Showing 1743 items matching "concrete"
-
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyImage, c1990
This photograph is a general view of the machinery of the Gold Battery. The Bergin Pan is on the left, Stamper Box and in foreground concrete bed for Wilfrey table which has been removed. This is one of a series of photographs of the Rutherglen Gold Battery. The battery's purpose was to crush quartz from nearby quartz reefs and extract gold from within. The battery was erected in 1908 and consists of a five-head battery, Wilfrey table, Bergin pan, portable steam engine and shed. The battery was restored in 2011/12 and can be viewed daily between 9.00am and 5.00pm. See website for details.Colour photograph of a number of large pieces of machinery inside a buildinggold battery, gold processing -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, International Correspondence Schools Ltd, I.C.S. Reference LibraryL Specifications, 1907
Purple hard cover book with leather spineengineering, rex jolioake, r.c. smith, concrete, titles, drans, bricks, tiler, plumber, gas fitter, plasterer, glazer, painter, paper hanger -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, McGraw-Hill Book Company, Civil Engineering Handbook, 1940
Dark Green book of 877 pages,non-fictionengineering, rex hollioake, surveying, railway, highway, mechanics, hydraulics, framed structures, steel design, concrete, foundations, sewerage, water supply, purification -
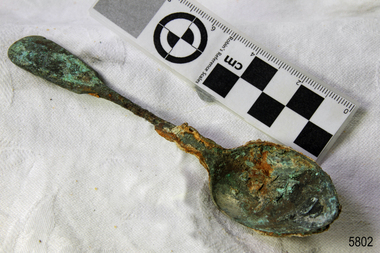 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Spoon, c. 1878
This tea spoon is from the wreck of the LOCH ARD, a Loch Line ship of 1,693 tons which sailed from Gravesend, London, on 2 March 1878 with 17 passengers and a crew of 36 under Captain George Gibbs. “The intention was to discharge cargo in Melbourne, before returning to London via the Horn with wool and wheat”. Instead, on 1 June 1878, after 90 days at sea, she struck the sandstone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on the south west coast of Victoria, and sank with the loss of 52 lives and all her cargo. The manifest of the LOCH ARD listed an array of manufactured goods and bulk metals being exported to the Colony of Victoria, with a declared value of £53,700. (202 bills of lading show an actual invoice value of £68, 456, with insurance underwriting to £30,000 of all cargo). Included in the manifest is the item of “Tin hardware & cutlery £7,530”. This teaspoon is one of 482 similar items of electro-plated cutlery from the LOCH ARD site, comprising spoons and forks of various sizes but all sharing the same general shape or design and metallic composition. 49 of these pieces display a legible makers’ mark — the initials “W” and “P” placed within a raised diamond outline, which is in turn contained within a sunken crown shape — identifying the manufacturer as William Page & Co of Birmingham. An electroplater’s makers’ marks, unlike sterling silver hallmarks, are not consistent identifiers of quality or date and place of manufacture. A similar line of five impressions was usually made to impress the consumer with an implication of industry standards, but what each one actually signified was not regulated and so they varied according to the whim of the individual foundry. In this case, the maker’s marks are often obscured by sedimentary accretion or removed by corrosion after a century of submersion in the ocean. However sufficient detail has survived to indicate that these samples of electro-plated cutlery probably originated from the same consignment in the LOCH ARD’s cargo. The following descriptions of maker’s marks are drawn from 255 tea spoons, 125 dessert spoons, and 99 table forks. These marks are clearly visible in 66 instances, while the same sequence of general outlines, or depression shapes, is discernible in another 166 examples. 1. A recessed Crown containing a raised Diamond outline and the initials “W” and “P” (the recognised trademark of William Page & Co) 2. An impressed Ellipse containing a raised, pivoted, Triangle in its lower part and bearing a Resurrection Cross on its upper section (a possible dissenting church symbol reflecting religious affiliation); OR a rounded Square impression containing a raised, ‘lazy’, letter “B” (possibly mimicking sterling silver hallmark signifying city of manufacture i.e. Birmingham) 3. An impressed rounded Square filled with a raised Maltese Cross (the base metal composite of nickel silver was also known as ‘German silver’ after its Berlin inventors in 1823) 4. A recessed Circle containing a Crab or Scarab Beetle image; OR a recessed Circle containing a rotated ‘fleur de lys’ or ‘fasces’ design 5. A depressed Diamond shape enclosing a large raised letter “R” and a small raised letter “D” (mimicking the U.K. Patent Office stamp which abbreviated the term ‘registered’ to “RD”, but also included date and class of patent) Suggested trade names for William Page & Co’s particular blend of brass plating are ‘roman silver’ or ‘silverite’. This copper alloy polishes to a lustrous gold when new, discolouring to a murky grey with greenish hue when neglected. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only seven in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance – Victorian Heritage Register S 417. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Unrestored tea spoon from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The spoon design has a flattened fiddle-back handle, with a thin stem or shank, flared collar, and elongated bowl. The spoons metallic composition is a thin layer of brass alloy which has partially corroded back to a nickel-silver base metal. Red stained limestone concretion covering 40% of spoon surface area. Some verdigris. Stem is bent and thinned by corrosion. Outline of four makers marks are visible but detail is obscured.flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, loch ard gorge, electroplated cutlery, loch ard, nickel silver, william page and company, birmingham brass plating, makers marks, tea spoons -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Spoon, circa 1878
This tea spoon is from the wreck of the LOCH ARD, a Loch Line ship of 1,693 tons which sailed from Gravesend, London, on 2 March 1878 with 17 passengers and a crew of 36 under Captain George Gibbs. “The intention was to discharge cargo in Melbourne, before returning to London via the Horn with wool and wheat”. Instead, on 1 June 1878, after 90 days at sea, she struck the sandstone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on the south west coast of Victoria, and sank with the loss of 52 lives and all her cargo. The manifest of the LOCH ARD listed an array of manufactured goods and bulk metals being exported to the Colony of Victoria, with a declared value of £53,700. (202 bills of lading show an actual invoice value of £68, 456, with insurance underwriting to £30,000 of all cargo). Included in the manifest is the item of “Tin hardware & cutlery £7,530”. This teaspoon is one of 482 similar items of electro-plated cutlery from the LOCH ARD site, comprising spoons and forks of various sizes but all sharing the same general shape or design and metallic composition. 49 of these pieces display a legible makers’ mark — the initials “W” and “P” placed within a raised diamond outline, which is in turn contained within a sunken crown shape — identifying the manufacturer as William Page & Co of Birmingham. An electroplater’s makers’ marks, unlike sterling silver hallmarks, are not consistent identifiers of quality or date and place of manufacture. A similar line of five impressions was usually made to impress the consumer with an implication of industry standards, but what each one actually signified was not regulated and so they varied according to the whim of the individual foundry. In this case, the maker’s marks are often obscured by sedimentary accretion or removed by corrosion after a century of submersion in the ocean. However sufficient detail has survived to indicate that these samples of electro-plated cutlery probably originated from the same consignment in the LOCH ARD’s cargo. The following descriptions of maker’s marks are drawn from 255 tea spoons, 125 dessert spoons, and 99 table forks. These marks are clearly visible in 66 instances, while the same sequence of general outlines, or depression shapes, is discernible in another 166 examples. 1. A recessed Crown containing a raised Diamond outline and the initials “W” and “P” (the recognised trademark of William Page & Co) 2. An impressed Ellipse containing a raised, pivoted, Triangle in its lower part and bearing a Resurrection Cross on its upper section (a possible dissenting church symbol reflecting religious affiliation); OR a rounded Square impression containing a raised, ‘lazy’, letter “B” (possibly mimicking sterling silver hallmark signifying city of manufacture i.e. Birmingham) 3. An impressed rounded Square filled with a raised Maltese Cross (the base metal composite of nickel silver was also known as ‘German silver’ after its Berlin inventors in 1823) 4. A recessed Circle containing a Crab or Scarab Beetle image; OR a recessed Circle containing a rotated ‘fleur de lys’ or ‘fasces’ design 5. A depressed Diamond shape enclosing a large raised letter “R” and a small raised letter “D” (mimicking the U.K. Patent Office stamp which abbreviated the term ‘registered’ to “RD”, but also included date and class of patent) Suggested trade names for William Page & Co’s particular blend of brass plating are ‘roman silver’ or ‘silverite’. This copper alloy polishes to a lustrous gold when new, discolouring to a murky grey with greenish hue when neglected. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only seven in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance – Victorian Heritage Register S 417. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Unrestored tea spoon from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The spoon design has a flattened fiddle-back handle, with a thin stem or shank, flared collar, and elongated bowl. The spoons metallic composition is a thin layer of brass alloy which has partially corroded back to a nickel-silver base metal. Interior of bowl bears red-rust stained sedimentary concretion. Corrosion has perforated edges of bowl near neck, top of handle, and thinned stem. Some verdigris. flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, electroplated cutlery, loch ard shipwreck, nickel silver, william page & co, makers marks, william page & co -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Spoon, circa 1878
This table spoon is from the wreck of the LOCH ARD, a Loch Line ship of 1,693 tons which sailed from Gravesend, London, on 2 March 1878 with 17 passengers and a crew of 36 under Captain George Gibbs. “The intention was to discharge cargo in Melbourne, before returning to London via the Horn with wool and wheat”. Instead, on 1 June 1878, after 90 days at sea, she struck the sandstone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on the south west coast of Victoria, and sank with the loss of 52 lives and all her cargo. The manifest of the LOCH ARD listed an array of manufactured goods and bulk metals being exported to the Colony of Victoria, with a declared value of £53,700. (202 bills of lading show an actual invoice value of £68, 456, with insurance underwriting to £30,000 of all cargo). Included in the manifest is the item of “Tin hardware & cutlery £7,530”. This table spoon is one of 482 similar items of electro-plated cutlery from the LOCH ARD site, comprising spoons and forks of various sizes but all sharing the same general shape or design and metallic composition. 49 of these pieces display a legible makers’ mark — the initials “W” and “P” placed within a raised diamond outline, which is in turn contained within a sunken crown shape — identifying the manufacturer as William Page & Co of Birmingham. An electroplater’s makers’ marks, unlike sterling silver hallmarks, are not consistent identifiers of quality or date and place of manufacture. A similar line of five impressions was usually made to impress the consumer with an implication of industry standards, but what each one actually signified was not regulated and so they varied according to the whim of the individual foundry. In this case, the maker’s marks are often obscured by sedimentary accretion or removed by corrosion after a century of submersion in the ocean. However sufficient detail has survived to indicate that these samples of electro-plated cutlery probably originated from the same consignment in the LOCH ARD’s cargo. The generally common range of marks are drawn from 255 tea spoons, 125 dessert spoons, and 99 table forks. These marks are clearly visible in 66 instances, while the same sequence of general outlines, or depression shapes, is discernible in another 166 examples. Suggested trade names for William Page & Co’s particular blend of brass plating are ‘roman silver’ or ‘silverite’. This copper alloy polishes to a lustrous gold when new, discolouring to a murky grey with greenish hue when neglected. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only seven in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's shipwreck The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance – Victorian Heritage Register S 417 Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Unrestored table spoon from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The spoon design has a flattened fiddle-back handle, with a thin stem or shank, flared collar, and a shallow rounded bowl. The spoons metallic composition is a thin layer of brass alloy which has partially corroded back to a nickel-silver base metal. Some verdigris and red-stained concretion on front and back of spoon. Only 5% of original plate remains, with balance covered in dark green silver-oxide.flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, electroplated cutlery, loch ard shipwreck, william page and co, birmingham brass plating, table spoons -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Spoon, circa 1878
This table spoon is from the wreck of the LOCH ARD, a Loch Line ship of 1,693 tons which sailed from Gravesend, London, on 2 March 1878 with 17 passengers and a crew of 36 under Captain George Gibbs. “The intention was to discharge cargo in Melbourne, before returning to London via the Horn with wool and wheat”. Instead, on 1 June 1878, after 90 days at sea, she struck the sandstone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on the south west coast of Victoria, and sank with the loss of 52 lives and all her cargo. The manifest of the LOCH ARD listed an array of manufactured goods and bulk metals being exported to the Colony of Victoria, with a declared value of £53,700. (202 bills of lading show an actual invoice value of £68, 456, with insurance underwriting to £30,000 of all cargo). Included in the manifest is the item of “Tin hardware & cutlery £7,530”. This table spoon is one of 482 similar items of electro-plated cutlery from the LOCH ARD site, comprising spoons and forks of various sizes but all sharing the same general shape or design and metallic composition. 49 of these pieces display a legible makers’ mark — the initials “W” and “P” placed within a raised diamond outline, which is in turn contained within a sunken crown shape — identifying the manufacturer as William Page & Co of Birmingham. An electroplater’s makers’ marks, unlike sterling silver hallmarks, are not consistent identifiers of quality or date and place of manufacture. A similar line of five impressions was usually made to impress the consumer with an implication of industry standards, but what each one actually signified was not regulated and so they varied according to the whim of the individual foundry. In this case, the maker’s marks are often obscured by sedimentary accretion or removed by corrosion after a century of submersion in the ocean. However sufficient detail has survived to indicate that these samples of electro-plated cutlery probably originated from the same consignment in the LOCH ARD’s cargo. The generally common range of marks are drawn from 255 tea spoons, 125 dessert spoons, and 99 table forks. These marks are clearly visible in 66 instances, while the same sequence of general outlines, or depression shapes, is discernible in another 166 examples. Suggested trade names for William Page & Co’s particular blend of brass plating are ‘roman silver’ or ‘silverite’. This copper alloy polishes to a lustrous gold when new, discolouring to a murky grey with greenish hue when neglected. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only seven in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register most valuable. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only seven in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register most valuable. The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance – Victorian Heritage Register S 417. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Unrestored table spoon from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The spoon design has a flattened fiddle-back handle, with a thin stem or shank, flared collar, and a shallow rounded bowl. The spoons metallic composition is a thin layer of brass alloy which has partially corroded back to a nickel-silver base metal. Minimal original plate remains. Some verdigris (15%) and concretion (40%) on front and back of spoon. Spoon is bent and balance is covered in Silver Oxide.flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, electroplated cutlery, loch ard shipwreck, william page and co, birmingham brass plating, table spoons -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Spoon, circa 1878
This table spoon is from the wreck of the LOCH ARD, a Loch Line ship of 1,693 tons which sailed from Gravesend, London, on 2 March 1878 with 17 passengers and a crew of 36 under Captain George Gibbs. “The intention was to discharge cargo in Melbourne, before returning to London via the Horn with wool and wheat”. Instead, on 1 June 1878, after 90 days at sea, she struck the sandstone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on the south west coast of Victoria, and sank with the loss of 52 lives and all her cargo. The manifest of the LOCH ARD listed an array of manufactured goods and bulk metals being exported to the Colony of Victoria, with a declared value of £53,700. (202 bills of lading show an actual invoice value of £68, 456, with insurance underwriting to £30,000 of all cargo). Included in the manifest is the item of “Tin hardware & cutlery £7,530”. This table spoon is one of 482 similar items of electro-plated cutlery from the LOCH ARD site, comprising spoons and forks of various sizes but all sharing the same general shape or design and metallic composition. 49 of these pieces display a legible makers’ mark — the initials “W” and “P” placed within a raised diamond outline, which is in turn contained within a sunken crown shape — identifying the manufacturer as William Page & Co of Birmingham. An electroplater’s makers’ marks, unlike sterling silver hallmarks, are not consistent identifiers of quality or date and place of manufacture. A similar line of five impressions was usually made to impress the consumer with an implication of industry standards, but what each one actually signified was not regulated and so they varied according to the whim of the individual foundry. In this case, the maker’s marks are often obscured by sedimentary accretion or removed by corrosion after a century of submersion in the ocean. However sufficient detail has survived to indicate that these samples of electro-plated cutlery probably originated from the same consignment in the LOCH ARD’s cargo. The generally common range of marks are drawn from 255 tea spoons, 125 dessert spoons, and 99 table forks. These marks are clearly visible in 66 instances, while the same sequence of general outlines, or depression shapes, is discernible in another 166 examples. Suggested trade names for William Page & Co’s particular blend of brass plating are ‘roman silver’ or ‘silverite’. This copper alloy polishes to a lustrous gold when new, discolouring to a murky grey with greenish hue when neglected. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only seven in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register most valuable. The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance – Victorian Heritage Register S 417. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Unrestored table spoon from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The spoon design has a flattened fiddle-back handle, with a thin stem or shank, flared collar, and a shallow rounded bowl. The spoons metallic composition is a thin layer of brass alloy which has partially corroded back to a nickel-silver base metal. Approximately 10% of original plate remains. Some verdigris (5%) and a large amount of sedimentary concretion (60%) is on front and back of spoon. Balance is covered in dark green oxidisation.flagstaff hill maritime museum, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, electroplated cutlery, loch ard shipwreck, william page and co, birmingham brass plating, table spoons -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSpoon, circa 1878
This medium-sized dessert spoon is from the wreck of the LOCH ARD, a Loch Line ship of 1,693 tons which sailed from Gravesend, London, on 2 March 1878 with 17 passengers and a crew of 36 under Captain George Gibbs. “The intention was to discharge cargo in Melbourne, before returning to London via the Horn with wool and wheat”. Instead, on 1 June 1878, after 90 days at sea, she struck the sandstone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on the south west coast of Victoria, and sank with the loss of 52 lives and all her cargo. The manifest of the LOCH ARD listed an array of manufactured goods and bulk metals being exported to the Colony of Victoria, with a declared value of £53,700. (202 bills of lading show an actual invoice value of £68, 456, with insurance underwriting to £30,000 of all cargo). Included in the manifest is the item of “Tin hardware & cutlery £7,530”. This dessert spoon is one of 482 similar items of electro-plated cutlery from the LOCH ARD site, comprising spoons and forks of various sizes but all sharing the same general shape or design and metallic composition. 49 of these pieces display a legible makers’ mark — the initials “W” and “P” placed within a raised diamond outline, which is in turn contained within a sunken crown shape — identifying the manufacturer as William Page & Co of Birmingham. An electroplater’s makers’ marks, unlike sterling silver hallmarks, are not consistent identifiers of quality or date and place of manufacture. A similar line of five impressions was usually made to impress the consumer with an implication of industry standards, but what each one actually signified was not regulated and so they varied according to the whim of the individual foundry. In this case, the maker’s marks are often obscured by sedimentary accretion or removed by corrosion after a century of submersion in the ocean. However sufficient detail has survived to indicate that these samples of electro-plated cutlery probably originated from the same consignment in the LOCH ARD’s cargo. The generally common range of marks are drawn from 255 tea spoons, 125 dessert spoons, and 99 table forks. These marks are clearly visible in 66 instances, while the same sequence of general outlines, or depression shapes, is discernible in another 166 examples. Suggested trade names for William Page & Co’s particular blend of brass plating are ‘roman silver’ or ‘silverite’. This copper alloy polishes to a lustrous gold when new, discolouring to a murky grey with greenish hue when neglected. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only seven in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register most valuable. The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance – Victorian Heritage Register S 417. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Unrestored dessert spoon from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The spoon design has a flattened fiddle-back handle, with a thin stem or shank, flared collar, and a shallow rounded bowl. The spoons metallic composition is a thin layer of brass alloy which has partially corroded back to a nickel-silver base metal. Some 5% verdigris and 15% reddish stained concretion, with balance of spoon showing blackened nickel silver base metal. There is a plain heraldic shield embossed on rear of collar.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, electroplated cutlery, loch ard shipwreck, william page and co, birmingham brass plating, dessert spoons -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Spoon, circa 1878
This medium-sized dessert spoon is from the wreck of the LOCH ARD, a Loch Line ship of 1,693 tons which sailed from Gravesend, London, on 2 March 1878 with 17 passengers and a crew of 36 under Captain George Gibbs. “The intention was to discharge cargo in Melbourne, before returning to London via the Horn with wool and wheat”. Instead, on 1 June 1878, after 90 days at sea, she struck the sandstone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on the south west coast of Victoria, and sank with the loss of 52 lives and all her cargo. The manifest of the LOCH ARD listed an array of manufactured goods and bulk metals being exported to the Colony of Victoria, with a declared value of £53,700. (202 bills of lading show an actual invoice value of £68, 456, with insurance underwriting to £30,000 of all cargo). Included in the manifest is the item of “Tin hardware & cutlery £7,530”. This dessert spoon is one of 482 similar items of electro-plated cutlery from the LOCH ARD site, comprising spoons and forks of various sizes but all sharing the same general shape or design and metallic composition. 49 of these pieces display a legible makers’ mark — the initials “W” and “P” placed within a raised diamond outline, which is in turn contained within a sunken crown shape — identifying the manufacturer as William Page & Co of Birmingham. An electroplater’s makers’ marks, unlike sterling silver hallmarks, are not consistent identifiers of quality or date and place of manufacture. A similar line of five impressions was usually made to impress the consumer with an implication of industry standards, but what each one actually signified was not regulated and so they varied according to the whim of the individual foundry. In this case, the maker’s marks are often obscured by sedimentary accretion or removed by corrosion after a century of submersion in the ocean. However sufficient detail has survived to indicate that these samples of electro-plated cutlery probably originated from the same consignment in the LOCH ARD’s cargo. The generally common range of marks are drawn from 255 tea spoons, 125 dessert spoons, and 99 table forks. These marks are clearly visible in 66 instances, while the same sequence of general outlines, or depression shapes, is discernible in another 166 examples. Suggested trade names for William Page & Co’s particular blend of brass plating are ‘roman silver’ or ‘silverite’. This copper alloy polishes to a lustrous gold when new, discolouring to a murky grey with greenish hue when neglected. The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance – Victorian Heritage Register S 417.Unrestored dessert spoon from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The spoon design has a flattened fiddle-back handle, with a thin stem or shank, flared collar, and a shallow rounded bowl. The spoons metallic composition is a thin layer of brass alloy which has partially corroded back to a nickel-silver base metal. 50% original plate, 20% concretion, and 15% verdigris. There is a plain heraldic shield embossed on upper rear of spoon bowl (ratstail). Spoon is slightly bent.flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, electroplated cutlery, loch ard shipwreck, william page and co, birmingham brass plating, dessert spoons -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSpoon, circa 1878
This medium-sized dessert spoon is from the wreck of the LOCH ARD, a Loch Line ship of 1,693 tons which sailed from Gravesend, London, on 2 March 1878 with 17 passengers and a crew of 36 under Captain George Gibbs. “The intention was to discharge cargo in Melbourne, before returning to London via the Horn with wool and wheat”. Instead, on 1 June 1878, after 90 days at sea, she struck the sandstone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on the south west coast of Victoria, and sank with the loss of 52 lives and all her cargo. The manifest of the LOCH ARD listed an array of manufactured goods and bulk metals being exported to the Colony of Victoria, with a declared value of £53,700. (202 bills of lading show an actual invoice value of £68, 456, with insurance underwriting to £30,000 of all cargo). Included in the manifest is the item of “Tin hardware & cutlery £7,530”. This dessert spoon is one of 482 similar items of electro-plated cutlery from the LOCH ARD site, comprising spoons and forks of various sizes but all sharing the same general shape or design and metallic composition. 49 of these pieces display a legible makers’ mark — the initials “W” and “P” placed within a raised diamond outline, which is in turn contained within a sunken crown shape — identifying the manufacturer as William Page & Co of Birmingham. An electroplater’s makers’ marks, unlike sterling silver hallmarks, are not consistent identifiers of quality or date and place of manufacture. A similar line of five impressions was usually made to impress the consumer with an implication of industry standards, but what each one actually signified was not regulated and so they varied according to the whim of the individual foundry. In this case, the maker’s marks are often obscured by sedimentary accretion or removed by corrosion after a century of submersion in the ocean. However sufficient detail has survived to indicate that these samples of electro-plated cutlery probably originated from the same consignment in the LOCH ARD’s cargo. The generally common range of marks are drawn from 255 tea spoons, 125 dessert spoons, and 99 table forks. These marks are clearly visible in 66 instances, while the same sequence of general outlines, or depression shapes, is discernible in another 166 examples. Suggested trade names for William Page & Co’s particular blend of brass plating are ‘roman silver’ or ‘silverite’. This copper alloy polishes to a lustrous gold when new, discolouring to a murky grey with greenish hue when neglected. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only seven in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register most valuable. The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance – Victorian Heritage Register S 417. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Unrestored dessert spoon from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The spoon design has a flattened fiddle-back handle, with a thin stem or shank, flared collar, and a shallow rounded bowl. The spoons metallic composition is a thin layer of brass alloy which has partially corroded back to a nickel-silver base metal. Only 10% of original plate is visible, along with 10% verdigris and 60% concretion (lumps on spoon bowl). Outlines of four makers marks are evident but details are not discernible.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, electroplated cutlery, loch ard shipwreck, william page and co, birmingham brass plating, dessert spoons -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyPhotograph, Beauville Avenue, 34, Murrumbeena, 2001
Originally labelled "Beauville Estate, Established 1936, Still Thriving 65 years on, 10th March 2001", the Beauville Estate Album contains colour photographs of houses in the Estate. They were taken around the time of the Beauville Estate’s 65th Heritage Celebration held on 10/03/2001 and donated to the Caulfield Historical Society shortly afterwards. Photographer unknown.City of Glen Eira’s Heritage Management Plan Vol 2 p79 (this is p84 of the pdf version) – HO12 Beauville Estate and environs, Murrumbeena: The Beauville Historic Area is important at the State level as the first large housing estate undertaken by the AV Jennings Construction Co, later Jennings Group Limited, Victoria’s largest home builder. It is important also as a very early estate development incorporating a range of features other than houses and including made roads, shops and recreation facilities. In this respect it was the forerunner of the comprehensively planned housing estate of the post war era. The estate is distinguished by its aesthetic values, as is the earlier and comparable Hillcrest Estate, which are formed by a combination of restrained diversity in house styles, with the exception of no. 30 in the emerging International style, and by a landscaped garden environment. Colour photograph of white rendered, corner house with unpainted variegated brown brick features. Other features include a wide arched porch, tiled roof, tall brick chimney, cast iron work black porch door, window awnings and low unpainted matching brick fence in the foreground with "34" on the white metal letterbox on top of the right brick pillar beside the concrete pathway leading to the porch. Well-established garden including 2 matching pencil pines.murrumbeena, houses, beauville avenue, architectural styles, 1930's, inter war style, a.v. jennings, av jennings, jennings, brick houses, beauville estate, porches, sir albert victor jennings, a v jennings construction co, beauville estate heritage area, glen eira city council, architectural features, jennings group limited, land subdivision, gardens, beauville historic area, rendered houses, corner houses, brick features, awnings, brick fences, metal letterboxes, trees, cast iron work door -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - DEEBLE'S PYRITES WORKS, approx. 1950's
black and white photo - enlargement - of Deeble's Pyrites Works. Concrete vats near foregound and middle distance, elevatged building in background,. Two male adults at left middle distance. Carboys ( acid ) planks, tall weatherboard building and brick decorated chimney towards RH side of image. On back in grey lead 'Deebles Pyrites Works/1889. James Lerks identified this as being Spargo's Pyrites - the picture appears in 'Bendigo's Gold Story' by Ralph W Birrell and James A Lerk.cottage, miners -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - DEEBLE'S PYRITES TREATMENT PLANT: BENDIGO, approx. 1950's
black and white photo - Deebles Pyrites Works, concrete vats in near and middle ground. Elevated building in back ground, two male adults at left in middle distance. Carboys siphoning, planks,, tall weatherboard building, brick decorated chimney towards right hand side of image. On back in grey lead ' Deeble's Pyrites Works, approx. 1889' James Lerk identified this as being Spargo's Pyrites - the picure appears in 'Bendigo's Gold Story' by Ralph W Birrell and James A Lerk.cottage, miners -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - STATE RIVERS AND WATER SUPPLY COMMISSION VICTORIA : CENTRAL PLANT WORKSHOPS
State Rivers and Water Supply Commission of Victoria. Brochure titled 'Central Plant Workshops'. Double-sided, three pages on each. Information about the workshops (CPW for short) and the setting up of the Bendigo site from 1946. There is a map of the layout of the site, and information given under the following headings - Central Plant Workshops, Work of the CPW, Meter Wheels, Pump Station Equipment, Steel Fabrication, Precast Concrete, and the Area and its Equipment. The brochure is dated June, 1968.state infrastructure, water supply, coliban system, state rivers and water supply commission of victoria. coliban system. central plant workshops. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - Historical Society Field Trip to the Springs at Sedgwick, Abt 2009
The Phil Wilkin Collection contains a series of 11 Items. The related items can be found by clicking on the reference link below. The following history of the Young family and their descendants who lived at the Springs is provided by Phil Wilkin. His Great Grandparents were Frances Young and August Wirth. Phil has also provided notes on the Wilkin Family and some history of the gold mining in Sedgwick. Frances Young's parents Joseph and Margaret Young owned the property called "The Old Place, Preston Vale or Wellington Flat" at Sedgwick near the Springs. Joseph Young owned and Managed the Standard Brewery which was located at Campbells Creek during the late 1800’s early 1900’s. Joseph and Margaret are buried in the Harcourt cemetery. In 1880 August Wirth lived at Mosquito Creek (Lake Eppalock, Victoria) when he married Frances Young. In 1902 they moved to part of Joseph Young's property. They milked cows and sold cattle for a living. One of their children Charles Wirth (Phil Wilkin's Grandfather) bought the land in 1935 after his parents had died. Charles Wirth was a councillor and also was president of the Shire of Strathfieldsaye. The "Old Place" was part of the property owned by members of the family. The old house at the Springs was burnt out by bushfire in January 1944 and much of the stonework was later vandalized by campers. The original Coliban Water Works were designed in 1863 by the Irish engineer Joseph Brady. The system included 70 kilometres of open water channels, aqueducts, syphons and tunnels to carry water (by gravity) from the Coliban River at Malmsbury, north to Castlemaine and Bendigo. Sedgwick is a locality in Central Victoria, Australia. It is located in the City of Greater Bendigo. Facilities include a public hall that opened in 1958 and CFA Rural fire station. It was named Upper Emu Creek until 1901 when it was renamed as Sedgwick after British geologist Adam Sedgwick.Twenty nine photos taken on a field trip by the Bendigo Historical Society to "The Springs" on the main Coliban water channel from Malmsbury to the Sandhurst Reservoir in Bendigo. The water race descends through a concrete chute, and continues sharply around the contour of the hills. Once it descended into a syphon across the gully. The are 182 photos in this series and can be found at 8683.1 to 8683.11. The series also includes photos of the surrounding farming land and the remains of an old house. There are also some notes on the pioneers of the district.history, bendigo, coliban water, joseph brady, irrigation, the springs, sedgwick -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - Historical Society Field Trip to the Springs at Sedgwick, Abt 2009
The Phil Wilkin Collection contains a series of 11 Items. The related items can be found by clicking on the reference link below. The following history of the Young family and their descendants who lived at the Springs is provided by Phil Wilkin. His Great Grandparents were Frances Young and August Wirth. Phil has also provided notes on the Wilkin Family and some history of the gold mining in Sedgwick. Frances Young's parents Joseph and Margaret Young owned the property called "The Old Place, Preston Vale or Wellington Flat" at Sedgwick near the Springs. Joseph Young owned and Managed the Standard Brewery which was located at Campbells Creek during the late 1800’s early 1900’s. Joseph and Margaret are buried in the Harcourt cemetery. In 1880 August Wirth lived at Mosquito Creek (Lake Eppalock, Victoria) when he married Frances Young. In 1902 they moved to part of Joseph Young's property. They milked cows and sold cattle for a living. One of their children Charles Wirth (Phil Wilkin's Grandfather) bought the land in 1935 after his parents had died. Charles Wirth was a councillor and also was president of the Shire of Strathfieldsaye. The "Old Place" was part of the property owned by members of the family. The old house at the Springs was burnt out by bushfire in January 1944 and much of the stonework was later vandalized by campers. The original Coliban Water Works were designed in 1863 by the Irish engineer Joseph Brady. The system included 70 kilometres of open water channels, aqueducts, syphons and tunnels to carry water (by gravity) from the Coliban River at Malmsbury, north to Castlemaine and Bendigo. Sedgwick is a locality in Central Victoria, Australia. It is located in the City of Greater Bendigo. Facilities include a public hall that opened in 1958 and CFA Rural fire station. It was named Upper Emu Creek until 1901 when it was renamed as Sedgwick after British geologist Adam Sedgwick.Twenty five photos taken on a field trip by the Bendigo Historical Society to "The Springs" on the main Coliban water channel from Malmsbury to the Sandhurst Reservoir in Bendigo. The water race descends through a concrete chute, and continues sharply around the contour of the hills. Once it descended into a syphon across the gully. The are 182 photos in this series and can be found at 8683.1 to 8683.11. The series also includes photos of the surrounding farming land and the remains of an old house. There are also some notes on the pioneers of the district.history, bendigo, coliban water, joseph brady, irrigation, the springs, sedgwick -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - Historical Society Field Trip to the Springs at Sedgwick, Abt 2009
The Phil Wilkin Collection contains a series of 11 Items. The related items can be found by clicking on the reference link below. The following history of the Young family and their descendants who lived at the Springs is provided by Phil Wilkin. His Great Grandparents were Frances Young and August Wirth. Phil has also provided notes on the Wilkin Family and some history of the gold mining in Sedgwick. Frances Young's parents Joseph and Margaret Young owned the property called "The Old Place, Preston Vale or Wellington Flat" at Sedgwick near the Springs. Joseph Young owned and Managed the Standard Brewery which was located at Campbells Creek during the late 1800’s early 1900’s. Joseph and Margaret are buried in the Harcourt cemetery. In 1880 August Wirth lived at Mosquito Creek (Lake Eppalock, Victoria) when he married Frances Young. In 1902 they moved to part of Joseph Young's property. They milked cows and sold cattle for a living. One of their children Charles Wirth (Phil Wilkin's Grandfather) bought the land in 1935 after his parents had died. Charles Wirth was a councillor and also was president of the Shire of Strathfieldsaye. The "Old Place" was part of the property owned by members of the family. The old house at the Springs was burnt out by bushfire in January 1944 and much of the stonework was later vandalized by campers. The original Coliban Water Works were designed in 1863 by the Irish engineer Joseph Brady. The system included 70 kilometres of open water channels, aqueducts, syphons and tunnels to carry water (by gravity) from the Coliban River at Malmsbury, north to Castlemaine and Bendigo. Sedgwick is a locality in Central Victoria, Australia. It is located in the City of Greater Bendigo. Facilities include a public hall that opened in 1958 and CFA Rural fire station. It was named Upper Emu Creek until 1901 when it was renamed as Sedgwick after British geologist Adam Sedgwick.Twenty six photos taken on a field trip by the Bendigo Historical Society to "The Springs" on the main Coliban water channel from Malmsbury to the Sandhurst Reservoir in Bendigo. The water race descends through a concrete chute, and continues sharply around the contour of the hills. Once it descended into a syphon across the gully. The are 182 photos in this series and can be found at 8683.1 to 8683.11. The series also includes photos of the surrounding farming land and the remains of an old house. There are also some notes on the pioneers of the district.history, bendigo, coliban water, joseph brady, irrigation, the springs, sedgwick -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - Historical Society Field Trip to the Springs at Sedgwick, Abt 2009
The Phil Wilkin Collection contains a series of 11 Items. The related items can be found by clicking on the reference link below. The following history of the Young family and their descendants who lived at the Springs is provided by Phil Wilkin. His Great Grandparents were Frances Young and August Wirth. Phil has also provided notes on the Wilkin Family and some history of the gold mining in Sedgwick. Frances Young's parents Joseph and Margaret Young owned the property called "The Old Place, Preston Vale or Wellington Flat" at Sedgwick near the Springs. Joseph Young owned and Managed the Standard Brewery which was located at Campbells Creek during the late 1800’s early 1900’s. Joseph and Margaret are buried in the Harcourt cemetery. In 1880 August Wirth lived at Mosquito Creek (Lake Eppalock, Victoria) when he married Frances Young. In 1902 they moved to part of Joseph Young's property. They milked cows and sold cattle for a living. One of their children Charles Wirth (Phil Wilkin's Grandfather) bought the land in 1935 after his parents had died. Charles Wirth was a councillor and also was president of the Shire of Strathfieldsaye. The "Old Place" was part of the property owned by members of the family. The old house at the Springs was burnt out by bushfire in January 1944 and much of the stonework was later vandalized by campers. The original Coliban Water Works were designed in 1863 by the Irish engineer Joseph Brady. The system included 70 kilometres of open water channels, aqueducts, syphons and tunnels to carry water (by gravity) from the Coliban River at Malmsbury, north to Castlemaine and Bendigo. Sedgwick is a locality in Central Victoria, Australia. It is located in the City of Greater Bendigo. Facilities include a public hall that opened in 1958 and CFA Rural fire station. It was named Upper Emu Creek until 1901 when it was renamed as Sedgwick after British geologist Adam Sedgwick.Twenty six photos taken on a field trip by the Bendigo Historical Society to "The Springs" on the main Coliban water channel from Malmsbury to the Sandhurst Reservoir in Bendigo. The water race descends through a concrete chute, and continues sharply around the contour of the hills. Once it descended into a syphon across the gully. The are 182 photos in this series and can be found at 8683.1 to 8683.11. The series also includes photos of the surrounding farming land and the remains of an old house. There are also some notes on the pioneers of the district.history, bendigo, coliban water, joseph brady, irrigation, the springs, sedgwick -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - Historical Society Field Trip to the Springs at Sedgwick, Abt 2009
The Phil Wilkin Collection contains a series of 11 Items. The related items can be found by clicking on the reference link below. The following history of the Young family and their descendants who lived at the Springs is provided by Phil Wilkin. His Great Grandparents were Frances Young and August Wirth. Phil has also provided notes on the Wilkin Family and some history of the gold mining in Sedgwick. Frances Young's parents Joseph and Margaret Young owned the property called "The Old Place, Preston Vale or Wellington Flat" at Sedgwick near the Springs. Joseph Young owned and Managed the Standard Brewery which was located at Campbells Creek during the late 1800’s early 1900’s. Joseph and Margaret are buried in the Harcourt cemetery. In 1880 August Wirth lived at Mosquito Creek (Lake Eppalock, Victoria) when he married Frances Young. In 1902 they moved to part of Joseph Young's property. They milked cows and sold cattle for a living. One of their children Charles Wirth (Phil Wilkin's Grandfather) bought the land in 1935 after his parents had died. Charles Wirth was a councillor and also was president of the Shire of Strathfieldsaye. The "Old Place" was part of the property owned by members of the family. The old house at the Springs was burnt out by bushfire in January 1944 and much of the stonework was later vandalized by campers. The original Coliban Water Works were designed in 1863 by the Irish engineer Joseph Brady. The system included 70 kilometres of open water channels, aqueducts, syphons and tunnels to carry water (by gravity) from the Coliban River at Malmsbury, north to Castlemaine and Bendigo. Sedgwick is a locality in Central Victoria, Australia. It is located in the City of Greater Bendigo. Facilities include a public hall that opened in 1958 and CFA Rural fire station. It was named Upper Emu Creek until 1901 when it was renamed as Sedgwick after British geologist Adam Sedgwick.Twenty six photos taken on a field trip by the Bendigo Historical Society to "The Springs" on the main Coliban water channel from Malmsbury to the Sandhurst Reservoir in Bendigo. The water race descends through a concrete chute, and continues sharply around the contour of the hills. Once it descended into a syphon across the gully. The are 182 photos in this series and can be found at 8683.1 to 8683.11. The series also includes photos of the surrounding farming land and the remains of an old house. There are also some notes on the pioneers of the district.history, bendigo, coliban water, joseph brady, irrigation, the springs, sedgwick -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - Historical Society Field Trip to the Springs at Sedgwick, Abt 2009
The Phil Wilkin Collection contains a series of 11 Items. The related items can be found by clicking on the reference link below. The following history of the Young family and their descendants who lived at the Springs is provided by Phil Wilkin. His Great Grandparents were Frances Young and August Wirth. Phil has also provided notes on the Wilkin Family and some history of the gold mining in Sedgwick. Frances Young's parents Joseph and Margaret Young owned the property called "The Old Place, Preston Vale or Wellington Flat" at Sedgwick near the Springs. Joseph Young owned and Managed the Standard Brewery which was located at Campbells Creek during the late 1800’s early 1900’s. Joseph and Margaret are buried in the Harcourt cemetery. In 1880 August Wirth lived at Mosquito Creek (Lake Eppalock, Victoria) when he married Frances Young. In 1902 they moved to part of Joseph Young's property. They milked cows and sold cattle for a living. One of their children Charles Wirth (Phil Wilkin's Grandfather) bought the land in 1935 after his parents had died. Charles Wirth was a councillor and also was president of the Shire of Strathfieldsaye. The "Old Place" was part of the property owned by members of the family. The old house at the Springs was burnt out by bushfire in January 1944 and much of the stonework was later vandalized by campers. The original Coliban Water Works were designed in 1863 by the Irish engineer Joseph Brady. The system included 70 kilometres of open water channels, aqueducts, syphons and tunnels to carry water (by gravity) from the Coliban River at Malmsbury, north to Castlemaine and Bendigo. Sedgwick is a locality in Central Victoria, Australia. It is located in the City of Greater Bendigo. Facilities include a public hall that opened in 1958 and CFA Rural fire station. It was named Upper Emu Creek until 1901 when it was renamed as Sedgwick after British geologist Adam Sedgwick.Twenty five photos taken on a field trip by the Bendigo Historical Society to "The Springs" on the main Coliban water channel from Malmsbury to the Sandhurst Reservoir in Bendigo. The water race descends through a concrete chute, and continues sharply around the contour of the hills. Once it descended into a syphon across the gully. The are 182 photos in this series and can be found at 8683.1 to 8683.11. The series also includes photos of the surrounding farming land and the remains of an old house. There are also some notes on the pioneers of the district.history, bendigo, coliban water, joseph brady, irrigation, the springs, sedgwick -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncPhotograph, Cato Lake -- with palms & trees -- Coloured
Coloured Postcard Murray Views No. 7. Cato Park Stawell Victoria. The three black and white photos are missing the larger palm tree on the right in the foreground. The view is of the lake surrounded by trees and bench seating. One colour post card Murray View No 7 Cato Park Stawell Victoria plus two similar black & white photos one smaller the other an enlargement. Also a small B&W photograph in Album 14, p28. The post card is a view of a section of the lake surrounded by willows, 2 tall pine trees and one large palm tree on the right. The lake is also surrounded by 3 concrete & wood bench seats with maybe a 4th in the distance. Murray View No 7 Cato Park Stawell Vic. On the back "Post Card Real Photograph produced in Australia by Murray View, Gympie, Q".stawell -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncPhotograph, Cato Lake with the Swimming Pool c 1950's
Two black and white post cards of the Olympic swimming pool in Cato lake c 1950's. The Rose Series P 14901 shows the swimming pool and lake with the swimming pool dominating the photograph. Four flag posts are clearly visible and the pool connected to the edge of the lake. The Rose Series P 14012 also shows the Olympic pool but more of the lake and boundary. with seating around the lake. In March 1957 Cato Lake was emptied for construction of the Olympic pool and officially opened on 15.11.1958. Twenty seven years later In January 1985 the pool was found to be leaking and Borough Council in February banned further use of the Olympic pool. Eventually the Olympic pool was demolished in April 1988.Two black & white Rose series post cards of Cato Olympic swimming pool Stawell Vic. c 1950's. Series P 14901 is nearly a complete view of the Olympic pool with four flag posts in view and trees and buildings in the distance. Series P 14012 has only a small section of the Olympic pool in the photograph with just 3 flag poles in view. There are 2 concrete and timber seats in the foreground and Cato lake is very still, reflecting the distance trees.The Rose Series P 14901 Swimming Pool Stawell Vic. and The Rose Series P 14912 Cato Park and swimming pool Stawell, Vic. Both post cards were Published by Rose Stereograph Co., Armadale, Victoria. The "Rose" series De Luxe.stawell -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Colour Print/s - set of 5, Carolyn Dean, Nov. 1978
Set of five colour print of the construction of the foundation and pit of the "new shed" Nov. 1978. On Kodak paper. Date from printing date on rear of photograph. Photographer unknown. .1 - No. 4 road pit base with formwork for pump pit. .2 - Pits excavated 4 and 5 road and sand base installed. .3 - Excavating pits etc from South West corner of shed. .4 - No. 4 road pit poured. .5 - Placing concrete in No. 4 road pit. btm depot, construction, buildings -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - IAN DYETT COLLECTION: AUCTION CATALOGUE - COLIBAN WATER
White catalogue with blue printing for a sale on the 8th October, 1996 on account of Coliban Water, Golden Square. For sale were motor vehicles and trucks, survey equipment, trailers, generators, pumps, power tools, chainsaws, concrete mixers, parts, pipe, brass meters, ferrous & non ferrous scrap, office furniture, hand tools and sundries. J. H. Curnow & Son P/L were the auctioneers. Directions how to get to the Coliban Water Depot on the back cover.business, auctioneers, j h curnow & son pty ltd, ian dyett collection - auction catalogue - coliban water, barry breen, j h curnow & son p/l -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumEquipment - Tram Track Materials, Pandrol Australia, Sydney
Tramway Track materials used to reconstruct or replace Ballarat Tramway Museum track between Carlton St and Depot Junction Sept 2019. Follows the current practice in Melbourne.Demonstrates the materials used to replace BTM Tramway Track during 2019. Same materials used during the reconstruction of 2022.Group of rail fittings used during 2019 track relay by Fulton Hogan between Carlton St and Depot Junction. .1 - Section of tram rail - Ri57A - cut from an 18m long rail section. Rolled by voestalpine Railway Systems, Austria .2 - Group of three different sized Pandrol Rail insulators used between the rail and the clip. .3 - Pandrol resilient pad used between the concrete sleeper and the rail .4 - Pandrol clip used to secure the rail to the sleeper.tramways, ballarat, btm, trackwork, tramway rails, pandrol, voestalpine -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncAlbum - Hume Reservoir Australia Album - Plans and Progress Photos - River Murray Water Scheme, Department of Public Works, N.S.W, 1927
This set of photos is from a leather bound album bearing the inscription "HUME RESERVOIR AUSTRALIA" plus 'The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M .P.' all inscribed in gold. It was presented to The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M. P, Secretary of State for Dominion Affairs on the occasion of his visit to the Hume Reservoir on 2nd November 1927. This album is of local and national significance as it documents the planning and development of the Hume Reservoir up to 1927. It was the largest water reservoir in the British Empire. The album records the pioneering engineering work that went into its construction.1. Locality Plan and Plan of Dam. The dam is about ten miles by road upstream from Albury and about three-quarters of a mile below the confluence of the Mitta Mitta River and the Murray River. Its main features consist of a concrete portion across the bed of the river with earth embankment at both ends. The foundations throughout are on hard granite, found at an average depth of about 40 feet below the surface, the centre line being located to take advantage of the most favourable rock levels.Heading on page "WORKS UNDER RIVER MURRAY WATERS AGREEMENT/HUME RESERVOIR" Beneath top diagram "FIG. 1. ELEVATION" Beneath second diagram "FIG. 2. PLAN" On map "LOCALITY PLAN"hume reservoir australia, river murray waters scheme, hume weir diagrams, hume weir location -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncAlbum - Hume Reservoir Australia Album - Earth embankment, Victoria, August 1927
This set of photos is from a leather bound album bearing the inscription "HUME RESERVOIR AUSTRALIA" plus 'The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M .P.' all inscribed in gold. It was presented to The Rt. Hon. L. C. M. S. Amery, P. C., M. P, Secretary of State for Dominion Affairs on the occasion of his visit to the Hume Reservoir on 2nd November 1927. This album is of local and national significance as it documents the planning and development of the Hume Reservoir up to 1927. It was the largest water reservoir in the British Empire. The album records the pioneering engineering work that went into its construction.DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC WORKS, N.S.W. RIVER MURRAY WATERS SCHEME. HUME RESERVOIR. 32. Earth Embankment, Victoria. Looking down on the earth embankment and core wall. The earth is conveyed to the bank by rail, tipped out and then put in place by wheeled scoops, the horses and wheels treading and rolling the material into a very compact form while hoses play water on the mass to keep it moist. The concrete pillar with Tail Tower, and North Wing Wall, look very small in the distance. August 1927.hume reservoir australia, river murray waters scheme, hume reservoir construction -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPostcard - Lakes Entrance, Bulmer H D, 1940c
From a wallet of minitiature postcards published by Bulmer for sale to tourists. Also enlarged black and white copy 18.5 x 25 cm,Black and white mini postcard of Esplanade, showing timber groynes for sand control at edge of lake at walking path of concrete slabs. Across the highway from left to right is Kia-Ora House, Heyfield House, Coate Bros Garage, Robin Hood Inn, Vizes Cafe, Vic Carstairs, Miss Brown's (subagent for Statebank), Methodist Church, Bellevue Guest House, Police Station, Maranui Guest House, Glenara Guest House. Lakes Entrance Victoriatownship, waterfront, accommodation -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Report, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), "Trial Installation of Barrier Kerbing, Nicholson Street - Fitzroy", Nov. 197
Report, manila covers, A4 paper, white comb binder, 30 pages, 1 photograph page of Nicholson St, looking north with a Z class tram in the distance, tables of traffic timing, looking at the impact of concrete barrier kerbs laid along the eastern side of Nicholson St Fitzroy between Alexandra Parade and Victoria Parade, 12 month trial. Report dated November 1976. Includes impact on traffic and tram services. 2nd copy added 23/10/2014.Marked number "85" in top right hand corner and stamped on cover and inside cover page "Discarded from PTC Library 22 Oct 1989". 2nd copy ex AETA marked "4E13" in top right hand corner of cover.trams, tramways, mmtb, nicholson st, fitzroy, traffic control
