Showing 374 items
matching law family
-
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomCD, Interview: David Chambers, 11 March 1998
CD Oral History Interview of No 231 Trumpeter David Lee Chambers, 4th Australian Light Horse by his son-in-law Eric Lehmann,Presented to the Lighthorse Museum From the family of David Chambers Lisa Moloney 03 98738576 Carole Lehmann 03 95476042oral history, david chambers, 4th light horse, lehmann -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Functional object - Spirit Level
This item was given to the Historical Society in 1972, with the donor indicating that the spirit level belonged to the Henty family. The Hentys of Portland are regarded as the first permanent settlers in the State of Victoria (1834). Stephen Henty, with his brother Edward, was involved in the whaling industry in Portland. He also had shipping interests, operating a regular Western District shipping service (‘Champion’, ‘Lady Bird’, ‘Western’, ‘Edina’ etc) and a property ‘Cadnook’, near Harrow. Stephen Henty had close connections with Warrnambool not only because of his shipping interests but also because he was the brother-in-law of an early Warrnambool Harbour Master, Captain Frank Helpman. A spirit level was an essential tool for early settlers as they often built their own homes and constructed the roads nearby, needing to ascertain if what was being constructed was on level ground.It does not seem possible to establish whether this item belonged to the Henty family or to a Henty property. But in the Historical Society collection we have a piece of sheet music which includes the handwriting ‘Mrs Smalpaige, Cadnook’, ‘S. J. Henty’ and the date ‘8th August 1859’. Also the Warrnambool Art Gallery has an authentic Henty piano dating from 1837 and Stephen Henty’s wife died in Hamilton in 1906 so it is possible that the spirit level came to us from a Henty family descendant living nearby via Mr N. Kelly. If the Henty provenance can be proved then this item is of high significance.This is an unvarnished wooden spirit level, apparently home made, with a bubble in the centre. The top has been attached with eight screws, now much rusted. There appears to be some letters in the bubble area but they have not been deciphered “Hentys spirit level, oldest in Australia” is written in ink on the back of the objectspirit level, henty brothers portland, warrnambool, henty family -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Functional object - Bottle, Reeves Dry Ginger, Circa late 20th century
Ralph Reeves purchased an established cordial factory in the early 1900’s from the estate of J Fletcher. It was operated by the Reeves family, firstly Reginald, followed by his son-in-law Murray Moon until the latter part of the 20th century. A common object familiar to a large number of people in the Warrnambool area with links to one of Warrnambool’s longest established family businesses.Two clear glass bottles with rib pattern and circles at bottom of neck. Transfer label with small white circles and one larger red one. Top is white with orange writing. Contains Dry Ginger.Enjoy Reeves’ ice cold on the front, Bottled by R.J Reeves Warrnambool. Preservative added artificially coloured. Net contents 7 FL. OZ. warrnambool, reeves, reeves soft drink, reeves cordial. -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Functional object - Bottles, Syphon R.J Reeves, Early to mid 20th Century
Ralph Reeves purchased an established cordial factory in the early 1900’s from the estate of J Fletcher. It was operated by the Reeves family, firstly Reginald, followed by his son-in-law Murray Moon until the latter part of the 20th century.A common object familiar to a large number of people in the Warrnambool area with links to one of Warrnambool’s longest established family businesses. Two clear glass. Cylindrical with 12 ribs. Chrome metal top with lever and spout. Logo etched on front of bottles Inscriptions and Markings: “R. J. Reeves” engraved on side of lid. “R. J. Reeves Warrnambool in oval surrounding RJR. This syphon remains the property of R. J. Reeves Warrnambool and its use by others is prohibited.British syphon company Limited London.warrnambool, reeves, soda syphon, reeves soft drink, reeves cordial. -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybook, Constitution of Rechabites, 1906
This item belonged to Alan Richardson, a sawmiller at Tabbara. He helped to build and held a ticket for the paddle steamer "Curlip". He was a member of the Rechabites from March 3 1892. The Independent Order of Rechabites began in Salford, England in 1835. It was named after Rechab, a leader in the Old Testament, who instructed his tribe to refrain from drinking alcohol. During the Industrial Revolution the idea of temperance became popular as damage was caused to families by alcohol. In Australia it was first established in Tasmania in the mid 1800s. In 1847 a branch was created in Victoria, and it then spread to other States. Members were provided with assistance during times of sickness, death and hardship. This item is associated with the Richardson family, early settlers in the Orbost district.A small grey book with a black spine. The title and details are in black print. Inside is a magazine cutting - "The Rechabite July 1st 1931". This book is the "Constitution of the Victorian District, No 82" and contains the district by-laws."This is to certify that Bro. A.J. Richardson was admitted clearance a member of the Orbost.........."richardson-alan rechabites -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societymagazine, The Argus and Australasian Coronation Souvenir 24 May 1937, 24 May 1937
The Argus was a morning daily newspaper in Melbourne that was established in 1846 and closed in 1957 and was considered to be the general Australian newspaper of record for this period. Widely known as a conservative newspaper for most of its history. George VI became King after his brother, King Edward VIII, abdicated in 1936. The coronation of King George VI and Queen Elizabeth as King and Queen of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Commonwealth and as Emperor and Empress of India took place at Westminster Abbey, London, on 12 May 1937. King George ascended the throne upon the abdication of his brother, King Edward VIII, on 10 December 1936, three days before his 41st birthday. Edward's coronation had been planned for 12 May 1937 and it was decided to continue with his brother and sister-in-law's coronation on the same date. This newspaper provides a detailed pictorial representation of the coronation of King George V1 in London on 12 May, 1937. The commonwealth countries, including Australia joined in the celebration. Saving an item dedicated to the royal family is typical of the general feeling of respect and admiration felt by the rural communities towards the British Royal Family.A special edition souvenir newspaper which is a forty page pictorial commemorating the Coronation of King George VI. It is titled "THE ARGUS and AUSTRALIAN CORONATION SOUVENIR". On the front cover is a coloured painting /print of a horse parade/procession with banners printed by "ROWED". In the bottom right corner is the cost - 1/-. It contains a complete record of the ceremonies as well as large portrait photos of the royal family designed for framing. argus-newspaper george-v1 coronation -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Caulking Tool, Ward & Payne Ltd, Late 19th century
Caulking is the traditional technique used on wooden vessels built with butted or clinker-built planks to fill the gaps between these planks while still allowing the wood to flex and move. This involved driving the irons, hammered in with the mallet, deep into the seams to open them up. After this, spun yarn, oakum (hemp) or cotton was driven deep into the gaps. The hemp or cotton was soaked in creosote or pine tar to make the joins watertight. Caulking also played a structural role in tightening up the hull or deck by reducing the longitudinal movement of the neighbouring planks. The subject item was made by Ward & Payne of the Limbrick Works at Hillsborough, Sheffield England manufacturers of hand-forged tools. Their trademark registered in 1850 was a Letter "W" & "P" stamped into the steel. The firm was established by David Ward (1767-1822) in 1803 the company became David Ward & Sons, in 1837 after Ward's son Edward joined the firm. In 1845 Henry Payne the founder's son-in-law became a partner but died in 1850 after which the company reverted to the Ward family. The business then concentrated on making carving tools, chisels and gouges. In 1882 David Ward's grandson David Ward Jr. (1835-1889) purchased land and built a factory at Sheffield North known as the "Limerick Wheel". For a time Wards operated from both 106-114 West Street Sheffield and at Limbrick Road, Hillsborough on the river Loxley. By 1911 they had expanded into making spades, forks, sheep shears and many other types of edged tools including drills and wood planes. In 1967 Wilkinson Sword purchased all the company's share capital and continued to sell Ward & Payne tools until 1970 when a fire burned the factory down and housing development was built on the site. The subject item is significant as it gives a snapshot of the technological development of sailing ships and their operation before steam-powered vessels took over around the world. Tools such as the subject item demonstrate the traditional craftsmanship and skill of the shipwright and the aesthetic quality of the timber ships designs of the time. Caulking tool with square end"WARD Sheffield"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, james s steele, caulking iron, caulking tool, shipwright tools, ward & payne sheffield, forged tools -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDog, 19th century
This toy dog was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife.Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history.China toy dog salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. This moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and is tan in colour. The dog is solid with a pitted surface1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Knife, Made on or before September 1891
This sheath knife belonging originally to German seaman Julius Gebauhr and an artifact associated with the story of the survivors of the wreck of Fiji. A three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a varied cargo consisting of cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, various spirits, sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos and other musical instruments. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in a squally and boisterous south-west wind, the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers' calculation of his position. At about 2:30 am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed Fiji struck rock only 274 meters from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Efforts were made to lower boats but all capsized or became swamped two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after the line broke. The other, 17-year-old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt without a line, which he had cut loose with his sheath-knife when it becomes tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the cliffs in search of help. At about 10 am on Sunday a party of land selectors including F. J. Stanmore, Leslie Dickson found Gebauer. They were on their travels back from Princetown towards Moonlight Head. Gebauer was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in a singlet, socks, belt and his sheath-knife. His rescues gave him food and brandy and some clothing and gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stanmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and was set up on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line the light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, as many as five at a time, however, some were washed off. Only 14 of the 24 men who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. The wreck of Fiji has smashed apart within 20 minutes of the last man being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6 m of water. Of the 26 men on Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach. They were buried on the clifftop above the wreck. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship and his Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe who had dragged the captain out of the surf with his silver cased pocket watch, the only possession that he had left, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother in law Gilbert Hulands as payment of a debt. Since that time it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stanmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle has a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200 m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are china miniature animals, limbs from small china dolls, rubber balls, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with this sheath knife and Captain Vickers’ pocket watch. Flagstaff Hill’s collection from the wreck of the Fiji and Julius Gebauhr knife is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the vessel, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S 259). The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th-century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo still evident. Also the story of the heroic attempt by many to save the crew of the Fiji. The knife also represents an aspect of shipping history and fits in well with Victoria's framework of historical themes of living with natural processes as items such as these contribute to a better understanding of Victoria’s cultural history.Knife, metal with black wooden handle. Handle is riveted to knife in 3 places, with shaft of knife between the 2 parts of the handle. The handle also has a carved ring around the end, possibly for attaching a wrist strap. Knife blade is pointed in the centre of the tip and is rusty. The knife has a rectangular metal plaque on handle with inscription. The hand crafted dark brown, soft leather sheath is shaped to fit the knife and joined at the back with cross stitching. The sheath also has a leather belt strap that has come away from the sheath at one end.Metal plaque “FROM JULIUS GEBAUHR/”FIJI” /TO F.J.S.” (F J Standmore recipient)1891, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, knife, fiji, pocket watch, moonlight head, gebauhr, stansmore, wreck bay, sheath knife -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTextile - Rope Sample, After September 1891
The light line or rope used to construct this Turk’s Head knot was part of the line line-throwing apparatus used by the Rocket Rescue Crew. In normal operation a rocket carrying the line was fired over a ship, fastened to the ship, then hauled by the crew to pull a heavier rope from shore, which would have a canvas ‘breaches buoy’ attached to it. A tripod or triangle would be used to keep it free from breakers and rocks. One by one the crew on the wreck would sit in the buoy and be hauled safely back to shore. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the last man being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967.This rope is part of the collection of artefacts from the wreck of the Fiji. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Rope salvaged from the distress rocket rope line used in the rescue of the crew of the sailing ship “Fiji”. The light-weight brown rope has been crafted into a decorative 'Monkey fist' or 'Turk’s head' knot using three interwoven strands. 1891, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, rope, moonlight head, wreck bay, distress rocket, line, light line, rocket rescue apparatus, rocket equipment, rocket line -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCandlestick holder, Made on or before 1891
This candlestick holder is one of the artefacts salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the last man being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are china miniature animals, limbs from small china dolls, rubber balls, a glass bottle and a sample of rope from the distress rocket. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife.This candlestick holder is Artefact Reg No Fiji/2, part of the Fiji collection. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Candlestick holder or Chamber Candle. Made of china, off white in colour with crazed glazing. The round concave dish has the base of a round candle holder in centre (remainder of holder has been broken off). The base of a circular china finger ring is attached to both the rim and the dish, about ¾ of the way towards the centre - the top 2/3rds of the finger ring is broken off. A conical thimble-like spike, placed about a quarter of the way around from the finger ring, is intact. This spike was probably used to hold a candle snuffer of similar but larger size and shape. The candlestick holder was recovered from the wreck of the Fiji.1891, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, fiji, pocket watch, moonlight head, candlestick holder, candle holder, chamber candle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBottle, circa 1885 - 1891
This bottle was one of the items salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji in 1891. Joseph Bosisto began manufacturing Eucalyptus Oil in Australia from 1854. This bottle is marked ‘J. BOSISTO”, which probably dates it from 1885 when the company J. Bosisto & Co. was formed. The marking on the bottom of the bottle “GERMAN/B_ _ E” could mean that the bottle was imported by J. Bosisto from Germany. In the early years bottles were imported from overseas countries including England and Germany. In 1872 the Melbourne Bottle Works was established to supply the bottles locally and more cheaply but had difficulty keeping up with the supply. From 1865 Australian-made Bosisto’s Eucalyptus Oil began to be exported to England then later to Germany and other countries. Bosisto’s Eucalyptus Oil won many prizes at exhibitions between 1854 – 1891. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the last man being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are china miniature animals, limbs from small china dolls, rubber balls, this glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. The glass bottle is registered as “Artefact Reg No Fiji/1”. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Clear glass oval medical bottle with rounded corners and flattened sides on front and back surfaces. Opening of bottle has a lip around it and could have been sealed with a stopper. There is a chip in the lip. One face of the bottle has a rectangular border with a name embossed vertically on it, “J. BOSISTO / RICHMOND”. The oval base of the bottle also has letters embossed on it “GE_ _AN” “B _ _ _ _ _”. There is also a large chip out of the base. The sides of the bottle have a vertical joining line. The bottle was recovered from the wreck of the Fiji.Flat side of bottle has rectangular border with “J BOSISTO / RICHMOND” embossed in the centre. The base of the bottle has “G E . . A N/B . . . . . .” embossed on it. Other letters have been removed with the chip. (probable wording was ‘GERMAN/BOTTLE)warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, fiji, 1891, glass bottle, medicine bottle, bosistos, j bosistos, german bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDoll's leg, Bisque dolls were being made from the 1860’s
This doll’s leg was part of the cargo from the Fiji and was part of the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife.Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Doll’s leg salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. This moulded leg, made of bisque (sometimes described as china or porcelain) is for a small doll. The leg is solid rather than jointed, and goes from the lower thigh down to the foot, which has a shoe-shaped heel. The white coloured leg is finished with glazed paint and the shoe of the foot is painted black. The leg is discoloured in places with a tan colour. There is a groove around the top of the leg, which would enable the leg to be attached to the cloth body of a doll.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, doll, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, dolls limb, dolls leg, toys, doll's leg, doll's limb -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDoll's arm, Bisque dolls were being made from the 1860’s
This doll’s arm was part of the cargo from the Fiji and was part of the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Doll’s arm salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. This moulded arm, made of bisque (sometimes described as china or porcelain) is for a small doll. Its hand has the fingers touching each other with the thumb tucked into the palm. The white coloured arm is finished with glazed paint. The arm is discoloured in places with a tan colour. The arm is solid rather than jointed and goes from hand to upper arm. There is a groove around the top of the arm, which would enable the arm to be attached to the cloth body of a doll.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, doll, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, doll's arm, doll's limb -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDoll's leg, Bisque dolls were being made from the 1860’s
This doll’s leg was part of the cargo from the Fiji and was part of the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Doll’s leg salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. This moulded, shapely leg, made of bisque (sometimes described as china or porcelain) and tan in colour, is for a small doll. It has a shoe shaped foot complete with heel. The leg would have probably been finished with paint and the shoe would also be painted on. However this leg has no paint remaining. The leg is solid rather than jointed and goes from foot to lower thigh. Around the top edge of the thigh is a groove, which would enable the leg to be attached to the cloth body of a doll.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, doll, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, dolls limb, dolls leg, toys, doll's limb, doll's leg -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSlate pencil, Made on or before May 1891
Slate pencils were made from a rod of soft slate material and used for writing on thin slate boards. The slate boards were approximately 9cm x 12cm used in schools for writing practice in place of pencil and paper, which were more expensive and less durable. They could be used then easily erased for re-use. In work places, slate boards were sometimes bound into slate books The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are china miniature animals, limbs from small china dolls, rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Remnants of a black slate pencil salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. Pencil has no casing and is in three pieces. One piece is broken laterally and has a rounded end. The other two pieces have a longitudinal break and fit together. (The nature of the break indicates a material of natural formation, for example sedimentary rock such as slate.) flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, slate pencil, pencil, slate board, writing, stationery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLeisure object - Monkey, ca. 1891
This toy monkey was part of the cargo from Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool-based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation of Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous southwest winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30 am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17-year-old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut loose with his sheath knife when it became tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach and then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10 am on Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in a singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath knife, ready for all emergencies. At first, they were concerned about his wild and shaggy-looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 remaining on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29-year-old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26-year-old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of Fiji smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Master's Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism of the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue were in half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. The essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers' homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the lootings, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand-crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, and limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, a sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Toy white China monkey in a seated pose. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and is creamy sand colour with a rust-coloured mark on its face. The surface is slightly pitted. It was salvaged from the wreck of the ship FIJI. 1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, monkey -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMonkey, 19th Century
This toy monkey was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. This toy monkey is classified as Fiji 5 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Ceramic toy monkey salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The monkey is in a seated pose with its arms around its knees. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and the material is an orange colour. The surface is slightly pitted.ceramic, china, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, bisque, toys, miniature animals, monkey, ornament -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMonkey, 19th century
This toy monkey was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. This toy monkey is classified as Fiji 5 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. China toy monkey salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The monkey is in a seated pose with its arms around its knees. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and the material is an pinkish brown colour with darker orange in its lap. The surface is worn and slightly pitted.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, monkey -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageRabbit, 19th century
This toy rabbit was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife This toy rabbit is classified as Fiji 4 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. China toy rabbit salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The rabbit is in a lying pose. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and the material is an orange-sandy colour with darker orange markings. The surface is slightly pitted.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, rabbit -
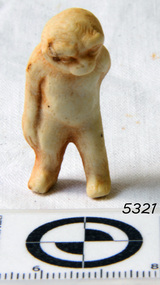 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageGorilla, 19th century
This toy gorilla was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife This toy gorilla is classified as Fiji 7 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. China toy gorilla salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The gorilla is in a standing pose. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and the material is pale creamy colour with a slightly pitted surface.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, gorilla -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCat, 19th century
This toy cat was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife.This toy cat is classified as Fiji 10 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. China toy cat salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The cat is in a resting pose. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and the material is tan in colour with a slightly pitted surface.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, cat -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageRubber ball, 19th century
This rubber ball was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. A press report notes that the balls collected from the Fiji’s cargo were originally red and white. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. This toy rubber ball is classified as Fiji 3 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Rubber ball salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The rubber is perishing and the surface is pitted and bumpy. The material is tan in colour with a slightly pitted surface. 1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, rubber ball -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageRubber ball, 19th Century
This rubber ball was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. A press report notes that the balls collected from the Fiji’s cargo were originally red and white. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. This toy rubber ball is classified as Fiji 3 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Rubber ball salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The rubber is perishing and the surface is pitted and bumpy. The material is tan in colour with a slightly pitted surface. warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, wreck bay, moonlight head, 1891, cargo, rubber ball, toy, fiji, captain vickers, william vickers -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph, Joseph Jordan Photographic Studio, Miss Christina Giles, before May 1899
This photograph is of Christina Giles, who died in Wangoom, Warrnambool, in 1899 at 7 years, 5 months and 4 days old and is one of many 19th century items of furniture, linen and crockery donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by, Vera and Aurelin Giles. The items are associated with Warrnambool and the Giles Family history. Items donated by the family have come to be known as the “Giles Collection”. Many items in the Lighthouse Keeper’s Cottage were donated by Vera and Aurelin Giles and mostly came from the home of Vera’s parents-in-law, Henry Giles and his wife Mary Jane (nee Freckleton) who married in 1880 and whose photos are on display in the parlour. Henry was born at Tower Hill in 1858, and was a labourer on the construction of the Warrnambool Breakwater before leaving in 1895 for around seven years to build bridges in NSW. Mary Jane was born in 1860 at Cooramook and she attended Mailor’s Flat State School and where she eventually was to become a student teacher. After which she became a governess at “Injemiara” where her grandfather, Francis Freckleton, had once owned land. Henry and Mary’s family consisted of six, some of the children were born at Mailor’s Flat and later some children at Wangoom. They lived with their parents at Wangoom and Purnim west, and this is where Henry died in 1933 and Mary Jane in 1940. Jordan, Warrnambool refers to Joseph Jordan who operated a photographic studio in Warrnambool from the late 1880s. His work was prevelent in Victoria's Western District of Victoria.This photograph of Christina Giles is of social significance at a local level, because it not only illustrates the level of material support the Warrnambool community gave to Flagstaff Hill during it’s establishment. But the Giles collection also gives us today a snapshot into what domestic life was like in early colonial times prior to Federation and the high mortality rates amongst children during the early years of colonial settlement. The photograph is also significant for is association with renowned Western District photographer, Joseph Jordan.Photograph of Christina Giles standing on chair in a decorative carved wood frame with floral design in abstract shape. Photo by Jordan of Warrnambool. Christina Giles died in Warrnambool in 1899 at 7 years, 5 months, 4 days of age. It is part of the Giles Family Collection. "Jordan Warrnambool" ( Photographers) flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, christina giles, giles collection, giles family, giles history, henry and mary giles, henry giles, tower hill, cooramook, warrnambool breakwater, mailor’s flat, wangoom, 19th century personal effects, joseph jordan, jordan photography -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Mrs Mary Jane Giles of Woodford, International Art Company, Circa 1880
The pair of photographs of Mr Henry and Mrs Mary Jane Giles was made by the International Art Company, the price was 30 shillings and the choice of frame was Rosewood. It is part of the Giles Collection, which also includes a photograph of the couple's daughter Christina Giles, who died in 1899 aged seven years. There are many 19th century items of furniture, linen and crockery donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by, Vera and Aurelin Giles. The items are associated with Warrnambool and the Giles Family history. Items donated by the family have come to be known as the “Giles Collection”. Many items in the Lighthouse Keeper’s Cottage were donated by Vera and Aurelin Giles and mostly came from the home of Vera’s parents-in-law, Henry Giles and his wife Mary Jane (nee Freckleton) who married in 1880 and whose photos are on display in the parlour. Henry was born at Tower Hill in 1858, and was a labourer on the construction of the Warrnambool Breakwater before leaving in 1895 for around seven years to build bridges in NSW. Mary Jane was born in 1860 at Cooramook and she attended Mailor’s Flat State School and where she eventually was to become a student teacher. After which she became a governess at “Injemiara” where her grandfather, Francis Freckleton, had once owned land. Henry and Mary’s family consisted of six, some of the children were born at Mailor’s Flat and later some children at Wangoom. They lived with their parents at Wangoom and Purnim west, and this is where Henry died in 1933 and Mary Jane in 1940.This photograph is locally significant due to its association with a local pioneering family. The Giles family collection is of social significance at a local level, because it not only illustrates the level of material support the Warrnambool community gave to Flagstaff Hill during it’s establishment. But the Giles collection also gives us today a snapshot into what domestic life was like in early colonial times prior to Federation. The photograph itself is of added significance as we can see the faces of the family whose lives the collection represents . Portrait photograph mounted in an oval rosewood frame, one of a pair. This photograph is Mary Jane Giles, dressed formally showing chest to head. Her hair is tied back hair and she has a neck band. The couple in the pair of photographs is Mr and Mrs Giles of Woodford, Victoria. The photographic studio was the International Art Company. It is part of the Giles Collection.Inscription on back of frame "International Art Company 30/-" "Rosewood"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, photograph late 1800s, oval wooden frame, portrait, mrs mary jane giles of woodford victoria, giles collection, henry giles, tower hill, cooramook, warrnambool breakwater, mailor’s flat, wangoom, 19th century personal effects, mary giles, christine giles -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ceramic Bottle (Chinese Style), Minton Potteries, Late 19th century
The subject item is believed to be a "Chinese style stoneware liquor bottle used to store "Tiger Whiskey" (rice wine). These Chinese liquor jugs are made of glazed pottery known as brown stoneware and have been made throughout the centuries by many makers until well after American Prohibition. Later varieties from the mid 20th century are commonly found in the USA with the raised lettering "Federal Law Forbids Sale Or Re-use of this bottle" a sure sign of post-1934 manufacture. This example is interesting as it has a British Minton mark of two triangles on the base indicating a date of 1879 and was likely exported to Australia by Minton. These ceramic bottles virtually always have irregularities and flaws which indicate a product has been hastily manufactured, in any event, this is a fine example of a relatively common item that may have been copied by Minton and sold as a decorative domestic item for display or mass produced for storing liquor. Giles Family: The pair of ceramic bottles were given to Vera Giles by Jim Thompson and are just many 19th century items of furniture, linen and crockery donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by, Vera and Aurelin Giles. The items are associated with Warrnambool and the Giles Family history. Items donated by the family have come to be known as the “Giles Collection”. Many items in the Lighthouse Keeper’s Cottage were donated by Vera and Aurelin Giles and mostly came from the home of Vera’s parents-in-law, Henry Giles and his wife Mary Jane (nee Freckleton) who married in 1880 and whose photos are on display in the parlour. Henry was born at Tower Hill in 1858, and was a labourer on the construction of the Warrnambool Breakwater before leaving in 1895 for around seven years to build bridges in NSW. Mary Jane was born in 1860 at Cooramook and she attended Mailor’s Flat State School and where she eventually was to become a student teacher. After which she became a governess at “Injemiara” where her grandfather, Francis Freckleton, had once owned land. Henry and Mary’s family consisted of six, some of the children were born at Mailor’s Flat and later some children at Wangoom. They lived with their parents at Wangoom and Purnim west, and this is where Henry died in 1933 and Mary Jane in 1940. A significant item of lead-glazed ceramic with the possibility it was made by the Minton potteries in England who were renowned for making quality pottery. The item style is in all probability a copy of a Chinese liquor bottle that was in common use throughout the British colonies and America up until the mid 20th Century. The Giles family collection has social significance at a local level, because it illustrates the level of material support the Warrnambool community gave to Flagstaff Hill when the Museum was established.Chinese liquor bottle one of a pair, lead glazed ceramic, dark brown and blue/black. Part of the Giles Collection.Mark of a double triangle, apex touching, on base, (Minton mark for 1879).flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, vase, pottery, ceramic ornament, domestic ware, late 19th - early 20th centuy ornament, giles collection, henry giles, tower hill, cooramook, warrnambool breakwater, mailor’s flat, wangoom, 19th century household goods -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFurniture - Sideboard, Circa 1880
This sideboard was from the home of Henry and Mary Jane Giles, who lived in Mailor's Flat, Wangoom, and Purnim West, Victoria, and is part of the many 19th century items of furniture, linen, and crockery donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by, Vera and Aurelin Giles. The items are associated with Warrnambool and the Giles Family history. Items donated by the family have come to be known as the “Giles Collection”. Many items in the Lighthouse Keeper’s Cottage were donated by Vera and Aurelin Giles and mostly came from the home of Vera’s parents-in-law, Henry Giles, and his wife Mary Jane (nee Freckleton) who married in 1880 and whose photos are on display in the parlour. Henry was born at Tower Hill in 1858, and was a labourer on the construction of the Warrnambool Breakwater before leaving in 1895 for around seven years to build bridges in NSW. Mary Jane was born in 1860 at Cooramook and she attended Mailor’s Flat State School and where she eventually was to become a student-teacher. After which she became a governess at “Injemiara” where her grandfather, Francis Freckleton, had once owned land. Henry and Mary’s family consisted of six, some of the children were born at Mailor’s Flat, and later some children at Wangoom. They lived with their parents at Wangoom and Purnim west, and this is where Henry died in 1933 and Mary Jane in 1940.The Giles family collection is of social significance at a local level, because it not only illustrates the level of material support the Warrnambool community gave to Flagstaff Hill during it’s establishment. But the Giles collection also gives us today a snapshot into what domestic life was like in early colonial times prior to Federation.Kauri Pine Mirror Backed Sideboard, two drawers and two doors to the base, the doors being carved in the traditional manner with a leaf design, brass swing handles are fitted to each of the drawers. The back has two shelves each supported on two turned columns, three mirrors are fitted into carved panels matching design as doors.The pediment is also carved in the same manner finishing with scrolled edges. Circa 1880. This item is part of the Giles Collection.Marked "Villa Rica" "Ambassadors" "Claro" "50" In pencilflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, sideboard, furniture, dresser, giles collection, henry giles, vera giles, tower hill, cooramook, mailor’s flat, wangoom, 19th century furniture, purnim west, 1880s furniture -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Adze, Ward & Payne Ltd, Between 1843 to Mid 20th Century
An adze is an ancient and versatile cutting tool and has been in use for thousands of years. Adze are similar to an axe but with the cutting edge perpendicular to the handle rather than parallel. They have been used since the Stone Age. Adzes are hand tools used for smoothing or carving wood. The subject item was made by Ward & Payne of the Limbrick Works at Hillsborough, Sheffield England manufacturers of hand-forged tools. Their trademark registered in 1850 was a Letter "W" & "P" stamped into the steel. The firm was established by David Ward (1767-1822) in 1803 the company became David Ward & Sons, in 1837 after Ward's son Edward joined the firm. In 1845 Henry Payne the founder's son-in-law became a partner but died in 1850 after which the company reverted to the Ward family. The business then concentrated on making carving tools, chisels and gouges. In 1882 David Ward's grandson David Ward Jr. (1835-1889) purchased land and built a factory at Sheffield North known as the "Limerick Wheel". For a time Wards operated from both 106-114 West Street Sheffield and at Limbrick Road, Hillsborough on the river Loxley. By 1911 they had expanded into making spades, forks, sheep shears and many other types of edged tools including drills and wood planes. In 1967 Wilkinson Sword purchased all the company's share capital and continued to sell Ward & Payne tools until 1970 when a fire burned the factory down and housing development was built on the site.The subject item is significant as it gives a snapshot of the technological development of sailing ships and their operation before steam-powered vessels took over around the world. Tools such as the subject item demonstrate the traditional craftsmanship and skill of the shipwright and the aesthetic quality of the timber ships designs of the time. Adze with wooden handle curved painted green with patent number and maker's name inscribed on inside curve of blade. Inscribed "Patd 561 Ward" "2w". flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, smoothing tool, hand tool, carpenders tool, adze, coopers tool, woodworking tools -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFurniture - Linen Chest, First half of the 19th Century
This chest came from County Cavan, North Ireland, with Jane Fleming, when she migrated to Australia arriving at Port Fairy in approximately 1863. Jane Flemming was about 6 or 7 years old at the time and later was to become the mother of Mary Jane Giles (nee Flemming). This chest is one of many 19th century items of furniture, linen and crockery donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by, Vera and Aurelin Giles. The items are associated with Warrnambool and the Giles Family history. Items donated by the family have come to be known as the “Giles Collection”. Many items in the Lighthouse Keeper’s Cottage were donated by Vera and Aurelin Giles and mostly came from the home of Vera’s parents-in-law, Henry Giles and his wife Mary Jane (nee Freckleton) who married in 1880 and whose photos are on display in the parlour. Henry was born at Tower Hill in 1858, and was a labourer on the construction of the Warrnambool Breakwater before leaving in 1895 for around seven years to build bridges in NSW. Mary Jane was born in 1860 at Cooramook and she attended Mailor’s Flat State School and where she eventually was to become a student teacher. After which she became a governess at “Injemiara” where her grandfather, Francis Freckleton, had once owned land. Henry and Mary’s family consisted of six, some of the children were born at Mailor’s Flat and later some children at Wangoom. They lived with their parents at Wangoom and Purnim west, and this is where Henry died in 1933 and Mary Jane in 1940.The chest is of historical significance as an example of an early piece of furniture brought to Australia by Jane Flemming when she migrated to Australia during the mid 19th century. The chest is associated with the Giles family as Jane later was to become the mother Of Mary Jane Giles (nee Flemming). The Giles family collection is of social and historical significance at a local level, because it not only illustrates the level of material support the Warrnambool community gave to Flagstaff Hill during it’s establishment. But the Giles collection also gives us today a snapshot into what domestic life was like in early colonial times prior to Federation. Linen chest wood construction with hinged lid and lock. Hinges are brass. Painted black. ( Giles Collection)Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, wooden chest, cabin trunk, giles collection, henry giles, tower hill, cooramook, mailor’s flat, wangoom, 19th century household goods, jane flemming, mary jane giles, linen chest
