Showing 218 items matching "weights and scales"
-
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Tin, Boot polish Cramond & Dickson, Early 20th century
This tin of boot polish was a common household item in the 20th century (and is still used to a lesser extent today). This tan boot polish was sold under the brand name of ‘C & D’ at the general store of Cramond and Dickson in Liebig Street, Warrnambool. John Glass Cramond and James Dickson established their business in Warrnambool in 1855 and this general store operated (firstly in Timor Street and later in Liebig Street) until 1973, making it one of the longest-running and one of the most important businesses in Warrnambool’s history. By 1868 a London agency had been established and direct imports from England began on a large scale. Many of the articles they sold, including the boot polish, were made expressly for the Cramond and Dickson store. This tin of boot polish is of great interest as an example of the goods sold by Cramond and Dickson that were made expressly for the Warrnambool store. Cramond and Dickson were one of the most important stores ever to operate in Warrnambool.This is a round metal tin originally gold-coloured and with a red tape binding to prevent its opening. The front of the tin has printing and the image of a stylized rising sun and the bottom has more printing. The bottom of the tin is indented to allow the tin to rest on the rim only. The printing is legible but much faded. The tin contains the original polish. Top: ‘Use only C & D brand of Tan Boot Polish, Cramond & Dickson, Warrnambool. Port Fairy and London’ Bottom: ‘For best results remove all dust, apply a little C & D dressing, brush briskly. Rubbing finally with a soft cloth produces a brilliant surface. Weight when packed 1½ ozs. net’ cramond and dickson store -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Tin, Boot polish Cramond & Dickson
A tin of boot polish was a common household item in the 20th century (and is still in use to a lesser extent today). This dark tan boot polish was sold under the brand name of ‘C & D’ at the general store of Cramond and Dickson in Liebig Street, Warrnambool. John Glass Cramond and James Dickson established their business in Warrnambool in 1855 and this general store operated (firstly in Timor Street and later in Liebig Street) until 1973, making it one of the longest-running and one of the most important businesses in Warrnambool’s history. By 1868 a London agency had been established and direct imports from England began on a large scale. Many of the articles they sold, including the boot polish, were made expressly for the Cramond and Dickson store.This tin of boot polish is of great interest as an example of the goods sold by Cramond and Dickson that were made expressly for the Warrnambool store. Cramond and Dickson were one of the most important stores ever to operate in Warrnambool. This is a round metal tin, originally gold-coloured and with a red tape binding to prevent its opening. The front of the tin has printing and the image of a stylized rising sun and the bottom has more printing. The bottom of the tin is indented to allow the tin to rest on the rim only. The printing is legible but much faded. The tin contains the original polish. Top: ‘Use only C & D brand of Dark Tan Boot Polish, Cramond & Dickson, Warrnambool, Port Fairy and London’ Bottom: ‘For best results remove all dust, apply a little C & D dressing, brush briskly. Rubbing finally with a soft cloth produces a brilliant surface. Weight when packed 1½ ozs. net’ cramond and dickson store, warrnambool -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyScales - Educational - Mathematics
... scales ...Teaching aid to measure weight.Plastic yellow base and T shaped stand. Stand can be lifted off base. Base is 'rectangular' with each side curving inwards. Apex of T has steel rod enabling the cross arm to move. Each end of arm has a hole with steel ring attached. Also in ring are the end of 3 chains hanging down and attached to white enamel plates.Embossed on upright 'Invicta / Simple Scale' mt beauty primary school, teaching aid, mathematics, scales -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyWeights - dish
Dish used to weigh goods in a shop or farm produce store prior to packaging.Historical: Goods were weighed in shops prior to packaging of goods.Steel curved dish joined in the centre forming a shallow oval shape. weights. shop. farm produce store. scales. -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyWeights - 2 in Set
Used as a weight to measure goods in a store prior to the introduction of packaging.Imperial weight used to weigh goods prior to packaging.Cast iron solid bell shaped weight with a handle at the narrow end at the top. There is a large one and smaller one.Large one has 7 lb inscribed on the handle.weights. shop. store. scales. -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyWeights - 3 in Set
Used to weigh goods in a shop or farming produce store.Imperial weights were used prior to decimalisation. Weights were used to weigh goods prior to packaging.Cast iron solid circular weights with rim around circumference and slightly narrower at the base.Largest - 4 lb Middle - 4 lb (None on smallest)weights. shop. store. scale. -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyWeights - 3 in Set
These weights were used to measure goods in a shop or farm produce store.Historical: These weights were used prior to decimalisation and prior to packaging of goods.Solid cast iron brown weights with rim around the circumference. Embossed inside the rim at the top with the maker and weight. Slightly narrower at the base.4 lb / Crane F Co. / Wolverhampton 2 lbs / Imperial / Standard 1 lb / Imperial / Standardweights. store. shop. scales. -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook - Catalogue, Price List of Assay Material, Balances, Chemical & Scientific Apparatus and Pure Chemicals, Fourth Edition, c1905
... scales ...Red hardcovered 110 page catalogue from the Felton, Grimwade & Co.. Includes numerous line and photographic illustrations.non-fictionj.w. glover, john w. glover, assay, chemistry, mining, felton grimwade & co, assay moulds, tongs, tools, balances, oertling, balance weight, compressed oxygen, crucibles, furnaces, muffles, scales, hammers, gas burners -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionSlide, Welcome Stranger Monument, c1970
The first recorded discovery of gold in Moliagul was in September 1852 and, before long, the area was flooded with over 4,000 miners. Two of those miners, John Deason and Richard Oates, had arrived in Bendigo in 1954 seeking their fortune. After eight years of little success, the friends moved to Moliagul and pegged a puddling claim. On 05 February 1869, Deason discovered a nugget near the roots of a tree, just 3cm beneath the soil. With the help of Oates, he uncovered the largest recorded alluvial gold nugget – known as the Welcome Stranger. The 61cm x 31cm nugget was taken to Dunolly to be measured on the bank’s scales, however at 69kg the gold needed to be broken on an anvil to actually fit on the scales.Photograph of the monument for the Welcome Nugget, a large gold nugget found by John Deason and Richard Oates at Moliagul.Obelisk inscription Welcome Stranger Nugget On this spot the largest nugget of gold in the world was discovered on the 5th February 1869 by John Deason and Richard Oates. Weight 2316 oz, Value £9553 Erected by the Mines Department 1897 Henry Foster Minister of Mines, D. J. Duggan M.L.A. Member for Dunollywelcome nugget, welcome nugget monument, john deason, richard oates -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Sample, Before 1878
On a piece of paper subsequently glued near one end of its curved upper face, this length of planed and polished hardwood timber bears the inscription: “A [p]iece of w[r]ec[k] of the Loch Ard wrecked near Sherbroke River”. The timber is carefully worked with rich dark colouring and a uniformly moulded design, suggesting that it was part of a fitting or furnishing that was publicly visible and prominent. If the artefact is what it is declared to be, then it is possible that it formed part of the ship’s railings or companionway stairs. The LOCH ARD was a 1,693 ton, 3 masted barque, built on the Clyde in 1873. In an age of increasing competition for the emigrant passenger trade from steam-driven vessels, special attention was paid to her wooden furnishings and fittings. The Loch Line owners prided themselves on their attractive, distinctively painted, sailing ships. Below decks, where cargo and third class passengers were stowed, was made of iron. But everything above deck, and on show to the saloon and second class passengers, was carved and varnished timber. Captain Daish’s 1878 report for the ship’s underwriters notes “a quantity of general Cargo washed up in a confused mass” in the cove and “a number of Cases, Casks and Bales; also deals and boards floating about in some of the gorges” further west of the shipwreck. Contemporary newspaper accounts also reported a large quantity of cargo and timber washed ashore in the days following the LOCH ARD shipwreck, adding “but those were speedily removed by persons who came down from Port Campbell, Scott’s Creek and other places with carts and pack horses”. The appearance and good condition of this wood artefact, and the aged patina and dated hand-writing style of its pasted on inscription, support the suggestion that it was ‘souvenired’ from the floating debris of the LOCH ARD at or near the 1878 date of its foundering off Mutton Bird Island. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The Loch Ard wreck is of state significance – Victorian Heritage Register S417. However there is a lack of documented provenance that limits the interpretive value of this piece of timber (for example, its potential to interpret nineteenth century souveniring and scavenging from shipwrecks along the south west coast of Victoria). Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. A length of hardwood timber, planed and varnished to smooth finish on three sides, with two unfinished tongues protruding from each end (one broken off), possibly from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The front or upper face is moulded and routed to a regular, linear (skirting board type) design along its entire length, the two sides flat planed. One side contains two inserted dowel rods that have been broken off. The bottom face has not been finished to the same standard. The sample is good quality wood that has retained its density and weight and shows no evidence of having been submerged in seawater for any length of time. Glued on to the upper face of the length of timber near the right hand end is a deteriorated square of paper bearing an inscription. The paper, peeling back and with torn edges, is stuck over an original wood stain but under a subsequent layer of varnish. The faded ink words are indecipherable where paper is missing, but written carefully in an old fashioned cursive script.The inscription on the paper reads: “A [p]iece of w[r]ec[k] of the Loch Ard wrecked near Sherbroke River”. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, nineteenth-century souveniring, shipwreck scavenging, loch line sailing ships, wood sample -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyscales, 1930's
... scales ...These cast iron scales were made for domestic use as they are quite basic and not accurate enough for commercial use.This item is an example of a common domestic kitchen appliance no longer in use.Large black kitchen scales with large dish that sits in metal claw.Underneath weights plates - 1lb 14ozscales instruments-weighing domestic kitchen -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyscales, c. 19th century
... scales ...Possibly used in a shop or as a travelling set of scales for a hawker.This item is an example of an early device used for measurement.A set of hanging scales. Two copper containers are suspended one from each end of a beam. In the centre of the beam is a hanging rod to the top and a pointer at the bottom.A number of scroll designs are imprinted into the beam. scales weight-measure hanging-scales -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyscales, 19th century
... scales ...This is a MANCUR spring balance. They were used for rough weighing on farms, in kitchens, on hunting trips for animals or hides. Large numbers of Mancur scales were made in America and Europe during the latter half of the nineteenth century, and they were generally used by farmers.This item is an example of an early type of hanging scale.A set of small round hanging scales with a hanging hook. It has two suspension rings and two load hooks. It has a brass crescent shaped plate in the centre calibrated in lbs, a needle as pointer which is hinged to the C spring. It has double sided measurements with graduations in pounds. scale-mancur measurement weight hanging-scales -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDecorative object - Weight, 19th to mid-20th centuries
W3ights such as this one were used to measure goods sold or purchased. They were used in Australia in homes and stores, and government organisations, until the mid 1960s when the Nation converted to metric measures. Weight; one pound imperial measure with inscription around perimete."1 lb" (Other marks are Indecipherable)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, weight, pound, pound weight, weights and measures, measurement, scale, imperial measure -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph, Ballarat School of Mines Balance Room, c1907
... scales ...This image was reproduced in the 1908 Ballarat School of Mines Calendar. During the early 1900s the Ballarat School of Mines had an international reputation for producing quality mining graduates. The graduates had much sought after practical experience. Their studies included 'real' experience in the Ballarat School of Mines Mining Laboratory, Assay Room, Balance Room, etc. This image was reproduced in the 1908 Ballarat School of Mines Annual Report. It is a room in the building now known as the "Old Chemistry Building'.Black and white photograph showing three men working at balances while assaying in the Ballarat School of Mines Balance Room. "Plate 117 Balance Rooms, School of Minesballarat school of mines, scientific equipment, assaying, assay, weigh, weight, scales, assay laboratory, old chemistry building, mining -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Glenfine South and South Berry Journal
This Book is associated with former Ballarat School of Mines Student Richard Squire (1875-1876). Gift of the Squire FamilyGreen water marked linen covered journal with maroon spine with red feint lined blue pages. Label on front cover is cream with black printing JOURNAL with handwritten DATA RISIS GLENFINE SOUTH -SOUTH BERRY G.S & S.B Hand written in black and red ink. Plan in back with scale 20 chains to one inch - Has an index. Handwritten on title page in black ink Address of sawmiller T. J. Brown, Mount Rowan D. W. Hambly 317 Ligar St, Ballarat J. Freeman, C/O Mrs H Simons, Lynch St, Footscray Sleemans Prescription for the bladder in 19009 Mixture No 55983 Tabloids No 55982glenfine south, south berry, sleemans, mining, gold mining, glenfine consols, reef, weights of quartz, blacksmiths tools, australian and eagle, davies south east reef drive, brawns, eaglehawk junction, simons letter, machinery, puddlng plant, poppet heads, winding plant, creswick, mosquito creek, frenchmans gully, spring hill, a. h. welsh, squire, petticoat gully -
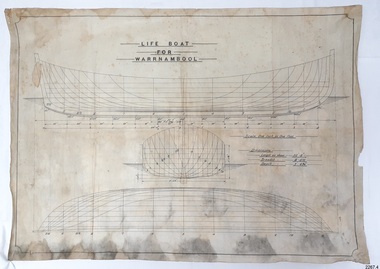 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePlan - Vessel Line Drawing, Life Boat for Warrnambool, ca. 1900-1909
The plans were used for the construction of the lifeboat ‘Warrnambool’, which began 15th September 1909 and was completed almost 12 months later 1st September 1910. It was built at the Government Dockyard in Williamstown, Victoria, along the lines designed by Great Britain’s Royal Lifeboat Institution, and included whaleback decks fore and aft, mast and centreboard, and rudder and tiller hung from the sternpost. It could be propelled by both sail and oar. At that time Captain Ferguson was Chief Harbour Master and Mr Beagley was the foreman boat builder. Mr Beagley built the lifeboat with his fellow workmen. The boat was described as “… a fine piece of workmanship and does credit to her builders and designers…” It had all the latest improvements in shape, disposition of weight and watertight compartments, and it had space for a large number of people in addition to the crew. It appears that 'H Meiers' whose signature was on the plaque that was found concealed in the hull, was involved with the building of the lifeboat. His signature and the dates of the start and finish of the boat’s construction are pencilled on the raw timber 'plaque' found in the hull in the early 1990s when the lifeboat was being restored. It is interesting that the ‘Melbourne Directory’ of 1911, published by Sands and MacDougal, lists McAuley and Meiers, boat builders, Nelson Place foreshore, between Pasco and Parker Streets, Williamstown, (Victorian Heritage Database, ‘Contextual History, Maritime Facilities’), It is quite possibly the business of the person whose name is inscribed on the lifeboat plaque. Flagstaff Hill’s documentation also mentions that the keel was laid at ‘Harry Myers, boat builders, Williamstown, Melbourne’ – the name ‘Myers’ can also be spelled ‘Meiers’, which could be the same person as the Meiers in “McAuley and Meiers” (as mentioned in genealogy lines of Myers). The new lifeboat, to be named ‘Warrnambool’ was brought to town by train and launched at the breakwater on 1st March 1911 using the Titan crane (the old lifeboat built in 1858, was then returned to Melbourne in 1911). This new lifeboat was stationed at Warrnambool in a shed located at the base of the Breakwater, adjacent to the slipway. A winch was used to bring it in and out of the water. The lifeboat ‘Warrnambool’ was similar in size to the old lifeboat but far superior in design, build and sea-going qualities such as greater manoeuvrability. The ‘self-righting, self-draining design was “practically non-capsizeable” and even if the boat overturned it would right itself to an even keel and the water would drain away. The hull was built of New Zealand Kauri, using double diagonal planking, laid in two layers at right angles, with a layer of canvas and red lead paint between the timbers to help seal the planking. It has “… plenty of freeboard area, high watertight spaces between the deck and bottom… through which pipes lead…” The backbone timbers were made of Jarrah. The lifeboat Warrnambool was one of several rescue boats used at Port Fairy and Warrnambool in the early 1900s. In late 1914 the Warrnambool lifeboat and crew were used to help find what was left of the tragic wreckage of the Antares and were able to discover the body of one of the crewmen, which they brought back to Warrnambool. Between 1951 and 1954 the lifeboat was manned under the guidance of Captain Carrington. He held lifeboat practice each month on a Sunday morning, to comply with the Ports and Harbour’s request that lifeboats be manned by a strong and competent crew, ready for action in case of emergency. In the early 1960’s it ended its service as a lifeboat and was used in Port Fairy as a barge to help dredge the Moyne River, bolted to the Port Fairy lifeboat. Flagstaff Hill obtained the Warrnambool in 1975. In 1984 it was on display at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. On 23rd May 1990, she was lifted from the water and placed in a cradle for restoration. The name ‘WARRNAMBOOL could be seen faintly on the lifeboat before it was restored. It was during the restoration that Flagstaff Hill's boat builder discovered the 'plaque' inside the hull. A copy of the blueprint plans has the name “V.E.E. Gotch” printed on it. His advertisement in Footscray’s ‘Independent’ newspaper of Saturday 11th May 1901 states he is “Principal and Skilled member (Naval Architect) to the Court of Marine Inquiry of Victoria and holds classes for naval architectural drawing and arithmetic.” The line drawing is significant for its connection with the lifeboat WARRNAMBOOL. The lifeboat is very significant to local and state history for its use in the lifesaving rescues of seafarers, particularly in Lady Bay. It was part of the local rescue equipment. It gave a half-century of service to the local community as a lifesaving vessel, including its involvement in retrieving the body of a shipwrecked crew member of the ANTARES. Line drawing in black ink and pencil on rectangular parchment or waxed linen. Drawing has diagrams of three profiles of a vessel, with measurements and connecting pencil lines on the left quarter. The plan is for the lifeboat named “Warrnambool”, which was built in Melbourne and completed in 1910. Old blue copies of the Lifeboat plan are archived also.“LIFE BOAT / FOR / WARRNAMBOOL” “Scale, One Inch to One Foot” “ “Length as shown 30’ – 8” “ “Breadth “ “ 8’ – 6 ½ “ “ “Depth “ “ 3’ – 4 ¾” “flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, lifeboat, warrnambool lifeboat, boat plans, lifeboat plans, boat construction, boat building, line drawing, plan for lifeboat, life boat, life boat 'warrnambool', clinker design, 1910 lifeboat, life saving equipment, shipbuilding -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Letter Scale, Philip Jakob, Maul, 1930s
Jakob Maul (1866-1953) founded a metal works factory in 1912 at Zell in Odenwald not far from Frankfurt. He was born the son of a winegrower from the Rheinhessen region of Germany that lies on the left bank of the river Rhine. At the age of 45, he started a metal works factory to produce various types of scales but during the second world war the factory was bombed and production ended. Production for the manufacture of scales resumed in 1948. In 1953 at his death Jakobs son Fritz Scharmann an engineer who had been working with his father since 1923 took over the management of the Maul companies. In 1970 the production responsibilities for Philip J Maul was taken over by Porti Office Equipment who was based in Hamburg. The company has undergone several integrations with subsidiary companies. Today the company has diversified into different areas one of which is manufacturing solar scales. An original postal scale made in Germany before the Second World War and regarded today as a collector's item. It is significant as it is a snapshot into the past and how everyday vintage items were used and interacted within society in the 1930s.Antique German Jacob Maul "Concav" brass postal or letter scale, quadrant type, with pendulum, measuring up to 9ozs. The scale has a level-adjusting screw.The balance is marked "CONCAV" and graduated in imperial ounces to 9 ozflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, scale, quadrant scale, postal weight, 9 oz, philip jakob, maul, scale manufacturer, german industry, weighing instrument, inclination scale -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Pipe, Before 1878
HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD: - The Loch Ard got its name from ”Loch Ard” a loch that lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and to the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic. The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold their position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as Loch Ard Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the Loch Ard tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of Loch Ard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up into Loch Ard Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck, it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artifact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register.The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we are able to interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collections historically significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history. Heavy duty brass sleeve retrieved from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. It is pinched and broken off at one end, enclosing an extendable inner sleeve, which is connected to a brass bracket fixed at right angles. The circular enclosing bracket would hold (and fix by an adjustable brass screw) a through or cross pipe of similar diameter to the outer sleeve. The artefact is a structural piece delivering vertical support to a horizontal rail (missing) and not for transporting gas. It is constructed of thick gauge metal suitable for weight/load bearing and its sliding sleeve design is similar to a modern shock absorber, or a telescopic leg supporting a surveying instrument. There is concreting sediment immobilising the sleeves and lining the inner surface of the bracket. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, brass fitting, brass pipe, 1878 shipwreck -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Mariner's astrolabe
This representative example demonstrates a mariner’s astrolabe. Historical examples are rare. There are less than one hundred known to exist and most of these have been recovered from shipwrecks, many from Spanish and Portuguese vessels. An astrolabe is a measuring device once used to navigate the seas by observing the sun and stars to measure their altitude. The measurement of altitude could then be used to calculate the ship’s latitude but at that time in history there was no means of measuring longitude. The body of the navigational astrolabe was cast brass and much heavier, and less complicated than the variety used on land. The heavier weight and cut-away shape reduced the effect of the wind and waves when trying to use it at sea. A mariner’s astrolabe or ‘star finder’ is a simplified version than that used by Arabic astronomers to find the altitude of the sun and stars above the horizon, and time of the sunrise and sunset. It is a forerunner to the quadrant, octant and sextant and was popular for about 200 years over the 1500s and 1600s to find the latitude of a ship at sea. The user held the astrolabe at eye level and, usually with assistance, aligned the stars through the two small sights (pinnules), then read the altitude indicated by the pointer on the arm. It could also be used to sight the sun by holding it lower down, aiming it at the sun, and adjusting it until the sun shone through both pinnules. This astrolabe is an example used to demonstrate the mariner’s astrolabe, which was navigational tool of the 1500s and 1600s, in the time before longitude was able to be determined. It is a forerunner to modern navigation technology. Mariner’s astrolabe – a representative example. A gold painted, disc shaped object with cut outs and revolving arm in centre. The arm has two sights attached at right angles. The top has a ring attached. Measurements are marked in degrees in a circular scale around outer edge.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, navigation instrument, navigation tool, navigation, astrolabe, mariner’s astrolabe, measure latitude, measure altitude, arabic navigation, measuring device, star finder, astronomy, marine tool, marine instrument -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionScientific Object, Scales
... Scales...scales ...Used at Ballarat School of Mines / University of Ballarat2 pound weigh scale; yellow gold gunmetal base, brass pans. Black pointer indicates balance."AVERY" and "TO WEIGH 2LB MADE IN ENGLAND".scales, brass, avery, england, weight, weigh, ballarat school of mines, university of ballarat, school of business, office equipment -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Tool - WEIGHTS FOR WEIGHING GOLD
... Scales ...Brass weights used for weighing gold. Smallest weights a 4 'grain' and 5 'grain' square weights. Rectangular 1 pennyweight weights (brass lozenge apothecary style weights ) through to round, flat 2 ounces. Weights enclosed in an oval shaped tin with side clasp.gold mining, scales, brass weight for weighing gold -
 Creswick Museum
Creswick MuseumChinese Opium or Gold Scale, circa 1840 - 1880
Probably brought to the area by Chinese miners or shopkeepers. It was used to weigh small items at a time when goods were often paid in gold. In could also be used for weighing opium. In China it was known as a Dotchin. Creswick had a large Chinese population which arrived circa 1855 and established the Chinese Camp (now Calembeen Park) plus other satelite camps in the area. In 1859 there was over 1,000 residents in the area and many operated as shopkeepers. Joined pieces of wood (bamboo), violin shape case joined with brass rivet together. The case features a long section to house the ivory rod with the bulbous section to house metal dish with four holes. Ivory rod. Metal weight is missingIvory rod has markings to indicate weight. Metal dish has four holesscale, goldrush, gold, miners, opium smoking, shopkeeping -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumScales, H. L. Becker Fils & Co
... Scales...scales ...Scientific Apparatus 2 tins with weights with appropriate numbersscales, flour mill scales -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumEquipment - BOX OF WEIGHTS AND TWEEZERS, GRIFFEN & TATLOCK
WEIGHTS USED IN DYEING THE MATERIAL (WOOL) BEFORE KNITTING HOSIERY AT CLUNES INTERKNIT HOSIERY MILL.BLACK BAKELITE BOX CONTAINING NINE BRASS MICRO.0 METRIC WEIGHTS 100. 50. 20. 10. 10. 5. 2. 2. 1 GRAMS DIFFERENT WEIGHTS ON INSIDE LID AND BASE OF CONTAINER AND SET OF TWEEZERS. CONTAINER OF WEIGHTS HOUSED IN GLASS CABINETlocal history, textile, equipment, weights and scales, knitting mill interknit hosiery co. -
 Nillumbik Shire Council
Nillumbik Shire CouncilPrint (Lithograph): John Olsen (b.1928 NSW), John Olsen, Tropical Rain Shower from The Bodford Terrace Suite, 1978
A typical Olsen painting combines an implied aerial view with an ambiguous and seemingly unpremeditated figuration. His characteristically quizzical line and irregular squiggles and dots deftly render countless organisms, large and minute. Their environment is conjured through loosely brushed and stained expanses of colour (on canvas or hardboard) and lines which sometimes read as geological mappings. In Olsen's work there is no foreground/ middle ground/ background, nor any sign of European landscape's concern with "human scale." Instead he employs simultaneously the contrary vantages of naturalist and geographer. 'Tropical Rain Shower' by John Olsen forms one of the eight artworks represented in the Bodford Terrace Suite. Eight of Australia's finest artists were brought together to create a folio of lithographic prints to celebrate the restoration of historic Bodford Terrace. Printed at the Druckma Press by John Robinson under the supervision of master printer Jock Abbott. The folio edition was limited to 300 signed and numbered folios. The lithographs were printed on special heavy weight french Arche's paper in accordance with the tradition of this artistic medium. Lithographic print on paper.Signed John Olsen '78, lower right hand corner. Edition 179/300bodfford terrace collection, john olsen, tropical rain shower -
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyWeighing machine, Reliance Automatic Personal Scale, Before 1975
... Scales ...Thought to have been used at Rutherglen Railway StationStep-on commercial weighing machine, clock face showing weight in stones, coin operated (pennies). Plate under face listing average weights. Dunlop rubber mat on platform. Manufactured. Painted enamel, metal rim round glass over faceNumbers around dial. "Penny" "Check Your Health / The Reliance / Automatic Personal Scale / British Made / in / Leicester" / "Zero". On back: "1081"scales, personal weight -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Tracks, Ballarat Railway Station, H. Pooley & Sons, London
... Scales ...ballarat railway station, scales, weight, pooley & son, h. pooley -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Tool - GOLD SCALES
... scales ...Beam scales for weighing gold, copper dishes.weighing, weights & measures, scales -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Tool - GOLD SCALES
... scales ...Small brass beam gold scales.weighing, weights & measures, scales
