Showing 1480 items
matching potential for museum
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionLetter - Correspondence, Letter Concerning Potential Donation of Aboriginal Artefacts to the Ballarat School of Mines Museum, 1954, 11/02/1954
The collection of artefacts formely belonged to the writers father, J.M. Marshall of Sturt Street. He was born and lived in Ballarat most of his life, and was interested in the Ballarat School of Mines Museum during the era of Professor Alfred Mica Smith. The response to this letter foreshadows the closure of the Ballarat School of Mines Museum. Alan Sonsee of the Ballarat Teachers' College was a Field Naturalist and collector of Aboriginal artefacts, and may have been associated with the decision. Handwritten letter from Jessie Marshall of Adelaide offering a collection of Australian "Native Weapons and Curios" to the Ballarat School of Mines Museum. The writer describes the collection as "not a large collection but a very good one - there are also some lovely shells." Ballarat School of Mines Registrar, F.E. Ferguson, declined the offer on behalf of the School Council, suggesting the Ballarat Teachers' College (Dana Street) would like to have the weapons, etc.C/- Collison & Co 32 Waymouth St Adelaide 11/2/54 Sear Sir A am writing this to offer a collection of Native Weapons and Curious - Australian - the Islands and S. Africa - the the Museum as a gift - they originally belonged to my father J.M. Marshall - formerly of Sturt Stree - who was born and lived in Ballarat most of his life and who was always interested i nthe Museum and School of Mines back in Prof. Mica Smith's time. This is not a large collection but a very good one - there are also some lovely shells. They have beenin stroage since his death and I feel he would have liked them to be of some use + give pleasure to someone + I can think of no better plance than your museum. Would you be goodenough to put this offer to your Committee + let me know if that are interested. I am yours Jessie Marshall PS I've made enquiries + there is plenty of motor transport available J.M.ballarat school of mines, aboriginal artefacts, ballarat school of mines museum, jessie marshall, i.m. marshall, ballarat teachers' college, f.e. ferguson, museum closure, alan sonsee, ballarat teachers college, museum, shells, j.m. marshall -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Tools, Chain pipe wrench c1900, c1900
The heavy duty chain wrench has a double jaw that gives fast, ratchet-like action in either direction The "cable chain" is preferable for working with fittings and other irregular forms related to pipe where flat chain is better suited for pipe. The side plates connect to the handle with dovetails; the bolt's primary function is to keep the jaws in position rather than carrying the strain. The free end of the chain connects to the handle behind the attachment point for the fixed end of the chain to avoid potential for the chain to "lock" on pipe. This chain pipe wrench is typical of the type used by early settlers in Moorabbin Shire c1900Heavy steel chain pipe wrench c1900wrenches, spanners, chain pipe wrench, early settlers, market gardeners, blacksmiths, tools, building equipment, hammers, moorabbin shire, bentleigh, mckinnon, highett, cheltenham,mcewan james pty ltd, melbourne, bunnings pty ltd, -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Cow Bell, James Barwell, 1860s-1878
This brass cow bell was recovered from the wreck of the sailing ship ‘Loch Ard’ at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria, from late 1960s to early 1970s. Cow bells were listed as part of the cargo on board the Loch Ard. This bell is now part of the John Chance collection. Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s divers also recovered similar bells from the Loch Ard wreck in 1973. One of them was found in a sandy hole in the centre of the wreck site. All of the recovered cow bells are without their hangers. A bell of this size could have been used by horse or cattle teams. Cow bells were a common Colonial item. They were hung around the necks of grazing domestic cows and goats, bullock and horse teams, even camel teams so that they could be found again. Sheep and cattle drovers used them as a warning for night time disturbances such as wild animals. The maker of the cow bell, James Barwell, was a bell founder established in Birmingham, England, from 1784. In 1842 he acquired Fiddian’s firm of ‘Steam and Water’, keeping its name and stamping it on some of his products. According to his advertisement in the Exhibitors guide for the Church Congress of 1887, he made bells and fittings for churches and schools. He also made bells for cloches and chimes, and made tuned musical handbells. He repaired and reproduced bells, and he had a team of experienced ringers to “inspect towers and report upon the tone and condition of bells and fittings.” In 1903 he became incorporated as a Limited Company, ‘engineers’ and plumbers’ brasswork, and bell founders.’ In 1914 he advertised as ‘Cock and Bell Founders’, specialising in plumbing and engineering fittings, church bells, and “every description of hanging and hand bells.” Some of Barwell’s products were stamped with his maker’s mark (his initials J. B. either side of a cross entwined with a ‘B’ in an oval of oak leaves (for Birmingham)). James Barwell bells were no longer made after 1920. James Barwell was among makers who exported bells to the Australian colony from the 1860s. Early Australian iron animal bells were also made from the 1860s by blacksmiths such as Anthony Morgan from 1861, August Menneke from 1867, and Samuel Jones from 1868. Few brass bells were produced here in those times. This bell is historically significant as typical of a cow bell used by farmers and herdsmen in Colonial Victoria. Its significance is increased by being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late 1960s to early 1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The cow bell is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Cow bell; heavy brass, flat top, pyramid shape, rectangular head, shoulders flare out to rectangular mouth. The head has two same-sized tooled holes for adding the hanging yoke. Inscription on top and one side. Encrustations are on the metal in places. The hanger and clapper are missing. Made by James Barwell of Birmingham.Stamped on the head "BARWELL / - - - / - - -- ING" [Perhaps BARWELL - - - BIRMING. Could size be in centre? 3 3/4 IN?] Stamped on side [motif] (undecipherable) flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, john chance, loch ard, mutton bird island, glenample, eva carmichael, tom pearce, james barwell, cow bell, horse bell, bell founder, bell smith, vintage bell, birmingham bell foundry, farmer, shepherd, drover, stock bell -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1840s to 1878
This handmade black glass bottle was recovered between the late 1960s to early 1970s from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. The ship was wrecked in 1878 and its remains are located at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria and bottles of liquor were listed as part of the Loch Ard’s cargo. This bottle is now part of the John Chance collection. Black glass is one of the oldest bottle colours and dates back to the early 17th century. In the 1840s to late-1870s black glass bottles were mainly used for liquor and ale. All glass is made from silica, which is found in quartz sand. The naturally occurring sand has impurities, such as iron, that determine the colour of the glass. Residual iron leads to green or amber coloured glass, and carbon in the sand makes that glass appear as ‘black’. A strong light behind the glass will show its colour as dark green or dark amber. This handmade bottle appears to have been made in a dip mould, with the molten glass blown into a seamless shoulder-height mould to give the body a uniform symmetrical shape and size. After the body is blown, the glass blower continues blowing free-form (without the mould) to form the shoulder and neck, then the base is pushed up with a tool, and the finish for the mouth is added with his tools. The dip mould gives the body a slightly textured surface, with the free blown shoulders and neck being smoother and shinier. There is usually a line around the shoulder where the mould of the body meets the shoulder, and a lump or mark in the centre of the base, called a pontil mark, where the push-up tool was removed. The ship Loch Ard was built on the River Clyde in Scotland in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. It sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. This bottle is historically significant as an example of liquor bottles imported into to Colonial Victoria in the mid-1800s to early-1900s. Its significance is increased by also being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late-1960s to early-1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The bottle is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Loch Ard, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. The collection is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417. The collection has additional significance because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The shipwreck is one of the worst, and best known, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Bottle, black glass. Thick matt body, with slightly bumpy texture, areas with sheen, colour imperfections. Tooled cork-top finish with ring below, slightly bulged neck. Shoulder has some diagonal creases and a line where shoulder meets body. Body tapers inwards to base. Heel varies in width. Pushed up base has pontil mark. Base is uneven. Handmade, dip mould. No inscriptions.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, mutton bird island, eva carmichael, tom pearce, john chance, bottle, black glass, antique bottle, bulge neck bottle, handmade, dip mould, mouth blown, pontil base, blown bottle, liquor bottle, ale bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1840s to 1878
This handmade black glass bottle was recovered between the late 1960s to early 1970s from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. The ship was wrecked in 1878 and its remains are located at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria and bottles of liquor were listed as part of the Loch Ard’s cargo. This bottle is now part of the John Chance collection. Black glass is one of the oldest bottle colours and dates back to the early 17th century. In the 1840s to late-1870s black glass bottles were mainly used for liquor and ale. All glass is made from silica, which is found in quartz sand. The naturally occurring sand has impurities, such as iron, that determine the colour of the glass. Residual iron leads to green or amber coloured glass, and carbon in the sand makes that glass appear as ‘black’. A strong light behind the glass will show its colour as dark green or dark amber. This handmade bottle appears to have been made in a dip mould, with the molten glass blown into a seamless shoulder-height mould to give the body a uniform symmetrical shape and size. After the body is blown, the glass blower continues blowing free-form (without the mould) to form the shoulder and neck, then the base is pushed up with a tool, and the finish for the mouth is added with his tools. The dip mould gives the body a slightly textured surface, with the free blown shoulders and neck being smoother and shinier. There is usually a line around the shoulder where the mould of the body meets the shoulder, and a lump or mark in the centre of the base, called a pontil mark, where the push-up tool was removed. The ship Loch Ard was built on the River Clyde in Scotland in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. It sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. This bottle is historically significant as an example of liquor bottles imported into to Colonial Victoria in the mid-1800s to early-1900s. Its significance is increased by also being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late-1960s to early-1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The bottle is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Loch Ard, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. The collection is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417. The collection has additional significance because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The shipwreck is one of the worst, and best known, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Bottle, black glass. Thick matt body, with slightly bumpy texture, areas with sheen, colour imperfections. Tooled cork-top finish with ring below, slightly bulged neck. Shoulder has a line where shoulder meets body. Body tapers inwards to base. Heel varies in width. Pushed up base has pontil mark. Handmade, dip mould. No inscriptions.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, mutton bird island, eva carmichael, tom pearce, john chance, bottle, black glass, antique bottle, bulge neck bottle, handmade, dip mould, mouth blown, pontil base, blown bottle, liquor bottle, ale bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1840s to 1878
This handmade black glass bottle was recovered between the late 1960s to early 1970s from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. The ship was wrecked in 1878 and its remains are located at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria and bottles of liquor were listed as part of the Loch Ard’s cargo. This bottle is now part of the John Chance collection. Black glass is one of the oldest bottle colours and dates back to the early 17th century. In the 1840s to late-1870s black glass bottles were mainly used for liquor and ale. All glass is made from silica, which is found in quartz sand. The naturally occurring sand has impurities, such as iron, that determine the colour of the glass. Residual iron leads to green or amber coloured glass, and carbon in the sand makes that glass appear as ‘black’. A strong light behind the glass will show its colour as dark green or dark amber. This handmade bottle appears to have been made in a dip mould, with the molten glass blown into a seamless shoulder-height mould to give the body a uniform symmetrical shape and size. After the body is blown, the glass blower continues blowing free-form (without the mould) to form the shoulder and neck, then the base is pushed up with a tool, and the finish for the mouth is added with his tools. The dip mould gives the body a slightly textured surface, with the free blown shoulders and neck being smoother and shinier. There is usually a line around the shoulder where the mould of the body meets the shoulder, and a lump or mark in the centre of the base, called a pontil mark, where the push-up tool was removed. The ship Loch Ard was built on the River Clyde in Scotland in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. It sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. This bottle is historically significant as an example of liquor bottles imported into to Colonial Victoria in the mid-1800s to early-1900s. Its significance is increased by also being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late-1960s to early-1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The bottle is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Loch Ard, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. The collection is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417. The collection has additional significance because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The shipwreck is one of the worst, and best known, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Bottle, black glass. Thick matt body, with slightly bumpy texture, areas with sheen, colour imperfections. Mouth has cork seal. Tooled cork-top finish with ring below, slightly bulged neck. Shoulder a line where shoulder meets body. Body tapers inwards to base. Heel varies in width. Pushed up base has pontil mark. White discolouration in a narrow line down the body. Handmade, dip mould. No inscriptions.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, mutton bird island, eva carmichael, tom pearce, john chance, bottle, black glass, antique bottle, bulge neck bottle, handmade, dip mould, mouth blown, pontil base, blown bottle, liquor bottle, ale bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1840s to 1878
This handmade black glass bottle was recovered between the late 1960s to early 1970s from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. The ship was wrecked in 1878 and its remains are located at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria and bottles of liquor were listed as part of the Loch Ard’s cargo. This bottle is now part of the John Chance collection. Black glass is one of the oldest bottle colours and dates back to the early 17th century. In the 1840s to late-1870s black glass bottles were mainly used for liquor and ale. All glass is made from silica, which is found in quartz sand. The naturally occurring sand has impurities, such as iron, that determine the colour of the glass. Residual iron leads to green or amber coloured glass, and carbon in the sand makes that glass appear as ‘black’. A strong light behind the glass will show its colour as dark green or dark amber. This handmade bottle appears to have been made in a dip mould, with the molten glass blown into a seamless shoulder-height mould to give the body a uniform symmetrical shape and size. After the body is blown, the glass blower continues blowing free-form (without the mould) to form the shoulder and neck, then the base is pushed up with a tool, and the finish for the mouth is added with his tools. The dip mould gives the body a slightly textured surface, with the free blown shoulders and neck being smoother and shinier. There is usually a line around the shoulder where the mould of the body meets the shoulder, and a lump or mark in the centre of the base, called a pontil mark, where the push-up tool was removed. The ship Loch Ard was built on the River Clyde in Scotland in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. It sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. This bottle is historically significant as an example of liquor bottles imported into to Colonial Victoria in the mid-1800s to early-1900s. Its significance is increased by also being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late-1960s to early-1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The bottle is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Loch Ard, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. The collection is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417. The collection has additional significance because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The shipwreck is one of the worst, and best known, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Bottle, black glass. Thick matt body, with slightly bumpy texture, areas with sheen, colour imperfections. Mouth has cork seal. Tooled cork-top finish with ring below, slightly bulged neck. Shoulder has a line with a long bump where shoulder meets body. Body tapers inwards to base. Pushed up base has pontil mark. Handmade, dip mould. No inscriptions.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, mutton bird island, eva carmichael, tom pearce, john chance, bottle, black glass, antique bottle, bulge neck bottle, handmade, dip mould, mouth blown, pontil base, blown bottle, liquor bottle, ale bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1840s to 1878
This handmade black glass bottle was recovered between the late 1960s to early 1970s from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. The ship was wrecked in 1878 and its remains are located at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria and bottles of liquor were listed as part of the Loch Ard’s cargo. This bottle is now part of the John Chance collection. Black glass is one of the oldest bottle colours and dates back to the early 17th century. In the 1840s to late-1870s black glass bottles were mainly used for liquor and ale. All glass is made from silica, which is found in quartz sand. The naturally occurring sand has impurities, such as iron, that determine the colour of the glass. Residual iron leads to green or amber coloured glass, and carbon in the sand makes that glass appear as ‘black’. A strong light behind the glass will show its colour as dark green or dark amber. This handmade bottle appears to have been made in a dip mould, with the molten glass blown into a seamless shoulder-height mould to give the body a uniform symmetrical shape and size. After the body is blown, the glass blower continues blowing free-form (without the mould) to form the shoulder and neck, then the base is pushed up with a tool, and the finish for the mouth is added with his tools. The dip mould gives the body a slightly textured surface, with the free blown shoulders and neck being smoother and shinier. There is usually a line around the shoulder where the mould of the body meets the shoulder, and a lump or mark in the centre of the base, called a pontil mark, where the push-up tool was removed. The ship Loch Ard was built on the River Clyde in Scotland in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. It sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. This bottle is historically significant as an example of liquor bottles imported into to Colonial Victoria in the mid-1800s to early-1900s. Its significance is increased by also being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late-1960s to early-1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The bottle is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Loch Ard, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. The collection is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417. The collection has additional significance because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The shipwreck is one of the worst, and best known, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Bottle, black glass. Thick matt body, with slightly bumpy texture, areas with sheen, colour imperfections. Mouth has cork seal, partly removed, with content remnants inside. Tooled cork-top finish with ring below, slightly bulged neck. Shoulder a line where shoulder meets body. Body tapers inwards to base. Heel varies in width. Base is uneven. Pushed up base has pontil mark. Handmade, dip mould. No inscriptions.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, mutton bird island, eva carmichael, tom pearce, john chance, bottle, black glass, antique bottle, bulge neck bottle, handmade, dip mould, mouth blown, pontil base, blown bottle, liquor bottle, ale bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1840s to 1878
This handmade black glass bottle was recovered between the late 1960s to early 1970s from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. The ship was wrecked in 1878 and its remains are located at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria and bottles of liquor were listed as part of the Loch Ard’s cargo. This bottle is now part of the John Chance collection. Black glass is one of the oldest bottle colours and dates back to the early 17th century. In the 1840s to late-1870s black glass bottles were mainly used for liquor and ale. All glass is made from silica, which is found in quartz sand. The naturally occurring sand has impurities, such as iron, that determine the colour of the glass. Residual iron leads to green or amber coloured glass, and carbon in the sand makes that glass appear as ‘black’. A strong light behind the glass will show its colour as dark green or dark amber. This handmade bottle appears to have been made in a dip mould, with the molten glass blown into a seamless shoulder-height mould to give the body a uniform symmetrical shape and size. After the body is blown, the glass blower continues blowing free-form (without the mould) to form the shoulder and neck, then the base is pushed up with a tool, and the finish for the mouth is added with his tools. The dip mould gives the body a slightly textured surface, with the free blown shoulders and neck being smoother and shinier. There is usually a line around the shoulder where the mould of the body meets the shoulder, and a lump or mark in the centre of the base, called a pontil mark, where the push-up tool was removed. The ship Loch Ard was built on the River Clyde in Scotland in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. It sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. This bottle is historically significant as an example of liquor bottles imported into to Colonial Victoria in the mid-1800s to early-1900s. Its significance is increased by also being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late-1960s to early-1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The bottle is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Loch Ard, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. The collection is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417. The collection has additional significance because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The shipwreck is one of the worst, and best known, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Bottle, black glass. Thick matt body, with slightly bumpy texture, areas with sheen, colour imperfections. Mouth is sealed, and has remnants of tape on outside. Tooled cork-top finish with ring below. Slightly bulged neck. Shoulder has some diagonal creases and a distinct line where shoulder meets body. Body tapers inwards to base. It has a bubble and diagonal crease lines. Base is uneven. Pushed up base has pontil mark. Handmade, dip mould. No inscriptions.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, mutton bird island, eva carmichael, tom pearce, john chance, bottle, black glass, antique bottle, bulge neck bottle, handmade, dip mould, mouth blown, pontil base, blown bottle, liquor bottle, ale bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1840s to 1878
This handmade black glass bottle was recovered between the late 1960s to early 1970s from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard. The ship was wrecked in 1878 and its remains are located at Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell, Victoria and bottles of liquor were listed as part of the Loch Ard’s cargo. This bottle is now part of the John Chance collection. Black glass is one of the oldest bottle colours and dates back to the early 17th century. In the 1840s to late-1870s black glass bottles were mainly used for liquor and ale. All glass is made from silica, which is found in quartz sand. The naturally occurring sand has impurities, such as iron, that determine the colour of the glass. Residual iron leads to green or amber coloured glass, and carbon in the sand makes that glass appear as ‘black’. A strong light behind the glass will show its colour as dark green or dark amber. This handmade bottle appears to have been made in a dip mould, with the molten glass blown into a seamless shoulder-height mould to give the body a uniform symmetrical shape and size. After the body is blown, the glass blower continues blowing free-form (without the mould) to form the shoulder and neck, then the base is pushed up with a tool, and the finish for the mouth is added with his tools. The dip mould gives the body a slightly textured surface, with the free blown shoulders and neck being smoother and shinier. There is usually a line around the shoulder where the mould of the body meets the shoulder, and a lump or mark in the centre of the base, called a pontil mark, where the push-up tool was removed. The ship Loch Ard was built on the River Clyde in Scotland in 1873 for the prestigious Loch Line of colonial clipper ships, designed for the Australian run. It sailed from England on 1 March 1878 carrying 37 crew, 17 passengers and a diverse general cargo ranging from luxury items to bulk railway iron. On 1 June 1878, emerging from fog and hearing too late the sound of breakers against the tall limestone cliffs, the vessel struck the southern foot of Mutton Bird Island and sank in 23 metres of water. Of the fifty-four people on board only two survived, one young male crewman, Tom Pearce, and one young female passenger, Eva Carmichael. This bottle is historically significant as an example of liquor bottles imported into to Colonial Victoria in the mid-1800s to early-1900s. Its significance is increased by also being an artefact recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Loch Ard and other wrecks in the late-1960s to early-1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. The bottle is also significant for being part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Loch Ard, which is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. The collection is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417. The collection has additional significance because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The shipwreck is one of the worst, and best known, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Bottle, black glass. Thick matt body, with slightly bumpy texture, areas with sheen, colour imperfections, bubble in glass. Bottle has foul smelling contents inside. Mouth has hard capped cork seal with black, hard rubber capped stopper. Side of mouth has ship or mark. Tooled cork-top finish with ring below, slightly bulged neck. Shoulder has some diagonal creases and a line where shoulder meets body. Body tapers inwards to base. Heel varies in width. Base is uneven. Pushed up base has pontil mark. Handmade, dip mould. No inscriptions.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, mutton bird island, eva carmichael, tom pearce, john chance, bottle, black glass, antique bottle, bulge neck bottle, handmade, dip mould, mouth blown, pontil base, blown bottle, liquor bottle, ale bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Latch, before 1890
In Flagstaff Hill’s collection are items associated with the Ancient Wreck, (also called the Gold Ship, Mahogany Ship or Ancient Vessel). Three relics were located in 1890, due to the ‘interest of a public works inspector, James Gilroy, who dug in the ship’s remains’. One of the relics was a heavily oxidated ‘quantity of ironwork’. The other two, now part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection, are - an iron latch probably from a galley oven door or fireplace - a bronze bolt (spike or pin) Both of these relics are listed on the same page in the records of the Old Warrnambool Museum, found by K.A.G. (or H.A.G.) on the site of the Ancient wreck in 1890. Interestingly, another item in these records is ‘Notes on Ancient wreck, near Gorman’s Lane’. Gorman’s Lane is just inland from the sand dunes of the Coastal Reserve at Tower Hill. The current location of these Notes is unknown. Another item thought to be a relic from the Mahogany Ship was the amphora or jug, also in Flagstaff Hill's collection. It was found in 1934 on a local property and donated in 1985. The Museum opened in 1886 and continued until 1963, when it was closed by the Warrnambool City Council and the whole collection was put into storage. The council then transferred items to various places including Flagstaff Hill and the current Warrnambool Art Gallery. Flagstaff Hill’s early Accession Records book lists the items as being received from the Old Warrnambool Museum collection; the Latch is record 152 and the Pin is record 153. An article, ‘Birthplace of our History’ by Don Dean, is on file in the Warrnambool and District Historical Society. It was published in the Australian POST, on March 17, 1955. This article describes the finding of the items going back to 1890, along with other information about sightings of what has come to be known as the Mahogany Ship. The mystery of the Mahogany Ship began in 1836 when two shipwrecked sealers discovered the remains of an “ancient vessel” in the sand dunes about four miles west of Warrnambool. Since the last recorded sightings in the 1880’s the true origin of the Mahogany Ship has remained one of Australia’s most famous historical mysteries. One of the more recent theories is that the vessel was one of the Portuguese ships exploring the Australian coast in 1522. For over one hundred years searchers have attempted to locate and identify the wreck. The search continues for the tangible evidence which will once and for all establish the Mahogany Ship’s place in Australia’s History. The latch has local historic significance as it was found in the sand dunes of Warrnambool in 1890. The latch is also significant for being part of the original 1886 Warrnambool Museum's collection. The latch is significant for its possible link to one of Victoria’s and Australia’s maritime mysteries, the Mahogany Ship (also known as the Ancient Wreck). It is one of very few known relics that could give evidence of the existence and history of the vessel. It is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register S438 as it is one of Victoria’s oldest recorded shipwrecks. The identity of the vessel has the potential to change Australia’s history.Latch, iron. Flat iron latch tapers inward from loop handle to narrow end with prongs. Handmade. warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, mahogany ship, latch, relic, old warrnambool museum, ancient vessel, ancient wreck, oven latch, fireplace latch, galley oven, gold ship, gorman's lane, coastal reserve, tower hill -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Bolt, before 1890
Flagstaff Hill’s collection has items that are thought to be relics from the Ancient Wreck, (also called the Gold Ship, Mahogany Ship or Ancient Vessel). Three relics were located in 1890, due to the ‘interest of a public works inspector, James Gilroy, who dug in the ship’s remains’. One of the relics was a heavily oxidated ‘quantity of ironwork’. The other two, now part of Flagstaff Hill’s collection, are - an iron latch probably from a galley oven door or fireplace - a bronze bolt (spike or pin) Both of these relics are listed on the same page in the records of the Old Warrnambool Museum, found by K.A.G. (or H.A.G.) on the site of the Ancient wreck 1890. Interestingly, another item in these records is ‘Notes on Ancient wreck, near Gorman’s Lane’. Gorman’s Lane is just inland from the sand dunes of the Coastal Reserve at Tower Hill. The current location of these Notes is unknown. Another relic is thought to be the amphora, discovered in 1934 on a local property. The Museum opened in 1886 and continued until 1963, when it was closed by the Warrnambool City Council and the whole collection was put into storage. The council then transferred items to various places including Flagstaff Hill and the current Warrnambool Art Gallery. Flagstaff Hill’s early Accession Records book lists the items as being received from the Old Warrnambool Museum collection; the Latch is record 152 and the Pin is record 153. An article, ‘Birthplace of our History’ by Don Dean, is on file in the Warrnambool and District Historical Society. It was published in the Australian POST, March 17, 1955. This article describes the finding of the items going back to 1890, along with other information about sightings of what has come to be known as the Mahogany Ship. The mystery of the Mahogany Ship began in 1836 when two shipwrecked sealers discovered the remains of an “ancient vessel” in the sand dunes about four miles west of Warrnambool. Since the last recorded sightings in the 1880’s the true origin of the Mahogany Ship has remained one of Australia’s most famous historical mysteries. One of the more recent theories is that the vessel was one of the Portuguese ships exploring the Australian coast in 1522. For over one hundred years searchers have attempted to locate and identify the wreck. The search continues for the tangible evidence which will once and for all establish the Mahogany Ship’s place in Australia’s History. The bolt has local historic significance as it was found in the sand dunes of Warrnambool in 1890. The bolt is also significant for being part of the original 1886 Warrnambool Museum's collection. The bolt is significant for its possible link to one of Victoria’s and Australia’s maritime mysteries, the Mahogany Ship (also known as the Ancient Wreck). It is one of very few known relics that could give evidence of the existence and history of the vessel. It is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register S438 as it is one of Victoria’s oldest recorded shipwrecks. The identity of the vessel has the potential to change Australia’s history.Bolt, also referred to as spike or pin. Bronze bolt, round body with head on one end that has straight sides, tapers to a point at the other end.warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, mahogany ship, relic, pin, spike, old warrnambool museum, nail, ancient vessel, ancient wreck, portuguese ship, gold ship, gorman’s lane, coastal reserve, tower hill -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Fork, c. 1878
This fork was recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard. It is the Old English design that has been very popular since the 19th century. It has been restored to resemble its original state prior to the disaster in 1878. The for was originally plated with silver, which is when a base metal such as nickel or nickel alloy with copper and/or zinc has been plated or coated with a thin layer of silver. Wear on the metal will cause the base metals to appear through the silver plating. Some manufacturers gave a warranty that the cutlery was ‘white throughout’ but didn’t necessarily say it was solid silver. LOCH ARD 1873-1878 – The Scottish-built clipper ship Loch Ard was bound for Melbourne in 1878 with 54 people on board. The mixed cargo it carried included items for the 1880 International Exhibition in Melbourne, one of which was the now famous Majorca ware Minton ‘Peacock’ statue. The Loch Ard was wrecked on June 1st when the ship crashed into Mutton Bird Island, east of Port Campbell. The only survivors were Tom Pearce, a crew member, and Eva Carmichael, a young passenger who was rescued by Pearce. The Gibsons, owners of nearby Glenample Homestead, cared for Tom, and for Eva who stayed longer before returning to Ireland. The wreck of the Loch Ard was discovered in 1967, before the introduction of the Victorian historic shipwreck legislation. In 1969 it was decided that all recovered material should be lodged with the Receiver of Wrecks. In 1980 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum Divers received a permit to recover artefacts from the wreck to safeguard them from looters. In 1982 the site was listed as a Historic Shipwreck, and the Maritime Archaeology Unit recovered loose artefact material. The fork is recognised as being historically significant as an example of cutlery either as part of the flatware service of the ship ‘Loch Ard’ or part of the ship’s cargo, imported for use in Colonial Victoria in the 19th to early 20th century. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Fork; silver plated. The fork is the Old English design and is embossed with several marks. it has recently been restored. Shipwreck artefact from the Loch Ard. 3 letters within an oval (- - S) 4 letters within circles (E) (P) (N) (S) 1 letter within a shield appears to be a [B] flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, victoria, eva carmichael, tom pearce, cutlery, silver flatware, silver plate, antique, old english flatware pattern, eating utensil, fork, silverware, dining utensil -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Light Fitting, c. 1878
This light hanging mechanism could have been used for an adjustable chandelier with candle holders. It would likely be attached to the ceiling by its long stem to suspend the light fitting. A chain would have been threaded around each pulley, with one end joined to the top of the light fitting and the other end joined to a counter weight. The four counter weights would allow the light fitting to be raised or lowered to the desired height with little effort, to allow for lighting the candles or change the intensity of the light. This light fitting was once installed on the famous sailing ship, the Loch Ard, which was built in 1873 and tragically wrecked in 1878.The fitting was recovered from the wreck almost 100 years later, at the time it was discovered. LOCH ARD 1873-1878 – The Scottish-built clipper ship Loch Ard was bound for Melbourne in 1878 with 54 people on board. The mixed cargo it carried included items for the 1880 International Exhibition in Melbourne, one of which was the now famous Majorca ware Minton ‘Peacock’ statue. The Loch Ard was wrecked on June 1st when the ship crashed into Mutton Bird Island, east of Port Campbell. The only survivors were Tom Pearce, a crew member, and Eva Carmichael, a young passenger who was rescued by Pearce. The Gibsons, owners of nearby Glenample Homestead, cared for Tom, and for Eva who stayed longer before returning to Ireland. The wreck of the Loch Ard was discovered in 1967, before the introduction of the Victorian historic shipwreck legislation. In 1969 it was decided that all recovered material should be lodged with the Receiver of Wrecks. In 1980 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum Divers received a permit to recover artefacts from the wreck to safeguard them from looters. In 1982 the site was listed as a Historic Shipwreck, and the Maritime Archaeology Unit recovered loose artefact material. The light fitting is recognised as being historically significant as an example of lighting either as part of the ship ‘Loch Ard’ or part of the ship’s cargo, imported for use in Colonial Victoria in the 19th to early 20th century. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Light fitting; hanging mechanism with simple pulley wheels for pendant light. Metal pipe, closed and hooked at one end, stem has three decorative rings, and open end has a short narrower metal pipe inserted. Narrow pipe has a three tiered, scallop-edged dome attached to the end. The dome encloses remnants of broken chain length and is attached to a set of four pulley wheels arrayed in a circle with their edge sat right angles to each other. The light fitting was recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, victoria, eva carmichael, tom pearce, lighting, lidht fitting, pendant light, chandelier, pulley light, adjustable height light -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Candle Bracket, c. 1878
This candle bracket was recovered from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard after the to the disaster in 1878. The bracket has been hand forged into a pleasing shape and design. The candle holder on the arm of the bracket cn swivel from side to side allowing the light to be adjusted. LOCH ARD 1873-1878 – The Scottish-built clipper ship Loch Ard was bound for Melbourne in 1878 with 54 people on board. The mixed cargo it carried included items for the 1880 International Exhibition in Melbourne, one of which was the now famous Majorca ware Minton ‘Peacock’ statue. The Loch Ard was wrecked on June 1st when the ship crashed into Mutton Bird Island, east of Port Campbell. The only survivors were Tom Pearce, a crew member, and Eva Carmichael, a young passenger who was rescued by Pearce. The Gibsons, owners of nearby Glenample Homestead, cared for Tom, and for Eva who stayed longer before returning to Ireland. The wreck of the Loch Ard was discovered in 1967, before the introduction of the Victorian historic shipwreck legislation. In 1969 it was decided that all recovered material should be lodged with the Receiver of Wrecks. In 1980 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum Divers received a permit to recover artefacts from the wreck to safeguard them from looters. In 1982 the site was listed as a Historic Shipwreck, and the Maritime Archaeology Unit recovered loose artefact material. The candle bracket is an example of light fittings from the ship ‘Loch Ard’ or from part of the ship’s cargo, imported for use in Colonial Victoria in the 19th to early 20th century. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Candle bracket, bronze with fancy floral design. Bracket has been hand wrought with varying widths of flat iron. Bracket’s arm swivels on a pin front of bracket. Bracket was recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, loch ard, victoria, eva carmichael, tom pearce, antique, candle holder, candle bracket, candlestick holder, lighting, ship lighting, ship hardware -
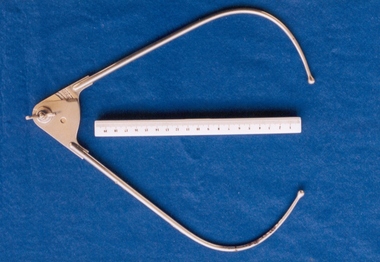 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Pelvimeter used by Box Hill Hospital labour ward
A pelvimeter is used in obstetrics for measurement of the female pelvis, with the aim of attempting to determine whether there will be any potential issues with a vaginal birth. The style of this pelvimeter is similar to Collyer's pelvimeter as depicted in Aesculapius Surgical Instruments p. 2195. This instrument was included with other obstetric instruments, mostly destructive instruments, given to RANZCOG from Box Hill Hospital labour ward in February- March 1998. The maternity service at Box Hill Hospital combined with St George's Hospital in Kew to be known as Birralee Maternity Service. These instruments were collected by Julie Collette, Unit Manager, St George's Kew and given to RANZCOG Museum Curator, Susan Barnett.Pelvimeter. Similar in style to Collyer's pelvimeter. Has adjustable arms hinged with a wingnut, and a scale graduated in inches and centimetres.obstetrics -
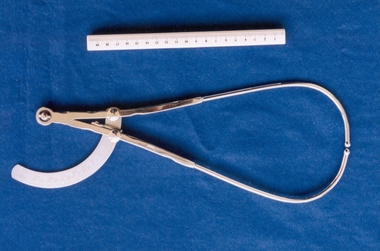 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - 'Ramsay' pelvimeter used by Box Hill Hospital labour ward, Ramsay
A pelvimeter is used in obstetrics for measurement of the female pelvis, with the aim of attempting to determine whether there will be any potential issues with a vaginal birth. This pelvimeter is similar in style to Martin's pelvimeter (see Aesculapius). This instrument was included with other obstetric instruments, mostly destructive instruments, given to RANZCOG from Box Hill Hospital labour ward in February- March 1998. The maternity service at Box Hill Hospital combined with St Geroge's Hospital in Kew to be known as Birralee Maternity Service. These instruments were collected by Julie Collette, Unit Manager, St George's Kew and given to RANZCOG Museum Curator, Susan Barnett.Pelvimeter, manufactured by Ramsay. Metal device with calibrator graduated to 18 inches/ 45 cms. Inscribed " Ramsay" upper arm."Ramsay"obstetrics -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane, 1957
The Alexander Schleicher K4 was designed in the mid 1950s by Rudolf Kaiser as a club training glider and several hundred were built. The Australian Gliding Museum’s K4, VH-IKK, serial number 55, was built in 1957 and purchased by the RAF Air Training Corp. U.K. After some years it was sold to a New Zealand Gliding Club and in 1990 with over 4800 hours, number of launches unknown, it was purchased by the Brisbane Valley Soaring Club and in 1994 was transferred to the Far North Queensland Soaring Centre who operated it from the Mareeba airfield. On 9 January 2000 it was donated to Vintage Gliders Australia by Kevin Sedgman at a presentation ceremony with Alan Patching receiving the glider during the Rally at Lake Keepit. It has been flown regularly at vintage glider rallies and on several occasions at Museum open days. However, it has subsequently been grounded on account of potential structural defects. VH-IKK is one of two K4s in Australia, the other being VH-XJP which is believed to be in storage in Queensland in a damaged condition. When restored, this exhibit will be representative example of the AS-K4 glider-sailplane type.Tandem two seat high wing strutted glider consisting of wood with plywood and fabric wings, tailplane / elevators, fin / rudder, and tubular steel framed, fabric covered fuselage. Prior to restoration work, the glider was finished in a white, green and yellow paint scheme. “Vintage Gliders Australia” name in white lettering on fuselage sides and registration VH-IKK in black lettering on rudderaustralian gliding, glider, sailplane, alexander schleicher, k4, kaiser, raf air training corp, brisbane valley soaring club, far north queensland soaring centre, vintage gliders australia, sedgman, patching -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane, 1960
The Ka 2, a tandem two seat training sailplane of 15 metre wing span, was designed by Rudolf Kaiser for Schleicher in 1953. It was a versatile craft due to its good cross country soaring capability. With the Ka 2B, the design was improved in 1955 by lengthening the wing span to 16 metres and increasing the dihedral and tip washout. The fuselage was lengthened slightly as well. Schleicher built 42 Ka2s from 1953 to 1955 and 75 Ka 2Bs from 1955 to 1957. In addition Schleicher supplied kits for construction of the sailplane by independent builders. The Australian Gliding Museum’s example is the single Ka 2b built in Australia from plans and is designated as GFA-HB-47. The club concerned was the Illawarra Soaring Club of Sydney. The glider registered as VH-GHO and first flew in October 1960. However, within a short time it was badly damaged and needed major repairs which took over a year to complete. After lengthy service at Illawarra Soaring Club it was transferred to the Stirling Gliding Club in Western Australia in August 1976. Again it suffered damage in a landing accident in 1978. The damaged glider was put into storage at Northam where it remained for approximately 11 years. It was acquired by Mike Valentine in 1989 and brought back to flying condition at Bacchus Marsh, Victoria. The last entry in the log book is dated January 1997 at which time it had accumulated 1170 hours from 2446 flights. The last owner prior to transfer to the Australian Gliding Museum was John Ashford of the Geelong Gliding Club. The Museum's Ka 2B sailplane is a potentially airworthy example of this German 1950s sailplane type. It is a rarity in Australia as the only Ka 2b appearing on the Australian register.Tandem two seat sailplane of wood and fabric construction finished in cream and red colour schemeRegistration VH-GHO (with "HO" letters painted on the fin / rudder) Serial number - GFA HB 47 australian gliding, glider, sailplane, schleicher, kaiser, ka 2, illawarra soaring club, stirling gliding club, valentine, ashford -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (Item) - Potential New Workload Estimates For Gaf
Description: A magazine commemorating 50 years of RFDS in WA. History of RFDS and the technologies used. Published by the RFDS in 1985. 84 pages. Significance: GAF Nomad used by RFDS. Level of Importance: . -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Photograph, Potential Recruits - RAAF Personnel 1969, 1969
Framed Colour Photograph of six Vietnamese children standing in front of a RAAF Caribou. Three RAAF Personnel look on.My Vietnam Collection- Norm Cooperraaf, caribou, vietnamese children -
 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryGlass, Bottle
Acriflavine was developed in 1912 by German Paul Erlich. It was an early antiseptic agent before the discovery of penicillin. It was also very effective. In recent years there has been a lot of research on acriflavine for its potential to fight "super bugs", as well as its potential to prevent contracting the common cold. This research is still underway.Amber glass, triangular bottle with black bakelite screw-top lid. Two sides of the bottle are dimpled and the words "NOT TO BE TAKEN" are moulded into the bottle. There is a white [discoloured] manufacturer's label with red printed text and black handwritten text. The bottle is empty.antibacterial, paul erlich, world war i, super bugs -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesPeriodical, Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies, Australian Aboriginal studies : journal of the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies, 2007
1. The moral lexicon of the Warlpiri people of central Australia LR Hiatt This paper discusses words that match ?Good? and ?Bad?; examples of ?Good? and ?Bad? behaviour; morality and law; and egalitarianism and dominance. It also presents a comparison with Gidjingarli (Burarra). 2. Mobs and bosses: Structures of Aboriginal sociality Patrick Mullins (Mount Druitt, NSW) A commonality of Aboriginal social organisation exists across the continent in communities as different as those from the Western Desert across to Cape York, from the towns of New South Wales and Western Australia to cities like Adelaide. This is found in the colloquial expressions ?mob? and ?boss?, which are used in widely differing contexts. Mobbing is the activity where relatedness, in the sense of social alliances, is established and affirmed by virtue of a common affiliation with place, common experience and common descent, as well as by the exchange of cash and commodities. Bossing is the activity of commanding respect by virtue of one?s capacity to bestow items of value such as ritual knowledge, nurturance, care, cash and commodities. Mobbing and bossing are best understood as structures in Giddens? sense of sets of rules and resources involved in the production of social systems, in this case social alliances. Mobbing and bossing imply a concept of a person as a being in a relationship. Attention needs to be given to the way these structures interact with institutions in the wider Australian society. 3. Recognising victims without blaming them: A moral contest? About Peter Sutton?s ?The Politics of Suffering: Indigenous Policy in Australia since the 1970s? and Gillian Cowlishaw?s replies Ma�a Ponsonnet (Universit� Paris- 8-Saint-Denis) Peter Sutton?s texts on Aboriginal violence, health and their politicisation are replied to using his methodology, and acknowledging his convincing points. Sutton rightly denounces a lack of lucidity and scientific objectivity in anthropological debates. These inadequacies impede identification of what Aboriginal groups can do to improve their situations for fear that this identification would lead to blame the victims. At the other end of the ethical spectrum, those who advocate a broader use of what I will call a ?resistance interpretation? of violence fail to recognise victims as such, on the implicit grounds that seeing victims as victims would deprive them of any agency, on the one hand, and entail blame, on the other hand. I aim to define a middle road between those views: the idea that victims should be acknowledged as such without being denied their agency and without being blamed for their own condition. This middle road allows identification of the colonisers? responsibilities in the contemporary situation of Indigenous communities in Australia, and to determine who can do what. Secondly, I show that Sutton?s texts convey, through subtle but recurrent remarks, an ideology of blame rather than a mere will to identify practical solutions. As a consequence, some of his proposals do not stand on a solid and objective causal analysis. 4. 'You would have loved her for her lore?: The letters of Daisy Bates Bob Reece (Murdoch University) Daisy Bates was once an iconic figure in Australia but her popular and academic reputation became tarnished by her retrograde views. Her credibility was also put in doubt through the exposure of her fictionalised Irish background. In more recent times, however, her ethnographic data on the Aborigines of Western Australia has been an invaluable source for Native Title claims, while her views on Aboriginal extinction, cannibalism and ?castes? are being seen as typical of her time. This article briefly reviews what has been the orthodox academic opinion of her scientific achievement before summarising what is reliably known of her early history and indicating what kind of person is revealed in the 3000 or more letters that she left behind. 5. What potential might Narrative Therapy have to assist Indigenous Australians reduce substance misuse? Violet Bacon (Curtin University of Technology) Substance misuse is associated with adverse consequences for many Australians including Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples. Extensive research has been conducted into various intervention, treatment and prevention programs to ascertain their potential in reducing substance misuse within Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal communities. I explore the potential of Narrative Therapy as a counselling intervention for assisting Indigenous Australians reduce the harm associated with substance misuse. 6. Bone points from the Adelaide River, Northern Territory Sally Brockwell (University of Canberra) and Kim Akerman (Moonah) Large earth mounds located next to the vast floodplains of the lower Adelaide River, one of the major tropical rivers draining the flat coastal plains of northern Australia, contain cultural material, including bone points. The floodplains of the north underwent dynamic environmental change from extensive mangrove swamps in the mid-Holocene, through a transition phase of variable estuarine and freshwater mosaic environments, to the freshwater environment that exists today. This geomorphological framework provides a background for the interpretation of the archaeology, which spans some 4000 years. 7. A different look: Comparative rock-art recording from the Torres Strait using computer enhancement techniques Liam M Brady (Monash University) In 1888 and 1898, Cambridge University?s Alfred C Haddon made the first recording of rock-art from the Torres Strait islands using photography and sketches. Systematic recording of these same paintings and sites was carried out from 2000 to 2004 by archaeologists and Indigenous Torres Strait Islander and Aboriginal communities as part of community-based rock-art recording projects. Computer enhancement techniques were used to identify differences between both sets of recordings, to reveal design elements that Haddon missed in his recordings, and to recover images recorded by Haddon that are today no longer visible to the naked eye. Using this data, preliminary observations into the antiquity of Torres Strait rock-art are noted along with recommendations for future Torres Strait region rock-art research and baseline monitoring projects. 8. Sources of bias in the Murray Black Collection: Implications for palaeopathological analysis Sarah Robertson (National Museum of Australia) The Murray Black collection of Aboriginal skeletal remains has been a mainstay of bio-anthropological research in Australia, but relatively little thought has been given to how and why this collection may differ from archaeologically obtained collections. The context in which remains were located and recovered has created bias within the sample, which was further skewed within the component of the collection sent to the Australian Institute of Anatomy, resulting in limitations for the research potential of the collection. This does not render all research on the collection unviable, but it demonstrates the importance of understanding the context of a skeletal collection when assessing its suitability for addressing specific research questions.maps, b&w photographs, colour photographs, illustrations, graphs, chartswarlpiri, sociology, daisy bates, substance abuse, narrative therapy, rock art, technology and art, murray black collection, pleistocene sites, watarrka plateau -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumFlyer - LEAFLET
COLLECTION OF TOURIST ATTRACTIONS OF TALBOT & CLUNES SHIRE. COLLECTED BY TALBOT & CLUNES TO ANNOUNCE THE MEMBERSHIP WITH MARYBOROUGH AND DISTRICT DEVELOPMENT COMMITTEE TO SUPPORT AND DEVELOP THE BUSINESS AND TOURIST POTENTIAL IN CENTRAL VICTORIAlocal history, document, leaflet, tourism -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumReport, Australian Wool Corporation survey for market potential of wool minority blends
"Australian Wool Corporation survey for market potential of wool minority blends " - WD Scott & Co Pty Ltd : a survey of Australian garment manufacturers and retailers.textile industry fashion textile fibres textile fibres - synthetic, cloth - woollen, cloth - worsted, textile industry, fashion, textile fibres, textile fibres - synthetic -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumSlide, Lincoln
Slide of a longwoolled, Lincoln sheep. Longwools are usually mated to merino ewes to produce large-framed vigorous, first-cross sheep which produce better and finer wool than the longwool and have better meat potential than the merino. Slide printed by Audio Visual Education Centre, Education Department of Victoria. Formerly stored in presentation folder as part of "British Breeds of Sheep Set No. 448" series by the Audio Visual Education Centre, Education Department of Victoria.Slide of a Lincoln sheep.BRITISH BREEDS OF SHEEP / Set No. 448 / No. 1 / Lincoln VISUAL EDUCATION CENTRE / EDUCATION DEPT. OF VICTORIAlincoln sheep, sheep, british, slide, sheep - british -
 Ambulance Victoria Museum
Ambulance Victoria MuseumBrochure, Station Officer Certificate Course, Circa 1983
Used to provide careers information to potential Ambulance station officersFold out brochure. Ambulance Service Victoria logo top left corner. Ambulance Officers Traing Centre logo lower right cornerSTATION OFFICER CERTIFICATE COURSE ambulance officers training centre -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumBook (Item) - Airline Theory Book, David Robson, In Safe Hands: The How and Why of Airline Travel, 02/1999
Seems to be a book designed to offer reassurance to potential passengers about the safety of flight. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumBooklet (Item) - Discount fares and the potential for profit and loss, Boeing 737-200
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumBooklet (Item) - Analysis of air cargo potential, Boeing Europe- Pacific rim Australasia
