Showing 1812 items matching "planning and development"
-
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncArchive (Sub-series) - Subject File, Development (Kew), 1958
Various partiesReference, Research, InformationSecondary Values (KHS Imposed Order)Subject file consisting largely of newspaper clippings/articles relating to houses in Kew. The earliest original newspaper article dates from 1923 and relates to housing shortages. The file contains some interesting Council records and correspondence relating to community action in response to development. These include the proposed lease of the Ground Floor of the Kew Civic Buildings as a postal delivery centre (1992), the development of flats in Studley Ward (1977), a proposed motel in Studley Park Road (1983)kew post office, heritage, planning and developmentkew post office, heritage, planning and development -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
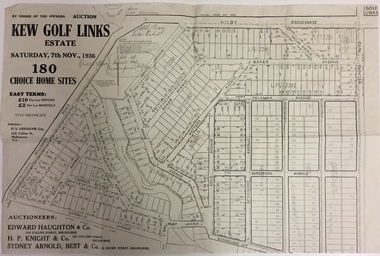
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Kew Golf Links Estate, 1936, 1936
The Kew Golf Links Estate was a major subdivision in North Kew. It derived its title due to the land being previously occupied by the Kew Golf Club, which transferred its course to a number of locations before occupying its current site. The Plan advertises 180 choice home sites. The street names are somewhat different today as those on the map are named after the proposed Kodak Factory to be built on the site. The subdivision of the Kew Golf Links Estate was a major subdivision of farmland in Kew. The site was at one stage designated for industrial development and the building of a new Kodak factory. The decision by Council to oppose the redevelopment makes the beginning of the period when all industrial development was banned in Kew.Monochrome printed, folded subdivision plan for the Kew Golf Links Estate, to be auctioned on 7 November 1936. Streets named include: Carnegie Avenue, Willsmere Road, Kilby Boulevarde, Kodak Avenue, Coleman Avenue, Beresford Avenue, McConchie Avenue, Cole Avenue, White Avenue, Baker Avenue, Spruzen Avenue, Tanner Avenue, Ratten Avenue, Mathers Avenue, Railway Avenue, Sutherland Avenue, and Belford Road. The position of the Yarra River and a large Drainage Reserve are marked on the plan. Lots for sale are numbered. Existing buildings are designated with a square.subdivision plans - kew (vic), kodak factory - kew (vic) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncBooklet, Duncan & Weller Pty Ltd, Old Kew Golf Links Estate, 1927, 1927
The booklet advertises the third sale within the Old Golf Links Estate which was a major subdivision of farmland in North Kew in the 1920sThe subdivision of the Kew Golf Links Estate was a major subdivision of farmland in Kew. The site was at one stage designated for industrial development and the building of a new Kodak factory. The decision by Council to oppose the redevelopment makes the beginning of the period when all industrial development was banned in Kew.6 page illustrated brochure advertising the third section of a major subdivision in Kew in 1927 including 75 charming home allotments and 7 valuable building sites. The brochure includes the subdivision plan. The front cover includes a colour illustration of the almost completed houses in Woolcock Avenue. Streets named include: Kilby Road, Kodak Avenue, Baker Avenue, Mathers Avenue, Coleman Avenue, White Avenue and Belford Road. Lots for sale are numbered. Existing buildings are designated with a square.subdivisions - kew (vic), kew golf links estate -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncJournal, Kewriosity : September 1992
Opportunity for employers & unemployed young people / p1.Kew Festival and education / p1. Kew's Community Bus / p1. Chief Executive's Column [Influences on rates and charges for 1992/93]; City of Kew Streetscaping Committee / Malcolm Hutchinson p2. Mayor's Comment / Cr Roger Streeton p3. Diary Dates for September/October [1992] / p4. Municipal Health Plan have your say? / p5. Volunteer wanted [Kew Cottges] / p5. Work at home as a family day care giver / p5. Nutrition information win prizes / p6. Holiday fun for children & teenagers / p7. What do women at mid-life want? / p7. Be wise with medicines month / p7. 12 month trials of multi-dwelling development code / p7. Pictures of Kew [Mrs June Stratford, Head of Carey Junior School; Octagonal shelter, Boroondara Cemetery; St Anthony's Home for Children 1922-76; The Hartwell Players] / p8.Kewriosity was a local newsletter combining Kew Council and community news. It was published between November 1983 and June 1994, replacing an earlier Kewriosity [broad] Sheet (1979-84). In producing Kewriosity, Council aimed to provide a range of interesting and informative articles covering its deliberations and decision making, together with items of general interest and importance to the Kew community and information not generally available through daily media outlets.non-fictionOpportunity for employers & unemployed young people / p1.Kew Festival and education / p1. Kew's Community Bus / p1. Chief Executive's Column [Influences on rates and charges for 1992/93]; City of Kew Streetscaping Committee / Malcolm Hutchinson p2. Mayor's Comment / Cr Roger Streeton p3. Diary Dates for September/October [1992] / p4. Municipal Health Plan have your say? / p5. Volunteer wanted [Kew Cottges] / p5. Work at home as a family day care giver / p5. Nutrition information win prizes / p6. Holiday fun for children & teenagers / p7. What do women at mid-life want? / p7. Be wise with medicines month / p7. 12 month trials of multi-dwelling development code / p7. Pictures of Kew [Mrs June Stratford, Head of Carey Junior School; Octagonal shelter, Boroondara Cemetery; St Anthony's Home for Children 1922-76; The Hartwell Players] / p8. publications -- city of kew (vic.), kewriosity, council newsletters, community newsletters -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncJournal, Kewriosity : April 1990
Rates reminder / p1. The greening of Kew / p1. Dates for April / p2. Dog fees due / p2. Streetscaping plan / p3. Commentary / Cr Michael Montalto / p3 Residential policies review / p3 . Community bus / p3. High Street parking changes / p3. [Easter] Holiday Program / p4. Library corner / p4. Notices [Anniversary fete] / p4. The view from the dome [Sacred Heart Church] / p4. Car control course for young drivers / p4. Singles talk / p4. Anzac Day / p5. Office [development] Policy launched / p5. Federal Minister in firing line [Family Day Care programs] / p5. Possums playgroup / p5. World focus on literacy this year / p6. Credit card debt a nightmare / p6. Garden weddings fee [Alexandra Gardens] / p6. Siena [College] is 50 / p6. Painting for Kew Library [Studley Park Conservation Society, Louise Folleta - 'Yarra River at Studley Park'] / p7. One year on for women's club [Kew Ladies Probus Club] / p7. In Brief / p7. Council strengthens YMCA links [Kew Recreation Centre] / p7. Neighbourhood Watch / p8. Traffic Management update / p8. Consumer matters / p8. Back care seminar / p8. Introducing the "Fact Pack" [Youth Services] / p8.Kewriosity was a local newsletter combining Kew Council and community news. It was published between November 1983 and June 1994, replacing an earlier Kewriosity [broad] Sheet (1979-84). In producing Kewriosity, Council aimed to provide a range of interesting and informative articles covering its deliberations and decision making, together with items of general interest and importance to the Kew community and information not generally available through daily media outlets.non-fictionRates reminder / p1. The greening of Kew / p1. Dates for April / p2. Dog fees due / p2. Streetscaping plan / p3. Commentary / Cr Michael Montalto / p3 Residential policies review / p3 . Community bus / p3. High Street parking changes / p3. [Easter] Holiday Program / p4. Library corner / p4. Notices [Anniversary fete] / p4. The view from the dome [Sacred Heart Church] / p4. Car control course for young drivers / p4. Singles talk / p4. Anzac Day / p5. Office [development] Policy launched / p5. Federal Minister in firing line [Family Day Care programs] / p5. Possums playgroup / p5. World focus on literacy this year / p6. Credit card debt a nightmare / p6. Garden weddings fee [Alexandra Gardens] / p6. Siena [College] is 50 / p6. Painting for Kew Library [Studley Park Conservation Society, Louise Folleta - 'Yarra River at Studley Park'] / p7. One year on for women's club [Kew Ladies Probus Club] / p7. In Brief / p7. Council strengthens YMCA links [Kew Recreation Centre] / p7. Neighbourhood Watch / p8. Traffic Management update / p8. Consumer matters / p8. Back care seminar / p8. Introducing the "Fact Pack" [Youth Services] / p8. publications -- city of kew (vic.), kewriosity, council newsletters, community newsletters -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncJournal, Kewriosity : November 1989
Paper collections / p1. Community Assistance Grants / 1. Stop Press [Community Services Department, Planning and Development Department] / p1. Dates for November / p2. Residential policies review / p2. Cotham/Glenferrie traffic plans / p2. Christmas cards / p2. And more Christmas cards / p2. History tapestry nears completion [bicentennial project, Kew Historical Society] / p2. Commentary / Cr Michael Montalto [Council finances] / p3. Municipal Offices temporarily relocate [asbestos] / p3. Osteoporosis apparatus installed at St George's [Hospital] / p4. Camberwell joins holiday program [Teenage Holiday Program] / p3. Notices / p4. Early parenting / p4. Roadworks for Kew / p4. Where are you Clark Kent? [Interchange Inner East] / p5. Bushwalkers clean up [Studley Park] / p5. [St George's] Hospital signs first health agreement / p5. [Royal Women's] Hospital honours work of Kew women / p6. Council waste disposal costs up 30% / p6. Merri Yarra [Municipal Protection] Committee disbands / p6. Keeping you informed [Citizens' Advice Bureaux] / p7. Overdevelopment review put on hold / p7. Kew's Parks - Is there room for improvement / p7. [Woodlands Avenue] Playgroup enrolments open / p7. Neighbourhood Watch / p8. Bowls at East Kew [Kew East Bowling Club] / p8. [Kew Bowling Club] / p8. Kew brothers rowed for gold [Bradley Kinninmonth, Eugene Kinninmonth] / p8.Kewriosity was a local newsletter combining Kew Council and community news. It was published between November 1983 and June 1994, replacing an earlier Kewriosity [broad] Sheet (1979-84). In producing Kewriosity, Council aimed to provide a range of interesting and informative articles covering its deliberations and decision making, together with items of general interest and importance to the Kew community and information not generally available through daily media outlets.non-fictionPaper collections / p1. Community Assistance Grants / 1. Stop Press [Community Services Department, Planning and Development Department] / p1. Dates for November / p2. Residential policies review / p2. Cotham/Glenferrie traffic plans / p2. Christmas cards / p2. And more Christmas cards / p2. History tapestry nears completion [bicentennial project, Kew Historical Society] / p2. Commentary / Cr Michael Montalto [Council finances] / p3. Municipal Offices temporarily relocate [asbestos] / p3. Osteoporosis apparatus installed at St George's [Hospital] / p4. Camberwell joins holiday program [Teenage Holiday Program] / p3. Notices / p4. Early parenting / p4. Roadworks for Kew / p4. Where are you Clark Kent? [Interchange Inner East] / p5. Bushwalkers clean up [Studley Park] / p5. [St George's] Hospital signs first health agreement / p5. [Royal Women's] Hospital honours work of Kew women / p6. Council waste disposal costs up 30% / p6. Merri Yarra [Municipal Protection] Committee disbands / p6. Keeping you informed [Citizens' Advice Bureaux] / p7. Overdevelopment review put on hold / p7. Kew's Parks - Is there room for improvement / p7. [Woodlands Avenue] Playgroup enrolments open / p7. Neighbourhood Watch / p8. Bowls at East Kew [Kew East Bowling Club] / p8. [Kew Bowling Club] / p8. Kew brothers rowed for gold [Bradley Kinninmonth, Eugene Kinninmonth] / p8. publications -- city of kew (vic.), kewriosity, council newsletters, community newsletters -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncJournal, Kew Historical Society, Newsletter No.105, December 2013
Development in Studley Ward / Robert Baker p1-2. Society Activities: Exhibitions [Kew Living 25 years on; Kew High School]; Past meetings; Future meetings; McIntyre Lecture / p3. Wilton [Kew RSL] / Don Garden p4-5. Did you know? [Dickens Village; Jellis' Bakeries; Images of Kew / p5. President's 54th Annual Report 2012-13 / Alex Wilson OAM p6-7. Vale [Ray Boothroyd; Beth Brodribb OBE; Robert (Bob) Johnson] / Judith Vimpani p7. Subdivision plans / Robert Baker p8. The Kew Flyer / Tony Michael & Robert Baker p9-10. It happened in the past [50-years ago; 100-years ago] / p11. Support Kew's History / p11. Tara Hall / p12. Book sale / p12.Published quarterly since 1977, the newsletters of the Kew Historical Society contain significant research by members exploring relevant aspects of the Victorian and Australian Framework of Historical Themes. Frequently, articles on people, places and artefacts are the only source of information about an aspect of Kew, and Melbourne’s history.non-fictionDevelopment in Studley Ward / Robert Baker p1-2. Society Activities: Exhibitions [Kew Living 25 years on; Kew High School]; Past meetings; Future meetings; McIntyre Lecture / p3. Wilton [Kew RSL] / Don Garden p4-5. Did you know? [Dickens Village; Jellis' Bakeries; Images of Kew / p5. President's 54th Annual Report 2012-13 / Alex Wilson OAM p6-7. Vale [Ray Boothroyd; Beth Brodribb OBE; Robert (Bob) Johnson] / Judith Vimpani p7. Subdivision plans / Robert Baker p8. The Kew Flyer / Tony Michael & Robert Baker p9-10. It happened in the past [50-years ago; 100-years ago] / p11. Support Kew's History / p11. Tara Hall / p12. Book sale / p12. kew historical society (vic.) -- periodicals., kew historical society (vic.) -- newsletters, kew historical society (vic.) -- journals -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncJournal, Kewriosity : July 1987
Kew needs more caregivers [Kew Family Day Care Service] / p1. Aquatic Centre go ahead [Kew Recreation Centre] / p1. Dates for July / p2. Holiday Program [activities] / p2. Commentary - Rewarding year almost over / Cr Joe Ormando, Mayor of Kew p3. Nominations close [Kew Council elections] / p3. Traffic Plans / p3. Streetscapes [Derby Street, Pakington Street, Mawson Street, Ridgeway Avenue upgrades] / p3. Living by faith and prudence Carmelite Sisters say / p4. Mothers mark day [Nursing Mothering Week] / p4. Volunteers [Royal Talbot Hospital Auxiliary] / p4. Kew President [Janet Stearn, Victorian Penguin Club] / p5. Art ideas/ / p5. [Kew] Library re-opens / p5. Kew [Community] Bus / p5. Kew Community House - Drop-in Centre / Janet Price / p6. Rec[reation] Program / p6. Dance class [Susan Crouch, Naomi Aitchison] / p6. [Kew Community] Action Group / Rhonda McCaw p6. Integration a two way street [Wheelchair basketball, Victorian Netball Association] / p7. Opera for Kew [Ian Lowe] / p7. Bicentennial plans [Kew Bicentennial Committee] / Gerard Petrie p7. Dance therapy [Dance Therapy Development Group] / p7. Footy news [Kew Football Club] / p8. Keeping you informed [Kew Citizens' Advice Bureau] / p8. Cheque for Red Cross [Kew Red Cross Appeal Committee] / p8. Preparing [garden] beds for Spring / Peter Davies p8.Kewriosity was a local newsletter combining Kew Council and community news. It was published between November 1983 and June 1994, replacing an earlier Kewriosity [broad] Sheet (1979-84). In producing Kewriosity, Council aimed to provide a range of interesting and informative articles covering its deliberations and decision making, together with items of general interest and importance to the Kew community and information not generally available through daily media outlets.non-fictionKew needs more caregivers [Kew Family Day Care Service] / p1. Aquatic Centre go ahead [Kew Recreation Centre] / p1. Dates for July / p2. Holiday Program [activities] / p2. Commentary - Rewarding year almost over / Cr Joe Ormando, Mayor of Kew p3. Nominations close [Kew Council elections] / p3. Traffic Plans / p3. Streetscapes [Derby Street, Pakington Street, Mawson Street, Ridgeway Avenue upgrades] / p3. Living by faith and prudence Carmelite Sisters say / p4. Mothers mark day [Nursing Mothering Week] / p4. Volunteers [Royal Talbot Hospital Auxiliary] / p4. Kew President [Janet Stearn, Victorian Penguin Club] / p5. Art ideas/ / p5. [Kew] Library re-opens / p5. Kew [Community] Bus / p5. Kew Community House - Drop-in Centre / Janet Price / p6. Rec[reation] Program / p6. Dance class [Susan Crouch, Naomi Aitchison] / p6. [Kew Community] Action Group / Rhonda McCaw p6. Integration a two way street [Wheelchair basketball, Victorian Netball Association] / p7. Opera for Kew [Ian Lowe] / p7. Bicentennial plans [Kew Bicentennial Committee] / Gerard Petrie p7. Dance therapy [Dance Therapy Development Group] / p7. Footy news [Kew Football Club] / p8. Keeping you informed [Kew Citizens' Advice Bureau] / p8. Cheque for Red Cross [Kew Red Cross Appeal Committee] / p8. Preparing [garden] beds for Spring / Peter Davies p8. publications -- city of kew (vic.), kewriosity, council newsletters, community newsletters -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncDocument, Kew Historical Society Collection : Preservation Needs Assessment, 2021
Following a Significance Assessment, in 2020, Kew Historical Society received a Community Heritage Grant from the National Library of Australia for a Preservation Needs Assessment, prepared by Grimwade Conservation Services (GCS). The purpose of the assessment was to consider the physical condition of the collection, the suitability of the current housing and storage facilities and to make recommendations for the development of a conservation program.Illustrated 87-page Final Report by Vanessa Kowalski (Grimwade Conservation Services), including - Executive Summary / p5. Key recommendations / p7. Policies and Procedures / p9. Collection / p11. Building (Repository Structure) / p25. Environment / p33. Storage / p41. Display/Exhibitions / p54. Housekeeping / p58. Visitor Impact / p51. Disaster Preparedness / p63. Training Needs/Skills Assessment / p65. Action Plan / p67. Authorship / p71. References / p73. Appendices / p75. non-fictionFollowing a Significance Assessment, in 2020, Kew Historical Society received a Community Heritage Grant from the National Library of Australia for a Preservation Needs Assessment, prepared by Grimwade Conservation Services (GCS). The purpose of the assessment was to consider the physical condition of the collection, the suitability of the current housing and storage facilities and to make recommendations for the development of a conservation program.preservation needs assessments, kew historical society -- collections, kew historical society - conservation, community heritage grants -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncJournal, Kewriosity : October 1984
[Kew] Recreation Centre update [The Committee; Resident Attitude Survey] / p1. [Anglican] Archbishop's first visit to East Kew [St Paul's Church] / p1. Community [Asian Evangelical Fellowship; Hyde Park Fellowship; Kew Baptist Church; Kew Native Plant Group; Kew Garden Club; Kew (Daytime) Garden Club; Fashion Parade; The Rheumatism and Arthritis Foundation of Victoria; Retiring?; Anyone for tennis?; Games evening] / p2. Council - Mayoral Column / Cr Robin Saunders / p3. New Depot / p3. Library News / p3. Calling on people with disabilities in Kew / p3. Dieback in Kew's Plane Trees / p3. Kew's new Councillors - Roger Streeton; Chester Keon-Cohen] / p4. Kew Junction Shopping Centre - Liftout Guide / p5-6, 11-12. Youth Pages - Welcome / p7. Earth Club Camps / Phil Smith p7. Training the oldies / Elizabeth Trapani p7. Holiday fun around Kew / p8&9. Things to do in Kew / p10. A bit further afield / p10. Community - Artisst take dance , drama & art to the streets / p13. Asthma Foundation / p13. Council - More thoughts about the Community House / p14. 1985 Kew Festival / p14. Development Plan for Lower Yarra / p15. Jackie Kookaburra goes to Sea / p15. Migrant woman candidate for Kew [Anna-Maria Dierer, ALP] / p15. Council/Community - Traffic Management; New Residents' Kit; Family Fun Day [East Kew Uniting Church]; Older Person's Action Centre; Kew Citizens' Band - Engagement list / p16.Kewriosity was a local newsletter combining Kew Council and community news. It was published between November 1983 and June 1994, replacing an earlier Kewriosity [broad] Sheet (1979-84). In producing Kewriosity, Council aimed to provide a range of interesting and informative articles covering its deliberations and decision making, together with items of general interest and importance to the Kew community and information not generally available through daily media outlets.non-fiction[Kew] Recreation Centre update [The Committee; Resident Attitude Survey] / p1. [Anglican] Archbishop's first visit to East Kew [St Paul's Church] / p1. Community [Asian Evangelical Fellowship; Hyde Park Fellowship; Kew Baptist Church; Kew Native Plant Group; Kew Garden Club; Kew (Daytime) Garden Club; Fashion Parade; The Rheumatism and Arthritis Foundation of Victoria; Retiring?; Anyone for tennis?; Games evening] / p2. Council - Mayoral Column / Cr Robin Saunders / p3. New Depot / p3. Library News / p3. Calling on people with disabilities in Kew / p3. Dieback in Kew's Plane Trees / p3. Kew's new Councillors - Roger Streeton; Chester Keon-Cohen] / p4. Kew Junction Shopping Centre - Liftout Guide / p5-6, 11-12. Youth Pages - Welcome / p7. Earth Club Camps / Phil Smith p7. Training the oldies / Elizabeth Trapani p7. Holiday fun around Kew / p8&9. Things to do in Kew / p10. A bit further afield / p10. Community - Artisst take dance , drama & art to the streets / p13. Asthma Foundation / p13. Council - More thoughts about the Community House / p14. 1985 Kew Festival / p14. Development Plan for Lower Yarra / p15. Jackie Kookaburra goes to Sea / p15. Migrant woman candidate for Kew [Anna-Maria Dierer, ALP] / p15. Council/Community - Traffic Management; New Residents' Kit; Family Fun Day [East Kew Uniting Church]; Older Person's Action Centre; Kew Citizens' Band - Engagement list / p16. publications -- city of kew (vic.), kewriosity, council newsletters, community newsletters -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncJournal, The Kewriosity Sheet Vol.2 No.7 : December 1980
Stop Press! / Editor p1. Kew Traffic School / p1.Mobile New Games Trailer / p1. Recreation Programmes [Playcentre; Sports Coaching Kew Tennis Club; Toddler Play Groups; Films] / p1. Art, Craft & Home Produce Market [Kew High School] / p2. Kew Croquet Club / p2. What's doing in Kew for December / p2. For sale - 'Boroondara Place of Shade' [Boroondara General Cemetery] / by Elizabeth Mackie p3. Xmas garbage / p3. Street Party [St Hilary's Church] / p3. Which Way? [Extract - Alice in Wonderland] / p3. Rhymes Without Reason / from David's Joke Book / p3. Kew Junction Development Planning [Background; Public Participation Programme] / p4.The Kewriosity Sheet (1979-83) was first published in the City of Kew (Victoria) in June 1979 as a two-sided 'community newssheet'. It aimed to: 'share news about Kew happenings and Kew people, and to exchange ideas about living in Kew'. Later issues gradually evolved into a 4-page, quarto sized publication. The Kewriosity Sheet was superseded by the Kew Council publication 'Kewriosity' (1983-1994).non-fictionStop Press! / Editor p1. Kew Traffic School / p1.Mobile New Games Trailer / p1. Recreation Programmes [Playcentre; Sports Coaching Kew Tennis Club; Toddler Play Groups; Films] / p1. Art, Craft & Home Produce Market [Kew High School] / p2. Kew Croquet Club / p2. What's doing in Kew for December / p2. For sale - 'Boroondara Place of Shade' [Boroondara General Cemetery] / by Elizabeth Mackie p3. Xmas garbage / p3. Street Party [St Hilary's Church] / p3. Which Way? [Extract - Alice in Wonderland] / p3. Rhymes Without Reason / from David's Joke Book / p3. Kew Junction Development Planning [Background; Public Participation Programme] / p4. community publications --- kew (vic.), the kewriosity sheet, newsletters - kew (vic.) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncJournal, The Kewriosity Sheet Vol.4 No.6 : February 1983
Kew Recreation Program / p1&2. [1983] Kew Festival / p1. East Kew Uniting Church / p1. Emergency overnight accommodation/ Foster care for children [Greek Orthodox Community) / p2. What's doing in Kew for February / p2&3. Kew Garden Club / p3. Kew (Daytime) Gardening Club / p3. Native Plant Group / p3. Are you interested in poetry / p3. Scrabble / p3. Save the Children Fund / p3. Institute of Early Childhood Development (short courses) / p4. Make Today Count (health & wellbeing) / p4. Kew Library (family history; genealogy) / p4. Hyde Park Fellowship (Hyde Park Uniting Church) / p4. Early Planning for Retirement Group / p4. Uniting Church East Kew / p4.The Kewriosity Sheet (1979-83) was first published in the City of Kew (Victoria) in June 1979 as a two-sided 'community newssheet'. It aimed to: 'share news about Kew happenings and Kew people, and to exchange ideas about living in Kew'. Later issues gradually evolved into a 4-page, quarto sized publication. The Kewriosity Sheet was superseded by the Kew Council publication 'Kewriosity' (1983-1994).non-fictionKew Recreation Program / p1&2. [1983] Kew Festival / p1. East Kew Uniting Church / p1. Emergency overnight accommodation/ Foster care for children [Greek Orthodox Community) / p2. What's doing in Kew for February / p2&3. Kew Garden Club / p3. Kew (Daytime) Gardening Club / p3. Native Plant Group / p3. Are you interested in poetry / p3. Scrabble / p3. Save the Children Fund / p3. Institute of Early Childhood Development (short courses) / p4. Make Today Count (health & wellbeing) / p4. Kew Library (family history; genealogy) / p4. Hyde Park Fellowship (Hyde Park Uniting Church) / p4. Early Planning for Retirement Group / p4. Uniting Church East Kew / p4.community publications --- kew (vic.), the kewriosity sheet, newsletters - kew (vic.) -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
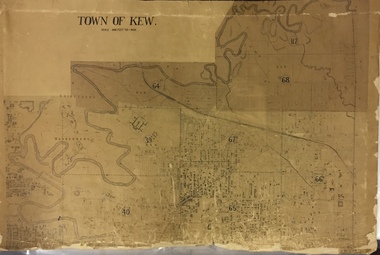
Kew Historical Society IncMap, MMBW, MMBW Town of Kew, 1910-21
The Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) was established by an act of the Victorian Parliament in 1890 to prepare for and to implement a sewerage and water reticulation system across what was then inner Melbourne, its surrounding and middle distance suburbs, including Kew. The MMBW was disbanded in 1991.The map collection of the Kew Historical Society has at its core the historic maps assembled and originally stored in the City Engineer's Department of the City of Kew. These include maps in a number of scales. The vast majority of maps were produced by the MMBW in the first two decades of the twentieth century, and are solid working maps, backed by linen for durability. These maps are historically significant to Kew, the City of Boroondara and to the history of the development of state utilities in Victoria. A number of the Kew maps have additional details added by former municipal officers, including the levels reached by various floods. As these were working documents, information was added to them long after the period of their initial production and distribution.Early map of the Town of Kew, created after 1910, at a scale 440 ft to 1 inch. The 'assembled' map by the City of Kew Engineer's Department includes scaled down copies of The Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works maps, Nos. 39, 40, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, and 117. The map covers the entirety of the Town of Kew, bordered on its north and west by the River Yarra, by Burke Road in the East and Barkers Road in the south. The map shows the extent of urban development by that time, prominent institutions and the outlines of built structures in the municipality. TOWN OF KEW / SCALE 400 FEET TO 1 INCHmelbourne & metropolitan board of works, mmbw maps, mmbw plans, town of kew, cartography -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
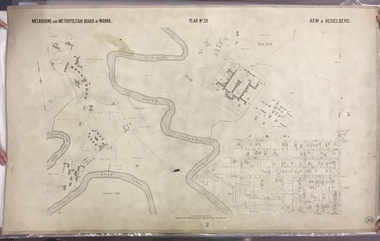
Kew Historical Society IncMap, MMBW, MMBW Plan No.39 Kew & Heidelberg, 1900-1910
The Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) was established by an act of the Victorian Parliament in 1890 to prepare for and to implement a sewerage and water reticulation system across what was then inner Melbourne, its surrounding and middle distance suburbs, including Kew. The MMBW was disbanded in 1991.The map collection of the Kew Historical Society has at its core the historic maps assembled and originally stored in the City Engineer's Department of the City of Kew. These include maps in a number of scales. The vast majority of maps were produced by the MMBW in the first two decades of the twentieth century, and are solid working maps, backed by linen for durability. These maps are historically significant to Kew, the City of Boroondara and to the history of the development of state utilities in Victoria. A number of the Kew maps have additional details added by former municipal officers, including the levels reached by various floods. As these were working documents, information was added to them long after the period of their initial production and distribution.Early map of part of the Borough of Kew, created in the first decade of the twentieth century, at a scale 160 ft to 1 inch. The map covers what was then the north western section of Kew, bordered on its north by Wills Street and the Kew Lunatic Asylum, in the west by the River Yarra [and the later added Yarra Boulevard] , by Princess Street in the East and Holroyd Street in the south. The map shows the extent of urban development by that time, prominent institutions and the outlines of built structures in the municipality. Contour lines were added in ink to the map at a later stage.MELBOURNE AND METROPOLITAN BOARD OF WORKS / PLAN NO. 39 / KEW & HEIDELBERGmelbourne & metropolitan board of works, mmbw maps, mmbw plans, borough of kew, cartography -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
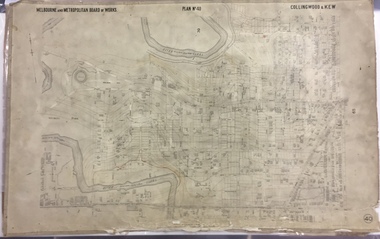
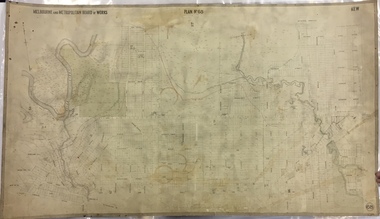
Kew Historical Society IncMap, MMBW, MMBW Plan No.40 Collingwood & Kew, 1900-1910
The Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) was established by an act of the Victorian Parliament in 1890 to prepare for and to implement a sewerage and water reticulation system across what was then inner Melbourne, its surrounding and middle distance suburbs, including Kew. The MMBW was disbanded in 1991.The map collection of the Kew Historical Society has at its core the historic maps assembled and originally stored in the City Engineer's Department of the City of Kew. These include maps in a number of scales. The vast majority of maps were produced by the MMBW in the first two decades of the twentieth century, and are solid working maps, backed by linen for durability. These maps are historically significant to Kew, the City of Boroondara and to the history of the development of state utilities in Victoria. A number of the Kew maps have additional details added by former municipal officers, including the levels reached by various floods. As these were working documents, information was added to them long after the period of their initial production and distribution.Early map of part of the Borough of Kew, created in the first decade of the twentieth century, at a scale 160 ft to 1 inch. The map covers what was then the south western section of Kew, bordered on its north by Studley Park Road, in the west by Walmer Street and the River Yarra, by High Street South and Princess Street in the East and Barkers Road in the south. The map shows the extent of urban development by that time, prominent institutions and the outlines of built structures in the municipality. Contour lines and historic flood levels were added in ink to the map at a later stage.MELBOURNE AND METROPOLITAN BOARD OF WORKS / PLAN NO. 40 / COLLINGWOOD & KEWmelbourne & metropolitan board of works, mmbw maps, mmbw plans, borough of kew, cartography -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncMap, MMBW, MMBW Plan No.64 Kew & Heidelberg, 1900-1910
The Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) was established by an act of the Victorian Parliament in 1890 to prepare for and to implement a sewerage and water reticulation system across what was then inner Melbourne, its surrounding and middle distance suburbs, including Kew. The MMBW was disbanded in 1991.The map collection of the Kew Historical Society has at its core the historic maps assembled and originally stored in the City Engineer's Department of the City of Kew. These include maps in a number of scales. The vast majority of maps were produced by the MMBW in the first two decades of the twentieth century, and are solid working maps, backed by linen for durability. These maps are historically significant to Kew, the City of Boroondara and to the history of the development of state utilities in Victoria. A number of the Kew maps have additional details added by former municipal officers, including the levels reached by various floods. As these were working documents, information was added to them long after the period of their initial production and distribution.Early map of part of the Borough of Kew, created in the first decade of the twentieth century, at a scale 160 ft to 1 inch. The map covers what was then the northern most part of Kew, bordered on its north and west by the Yarra River, in the East by Connor's Creek and by the Asylum in the south. The map shows the extent of urban development by that time, prominent institutions and the outlines of built structures in the municipality. Contour lines and historic flood levels were added in ink to the map at a later stage.MELBOURNE AND METROPOLITAN BOARD OF WORKS / PLAN NO. 64 / KEW & HEIDELBERGmelbourne & metropolitan board of works, mmbw maps, mmbw plans, borough of kew, cartography -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
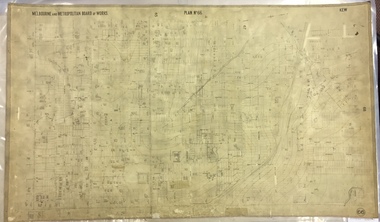
Kew Historical Society IncMap, MMBW, MMBW Plan No.65 Kew & Heidelberg, 1900-1910
The Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) was established by an act of the Victorian Parliament in 1890 to prepare for and to implement a sewerage and water reticulation system across what was then inner Melbourne, its surrounding and middle distance suburbs, including Kew. The MMBW was disbanded in 1991.The map collection of the Kew Historical Society has at its core the historic maps assembled and originally stored in the City Engineer's Department of the City of Kew. These include maps in a number of scales. The vast majority of maps were produced by the MMBW in the first two decades of the twentieth century, and are solid working maps, backed by linen for durability. These maps are historically significant to Kew, the City of Boroondara and to the history of the development of state utilities in Victoria. A number of the Kew maps have additional details added by former municipal officers, including the levels reached by various floods. As these were working documents, information was added to them long after the period of their initial production and distribution.Early map of part of the Borough of Kew, created in the first decade of the twentieth century, at a scale 160 ft to 1 inch. The map covers what was then the south central part of Kew, bordered on its north by Malmsbury Street, in the west by Florence Avenue, in the south by Barkers Road, and in the east by Princess Street. The map shows the extent of urban development by that time, prominent institutions and the outlines of built structures in the municipality. Contour lines were added in ink to the map at a later stage.MELBOURNE AND METROPOLITAN BOARD OF WORKS / PLAN NO. 65 / KEW & HEIDELBERGmelbourne & metropolitan board of works, mmbw maps, mmbw plans, borough of kew, cartography -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
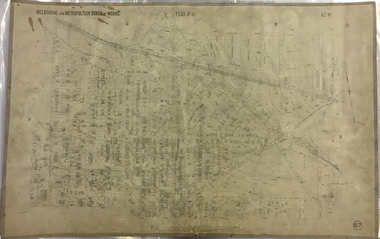
Kew Historical Society IncMap, MMBW, MMBW Plan No.66 Kew, 1900-1910
The Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) was established by an act of the Victorian Parliament in 1890 to prepare for and to implement a sewerage and water reticulation system across what was then inner Melbourne, its surrounding and middle distance suburbs, including Kew. The MMBW was disbanded in 1991.The map collection of the Kew Historical Society has at its core the historic maps assembled and originally stored in the City Engineer's Department of the City of Kew. These include maps in a number of scales. The vast majority of maps were produced by the MMBW in the first two decades of the twentieth century, and are solid working maps, backed by linen for durability. These maps are historically significant to Kew, the City of Boroondara and to the history of the development of state utilities in Victoria. A number of the Kew maps have additional details added by former municipal officers, including the levels reached by various floods. As these were working documents, information was added to them long after the period of their initial production and distribution.Early map of part of the Borough of Kew, created in the first decade of the twentieth century, at a scale 160 ft to 1 inch. The map covers what was then the south eastern part of Kew, bordered on its north by Adeney Avenue, in the west by Sackville Street, in the south by Barkers Road, and in the east by Burke Road. The map shows the extent of urban development by that time, prominent institutions and the outlines of built structures in the municipality. Contour lines were added in ink to the map at a later stage.MELBOURNE AND METROPOLITAN BOARD OF WORKS / PLAN NO. 66 / KEW melbourne & metropolitan board of works, mmbw maps, mmbw plans, borough of kew, cartography -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
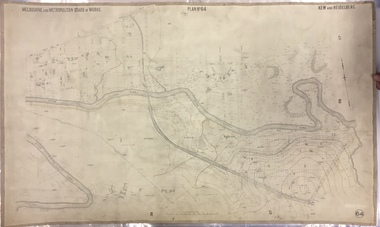
Kew Historical Society IncMap, MMBW, MMBW Plan No.67 Kew, 1900-1910
The Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) was established by an act of the Victorian Parliament in 1890 to prepare for and to implement a sewerage and water reticulation system across what was then inner Melbourne, its surrounding and middle distance suburbs, including Kew. The MMBW was disbanded in 1991.The map collection of the Kew Historical Society has at its core the historic maps assembled and originally stored in the City Engineer's Department of the City of Kew. These include maps in a number of scales. The vast majority of maps were produced by the MMBW in the first two decades of the twentieth century, and are solid working maps, backed by linen for durability. These maps are historically significant to Kew, the City of Boroondara and to the history of the development of state utilities in Victoria. A number of the Kew maps have additional details added by former municipal officers, including the levels reached by various floods. As these were working documents, information was added to them long after the period of their initial production and distribution.Early map of part of the Borough of Kew, created in the first decade of the twentieth century, at a scale 160 ft to 1 inch. The map covers what was then the north central part of Kew, bordered on its north by the Outer Circle Railway Spruzen and Beresford Avenues, in the west by Princess Street, in the south by High Street, and in the east by (about) Belford Road. The map shows the extent of urban development by that time, prominent institutions and the outlines of built structures in the municipality. Contour lines were added in ink to the map at a later stage.MELBOURNE AND METROPOLITAN BOARD OF WORKS / PLAN NO. 67 / KEW melbourne & metropolitan board of works, mmbw maps, mmbw plans, borough of kew, cartography -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncMap, MMBW, MMBW Plan No.68 Kew, 1900-1910
The Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) was established by an act of the Victorian Parliament in 1890 to prepare for and to implement a sewerage and water reticulation system across what was then inner Melbourne, its surrounding and middle distance suburbs, including Kew. The MMBW was disbanded in 1991.The map collection of the Kew Historical Society has at its core the historic maps assembled and originally stored in the City Engineer's Department of the City of Kew. These include maps in a number of scales. The vast majority of maps were produced by the MMBW in the first two decades of the twentieth century, and are solid working maps, backed by linen for durability. These maps are historically significant to Kew, the City of Boroondara and to the history of the development of state utilities in Victoria. A number of the Kew maps have additional details added by former municipal officers, including the levels reached by various floods. As these were working documents, information was added to them long after the period of their initial production and distribution.Early map of part of the Borough of Kew, created in the first decade of the twentieth century, at a scale 160 ft to 1 inch. The map covers what was then the north central part of Kew, bordered in the north by Oak Avenue, in the west by the Yarra River and Connor's Creek, in the south by Beresford and Carnegie Avenues, and in the east by Glass's Creek and Burke Road. The map shows the extent of urban development by that time, prominent institutions and the outlines of built structures in the municipality. Contour lines and the levels of historic floods were added in ink to the map at a later stage.MELBOURNE AND METROPOLITAN BOARD OF WORKS / PLAN NO. 68 / KEW melbourne & metropolitan board of works, mmbw maps, mmbw plans, borough of kew, cartography -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncMap, MMBW, MMBW Plan No.117 Heidelberg & Kew, 1900-1910
The Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) was established by an act of the Victorian Parliament in 1890 to prepare for and to implement a sewerage and water reticulation system across what was then inner Melbourne, its surrounding and middle distance suburbs, including Kew. The MMBW was disbanded in 1991.The map collection of the Kew Historical Society has at its core the historic maps assembled and originally stored in the City Engineer's Department of the City of Kew. These include maps in a number of scales. The vast majority of maps were produced by the MMBW in the first two decades of the twentieth century, and are solid working maps, backed by linen for durability. These maps are historically significant to Kew, the City of Boroondara and to the history of the development of state utilities in Victoria. A number of the Kew maps have additional details added by former municipal officers, including the levels reached by various floods. As these were working documents, information was added to them long after the period of their initial production and distribution.Early map of part of the Borough of Kew, created in the early twentieth century, at a scale 160 ft to 1 inch. The map covers what was then the north eastern part of Kew showing the natural landscape and limited development on the south side of the Yarra River. In the Kew section, south of the river, the land is occupied currently by the Greenacres and Kew Golf Clubs. The map shows the extent of urban development by that time and the outlines of the few built structures in the municipality. The height above sea level of all parts of the landscape are indicated numerically in feet. Contour lines and the levels of historic floods were added in ink to the map at a later stage. MELBOURNE AND METROPOLITAN BOARD OF WORKS / PLAN NO. 117 / HEIDELBERG & KEW melbourne & metropolitan board of works, mmbw maps, borough of kew, cartography, mmbw plan no. 117, kew (vic.) -- maps, heidelberg (vic.) -- maps -
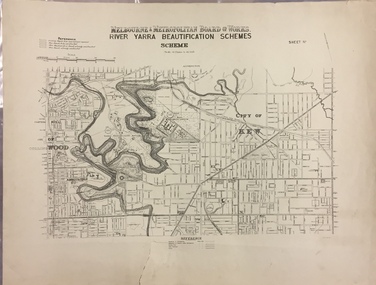 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncMap, MMBW, River Yarra Beautification Schemes, c.1913
The Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) was established by an act of the Victorian Parliament in 1890 to prepare for and to implement a sewerage and water reticulation system across what was then inner Melbourne, its surrounding and middle distance suburbs, including Kew. The MMBW was disbanded in 1991.The map collection of the Kew Historical Society has at its core the historic maps assembled and originally stored in the City Engineer's Department of the City of Kew. These include maps in a number of scales. The vast majority of maps were produced by the MMBW in the first two decades of the twentieth century, and are solid working maps, backed by linen for durability. These maps are historically significant to Kew, the City of Boroondara and to the history of the development of state utilities in Victoria. A number of the Kew maps have additional details added by former municipal officers, including the levels reached by various floods. As these were working documents, information was added to them long after the period of their initial production and distribution.Map of the City of Kew showing part of the River Yarra Beautification Schemes. The map shows development to date and the flood levels reached in 1923 and 1924. This map may have been adapted from an earlier map, as most development in central Kew and Studley Park had occurred by this date yet numerous streets are not represented. Public buildings and institutions are clearly represented and named on the map as are significant public transport infrastructure (eg the Outer Circle railway).MELBOURNE AND METROPOLITAN BOARD OF WORKS / RIVER YARRA BEAUTIFICATION SCHEMES / SCHEME / SCALE 10 CHAINS TO AN INCHmelbourne & metropolitan board of works, mmbw maps, mmbw plans, city of kew, flood levels -- kew (vic.), cartography -
 Queen Victoria Women's Centre
Queen Victoria Women's CentreNewspaper excerpt, The Sunday Age, Car Chaos fear at Queen Victoria Site: Lonsdale Street's Greek quarter feels threatened by development plans, 29 October 2000
Newspaper excerpt from The Sunday Age. Page 5 and a smaller introduction probably from the front page. Smaller excerpt colour photo of blue-stone and cast-iron wall which was to be demolished. Larger excerpt, a black and white aerial view of QVWC and the block where it is situated. building construction, building permits, historic building -
 City of Warrnambool Rowing Club
City of Warrnambool Rowing ClubDevelopment Plaque, 16 july 2017
The people are L to R: Kathy McMeel (secretary), Annie Blanch (Boat Captain), Joanne Bone (president), James Tait (director of Gwen and Edna Jones and Ray and Joyce Uebergang Foundations, Susan Finnigan (Grants Officer) and Clive Wooster (treasurer). • In February 2017 the club filled the base of the boathouse and poured a new concrete floor. • They had an opening to thank the donors, especially the Gwen and Edna Jones and Ray and Joyce Uebergang Foundations and to celebrate with the community and rowers, past and present • Since 1996 rowers had to wade in foul, ankle to thigh high water to access the boat shed- this was for 3-5 months of every year- our facilities are now accessible and Warrnambool has a sporting venue for rowers that is safe and one the public can be proud of. • The Club thanked Barry Wilson for generously donating the plans and acknowledged the ‘term deposit’ raised over the last 10 years, by past and present members, which allowed the Club to contribute the additional funding required. • In particular The Foundations assistance made the project possible. The two philanthropic Foundations are a treasure for the community as they can step in and fill the gap where other funding sources cannot. In our case they were the major donors and we could not have contemplated this project without their assistance. We are truly grateful for the assistance of The Gwen and Edna Jones and Ray and Joyce Uebergang Foundation. • Mr James Tait, a director of both Foundations to unveiled the commemorative plaque. Color photograph taken at the opening of the Redeveloped City of Warrnambool Rowing Club. Includes a brass plaque. The people are L to R: Kathy McMeel (secretary), Annie Blanch (Boat Captain), Joanne Bone (president), James Tait (director of Gwen and Edna Jones and Ray and Joyce Uebergang Foundations, Susan Finnigan (Grants Officer) and Clive Wooster (treasurer).james tait, warrnambool, city of warrnambool rowing club, warrnambool rowing club, boathouse, boathouse redevelopment, gwen and edna jones foundation, ray and joyce uebergang foundation -
 Glen Eira City Council History and Heritage Collection
Glen Eira City Council History and Heritage CollectionDocument - Booklet, "THE CAULFIELD ARTS COMPLEX / CITY OF CAULFIELD", After 1987
Considered to be of historical and social significance. Provides information on the development of the current Town Hall Auditorium and the Glen Eira Gallery.1 x Maroon coloured booklet with gold lettering on cover published by the City of Caulfield. Inside are 14 paper pages with colour concept drawings of the proposed Caulfield Arts Complex, Concept Plans and printed text. Dated May 1987 in the opening page with an Introduction by the Mayor of Caulfield, Cr Jack Campbell. -
 Beechworth Honey Archive
Beechworth Honey ArchivePublication, Honeybee RD&E plan: 2012 to 2013. (Rural Industries Research and Development Corporation). Canberra, 2012, 2012
24 pages. -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPlan, Rainforest Garden Development VCAH Burnley, 1990-1992
Some of these plans were held in P. Tulk's office, used by Honours Student, Linda Hipwell in 1999. (1a) Rough sketch on tracing paper. (1) Rainforest Project drawn by G. Olive, rough sketch pen and pencil on paper. (2) 1 tracing paper and 2 paper copies, Rainforest Garden Development Plant Schedule Key by type of plant. (3) Blueprint of Rainforest Garden Development, plant names beside plants, note to P. Tulk from J. Kellow. (4) Native Garden Burnley VCAH Hort Eng. II. Surveying by Gail, John, Rebecca, Sean, Tim (Students). g. olive, phil tulk, linda hipwell, vcah, students, rainforest, gardens -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPlan, Landscape Construction Facility/Field Station Entry Development Proposal, 1997-1998
The same plan, coloured, drawn by Phil Tulk with different dates: 27.11.1997 and 18.05.1998.phil tulk, field station, landscape construction facility -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesBooklet, Yuncken Freeman Architects, Yarra Valley Metropolitan Park Development Plan - Guidelines for Environs Draft Brief, 1976
parks, yuncken freeman architects -
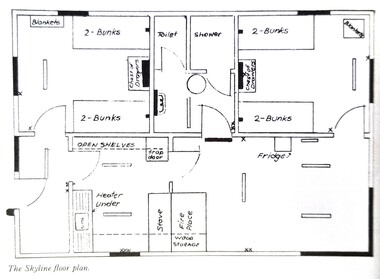 Falls Creek Historical Society
Falls Creek Historical SocietyPlan - Floor plan Skyline Lodge, Bogong High Plains
MEYER COLLECTION - FALLS CREEK PHOTOS In 1947 a determined group of like-minded State Electricity Commission (SEC) staff including Ray Meyer, the chief surveyor of the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme, had a common interest that revolved around the skiing potential of the snow-covered high plains which included what is now the resort of Falls Creek. The six SEC employees, Toni St Elmo, Ray Meyer, Jack Minogue, Lloyd Dunn, Adrian Ruffenacht and Dave Gibson (together with their families) banded together to secretly build a 'hut' that was the first ski lodge at Falls Creek. Using a road built in 1930s to gain access to Falls Creek, their hut project was carried out in secret as efforts by other skiers were blocked by H.H.C. Williams – the engineer in charge of the Hydro Scheme. In 1946 Ray Meyer made a trip to the Lands Office in Melbourne. He came away with a 99-year lease on three acres that was ideally suited for a hut designed by Lloyd Dunn. Adrian Ruffenacht (Design Engineer for the KHS) had suggested where the group should build because of easy access to a spring for water. Much of the building material required was scavenged from derelict huts on the high plains. Due to the need for secrecy, the determined group worked on the hut in the evenings and weekends to avoid detection. During the building period the group had met at Echidna Rock (now known as Eagle Rock) where Skippy St Elmo announced, "This is my favourite ‘Skyline’.” And so the first lodge in the area at Falls Creek Ski Resort came into existence. With the development of the International Poma in the 1970s, the Skyline Lodge, which was sited between the ski-lift’s pole one and pole two, was demolished. However, the legacy of Ray Meyer, Toni St Elmo, Jack Minogue, Lloyd Dunn, Adrian Ruffenacht and Dave Gibson and Skyline lives on in the vibrant atmosphere of Falls Creek Resort. The MEYER COLLECTION documents developments on the Kiewa Hydro Scheme and their life at Falls Creek from the mid 1930s to 1960s.This image is significant because it depicts developments made to "Skyline", the first lodge at Falls Creek.A floor plan of Skyline Lodge, probably after renovations were carried out by the Ski Club of Victoria which bought in to Skyline in 1950. In 1951 - 1952 a road up to the Lodge as well as drains, trenches and culverts were added. renovations to the lounge, basement drainage and porch resurfacing were completed in 1955. falls creek, victorian snowfields, skyline lodge
