Showing 1907 items matching " war work"
-
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Book, Sheehan, Neil, Two Cities: Hanoi and Saigon, 1992
This is a grimly honest book, providing vivid glimpses of ordinary people trying to make a non-existent system work.This is a grimly honest book, providing vivid glimpses of ordinary people trying to make a non-existent system work.vietnam war, 1961-1975., vietnam -- ho chi minh city, hanoi, saigon -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Textile, Handkerchief white edge, Circa 1918
Hankerchiefs have been used for centuries as a piece of cloth deemed useful for personal hygiene. They are usually kept in one's pocket but at times through history have been fluttered to attract attention or send a message. In harder times they proved to be a cheap item often used to add interest to an outfit. This item is one of five hankerchiefs which were brought back from France after WW1 by great uncles of Gloria Redman and have been passed down through her grandmother and mother. This item has significance as an item linked to a local family and World War 1 and as such has social, and historical significance. It is well provenanced and can be used to provide interest to the relating of a fairly common story whereby many soldiers brought or sent back small items such as hankerchiefs to their loved ones at home. Cream silk handkerchief with cream blanket stitched edge with three cream and one pink flower embroidered in each corner. Stems and leaves worked in green.redman, hankerchief, warrnambool, ww1 hankerchief, souvenir ww1 -
 Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub Branch
Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub BranchLiterary work - Framed poem, Dutch Resistance Fighters Poem
The poem was written in 1942 by Jan Remco Theodoor Campert before he and seventeen other Dutch Resistance Fighters were condemed to death. Jan Campert was a Dutch journalist ,theatre critic and writer who lived in Amsterdam. During the German Occupation of the Netherlands in World War ii he was arrested for aiding the Jews. He was held in the Neuengamme concentration camp where he died in 1943.Wooden framed poem.On rear of object - Donated by W.J.L. Verhoef Sen. To honor those resistance fighters who offered their lives during the years 1940 -1945 so we could live in freedom and peace. On the day of the official opening of this centre. September 26th 1987. -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPainting - Panoramic View of Kew and Abbotsford from the garden of Rockingham, V Maloney, 1952
The extensive formal landscaped gardens of Rockingham had been created in the 1860s, and by the 1950s remained bordered to the south by the Barkers Road cutting, and to the north by Blytheswood, the neighbouring Syme family property, By 1940, the Syme family were no longer the occupiers of Rockingham. John Herbert Syme had died in October 1939, and by August the following year, his wife had made the house and garden available, rent free to the Red Cross as a convalescent home for Australian soldiers injured in the Second World War. At the time, the house was described as containing twenty rooms, including a ballroom and a billiards room, with a garden of eight acres overlooking the Yarra. The task of renovating the house to conform to its new function as a convalescent home took a year, finally opening in August 1941. Community support for Rockingham was widespread and included the decision by the National Gallery of Victoria to loan pictures from its collection to decorate the walls. Calls were made for women around Victoria to donate fruit and vegetables from their gardens, which the railways agreed to freight for free. Other local support included the work by a team of boys to establish a three-acre vegetable garden within the formal terraced gardens. From the beginning, occupational therapy formed a key component of the rehabilitation of psychologically injured soldiers. This is confirmed by contemporary newspaper accounts of weaving, ironwork, leatherwork, basketry and gardening by patients. Numerous photographs, held by the Australian War Memorial (AWM) and the State Library of Victoria (SLV), record the importance of these rehabilitation activities. The painting of the view across the river to Abbotsford may have been painted in one of these occupational therapy sessions. For many decades it hung in the occupational therapy room. It must have been on view following the sale of Rockingham by the Syme family to the Red Cross in 1955, and subsequently, until the house was demolished and its grounds finally subdivided in 1977.View of Abbotsford from the garden of Rockingham (1952) was created by V Maloney. The vantage point of the artist was the garden of Rockingham, one of two mansions overlooking the Yarra owned by the Syme family. The artwork depicts a number of sites - especially factories - that have since been demolished.Signed by the artist, lower right "V Maloney"rockingham red cross convalescent home, hospitals - kew (vic), rosemary lade, art therapy -
 St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne Archives
St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne ArchivesArtwork, other - Painting, Circa 1966-1967
This painting was presented to the St Vincent's civilian medical team by the people of An Giang Province, Vietnam, in recognition of their work in the area. St Vincent's sent four civilian clinical teams to Long Xuyen, South Vietnam, 1965 - 1966 as part of an aid program administered by the Australian Department of External Affairs to assist Vietnamese medical and paramedical personnel and provide medical aid to everyone who needed it. The service of the Australian civilian teams who went to Vietnam 1964 - 1972 was recognised with a special plaque within the grounds of the Australian War Memorial in October 2008. This item has historical significance because it is a memento of the hospital's involvement in a nationally significant wartime aid program to South Vietnam. Landscape painting of deer near a forest stream. Painted in the traditional Vietnamese style using lacquer and paint. Artwork is framed in a black frame but is not behind glass. The artist is unknown.Plaque is attached at lower left corner and translated reads: The people of An Giang Province / are extremely grateful to the Australian Surgical Team.st vincent's hospital melbourne, paintings, artworks, south vietnam, medical aid -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Personal Papers, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), "Sequence of Acts of Parliament", c1955
Set of personal papers - set of 7 handwritten papers pinned in top left hand corner, titled "Sequence of Acts of Parliament" dated up to 11/5/1954, Orders in Council and National Security repeal Act of 1945. Compiled by H. S. McComb as part of his work on the consolidation of the MMTB Act in the mid 1950's.trams, tramways, mmtb, tramways, parliament, order in council, world war 2 -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumBook, Murray Views, "See Australia First - Melbourne Victoria", c1950
Book - 16 pages, including grey card covers, titled "See Australia First - Melbourne Victoria" featuring 12 pages of postcard photographs of Melbourne. Inside rear cover has a details of Melbourne's history, the city and its features. Produced by Murray Views of Gympie Qld, printed by Samuel Lee and Co. Images post second world war - late 1940's to early 1950's. Features images of: Alexandra Gardens River Yarra and Princes Bridge Flinders St Station St Kilda Road - tram track work being undertaken Flinders St and the Forum theatre The Exhibition Buildings Collins St Parliament House Bourke St - with cable tram tracks and the Metropole Hotel, Myer, Foys Aerial view of Melbourne Captains Cook's Cottage St Kilda Road with W2 287 Burns Memorial St Kilda Road St Paul's and Princes Bridge Town Hall Royal Melbourne Hospital Collins St with W2 turning Queen Victoria Gardenstrams, tramways, melbourne, flinders st station, collins st, town hall, princes bridge, st kilda rd -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Report, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), "Rolling Stock Department - Annual Report", Jul. 1940
Report - six foolscap sheets stapled in the top left hand corner enclosed by folder protective corner, titled "Rolling Stock Department - Annual Report for the year ending 30 June 1940". Gives details of the trams maintained and built, the workshops, running sheds, availability, buses, new buses, improvements to the rolling stock, defence work, work for other departments, foundry, laboratory, drawing office cable system and staffing. Last sheet details various classes available for service and those under construction.trams, tramways, workshops, staff, new trams, world war 2, buses -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Radio Transcript, Australian Broadcasting Commission, "Woman at War - Melbourne Tram Conductress", May. 1943
... the war. Demonstrates the work of the ABC during 1943 and has ...Interview titled "Woman at War - by Catherine Duncan - Interviews with women in Industry No. 1 - interviews Mrs. Hammond a Melbourne Tram Conductress", dated 5/1943. ABC Shortwave Division. An announcer introduces Catherine Duncan, who then introduces Nita Hammond who featured in a poster on the tram called "She's Helping You". Her husband is serving overseas, prior to becoming a conductress, was just an ordinary housewife, describes the training, learning on the job to collect fares, making friends son the job, was stationed at Head Office, American servicemen, finishing up after the war.Demonstrates the work of the ABC during 1943 and has a close association with Catherine Duncan and Nita Hammond.Radio Transcript or script, 7 foolscap pages, duplicated. A4 photocopy held as well.trams, tramways, world war 2, conductresses, radio stations, abc radio news -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumMagazine, Truck and Bus Transportation, "Trams to Replace buses in Melb's Bourke St Lines", Sep. 1943
Magazine cutting or photocopy of an article titled "Trams to Replace buses in Melb's Bourke St Lines", from the September 1943 issue of Truck and Bus Transportation. Quotes MMTB Chairman Mr Bell, Premier Mr. Dunstan. Notes problems with the extra war time traffic, not coping with maintenance issues, problems with double deck passengers, passengers not wanting to use upstairs, trams superior for the short haul, Fisherman's Bend services, number of buses and that the Board is building new trams, the SW6. Notes service schedules to Northcote, could operate Bourke St with 55 trams instead of 74 buses. Notes the work to consider replacement done by Mr. Simpson, the Acting Manager. Has photo of Mr Bell and the exterior and interior of an SW6 class tram. Has adverts for General Motors Holdens making bomber parts, Better Brakes and Hastings Deerings. 2nd copy added 8/4/2021trams, tramways, bourke st, sw6 class, buses, double deck buses, conversion, northcote, services, general motors -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Form/s, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), "Memorandum to Official and Clerical Staff - Classification of Officers", 2/1920 and 7/1920
.1 - Memorandum printed on quarto paper, duplicated, titled "Memorandum to Official and Clerical Staff - Classification of Officers", dated 28/7/1920 asking the enclosed card to be completed. Shows that the MMTB was trying to get on top of who they had working for them. Notes the system that the person was working for. Two copies held. Machined stamped with "W.O.Srangward" signature as Secretary. .2 - Record card - form number 1168, printed on heavy card, asking for the persons details, age, war service, salary, hours of work, occupation, date joining etc. On rear has space for Head Office notes. .3 - Notice dated 23/2/1920, advising of the proposed classification - typed on a half foolscap sheet.trams, tramways, mmtb, employees, officers, records, personnel, wages -
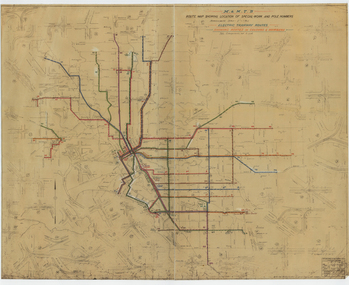 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDrawing, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), "Route Map showing location of special work and pole numbers" "Electric Tramway Routes - showing routes in colours and numbers", late 1941
Map of the system shown at two inches = 1 mile. Drawing No. P5799. Shows crossovers, track layouts at junctions, signal cabins roads, railways and stations. Originally signed by Perway Engineer - 20/12/1940, though originally drawn in 1922. Has been marked up in coloured pencil to show the routes and route numbers. The plan shows the lines to Maribyrnong Munitions works along Cordite Ave and Wests Road and the track from Moonee Ponds to Union Road, which opened in July 1941, but not the extension to Essendon Airport built-in 1942. See Reg Item 1561 for a 1963 version and 1683 for a 1987 versionDemonstrates the use of a MMTB drawing to show tram routes and their route numbers at the time.Drawings - dyeline cloth backed print - titled - "Route Map showing location of special work and pole numbers" and subtitled - "Electric Tramway Routes - showing routes in colours and numbers". trams, tramways, mmtb, trackwork, tramways, junction, map, world war 2 -
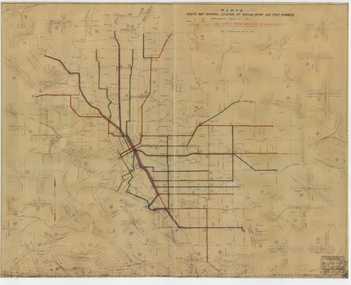 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDrawing, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), "Route Map showing location of special work and pole numbers" "All night tram routes in colours", late 1941
Map of the system shown at two inches = 1 mile. Drawing No. P5799. Shows crossovers, track layouts at junctions, signal cabins roads, railways, and stations. Originally signed by Perway Engineer - 20/12/1940, though originally drawn in 1922. Has been marked up in colour pencil to show the all-night routes and the individual services. The plan shows the lines to Maribyrnong Munitions works along Cordite Ave and Wests Road and the track from Moonee Ponds to Union Road, opened in July 1941, but not the extension to Essendon Airport built in 1942.Demonstrates a detail drawing of Melbourne tramways, junctions and pole numbers.Drawings - dyeline cloth-backed print - titled - "Route Map showing the location of special work and pole numbers" and subtitled - "All night tram routes in colours". trams, tramways, mmtb, trackwork, tramways, junction, map, world war 2, night trams -
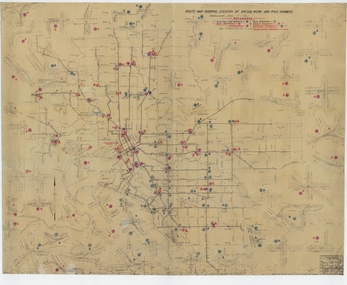 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDrawing, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), "Route Map showing location of special work and pole numbers" "substations", late 1942
Map of the system shown at two inches = 1 mile. Drawing No. P5799. Shows crossovers, track layouts at junctions, signal cabins roads, railways, and stations. Originally signed by Perway Engineer - 20/12/1940, though originally drawn in 1922. The plan shows the lines to Maribyrnong Munitions works along Cordite Ave and Wests Road and the track from Moonee Ponds to Union Road, opened in July 1941, and the extension to Essendon Airport built in 1942, but not the Queen St North Essendon substation. Shows underground cables, tram and bus depot, workshop locations, and substation locations and their priority.Yields information about the MMTB substation locations in 1942.Drawing - dyeline cloth backed print - titled - "Route Map showing location of special work and pole numbers" and subtitled - "Substations". trams, tramways, mmtb, trackwork, tramways, junction, map, world war 2, substation -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumFunctional object - Rolleicord Camera, Franke & Heidecke, late 1930s
Used by the MMTB Supply Department for photograpy. Based on the wikipedia reference and the markings on top of the front face of the camera, made prior to the Second World War. Camera takes 120 film.Demonstrates the type of equipment the MMTB used to record their work, problems and to illustrate reports etc.Camera - metal frame, twin lenses folding view finder within a leather caseMarked "Melbourne Tramways Australia" on the top of the leather cover, and the full name of the MMTB , Melbourne Australia on one side of the camera.mmtb, camera, photography -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Photocopy, Roger J. Jones, "Back in Them Days' ", c1992/93
... the depression, and work done during the war...., and work done during the war. "Back in Them Days' " Document ...Photocopy of cover and five pages extracted from a publication - "Back in Them Days' " - an oral history of Preston edited by Roger J. Jones. Extract features "Tram building" at Preston workshops, features an interview with Clive Boxer. Worked at the workshops 1925 for 6 years, through to 1974, described the construction of trams, working conditions, working hours, the bosses, Industrial relations, wages, repairs, overhauls, working during the depression, and work done during the war.Has in ink on the front cover "Please return to John" item "Tram building" by Clive Boxer, recorded c 1992/93.trams, tramways, preston workshops, oral history, preston, tram bodies -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumAdministrative record - Annual Report/s, Footscray Tramway Trust, "Footscray Tramway Trust", 1918
Second Annual Report of the Footscray Tramway Trust, for the year ending 30/9/1918. Lists the Trust Members, Consulting Engineers, and Secretary. Details the Trust's activities, finances and a short review of activities. Engineering report by Christie & Gardiner detailing the construction, supply of materials, rails, special work, and that 7 Combination Cars had been purchased along with motors and trucks. Has four pages of financial statements. The First World War restricted progress in acquiring materials. The tramcar bodies were purchased from the Hawthorn Tramway Trust (HTT). The change in Consulting Engineers was mostly likely due to issues that the firm of McCarty Underwood had with the HTT.Yields information about the construction of the Footscray Tramway Trust tramways.Ten foolscap sheets, duplicated, pinned with a removable foldable clip in top left hand corner.tramways, tramcars, ftt, footscray tramways trust, new tramways, rails, tramway construction, annual reports, htt -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - JENNY FOLEY COLLECTION: ON TOUR
Work started on the Lauriston Reservoir in 1939 as part of the Coliban water system and was officially opened by Victorian Premier, Albert Dunstan in 1941. Capacity was increased in 1946 when steel spillway gates were added. Although these had been part of the original design they could not be added at the time of the building because of post-war steel shortages.Bendigo Advertiser ''The way we were'' from 2003. on tour: school of mines civil engineering students visit the construction site of the Lauriston Reservoir in 1940. Left to right: Les Nankervis, Ron Watts, instructor Syd Power, an unknown student and Cliff Binks. The clip is in a folder.newspaper, bendigo advertiser, the way we were -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumCertificate - Digital Image, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), Certificate of Service - James Hacker Brownlie, 16/5/1960
Digital image of a MMTB tramway Certificate of Service presented to James Hacker Brownlie, who worked as a coach builder / foreman at Preston Workshop after 31 years on the job. Dated 16-5-1960. Mr Brownlie served in France during World War 1. Signed by the Chairman - Robert Risson, Deputy Chairman - D H Eakins, Board Member - K Brennan, Secretary W Aird.Demonstrates a certificate presented to MMTB employees upon retirement.Digital image of a MMTB certificate of Service, hand type set and printed, signed by the MMTB Chairman, Deputy Chairman, Board Member and the Secretary. The MMTB's seal has been affixed.mmtb, tramways, preston workshops, retirement, certificates, j h brownlie -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Research Notes, "The Footscray Tramway Trust - 1917 - 1920", c1990
Three page research report titled "The Footscray Tramway Trust - 1917 - 1920", outlining the work of the FTT in setting up the tramway system in Footscray, its authorised routes, MMTB takeover, the trams it ordered, transformers, delays due to WW1, development during WW2 and its decline and closure of most of its routes.trams, tramways, footscray, footscray depot, ftt, mmtb, world war 1, world war 2 -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumBooklet - A survey of the North Australian Coast on AK121 Aroetta, NT Force, NT Coastal Recce Unit RAE, 6 Aust Army Topo Survey Corps, AKA121 Aroetta, 28 Mar 1945
The work of the Australian Survey Corps is to make maps for the Army. At the outbreak of war very little of the mainland had been mapped, especially the northern parts. The best maps in existence of the N.T. coast in Dec "41 were those made by Matt Flinders in 1801 -1802. The Army soon got out new maps of all important areas including much of the inland. Later it was decided to bring the complete coastline up to date. Several parties put in between them six months on the coast during the dry season of "45 but a couple more months would be needed to complete the program when the "wet" interrupted the work. A small section from Buckingham Bay - Groote Eylandt was still untouched and this diary covers that section of the N.T. Coast. A survey party of four men was chosen who were to be transported from place to place by the AK121 Aroetta - a ketch of 25 tons belonging to an army unit called N.T. Coastal Recce whose work it was to patrol the coast and as well do air - sea rescue. The survey party: Lieut Jack Worsley (the Loot) Sgt Jack Love, Spr Jack Cook, Spr Pat Hede. Crew of Aroetta: Liet Ralph Warne (Skipper), Sgt Buckley (Buck) (First Mate and Orderly Rm), Sgt Jim Terjesen (Jumbo) Bosun, WO2 Tom Davis (Engineer), Cpl Kevin Monk (Artificer), L/Cpl Jack Cox (Deck Hand), Spr Jack Andrews (Signals), Spr Laurie Rament (Ass. Engineer), Spr McKenzie (Mac) (Cook). The complete history is not available after July 31 1945. The remainder of the notes are very badly water-damaged and in some places unreadable.A4 Booklet, plain paper with text and diagrams and half tone photograph of Lt Jack Worsley with plastic binderSigned by George Barton Maj. for LtCol GS. NT Forceroyal australian survey corps, rasvy, fortuna, army survey regiment, army svy regt, asr -
 Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub Branch
Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub BranchPainting - Large wooden framed painting
Michael Turner born in 1934 is a British painter and illustrator specialising in motoring and aviation paintings. After leaving school he attended Art College followed by National Service with the Royal Electrical and Mechanical Engineers for 2 years. On leaving National Service he worked with a London advertising studio before turning freelance in1957. The Bristol Blenheim depicted in the painting was a British light bomber used extensively for 2 years of the Second World War. It was powered by a pair of Bristol Mercury V111 air cooled radial engines capable of developing 860 bhp. armament was a combination of Vickers, Browning and Lewis machine guns in .303 ( 7.7mm ). A 1000lb (450kg ) could be carried in the internal bomb bay in the centre section of the fuselage. The 114 Squadron was a Squadron of the British Royal Air Force formed in India during the First World War. The Squadron was disbanded in 1971.Large wooden framed painting of an RAF WW2 bomber in flight.Below the painting is the wording " A 114 Squadron Blenheim 1V on a low level bombing run over the power station at Knapsack Cologne, in August 1941 - donated by Laurie Pillar". -
 Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub Branch
Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - HMAS Napier in Colombo Graving Dock
The wording " graving " refers to the ship being put into dry dock to clean and coat the bottom of the ship. The artist Roy Cecil Hodgkinson #VX93432 attained the rank of Captain. Saw action abroad during 1939 and 1945 and was repatriated .His occupation was a cartoonist illustrator. In 1942 Roy was appointed as an Official War Artist by the Australian War Memorial. During his appointment he served in Northern Australia, New Guinea, Ceylon , India and Burma.Framed work on paper depicting HMAS Napier in graving dock. Coloured crayons with water colour heightened with white on paper.Inscription below picture " HMAS Napier one of the five ' N' class fleet destroyers transferred on loan from the Royal Navy between 1940 and 1945, is eased into the Colombo graving dock" . -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageVehicle - Wagon, H.H. Smith & Co. Baker, Circa 1930s - 1940s
This baker’s wagon or cart transported and delivered bread and other baked goods in the Warrnambool area. It currently has advertising for H.H. Smith & Co. Henry Huntington Smith (1857-1941) owned and operated his Warrnambool bakery in the late 19th and early 20th century. However, the design of the wagon is similar to those used by local bakers in the 1930s and 1940s and probably originated from Stephenson’s Bakery in Warrnambool, which operated around that time. The wagon’s original internal shelves were removed in the early days of Flagstaff Hill so that children could have rides around the village in a horse-driven cart. BAKERS’ HISTORY There were many bakeries in Warrnambool in the 19th to mid-20th century. Each bread bakery made horse and cart deliveries in its allocated zone. SMITH’S BAKERY; – as shown on the wagon’s signage. Henry Huntington Smith (1857-1941) was born and educated in Warrnambool. He worked at Davis’ steam biscuit factory in Timor Street before he began his own bakery business in 1885 near the corner of Fairy and Koroit Streets. A few years later Smith built a new bakery on the corner of Fairy and Lava Street where it still stands today (2025) as Monaghan’s Pharmacy. The building was designed by James McLeod in 1892 as a bakehouse, shop and residence for Smith The address was known locally as Smith’s Corner. Next door to the bakery, at 136 Fairy Street, were stables built by Jobbins and McLeod in 1886 for William Cust. A photograph in the archives of the Warrnambool and District Historical Society shows the 1892 building with four fancy horse-drawn wagons on the street with white-clad drivers and a promotional stand erected with 5 bakers in uniform and the signage “H H Smith & Co, Pastry Cooks and Confectioners”. One of the wagons appears to have “H H Smith” painted on the side. H.H. Smith & Co. placed an Advertisement in the Weekly Times in December 1896 promoting its business as bakers, confectioners and pastry cooks, praising their shop as an ‘ornament to the town’ with ‘neat appointments’ and ‘dainty decorations’. It also boasted of supplying a large number of customers within a twelve-mile radius of Warrnambool. In November 1919 The Warrnambool Standard announced the marriage of Henry H Smith, Mayor of Warrnambool, to Jeannie Samson-Goodman in East Adelaide. In the same newspaper was a notice that Frank Crossley was to open as baker and pastry cook in H.H. Smith’s premises. As well as being the proprietor of the H.H. Smith Bakery, Henry Huntington Smith was a Councillor for the Warrnambool Municipality from 1913 to 1937 and Mayer for two terms. In December 1919 during his first term as Mayor, he was honoured for the work he had done with returning soldiers after World War I, receiving a document in recognition of this work, presented by the Mothers, Wives and Sisters of returned soldiers. Smith was very interested and involved in the community in many roles, including being the Vice President of the first Warrnambool and District Historical Society. STEPHENSON’S BAKERY: – believed to be the past owner of the wagon. The last owner of the bakery was Harold Stephenson. Stephenson was enlisted in the A.I.F. and was invalided home in 1943 before the end of the Second World War. He also served as a Councillor from 1958 to 1976, during which time he served six terms as Mayor for the City of Warrnambool (1966-1973) while he had the bakery. He was very involved in many local organisations including the Warrnambool Surf Life Saving Club and the Road Race Committee. He died in 1985, lauded as being one of Warrnambool’s “most distinguished civic leaders”. It has been said that the baker injured in World War II invented a special contraption to enable him to get up into the wagon and that he alerted his customers that he was in their vicinity by blowing a whistle. The customers would come out and choose their bread from the back of his wagon then pay him for it. However, another account is given by a man who once earned pocket money by helping the baker on his rounds. He says that it was Stephenson, the owner and manager of the bakery, and not the delivery baker who received a significant injury during the war, making him unable to climb the stairs of his upstairs accommodation at the bakery, therefore causing him to sleep downstairs. At this time in the early to late 1940 Stephenson’s bakery had three wagons, one for each of the delivery rounds. The wagons were painted black and yellow. Two of the drivers were Stan Lake and Ali (Alec) Dean who both had wagons with the covered cabin design. The third driver was Bill Lake who had a flat wagon. Stan Lake delivered in the area around Lava and Koroit Streets, Ali Dean had another round and Bill Lake had the Dennington area. Bread continued to be delivered into the 1960s but by this time the delivery vehicles were motorised. The goods produced at Stephenson’s bakery included bread baked in different shaped tins such as High Tin, Sandwich and Vienna. Some shapes were easily divided into half by breaking them apart, therefore the baker could make two-quarter loaves from a half loaf, satisfying different needs. There was the option of white or brown bread, sweet buns, fruit buns and Boston buns. The baker’s assistant was known to take great delight in ‘trimming’ the broken halves of excess bread and crust, enjoying his treat. THE BAKERY PREMISES: – Southeast corner of Fairy and Lava Streets, Warrnambool. The building retains the original cast iron veranda. Above the veranda, a motif of a wheat sheaf in ornamental plaster can be seen. Inside the building, there are still some of the original fittings. The building was classified by the National Trust in August 1979. After the Second World War, an official system of zoning was introduced as a fair way for the baking industry to operate. In 1949 different pricing was introduced by the Government for either delivered or retail purchased bread. Many of the small local bakeries went out of business after the Government banned zoning. The way was made open for the larger bread manufacturers to enter the local market with cheaper prices. Some of those companies were Mc Queens, Tip Top, Twisties, and Sunicrust, (Mc Queens ‘new’ bakery building was where the current Toyworld shop now stands, is, in the Ozone carpark.) O’Grady’s Bakery, later changing hands and known as Burkes Bakery, was on Fairy Street near the Timor Street intersection, on the North West side. There was also a bakery named Almay. The baker’s wagon is significant because of its association with H.H. Smith’s Bakery in Warrnambool.. The H.H. Smith’s Bakery building on the corner of Fairy and Lava Streets, built in 1892, is classified by the National Trust, August 1979. Smith Street Warrnambool was named after Henry Huntington Smith, who was a Warrnambool Councillor 1913 – 1937 and Mayor 1919 – 1921. Baker’s wagon, often referred to as a baker’s cart. Four wheeled horse-drawn delivery wagon, front wheels smaller than rear wheels. Wagon is clad with metal sheets and lined with varnished timber panels. Wheels have metal rims, wooden spokes and rear wheels have wooden brake pads. Horse shaft is timber with metal fittings. Front has a metal lamp holder, brake lever, metal hand grips and decorative metal foot plates. The wagon has suspension leaves on back and sides and double suspension leaves on the front. Driver’s area at front has a roof, glass side windows and wooden box seat with hinged compartment accessing wagon storage area. Door above back of seat has buckled leather handgrip strap attached, door slides open for access to wagon area. Back of wagon has a wooden step and a split door; top door has ventilation louvers, both doors have metal latches. Wagon is painted cream with brown trim and signage and green step. Remnants of red and green paint are visible; underside of seat panel is painted grey. Wagon advertises H.H. Smith & Co. Baker, a Warrnambool business established in 1885, but is of a more modern design seen around 1930’s and 1940’s and most likely belonging to Stephenson's bakery. Brown signwriting on sides of wagon “H.R. SMITH & CO. / BAKER” Brown signwriting across front of wagon “BAKER” warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, great ocean road, baker’s wagon, h.h. smith baker, warrnambool, henry h smith, jeannie samson-goodman, frank crossley, mayor of city of warrnambool, vice president of warrnambool and district historical society, stephenson’s bakery warrnambool, harold stephenson, warrnambool surf life saving club, road race committee, national trust building, stan lake, bill lake, ali dean, 19th and 20th century bakers, davies steam biscuit factory warrnambool, james mcleod building designer, jobbins and mcleod, william cust, h h smith & co, pastry cooks and confectioners, bakery trade, bread delivery wagon -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Diagram and Handwritten Notes
Handwritten notes and diagram relating to Kitty Hawk Plane by REID LIONEL : Service Number - 57094 : Date of birth - 13 Oct 1917 : Place of birth - CARLTON VIC :Handwritten notes and diagram contained in RAAF Fitters Manual II.A belonging to Reid. L. TFR 57094. Notes and diagram is on a A3 piece of paper.Kitty hawk span 37ft 3 1,2" Length 31ft.raaf, wwii, world war 2, kitty hawk -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchBook - Book - Cartoon, World at War, 1942
A history of sixty cartoons with text by David LOW a New Zealander of Scottish-Irish parentage. In 1919 he started work in London. His cartoons on world affairs had a wide reputation in Europe before the war were banned in Germany in 1936. Book without cover containing 60 plus cream coloured pages of cartoons World at War A history in Sixty Cartoons with a narrative text by LOWdavid low, world at war -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Surgical silks and sutures, Teleflex (manufacturers of Deknatel), Early 1900s
Through many millennia, various suture materials were used or proposed. Needles were made of bone or metals such as silver, copper, and aluminium bronze wire. Sutures were made of plant materials (flax, hemp and cotton) or animal material (hair, tendons, arteries, muscle strips and nerves, silk, and catgut).[citation needed] The earliest reports of surgical suture date to 3000 BC in ancient Egypt, and the oldest known suture is in a mummy from 1100 BC. A detailed description of a wound suture and the suture materials used in it is by the Indian sage and physician Sushruta, written in 500 BC. The Greek father of medicine, Hippocrates, described suture techniques, as did the later Roman Aulus Cornelius Celsus. The 2nd-century Roman physician Galen described sutures made of surgical gut or catgut. In the 10th century, the catgut suture along with the surgery needle were used in operations by Abulcasis. The gut suture was similar to that of strings for violins, guitars, and tennis racquets and it involved harvesting sheep or cow intestines. Catgut sometimes led to infection due to a lack of disinfection and sterilization of the material. Joseph Lister endorsed the routine sterilization of all suture threads. He first attempted sterilization with the 1860s "carbolic catgut," and chromic catgut followed two decades later. Sterile catgut was finally achieved in 1906 with iodine treatment. The next great leap came in the twentieth century. The chemical industry drove production of the first synthetic thread in the early 1930s, which exploded into production of numerous absorbable and non-absorbable synthetics. The first synthetic absorbable was based on polyvinyl alcohol in 1931. Polyesters were developed in the 1950s, and later the process of radiation sterilization was established for catgut and polyester. Polyglycolic acid was discovered in the 1960s and implemented in the 1970s. Today, most sutures are made of synthetic polymer fibers. Silk and, rarely, gut sutures are the only materials still in use from ancient times. In fact, gut sutures have been banned in Europe and Japan owing to concerns regarding bovine spongiform encephalopathy. Silk suture is still used today, mainly to secure surgical drains. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Surgical_suture#:~:text=Sutures%20were%20made%20of%20plant,a%20mummy%20from%201100%20BC. This tin contains a variety of surgical threads and accessories that were used by Dr W.R.Angus. It was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s SS Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The repair of open wounds is essential to prevent infection and death. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Black tin with hinged lid, containing reels and packets of surgical silk, gut and metal suture threads, scalpel blades, chamois and metal blade holder with tensioned chamois piece across top. (W.R. Angus Collection)‘MEDRAFIL, Dr MULLER- MEERNACH, Nr O, MADE IN GERMANY.’ printed on one of the paper bags in the box containing a suture bobbin. 'PEARSALL'S LONDON' printed on some bobbins. 'J A DEKNATEL & SON INC, QUEENS VILLAGE, LONG ISLAND NEW YORK' printed on others.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, surgical silks and sutures, dr w r angus, medical equipment, surgical instrument, dr ryan, ophthalmology, s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, flying doctor, medical history, medical treatment, mira hospital, medical education, sutures, surgical silk -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Thermometer, Late 19th - early 20th century
The Thermoscope The thermometer dates back to the early 1600s, with Galileo’s invention of the “thermoscope.” Galileo’s device could determine whether temperature was rising or falling, but was not able to detect the actual scale of the temperature. In 1612, Italian inventor and physician Sanctorius was the first to put a numerical scale on the thermoscope. His product was also designed for taking temperature from a patient’s mouth. However, neither Galileo’s nor Sanctorius’ thermoscopes were very accurate. Standardized Scales In 1709, Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit invented his first thermometer using alcohol. He later introduced the mercury thermometer in 1714, which was more accurate and predictable. The Fahrenheit temperature scale was standardized in 1724 with a freezing point of 32 degrees and a boiling point of 212 degrees. Fahrenheit’s mercury thermometer is recognized as the first modern thermometer with a standardized scale. The Celsius scale was invented in 1742 by Anders Celsius, with a freezing point of 0 degrees and a boiling point of 100 degrees. This scale was accepted into the international conference on weights and measurements in 1948. The Kelvin Scale, measuring extreme temperatures, was developed by Lord Kelvin in 1848. Registering Thermometers Early versions of the thermometer were not able to hold the temperature after they were moved. You can imagine how this made it hard for doctors to correctly read a patient’s temperature. The first thermometer that could register and hold onto temperature was built by James Six in 1782. Today, it is known as Six’s thermometer. Since then, the mercury thermometer was adapted to read a patients temperature after leaving the body. Registering thermometers are still used today and are reset by shaking down the mercury to the bottom of the tube. The Modern Devices Modern Day Thermometers This brings us to the first practical clinical thermometer, which was invented in 1867 by Sir Thomas Allbutt. The device was portable, about 6 inches long and was capable of recording a patient’s temperature in 5 minutes. Now, there are a few options for clinical and home use. Liquid filled thermometers have been adapted based on the designs of inventors like Fahrenheight and Six are still used today. Digital thermometers, like the Omron Compact Digital Thermometer, are capable of finding a temperature and producing an electronic number within a minute of use. Digital ear thermometers also produce a quick and accurate temperature. Dr. Jacob Fraden invented an infared thermometer called the Thermoscan Human Ear Thermometer in 1984. These thermometers use an infared light to scan the heat radiation in a patient’s ear or forehead. The thermometer, like many medical devices, has made strides in efficiency and accuracy. As medical technology continues to advance, businesses in the medical device industry must be prepared to move with it. This thermometer was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments, and material once belonging to Dr. Edward Ryan and Dr. Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr. Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr. Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr. Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at the University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr. Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr. Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was a physician, surgeon, and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as a new Medical Assistant to Dr. Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr. Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr. Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s SS Largs Bay. Dr. Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr. Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928. The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr. Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr. John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was a surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr. Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr. Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr. Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr. L Middleton was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital from 1926-1933 when he resigned. [Dr. Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr. Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr. Edward saw patients in his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2-bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr. Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital from 1884-1902. He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr. Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr. Edward and Dr. Tom Ryan work as surgeons including in eye surgery. Dr. Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital from 1902-1926. Dr. Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr. Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr. Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr. Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr. Ryan. Dr. Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr. T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr. Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr. Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon from 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10 am, 2-4 pm, 7-8 pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr. Edward Ryan and Dr. Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr. Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr. Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles were passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr. John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks, and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr. Angus had his own silkworm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr. Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness, and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr. Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and a surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital from 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence, he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist at Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr. Angus was elected a member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life, Dr. Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr. Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eyewitness from the late 1880s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr. Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks, and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr. Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as the Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council, and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments, and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Long cylindrical glass thermometer with mercury bulb, inside a light weight wooden cylinder with top, (W.R. Angus Collection) Temperature scale in fahrenheit. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, thermometer, dr w r angus, medical equipment, surgical instrument, dr ryan, ophthalmology, s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, flying doctor, medical history, medical treatment, mira hospital, medical education -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Medical Textbook, Young J. Pentland, Manual of Practical Anatomy, Vol. 2, Thorax, Head and Neck, 1894
This textbook was used by Doctor Angus during his medical studies at Adelaide University. It was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s SS Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Manual of Practical Anatomy, Vol. 2, Thorax, Head and Neck. D.J. Cunningham. Label Pub. 1894, Young J. Pentland, Edinburgh and London. Label "W.R. Angus/309 Koroit Street/Warrnambool/ Victoria, 3280". Name in pencil looks like “A S Cobbledick”. Pencil “W.R. ANGUS/MED SCHOOL/ADELAIDE UNI/1921" (W.R. Angus Collection)Label "W.R. Angus/309 Koroit Street/Warrnambool/ Victoria, 3280". Name in pencil looks like “A S Cobbledick”. Pencil “W.R. ANGUS/MED SCHOOL/ADELAIDE UNI/1921" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, dr w r angus, medical history, medical education, published 1894, young j. pentland, medical textbook -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Medical Textbook, His Majesty's Stationery Office, Recreation and Physical Fitness for Youths and Men, 1938
This medical book was used by Dr Angus in his practice in Warrnambool and was probably connected with his association with the National Fitness Council and his assistance with the National Fitness Campaign “Fit for Purpose”. It was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s SS Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Recreation and Physical Fitness for Youths and Men, Board of Education. Pub 1938, His Majesty's Stationery Office, Adastral House, Kingsway, London, W.C. 2, Label "EPWORTH BOOK DEPOT/BOOK SELLERS/PIRIE ST, ADELAIDE" Pencil "W.R. Angus" and on pge edges "A N. G U S" (W.R. Angus Collection) Label "EPWORTH BOOK DEPOT/BOOK SELLERS/PIRIE ST, ADELAIDE" Pencil "W.R. Angus" and on pge edges "A N. G U S" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, national fitness campaign, fit for a purpose, dr w r angus, medical history, medical treatment, medical education, his majesty's stationery office, medical textbook
