Showing 1703 items
matching heritage significance
-
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyAlbum - Album page, Congregational Church, Grange Road, Circa 1972
This photograph is part of the Caulfield Historical Album 1972. This album was created in approximately 1972 as part of a project by the Caulfield Historical Society to assist in identifying buildings worthy of preservation. The album is related to a Survey the Caulfield Historical Society developed in collaboration with the National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and Caulfield City Council to identify historic buildings within the City of Caulfield that warranted the protection of a National Trust Classification. Principal photographer thought to be Trevor Hart, member of Caulfield Historical Society. Most photographs were taken between 1966-1972 with a small number of photographs being older and from unknown sources. All photographs are black and white except where stated, with 386 photographs over 198 pages. This church has since become the Greek Orthodox Church. From Victorian Heritage Database: Citation for Greek Orthodox Church HO84 https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/43587 (as at 19/10/2020) The former Primitive Methodist, later Congregational, church at 152 Grange Road, Glen Huntly, is a small timber building, erected in 1885 (89?) in South Melbourne and relocated to Glenhuntly in 1909. It is a highly individual picturesque timber structure with distinctive spire and timber enrichment. It has aesthetic, historical and social significance. Its aesthetic value is derived from the choice of materials and picturesque Gothic Revival character showing American influence. Its historical value is derived from its survival as a rare example of a Primitive Methodist Church building whilst its social value hinges on its early roles as a place of worship for the Primitive Methodists in South Melbourne and the Congregationalists in Glenhuntly.Page 73 of Photograph Album with two photographs (both portrait) of front and side views of the spire of the Congregational Church on Grange RoadHand written: 73 [bottom left] trevor hart, congregational church, grange road, gothic revival, carnegie, glen huntly, glenhuntly, greek orthodox church, primitive methodist church, spire, timber buildings -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet - Report, Sturt Street Gardens, Ballarat, Victoria, Conservation and Landscape Management Plan, July 2007, 07/2007
The Sturt Street Gardens had its origins in the 1851 survey of Ballarat West by W.S. Urquhart. A generous reserve was allocated for the main streets of Ballarat, of which Sturt Street was the first. In the 1860s Sturt Street was planted with blue gums, with dual carriageway and central median Strip. Bandstands were soon erected.70 page report on the Ballarat Sturt Street gardens. The report includes an historical overview, Physical Analysis, Statement of Cultural Significance, and Consideration and Landscape Policies.queen alexandra bandstand, titanic memorial bandstand, sturt street, sturt street gardens, blue gum, statues, eight hour day memorial, boer war memorial, peter lalor statue, bluestone, bluestone guttering, william dunstan vc, time capsule, conservation management plan, landscape management plan -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Porthole, c 1888
This porthole was part of the ship's fittings when the Antares was constructed. THE ANTARES In mid-November 1914, after the beginning of the First World War, a young local man went one evening to fish near the Bay of Islands, west of Peterborough. He later arrived home hurriedly and in an agitated state declaring: "The Germans are coming!" His family laughed and disbelieved him, as this young fellow was prone to telling fictional tales. About a month later, on December 13th 1914, local farmers Phillip Le Couteur and Peter Mathieson were riding in the vicinity, checking on cattle. Phillip Le Couteur saw what he “thought was the hull of a ship below the cliffs.” He rode to Allansford and contacted police. The next day, two Constables and Phillip Le Couteur returned to the site, where they dug a trench near the top of the cliff and sank a log in it. To this they attached a rope, which they threw down the cliff face. Constable Stainsbury and Phillip Le Couteur then made the dangerous descent down the rope on the sheer cliff face. They found wreckage strewn around a small cove and a portion of a man's body under the cliffs. The hull of the ship could be seen about 300 metres out to sea. Some of the wreckage revealed the name Antares and the remains of the ship's dinghy bore the name Sutlej. During the next two weeks and with the help of the Warrnambool lifeboat and crew, two more bodies were found. Later investigations proved that the tragic wreck was indeed that of the Antares, reported overdue on the 207th day of her voyage from Marseilles, France, to Melbourne. She was a three masted, 1749 ton iron clipper, built in Glasgow in 1888 and originally named and launched as the Sutlej. Bought in 1907 by Semider Bros. from Genoa, Italy, she was refitted and renamed Antares. It was later realised that the local lad who a month earlier had declared he had seen German guns being fired, had probably seen distress flares fired from the deck of the Antares the night she was wrecked. She was last sailed under Captain Gazedo and wrecked at what is now known as Antares Rock, near the Bay of Islands. She had been carrying a large cargo of roofing tiles from France to Melbourne, consigned to Mullaly & Byrne. Many of them are now to be seen amongst the battered and scattered remains of the wreck. Some of the timbers were found to be blackened by fire. An Information Board has been erected on the cliff top near to the site of the Antares wreck, at the end of Radfords Rd, west of Peterborough. (Ref: Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s “Antares” fact sheet, Victorian Heritage Database, Information Board at Peterborough, Flagstaff Hill Significance Assessment 2010)The Antares was one of the last of the 'tall ships' to be lost along the south west coast of Victoria, and is the only wreck that took the lives of all people on board. She is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register VHS S34. The Antares is significant as a sail trader carrying an international inbound cargo. It is part of the Great Ocean Road Historic Shipwreck Trail. Porthole with glass, brass, screw dog broken off, glass has cracks through it, some encrustation. Artefact Reg No A/5, recovered from the wreck of the Antares.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, porthole, antares., tall ship, peterborough, 1914 shipwreck, phillip le couteur, peter mathieson, constable stainsbury, sutlej, antares rock., bay of islands, ship's fitting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Teacup, 1920s
This teacup is part of a four-piece place setting, comprising a teacup, saucer and plates, from a tea set. The tea set was given by Eva Carmichael, a survivor of the ship Loch Ard which was wrecked near Port Campbell in 1878, to Jane Shields, the young woman who supported Eva during her recovery from the ordeal. Ms Shields was Eva’s close companion while she was convalescing at Glenample Homestead. The friendship between the two women continued after Eva Carmichael returned to her home in Britain, became Mrs Townsend, and had three sons. Jane Shields also married, becoming Mrs John Osborne and bearing four daughters and two sons. In 1926-27, almost forty-eight years after the shipwreck, one of Jane’s daughters (Ella Marie Schulby nee Osborne) visited Eva in England. Eva gave her the tea set to take back home to her mother. Jane died in 1932 and her tea set was inherited by her daughters, who divided it between themselves, a four-piece place setting for each of them. A brief history of the Loch Ard: - The Loch Ard was named after a Scottish lake. It was one of the famous Loch Line of ships that sailed the long voyage from England to Australia. Barclay, Curdle and Co. built the three-masted iron ship in Glasgow in 1873. It had sailed three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of recently married, 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, and a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. Other cargo included items intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The Loch Ard had been sailing for three months and was close to its destination. At 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs expected to see land, but the Loch Ard ran into a fog that greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs became anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. The fog lifted at 4 am. A lookout announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view; the ship was much closer to them than Captain Gibbs expected. It was not long before the Loch Ard's bow swung towards land. Although the Captain tried to manage the vessel, his attempts didn’t work and the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. The top deck became loosened from the hull, and the masts and rigging crashed down, knocking passengers and crew overboard. The lifeboat was launched by Tom Pearce but crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce managed to cling to the lifeboat’s overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and the tide brought him back to what is now called Loch Ard Gorge. He swam to shore and found a cave for shelter. A passenger, Eva Carmichael, had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening and was confronted by towering cliffs above the ship. She was soon swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore and to the shelter of the cave. He revived Eva with a bottle of brandy from a case that had washed up on the beach. Tom scaled a cliff in search of help and followed some horse hoof prints. He came from two men from Glenample Station, three and a half miles away. He told the men of the tragedy and then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. They reached Loch Ard Gorge and took the two shipwreck survivors to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome and was presented with a medal and some money. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy.This blue china tea set, comprising a teacup, saucer and two plates, is of high significance as it is closely connected to the wreck of the Loch Ard, and to one of only two survivors, Eva Carmichael. Memorabilia connected to Eva Carmichael are precious and rare. The Loch Ard shipwreck is significant for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register (S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulations of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The group gives a snapshot of history, enabling us to interpret the story of this tragic event and the lives of the people involved. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allow us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collection's historical significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.The teacup is part of a china tea set place setting, which comprises the teacup, a saucer and two plates of slightly different sizes. The cup is a royal blue outer, white inside with gold lip, a gold ring around the base and a gold handle. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, china tea set, tea set, royal blue china, tom pearce, eva carmichael, jane shields, glenample, loch ard, place setting, teacup -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Saucer, 1920s
This saucer is part of a four-piece place setting, comprising a teacup, saucer and plates, from a tea set. The tea set was given by Eva Carmichael, one of only two survivors of the ship Loch Ard which was wrecked near Port Campbell in 1878, to Jane Shields, the young woman who supported Eva during her recovery from the ordeal. Ms Shields was Eva’s close companion while she was convalescing at Glenample Homestead. The friendship between the two women continued after Eva Carmichael returned to her home in Britain, became Mrs Townsend, and had three sons. Jane Shields also married, becoming Mrs John Osborne and bearing four daughters and two sons. n 1926-27, almost forty-eight years after the shipwreck, one of Jane’s daughters (Ella Marie Schulz nee Osborne) visited Eva in England. Eva gave her the tea set to take back home to her mother. Jane died in 1932 and her tea set was inherited by her daughters, who divided it between themselves, a four-piece place setting for each of them. This blue ceramic tea set, comprising a teacup, saucer and two plates, is of high significance as it is closely connected to the wreck of the Loch Ard, and one of only two survivors, Eva Carmichael. Memorabilia connected to Eva Carmichael are precious and rare. The Loch Ard shipwreck is significant for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register (S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulations of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collection gives a snapshot of history, enabling us to interpret the story of this tragic event and the lives of the people involved. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allow us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collection's historical significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.Saucer; this saucer is part of a ceramic tea set place setting, comprising a cup, saucer and two plates of slightly different sizes. The saucer is royal blue with a gold rim.warrnambool, maritime-museum, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, loch ard, shipwreck, tea set, ceramic, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, royal blue china, eva carmichael, jane shields, glenample, place setting, saucer, ceramic tea set -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Plate, 1920s
This plate is part of a four-piece place setting, comprising a teacup, saucer and plates, from a tea set. The tea set was given by Eva Carmichael, one of only two survivors of the ship Loch Ard which was wrecked near Port Campbell in 1878, to Jane Shields, the young woman who supported Eva during her recovery from the ordeal. Ms Shields was Eva’s close companion while she was convalescing at Glenample Homestead. The friendship between the two women continued after Eva Carmichael returned to her home in Britain, became Mrs Townsend, and had three sons. Jane Shields also married, becoming Mrs John Osborne and bearing four daughters and two sons. In 1926-27, almost forty-eight years after the shipwreck, one of Jane’s daughters (Ella Marie Schulz nee Osborne) visited Eva in England. Eva gave her the tea set to take back home to her mother. Jane died in 1932 and her tea set was inherited by her daughters, who divided it between themselves, a four-piece place setting for each of them. This blue china tea set, comprising a teacup, saucer and two plates, is of high significance as it is closely connected to the wreck of the Loch Ard, and one of only two survivors, Eva Carmichael. Memorabilia connected to Eva Carmichael are precious and rare. The Loch Ard shipwreck is significant for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register (S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulations of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collection gives a snapshot of history, enabling us to interpret the story of this tragic event and the lives of the people involved. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allow us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collection's historical significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history. Plate; this plate is part of a ceramic tea set place setting, comprising a cup, saucer and two plates of slightly different sizes. The plate is a royal blue colour with a gold rim.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, ceramic tea set, plate, tea set, royal blue china, eva carmichael, jane shields, glenample, loch ard, place setting, coffee cup plate -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Plate, 1920s
This plate is part of a four-piece place setting, comprising a teacup, saucer and plates, from a tea set. The tea set was given by Eva Carmichael, one of only two survivors of the ship Loch Ard which was wrecked near Port Campbell in 1878, to Jane Shields, the young woman who supported Eva during her recovery from the ordeal. Ms Shields was Eva’s close companion while she was convalescing at Glenample Homestead. The friendship between the two women continued after Eva Carmichael returned to her home in Britain, became Mrs Townsend, and had three sons. Jane Shields also married, becoming Mrs John Osborne and bearing four daughters and two sons. In 1926-27, almost forty-eight years after the shipwreck, one of Jane’s daughters (Ella Marie Schulz nee Osborne) visited Eva in England. Eva gave her the tea set to take back home to her mother. Jane died in 1932 and her tea set was inherited by her daughters, who divided it between themselves, a four-piece place setting for each of them. This blue china tea set, comprising a teacup, saucer and two plates, is of high significance as it is closely connected to the wreck of the Loch Ard, and one of only two survivors, Eva Carmichael. Memorabilia connected to Eva Carmichael are precious and rare. The Loch Ard shipwreck is significant for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register (S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulations of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collection gives a snapshot of history, enabling us to interpret the story of this tragic event and the lives of the people involved. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allow us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collection's historical significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.Plate; this plate is part of a ceramic tea set place setting, comprising a cup, saucer and two plates of slightly different sizes. The plate is a royal blue colour with a gold rim.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, ceramic tea set, plate, tea set, royal blue china, eva carmichael, jane shields, glenample, loch ard, place setting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Portrait, Burlington, Jane Osborne nee Shields, 1870's to 1923
This photograph of Jane Shields was taken at the Burlington Studio, Melbourne in the late 19th to early 20th century. Jane Shields became friends with Eva Carmichael in 1878, a friendship that continued throughout their lives. The item was created by layering fabric glued onto card, the the oval-cut photograph blued onto the fabric. A tea set was given by Eva Carmichael, a survivor of the ship Loch Ard which was wrecked near Port Campbell in 1878, to Jane Shields, who was the young woman who supported Eva during her recovery from the ordeal. Jane was Eva’s close companion while she was convalescing at Glenample Homestead. The friendship between the two women continued after Eva Carmichael returned to her home in Britain, became Mrs Townsend, and had three sons. Jane Shields also married, becoming Mrs John Osborne and bearing four daughters and two sons. In 1926-27, almost forty-eight years after the shipwreck, one of Jane’s daughters (Ella Marie Schulz nee Osborne) visited Eva in England. Eva gave her the tea set to take back home to her mother. Jane died in 1932 and her tea set was inherited by her daughters, who divided it between themselves, a four-piece place setting for each of them. This photograph of Jane Osborne nee Shields is significant for its connection with Eva Carmichael and the wreck of the Loch Ard in 1878. Memorabilia connected to Eva Carmichael are precious and rare. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard itself is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register (S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulations of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collection gives a snapshot of history, enabling us to interpret the story of this tragic event and the lives of the people involved. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allow us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collection's historical significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.Photograph; studio portrait of the upper torso of a female. The photograph has been has been cut into an oval shape, glued on rectangular fabric that was already glued onto card. The woman is wearing a light-coloured jacket, white blouse and bow tie. The figure is Jane Osbourne, nee Jane Shields, a friend of Eva Carmichael. An inscription is handwritten on the matt card. Burlington, Melbourne, produced the photograph."Burlington, Melb." flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, china tea set, tea cup, tea set, royal blue china, eva carmichael, jane shields, glenample, loch ard, place setting, eva townsend, jane osborne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Plate, Minton Potteries, ca 1878
This plate is one of a collection of plates with the Asiatic Pheasant design from recovered from the wreck o the Loch Ard. A brief history of the Loch Ard (1873-1878): - The sailing ship Loch Ard was one of the famous Loch Line ships that sailed from England to Australia. Barclay, Curdle and Co. built the three-masted iron vessel in Glasgow in 1873. It had sailed three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of recently married, 29-year-old Captain Gibbs. It was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, and a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. Other cargo included items intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The Loch Ard had been sailing for three months and was close to its destination on June 1, 1878. Captain Gibbs had expected to see land at about 3 am but the Loch Ard ran into a fog that greatly reduced visibility and there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. The fog lifted at 4 am and the sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast were much closer to them than Captain Gibbs expected. He tried to manage the vessel but failed and the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. The top deck loosened from the hull, and the masts and rigging crashed down, knocking passengers and crew overboard. The lifeboat was launched by Tom Pearce but crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. He clung onto its overturned hull and sheltered under it. He drifted out to sea and the tide brought him back to what is now called Loch Ard Gorge. He swam to shore and found a cave for shelter. A passenger, Eva Carmichael, had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening and was confronted by towering cliffs above the ship. She was soon swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He swam out and dragged her to the shelter of the cave. He revived her with a bottle of brandy from a case that had washed up on the beach. Tom scaled a cliff in search of help and followed some horse hoof prints. He came from two men from Glenample Station, three and a half miles away. He told the men of the tragedy and then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. They reached Loch Ard Gorge and took the two shipwreck survivors to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome and was presented with a medal and some money. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. This plate is significant for its connection to the potters Minton. It is also significant for its connection with the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. The Loch Ard shipwreck is significant for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register (S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulations of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The group gives a snapshot of history, enabling us to interpret the story of this tragic event and the lives of the people involved. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allow us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collection's historical significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.China dinner plate, scalloped rim. Floral arrangement with Asiatic Pheasant design, made by Middleport Pottery. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard. Within cartouche "B & L / MIDDLEPORT POTTERY" and an 'L" handwritten in black pen.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, plate, minton, loch ard, asiatic pheasant design -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Meat Dish, 1870-1873
The Asiatic Pheasant pattern on the plate is a transfer design and was the most popular design of the 18th & 19th centuries and is still being produced today. The design was produced as high-quality, decorative dinnerware by the potters in the Staffordshire area of England, from the late 1830s, but no one is sure exactly of the original designer's name. History of the Loch Ard: The Loch Ard got its name from ”Loch Ard” a loch that lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and to the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic. The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as recovered from the wreck of the Loch ArdGorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the recovery from the wreck of the Loch Ard tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of the Loch Ard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up and recovered from the Loch ArdGorge wreck. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck, it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artifact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register.The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we are able to interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collections historically significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history. Serving dish or meat dish; oval with scalloped edges. White Chine plate with a blue flora transfer design called "Asiatic Pheasant". Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard. Printed "W & S" (pattern is) "Asiatic Pheasants"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, serving dish, asiatic pheasant, meat dish, meat plate, serving plate, crockery, domestic item, dining -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDecorative object - Ceiling Rose, 1873
History of the Loch Ard: The Loch Ard got its name from ”Loch Ard” a loch which lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic. The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as recovered from the wreck of the Loch ArdGorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ardtragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up into recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition in. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artifact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collections historically significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history. Ceiling rose, cast brass, with hole in the centre and raised arrow shape geometric style patterning around the centre part of the top side of the ceiling rose. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, ceiling rose -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Deadeye/Bullseye, circa 1873
Context: A deadeye or bullseye is an item used in the standing and running of sail rigging in traditional sailing ships. It is a smallish round thick wooden disc (usually lignum vitae) with one or more holes through it, perpendicular to the plane of the disc. History of the Loch Ard: The Loch Ard got its name from ”Loch Ard” a loch which lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic. The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as recovered from the wreck of the Loch ArdGorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ardtragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up into recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition in. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artifact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collections historically significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history. Ship’s deadeye comprising a thick round wooden disc, pierced by 3 similarly sized and shaped holes from one flat side through to the other, in a triangle formation. It has been polished a rich dark colour and a crude mouth has been carved below the 'eyes' to create a curio effect. These alterations are most likely to have been made after the object was retrieved from the sea, (when it was used as a doorstop).Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, deadeye, loch ard, rigging -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePlaque - Nameplate, Circa 1886
... significance — Victorian Heritage Register No. S255. The Falls ...The brass letter “A” is from the starboard bow of the FALLS OF HALLADALE, a 2085-ton iron-hulled and four-masted sailing ship that was wrecked near Peterborough on 14 November 1908. Two companion pieces, the letters “S” and “D”, are also in the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village collection of shipwreck artefacts (as registered numbers 748 and 6596). The ship’s name originally appeared in these impressively large brass letters across the stern and both port and starboard bows of the vessel. The FALLS OF HALLADALE was built in 1886 by Russell & Co at their Greenock shipyards on the River Clyde. She was the seventh of nine similar cargo carriers produced for the owners of the Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow. All nine ships were named after waterfalls in Scotland. First was the FALLS OF CLYDE in 1878, then the FALLS OF BRUAR in 1879 (lost in 1887), the FALLS OF DEE in 1882 (sunk in 1917), the FALLS OF AFTON in 1882, the FALLS OF FOYERS in 1883 (disappeared in 1898), the FALLS OF EARN in 1884 (wrecked in 1892), the FALLS OF HALLADALE in 1886 (wrecked in 1908), the FALLS OF GARRY in 1886 (wrecked in 1911), and the last of the fleet, the FALLS OF ETTRICK (lost in 1906). The FALLS OF CLYDE is still afloat as an exhibit at the Hawaii Maritime Center in Honolulu. Russell & Co delivered the owners full-bottomed, economical ships of 1800 to 2000 tons, practically designed to minimise loss of speed while increasing seaworthiness and carrying capacity. The sturdily constructed FALLS OF HALLADALE had iron masts and wire rigging, allowing her to maintain full sail even in gale conditions, and square “warehouse-type” bilges to accommodate maximum bulk cargo on her long-haul voyages. This class of ship remained commercially competitive into the twentieth century despite the advantages of coal-fired steamships. When the 22 years old FALLS OF HALLADALE finally foundered on Victoria’s Shipwreck Coast in 1908, the Melbourne Court of Marine Inquiry held it was entirely due to Captain D.W. Thomson’s navigational error, rather than any technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck of the FALLS OF HALLADALE is of state significance — Victorian Heritage Register No. S255. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).A brass letter “A”, from the shipwreck FALLS OF HALLADALE, raised along the central axis to form three dimensional effect, in unrestored and fair condition. Of dull grey-green metal, bent and with irregularly worn edges, it has been subjected to amateur cleaning on the front face, with some remaining greenish copper oxidation and surface pitting. The rear face is uncleaned with a layer of sedimentary concretion, orange-red staining from the iron hull, and green copper oxidisation. Three sediment-filled bolt collars on the rear face are part of the original casting.warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck artefact, maritime museum, great ocean road, brass lettering, falls of halladale, 1908 shipwreck, russell & co., ship's nameplate, letter, letter a -
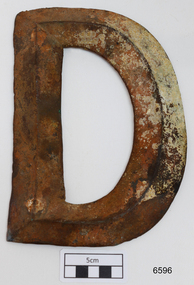 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePlaque - Nameplate, Circa 1886
... significance — Victorian Heritage Register No. S255. The Falls ...The brass letter “D” is from the starboard bow of the FALLS OF HALLADALE, a 2085 ton iron-hulled and four-masted sailing ship that was wrecked near Peterborough on 14 November 1908. Two companion pieces, the letters “S” and “A”, are also in the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village collection of shipwreck artefacts (as registered numbers 748 and 6595). The ship’s name originally appeared in these impressively large brass letters across the stern and both port and starboard bows of the vessel. The FALLS OF HALLADALE was built in 1886 by Russell & Co at their Greenock shipyards on the River Clyde. She was the seventh of nine similar cargo carriers produced for the owners of the Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow. All nine ships were named after waterfalls in Scotland. First was the FALLS OF CLYDE in 1878, then the FALLS OF BRUAR in 1879 (lost in 1887), the FALLS OF DEE in 1882 (sunk in 1917), the FALLS OF AFTON in 1882, the FALLS OF FOYERS in 1883 (disappeared in 1898), the FALLS OF EARN in 1884 (wrecked in 1892), the FALLS OF HALLADALE in 1886 (wrecked in 1908), the FALLS OF GARRY in 1886 (wrecked in 1911), and the last of the fleet, the FALLS OF ETTRICK (lost in 1906). The FALLS OF CLYDE is still afloat as an exhibit at the Hawaii Maritime Center in Honolulu. Russell & Co delivered the owners full-bottomed, economical ships of 1800 to 2000 tons, practically designed to minimise loss of speed while increasing seaworthiness and carrying capacity. The sturdily constructed FALLS OF HALLADALE had iron masts and wire rigging, allowing her to maintain full sail even in gale conditions, and square “warehouse-type” bilges to accommodate maximum bulk cargo on her long-haul voyages. This class of ship remained commercially competitive into the twentieth century despite the advantages of coal-fired steamships. When the 22 years old FALLS OF HALLADALE finally foundered on Victoria’s Shipwreck Coast in 1908, the Melbourne Court of Marine Inquiry found it was entirely due to Captain D.W. Thomson’s navigational error, rather than any technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck of the FALLS OF HALLADALE is of state significance — Victorian Heritage Register No. S255. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Large brass letter “D”, from the shipwreck FALLS OF HALLADALE, dented but in generally good unrestored condition. Front face of dull grey-green metal showing reddish oxide stain and some cream-coloured concretisation. Rear face has not been brushed clean and displays more encrustation.The four bolt collars for fixing letter to ship are filled with sediment.warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck artefact, maritime museum, great ocean road, brass lettering, falls of halladale, 1908 shipwreck, russell & co., ship nameplate, nameplate, letter, letter d -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Mug, 1878
History of the Loch Ard: The Loch Ard got its name from ”Loch Ard” a loch which lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic. The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ardstill lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up into recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition in. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artifact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The mug is significant as an example of an 1870s drinking vessel. It is also significant for its connection with the Loch Ard. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collection's historical significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history. Mug, China; white, glazed, with cast and raised wheat pattern embossed on outside, slight grooving on perimeter with handle on side. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, china mug, mug, drinking vessel, ceramic mug -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Jug
History of the Loch Ard: The Loch Ard got it’s name from ”Loch Ard” a loch which lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and to the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic.The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as Loch Ard Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the Loch Ard tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of Loch Ard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up into Loch Ard Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition in. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artifact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register.The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we are able to interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collections historically significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history. Jug, white glazed, ornately designed china cream jug, blue floral embossed around girth. Jug features a circular pedestal foot with six small feet attached around the circumference of the pedestal. Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, jug, china jug -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLeisure object - Toy Soldier, circa 1878
The toy soldier is a relic from the shipwreck of the LOCH ARD in 1878. It has a companion piece in the Flagstaff Hill collection. The toy soldier is unpainted, but the style of uniform, and the weapons carried (a musket and a basket-handled cutlass), indicate it is a representation of the Napoleonic Wars period from the beginning of the nineteenth century. Mass-produced toy soldiers made of cast metal (lead or tin) became popular during the 1800s. Heyde of Germany manufactured silhouette-shaped ‘flats’ early in the century; then Mignot of France released three-dimensional ‘solids’; and later (1893) Britain of England made ‘hollow cast’ figures. These innovations were designed to make sets of toy soldiers more affordable for middle and lower-class children, extending the market beyond the intricately made and hand-crafted replicas that were the preserve of the rich in the eighteenth century. Wooden military figures, specially carved and unpainted ones, were therefore not particularly common at the time when the LOCH ARD went down on Victoria’s southwest coast. Mignot was the first to sell unpainted soldiers, leaving their customers to fill in the colours according to their own patriotic preferences. If a similar attitude is assumed for the two virtually identical figures in the Flagstaff Hill collection, it is possible they were part of a new set intended for sale, rather than part of a passenger’s existing collection. A similarly light composite material of sawdust, glue and linseed oil (press-moulded onto a metal frame) was used by the German firm O & M Hausler to create toy soldiers, but this type of modelling was not commercialised until after 1912. The first heat-moulded plastic toy soldiers did not become available until after 1945.The toy soldier represents a 19th century child's interest in military history. The item is one of two toy soldiers recovered from the Loch Ard that are in Flagstaff Hill's collection. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck of which the subject items are a small part. The collections objects give us a snapshot of how we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. Through is associated with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.An unpainted replica or toy soldier, presented in a Napoleonic Wars era uniform. The moulded figure is in a standing posture and is bearing a musket at the slope-arms position, with a sabre or cutlass slung behind. It wears a plumed helmet, short-fronted coat with longer buttoned tails at the back, button-fastened bib-front trousers, a pair of crossed bandoliers, and tasselled shoulder epaulettes. The figure is a creamy colour with red-brown stains on the head and shoulder. There is a hole in the end of the musket. The model is detailed and sharp. It was recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard.Cataloguing numbers: “6599” on the rear of the left trouser leg “PWO 2308” on the sole of the left boot, (partially obscuring “R122” written in biro) “2218” on the sole of the right boot.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, loch ard, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, napoleonic uniform, toy soldier, replica soldier -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Nail, ca. 1855
When the ship Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the most perfect clipper ship ever to be built. James Blaine’s Black Ball Line had commissioned her to be built for their fleet of passenger liners. At a cost of £43,103, the Aberdeen builders designed her to sail faster than the quick clippers designed by North American Donald McKay. She was a three masted wooden clipper ship, built with diagonal planking of British oat with layers of Scottish larch. This luxury vessel was designed to transport emigrants to Melbourne in superior comfort. She had ventilation ducts to provide air to the lower decks and a dining saloon, smoking room, library and bathrooms for the first class passengers. At the launch of Schomberg’s maiden voyage, her master Captain ‘Bully’ Forbes, drunkenly predicted that he would make the journey between Liverpool and Melbourne in 60 days. Schomberg departed Liverpool on 6 October 1855 with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended the build the Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. The winds were poor as Schomberg sailed across the equator, slowing her journey considerably. She was 78 days out of Liverpool when she ran aground on a sand-spit near Peterborough, Victoria, on 27 December; the sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes’s map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the SS Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers were able to disembark safely. The Black Ball Line’s Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers’ baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo, but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. After two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1975, divers from Flagstaff Hill, including Peter Ronald, found an ornate communion set at the wreck. The set comprised a jug, two chalices, a plate and a lid. The lid did not fit any of the other objects and in 1978 a piece of the lid broke off, revealing a glint of gold. As museum staff carefully examined the lid and removed marine growth, they found a diamond ring, which is currently on display in the Great Circle Gallery. Flagstaff Hill also holds ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photograph from the Schomberg. Most of the artefacts were salvaged from the wreck by Peter Ronald, former director of Flagstaff Hill. The Schomberg, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S612), has great historical significance as a rare example of a large, fast clipper ship on the England to Australia run, carrying emigrants at the time of the Victorian gold rush. She represents the technical advances made to break sailing records between Europe and Australia. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is significant for its association with the shipwreck, The collection is primarily significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Schomberg. It is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international passenger Ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and for its association with the shipwreck and the ship, which was designed to be fastest and most luxurious of its day Copper nail with petrified wooden section attached. There is a washer on the end of the nail. It is covered in verdigris. The nail was recovered from the wreck of the Schomberg.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, petrified wood, schomberg, copper nail, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen, ship's nail, nail in wood sample -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Light Bracket, Before 1878
... is of State significance — Victorian Heritage Register S417. The gas ...This pressed brass artefact is a highly decorative side bracket for distancing a gas lamp flame from the internal wall of a building. It is hollow and made of light gauge metal, with an innovative aesthetic design, but no internal piping to transport gas. It was recovered from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. There are similar artefacts in the Flagstaff Hill collection. The LOCH ARD left Gravesend (London) on 2 March 1878, bound for Melbourne, with a crew of 37, 17 passengers, and a diverse and valuable cargo of manufactured goods, luxury items, and refined metal. Some of the cargo was destined for display at Melbourne’s first International Exhibition in 1880. At 3 am, 1 June 1878, the ship was wrecked against the high limestone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on Victoria’s south west coast near Port Campbell. Only two people survived the disaster — Tom Pearce, a male crew member, and Eva Carmichael, a female passenger. The cargo proved too difficult to salvage in the vessel’s exposed condition and was largely written off. The manifest of goods in the LOCH ARD’s holds included “Fittings gas (4 cases)”. The gas lighting of streets, public buildings, and the dwellings of wealthier private citizens was already well-advanced in the cities and major towns of the Australian colonies. In 1841 Sydney was the first to be gas-lit with 23 street lamps, 106 hotel lamps, and 200 private residences connected to the Darlinghurst “gasometer” by an underground network of metal pipes. “The dim days of oil and tallow are gone by!” pronounced one newspaper, flushed with civic pride. The 1850s Gold Rush promoted a similar attitude of confidence and affluence in the Colony of Victoria. In 1855 Melbourne was connected to its own system of subterranean gas pipes despite the same high rates of 25 shillings per 1000 cubic feet being charged, (reduced to 15 shillings in 1865 with cheaper sources of coal). By1858 Kyneton had its own gasworks to light the town (fuelled by eucalyptus leaves) and Geelong followed suit in 1860. Had the LOCH ARD reached its intended destination in 1878, it is probable that the 4 cases of brass gas light fittings on board would have found a ready market.The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance — Victorian Heritage Register S417. The gas light bracket is an example of lamp fittings and plumbing from the late 19th century.A pressed brass lighting bracket recovered from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. It would be used for attaching, but simultaneously offsetting, a gas nozzle to a wall. Highly decorative in an unusually ‘modern’ or ‘art-deco’ style, with sweeping curves dissected by angular geometric pattern, and supporting a short, vertical bar with a gas nozzle on top. It is constructed of light gauge metal, with splitting along seams, and some delicate tracery is missing. Outer surface has been polished, removing sediment, but greenish oxidation remains in dents and joins. warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck artefact, maritime museum, gas lamps, gas lighting, gas works, brass fittings, gas pipes, loch ard, 1878 shipwreck, victorian affluence, colonial gas lighting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Gas Fitting, Before 1878
The artefact is a short cross-section of part of a functional part of a brass fitting that suspended a gas lamp, providing structural support, and internally, supplying the gas for its ignition. It combines elegant design with the elements required for safe and efficient delivery of gas. It was recovered from the LOCH ARD shipwreck site. There are similar artefacts in the Flagstaff Hill collection. The LOCH ARD left Gravesend (London) on 2 March 1878, bound for Melbourne, with a crew of 37, 17 passengers, and a diverse and valuable cargo of manufactured goods, luxury items, and refined metal. Some of the cargo was intended for Melbourne’s first International Exhibition to be held in 1880. At 3 am, 1 June 1878, the ship was wrecked against the high limestone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on Victoria’s south west coast near Port Campbell. Only two people survived the disaster — Tom Pearce, a male crew member, and Eva Carmichael, a female passenger. The cargo proved too difficult to salvage in the vessel’s exposed condition and was largely written off. The manifest of goods in the LOCH ARD’s holds included “Fittings gas (4 cases)”. The gas lighting of streets, public buildings, and the dwellings of wealthier private citizens, was already well advanced in the cities and major towns of the Australian colonies. In 1841 Sydney was the first to be gas lit with 23 street lamps, 106 hotel lamps, and 200 private residences connected to the Darlinghurst “gasometer” by an underground network of metal pipes. “The dim days of oil and tallow are gone by!” pronounced one newspaper, flushed with civic pride. The 1850s Gold Rush promoted a similar attitude of confidence and affluence in the Colony of Victoria. In 1855 Melbourne was connected to its own system of subterranean gas pipes despite the same high rates of 25 shillings per 1000 cubic feet being charged, (reduced to 15 shillings in 1865 with cheaper sources of coal). By1858 Kyneton had its own gasworks to light the town (fuelled by eucalyptus leaves) and Geelong followed suit in 1860. Had the LOCH ARD reached its intended destination in 1878, it is probable that the 4 cases of brass gas light fittings on board would have found a ready market.The gas fitting is significant for its association with the LOCH ARD shipwreck, which is of State significance and is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register S417. The fitting is an example of a late 19th-century plumbing and light fitting.A pressed brass gas light fitting, recovered from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The elegant and functional fitting extends from an ornate 8cm diameter ceiling flange, and comprises two short lengths of fluted column pipe with a brass joiner that are severed (cut off) at the end. Within this decorative outer layer of 3cm diameter is a full length brass tube liner, which is in turn protecting a narrow 0.75cm copper gas pipe that also runs full length. The artefact is generally unrestored with reddish/cream sandstone concretion, but is in good condition.warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck artefact, maritime museum, gas lamps, gas lighting, gas works, brass fittings, gas pipes, loch ard, 1878 shipwreck, victorian affluence, colonial gas lighting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDeadeye, circa 1873
... of the LOCH ARD is of State significance. Victorian Heritage Register ...This example of a sailing ship’s ‘dead-eye’ is from the wreck of the LOCH ARD, which sank near Port Campbell in 1878. The vessel was an iron hulled clipper ship constructed for the Loch Line in 1873. It was part of a fleet of similar merchant ships owned by that company, which specialised in bringing passengers and goods from London via the Great Circle route to Melbourne, and returning to Britain via Cape Horn with the colony’s wool clip. Deadeyes were a common feature of sailing ship technology in the nineteenth century. They were a simple, cheap, and hard-wearing device that, in conjunction with another deadeye, provided an effective means of levering, or tightening, attached ropes and stays. Lower deadeyes were fixed to the sides of the ship by an encircling metal collar (inset in a flattish groove chiselled around the outer circumference of the disc), which was bolted to iron bars attached to the hull (called chain-plates). Upper deadeyes were looped by a strong hemp or wire rope (inset in a rounded groove carved around the outer circumference of the disc), which was joined to the bottom ends of the rigging which reached up to secure the masts into position (called shrouds or stays). Connecting a Lower deadeye to its corresponding Upper deadeye was a rope (called a lanyard) which looped up and down through the three “eyes” of each disc, to form a pulley system. The hitching of the two deadeyes with a looped lanyard provided the means of tightening, or loosening, the tension on the mast rigging ― essentially by pulling against the chain-plates bolted to the outside of the hull. It was a procedure that could be performed by sailors at sea and in emergencies. For example, after a gale the stays may have stretched and the masts worked loose, requiring retightening. Or, in the extreme circumstance of shipwreck, the lanyards might need to be released on the weather side, so that the masts fall away from the stricken vessel. The shipwreck of the LOCH ARD is of State significance. Victorian Heritage Register S417.A well-preserved ship’s deadeye with wire loop rope still attached. The original tar coating for water-proofing still remains, colouring the entire artefact black. It is wrapped in hessian cloth and hemp cord and is currently in storage under secure and stable conditions. This deadeye was recovered from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The artefact is a typical deadeye, comprising a thick round wooden disc, pierced by 3 similarly sized and shaped holes from one flat side through to the other, in a triangle formation. The survival of the wire cable loop-rope suggests it was an Upper Deadeye, connected to the shrouds (mast rigging). Previous number PWO 2388.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, deadeye, loch ard, rigging -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Cap Liner, ca 1908
A cap liner helps to seal the contents in a container to avoid spoiling and leakage. This cap liner was recovered from the Falls of Halladale shipwreck. The Falls of Halladale was an iron-hulled, four-masted barque, used as a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 bound for Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold was general cargo consisting of roofing tiles, barbed wire, stoves, oil, and benzene as well as many other manufactured items. After three months at sea and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland on the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members survived, but her cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson's navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The Falls of Halladale was built in1886 by Russell & Co., at Greenock shipyards on the River Clyde, Scotland for Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow. She was one of several designs of the Falls Line of ships named after waterfalls in Scotland. The company had been founded between 1870- 1873 as a partnership between Joseph Russell, Anderson Rodger, and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co. standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships during that time. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and was able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the 'windjammers' that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck in stormy conditions. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes from Europe and the Americas. Also of significance is that the vessel was one of the first ships to have fore and aft lifting bridges as a significant safety feature still in use on modern vessels today. The subject model is an example of an International Cargo Ship used during the 19th and early 20th centuries to transport goods around the world and representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. Glass cap liner, moulded disc with indented ring on the underside and a grip on top. Encrustation on surface. Glass has imperfection's and surface has a small amount of encrustations. Recovered from Falls of Halladale wreck. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, cap liner, russell & co., falls of halladale, ship wreck, glass liner, glass seal -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFootwear - Rubber Boot, 1900-1908
The Falls of Halladale was an iron-hulled, four-masted barque, used as a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 bound for Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold was general cargo consisting of roof tiles, barbed wire, stoves, oil, and benzene as well as many other manufactured items. After three months at sea and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland on the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members survived, but her cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson's navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The Falls of Halladale was built in1886 by Russell & Co., at Greenock shipyards on the River Clyde, Scotland for Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow. She was one of several designs of the Falls Line of ships named after waterfalls in Scotland. The company had been founded between 1870- 1873 as a partnership between Joseph Russell, Anderson Rodger, and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co. standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships during that time. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and was able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the 'windjammers' that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck in stormy conditions. This rubber boot is significant for being the only rubber boot in our collection. It is remarkable that it has survived almost seventy years underwater. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes from Europe and the Americas. Also of significance is that the vessel was one of the first ships to have fore and aft lifting bridges as a significant safety feature still in use on modern vessels today. The subject model is an example of an International Cargo Ship used during the 19th and early 20th centuries to transport goods around the world and represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. Rubber boot, left foot, Boot is ankle height and adult size. The heel appears to be solid rubber and the inner sole resembles leather. The rubber has come away from the outer boot in places, revealing a fabric base. Recovered from the Falls of Halladale. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, russell & co., rubber boot, protective footwear, shipwreck artefact -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Glass, drinking, 1886-1908
The Falls of Halladale was an iron-hulled, four-masted barque, used as a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 bound for Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold was general cargo consisting of roofing tiles, barb wire, stoves, oil, and benzene as well as many other manufactured items. After three months at sea and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland on the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members survived, but her cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson's navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The Falls of Halladale was built in1886 by Russell & Co., at Greenock shipyards on the River Clyde, Scotland for Wright, Breckenridge & Co of Glasgow. She was one of several designs of Falls Line of ships named after waterfalls in Scotland. The company had been founded between 1870- 1873 as a partnership between Joseph Russell, Anderson Rodger, and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co. standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships during that time. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the 'windjammers' that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck in stormy conditions. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes from Europe and the Americas. Also of significance is that the vessel was one of the first ships to have fore and aft lifting bridges as a significant safety feature still in use on modern vessels today. The subject model is an example of an International Cargo Ship used during the 19th and early 20th centuries to transport goods around the world and representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. Small drinking glass, rebated around lip with encrustation and a small chip out of the lip. Inscriptions on attached sticker. The handmade glass has been blown into a mould.""F/15" "SS 3/2-74"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale, glass, russell & co., wreck, artifact, shot glass, handmade, blown glass, shipwreck artefact -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Wagon Wheel Spoke, ca. 1908
This wagon wheel spoke was recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. Buggy wheels and spokes here amongst the varied cargo carried on the ship. The Falls of Halladale was an iron-hulled, four-masted barque, used as a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 bound for Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold was general cargo consisting of roofing tiles, barb wire, stoves, oil, and benzene as well as many other manufactured items. After three months at sea and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland on the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members survived, but her cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson's navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The Falls of Halladale was built in1886 by Russell & Co., at Greenock shipyards on the River Clyde, Scotland for Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow. She was one of several designs of Falls Line of ships named after waterfalls in Scotland. The company had been founded between 1870- 1873 as a partnership between Joseph Russell, Anderson Rodger, and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co. standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships during that time. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and was able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the 'windjammers' that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck in stormy conditions. The wheel spoke was part of the cargo on the ship, Falls of Halladale, along with buggy wheels. These are examples of parts of vehicles used at the beginning of the 20th century and could have been built components for buggies or wagons if delivered to their destinations of Melbourne or Sydney. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes from Europe and the Americas. Also of significance is that the vessel was one of the first ships to have fore and aft lifting bridges as a significant safety feature still in use on modern vessels today. The subject model is an example of an International Cargo Ship used during the 19th and early 20th centuries to transport goods around the world and represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. Wagon wheel spoke, light coloured wood, flat length, tongue shaped at the end. It was recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, russell & co., spoke, wagon wheel spoke, wreck artifact, falls of halladale, buggy wheel spoke, wheel spoke, cargo -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Clock Frame, ca. 1908
This clock face was recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. There were twenty boxes of clocks carried on the ship as cargo, destined for the ports of Melbourne and Sydney. The Falls of Halladale was an iron-hulled, four-masted barque, used as a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 bound for Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold was general cargo consisting of roofing tiles, barbed wire, stoves, oil, and benzene as well as many other manufactured items. After three months at sea and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland on the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members survived, but her cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson's navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The Falls of Halladale was built in1886 by Russell & Co., at Greenock shipyards on the River Clyde, Scotland for Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow. She was one of several designs of Falls Line of ships named after waterfalls in Scotland. The company had been founded between 1870- 1873 as a partnership between Joseph Russell, Anderson Rodger, and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co. standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships during that time. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and was able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the 'windjammers' that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck in stormy conditions. Twenty cases of clocks were carried amongst the cargo of the Falls of Halladale, an example of the need for people in the early 20th century to have easy access to the current time. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes from Europe and the Americas. Also of significance is that the vessel was one of the first ships to have fore and aft lifting bridges as a significant safety feature still in use on modern vessels today. The subject model is an example of an International Cargo Ship used during the 19th and early 20th centuries to transport goods around the world and represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. Section of a clock frame, brass, with drilled holes and cutout shapes and an arched base. It was recovered from the wreck of the Falls of Halladale. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, clock frame, russell & co., falls of halladale wreck, artifact, clock part, time keeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Sauce Bottle, 1878
This Worcestershire Sauce bottle was made by Lee & Perkins. It was hand blown into a two-piece mould, snapped off the blowing rod and then had a separate mouth applied to the neck, as evidenced by the side seams, ripples in the body, join below the mouth, bubbles in the glass and a push-up base that is uneven in thickness. The Loch Ard got its name from ”Loch Ard” a loch that lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic. The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold their position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as Loch Ard Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the Loch Ard tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of Loch Ard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up into Loch Ard Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck, it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artifact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collections historically significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.Clear glass bottle with a green tinge. The bottle has an applied mouth, seams from base to mouth, bubbles and impurities in the glass, and uneven glass thickness. Vertical and horizontal inscriptions are raised. The bottle once contained Worcestershire Sauce and was made by Lea and Perkins. Vertical; "LEA & PERKINS" and around shoulder "WORCESTERSHIRE SAUCE" flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, sauce bottle, worcestershire sauce, shipwreck artefact, condiment bottle, loch ard artifacts, lea and perkins -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Container
When the Schomberg was launched in 1855, she was considered the "Noblest” ship that ever floated on the water. Schomberg's owners, the Black Ball Line had commissioned the ship for their fleet of passenger liners. She was built by Alexander Hall of Aberdeen for £43,103 and constructed with 3 skins. One planked fore and aft and two diagonally planked, fastened together with screw-threaded trunnels (wooden rails). Her First Class accommodation was simply luxurious with velvet pile carpets, large mirrors, rosewood, birds-eye maple and mahogany timbers throughout, soft furnishings of satin damask, and oak-lined library with a piano. Overall she had accommodation for 1000 passengers. At the launch, the Schomberg's 34-year-old master, Captain 'Bully' Forbes, had promised to reach Melbourne in sixty days stating, "with or without the help of God." Captain James Nicol Forbes was born in Aberdeen in 1821 and rose to fame with his record-breaking voyages on the famous Black Ball Line ships; Marco Polo and Lightning. In 1852 in the Marco Polo, he made the record passage from London to Melbourne in 68 days. Unfortunately, there were 53 deaths on the voyage, but the great news was off the record passage by Captain Forbes. In 1854 he took the clipper “Lighting” to Melbourne in 76 days and back in 63 days, this record was never beaten by a sailing ship. He often drove his crew and ship to breaking point to beat his previous records. He cared little for the comfort of the passengers. On this, the Schomberg's maiden voyage, he was determined to break existing records. Schomberg departed Liverpool on her maiden voyage on 6th October 1855 flying a sign that read "Sixty Days to Melbourne". She departed with 430 passengers and 3000 tons cargo including iron rails and equipment intended to build the Melbourne to Geelong Railway and a bridge over the Yarra from Melbourne to Hawthorn. She also carried a cow for fresh milk, pens for fowls and pigs, 90,000 gallons of water for washing and drinking. She also carried 17,000 letters and 31,800 newspapers. The ship and cargo were insured for $300,000 a fortune for the time. The winds were poor as she sailed across the equator, slowing Schomberg's journey considerably. The land was first sighted on Christmas Day, at Cape Bridgewater near Portland, Captain Forbes followed the coastline towards Melbourne. Forbes was said to be playing cards when called by the third mate Henry Keen, who reported land about 3 miles off. Due in large part to the captain's regarding a card game as more important than his ship, it eventually ran aground on a sand spit near Curdie's Inlet (about 56 km west of Cape Otway) on 26th December 1855, 78 days after leaving Liverpool. The sand spit and the currents were not marked on Forbes's map. Overnight, the crew launched a lifeboat to find a safe place to land the ship’s passengers. The scouting party returned to Schomberg and advised Forbes that it was best to wait until morning because the rough seas could easily overturn the small lifeboats. The ship’s Chief Officer spotted the SS Queen at dawn and signalled the steamer. The master of the Queen approached the stranded vessel and all of Schomberg’s passengers and crew disembarked safely. The Black Ball Line's Melbourne agent sent a steamer to retrieve the passengers' baggage from the Schomberg. Other steamers helped unload her cargo until the weather changed and prevented the salvage teams from accessing the ship. Later one plunderer found a case of Wellington boots, but alas, all were for the left foot. Local merchants Manifold & Bostock bought the wreck and cargo but did not attempt to salvage the cargo still on board the ship. They eventually sold it on to a Melbourne businessman and two seafarers. In 1864 after two of the men drowned when they tried to reach Schomberg, salvage efforts were abandoned. In 1870, nearly 15 years after the wreck parts of the Schomberg had washed ashore on the south island of New Zealand. The wreck now lies in 825 metres of water and although the woodwork is mostly disintegrated the shape of the ship can still be determined due to the remaining railway irons, girders and the ship’s frame. A variety of goods and materials can be seen scattered about nearby. There have been many other artefacts salvaged from the wreck include ship fittings and equipment, personal effects, a lithograph, tickets and photographs from the Schomberg. This ceramic container was retrieved from the shipwreck site during early salvage efforts on the vessel. And was donated to the Flagstaff Hill collection of Schomberg shipwreck artefacts.The ceramic container is particularly significant in that along with other items from the wreck have helped in part to having legislation changed to protect shipwrecks, with far tighter controls being employed to oversee the salvaging of wreck sites. This item forms part of the Schomberg collection at Flagstaff Hill maritime museum. The collection as a whole is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Schomberg is also significant for its association with the Victorian Heritage Registered Schomberg shipwreck (VHR S 612). The collection is of additional significance because of the relationship between the objects salvaged, as together they help us to interpret the story of the Schomberg. The collection as a whole is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria's maritime history and its potential to interpret social and historical themes from society at the time of the wreck.Stoneware Container with lid, white in colour,Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, container, shipwrecked-artefact, schomberg, clipper ship, black ball line, 1855 shipwreck, aberdeen clipper ship, captain forbes, peterborough shipwreck, ss queen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLetter
... is of State significance ― Victorian Heritage Number S417 flagstaff ...This letter was written to Alisdair Loch, 10 Beaconsfield Parade, Lindfield (Sydney) NSW, from Frank Townshend Esq., 3 The Square, Holywell, Wotton-under-Edge, Gloucestershire, England. Its author is a son of Eva Carmichael/Townshend, sole female survivor of the LOCH ARD shipwreck in 1878. It tells of Eva’s struggle in the sea after the LOCH ARD hit the rocks, and of her rescue by the only other survivor, young seaman Tom Pearce. It also relates her return to a privileged life in Ireland, her subsequent marriage to another member of the Anglo-Irish ascendancy, and her three sons. In some places the letter seems in historical error, which is not surprising given the dates involved and the time that elapsed between them (Eva shipwrecked 1878, Son’s birth 1887, Eva’s death 1934, Son’s letter 1962). The writer makes clear he is relying on his memory of what his mother had told him, and he is usually forthright in declaring those things he cannot remember, or remembers indistinctly. An interesting paragraph in the letter answers the contemporary newspaper speculation about a possible romance between the two survivors: “She [his mother, Eva Carmichael] received many proposals of marriage, perhaps a dozen, including one from Tom Pearce. Tom Pearce was, I think, an apprentice. She spoke of him sometimes as a ‘cabin boy’. From his photograph, he was a fine, handsome young man. The reason she declined his offer of marriage was largely the fruit of class distinction, I think; class prejudice being very strong in Ireland, in those days.” The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance ― Victorian Heritage Number S417Typed copy of a letter from Frank Townshend, LOCH ARD survivor Eva Carmichael’s son in England, to Alasdair Loch, Sydney NSW. It is dated 8 March 1962 and consists of four pages. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, letter, frank townshend, eva carmichael, loch ard, alasdair loch, tom pearce -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLetter
... of the LOCH ARD is of State significance ― Victorian Heritage Number ...This letter is a photographed copy of a typed transcript of an original. It is dated 28 March 1962 and was written by Ian F. Sloane Esq. of Savernake Station, NSW. Sloane’s great uncle, Hugh Gibson, was the owner of Glenample Station, Vic., where Eva Carmichael stayed to recuperate from her ordeal as the only female survivor of the LOCH ARD shipwreck in 1878. The letter is in reply to an earlier inquiry for information about the LOCH ARD tragedy from Alasdair Loch, 10 Beaconsfield Parade, Lindfield NSW. Most of the letter consists of tantalising asides: about trips to Glenample in 1916 and 1917 and the digging up of an old piano at Loch Ard Gorge; the possession of his uncle’s personal account of the shipwreck and its aftermath; the existence of a painting of Eva when she was staying at the Glenample homestead in 1878; and the disputed ownership of “a very old black iron box” containing letters from relatives of the shipwreck victims (who Hugh Gibson had written to advising of their unhappy fate). Unfortunately the letter, written in haste prior to Sloane’s departure overseas, contains no substantive information. However it concludes with an interesting footnote concerning Eva’s emotional recovery at Glenample. Sloane’s postscript states: “Miss Carmichael was very well after the wreck, full of fun and laughter, until she suddenly cracked, and had a nervous breakdown…Mrs Gibson…got a young girl, the same age as Eva, as her companion[…She] proved trumps and saved Eva’s mind. They became lifelong friends. Both wrote to my aunt till they died. Miss Carmichael stayed about 6 months at Glenample I think.” The shipwreck of the LOCH ARD is of State significance ― Victorian Heritage Number S417A photographic copy of a typed letter-transcript. The original letter was written to Alasdair Loch, Lindfield NSW, and is from Ian F. Sloane Esq. of Savernake Station NSW. It is dated 28 March 1962 and is two pages long.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, letter, alasdair loch, ian f sloane, sloane, loch ard, hugh gibson, eva carmichael, glenample station, tom pearce, glenample homestead
