Showing 1088 items matching "geological"
-
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumMap - SURVEYERS MAP OF CLUNES, J. FINNIE, 1883
A SURVEYORS MAP OF CLUNES. GEOLOGICALLY AND TOPOGRAPHICALLY SURVEYED BY R.A.F. MURRAY.LITHOGRAPHED BY R. SHEPHERD AND PRINTED BY J. FINNIE MINING DEPARTMENT, MELBOURNE,1883document, surveyers map of clunes, map of clunes -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Coorongite
... geological ...Coorongite is a dark, rubber-like, highly resilient structureless algal deposit. In the Coorong district of South Australia it occurs in moderate quantities associated with the coastal swamps and sand dunes which extend for a considerable distance east of the mouth of the Murray. This particular specimen was recovered from the south of the Coorong River, South Australia. A type of sediment rich in organic matter, Coorongite is the unlithified end-member of the sapropelic coal series. The members of the sapropelic coal series can be ranked in order as sapropel (the unlithified form), sapropelic-lignite, and sapropelic-coal (the lithified forms) based on increasing carbon content and decreasing volatile content. Sapropel (Coorongite) is an unlithified dark, pulpy, fine organic mud containing concentrations of algae and miospores that are more or less identifiable. Coorongite is typically found as an algae like substance, that can be found in irregular size pieces. Coorongite was believed to be dried up oil due to its rubber-like texture. The Coorongite is also soft to the point where it can be cut into with a knife or it can be broken and torn by hand. Otherwise known as 'Kurangk', the Coorong River is home to the Ngarrindjeri people, which acts as both a place for gathering food and a spiritual place. In 1852 the first sight of Coorongite was found along the Coorong River. The finders mistook the Coorongite for dried up oil, which lead to the belief that there were oil reserves under the Coorong River. Between the 1860s and the 1930s the Coorong River became a place where mining oil and Coorongite became precedent. Nowadays, the local council and the South Australian Government are working together with the Ngarrindjeri people to sustain and preserve the Coorong River and the culture that is with it. Soon after gold was discovered in 1851, Victoria’s Governor La Trobe wrote to the Colonial Office in London, urging ‘the propriety of selecting and appointing as Mineral Surveyor for this Colony a gentleman possessed of the requisite qualifications and acquaintance with geological science and phenomena’. Alfred Selwyn was appointed geological surveyor in Australia in 1852 which began the Geological Survey of Victoria. Selwyn went on to collect geological samples and catalogue thousands of specimens around Australia. In 1853-69 the Geological Survey issued under Selwyn's direction sixty-one geological maps and numerous reports; they were of such high standard that a writer in the Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society of London bracketed the survey with that of the United States of America as the best in the world. During his years spent in Australia, Selwyn collected numerous significant geological specimens, examples of which are held in collections such as the Burke Museum.Coorongite is considered to be a mineral with a unique texture, where it can be both hard and soft. Coorongite can also be considered to be a rare mineral, as it is only located along the Coorong River and due to the mining of it, has left very few sources. It was believed at one point that Coorongite could be used to replace oil. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.Three solid varyingly hand-sized pieces of wooden appearing organic matter derived from the river in the Coorong District in South Australia. A rubber-like, highly resilient structureless algal deposit.Specimen 245 page 69 / in Descriptive Register / "Elcestic Bitumen, / Coorangite" South of / Coorung River, South Australia . / C. WIllman / 15/4/21burke museum, beechwoth, indigo shire, beechworth museum, geological, geological specimen, mineraology, coorong, coorong river, kurangk, ngarrindjeri, south australia, coorongite, coorongite specimen -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet - Booklet - Prospectus, Bairnsdale District School of Mines, Prospectus, 1904, 1904
Higher education in east Gippsland dates back to 1890, and the opening of the Bairnsdale District School of Mines, In 1986 the Bairnsdale School of Mines and the Sale and Bairnsdale Technical schools amalgamated to form the East Gippsland Community College of TAFE. In 1995 it became the East Gippsland Institute of Technology, and in 2011 changed its name to Advance TAFE. The Bairnsdale District School of Mines Prospectus includes the members of council, a photographic image of the school, teaching staff, rules relating to students and instructors, Constitution, and a prospectus of subjects including Mining and Science Subjects, Diploma Courses, Preliminary Training, Metallurgy Course, Mining Engineering Course, Battery Manager's Certificate, Assayer's Certificate. It also includes a scale of fees, information on the Metallurgical Plant, Chemistry, Assaying and Metallurgy, Geology, Mining Geology, Mining, Petrology, Dynamics and Heat, Magnetism & Electricity, Mechanics Applied to Mining, Land Surveying, Mine Surveying, Algebra, Euclid, Trigonometry, Mechanical Drawing, Practical Plane Geometry, Practical Solid Geometry, Engineering Drawing, Art Subjects, and a list of certificates issued by the school since 1892.Grey soft covered book of 68 pages. The Bairsndale District School of Mines Prospectus includes the members of council, an photographic image of the school, teaching staff, rules relating to students and instructors, Constitution, and a prospectus of subjects including Mining and Science Subjects, Diploma Courses, Preliminary Training, Metallurgy Course, Mining Engineering Course, Battery Manager's Certificate, Assayer's Certificate. It also includes a scale of fees, information on the Metallurgical Plant and its chares, Chemistry, Assaying and Metallurgy, Geology, Mining Geology, Mining, Petrology, Dynamics and Heat, Magnetism & Electricity, Mechanics Applied to Mining, Land Surveying, Mine Surveying, Algebra, Euclid, Trigonometry, Mechanical Drawing, Practical Plane Geometry, Practical Solid Geometry, Engineering Drawing, Art Subjects, and a list of certificates issued by the school since 1892.bairnsdale district school of mines, bairnsdale, school of mines, donald clark, francis w. sewell, j.v.r. anderson, a.d. pleydell, walter seehusen, director, mining engineering, metallurgy, academy of arts, municipal surveyor, 1914 -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Hyalite in Basalt
According to the 1912 Department of Mines Bulletin of the Geological Survey of Victoria, basalt covers a considerable portion of the Macedon area including Mount Macedon. Basalt is the most common form of rock underlying the earth's surface and is found in three kinds of rock forming environments: ocean divergent boundaries, oceanic hotspots, and mantle plumes and hotspots beneath continents.This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid mass, geological specimen in shades of grey and white. Hyalite is a colourless variety of opal. It occurs as globular and botryoidal masses and irregular crusts in volcanic and pegmatite environments where the silica deposits from the gas phase. Basalt is dark in colour, fine-grained igneous rock composed of plagioclase and pyroxene minerals. It is commonly formed as an extrusive rock, such as lava flow. It is one of the most common forms of rock underlying the earth's surface.burke museum, geological specimen, department of mines, geological survey of victoria, basalt, mount macedon, beechworth -
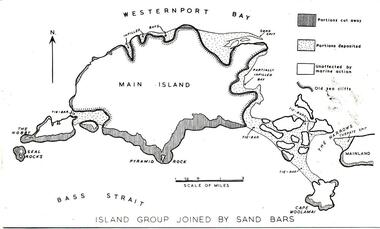 Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.
Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.Photograph
One of a collection of over 400 photographs in an album commenced in 1960 and presented to the Phillip Island & Westernport Historical Society by the Shire of Phillip IslandPhotograph of a map of Phillip Island showing a late stage in the geological formationlocal history, photography, phillip island, black & white photograph, phillip island geology, map, map of phillip island, john jenner, bryant west -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet, Northern Territory ... The Tanami Gold Country with Plans, 1909, 1909
Pink foolscap report of 12 pages, includes geological map from Pine Creel to Sturt's Creek by H.Y. L. brown; geological map between Mucka and Gordon Downs Station and Tanami by W.R. Murray; geological map of Tanami and surrounding country by W.R. Murray, and Plan of Lawne's Gold Prospecting Claim at Tanami by W.R. Murray pine creek, sturt's creek, tanami, northern territory, tanami gold country -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionInstrument - Scientific Object, TOWER, Petrographic Microscope
Used in the mid-seventies in petrology laboratories of BIAE.A petrographic optical microscope, with three objected lens turret. Black enameled frame, chrome components. Blonde polished wood storage box.TOWER No 19621. On frame self-adhesive sticker: "Ballarat CAE GEOLOGY"ballarat cae geology, microscope, petrographic microscope, scientific instruments, lens -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph, Geology Excursion near the Twelve Apostles, Great Ocean Road
A Geology Excursion associated with the Ballarat College of Advanced Education (later Federation University).geology, 12 apostles, twelve apostles, great ocean road -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncArchive (Sub-series) - Subject File, Kew Historical Society, Geology (Kew), 1958
Various partiesReference, Research, InformationSecondary Values (KHS Imposed Order)Subject file containing some secondary sources. These include a Parks Victoria brochure on the Geology of Yarra Bend Park and a printout of a web page about the Collingwood Children’s Farm that includes information about the geological formation of the region.kew historical society - archives, geology - kew (vic)kew historical society - archives, geology - kew (vic) -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Basalt (igneous-volcanic) containing Olivine, unknown
... geological ...This particular geological specimen was found in Mount Franklin or Lalgambook in Djadjawurrung, located between Daylesford and Newstead, approximately ninety minutes drive from Melbourne. The mountain is an example of a breached scoria cone (a steep conical hill of loose pyroclastic fragments) which was created by a volcanic eruption about 470,000 years ago, a date which may indicate the age of this geological specimen. The volcanic eruptions of Mount Franklin were most likely witnessed by members of the Dja Dja Wurrung Aboriginal tribe, who referred to this country as the 'smoking grounds'. Mount Franklin and the surrounding area appears to have been a place of considerable religious significance to Aboriginal people, there is evidence which indicates that frequent large ceremonial gatherings took place in the area. Basalt is the most common rock on Earth’s surface, more than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Basalt is an aphanitic extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. Specimens are black in colour and weather to dark green or brown. Basalt is rich in iron and magnesium and is mainly composed of olivine, pyroxene, and plagioclase. Olivine is the name of a group of rock-forming silicate minerals with compositions ranging between Mg2SiO4 and Fe2SiO4. Unlike other minerals, Olivine has a very high crystallisation temperature which makes it the first of the minerals to crystallise from magma. As magma cools, the crystals begin to form and settle on the bottom of the lava and form basalts that are abnormally enriched in olivine in the lower part of lava flows. According to H. M. King (on geology.com) "Olivine is thought to be an important mineral in Earth's mantle. Its presence as a mantle mineral has been inferred by a change in the behaviour of seismic waves as they cross the boundary between Earth's crust and mantle". Lava from Mount Franklin and other volcanoes in the area filled valleys and buried the gold bearing streams that became the renowned ‘deep leads’ of the gold mining era. In 1852, as part of the Victorian gold rush, gold was discovered in the immediate area, this gold was created by lava flows during the Newer Volcanic period, which were mined intensively during the nineteenth century. Around 1865 the presence of a deep lead in Mount Franklin was established. Deep lead mining was initially unsuccessful, and it was not until the late 1870s that the Franklinford Gold Mining Company mined at Mount Franklin on a significant scale. A few years later the Mount Franklin Estate Gold Mining Company also struck gold, followed by the Shakespeare and Great Western companies in the mid-1880s. By the late 1880s, however, deep lead mining had ceased in the area. Soon after gold was discovered in 1851, Victoria’s Governor La Trobe wrote to the Colonial Office in London, urging ‘the propriety of selecting and appointing as Mineral Surveyor for this Colony a gentleman possessed of the requisite qualifications and acquaintance with geological science and phenomena’. Alfred Selwyn was appointed geological surveyor in Australia in 1852 which began the Geological Survey of Victoria. In 1853-69 the Geological Survey issued under Selwyn's direction sixty-one geological maps and numerous reports; they were of such high standard that a writer in the Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society of London bracketed the survey with that of the United States of America as the best in the world. During his years spent in Australia, Selwyn collected numerous significant geological specimens, examples of which are held in collections such as the Burke Museum.This geological specimen is an example of basalt and olivine which shows the volcanic lava activity and geographical specific nature of Mt Franklin as a significant volcanic site. According to Agriculture Victoria 'The crater is one of the deepest in the Central Highlands area. It is a major megacryst site with some of the largest known Victorian examples of megacrysts of augite and an orthoclase. The small parasitic mound of Lady Franklin on the western flanks adds to the geological interest of the site'. This specimen also highlights the locality as a significant place for both indigenous activity and Victorian gold rush era mining practices. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.An angular, solid hand-sized piece of grey volcanic Basalt with green/brown Olivine phenocrysts along one flat edge.Olivine in basalt / - label is probably / correct. / C. Willman / 15/4/21burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, beechworth museum, geological, geological specimen, mineralogy, basalt, igneous rock, igneous-volcanic, volcanic geology, volcanic, olivine, olivine specimen, basaltoid -
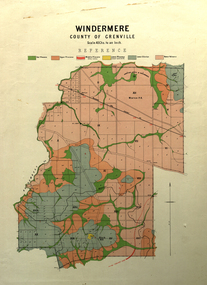 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMap, Windermere, County of Grenville
Coloured geological map of Windermere, County of Grenville. Scale is 40 chains to 1 inchwindermere, grenville, krause, plan, map -
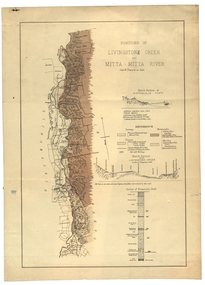 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPlan, Livinstone Creek and Mitta Mitta River
Plan showing geological eras and soil types. Scale 80 chains to 1 inchmitta mitta, mitta mitta river, hinnomunjie flats, mining, shafts, livingstone creek -
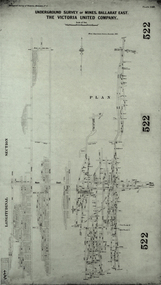 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPlan, Underground Survey of Mines, Ballarat East. The Victoria United Company, 1903
Underground Survey of The Victoria United Company from Geological Survey of Victoria, Memoirs No. 4.ballarat east, victoria united company, cgt, mining, geological survey, longitudinal section -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, Principles of Geology
This item is from the ‘Pattison Collection’, a collection of books and records that was originally owned by the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute, which was founded in Warrnambool in 1853. By 1886 the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) had grown to have a Library, Museum and Fine Arts Gallery, with a collection of “… choice productions of art, and valuable specimens in almost every branch and many wonderful national curiosities are now to be seen there, including historic relics of the town and district.” It later included a School of Design. Although it was very well patronised, the lack of financial support led the WMI in 1911 to ask the City Council to take it over. In 1935 Ralph Pattison was appointed as City Librarian to establish and organise the Warrnambool Library as it was then called. When the WMI building was pulled down in 1963 a new civic building was erected on the site and the new Warrnambool Library, on behalf of the City Council, took over all the holdings of the WMI. At this time some of the items were separated and identified as the ‘Pattison Collection’, named after Ralph Pattison. Eventually the components of the WMI were distributed from the Warrnambool Library to various places, including the Art Gallery, Historical Society and Flagstaff Hill. Later some were even distributed to other regional branches of Corangamite Regional Library and passed to and fro. It is difficult now to trace just where all of the items have ended up. The books at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village generally display stamps and markings from Pattison as well as a variety of other institutions including the Mechanics’ Institute itself. RALPH ERIC PATTISON Ralph Eric Pattison was born in Rockhampton, Queensland, in 1891. He married Maude Swan from Warrnambool in 1920 and they set up home in Warrnambool. In 1935 Pattison accepted a position as City Librarian for the Warrnambool City Council. His huge challenge was to make a functional library within two rooms of the Mechanics’ Institute. He tirelessly cleaned, cleared and sorted a disarrayed collection of old books, jars of preserved specimens and other items reserved for exhibition in the city’s museum. He developed and updated the library with a wide variety of books for all tastes, including reference books for students; a difficult task to fulfil during the years following the Depression. He converted all of the lower area of the building into a library, reference room and reading room for members and the public. The books were sorted and stored using a cataloguing and card index system that he had developed himself. He also prepared the upper floor of the building and established the Art Gallery and later the Museum, a place to exhibit the many old relics that had been stored for years for this purpose. One of the treasures he found was a beautiful ancient clock, which he repaired, restored and enjoyed using in his office during the years of his service there. Ralph Pattison was described as “a meticulous gentleman whose punctuality, floorless courtesy and distinctive neat dress were hallmarks of his character, and ‘his’ clock controlled his daily routine, and his opening and closing of the library’s large heavy doors to the minute.” Pattison took leave during 1942 to 1942 to serve in the Royal Australian Navy, Volunteer Reserve as Lieutenant. A few years later he converted one of the Museum’s rooms into a Children’s Library, stocking it with suitable books for the younger generation. This was an instant success. In the 1950’s he had the honour of being appointed to the Victorian Library Board and received more inspiration from the monthly conferences in Melbourne. He was sadly retired in 1959 after over 23 years of service, due to the fact that he had gone over the working age of council officers. However he continued to take a very keen interest in the continual development of the Library until his death in 1969. The Pattison Collection, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. The Warrnambool Mechanics Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and the important role it played in the intellectual, cultural and social development of people throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance. Principles of Geology Author: Sir Charles Lyell Publisher: John Murray Date: 1853 Label on spine with typed text PAT 550 LYE Inside front endpaper has a sticker from Corangamite Regional Library Service warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, pattison collection, warrnambool library, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, ralph eric pattison, warrnambool city librarian, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, sir charles lyell, principles of geology -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - STRUGNELL COLLECTION: BENDIGO GOLD FIELD GEOLOGICAL SURVEY, 1936
BHS CollectionBendigo Goldfieds Geological Survey. Prepared in the Bendigo Office Bottom Section of original map.Dept of Mines Victoriabendigo, gold mining, geological map -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - STRUGNELL COLLECTION: BENDIGO GOLD FIELD GEOLOGICAL SURVEY, 1936
BHS CollectionBendigo Goldfieds Geological Survey. Prepared in the Bendigo Office Top Section of original map.Dept of Mines Victoriabendigo, gold mining, geological map -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Black and White Photograph, Students, c1974
.1) A class of seven students and one lecturer, c1980 .2) A female in a hard hat, kneeling at a cutting face, with a geological hammer, c1980 .3) A male at a geological microscope, c1973 .4) 3 males in a geology laboratory, with microscopt and VDU, c1978 .5) Five males in a field locationwith electric resistance apparatus, c1974 .6) A male in grey overall at a lapping machine, c1978 geology, geolological microscope, resistance apparatus, rudi lennards, noone, stafford mcknight, julia gleeson, phillip edward petrie, kenneth heighway, alumni, mount helen campus, student activity -
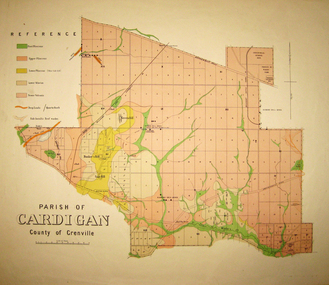 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMap - Geological survey, Parish of Cardigan, County of Grenville, c1889
Geological map of the Parish of Cardigan on a cadastral base showing quartz reefs, shafts, alluvial deposits.cardigan, winter's creek, ballarat cattle yards railway, prince of wales park, ballarat, friendly societies reserve, ballarat industrial school reserve, green hill, bunker's hill, sago hill, diamond drill bores, cardigan propriety, half way house, ti tree creek, albion consols, prince imperial, winter's freehold company -
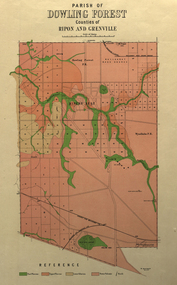 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPlan, Parish of Dowling Forest, County of Ripon and Grenville, 19
Scale [1:31 680]. 40 chains to 1 in.Geological map on a cadastral base, showing the occurence of reefs, and alluvial deposits. Relief shown by contours.dowling forest, wyndholm, wyndholm pre-emptive right, miners rest, ballarat racecourse, winter's swamp, police reserve, miner's rest, winters swamp, geology -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph, Dr Brian Chappel, 03/1982
Photograph of Dr Brian Chappel, University of Ballarat Science & Engineering (Geology/Mining) staffmember. rresearch, consulting, brian chappell, invention, science and engineering -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, Victoria Geology and Physical Geography
Victoria Geology and Physical Geography Author: Reginald Murray Publisher: Government Printer Date: 1887Label on spine with typed text RA 551.09945 MUR Inside front cover has a sticker from Warrnambool Mechanics Institute and Free Library warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, reginald murray, victoria geology and physical geography -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - MCCOLL, RANKIN AND STANISTREET COLLECTION: MINING AND GEOLOGICAL JOURNAL, 1970
McColl Rankin & Stanistreet, Mining and Geological Journal, Vol 6, No 6, contains articles on mining.organization, business, industrial, mccoll rankin & stanistreet, mining & geological journal -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncMap, Department of Mines Victoria, Alluvial Map Stawell Region, 1870's
c1870 Coloured map showing Black Range North to Stawell and Illawarra. Shows geological layout.Department Mines Victoria 1952/G/2 mining, gold, map -
 University of Melbourne, School of Chemistry
University of Melbourne, School of ChemistryGeological Specimens
Set of geological specimens on microscopic slides stored in wooden box with hinged lid, at least 1913. -
 Tarnagulla History Archive
Tarnagulla History ArchivePhotocopy of booklet: List of Nuggets Found in Victoria, List of Nuggets Found in Victoria, 1912 (original)
Murray Comrie Collection. Photocopy of the publication 'List of Nuggets Found in Victoria ' being No. 12 in the Memoirs of the Geological Society of Victoria.tarnagulla, nuggets, gold, mining, prospecting -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Ilvaite
Ilvaite has acquired its name from Ilva (Latin for Elba) Island, Greece, where Ilvaite is most commonly found. The geological setting in which Ilvaite occurs is through contact with magnetite, zinc and copper ore deposits, along with contact metamorphic deposits and zeolite zones. llvaite crystallizes in the form of black prismatic crystals and columns . This specimen was retrieved from Broken hill, known as the world's richest and largest zinc-lead ore deposit. Because of Ilvaite's often unaesthetic crystal formations compared to other minerals, Ilvaite is uncommon in most rock collections, particularly specimens that are not well formed, such as this one. Ilvaite is also a member of the Sorosilicate subclass of the silicate minerals, which have an unusual basic unit of Si2O7, making Ilvaite a unique mineral. Given that Ilvaite is not commonly found in Australia, it marks a unique contribution to an Australian collection of minerals. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid hand-sized ferrous iron analogue mineral with of black with shades of beige Ilvaite is a brittle, opaque rock formation that has acquired its name from Ilva (Latin for Elba) Island, Greece, where Ilvaite is most commonly found. The geological setting in which Ilvaite occurs is through contact with magnetite, zinc and copper ore deposits, along with contact metamorphic deposits and zeolite zones. llvaite crystallizes in the form of black prismatic crystals and columns rock, mineral, ilvaite, ilvaite specimen -
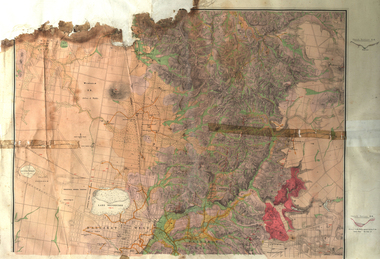 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMap, Ballarat Goldfield, c1898
This map shows geological features, suggests the last basalt flow, and includes alotments and names of Mining Companies. Although this map has no date on it the Ballarat Industrial School is used for dating purposed. The Ballarat Industrial School ran from 1869-1879, but the term Ballarat Industrial School Reserve was still in use in 1898 and possibly beyond.Geological Map of Ballarat with 3 holes in the left hand side. The map indicates the position of Lake Wendouree, Township of Warrenheip, Ballarat East, Industrial School Reserve, Winters Swamp, Police Paddock, Wyndholm Premptive Right (Salton and Waldie), Black Hill, Vale Park Reserve, Pennyweight Hill, Little Bendigo, Black Swamp Lead, monte Christo Reef, Chinaman's Gully, Miners Rest, Pincotts Dam, Northumberland Gully. It also show the following goldmining companies: City of Ballarat, Kohinor, Hand and Band, Great North West, Northern Junction, Kneeshaw, Rossers Freehold, Silurial.ballarat, warrenheip, lake wendouree, ballarat east, winters swamp, winter swamp, wyndholm premptive right, cemetery, vale park reserve, little bendigo, kneeshaw co., industrial school reserve, kirks dam, pincotts dam, black hill, wombat hill, dead horse gully, miners rest, mt rowan, salton and waldie, rose hill co, great north west no 1, rose's freehold co, hand and band co, police reserve, police paddock, mount rowan, ballarat industrial school reserve, market reserve, winter's swamp, kneeshar co, monte cristo line of reef, chinaman's gully or black snake, milkmaid's gully, ballarat gold field, bakery hil lead, old gravel pits lead, golden point lead, eureka lead, miner's rest, yarrowee creek, leigh creek, black swamp lead, yorkshire reef, nil desperandum reef, cockatoo lead, hit or miss gully, herbert werner frederick de nully, pennyweight hill, esmond's lead, ash's lead, nightingale lead, john bull gully, gladstone reef, whitehorse reef, petticoat creek, pincott's dam, frenchman's gully, tim's crushing plant, jenkin's gully, california gully, drake's creek, sulton and waldie, ballarat undustrial school, ballarat & mariborough railway -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Anthracite crystal, Unknown
... geological ...Anthracite typically occurs in geologically deformed areas due to extreme heating – with temperatures ranging from 170 to 250 °C – caused by igneous intrusions or high geothermal gradients. It is most commonly found in northeastern Pennsylvania in the United States; however, smaller amounts are also found in Australia, China, eastern Ukraine, South Africa, western Canada, and other countries. This specimen was recovered from Tasmania and is 85-95% carbon.Anthracite is the mineral name for hard coal and is the least plentiful of all coal types. It is clean to the touch and, when polished, is used for decorative purposes. Before natural gas and electricity, anthracite was used for domestic heating as it produces little dust, burns slowly, and gives off a minor amount of smoke. However, it is also limited in abundance and expensive. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A hand-sized highly metamorphosed coal mineral with a black/steel-grey shiny metallic lustre.geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, geological, mineralogy, victoria, alfred selwyn, anthracite -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - MINING & GEOLOGICAL JOURNAL, 1940
Mining & Geological Journal January 1940 Vol.2 No.2 Mine reports Chewton Gold Field, Geological Glossary, Flotation Process, Wonthaggi Coal Field published hald yearly by he Department of Mines Victoria contains photographs, maps and illustrations.gold, mining, journal -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Unknown, possible Carnelian Agate or Chalcedony
Although it is not known where these specimens were collected, Victoria and other regions of Australia were surveyed for sites of potential mineral wealth throughout the 19th Century. The identification of sites containing valuable commodities such as gold, iron ore and gemstones in a locality had the potential to shape the development and history of communities and industries in the area. The discovery of gold in Victoria, for instance, had a significant influence on the development of the area now known as 'the goldfields', including Beechworth; the city of Melbourne and Victoria as a whole. Agate occurs when amygdales (gas pockets) form in the upper levels of basaltic lava flows. If these pockets or bubbles are iniltrated by water bearing silica in solution, the fluid dries and hardens in layers, forming round or egg shaped nodules or geodes within the rocky matrix. Agate is formed of a silica mineral chalcedony similar to quartz. The term carnelian primarily refers to the reddish shading of the stone; whether the stone is termed an agate or chalcedony type is often influenced by the degree of colour banding the specimen shows. The specimens are significant as examples of surveying activity undertaken to assess and direct the development of the mineral resource industries in Victoria and Australia, as well as the movement to expand human knowledge of earth sciences such as mineralogy and geology in the nineteenth century.Three small geological specimens that appear visually consistent with images of rough or unpolished Carnelian Agate or Chalcedony. geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, north-east victoria, gemstones, agate, carnelian
