Showing 645 items
matching pressure
-
 Tennis Australia
Tennis AustraliaBall container, Circa 1945
An unsealed Slazenger (U.K.) 'Lawn Tennis Ball' container. Originally packed under pressure (solder spot on base). Lid and balls missing. Materials: Metal, Paint, Rubber, Felttennis -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionFunctional object - Barograph, n.d
Port of Portland Collection A barograph is a barometer that records the barometric pressure over time in graphical form. This instrument is also used to make a continuous recording of atmospheric pressure.Wooden case, glass sided (front and ends). Steel handle on top (brass plated) used from circa 1950's.port of portland, maritime, barograph -
 Upper Yarra Museum
Upper Yarra MuseumRacket, Wooden press, Alexander Patent
rackethttp://www.utas.edu.au/docs/library/companion_to_tasmanian_history/A/Alexander%20Patent%20Racket%20Company.htm extract..The Alexander Patent Racket Company made sporting equipment, notably the world's first laminated tennis racquet. In the early 1920s Alfred Alexander invented the process, patented it and began making racquets. In 1926 the Company was formed and production expanded at the factory in Wentworth Street, Newstead. Success depended on the use of imported English ash Wooden press with 1 fixed side. The racket slides in and the frame is tightened with a wing nut. This was used to store the rackets as the laminated wooden frame warped due to pressure of the strings and damp conditions. racket wooden press alfred alexander alexander patent racket company -
 Friends of Kurth Kiln
Friends of Kurth KilnTusons Gas Producer Unit, Tusons
In conversation with Mr Tibbett we found out that he obtained this particular unit at an auction in Sydney and brought it home with the intention of one day getting it going again. 'One day' never seemed to come, so he decided to let us have it for our display, rather than jjust collecting dust in his shed.This unit is again of a different manufacturer and construction, highlighting the versatile nature of charcoal producer gas and its applications. A commercially made cast iron unit with a solid round hopper/boiler on a steelframe base. It has a pressure-cooker lid and a car type radiator. Solid built, but rust affected in partsMake: Tysons Cross Draught Model: Official 30hp Heavy Duty Serial: 1368 -
 Tennis Australia
Tennis AustraliaBall container, Ball, Circa 1945
An unsealed Slazenger (U.K.) 'Lawn Tennis Ball' container. Originally packed under pressure (solder spot on base). Contains three unbranded balls. Materials: Metal, Paint, Rubber, Felttennis -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumDomestic object - LAUNDRY MANGLE
Laundry equipmentLarge green wrought iron mangle with wooden rollers and metal pressure bar. Wheel to turn metal cogs to work rollers. Wooden shelf at base. Metal castors to maneuver into position.Trademark Wertheimlaundry, washing -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionBering Burner
Used for planned burning operationsPressurised Bering burner wand, with pump and pressure gauge Adaption of a commercial garden weed burner Bering Engineering Ltd we’re originally based at Doman road, Camberley in Surrey, UKforests commission victoria (fcv), planned burning, bushfire, hand tools -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionHose pressure testing kit
After the 1939 bushfires the Forests Commission placed orders for 130,000 feet (nearly 40 km) of 1½ inch canvas hose in Britain to accompany over 200 new pumps of various types. The Altona workshop became a major centre for fabrication, repair and storage of hose. But lack of standardisation of hose couplings plagued Australian firefighters for decadesHose pressure testing kit. Canvas hose needs to be washed, dried, rolled and stored properly after it has been used otherwise it will rot. Unrolled hose is notorious for becoming tangled.FCVforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, fire pump, fire tanker -
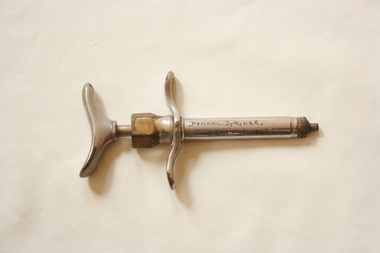 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryEquipment - Dental syringe, sectioned
Sectioned by Dr. Geoffrey Kaye in 1946.Cross-sectioned silver metal dental syringe, which injects at a high pressure of c.10 atmospheres. It was used for raising intradermal wheals, injecting the cranial foramina and infiltrating fibrous tissues. Hand-written inscription on barrel. "DENTAL SYRINGE/G Kaye sect. 1946"anaesthesia, dentistry, dental -
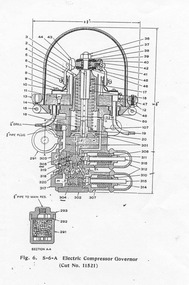 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumDocument - Instruction, Ballarat Tramway Museum (BTM), "S-6-A Electric Compressor Governor", 2009
Yields information about a compressor governor that is fitted to some Ballarat Trams, Westinghouse.Two A4 photocopied sheets, giving a side elevation of the Westinghouse "S-6-A Electric Compressor Governor" and the setting or the regulation and adjustment, installation and maintenance of the Governor. Commonly known as a "Bettleback" Governor. Dates from 1916. See Reg Item 703 for a MMTB drawing. WAD’s thoughts on setting Beetle back compressor Governors – 19/12/2009. Refer to instructions as well. Set both valves to approximately the same tension or thread length If when pumping up, both valves start to chatter, screw down the back valve further. When working satisfactorily, but pressures not right, that is, the governor is cutting out without valves chattering or with excessive range or pressure too high. Adjust the front valve until the desired cut out pressure arrived at. The cap must be on this valve for it to work. Adjust the back valve to adjust the cutting in setting, screw down for high cut in pressure. Adjust both as necessary to obtain your desires! And best of luck, it can be done, but is frustrating!!!!!trams, tramways, governors, westinghouse, air compressors, instructions -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, McGraw-Hill Book Company, Hydraulics: A Text on Practical Fluid Mechanics, 1937
The book was used by Charles Bacon who studied at the University of Nevada in the late 1930s/early 1940s. Bacon worked at Bunker Hill Mines and Kellogg Idaho, before arriving in Australian in 1951. He worked for CN Myers, a company involved with paper converting. CN Myers was a family business (on Charles Bacon's maternal line).Blue hard-covered book of 460 pages. Chapters include Properties of Fluids, intensity of Pressure, Hydrostatic Pressure of Areas, Dams, Kinematics of fluid Flow, Dynamics of Fluid Flow, Applications of Hydrokinetics, Friction Losses in Pipes, Flow Through Pipes, Uniform Flow in Open Channels. Nonuniform Flow in Open Channels, Unsteady Flow, Dynamic Forces, Description of the Impulse Wheel, Theory of the Impulse Wheel, water Power Plants, centrifugal Pump and more.Inside Front Cover "Charles Bacon, Mackay school of Mines Reno, Nevada."charles bacon, mining engineering, metallurgy, university of nevada, mackay school of mines -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societymangle, Early 20th century
A mangle or wringer is a mechanical laundry aid consisting of two rollers in a sturdy frame, connected by cogs and, in its home version, powered by a hand crank or electrically. A household mangle/wringer could be attached to a bench for easier use. The washing process itself involved lifting the items from the cold soak and wringing or mangling each item before transferring them, with more soap flakes, into the copper for boiling. Items that remained soiled, even after an overnight soak, were rubbed on a scrubbing board before being transferred to the copper. The clothes mangle would be used to squeeze out all the excess water. Clothes would then be hung out to dry on a clothes line, or laid over a clothes-horse next to the kitchen or living room fire. This one was owned by the mother of Bob Clarke, an Orbost resident.This item is an example of the typical laundry equipment used by families in the Orbost district in the early 20th century.Clothes mangle [wringer] which has a wooden and metal turning handle. It has a ratchet and 2 tap screws for pressure. It has of two rollers in a frame, connected by cogs and is powered by a hand crank.On top - "No. Hardwood Rolls 124" Front - "Household Clothes Mangle Steel ball bearings The American Wringer Company New York USA"laundry wringer mangle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLamp
Lamp with large disc for radiating heat. Heavy circular base, tank with fuel inlet and pressure pump. Mantle type wick with half-spherical mantle. "Companion" inscribed onto fuel tank.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, lighting, lamp, companion -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPamphlet, Our City - Ringwood (1972), 1972
Community information brochure issued in 1972 by Ringwood Council outlining local services, sporting, and cultural facilities. Includes names of Ward Councillors, and two City of Ringwood Free Tipping Vouchers valid until the end of 1973."Frontpiece: New bridge of pressure treated pine over Ringwood Lake." "Ringwood Must Grow, Not Go! With your money, Council provides these vital Services."rinx -
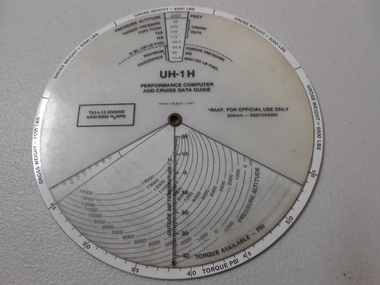 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Equipment - Performance Computer And Cruise Data Guide
White 20cm round plastic disc with information on Weight plus Torque PSI plus Hover Gross Weight and Pressure Altitude for a UH - IH Huey Helicopter for use of The Royal Australian Air Force.UH-IH Performance Computer + Cruise data guide.computer and cruise data guide, uh-1h helicopter, raaf -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPolisher Floor, Hoover Appliances, Meadowbank
This appliance was a time saving method of cleaning floors. It appeared at a time (after World War II) when the domestic pressures faced by mothers and domestic staff was on the increase. The necessary "working parents" was through necessity becoming part of the "typical" family environment. It was the start of the ever increasing demand, from an economical reason, for both parents to work outside their property. Historically the period of the 1950s was one of extreme changes. It was an era where established role models were under pressure from an ever increasing demand for new and advancing consumerism. Communication levels via radio, newspapers and television was expanding at an ever increasing rate. Relatively isolated rural areas were opening up (post war) to foreign ideologies of consumerism. The basic restraints of "this will be alright mate, she'll do" was under a slow but effective take over. "I can get this done faster by this new whiz bang gadget that I saw on the TV last night!" was the new way to live by.This item is very significant in that it demonstrates the new consumerism at its infant stage of the social changes occurring due to greater communication levels between the rural Australian communities and other advancing communities world wide. The Kiewa Valley residents (mainly from the intermingling of rural and post World War II refugees working at the construction of the Victorian Hydro electricity installations, resulted in this rural area becoming integrated to new ways of living (both socially and economically). Once the attitude of "we have always done it this way mate!" was challenged and overcome, the acceptance of new time saving "gadgets" which started to pour in from foreign markets, the relative isolation of the Kiewa Valley (being mainly psychological entrenched), was over.This hoover electric floor scrubber and polisher has a main base containing two brushes (can be replaced with polishing pads). The two brushes/pads are fastened or removed from the base unit by pulling/pushing the heads from the small hexagonal shaft on the bottom of the machine motor. A pressure sensitive wire is inlaid at the brush/pad end to hold the brush/pad unit onto the shaft. The discs body and main body covering the electric motor are made from sturdy plastic. The rest of the appliance materials i.e. upright handle and the u framed attaching arm are made from lightweight powder coated steel. A small (350mm) red coloured foot switch protrudes from the back of the motor to release the the upright handle from the storage position to the action position.There are two fork shaped brackets on the rear of the handle, for securing the 6.5 metre long electrical cord and plug. There is no on/off switch on the appliance. A small stainless steel "u" framed clip (for hanging the appliance in the vertical position) for cupboard storage. Within the circle of the cleaning brush is stamped "1 above S.A.B.351" and on the opposite side P/No: 5023792". On the main plastic head of the brush discs are "TO CLEAN" and under this "USE ONLY WARM(underlined) WATER AND SOAP" on the opposite side, and within a circle is the Hoover Trademark. On the front of the blue coloured plastic dome covering the electric motor is (on a raised domed shaped plaque (on a red background) Hoover in slanted print from left to right(in a diagonal level)domestic appliances, floor cleaning, electric floor scrubbers and polishers -
 Maldon Vintage Machinery Museum Inc
Maldon Vintage Machinery Museum IncBlower - Centrifugal
Centrifugal blower direct coupled to an electric motor. Painted dark blue with an anti-clockwise direction arrow picked out in white on the front.Operating details - speed range 2850 - 3500 RPM. Working pressure range 14 - 25 PSI? Working voltage 210 - 350 volts. Dawn No. 2F.machinery; blower; centrifugal; metalwork -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - LA TROBE UNIVERSITY BENDIGO COLLECTION: THEY WANT WORD ON THE MERGER
A newspaper article titled 'They want word on the merger'. Pressure is being put on the Minister of Education Mr. Lindsay Thompson to announce the merger of State College of Victoria Bendigo and Bendigo Institute of Technology. 4/5/74.bendigo, education, bit and btc merger, la trobe university bendigo collection, collection, bendigo, education, tertiary education, state college of victoria bendigo, bendigo institute of technology, mr. lindsay thompson, merger -
 Tennis Australia
Tennis AustraliaBall container, Ball, Circa 1948
An unsealed Slazenger (U.K.) 'Lawn Tennis Ball' container. Originally packed under pressure (solder spot on base). Lid missing. Contains three of four original balls. Materials: Metal, Paint, Rubber, Felttennis -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPeat Spears (various)
After the 1939 bushfires the Forests Commission placed orders for 130,000 feet (nearly 40 km) of 1½ inch canvas hose in Britain to accompany over 200 new pumps of various types. The Altona workshop became a major centre for fabrication, repair and storage of hose, pumps and specialised equipment.Underground peat fires are very difficult to extinguish Water tends to just run off and not penetrate when sprayed onto the surface Peat spears are driven into the ground and connected to high pressure hose to inject waterforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, fire pump, fire tanker -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Photograph, Gibbons, Denis, Hoi My Southern Cross Windmill 1
Denis Gibbons (1937 – 2011) Trained with the Australian Army, before travelling to Vietnam in January 1966, Denis stayed with the 1st Australian Task Force in Nui Dat working as a photographer. For almost five years Gibbons toured with nine Australian infantry battalions, posting compelling war images from within many combat zones before being flown out in late November 1970 after sustaining injuries. The images held within the National Vietnam Veterans Museum make up the Gibbons Collection.A black and white photograph of the Hoi My Southern Cross Windmill water pump and the water pressure header tower. Pipes and taps were laid from the header tank to various access points throughout the village.photograph, 1st australian civil affairs unit, hoi my southern cross windmill, gibbons collection catalogue, denis gibbons, photographer, vietnam war -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionInstrument - Ships Barometer
Since the mid-1600s, barometers have been a useful tool for boaters to measure air pressure in order to predict weather changes out on the sea. A change in pressure causes the dial's indicator hand to move. Aneroid barometers have a circular display face much like a clock that indicates the current atmospheric pressure. Part of a collection of objects belonging to Robert Hodgson. He was a fisherman and part of Shore Line Engineering.A circular white round face with black numbers around the edge starting at 80 and going up in 1 number increments to 106. Language is in Russian. A thermometer is on the face of the lower half starting at -10 degrees Celsius and up to 40 degrees Celsius going up in 10 number increments. A glass panelsits above the whit face and it is held together by a metal edge. The back of the barometer is black bakelite. -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyHorse Equipment - straps
A harness distributes pressure over a large area of the horseHorses were used by farmers in the Kiewa Valley prior to motorised vehicles.Unidentified horse straps - leather with steel buckles. Possibly part of a harness that connects a horse to a horse drawn vehicle.horse harness, horse equipment -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumGauge, Pressure
Bourdon pressure gauge. Lbs per ounce. No. 13057. -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPhotograph - 133 Myers St. Lakes Entrance, 1970
This tank provided good pressure for the house and septic tankColour photograph of cottage at 133 Myer Street showing stainless steele milk vat on high tank stand to collect water from town water supply Lakes Entrance Victoriabusinesses, roads and streets -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomInformation Sheets, Army School of Catering, Student Study Guide, abt 1980's
A set of photocopied study guides and precis on various implements used by catering staff in a field environment, including, immersion heaters, pressure lamps (Austramax) M2A modified burner and a page on immediate first aid for snake bitecatering equipment -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Photograph, Gibbons, Denis, Vung Tau Shopping
Denis Gibbons (1937 – 2011) Trained with the Australian Army, before travelling to Vietnam in January 1966, Denis stayed with the 1st Australian Task Force in Nui Dat working as a photographer. For almost five years Gibbons toured with nine Australian infantry battalions, posting compelling war images from within many combat zones before being flown out in late November 1970 after sustaining injuries. The images held within the National Vietnam Veterans Museum make up the Gibbons Collection. A colour photograph of Lt Terrie Roche, Capt Amy Pittendreigh, Lt Colleen Mealey and Lt Margaret Ahern, taking a break in Vung Tau from the contant pressures of the wounded and sick at 8 Field Ambulance Hospital.photograph, 8 field ambulance hospital, vung tau, lt terrie roach, capt amy pittendreigh, lt colleen mealey, lt margaret ahern, nurses, gibbons collection catalogue, denis gibbons, photographer, vietnam war -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Pressure Gauge, Barclay Curle & Co shipbuilders, Circa 1873
The Loch Ard got its name from "Loch Ard" a loch that lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic. The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curle & Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen, and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead, and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold their position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as Lochard Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy that had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost families in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce, and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the Lochard tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of Lochard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up into Lochard Gorge. Cargo and artifacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artifact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register.The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artifacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artifacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck of which the subject items are a small part. The collection's objects give us a snapshot of how we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. Through is associated with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.Pressure gauge; round brass instrument with brass fittings: gate valve and handle. The two separate parts include a small bracket. Encrustations are on the surface. The flat side has been lacquered. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, pressure gauge, mechanical instrument -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePressure Gauge
Pressure Gauge section, circular section of gauge with glass missing attached to a gate-valve. H 205mm x W 130mm x D 30mm. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard. Previous number PWO 0349.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, pressure gauge, loch ard -
 Nhill Aviation Heritage Centre
Nhill Aviation Heritage CentreInstrument - Barometer, Aneroid Barometer, c1960s
Precision instrument used meteorological offices on air fields to measure barometric pressure141.1 Metal cube shape instrument with button switch attached is a cylindrical read out and adjuster knob. 141.2 Carry box with hinged lid and metal latch, has three hold down screws. 141.3 Stainless steel and glass thermometer 141.4 batteries 4x 15v. Standard batteries were HT Eveready B123 30v x3, LT Eveready LLII 1.5 v x1Aneroid Barometer, Type No. M.1991/A Range 800-1050mb. Ser No. 686/65, Mechanism Ltd, Made in Englandbarometer, instrument, aneroid barometer, thermometer
