Showing 1148 items matching "metal tools"
-
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybutton hook, 1895 – 1905
Button hooks were used to fastens buttons on boots and long gloves. It is a tool used for the closing of shoes, gloves or other apparel that uses buttons as fasteners. The steel hook end is inserted through the buttonhole to capture the button by the shank and draw it through the opening. This hook is most likely to have been used to do up bootsWomen and young girls generally wore boots that were either front laced or side buttoned, particularly in the period from the 1870s . Buttonhooks were needed to do up the buttons on buttoned boots and were used by poking the metal hook through the buttonhole, grabbing the button and pulling it through the eyelet. This item is an example of a commonly used accessory no longer relevant.A button hook made of metal with a beaten silver handle ornately decorated with scrolls and foliate design. At the top is a small ring on the handle end. This could have been for a lady to attach the item to her chatelaine at her belt, or on a necklace. clothing footwear gaiters boots button-hook -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societycontainer, First half 20th century
This may have a WW 1 military item (?). It seems to be an oil canister from a gun cleaning kit. It could be from a spare parts tool kit for a Bren Gun.This item is linked to WW1 ans is a reminder of those who played a role in that conflict.A small rectangular shaped metal container with screw top lid. It has one flat side and the lid has a textured grip. The dipstick unscrews.container-metal -
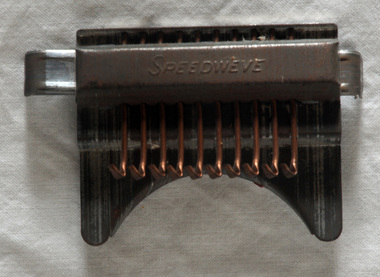 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyweaving tool, late 1940's - 1950's
The Speedweve is a tiny darning loom advertised as ‘Lancashire’s smallest loom’. It was manufactured by E & A Chesstok Ltd of Rusholme, Manchester in 1947/48. It is basically a little loom for mending socks and holes in clothing. - This item was a common household item used a time when people still felt it worth the effort to darn socks.A metal Speedweve - a small darning tool.The slide at the top pushes back and forth making the 10 copper hooks rotate one way then the other. There would have been a wooden disc for keeping the fabric flat. top - SPEEDWEVEdomestic weaving loom -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyhammer, 1920's
... hammer-ball-peen tool metal-work...-peen tool metal-work Wooden handled ball peen pein) hammer ...A ball-peen ) hammer, also known as a machinist's hammer, is a type of peening hammer used in metal-working. Its steel head is harder than that of a claw hammer, so is less likely to chip on impact. Ball peen hammers are commonly used to drive cold chisels, set rivets, and bend and shape metal. Before the advent of pneumatic rivet guns, ball peen hammers were commonly used for riveting. First the flat head drove the nail through, then the round ball was used to "peen over" the other side of the rivet. Before the advent of pneumatic rivet guns, ball peen hammers were commonly used for riveting. First the flat head drove the nail through, then the round ball was used to "peen over" the other side of the rivet. These hammers were made to last.Wooden handled ball peen pein) hammer. The handle has been nailed in and may not be the original. The metal head has one end shaped into a sphere and the other flat.hammer-ball-peen tool metal-work -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybuggy spanner, late 19th century -first half 20th century
... vehicles. buggy-spanner tool transport A metal buggy wheel spanner ...These were used on a horse-drawn wagons, carriages, stagecoaches, and carts. A wheelwright would use this tool to make or repair the wheels. Horse-drawn wagons are an important part of Australia’s agricultural history. Light buggies were popular with farmers for trips into town before the common use of motorised vehicles.A metal buggy wheel spanner for various applications.buggy-spanner tool transport -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyraker saw, c 1880 - 1940
Used in the timber industry in the Orbost district. This is a two person operated cross cut saw which functions as a pit saw. A log is placed over a pit lengthways. The man on the top walks along the log and pulls the saw upwards, and he man below pulls the saw downwards. This saw therefore cuts in both directions. This type of saw was often used in the ship building industry for cutting planks.A long raker saw which has been installed into the Slab Hut Shed in a vertical position as a pit saw. It has a metal handle extension at the top which has a wooden handgrip attached. Towards the bottom of the saw, a wooden handle had been added to the saw. timber-industry-tool raker-saw pit-saw -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societysignal lamps
Possibly used in the Orbost district. Railway lamps of this kind were hand signalling lamps used by train guards, shunters and sometimes signalmen and station staff. They could signal the locomotive crew at night to let them know what to do (move forward/move backward/right-of-way) when leaving a station, goods yard or siding. Railway lamps of this kind were significant railway items in their period of use as essential tools to the safe-working operations of the railway. Two railway signal lamps. These are kerosene burning lamps made of metal and painted red. Both lamps have carrying handles at the top. .1 has a green glass lens and .2 has a red glass lens. signals lamps communication railway transport kerosene-burning -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybutter press
This was found by Kevin Ingram while cleaning the Orbost Butter Factory site in 1991. The Orbost Butter and Produce Co. Ltd was registered on June 1st 1893 and was an important source of income to the Orbost district. A 1 lb butter press with a cylindrical metal handle on a square base. This tool fitted over the butter and pushed it out in a rectangular shape.orbost-butter_factory agriculture farming butter-press -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyhandsaw, !930's
Donated by the Harry Cameron family, Harry's father, James Cameron, came to Bellagoogan on Majors Creek in 1882. Bellagoogan was on Majors Creek near Orbost and was the site of the first race course. Like many other at the time, the Camerons bred race horses.Harry died in 1964 aged 75.Hand saw with a skew-back, steel blade and a wooden handle. It has three metal saw pins and a medallion marked 'warranted superior'. There is a chip carved wheat sheaf decorating the front hand grip. This handsaw is probably a Disston Keystone K-4 Air MasterOn a metal disc around a keyhole is "Warranted Superior".tool timber-industry handsaw -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societytobacco cutter, c. mid 19th century
Used to cut tobacco leaf or plugs into finer and more useable samples which could then be put into a pipe or made into a cigar or cigarette.Tobacco cutters were important tools for pipe smokers until self-made or manufactured cigarettes began to dominate the tobacco sales market from the 1920s. This item is a link to a previously common means of consuming tobacco.A metal blade cutter set onto a wooden base. The blade is rusty. tobacco-cutter tobacco-smoking -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Pliers, Henry Boker, late 19th to early 20th century
... for Boker tools in the 1950s. Museums Victoria has a Boker catalogue ...This unusual set of pliers was made in Germany by Henry Boker (Heinrich Boker). Boker hand tools were being produced in the 18th century in Remscheid, Germany. Boker tools were known for good quality and value for money. George A. Fox & Co., of 250 Victoria Street North Melbourne, were agents for Boker tools in the 1950s. Museums Victoria has a Boker catalogue in its collection dated circa 1954.These pliers are significant as an example of hand tools used in the early 20th centry or earlier. Pliers like this would typically be used in maritime trades.Pliers, double headed. This hand tool has two sets of jaws on its pair of handles. It was made by Henry Boker, Germany. Impressed into metal "HENRY BOKER / GERMANY"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, pliers, double headed pliers, henry boker, boker hand tool, german tool, german pliers, antique pliers, vintage pliers, victorian pliers, heinrich boker, tradesmen's tools -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Plane, Mid to late 19th Century
A jack plane (or fore plane) is a general-purpose woodworking bench plane, used for dressing timber down to the correct size in preparation for truing and/or edge jointing. It is usually the first plane used on rough stock, but in exceptional cases can be preceded by the scrub plane. Jack planes are 300–460 mm long and 64–76 mm wide, with wooden-stocked planes sometimes being slightly wider. The blade is 44–57 mm wide that is often slightly convex (or ground with rounded corners) to prevent digging in to or marking the work. The cut is generally set deeper than on most other planes as the plane's purpose is to remove stock rather than to gain a good finish (smoothing planes are used for that). In preparing stock, the jack plane is used after the scrub plane and before the joiner plane and smoothing plane. The carpenters' name for the plane is related to the saying "jack of all trades" as jack planes can be made to perform some of the work of both smoothing and joiner planes, especially on smaller pieces of work. Its other name of the fore plane is more generally used by joiners and may come from the fact that it "is used before you come to work either with the Smooth Plane or with the Joiner". Early planes were all wood, except for the cutter, or combined a wood base with a metal blade holder and adjustment system on top. Although there were earlier all-metal planes, Leonard Bailey patented many all-metal planes and improvements in the late 19th century. A jack plane came to be referred to as a "No. 5" plane or a "Bailey pattern No. 5" at the end of the 19th century. A vintage tool made by an unknown company, this item was made commercially for firms and individuals that worked in wood and needed a tool that could remove large amounts of timber. These jack or dressing planes came in various shapes and sizes to achieve a flat and even finish to timber surfaces before the use of smoothing planes and came in many sizes. A significant tool from the mid to late 19th century that is still in use today with early models sought after by collectors. It gives us a snapshot of how furniture and other finishes were created on timber by the use of cutting edged hand tools. Tools that were themselves hand made shows the craftsmanship used during this time not only to make a tool such as the subject item but also the craftsmanship needed to produce a decorative or even finish that was needed for the finishing of timber items. Jack Plane handle is attached by large screw there is a round piece of wood tacked to front. noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, jack plane -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Draw Knife, Prior to 1950
A draw knife or drawing knife, draw shave, shaving knife is a traditional woodworking hand tool used to shape wood by removing shavings. It consists of a blade with a handle at each end. The blade is much longer along the cutting edge than it is deep (from cutting edge to back edge). It is pulled or "drawn" toward the user. A draw knife is commonly used to remove large slices of wood for flat faceted work, to debark trees, or to create roughly rounded or cylindrical billets for further work on a lathe, or it can shave like a spokeshave plane, where finer finishing is less of concern than a rapid result. The thin blade lends itself to create complex concave or convex curves such as in making staves for barrels.A specialised tool used in many different types of wood working and in the making of barrels, this type of tool has been used for many hundreds of years by coopers and other woodworking craftsmen all around the world. It is a tool that has not changed in design during this time and is still used today by craftsmen in the making of wooden barrels for the storage of wines etc. However this item at this time cannot be associated with an historical event, person or place, provenance is unknown, item assessed as a collection asset as it is believed to have been produced before 1950.Draw knife with metal blade and two wooden handlesNoneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, draw knife, coopers tools, woodworking tools, knife, cooperage -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Bick Iron, Prior to 1950
A Bick or coopers anvil is a tool used to fabricate the iron hoops that a cooper would produce to hold a barrel together. The hoops are first cut to the required length and then beaten into shape and riveted on the Bick or Tee anvil. They are then driven into place on the barrel with a hammer and iron tipped, wedged shaped driver.The subject Item is used as a tool to produce steel hoops for wooden barrels but at this time cannot be associated with an historical event, person or place, provenance is therefore unknown, item assessed as a collection asset as it is believed to have been produced and used before 1950.Bick Iron or Coopers Anvil, attaches to a removeable wooden base, Metal anvil with pointed end & flat shaped topNoneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, brick iron, anvil, coopers tools, barrel making, barrels -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Screw Driver, F G Pearson & Co, 1902
... metal ferrule Tool Screw Driver F G Pearson & Co ...The subject item was made by G. Pearson and Co Ltd. of the Hope Works, Sheffield England. This company was established in 1854. By 1914 the company was manufacturing many differing types of edge tools, joiners' tools, forks and garden tools. Their specialities were hay, manure and coke forks, punches, armourers' tools etc. In 1938 the Company was styled F. G. Pearson and Co (Sheffield) Ltd and they were still making plane and other sharp edged blades as late as 1957, but by the 1970s they had gone out of business.A significant company based in Sheffield England and making tools of all types and exporting same to various countries around the world. This particular item is a vintage joiners screwdriver possibly used by a local Warrnambool carpenter (J Rob).Screw driver wooden handle shaped blade & brass metal ferrule1902 Sheffield marked on blade, F Rob owner Marked on handlewarrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, joiners tools, screwdriver, carpenters tools, f g pearson sheffield -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Spokeshave, Prior to 1950
A spokeshave was made with a wooden body and metal cutting blade. With industrialization metal bodies displaced wood in mass-produced tools. Spokeshaves can be made from flat-bottom, concave, or convex soles, depending on the type of job to be performed. They can include one or more sharpened notches along which the wooden shaft is pulled in order to shave it down to the proper diameter. Historically, spokeshave blades were made of metal, and the body and handles were wood. Unlike a drawknife, but like a plane, spokeshaves typically have a sole plate that fixes the angle of the blade relative to the surface being worked. By the twentieth-century metal handles and detachable blades had become the most common. A convex, wooden, variant of the spokeshave is called a travisher; at one time mostly used in chairmaking.A tool of the cooper and other woodworking tradesmen that has been in use since the making of barrels and wooden buckets for hundreds of years without much change to the design or how the tool is used.Spokeshave, with two wooden handles on either side. Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, coopers tools, spokeshave, barrel making, wood plane -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Marking Gauge, Prior to 1950
A marking gauge, also known as a scratch gauge, and] is used in woodworking and metalworking to mark out lines for cutting or other operations. The purpose of the gauge is to scribe a line parallel to a reference edge or surface. It is used in joinery and sheet metal operations. The gauge consists of a beam, a headstock, and a scribing or marking implement, typically a pin, knife, pen or wheel. The headstock slides along the beam, and is locked in place by various means: a locking screw, cam lever, or a wedge. The marking implement is fixed to one end of the beam.A tool that has been in use since woodworking began for hundreds if not thousands of years without much change to the design or how the tool is used. Its use to scribe a line in various material as a cutting guide and is still in use today by many trades. Wooden marking Gauge, smallNonewarrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, marking gauge, woodworking, carpenters tools, tool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Spokeshave, Prior to 1950
A spokeshave was made with a wooden body and metal cutting blade. With industrialization metal bodies displaced wood in mass-produced tools. Spokeshaves can be made from flat-bottom, concave, or convex soles, depending on the type of job to be performed. They can include one or more sharpened notches along which the wooden shaft is pulled in order to shave it down to the proper diameter. Historically, spokeshave blades were made of metal, and the body and handles were wood. Unlike a draw knife, but like a plane, spokeshaves typically have a sole plate that fixes the angle of the blade relative to the surface being worked. By the twentieth-century metal handles and detachable blades had become the most common. A convex, wooden, variant of the spokeshave is called a travisher, at one time mostly used in chair making.A tool of the joiner and other woodworking tradesmen that has been in use since the making of furniture for hundreds of years without much change to the design or how the tool is used to smooth and shape timber.Spokeshave, Marked AH, (believed to be owner)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Bow Saw, Prior to 1950
... of a Coopers tool kit and used in the production of making barrels ...A coopers turning or bow saw is a woodworking tool used for straight or curved cuts. A bow saw is a type of frame saw with a thin toothed blade that is held in tension by a frame with two long narrow handles called "cheeks" that are supported and separated by a thin stretcher in the center of the handles, making a wide H shape (the cheeks form the uprights of the H, the stretcher the crossbar of the H). The blade is kept in tension with a turnbuckle that runs parallel to the blade between the two cheeks but on the opposite side of the stretcher.An age old tool used for cutting timber for hundreds of years before the modern cross cut saws were invented. This design of saw was part of a Coopers tool kit and used in the production of making barrels. However this item at this time cannot be associated with an historical event, person or place, provenance is unknown, item assessed as a collection asset as it is believed to have been produced before 1950.Bow saw wooden handle with metal blade missingNonewarrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, bow saw, turning saw, coopers tools, cutting wood, sawing timber, coopering -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Coopers Flagging Iron, Prior to 1950
... metal painted black Tool Coopers Flagging Iron ...A cooper would use a flagging iron to insert reeds around the head of a barrel to tighten the head and stop any leaks. First the cooper removes the full and quarter metal hoops around the barrel, this loosens the staves and insert reeds around the head, prying the stave apart from the head with a flagging iron. Then he replaces the hoops to tighten the staves against the head and the inserted reeds to form a leakproof seal.An age old tool used for many hundreds of years in the making and repairing of wooden barrels and an essential tool in a coopers tool kit.Flagging iron metal painted black Nonewarrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, flagging iron, coopers tools, barrel making, repairing barrel leaks, barrel head tightening -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Leg Vice, Mid 19th Century
The blacksmith leg vise is also called the "solid box vise" and is one of the most important tools in the blacksmith's shop. It firmly holds hot iron while it is hammered, chiseled, or twisted. These are the only vises that are designed to take this kind of use day in and day out. A small 30-pound blacksmith's vise can survive pounding that would wreck a much heavier cast iron bench model. Three things make a blacksmith's vice special. One is that they are forgings, not cast iron or ductile iron. The second is the leg that provides support to the floor or from a sunken post. The last is the hinge, while not a perfect way to construct a vice the pin joint is durable and can take a considerable beating. If sheared it is easy to replace. These things all combine into a tool that can take decades of heavy use and abuse. Most in use is one to two hundred years old.Some of these vises were made by specialists such as Atwood of Stourbridge England, Steel City and Columbian in the U.S. and others were made in anvil manufacturing plants such as "Mousehole Forge" and "Peter Wright" in England and "Fisher-Norris" and others in North America. The design of these vises right down to the last chamfer seems to have been perfected in the 1600s and remained more or less the same until the 20th century. The bodies are forged wrought iron or mild steel and they have hard steel surfaces welded into the jaws. The jaws have little or very shallow serrations which are generally worn off.Around the turn of the 20th Century during the hey-day of the blacksmith shop in North America, these tools were considered so standard a commodity that they were sold without reference to the manufacturer. Very few were even marked with the maker's name. Size is best defined by weight as there is some variation in jaw size from manufacturer to manufacturer. They were sold by the pound and are still best judged by the pound.A vintage tool used in a Blacksmiths shop during the early 19th century to the beginning of the 20th century. Regarded as a significant into social history of the time.Leg Vice attached with screws to bench via a block of wood. Has large metal pole which practically reaches the floor. Also has a metal device to either tighten or slacken vice.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDrill Press, early to mid-20th century
... metal working tool... machine drill with gear driven flywheel forging tool metal working ...This post drill press has been made by Melbourne business, Dawn Manufacturing Company. It can be operated manually or by a pulley driven flywheel, with the aid of an engine connected to a power supply. In the late 1800s early 1900s a drill press like this would have been driven by steam from a boiler, the main power source for manufacturer’s power at that time. Dawn’s Golden Anniversary 1917-1967 Catalogue describes this model 611 drill as … “Ruggedly constructed with accurately reamed bearings. The coupling between the main spindle and feed screw engages the full circumference of the spindle, and embraces a ball-bearing thrust race. The pillar, as in all “Dawn Drilling Machines” is a solid bright steel bar, in place of the usual light tubing. Adjustable automatic feed.” And “F. & l. Pulleys extra, if required”. DAWN MANUFACTURING CO. The Dawn Manufacturing Co. was founded in Coburg, Melbourne, in 1917 by the four Blake brothers, who were all engineers. After World War I Dawn was supplying drills Australia wide and the company was growing at a healthy rate. During the depression they remained busy, with employees working 60-80 hour weeks. Dawn was contracted to supply vices and clamps to the Australian Defence Department and munitions factory during the World War II. - 1959 the company was taken over by G.N. Raymond Group. - 1967 the Dawn Manufacturing Co. had distributors in Australia and overseas, including USA, Canada, New Zealand, Asia and the Middle East. - 1973 the Siddons Ramset Limited acquired Dawn. - December 1991, Dawn became a unit of the United States owned Stanley Works Pty. Ltd. - November 1998 Dawn became 100 per cent Australian owned. The drill is a typical tool of a blacksmith, cart wright, wheelwright and garage business. It is an example of the tools of the blacksmiths’ trade in Victoria in the early to mid-20th century.Post type drill press machine with gear driven flywheel. Drill press is attached to a post and is fitted with a pulley belt and will run at a speed of maxim 200 r.p.m. The machine can also be manually operated. It has an aperture in the centre, a chuck, for the drill bit and has two metal handles at the centre, on the right hand side. Gear ratio 2:1 main drive, 6" diam, 3:1 reduction gear. Made by Dawn of Melbourne, Australia. Model No. 611, Code No. 9157"DAWN MFG COY”, “MELB. AUSTRALIA", " 611"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, blacksmiths, blacksmith’s drill, blacksmith tools, dawn drill model no. 611, dawn drill code no. 9157, dawn manufacturing coy melbourne, dawn manufacturing coy coburg, dawn post drill, drilling machine, drill with gear driven flywheel, forging tool, metal working tool, post drill, steam powered drill, trade tool, warrnambool district 1900s -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Mortice Machine, Mathieson and Son, 1910-1940
In 1792 John Manners had set up a workshop making woodworking planes at 14 Saracens Lane Glasgow. He also had employed an apprentice Alexander Mathieson (1773-1851). But in the following year at Saracen's Lane, the 1841 census describes Alexander Mathieson as a master plane-maker now at 38 Saracen Lane with his son Thomas Adam working with him as a journeyman plane-maker. Presumably, Alexander must have taken over the premises and business of John Manners. Now that the business had Thomas Adam Mathieson working with his father it gradually grew and became more diversified, and it is recorded at the time by the Post-Office Glasgow Annual Directory that by 1847-1848 Alexander Mathieson was a “plane, brace, bit, auger & edge tool maker” In 1849 the firm of James & William Stewart at 65 Nicolson Street, Edinburgh was taken over and Thomas was put in charge of the business, trading under the name Thomas A. Mathieson & Co. as plane and edge-tool makers. Thomas's company went on to acquire the Edinburgh edge-tool makers “Charles & Hugh McPherson” and took over their premises in Gilmore Street. In the Edinburgh directory of 1856/7, the business is recorded as being Alexander Mathieson & Son, plane and edge-tool makers at 48 Nicolson Street and Paul's Work, Gilmore Street Edinburgh. In the 1851 census, Alexander is recorded as working as a tool and plane-maker employing eight men. Later that year Alexander died and his son Thomas took over the business. Under the heading of an edge-tool maker in the 1852/3 Post-Office Glasgow Annual Directory the firm is now listed as Alexander Mathieson & Son, with further entries as "turning-lathe and vice manufacturers". By the early 1850s, the business had moved to 24 Saracen Lane. The directory for 1857/8 records that the firm had moved again only a few years later to East Campbell Street, off the Gallowgate area, and that through further diversification was also manufacturing coopers' and tinmen's tools. The ten-yearly censuses report the firm's growth in 1861 stating that Thomas was a tool manufacturer employing 95 men and 30 boys; in 1871 he had 200 men working for him and in 1881 300 men. By 1899 the firm had been incorporated as Alexander Mathieson & Sons Ltd, even though only Alexander's son Thomas appears ever to have joined the firm so the company was still in his fathers' name. In September 1868 Thomas Mathieson put a notice in the newspapers of the Sheffield & Rotherham Independent and the Sheffield Daily Telegraph stating that his firm had used the trade-mark of a crescent and star "for some time" and that "using or imitating the Mark would be proceeded against for infringement". The firm had acquired its interest in the crescent-and-star mark from the heirs of Charles Pickslay, the Sheffield cutler who had registered it with the Cutlers' Company in 1833 and had died in 1852. The year 1868 seems also to be the one in which the name Saracen Tool Works was first adopted; not only does it figure at the foot of the notice in the Sheffield press, it also makes its first appearance in the firm's entry in the Post-Office Glasgow Annual Directory in the 1868/9 edition. As Thomas Mathieson's business grew, so too did his involvement in local public life and philanthropy. One of the representatives of the third ward on the town council of Glasgow, he became a river bailie in 1868, a magistrate in 1870, and a preceptor of Hutcheson's Hospital in 1878. He had a passion for books and was an "ardent Ruskinian". He served on the committee handling the bequest for the setting up of the Mitchell Library in Glasgow. When he died at Coulter Maynes near Biggar in 1899, he left an estate worth £142,764. Company's later years: Both Thomas's sons, James Harper and Thomas Ogilvie were involved in the continuing life of the firm. James followed in his father's footsteps in becoming a local public figure. He was appointed Deputy Lieutenant of the County of the City of Glasgow and was made a deacon of the Incorporation of the Hammermen of Glasgow in 1919. His brother Thomas Ogilvie was recorded as a tool manufacturer and employer in the 1911 census. Thomas Ogilvie's son Thomas Alastair Sutherland Ogilvie Mathieson was born in 1908 took a rather different approach to engineering, however, by becoming a racing driver. In 1947 he wed the French film actress Mila Parély. The firm had won many awards at world fairs for their goods. At the Great Exhibition, London, 1851. Prize medal for joiners' tools in the class of Cutlery & Edge Tools, Great London Exposition, 1862. Prize medal honoris causa. International Exhibition, Melbourne, 1880. Gold medal International Exhibition of Industry, Science and Art, Edinburgh, 1886 Prize medal. See note section for Thomas McPherson Australian Retailer information: The firm of Alexander Mathieson & Sons was one of the leading makers of hand tools and later woodworking machines in Scotland. Its success went hand in hand with the growth of the shipbuilding industries on the Firth of Clyde in the nineteenth century and the emergence of Glasgow regarded as the "second city of the Empire". It also reflected the firm's skill in responding to an unprecedented demand for quality tools by shipyards, cooperages, and other industries, both locally and throughout the world. McPherson's started as an Australian retailer of hardware products in Melbourne going on to become a company that supplied machinery and other items for the establishment of major infrastructure projects in Australia during the early days of the colony that assisted in linking the various states and territories which became a precursor of Federation. From a humble beginning McPherson's became one of Australia's leading retail, and later manufacturing businesses that is still in existence today.Mortice machine metal with long metal lever handle with counter weight & 3 adjustment wheels & metal crank with wood end. Has 4 feet that can be bolted to floor & vertical moving piece that a cutting bit would fit into.Imprinted Alex Mathieson & Son Trademark Saracen Tool works Glasgow' also a brass plate "Thomas McPherson & Son Machinery Importer Melbourne"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Plough, Syracuse Chilled Plow Co, 1876-1900
... plough metal wheel in front. Tool Plough Syracuse Chilled Plow Co ...The Syracuse Chilled Plough Company was created in 1876 and specialised in the manufacture of agricultural ploughs. Harry Wiard invented the chilling process in plough manufacture. The company was originally founded as the Robinson Chilled Plough Company in 1876 and changed its name 3 years later. At its peak, in the early 20th century. The company made more than 100,000 horse-drawn ploughs and road scrapers of various designs that were sold from the Syracuse plant each year and exported around the world. The company slogan of the day was, “The sun never sets on a Syracuse plough." Eventually, other farming implements were added to the line. The company employed more than 300 people in its local plant, which covered a square block on the cities Near West Side. In 1910-11, Deere and Company began expanding its holdings, and with the success of the Syracuse Chilled Plough Company, Deere sought to acquire the company. The management of the Syracuse operation after John Deere took over remained in the hands of Wiard and Chase, and the manufacturing operations were left in Syracuse. The only change from previous Syracuse operations was the selling of the companies products through Deere retail outlets instead of directly to the trade. The factory in Syracuse continued to produce ploughs until 1955. The subject item in the Flagstaff collection is an early model Syracuse Chilled plough with a wooden beam frame it is very much lighter in weight and was adapted to work sandy or light loamy soil. This plough has a sloping landside, which tends to keep the clods and dirt from falling into the furrow, making the ploughman's work much more comfortable and easy. This design was made in eight sizes for both right and left-handed ploughing and became very popular in the far West and South of the USA. Note: The definition of a chill plough means : a plough having the share and mould-board of chilled semi steel or cast iron.The subject item is believed to be a very early plough given its wooden beam frame and was made before 1900 probably around 1880. This makes it a significant example of the types of plough that early settlers were using in Victoria. There would not be very many of this type of vintage plough left with a wooden beam and frame, making it today a desirable collector's item. Syracuse Wood Beam Chilled single furrow plough metal wheel in front. Syracuse Chiller Co Syracuse & 50 L stamped on ploughshare.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, plough, syracuse chiller co, chiller plourh, farm equipment, furrow -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Brace, 1859-1866
No contextual information available at this time give the items usual design and no makers markings writer believes item is from the 1860s either American, British or could be of continental origin.An early tool significant because of it's unique design writer cannot find one like it during researching the item.Metal Brace possibly for gas fitter has leather in centre, (owner installed)Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSpirit level
Spirit level, small, wood with metal around the ends and the glass levels. Comprises both verticle and horizontal levels. Horisontal level is divided into 2 by metal surround. Imperial measurements are impressed into wood on both sides of the ruler.Impreial measurements are impressed into the wood on both sides.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, spirit level, cabinet making, wood working, wood working tool, building tool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Compass, late 19th to early 20th century
This large compass is well made. It is now pitted and scratched, indication much use. Compasses were used to measure and mark out the head of the barrel by coopers. Very large compasses were used by block, spar and pump makers to help shave off angles left by axes and other tools on mast sides. Also they were used by blacksmiths in their work draftsmen, carpenters, engineers and navigators.This compass is an example of a drawing instrument that could have been used in the 19th and early 20th century by coopers and blacksmiths as well as navigators and ship smiths.Compass; large metal compass, 90-degree angle, two pointed arms hinged at the top. Inscription on the top of one arm.Stamped into the metal " J J E " ( or J J F )flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, compass, drawing instrument, measuring instrument, scientific instrument, draftsman, technical drawing, navigation, engineering, blacksmith, cooper, plumber -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - File, Early 20th century
This file would be used by a tradesperson or home handyman to smooth the edges of the wooden piece he or she was working on. The surfaces of the file would be of different abrasiveness to suit different stages of the job. A file would be part of a woodworker's tool kit.This design of this file has been used since at least the early 20th century and can be found in stores today.File; small metal three-sided file with wooden handle.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, file, three-sided file, carpentry, woodwork, guilding, tradesman -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Marking Gauge
This marking gauge has a round head. It is a hand-powered tool and is used to measure and mark a scribed line onto the surface of the wood for the purpose of cutting or aligning. It would have been used by a tradesperson such as a cabinet maker, wood worker or carpenter. The hand tool shows signs of much use. It appears to be appreciated as a tool due to the initials carved into the side of the block. The marking gauge is an example of a hand powered woodworking tool used over the past few centuriesMarking gauge: wooden staff with half-round block secured by a wedge. there is a metal marker on one end. Inscription "WS" crudely engraved in end of block.Carved "W.S."flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, shipwreck coast, hand tool, woodwork, marking gauge, w.s., measuring tool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Box plane, Stewart Spiers, mid-1900s
This small metal plane was manufactured in 1909 by Spiers-Stewart, Ayr, Ayrshire, Scotland. Stewart Spiers began making planes in Ayr in around 1840. The business continued successfully as a small operation until the mid-1930s.This plane is an example of tools made overseas and used in the 1900's. Box plane; hand operated small metal plane with round wooden knob. Plane has separate blade and blade cap. Inscription on blade cap is indecipherable. Originally marked as made by Spiers."SPIERS"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime-museum, maritime village, shipwreck coast, tradesman's tool, plane, box plane, tool, spiers-stewart, early 20th century, scotland, hand tool, stewart spiers, spiers, woodworking
