Showing 1662 items matching " gun"
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhoto Album, Ballarat Teachers' College Golden Jubilee Reunion 1947 - 1997, 22/03/1997
Students at the Ballarat Teachers' College in 1947 undertook one year training to become a primary school teacher. Hard covered white and grey photo album with photographs from the Ballarat Teachers' College Year of 1947 Golden Jubilee Reunion held at Craigs Hotel, Lydiard Street, Ballarat. The album includes a photograph of former residents of the Camp Street Hostel. (Margaret Palmer, Joyce Mathison, Beatrice Freeman, Gwen Pamphilon, Betty Perry, Nancy Kerr, Kath Crosetti, Neila Vallance, Ann McKinnon) The second half of the album include photos from the 1998 reunion. The back pages have autographs of those who attended the 1997 Jubilee reunion.ballarat teachers' college, 1947, nield, roddis, lelean, marshman, mclachlan, bunney, lynch, gleeson, welsh, pattenden, henning, pamphilon, fauld, mckenna, morrish, boyd, mathison, doney, batson, kennedy, kerr, surman, williams, vallance, freeman, hannan, harley, palmer, perry, watts, esmore, gunning, tobin, crosetti, mclachlan, hill, carless, rice, mallett, fraser, gleeson, martin, batson, perry, harley -
 Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright Museum
Bright & District Historical Society operating the Bright MuseumCup, siver trophy, 1911
Silver trophy cup with two handles on a stand. Highly decorated with oval shapes and floral pattern.B Main \ Won This Trophy \ on 3 Shootings at 500 yds \ Total 137 Scratched on the base.cup, silver, trophy, sport, gun club -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Case, Early 20th century
This small case is lined with a metal insert and shows remnants of a carry strap. It could have been used for storing and carrying fuses or cartridges for the life saving Rocket Launcher machine. The protective metal insert would help keep the contents dry or cool and protect from flame. It is part of the collection of rescue equipment in the Rocket House used by the life saving rescue crew. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - Rocket rescue became the preferred lifesaving method of the rescue crews, being much safer that using a lifeboat in rough seas and poor conditions. The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. . The British Board of Trade regularly published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle, determined by the Head of the crew and measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A continuous whip line was then sent out to the ship’s crew, who hauled it in then followed the instructions – in four languages - on the attached tally board. The survivors would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line with a tail block connected to it. They then secured the block to the mast or other strong part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the survivors fixed above the whip’s tail block. The hawser was then tightened by the crew pulling on it, or by using the hooked block on the shore end of the whip and attaching it to a sand anchor. The breeches buoy was attached to the traveller block on the hawser, and the shore crew then used the whip line to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. The rescue crew wore scarlet, numbered armbands and worked on a numerical rotation system, swapping members out to rest them. This small leather carrying case is significant for its connection with the rocket rescue equipment, local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Leather case, brown with contrasting stitching, protective metal insert divided into two compartments. Rectangular shape. Roller buckle on front with remnants of the matching strap. Also remnants of a leather strap on the side, possibly a shoulder strap.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, maritime accidents, shipwreck victim, rocket equipment, marine technology, rescue boat, lifeboat, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, rocket rescue method, shore to ship, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, line throwing mortar, mortar, rocket rescue apparatus, line thrower, line throwing, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, schermuly pistol, pistol rocket apparatus, line throwing cartridge, l.s.r.c., lsrc, leather case, cartridge case, fuse case, ammunition case -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Pistol, 1873-1884
Rollin White was an American gunsmith who invented a single shot bored-through revolver cylinder that allowed paper cartridges to be loaded from the rear of a revolver's cylinder. Wen his patent expired the Colt's Patent Fire Arms Manufacturing Company started working on its own metallic cartridge revolvers. Thus, after having introduced its first rear-loading pistols in 1871 the (Colt House/Cloverleaf revolver) and the 1872 (Colt Open Top revolver), in 1873 Colt launched the Colt Peacemaker along with a new line of pocket revolvers, sorted in five different calibers (.22, .30, .32, .38, .41 cal). Since it was an entirely new line of revolvers this model was called the Colt New Line. Circa 1884-1886 (the .32 cal was only made during 1873-1884). Submerged by the company's competitors' cheaper imitations and refusing to introduce a lower quality among its own firearms to match its competitors, the Colt company dropped the line and ceased production.The Colt New Line was one of the first metallic cartridge rear-loading revolvers manufactured by Colt. It demonstrates the evolution of firearm production and development of firearms as manufacturers moved away from percussion muzzle-loading firearms to those that would accept cartridges. That incorporated the bullet, propellant and primer all within a brass cylinder allowing the projectile to be loaded directly into a pistols cylinder, or a rifle magazine. Pistol or handgun, Colt New Line revolver, single action five shot spur trigger. The rimfire revolver is .32 calibre. It has a black handle. There maker's name is impressed into the textured handle and the name and model is impressed onto the barrel. Made by Colt.Inscriptions on side of barrel and top "No 18842", "Colt New .32" . On top "Colt's FT.F.AMFG.CC Hartford.Ct.USA"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, revolver, colt, colt new line revolver, cartridge casing, cartridge, new line revolver, pistol, matalic cartridge, firearm, rollin white, new line, hand gun, single shot -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet, ResMag, 2008, 2008
Black and white soft covered magazine of the Mt Helen Resident Society.mount helen resident society, peter gunning, sarah-jayne smith, owen hillier, katie sleep -
 Australian Commando Association - Victoria
Australian Commando Association - VictoriaBook - 6th Div, Shawn OLeary, To The Green Fields Beyond:The story of the 6th Division Cavalry Commandos
The comprehensive history of the 6th Australian Division Cavalry Commandos – a (now out of print) reprint of one of the rarer Armoured unit history books. This is the story of one of Australia’s most famous fighting regiments during World War II. As an armoured cavalry unit it fought the Italians and Germans in the sands of the African desert and the Vichy French in the mountains of Syria. Later as a dismounted commando unit it fought the Japanese in the terrifying jungles of New Guinea. The heroism of the men in its ranks and the actions in which they engaged are portrayed in a way which makes battle deeds leap realistically from the pages. “To The Green Fields Beyond” is a documented and detailed book which is of value to everyone who is interested in Australia’s story. Seldom before has such a contribution been made to record of our national history. The book has been approved and sponsored by the Australian War Memorial. The 6th Division Cavalry Regiment was formed in November 1939 and, just two months later, was sent overseas to the Middle East in January 1940. Arriving in Egypt, the regiment immediately went to Palestine, where it joined the rest of the 6th Division and trained using machine-gun carriers and, from October, six old Vickers light tanks. At the end of the year the regiment moved into the Western Desert, where it joined British forces ready for the major offensive to commence on 9 December. Two days later the regiment became the first unit of the 2nd Australian Imperial Force (AIF) to go into action when one of its squadron fought a sharp action against the Italians holding Garn el Grein and Fort Maddalina on 11 and 12 December. By 21 December British forces had captured Sidi Barrrani and the desert was now open for the 6th Division’s advance along the Libyan coast. On 3 January 1941 the division attacked and captured the Italian fort of Bardia. The regiment’s A Squadron, under the command of Major Denzil Macarthur-Onslow, who went on to command the 4th Armoured Brigade, supported the attack. Tobruk was the next Italian fort to be captured, with the regiment again in support and covering the 19th Brigade’s advance. The regiment, though, was under-equipped and without its full compliment of vehicles, using only machine gun carriers. To compensate for this, A Squadron was parity re-equipped with captured Italian light tanks, which had large kangaroos painted on the hulls and turrets to distinguish them from enemy vehicles. After Tobruk, the regiment was used as part of the advance guard in the capture of Derna and then Benghazi. In April the unit moved to Helwan, where it was equipped with Vickers light tanks and machine-gun carriers, and operated with British troops in capturing Sollum. Towards the end of May the regiment moved to Palestine, where it came under the command of the 7th Division for the imminent invasion of Syria. The regiment experienced its heaviest fighting during the Syrian campaign, which began on 7 June. A Squadron was attached to the 21st Brigade and advanced along the coast, where the rugged hills made it difficult to manoeuvre the tanks and carriers. The squadron was relieved by one of the 9th Division Cavalry Regiment’s squadrons on 13 and 14 June. C Squadron, meanwhile, was with the 25th Brigade, and advanced along the Rosh Pinna road, engaging strong enemy defences at Fort Khirbe. C Squadron was relieved by B Squadron, which was later attacked by Vichy French tanks that were supported by heavy artillery and machine-gun fire, which forced the Australians to withdrawal. Always willing or needing to improvise during the campaign, A and B Squadrons both operated three captured French R35 Renault light tanks, while C Squadron provided personnel for a horse troop, quickly nicknamed the “Kelly Gang”, to patrol the high, rugged hills near the Mardjayoun–Banis Road. The regiment remained in Syria as part of the occupation force and returned to Australia in March 1942. It was sent to the Adelaide River, in the Northern Territory, and then later to Murgon, in Queensland. In 1943 and 1944 divisional cavalry regiments were reorganised into cavalry (commando) regiments. In January 1944 the 6th Division Cavalry Regiment became the 2/6th Cavalry (Commando) Regiment. The regiment lost its vehicles and became the administrative headquarters for the 2/7th, 2/9th, and 2/10th Commando Squadrons. The regiment remained with the 6th Division and participated in the Aitpae–Wewak campaign, in New Guinea, during 1945. Includes Nominal Rollnon-fictionThe comprehensive history of the 6th Australian Division Cavalry Commandos – a (now out of print) reprint of one of the rarer Armoured unit history books. This is the story of one of Australia’s most famous fighting regiments during World War II. As an armoured cavalry unit it fought the Italians and Germans in the sands of the African desert and the Vichy French in the mountains of Syria. Later as a dismounted commando unit it fought the Japanese in the terrifying jungles of New Guinea. The heroism of the men in its ranks and the actions in which they engaged are portrayed in a way which makes battle deeds leap realistically from the pages. “To The Green Fields Beyond” is a documented and detailed book which is of value to everyone who is interested in Australia’s story. Seldom before has such a contribution been made to record of our national history. The book has been approved and sponsored by the Australian War Memorial. The 6th Division Cavalry Regiment was formed in November 1939 and, just two months later, was sent overseas to the Middle East in January 1940. Arriving in Egypt, the regiment immediately went to Palestine, where it joined the rest of the 6th Division and trained using machine-gun carriers and, from October, six old Vickers light tanks. At the end of the year the regiment moved into the Western Desert, where it joined British forces ready for the major offensive to commence on 9 December. Two days later the regiment became the first unit of the 2nd Australian Imperial Force (AIF) to go into action when one of its squadron fought a sharp action against the Italians holding Garn el Grein and Fort Maddalina on 11 and 12 December. By 21 December British forces had captured Sidi Barrrani and the desert was now open for the 6th Division’s advance along the Libyan coast. On 3 January 1941 the division attacked and captured the Italian fort of Bardia. The regiment’s A Squadron, under the command of Major Denzil Macarthur-Onslow, who went on to command the 4th Armoured Brigade, supported the attack. Tobruk was the next Italian fort to be captured, with the regiment again in support and covering the 19th Brigade’s advance. The regiment, though, was under-equipped and without its full compliment of vehicles, using only machine gun carriers. To compensate for this, A Squadron was parity re-equipped with captured Italian light tanks, which had large kangaroos painted on the hulls and turrets to distinguish them from enemy vehicles. After Tobruk, the regiment was used as part of the advance guard in the capture of Derna and then Benghazi. In April the unit moved to Helwan, where it was equipped with Vickers light tanks and machine-gun carriers, and operated with British troops in capturing Sollum. Towards the end of May the regiment moved to Palestine, where it came under the command of the 7th Division for the imminent invasion of Syria. The regiment experienced its heaviest fighting during the Syrian campaign, which began on 7 June. A Squadron was attached to the 21st Brigade and advanced along the coast, where the rugged hills made it difficult to manoeuvre the tanks and carriers. The squadron was relieved by one of the 9th Division Cavalry Regiment’s squadrons on 13 and 14 June. C Squadron, meanwhile, was with the 25th Brigade, and advanced along the Rosh Pinna road, engaging strong enemy defences at Fort Khirbe. C Squadron was relieved by B Squadron, which was later attacked by Vichy French tanks that were supported by heavy artillery and machine-gun fire, which forced the Australians to withdrawal. Always willing or needing to improvise during the campaign, A and B Squadrons both operated three captured French R35 Renault light tanks, while C Squadron provided personnel for a horse troop, quickly nicknamed the “Kelly Gang”, to patrol the high, rugged hills near the Mardjayoun–Banis Road. The regiment remained in Syria as part of the occupation force and returned to Australia in March 1942. It was sent to the Adelaide River, in the Northern Territory, and then later to Murgon, in Queensland. In 1943 and 1944 divisional cavalry regiments were reorganised into cavalry (commando) regiments. In January 1944 the 6th Division Cavalry Regiment became the 2/6th Cavalry (Commando) Regiment. The regiment lost its vehicles and became the administrative headquarters for the 2/7th, 2/9th, and 2/10th Commando Squadrons. The regiment remained with the 6th Division and participated in the Aitpae–Wewak campaign, in New Guinea, during 1945. Includes Nominal Rollww2, australian commandos, australian special forces, world war 2 -
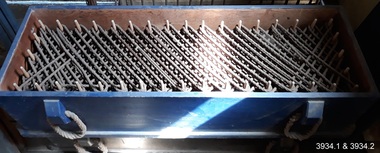 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Line faking box, Government of Victoria, 1860s
The rocket line faking box with lid has a frame inside with a specifically designed perimeter of faking pegs. The rocket shot line has been faked, or skilful wound, around these pegs to prevent it from tangling. The line is stored in the box, ready for attaching to the line throwing rocket. Some line faking boxes have a false base that is removed before firing the line-throwing pistol, leaving the line to feed out from the box when the rocket is fired. After the line is attached to the rocket the box tilted slightly and faced towards the wreck to allow it to be freely dispatched. The equipment often includes more that one faking box to make allowance for possible errors, broken lines or the need for a heavier line. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it. In 1858 the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for lifeboat stations in Victoria, and in 1864 a rocket house was built to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. This rocket line faking box is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Rocket line faking box with loose fitting lid, painted blue on the outside. Rectangular box has two rope handles within wooden rope holders fixed onto each long side and one at each end. The box has a hook and ring at the base each end for releasing the top from the inserted faking frame. The line faking frame is inside the box. It has seventeen wooden pegs along each long side of the frame and three pegs along each short side. A continuous length of rocket line has been faked around the pegs in a specific pattern.flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, petticoat breeches, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket shed, lifeboat men, rocket equipment, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, beach rescue set, traveller, hawser, faking, faking box, faked line, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, lifeboat warrnambool, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, shore to ship, italian hemp, line-throwing pistol, line throwing cartridge, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, tally board, light line, whip line, endless whip, petticoat buoy, traveller chair, traveller block, her majesty’s coast guard, harbour board, line thrower, line throwing, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, hawser cutter, life jacket, faking board, welsh hand barrow, rocket set, rocket line faking box, faking frame -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Line faking box, Government of Victoria, 1860s
The rocket line faking box has a frame inside with a specifically designed perimeter of faking pegs. The rocket shot line has been faked, or skilful wound, around these pegs to prevent it from tangling. The line is stored in the box, ready for attaching to the line throwing rocket. Some line faking boxes have a false base that is removed before firing the line-throwing pistol, leaving the line to feed out from the box when the rocket is fired. After the line is attached to the rocket the box tilted slightly and faced towards the wreck to allow it to be freely dispatched. The equipment often includes more that one faking box to make allowance for possible errors, broken lines or the need for a heavier line. Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built to house it. In 1858 the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for lifeboat stations in Victoria, and in 1864 a rocket house was built to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater area, and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifeboat and rocket crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. Some became local heroes but all served an important role. By the end of the 1950s the lifeboat and rescue equipment had become obsolete. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy and traveller block rocket rescue apparatus was in use. It was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket rescue method became the standard in Victoria. His two-stage rockets, charged by a gunpowder composition, could fire the line up to 500-600 yards, although 1000 yards range was possible. Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a light-weight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. This rocket line faking box is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Rocket line faking box with loose fitting lid, painted black on the outside. Rectangular box has two rope handles within wooden rope holders fixed onto each long side and one at each end. The box has a hook and ring at the base each end for releasing the top from the inserted faking frame. The line faking frame is inside the box. It has seventeen wooden pegs along each long side of the frame and three pegs along each short side. A continuous length of rocket line has been faked around the pegs in a specific pattern.flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, maritime accidents, rocket crew, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, rocket firing equipment, rocket rescue equipment, rocket apparatus, beach apparatus, petticoat breeches, breeches buoy, rocket house, rocket shed, lifeboat men, rocket equipment, rocket machine, rocket head, rocket launcher, rocket line, marine technology, line-firing pistol, line throwing gun, beach rescue set, traveller, hawser, faking, faking box, faked line, lady bay, warrnambool harbour, port of warrnambool, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, breakwater, lifeboat warrnambool, rocket rescue method, rocket rescue apparatus, shore to ship, italian hemp, line-throwing pistol, line throwing cartridge, rocket apparatus rescue, stranded vessel, tally board, light line, whip line, endless whip, petticoat buoy, traveller chair, traveller block, her majesty’s coast guard, harbour board, line thrower, line throwing, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, hawser cutter, life jacket, faking board, welsh hand barrow, rocket set, rocket line faking box, faking frame -
 Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub Branch
Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub BranchSub Machine Gun
Thompson 0.45 Automatic Cartridge US Model of 1928 A1SN 288693weapon, ww2, army -
 Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub Branch
Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub Branchre Maxim Machine Gun
Wooden Ammunition Box containing ammunitionequipment, ww1, army -
 Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub Branch
Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub BranchLight Machine Gun
Japanese Model 96 6.5mm SN4452weapon, 1940, army -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Model, M-102, 105mm Howitzer
Could be towed by a truck or carried in or under a Chinook heleicopter. They were often ferried to remote hilltops to create firebases to support ground troops. Range 11,000 metres. Maximum fire rate of ten rounds per minute, sustained fire three rounds per minute. Superior to M101A1.towed howitzer, artillery gun, m-102 105mm, model -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Manual, United States Army, Operator And Organisational Maintenance Repair Parts and Special Tool List for Submachine Guns, Caliber .45, M3 and M3A1 (2 copies), 1957
A cream coloured manual with black writing. There are three punch holes down the left hand side of the manual. There is a heading "Department of the Army Technical Manual at the top of the manual. the manual is stored in a plastic folder.military weapons, submachine guns -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & Museumtrophy/cup
The 10 locals names and their scores are engraved on the front. Fish Creek were the runners up. A total of 6 teams competed in the competion from around the area. This trophy/cup is of social significance because it relates to the local Korumburra community in 1926. rifle club, trophy, guns, -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - LYDIA CHANCELLOR COLLECTION: TYNTYNDYER HOMESTEAD
An article from a 'Supplement to Bendigo Advertiser' giving some insights into the history of Tyntyndyer Homestead which is in the Swan Hill district. It gives an insight into the early settlers and their struggles for survival. There is an advertisement within the supplement advertising the 'Historic Tyntyndyer Homestead and Museum.' Coloured and black and white photographs are included in this article which is dated 12/2/1969.history, australian, early farming settlement, lydia chancellor collection, collection, swan hill, aboriginal, aboriginal contact, australia, history, australian history, homesteads, building, house, houses, heritage, tourism, aborigines, settlers, weapons, guns, pastoralists, expedition, john holloway, andrew beveridge, peter beveridge, robert o'hara burke, narrinyeri tribe, bushrangers, relics, national trust, advertisement, exploration -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Craig Deayton, The battle of Messines : 1917, 2017
On 7 June 1917, the British Second Army launched its attack on Messines Ridge, detonating 19 giant mines beneath the German front-line positions. By the end of the day, one of the strongest positions on the Western Front had fallen, a place of such importance that the Germans had pledged to hold it at any cost. It was the greatest British victory in three years of war. The first two years of the First World War had represented an almost unending catalogue of disaster for the Australians. Messines was not only their first real victory, it was also the first test in senior command for Major General John Monash who commanded the newly formed 3rd Division and would later be hailed as Australia's greatest soldier. Messines was a baptism of fire for the 3rd Division which came into the line alongside the battle-scarred 4th Australian Division, badly mauled at Bullecourt just six weeks earlier in one of the worst defeats of the war. The fighting at Messines would descend into unimaginable savagery, a lethal and sometimes hand-to-hand affair of bayonets, clubs, bombs and incessant machine-gun fire, described by one Australian as '72 hours of Hell'. After their string of bloody defeats over 1915 and 1916, Messines would be the ultimate test for the Australians. Collapse summaryIndex, bibliography, ill (col), p.172.non-fictionOn 7 June 1917, the British Second Army launched its attack on Messines Ridge, detonating 19 giant mines beneath the German front-line positions. By the end of the day, one of the strongest positions on the Western Front had fallen, a place of such importance that the Germans had pledged to hold it at any cost. It was the greatest British victory in three years of war. The first two years of the First World War had represented an almost unending catalogue of disaster for the Australians. Messines was not only their first real victory, it was also the first test in senior command for Major General John Monash who commanded the newly formed 3rd Division and would later be hailed as Australia's greatest soldier. Messines was a baptism of fire for the 3rd Division which came into the line alongside the battle-scarred 4th Australian Division, badly mauled at Bullecourt just six weeks earlier in one of the worst defeats of the war. The fighting at Messines would descend into unimaginable savagery, a lethal and sometimes hand-to-hand affair of bayonets, clubs, bombs and incessant machine-gun fire, described by one Australian as '72 hours of Hell'. After their string of bloody defeats over 1915 and 1916, Messines would be the ultimate test for the Australians. Collapse summary world war 1914-1918- campaigns - western front, battles of messines - australian participation - 1917 -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Christopher Shores, British and empire aces of world war 1, 2001
At the outset of World War I the British had some 110 assorted aircraft, used mostly for the visual reconnaissance role. With the advent of faster and more agile single-seaters, the Allies and their adversaries raced to outdo each other in the creation of genuinely effective fighters with fixed forward-firing machine gun armament. It was not until 1917 that the British developed a truly effective interrupter gear, which paved the way for excellent single seaters such as the Sopwith Triplane Camel and the RAF S.E.5., later joined by the Bristol F.2B - the war's best two-seat fighter. This volume traces the rapid development of the fighter in World War I and the amazing exploits of the British and Empire aces who flew them.Ill, p.64.non-fictionAt the outset of World War I the British had some 110 assorted aircraft, used mostly for the visual reconnaissance role. With the advent of faster and more agile single-seaters, the Allies and their adversaries raced to outdo each other in the creation of genuinely effective fighters with fixed forward-firing machine gun armament. It was not until 1917 that the British developed a truly effective interrupter gear, which paved the way for excellent single seaters such as the Sopwith Triplane Camel and the RAF S.E.5., later joined by the Bristol F.2B - the war's best two-seat fighter. This volume traces the rapid development of the fighter in World War I and the amazing exploits of the British and Empire aces who flew them.worls war 1914-1918 - aerial operations - britain, fighter pilots - british empire -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Fremantle Arts Centre Press, The time of the soldier, 1991
An account of the author's experiences in two World Wars, as a Sergeant Major in a machine gun battalion and as a prisoner of the Japanese in Java, Singapore and Thailand.Ill, p.210.non-fictionAn account of the author's experiences in two World Wars, as a Sergeant Major in a machine gun battalion and as a prisoner of the Japanese in Java, Singapore and Thailand. world war 1939 – 1945 – personal narratives – australia, prisoners of war - australia -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Squadron/Signal Publications, US Self propelled guns in action, 1999
A pictorial and descriptive history of United states self propelled gunsill (b/w,col), p.49.non-fictionA pictorial and descriptive history of United states self propelled gunsarmoured vehicles - united states - history, self propelled guns - united states - history -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Uwe Feist, Nashorn, Hummel, Brumbar in action, 1973
A descriptive and pictorial history of German self propelled gunsill (b/w,col), p.47non-fictionA descriptive and pictorial history of German self propelled gunsarmoured warfare - germany - history, self propelled guns - germany -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Uwe Feist, Panzerjager in action, 1973
A descriptive and pictorial history of German self propelled gunsill (b/w,col), p.49.non-fictionA descriptive and pictorial history of German self propelled gunsarmoured warfare - germany - history, self propelled guns - germany -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Joachim Engelmann, German railroad guns in action, 1976
A descriptive and pictorial history of German railway gunsill (b/w, col), p.49.non-fictionA descriptive and pictorial history of German railway gunsarmoured warfare - germany - history, german railway guns -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Alistair MacLean, The guns of Navarone, 1958
The classic World War II thriller from the acclaimed master of action and suspense. Twelve hundred British soldiers isolated on the small island of Kheros off the Turkish coast, waiting to die. Twelve hundred lives in jeopardy, lives that could be saved if only the guns could be silenced. The guns of Navarone, vigilant, savage and catastrophically accurate. Navarone itself, grim bastion of narrow straits manned by a mixed garrison of Germans and Italians, an apparently impregnable iron fortress. To Captain Keith Mallory, skllled saboteur, trained mountaineer, fell the task of leading the small party detailed to scale the vast, impossible precipice of Navarone and to blow up the guns. The Guns of Navarone is the story of that mission, the tale of a calculated risk taken in the time of war...maps, p.270.fictionThe classic World War II thriller from the acclaimed master of action and suspense. Twelve hundred British soldiers isolated on the small island of Kheros off the Turkish coast, waiting to die. Twelve hundred lives in jeopardy, lives that could be saved if only the guns could be silenced. The guns of Navarone, vigilant, savage and catastrophically accurate. Navarone itself, grim bastion of narrow straits manned by a mixed garrison of Germans and Italians, an apparently impregnable iron fortress. To Captain Keith Mallory, skllled saboteur, trained mountaineer, fell the task of leading the small party detailed to scale the vast, impossible precipice of Navarone and to blow up the guns. The Guns of Navarone is the story of that mission, the tale of a calculated risk taken in the time of war... world war 1939-1945 - fiction, special operations - fiction -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Apike Milligan, Mussolini: His part in my downfall, 1980
The fourth volume of Spike Milligan's legendary account of his time in the army during World War Two begins as he and his regiment land in sunny Italy in 1943 ('The ship touched the beach very gently, so gently I suspect it's not insured'). After a bout of Sandfly Fever, from which he soon recovers ('I'm ready to be killed again'), our plucky hero is piddled on by a farm dog ('Mussolini's revenge?') before forging his way inland towards the enemy and the sound of guns ('We're getting near civilisation'), where matters suddenly take a dark turn ('I was not really me any more')ill., facsims, ports, 288 p. The fourth volume of Spike Milligan's legendary account of his time in the army during World War Two begins as he and his regiment land in sunny Italy in 1943 ('The ship touched the beach very gently, so gently I suspect it's not insured'). After a bout of Sandfly Fever, from which he soon recovers ('I'm ready to be killed again'), our plucky hero is piddled on by a farm dog ('Mussolini's revenge?') before forging his way inland towards the enemy and the sound of guns ('We're getting near civilisation'), where matters suddenly take a dark turn ('I was not really me any more')world war 1939-1945 - fiction, war stories -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, John Masefield, Gallipoli, 1978
The Gallipoli campaign began one fateful Sunday morning in April 1915. It was to be Australia's test of nationhood. The Allied soldiers landed in the dark, crossing beaches tangled with barbed wire, passing mines and scaled the precipitous cliffs under machine-gun fire. An intense five-month campaign ensued, the lines so close that there was no respite from battle. With access to military documents, the poet John Masefield published this moving account of the Allied efforts in the Dardanelles less than a year after the defeat. The book was a huge success, as it gave glory to the bravery and determination of the young men who endured heat, toil, thirst, disease and pestilence but were always ready and willing to die in exultation for their cause.. Moving account of the Allied efforts in Dardanelles after the defeat.Ill, map, p.183non-fictionThe Gallipoli campaign began one fateful Sunday morning in April 1915. It was to be Australia's test of nationhood. The Allied soldiers landed in the dark, crossing beaches tangled with barbed wire, passing mines and scaled the precipitous cliffs under machine-gun fire. An intense five-month campaign ensued, the lines so close that there was no respite from battle. With access to military documents, the poet John Masefield published this moving account of the Allied efforts in the Dardanelles less than a year after the defeat. The book was a huge success, as it gave glory to the bravery and determination of the young men who endured heat, toil, thirst, disease and pestilence but were always ready and willing to die in exultation for their cause.. Moving account of the Allied efforts in Dardanelles after the defeat. world war 1914-1918 - campaigns - gallipoli, anzac corps -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Allen & Unwin, The battle of Long Tan : as told by the commanders to Bob Grandin, 2004
This is the first time that those in direct command of Delta Company have shared their memories of the most significant battle fought by Australians in Vietnam, the Battle of Long Tan. Each of the commanders shares the experiences that brought them to Vietnam, and describes how the company commander, Harry Smith, drove Delta Company to become one of the most outstanding units in the Australian forces. Delta's superb military discipline, and its commanders' ability to think outside the square were decisive in holding a vastly superior number of enemies at bay. Each platoon played a crucial role in Delta Company's survival. The artillery's commitment in providing an unbroken wall of metal through which the enemy had to advance is told from the perspectives of both the forward controller and the gun positions. We fly with the RAAF helicopter pilots whose ammunition resupply was the turning point of the battle, and experience the carnage of the battlefield through the eyes of those in the relieving APCs. Delta Company's trauma on returning to the battlefield to claim their fallen was lightened only by the miraculous survival of two of their wounded. The trauma of the battle did not end with the action, however, as politics began to play their part in the drama. The valour of those directly involved in the battle has never been duly recognised - in some cases it has been belittled, in others denied. The ongoing efforts of the Long Tan commanders to right the many wrongs perpetrated in the wake of the battle, and their own journeys from the events of August 1966 draw the reader into a compelling dialogue on the aftermath of Vietnam. Collapse summaryIndex, ill, maps, p.332.non-fictionThis is the first time that those in direct command of Delta Company have shared their memories of the most significant battle fought by Australians in Vietnam, the Battle of Long Tan. Each of the commanders shares the experiences that brought them to Vietnam, and describes how the company commander, Harry Smith, drove Delta Company to become one of the most outstanding units in the Australian forces. Delta's superb military discipline, and its commanders' ability to think outside the square were decisive in holding a vastly superior number of enemies at bay. Each platoon played a crucial role in Delta Company's survival. The artillery's commitment in providing an unbroken wall of metal through which the enemy had to advance is told from the perspectives of both the forward controller and the gun positions. We fly with the RAAF helicopter pilots whose ammunition resupply was the turning point of the battle, and experience the carnage of the battlefield through the eyes of those in the relieving APCs. Delta Company's trauma on returning to the battlefield to claim their fallen was lightened only by the miraculous survival of two of their wounded. The trauma of the battle did not end with the action, however, as politics began to play their part in the drama. The valour of those directly involved in the battle has never been duly recognised - in some cases it has been belittled, in others denied. The ongoing efforts of the Long Tan commanders to right the many wrongs perpetrated in the wake of the battle, and their own journeys from the events of August 1966 draw the reader into a compelling dialogue on the aftermath of Vietnam. Collapse summary vietnam war 1961-1975 – australian involvement, vietnam war 1961-1975 – battles – long tan -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Michael K Cecil, Australian Military Equipment Profiles: Local pattern carriers 1939-1945, 1992
Illustrative and textual description of Australian local pattern carriers 1939-1945Ill, p.48non-fictionIllustrative and textual description of Australian local pattern carriers 1939-1945military weapons - australia, machine gun carriers - australia -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Chartwell Books, Classic fighters : the inside story, 2005
'Packed with fascinating facts, this volume contains incredibly detailed cutaway drawings of arguably the greatest fighter aircraft ever flown. Each drawing examines what's 'under the skin', clearly showing 'the inside story' - airframe structure, cockpit components, engines, fuel tanks, avionics, machine guns and cannon, missiles and bombs - revealing how the fighters were built, and the weapons they have carried into combat. Each significant component is given a number and is identified in an accompanying key. Moreover, together with stunning photographs, as well as detailed specifications, the absorbing in-depth development histories provide avid aviation enthusiasts all the information they could wish for about the most exciting warplanes spanning almost a hundred years. The aircraft themselves vary tremendously, from simple, wooden-framed, fabric-covered machines with open cockpits, often firing machine guns through whirring, propellers, to super-fast, highly maneuverable, sophisticated and stealthy fighters armed to the teeth with multi-barrel cannons and missiles that can destroy enemy aircraft from beyond visual range. In between are featured a host of combat-proven fighters, many of which have recorded a plethora of 'firsts' - first jet warplane, first supersonic fighter to enter service, first Mach 2 and even Mach 3 interceptors, first tail-less delta machine, first sweeping-wing machine, first missile-armed fighter, and many more. It is certainly an extraordinarily wide-ranging subject presented in such a fantastically individual manner that it is difficult to imagine a more striking volume in aviation publishing.Ill, p,253.non-fiction'Packed with fascinating facts, this volume contains incredibly detailed cutaway drawings of arguably the greatest fighter aircraft ever flown. Each drawing examines what's 'under the skin', clearly showing 'the inside story' - airframe structure, cockpit components, engines, fuel tanks, avionics, machine guns and cannon, missiles and bombs - revealing how the fighters were built, and the weapons they have carried into combat. Each significant component is given a number and is identified in an accompanying key. Moreover, together with stunning photographs, as well as detailed specifications, the absorbing in-depth development histories provide avid aviation enthusiasts all the information they could wish for about the most exciting warplanes spanning almost a hundred years. The aircraft themselves vary tremendously, from simple, wooden-framed, fabric-covered machines with open cockpits, often firing machine guns through whirring, propellers, to super-fast, highly maneuverable, sophisticated and stealthy fighters armed to the teeth with multi-barrel cannons and missiles that can destroy enemy aircraft from beyond visual range. In between are featured a host of combat-proven fighters, many of which have recorded a plethora of 'firsts' - first jet warplane, first supersonic fighter to enter service, first Mach 2 and even Mach 3 interceptors, first tail-less delta machine, first sweeping-wing machine, first missile-armed fighter, and many more. It is certainly an extraordinarily wide-ranging subject presented in such a fantastically individual manner that it is difficult to imagine a more striking volume in aviation publishing.fighter planes - history, fighter planes -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Grubb Street et al, Under the guns of the German aces : Immelmann, Voss, Göring, Lothar von Richthofen : the complete record of their victories and victims, 1997
Listing of the victims of the ace German fighter pilots in World war IIIndex, bib, ill, p.192.non-fictionListing of the victims of the ace German fighter pilots in World war IIfighter pilots - great britain - biography, fighter pilots - germany - biography -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Pan Books, The guns 1914-1918, 1971
A study of artillery in World War OneIll, p.159.non-fictionA study of artillery in World War Oneworld war 1914-1918 - military history, world war 1914-1918 - artillery
