, w. e. h. (william edward hanley), 1905-1981. | stanner, w. e. h. (william edward hanley), 1905-1981 -- bibliography. | stanner, w. e. h. (william edward hanley), 1905-1981. | anthropology. festschriften. | anthropology. | aboriginal australians. -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustBooklet, Baxter, Bruce [et al.]. (Aboriginal History Program), Matakupat : the Aboriginal history of the Swan Hill area, 1990
Traditional Aboriginal Society was an oral culture so that the history, stories, and songs and knowledge of Spirituality, Laws, Customs and Values were communicated verbally for thousands of years. The invasion of Europeans caused destruction of tribal groups by disease and killings. It limited the use of language, exchange of stories, land use and the important performance of rituals and ceremonies. Europeans used their world view as a mirror and through their observations, documents, diaries, reports and stories were full of racist comments and ignorant opinions of a lifestyle and culture of which they had little understanding. This book was the result of many months of research by a group of Swan Hill Aboriginal Educators. It is an attempt to present limited information about the history and lifestyles of the Wemba Wemba and Wathi Wathi people, the Tribes of the Swan Hill and Lake Boga areas.20 p. : ill., map ; 21 cm.Traditional Aboriginal Society was an oral culture so that the history, stories, and songs and knowledge of Spirituality, Laws, Customs and Values were communicated verbally for thousands of years. The invasion of Europeans caused destruction of tribal groups by disease and killings. It limited the use of language, exchange of stories, land use and the important performance of rituals and ceremonies. Europeans used their world view as a mirror and through their observations, documents, diaries, reports and stories were full of racist comments and ignorant opinions of a lifestyle and culture of which they had little understanding. This book was the result of many months of research by a group of Swan Hill Aboriginal Educators. It is an attempt to present limited information about the history and lifestyles of the Wemba Wemba and Wathi Wathi people, the Tribes of the Swan Hill and Lake Boga areas.1. aborigines, australian -- victoria -- swan hill -- history -- juvenile literature. 2. aborigines, australian -- victoria -- swan hill -- social life and customs -- juvenile literature. i. baxter, bruce. ii. title., other: wemba wemba tribe -- wathi wathi tribe -- aboriginal educators. -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustJournal - Serials, Department of Pacific and Southeast Asian History, Australian National University, Aboriginal History - Volume 10. 1-2 1986, 1986
A series of articles by leading writers on Aboriginal History.207 P.; bibs.; tables; ports.; footnotes; 25 cm.A series of articles by leading writers on Aboriginal History.government policy-aborigines, australia-race related. | missions-australia-aborigines-attitudes and treatment., | aborigines, australia-social security. | native police-victoria-history1838., | aborigines-gippsland-1860-1890-missions relations. | rowley, charles dunford (1906ð1985) | social identity - aboriginality | law - administrative law - commonwealth | social welfare | government policy - assimilation - 1926-1950 | government policy - assimilation - 1951-1971 | social behaviour - social control | social welfare - government - unemployment benefits | body - decoration - body modification | dance | death - mortuary / funeral ceremonies | death - mortuary / funeral ceremonies - mortuary objects - poles | sites - mortuary sites and cemeteries | weapons - spears | -
 Koorie Heritage Trust
Koorie Heritage TrustPamphlet, Barrett, Charles, The Australian Aborigine
... Federation Square, Melbourne melbourne Aboriginals Australia - social ...A general overview of some Aboriginal life and customs.21 p.; ill,; 25 cm.A general overview of some Aboriginal life and customs.aboriginals, australia - social life and customs
