Showing 23326 items
matching mader
-
 Tarnagulla History Archive
Tarnagulla History ArchivePostcard: Newbridge Brewery
David Gordon Collection. Original image made mid to late 19th C. Modern reprint. -
 The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical Collection
The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical CollectionSouvenir - Trophy, Star Piquet
Custom made timber stand to hold bullet riddled star piquetnil -
 The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical Collection
The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical CollectionPlaque - The Kings Regiment plaque
The Kings Regiment plaque is in the centre of the plaque, its made of dark wood, the -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyHandkerchief box, 1900
Wooden handkerchief box made and carved, with flowers by Mr. Striezel in 1900.handkerchief boxes, boxes -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncAward - Wodonga Darts Association Premiers 1985
The Terminus Hotel was one of the earliest hotels in Wodonga, with clear links to the establishment of the railway line. It was an important business and meeting place from the original construction in 1873 until 1st June 1998 the Terminus Hotel when it was destroyed by fire. It provided a popular venue for social activities, including competitive darts, both through its own competition and as part of the Albury-Wodonga District Darts Association. The remains of the building were demolished in 1999. This is perpetual trophy for the Terminus Dart club based at the Terminus Hotel in Wodonga. This trophy recognises the winners of the Albury-Wodonga Darts Association Premiers 1985.The Terminus Hotel was an important meeting place in Wodonga for more than 100 years. This item is representative of one of the social and sporting activities it provided for members of the local community.A trophy made from timber and metal with a representation of a darts player on the top.At base: "A.W.D.D.A 1985/ PREMIERS TERMINUS EASY BEATS Listed on front: I. BOSLEY (CAPT.) G. MULHOLLAND (V.C.) K. COOK R. HUDSON J. DE KRUIFF D. ROWE B. SAYERSterminus hotel wodonga, albury-wodonga district darts association, sport and recreation -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyFunctional object - Keyring, Legacy Appeal Keyring, 2015
A keyring issued by Legacy for fundraising during the Legacy Appeal and Badge Week. The donation value for the keyring is $5. The date is estimated to be approximate 2015. It was found in the archive as an example the types of items Legacy has used in fundraising. The badge of Legacy is the Torch and Wreath of Laurel. The Torch signifies the undying flame of service and sacrifice of those who gave their lives for their country. The Wreath of Laurel is the symbol of our remembrance of them.Example of Legacy items that were sold up to raise money for Legacy's work. Legacy Appeal keyring with a slouch hat made of copper coloured metal.Embossed on the reverse "www.legacy.com.au / Legacy / 1800 534 229"legacy appeal, fundraising, badge week -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumInstrument - Direct Current Galvanometer
Cylindrical and galvanometer made of green-gray enameled metal on a round base.Plaque on top of cylinder: 'DIRECT CURRENT GALVANOMETER / COIL RESISTANCE 20 OHMS / CRITICAL RESIST 120 OHMS / SENSITIVITY 200 m.m/μα / Instrument No. 1023 / J. L WILLIAM'j l william, scientific instruments, galvanometer, direct current galvanometer, australian instrument makers, ammeters -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionSculpture - Sculpture - Metal, 'Sculpture No. 9' by Cinnamon Francis
This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 2000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.Metal sculpture, made from found items, including musical instruments.art, artwork, cinnamon francis, sculpture, metalwork, alumni, cinnamon stephens -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumGalvanometer, Tinsley
Cylindrical reflecting galvanometer made of metal and covered in light green enamel.Label: “Purchased by Universities Commission” Engraved: “No. 79133” Plaque on front: “Reflecting Galvanometer, link in aperiodic link out ballistic, 3038 H. Tinsley & Co. Ltd No. 78,424” Attached tag: Diagram (see worksheet) “Rs - shunt resistance Rg = galvanometer resistance” -
 Friends of Westgarthtown
Friends of WestgarthtownHorseshoe
Two horseshoes made of steel, one is slightly larger than the other.No visible markingsrural industry, agriculture, both shoes heavily corroded and fragile to touch. -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesClothing - Lady's Jodphurs, c. 1930
Jodphurs worn by female students. Given to Archives by Alice Tucker (nee glascodine) who graduated in 1933 with Certificate of Competency in HorticulturePair of fawn cotton ladies jodphurs made by Rankine & Dobbie, MelbourneRankine & Dobbiejodphurs, pants, trousers, female students, alice tucker (née glascodine), 1933, uniform -
 Wannon Water
Wannon WaterTwo way radio
Front and back cover made of metal and held together at the back with a screw. Push Button on the left (Press to Talk), also red wheel for turning transistor on and adjusting volume. Aerial on the right at the top. Aerial 1.40 m long when extended. Front cover has inbedded a silver square metal mesh for hearing sound and speaking. Brown leather cover with zip for protection.Front: 9 Transistor/Sharp/ Model CBT-1A Back: Earphone/ Press to Talk/ Made in Japan Handwritten on a piece of tape: Batteries replaced 1-5-1968, 6-6-1975 -
 Wangaratta Urban Fire Brigade
Wangaratta Urban Fire Brigadeframe picture
Certificate that the Wang urban fire brigade 'dodge' made it to the top of Mt Buffalo in 1978simple brown frame with a certificate This is to certify that the 'W. F. B 1938 Dodge' made it to the top of Mt Buffalo during the Bushranger rally 1979. signed by D.S Saunders Director of National Parks (top right quarter) (illustration of winding road over the other 3/4) 1978, dodge -
 The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical Collection
The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical CollectionPlaque - Presentation Plaque, Reconnaissance Platoon 5TH 6TH Royal Victoria Regiment
Delta Company was reformed out of Support Company, of which recon platoon was a part ofShield shaped plaque made of varnished timber with a large badge affixed to its front The badge is a 5/6 colour patch being made up of a black rectangle on top of a red rectangle. Gold eyes and hands appear to be pearing through the bushes in the foregrond. This is the recon platoon logo. Below this badge is an engraved plaque made of brassRecon Platoon Best Section Canungra 20055/6rvr, support company, recon platoon, wark vc club, plaque -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Bed Pan, Early 20th century
This bed pan was used in the past for patients in hospitals and other places where there were bedridden people. Bed pans are still used in these circumstances but they are now made of materials that are more easily sterilized. This item has no known local provenance but it is an interesting example of hospital equipment used in the past and will be useful for display. This is a spherical-shaped white china bowl with a pointed end and with the opening partly covered at the smaller end. It has a china handle at the top section. There are three drainage holes at the bottom of the smaller end. Inside the bowl at the top section there is black printing. The New Slipper Bed Pan This slipper should be passed under the Patient in front between the legs. If a flannel cap is made for the blade fastened by strings under the handle considerable comfort will be afforded. vintage hospital equipment, history of warrnambool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTextile - Pillow Shams, 1844-1900
The two embroidered pillow shams were made by Betty Stones's mother Daisy (nee Dale) Welsh. A number of crocheted and embroidered articles were donated to Flagstaff Hill Museum by Betty Stone who advised that they cover a period of three generations from Sarah (nee Chamberlain) Lees, Ann (nee Lees) Dale, and Daisy Elvena (nee Dale) Welsh. All three were accomplished needlewomen, both Sarah Lees (born 1844) and her daughter, Ann (1865) these women crocheted a wide variety of articles for use in their homes. Today we have a few surviving examples of their skill that has survived the years.This item and others in the collection donated by Betty Stone are significant for their association with the early Warrnambool pioneering families of Chamberlain, Dale and Lees. These families are listed in the "Pioneers' Register" for Warrnambool Township and Shire, 1835-1900, and published by A.I.G.S. Warrnambool Branch. The item is a fine example of early 20th-century needlework and handmade domestic items.A pair of white pillow shams, rectangular in shape with a shallow scalloped crochet edge. The embroidered central design includes a bird motif. Made by Daisy Walsh (nee Dale). Part of the Chamberlain Dale Lees Collection.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, chamberlain family, dale family, lees family, betty stone, warrnambool pioneer, warrnambool genealogy, wangoom, chamberlain dale lees collection, glory box, handmade, craft, manchester, linen, haberdashery, needlework, crochet, pillow shams, bed linen, pillow covers, daisy dale, daisy welsh, betty stone's mother -
 Stratford and District Historical Society
Stratford and District Historical SocietySnakebone necklace
Makers of Snakebone Necklaces Two local women who made these necklaces were: Minnie Blucher (nee Wanke) (c.1891-1976) who lived at Briagolong in the 1940s. Highly artistic, she eagerly sought out snakes, killing many around Noble's Bridge. Peter Mills of Briagolong remembers that she would hang them on fences for maggots to eat away the fresh, and painted and dyed the bones. She also used spine bones from cattle for ornaments. Bella Buttsworth (1882-1951) was the daughter of Thomas and Rachel Mills of Briagolong, and the aunt of Ina Worseldine of Maffra. Ina remembers her making these necklaces in the 1920s, and that she placed beads in between the bones. The comment was also made that she often put large bones at the front and smaller ones to the back. Bella obtained the bones by boiling the dead snakes down, and then left the bones out on logs in the sun to bleach.A circular necklace made of spine bones from snakes and red beads, threaded onto copper wire. It contains 20 bones, each with a red bead between it and the next, with five red beads near a rough hook catch. The bones appear painted, possibly with calcomine.craft, handcrafts -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPhotograph - Colour print, Things are Never Down on the Farm at Burnley Horticultural School, 1934
Photograph made by A.P. Winzenried for, "Green Grows Our Garden," p73.Colour photograph. Copy made by A.P. Winzenried. Photograph appeared in the "Sun News Pictorial," July 10, 1934. The caption reads, "Things are never down on the farm at Burnley Horticultural School while Don, the old dray horse, is on the job carting his load of happy students back to the lecture room after a session of practical work. Most of the 30 pupils now at the school are engaged in the study of pruning." See B94.-902. A large group of male and female students seated on a cart darwn by a draught horse.a.p. winzenried, green grows our garden, don, dray horse, students working outside, draught horse, students, orchard, newspaper cutting -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumDocument, "Dem Tagebuch", 1945-1946
Made in Camp 1, Tatura to contain type written diary by Dr. Neumann, who, from Germany, had been appointed lecturer at Sydney University c.1937, until interned in 1939. This item remained in the possession of his daughter Ingrid until she brought it and presented to the Museum.Grey cardboard covers with red binding secured by cream plastic string, containing paper pages with hand written notes, mostly in German. Scrap book made and bound in Camp 1 with diary entries written fromOctober 1945 to 20.01.1946, by Dr. Neumann during his internment in Camp 1, Tatura.October 1945 (inside)camp 1 tatura, dr gerhard neumann, books, collections -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Rabbet Plane, Mathieson and Son, Late 19th to early 20th Century
In 1792 John Manners had set up a workshop making woodworking planes at 14 Saracens Lane Glasgow. He also had employed an apprentice Alexander Mathieson (1773-1851). But in the following year at Saracen's Lane, the 1841 census describes Alexander Mathieson as a master plane-maker now at 38 Saracen Lane with his son Thomas Adam working with him as a journeyman plane-maker. Presumably, Alexander must have taken over the premises and business of John Manners. Now that the business had Thomas Adam Mathieson working with his father it gradually grew and became more diversified, and it is recorded at the time by the Post-Office Glasgow Annual Directory that by 1847-1848 Alexander Mathieson was a “plane, brace, bit, auger & edge tool maker” In 1849 the firm of James & William Stewart at 65 Nicolson Street, Edinburgh was taken over and Thomas was put in charge of the business, trading under the name Thomas A. Mathieson & Co. as plane and edge-tool makers. Thomas's company went on to acquire the Edinburgh edge-tool makers “Charles & Hugh McPherson” and took over their premises in Gilmore Street. In the Edinburgh directory of 1856/7, the business is recorded as being Alexander Mathieson & Son, plane and edge-tool makers at 48 Nicolson Street and Paul's Work, Gilmore Street Edinburgh. The 1851 census Alexander is recorded as working as a tool and plane-maker employing eight men. Later that year Alexander died and his son Thomas took over the business. Under the heading of an edge-tool maker in the 1852/3 Post-Office Glasgow Annual Directory the firm is now listed as Alexander Mathieson & Son, with further entries as "turning-lathe and vice manufacturers". By the early 1850s, the business had moved to 24 Saracen Lane. The directory for 1857/8 records that the firm had moved again only a few years later to East Campbell Street, off the Gallowgate area, and that through further diversification was also manufacturing coopers' and tinmen's tools. The ten-yearly censuses report the firm's growth in 1861 stating that Thomas was a tool manufacturer employing 95 men and 30 boys; in 1871 he had 200 men working for him and in 1881 300 men. By 1899 the firm had been incorporated as Alexander Mathieson & Sons Ltd, even though only Alexander's son Thomas appears ever to have joined the firm so the company was still in his fathers' name. In September 1868 Thomas Mathieson put a notice in the newspapers of the Sheffield & Rotherham Independent and the Sheffield Daily Telegraph stating that his firm had used the trade-mark of a crescent and star "for some time" and that "using or imitating the Mark would be proceeded against for infringement". The firm had acquired its interest in the crescent-and-star mark from the heirs of Charles Pickslay, the Sheffield cutler who had registered it with the Cutlers' Company in 1833 and had died in 1852. The year 1868 seems also to be the one in which the name Saracen Tool Works was first adopted; not only does it figure at the foot of the notice in the Sheffield press, it also makes its first appearance in the firm's entry in the Post-Office Glasgow Annual Directory in the 1868/9 edition. As Thomas Mathieson's business grew, so too did his involvement in local public life and philanthropy. One of the representatives of the third ward on the town council of Glasgow, he became a river bailie in 1868, a magistrate in 1870 and a preceptor of Hutcheson's Hospital in 1878. He had a passion for books and was an "ardent Ruskinian". He served on the committee handling the bequest for the setting up of the Mitchell Library in Glasgow. When he died at Coulter Maynes near Biggar in 1899, he left an estate worth £142,764. Company's later years: Both Thomas's sons, James Harper and Thomas Ogilvie were involved in the continuing life of the firm. James followed in his father's footsteps in becoming a local public figure. He was appointed Deputy Lieutenant of the County of the City of Glasgow and was made a deacon of the Incorporation of the Hammermen of Glasgow in 1919. His brother Thomas Ogilvie was recorded as tool manufacturer and employer in the 1911 census. Thomas Ogilvie's son Thomas Alastair Sutherland Ogilvie Mathieson was born in 1908 took a rather different approach to engineering, however, by becoming a racing driver. In 1947 he wed the French film actress Mila Parély. The firm had won many awards at world fairs for their goods. At the Great Exhibition, London, 1851. Prize medal for joiners' tools in the class of Cutlery & Edge Tools, Great London Exposition, 1862. Prize medal honoris causa. International Exhibition, Melbourne, 1880. Gold medal International Exhibition of Industry, Science and Art, Edinburgh, 1886. Prize medalThe firm of Alexander Mathieson & Son was one of the leading makers of hand tools in Scotland. Its success went hand in hand with the growth of the shipbuilding industries on the Firth of Clyde in the nineteenth century and the emergence of Glasgow as the "second city of the Empire". It also reflected the firm's skill in responding to an unprecedented demand for quality tools by shipyards, cooperages and other industries, both locally and far and wide.Rabbet plane with a flat base. The blade wedge is inserted but without a blade. Made by A Mathieson and Son.Inscription "Alex Mathieson and Son" no longer visibleflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, cabinet makers tools, carpenders tools, wood planes, rabbeting plane, window making, tools, wood working, hand tool -
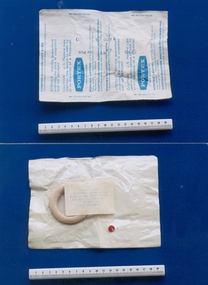 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Ring pessary associated with Dr Geoff Bishop, c. 1977, before 1977
This pessary came from Professor Geoff Bishop's rooms, Mollison House, 386 Albert Street, East Melbourne. As well as the UK, Portex had divisions in the USA and Canada. The pessary was originally regarded as an instrument and made from cork, ivory, hard rubber or gum-elastic. In later times, they were made from black vulcanite, flexible tin, soft copper wire covered with Indian rubber, and celluloid. The form of the pessary was and still is variable -either round, oval, or moulded in some cases combining three or four curves depending on the size of the pessary. In ancient time, medicated pessaries were made from emollient. astringent and aperient. Several of these are still used, but in more modem times are called vaginal suppositories. Anal suppositories are still used to suppress the pain of haemorrhoids.Portex brand ring pessary in original packaging. Consists of circular ring of cream vinyl, in sterile sealed pouch with transparent plastic at back. Stamped on pouch "PORTEX/MADE IN ENGLAND", and the text "USE BY JAN 77" and "CONTROL No 06 88". The ring is size 700/300/065 - 65mm. A sticker on the back of pouch gives instruction for cleaning the pessary. A red dot is also stuck to the back of the pouch.pessary, intrauterine device -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Plate
The Process of Making Pottery Decorating, Firing, Glazing, Making, Technical There is a rhythm and flow to clay. It can’t be done all at once! Even the making process! It can take weeks to get everything done, especially if you can only work on your pottery once a week! Even though we have three hour classes, it’s often just not enough time! Here is an overview of some of the processes so you have a bit more grasp on some of the technical stuff! Step One – Design There are SO many ideas out there for making stuff in clay! From delicate porcelain jewellery, through to heavy sculptural work and everything in between. Deciding your direction is sometimes not that easy – when you first start, try everything, you will naturally gravitate to the style that you enjoy! The options and variations are endless and can get a wee bit overwhelming too! Check in with me before you start to ensure your ideas will work, what order you might do things, how you could achieve the look you are seeking and any other technical data required! Step Two – Making Clay is thixotropic. This means that as you work with it, the clay first gets sloppier and wetter, before is begins to dry in the atmosphere. For most things, you simply can’t do all parts of the project at once. An example of work order might look like: Get last weeks work out from the shelves Prepare clay for today’s work – roll your clay, prepare balls for throwing, make the first stage of a pinch pot) Clean up last week’s work and put it on the shelf for bisque firing Check that you have any glazing to do – and do enough of it that you will have time to finish your main project Do the next step of your next project – there might be a further step that can’t be complete immediately, in that case, wrap your work well and put onto the shelves. Letting your work rest for a while can really help keep your work clean and professional looking. Many things require bagging under plastic to keep it ready for work the next week – put your name on the outside of the bag so you can find your work easily. We have stickers and markers. Consider how you want to decorate your work – coloured slip can be applied at a fairly wet stage (remembering that it will make your work even wetter!). Trying to apply slip to dry clay won’t work! If you want to do sgraffito – you will need to keep the work leather hard (a state of dryness where you can still work the clay with a little effort and a little water and care). Step Three – Drying Most of the time your work can go into the rack uncovered to let it dry out for the following week. If you want to continue forming or shaping you will need to double bag your work – put your work on a suitable sized bat and put the bat in a bag so the base of the bag is under the bat, then put another bag over the top of the work and tuck the top of the bag under the bat. If you want to trim (or turn) your thrown work the following week, it should also be double bagged. If your work is large, delicate, or of uneven thicknesses, you should lightly cover your work for drying. When considering the drying process, bare in mind the weather, humidity and wind! The hotter and dryer, the faster things dry and work can dry unevenly in the shelves – this can lead to cracking – another time to lightly cover your work for drying. Step Four – Trimming and Cleaning Up Your work is dry! It is called greenware now and it is at it’s most fragile! Handle everything with two hands. I often refer to soft hands – keep everything gentle and with your fingers spread as much as possible. Try to not pick up things like plates too much, and always with both hands! Before your work can be bisque fired it should be “cleaned up”. You work won’t go into the kiln if it has sharp edges – when glazed, sharp edges turn into razor blades! Use a piece of fly wire to rub the work all over – this will scratch a little so be light handed. Use a knife or metal kidney to scrape any areas that require a bit more dynamic treatment than the fly wire offers! Finally, a very light wipe over with a slightly damp sponge can help soften and soothe all of your edges and dags! Trimming thrown work: If you are planning to trim (or turn) your thrown work (and you should be), make sure you bag it well – your work should be leather hard to almost dry for easiest trimming. Use this step to finish the work completely – use a metal kidney to polish the surface, or a slightly damp sponge to give a freshly thrown look. Wipe the sponge around the rim after trimming, and check the inside of the pot for dags! Trimming slip cast work: Usually I will trim the rims of your work on the wheel the following day to make that stage easier, however you will still need to check your work for lumps and bumps. Last but not least – check that your name is still clearly on the bottom of your work. Step Five – Bisque Firing When the work is completely dry it can go into the bisque kiln. The bisque kiln is fired to 1000°C. This process burns off the water in the clay as well as some of the chemically bound water. The structure of the clay is not altered that much at this temperature. Inside the bisque kiln, the work is stacked a little, small bowl inside a larger bowl and onto a heavy plate. Smaller items like decorations or drink coasters might get stacked several high. Consideration is paid to the weight of the stack and shape of the work. A bisque kiln can fire about one and a half times the amount of work that the glaze kiln can fire. The firing takes about 10 hours to complete the cycle and about two days to cool down. Once it has been emptied the work is placed in the glaze room ready for you to decorate! Step Six – Glazing Decorating your work with colour can be a lot of fun – and time consuming! There are three main options for surface treatment at this stage: Oxide Washes Underglazes Glazes Washes and underglazes do not “glaze” the work – It will still need a layer of glaze to fully seal the clay (washes don’t need glaze on surfaces not designed for food or liquid as they can gloss up a little on their own). Underglazes are stable colourants that turn out pretty much how they look in the jar. They can be mixed with each other to form other colours and can be used like water colours to paint onto your work. Mostly they should have a clear glaze on top to seal them. Oxides are a different species – the pink oxide (cobalt) wash turns out bright blue for instance. They don’t always need a glaze on top, and some glazes can change the colour of the wash! The glazes need no other “glaze” on top! Be careful of unknown glaze interactions – you can put any combination of glaze in a bowl or on a plate, but only a single glaze on the outside of any vertical surface! Glazes are a chemical reaction under heat. We don’t know the exact chemicals in the Mayco glazes we use. I can guess by the way they interact with each other, however, on the whole, you need to test every idea you have, and not run the test on a vertical surface! Simply put, glaze is a layer of glass like substance that bonds with the clay underneath. Clay is made of silica, alumina and water. Glaze is made of mostly silica. Silica has a melting point of 1700°C and we fire to 1240°C. The silica requires a “flux” to help it melt at the lower temperature. Fluxes can be all sorts of chemicals – a common one is calcium – calcium has a melting point of 2500°C, however, together they both melt at a much lower temperature! Colourants are metal oxides like cobalt (blue), chrome (green through black), copper (green, blue, even red!), manganese (black, purple and pink) iron (red brown), etc. Different chemicals in the glaze can have dramatic effects. for example, barium carbonate (which we don’t use) turns manganese bright pink! Other elements can turn manganese dioxide brown, blue, purple and reddish brown. Manganese dioxide is a flux in and of itself as well. So, glazes that get their black and purple colours, often interact with other glazes and RUN! Our mirror black is a good example – it mixes really well with many glazes because it fluxes them – causes them to melt faster. It will also bring out many beautiful colours in the glazes because it’s black colouring most definitely comes from manganese dioxide! Glaze chemistry is a whole subject on it’s own! We use commercial Mayco glazes on purpose – for their huge range of colour possibilities, stability, cool interactions, artistic freedom with the ability to easily brush the glazes on and ease of use. We currently have almost 50 glazes on hand! A major project is to test the interactions of all glazes with each other. That is 2,500 test tiles!!!! I’m going to make the wall behind the wheels the feature wall of pretty colours! Step Seven – Glaze (Gloss or sometimes called “Glost”) Firing Most of the time this is the final stage of making your creation (but not always!) The glaze kiln goes to 1240°C. This is called cone 6, or midrange. It is the low end of stoneware temperatures. Stoneware clays and glazes are typically fired at cone 8 – 10, that is 1260 – 1290°C. The energy requirement to go from 1240°C to 1280°C is almost a 30% more! Our clay is formulated to vitrify (mature, turn “glass-like”) at 1240°, as are our glazes. A glaze kiln take around 12 hours to reach temperature and two to three days to cool down. Sometimes a third firing process is required – this is for decoration that is added to work after the glaze firing. For example – adding precious metals and lustres. this firing temperature is usually around 600 – 800°C depending upon the techniques being used. There are many students interested in gold and silver trims – we will be doing this third type of firing soon! After firing your work will be in the student finished work shelves. Remember to pay for it before you head out the door! There is a small extra charge for using porcelain clay (it’s more than twice the price of regular clay), and for any third firing process! Once your work has been fired it can not turn back into clay for millennia – so don’t fire it if you don’t like it! Put it in the bucket for recycling. https://firebirdstudios.com.au/the-process-of-making-pottery/Ceramics have evolved over thousands of years.White earthenware dinner plate. Crazing evident all over.Backstamped ‘Made in England S LTD’flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, ceramics, tableware -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Bowl, Broadhurst Staffordshire Ironstone Pottery, 1950s - 1960s
Broadhurst China was established in 1862 the firm was based at the Crown Pottery, Longton, Staffordshire until 1870 where James Broadhurst made a range of gold and silver lusterwares. In 1870 the firm moved to the Portland Pottery at Fenton, Staffordshire and continued to produce good quality earthenware. In 1897 "& Sons" was added to the company name and "Ltd" from C.1922. The full name, James Broadhurst & Sons Ltd. appears from 1957. In 1984 James Broadhurst & Sons Ltd became Churchill Tableware Ltd.Items made around 1950s or slightly later that are now collectors items made by one of the founders of ironstone pottery in England.Small ironstone willow pattern bowlThe back is stamped "WILLOW BROADHURST STAFFORDSHIRE IRONSTONE Made in England Detergent and Dishwasher Proof" Mass produce, Ceramic, Potteryironstone pottery, staffordshire pottery, flagstaff hill museum, crockery, dinner set, willow pattern -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomDomestic object - Silver Candelabra, 3 Stem
Set of 5 with catalogue no 0455, 0518, 0535, 0536. 3 stem, silver EPNS candelabra. Floral design around base and candle holders. Curved branches.Made in England Made in England by Ianthe of England On base: C31On candle holders: C34candelabra, mess -
 Slovenian Association Melbourne
Slovenian Association MelbourneSt Nicholas giving gifts to children 1958, St Nicholas - sv Miklavž giving gifts to Slovenian children 1958, 1958
St Nicholas is an old Christian tradition all over the world and Slovenians are very diligently keeping the tradition. The children were given presents, lollies and oranges, sometimes toys as well.Handmade outfit for St Nicholas still in use todaySt Nicholas giving gifts to Slovenian children in a hall, accompanied by angels and devils, much feared by children. The St Nicholas was MrSt Nicholas dressed in a home made outfit made by Dragica Gomizel in late 1950s.st nicholas, sv miklavž, slovenian custom, slovenian tradition -
 The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical Collection
The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical CollectionHeadwear - Steel Helmet, Olive colour RBR PASGT Helmet
Olive Green Steel Helmet, RBR PasgtDate July 2000, Lot No 3664, made by RBR International Ltd, Made in the UK -
 Heidelberg Golf Club
Heidelberg Golf ClubClothing - Necktie, Heidelberg Golf Club tie, Unknown
Heidelberg Golf Club members' tie with logo.One of a collection of various HGC members' ties.Navy blue necktie with yellow and brown diagonal stripe and single HGC logo.Manufacturer's tag on back of tie: "Holly Green, Made in Australia", "Man-made fibre"heidelberg golf club, memorabilia, vic mcgavin, neckties, club ties -
 Heidelberg Golf Club
Heidelberg Golf ClubClothing - Necktie, Heidelberg Golf Club tie, Unknown
Heidelberg Golf Club members' tie with logo.One of a collection of various HGC members' ties.Navy necktie with multiple yellow and red diagonal stripes and single HGC logo.Manufacturer's tag on back of tie: "Holly Green. Made in Australia. Man made fibre"heidelberg golf club, memorabilia, neckties, club ties -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Draw Knife, Hale Bros. (John Thomas Hale and Samuel Stafford Hale), 1940s or earlier
This draw knife once belonged to a Sough Australian family of coopers, or barrel makers surnamed Schahinger. The maker was Hale Bros. of Sheffield. The brothers, John Thomas Hale (1853-1919) and Samuel Stafford Hale (1855-1948) owned the Moorfield Works. The firm's Corporate Mark of a horse's head was granted in 1842 and came with the statement that "All tools marked with a "Horse's Head" are Guaranteed". The firm made tools for edgers and joiners, wall drills, cold chisels, files and rasps, printers' and publishers' tools, butchers' and bread knives, and table cutlery. This draw knife was used by a cooper in South Australia for making wooden barrels in the traditional manner. The makers had a family business of making knives, cutlery and tools for trades people. This draw knife is relevant to the trades represented in a maritime village of the late 19th century. Draw knife; cooper's steel draw knife with bulbous wooden handles that have scored rings as decoration. The straight blade is 13 inches long. Inscription and logo of a horse's head on centre of blade. Made by Hale Bros of Sheffield. "HALE BROS / SHEFFIELD / - - - - " Image [Horse's Head]flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime-museum, coopers, draw knife, barrel maker, hale bros., sheffield, moorfield works, john thomas hale, samuel stafford hale, knife makers -
 Otway Districts Historical Society
Otway Districts Historical SocietyBook, Hoppus's Practical Measurer
Manufactured by E. Hoppus the Hoppus's Practical Measurer, or measuring made easy by a new set of tables which show by looking the solid content of any piece of timber, stone, etc, either square, round or unequally sided, and the value at any price of cubic feet. The book also gives the superficial comtent of boards, glass, painting and plastering with explanations of the uses and applications of the tables. The contents are given in feet, inches, quarters and twelfth parts of an inch. It includes the measurment of timber by several dimensions together with tables showing the weight of iron by measure.Hoppus's Practical Measurer; or, Measuring made easy by a new set of tables, which show, at sight, the solid content of any piece of timber, stone, &c. W. Nicholson & Sons; London; nd. 238 p. Hard cover.e. hoppus; measurment; timber; stone; boards; glass; painting; plastering, iron;
