Showing 543 items matching "heat"
-
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Domestic object - Kitchen Equipment, 'Smoothwell' electric flat iron c1935, c1935
c1881 Henry W Seely, of New Jersey, USA, designed and patented an electric sad iron for pressing and smoothing material. He continued to modify and improve his designs, with his partner Richard Dyer, and other electrical appliance firms, e.g Hotpoint, began producing these flat irons that could provide continuous heat by connecting via an electrical flex to a light socket and hence without the need for hot fires, ash, or burning hot handles. Women with access to an electricity supply were delighted and their ironing chore became much less arduous No heat was felt at all from the iron as it is all concentrated on the bottom surface. By the early 20th century enthusiasm was building for the new electric smoothing irons: clean, powerful, adjustable, and labour-saving. This c1935 Premier System 'Smoothwell' flat iron was used by a resident of City of Moorabbin and is an example of the progress made from the sad irons used by the pioneers that are displayed beside it.A "Premier Smoothwell" electric flat iron with switched control lead and original box, c 1935 On plate of handle attached to Iron ' HARRODS Ltd. / LONDON On attached plate at rear of iron ' The "SMOOTHWELL" / "Premier System" /......... Plate on cord Plug " PREMIER/ FLAT IRON CONNECTOR/ THIS SIDE OUTWARDS/ (2 columns) 1) FOR 100-125 VOLTS/ USE THREE TERMINALS/ THUS ..... 2) FOR 200 - 240 VOLTS/ USE TWO RIGHT/ HAND TERMINALS/ ONLY/ THUS......seely henry w., sad irons, electric flat irons, dyer richard, edison thomas, hotpoint pty ltd., premier electric company birmingham england, pioneers, early settlers, moorabbin, bentleigh, cheltenham, laundry, sewing, craftwork, table ware, irons -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societycharcoal iron, early 20th century
Following the use of flat irons the base of the iron was made into a container to put glowing coals inside it and keep it hot a bit longer. This was called a charcoal iron. It had a hinged lid and air holes to allow the charcoal to keep smouldering. They are sometimes called ironing boxes, or charcoal box irons, and may come with their own stand.This item is an example of a domestic appliance in common usage before the advent of electricity.This is a charcoal iron which was heated by burning charcoal inside it. It is made of iron and has wooden handles, one on top for lifting it and one on the catch at the front that keeps the iron closed. Both of these handles were needed to load the iron with charcoal easily. As wood does not conduct heat well, these handles made the task of filling the iron much easier. The holes around the base of the iron are for letting the fumes out.Top- "M.G."iron-charcoal domestic -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet, Ballarat School of Mines and Industries, Prospectus, 1955, 1955
The Ballarat School of Mines is a predecessor institution of Federation University Australia. The Contents outline areas covered. The School Council, The Staff, Graduates of the School, Facts about the School, School Boards, General Regulations, Student Activities, Scholarships, Prizes, Courses of Instruction, Professional Diploma and Certificate Courses, Art Department, Trade Department, Juniot Technical School.R W Richards was the Principal and L C Garner was the Head Master of the Junior Technical School.Beige soft covered book of 67 pages. It includes information on the courses offered by the Ballarat School of Mines in 1955. Photographs include: 2 students on the steps to the Administration Building. The student on the top step is Alec Kinnane; Rear of the Administration Building, student activities; heat engines laboratory, Civil Engineering students, micro-examination of metals; Potter (Neville Bunning in background); machine shop; wool classing ballarat school of mines, prospectus, alec kinnane, wool classing, electrical engineering, surveying, courses, r w richards, principal, l c garner, head master, diploma courses, certificate courses -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPostcard, Bascands Ltd. Christchurch NZ, SECV 26
Colour postcard of SECV Ballarat No. 26, photographed in Wendouree Parade during possibly late 1975 by W.J.Kingsley for the BTPS postcard. Tram has St Aidans Drive destination and "TRAM RIDES" signs. Tram in SECV livery. Has "Nothing Beats Briquettes for heat" advertising board on side. On rear is a note regarding the tram, the BTPS and its operations, printers name and photographers name, with place for stamp and address. trams, tramways, wendouree parade, btps, postcards -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumSign, Hasco Foundry Ballarat, "Designed and Manufactured at the Tramways Board Workshops Preston", c2010
Replica Builders Plate, sign - cast brass with raised letters within two raised lines and four screw holes in each corner. Black painted background. "Designed and Manufactured at the Tramways Board Workshops Preston" Two copies held, both within plastic heat sealed envelopes with small label "Replica $20-" Produced by Tony Smith of the MTPA, c2010, cast by Hasco Foundry, Ballarat.trams, tramways, signs, tramcars, tramcar bodies, mmtb, new trams -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Kettle, Circa 1930
This kettle is a common household item and would have been used on the top of a wood stove. Copper was commonly used as it is an excellent conductor of heat. Elements of its construction would point to it being manufactured by hand. It could have originated from local plumber Alex Anderson who operated from Fairy St in the period 1920-1940. This is a common household item from the early 20th century when most household would have relied on wood stoves for cooking. As a handmade item it also has significance as an example of skills from earlier times.Circular copper kettle with lid with copper handle and handle with black bakelite handle which is eight ridges .The handle is rivetted to the body of the kettle.The base is rolled over the body of the kettle around the edge.The spout has a join along the top.warrnambool, copper kettle, alex anderson -
 Blacksmith's Cottage and Forge
Blacksmith's Cottage and ForgeTin, Stove Polish
One of the jobs of the housewife was to keep her stove-top looking clean and new, and a rich black colour. This was a source of pride amongst house-proud women, and also ensured a more efficient distribution of heat on their stove-tops for cooking. It was however one of the dirtiest jobs in the kitchen, requiring a lot of elbow-grease as well as a good polish paste. Local. The use of the magpie emblem denotes the emergence of a new nationalism, a pride in being Australian, as distinct from being "British", although Australians continued to see themselves as part of the greater British Empire and subjects of the King.Gold tin with push-in lid, with picture of magpie in black and white on branch. On front of tin: "Magpie" in white letters on a red background. "Stove Polish" in white letters on a blue background. 4 oz. Net. when packed. Made in Australia. On bottom of tin: "Grate & Stove Polishing Paste. Made in Australia." Side inscriptions give instructions for use. -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumDocument - Photocopy, Davis Urban Bus Service - timetables, 1971
Photocopies of the Davis Urban Bus Services to replace the tram services in Ballarat in 1971. Sebastopol - City - Lydiard St. North (routes 4 and 12) Sturt St West - City - Mt. Pleasant (routes 11 and 15) Wendouree West - City - Victoria St (routes 1 and 7) Timetables for Monday to Friday, Saturday and Sunday. Foolscap and quarto sheets photocopied with newspaper extracts in the background. Made on heat sensitive paper.trams, tramways, buses, timetables, ballarat, davis bus lines -
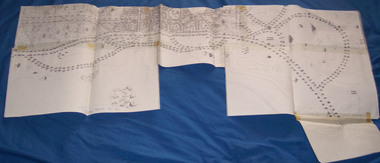 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumDocument - Photocopy, City of Ballaarat, Plan of Gardens, 1920s?
Photocopy - No Number, no date, other than BTM Number 228, No title – plan showing roads and trees in the Gardens area, early drawings, many roads on the east side of Lake Wendouree not built . Photocopy onto heat sensitive paper – 9 separate sheets joined with tape. An additional sheet added at the St. Aidans end showing roads – in pencil. Probably compiled for the BTPS by Bill Kingsley for planning purposes.Has “228” in biro on rear of sheet, and “Scale 100 foot to 1 inch” on front of sheet.trams, tramways, signals, forest city signals, equipment, electrical engineering -
 Musculoskeletal Health Australia (now held by the Glen Eira Historical Society)
Musculoskeletal Health Australia (now held by the Glen Eira Historical Society)Photograph - Object, 1987
This photo depicts the top centre-left panel of an Arthritis Foundation of Victoria multi-panel display board from 1987. The Foundation utilised freestanding display boards such as this to provide information about its programs and services at events.COL photo of one panel from a large freestanding display board. Using the words 'Self Help' as an acronym, the panel contains the following text: S STRESS MANAGEMENT. E EXERCISE. L LEARN ABOUT ARTHRITIS. F FIND THE FACILITIES. H HEAT HELPS PAIN. E EAT APPROPRIATELY. L LIVE! P PROTECT YOUR JOINTS. This is followed by some text in italics, "Can change your outlook".[On a white label, handwritten in blue ink] Self-help Display '87 Centre LEFT - LOWERarthritis foundation of victoria, afv, display board, information, resources, education, self help, pain management, pain relief, stress management, joint health, healthy food, healthy diet, exercise, recreation, rest, arthritis help book, 1987 -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietySoldering Irons x3
A soldering iron is a hand tool used in soldering. It supplies heat to melt solder so that it can flow into the joint between two workpieces. The iron was heated over a fire or in a charcoal brazier. Soldering irons were primarily used by tinsmiths and coppersmiths to work with thin sheet metal. These hand soldering irons have been replaced by electric ones.Used by coppersmiths and tinsmiths and workers in the Kiewa Valley.The soldering irons have a wooden handle, an iron rod and are made of copper at the pointy end (the bit).shaped like a pyramid.soldering iron, hand tool, coppersmith, tinsmith -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionScientific Instrument, Orsat Apparatus
The Orsat was returned to the Historical Collection by Len Taylor, former staff member of SMB. For a period of time it was with Gary Price who rebuilt the Orsat to working order. Gary used a similar apparatus at Sidchrome and Ballarat Heat Treatment Pty. The Orsat apparatus is used to measure volumes of Carbon Dioxide, Oxygen, and Carbon Monoxide within a fixed volume of a sample of gas.Timber box with lift up front revealing a number of valves, pressure measure and glass container of red liquid attached to hose. Gas analysis apparatusorsat, len taylor, gary price, carbon dioxide, oxygen, carbon monoxide, gas, measure, apparatus -
 Queenscliffe Maritime Museum
Queenscliffe Maritime MuseumEquipment - Sun valve
The light was powered by a kerosene lantern that had to be kept alight by the keepers until the introduction of bottled acetylene gas in 1925. The light operated for 111 years until 1985 when it was turned off for a trial period. It was never turned back on. A sun valve is a flow control activated by sunlight heat which automatically shuts off gas during daylight hours. Relic from the Hovell light run on acetylene from 1925 to 1985Sun valve from the Hovell Pile Lighthovell pile light, south channel, port phillip -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyContainer - Pottery Bottles, Unknown
One of the jobs of the housewife was to keep her stove-top looking clean and new, and a rich black colour. This was a source of pride amongst house-proud women, and also ensured a more efficient distribution of heat on their stove-tops for cooking. It was however one of the dirtiest jobs in the kitchen, requiring a lot of elbow-grease as well as a good polish paste or blacking ink.Two brown pottery blacking bottles, one with a light brown glaze and other is dark brown. Both have shaped wide necks with a lip at the edge for pouring. The contents were used to blacken a stove. blacking bottles, bottles, cooking equipment, cooking stoves, fuel cooking stoves, domestic ovens -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyDomestic object - Bread Tins, Unknown
This is an antique, bread baking tray. During the 19th century people used open flames for cooking or stoves. Stoves were gaining popularity in the 1800s, but they were not electric or gas like ours are now. Instead, they had either a wood fire or a coal fire inside. The stove allowed the heat to more uniformly cook and bake food than an open flame.This is an antique, bread baking tray. There are three tins joined by rivets to a heavy metal frame, so they cannot be separated. It shows considerable surface rust, but no holes and it can be used. It is very heavy, weighing close to 3 kgs. bread tins, baking tins, containers for baking bread -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncFunctional object - Bicycle Tool and Repair Kit, c1935
The first bicycles arrived in Australia in the 1860s. They gradually gained in popularity and by the 1890s they offered a cheap and relatively comfortable mode of transport. Far being just a means of leisure, long distance cycle travelling became a fact of life in rural areas for people such as sheep shearers and other agricultural labourers with migratory work. The bicycle and swag travelled much of Australia on dusty dirt tracks, long before the automobile was introduced. Today the bicycle continues to be an important item for general, cheap transport, sport and leisure. Tool kits such as those shown in the item, were and important piece of equipment for bicycle enthusiasts, particularly on a longer ride where assistance may not be close by if the rider experienced a punctured tyre. John Bull Rubber Co. Ltd. was a British tyre manufacturer based in Leicester. It was established in 1906 and was originally named Leicester Rubber Company. In 1915, a new factory was built in Evington Valley Road as indicated on the repair outfit tin in this kit. It was renamed John Bull Rubber in 1934 after its popular product of the same name. In 1958, the company was acquired by Dunlop Rubber. A leather bag containing tools and 2 tins containing rubber patches to repair bicycle tyres. The bag has 2 straps and metal buckles to attach it to the back of the bicycle seat.On tin 1: "The John Bull / Repair Outfit/ John Bull Rubber Co. Ltd./ Evington Valley Mills, Leicester" On tin 2: "ZENITH Repair Outfit / For Cycle and Rubber Repairs/ Self Vulcanizing" On tin 3: Around the DUNLOP logo "Six Self Lighting/ Patch Heat Units / For Cycle Tube/ Vulcaniser"bicycle history, bicycle repairs, john bull rubber, cycling leisure -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Notice, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), "Decorated Tram No. 1024 to be run from all depots - a/c Dulux Paints", 30/09/1971 12:00:00 AM
Photocopy on heat sensitive paper of Two page foolscap duplicated notice, titled "Decorated Tram No. 1024 to be run from all depots - a/c Dulux Paints", issued by The Traffic Manager to Depot Masters and other Officers, dated 30/9/1971 Details arrangements for the tram, transport between depots, maintenance, days in and run numbers. See also Reg Item 1525 for a TAA decorated tram and 1916 for other examples.trams, tramways, decorated trams, advertising trams, tram 1024 -
 Ithacan Historical Society
Ithacan Historical SocietyPhotograph, Stone house on Ithaca, c 1970s
The architecture of Ithaca has been influenced by various cultures in particular by the Venetian and British periods of rule. The house pictured is typical of many of the dwellings found on Ithaca built of stone which is sourced locally. Stone buildings are ideal for the climate of the island, retaining the heat in winter and cooler in summer. Sadly the catastrophic earthquakes of 1953 resulted in the widespread destruction on the many of the island's old buildings. Being one of the smaller and less accessible islands of Greece Ithaca fortunately has been spared inappropriate development and thus able to retain its authenticity and beautiful character. A coloured photograph of a double storey stone house with a tiled roof. A flight of stairs leads from the road to the elevated front door. At the bottom of the stairway there is a single storey stone building. Three trees are growing at the street level across the front of the house. architecture, houses -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Manufactured GLass, test tubes, mixers, 20thC
A test tube, also known as a culture tube or sample tube, is a common piece of laboratory glassware consisting of a finger-like length of glass or clear plastic tubing, open at the top, usually with a rounded U-shaped bottom. Test tubes are widely used by pharmacists to hold, mix, or heat small quantities of solid or liquid chemicals, especially for qualitative experiments and assays. Their round bottom and straight sides minimize mass loss when pouring, make them easier to clean, and allow convenient monitoring of the contents. The long, narrow neck slows down the spreading of vapours and gases to the environment. Test tubes are usually held in special-purpose racks, Test tubes for physics and chemistry are usually made of glass for better resistance to heat and corrosive chemicals and longer life. Tubes made from expansion-resistant glasses, such as borosilicate glass, can be placed directly over a Bunsen burner flame.8 clear glass test tubes of varied capacity with 3 glass mixers sitting in a wooden stand. A 1 metre length of clear plastic tubing is with this setglass manufacturers, test tubes, culture tubes, sample tubes, borosilicate glass, otto schlott, felton grimwade company, melbourne glass bottle works, laboratory glass, pharmacy, moorabbin, bentleigh, cheltenham, spotswood melbourne -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionEquipment - Model, 'Model Steam Engine' by Frederick Mitchell, 1886, c1892
Frederick Mitchell was born c1874 at Staffordshire Flat, Redcastle, near Heathcote. His father was an engineer from Cornwall, and had a quartz crushing battery at Staffordshire Flat from 1870 to at least the 1890s. Around 1886 Frederick Mitchell was an 18 year old "Engineer and Instrument Maker". He was awarded an 'Honorary Mention' at the Australian Juvenile Exhibition 1890-1. It was donated to the Ballarat School of Mines Museum in 1892. In the early 1960s the model was transferred to the Heat Engines Laboratory. All Heat Engines laboratory was moved from the Ballarat School of Mines to the Mt Helen Campus on October 1869. The model was accommodated in the thermodynamics laboratory. It was shown working during open days. The Ballarat School of Mines Calendar for 1893, page 66 refers to this item. There is correspondence between Frederick Mitchell's grandson, F.W. Mitchell; E.J. Barker, Director of the Ballarat College of Advanced Education; and Graham Beanland, Ballarat School of Mines.A working model of a vertical oscillating twin cylinder steam engine with fly wheel, mounted on a wood base board and covered in glass. Usually stored under a wood-framed glass cover. steam, model, engine, frederick mitchell, flywheel, ballarat school of mines museum -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Kitchen Equipment, curved sad iron, c1880
Sad-irons or "solid" irons were made by blacksmiths and used to smooth out material by pressing the hot iron over it. A piece of sheet -iron was placed over the kitchen fire and the irons placed on it could be heated whilst remaining clean of ash.. The women used 2 irons - one heating while the other was used. Thick cloth or gloves protected their hands from the hot irons. The handle was removed from the cool iron and re- attached to remove the hot iron from the fire. The cool iron was replaced on the fire or stove to heat again. These irons were cleaned with steel wool to prevent them marking the material. If the iron was too hot the material would scorch. Most homes set aside one day for ironing and some large households had an ironing room with a special stove designed to heat irons. However, most women had to work with a heavy, hot iron close to the fireplace even in summer.The Curtis family were early settlers in Moorabbin Shire c1880 and used sad ironsA small, curved, flat iron, with attached handle, used for cuffs, collars and frillsSILVESTER'S/ PATENT/ SALTERS / No 3 with the pretzel & a arrow going through the centresad iron, kitchen equipment, pioneers, early settlers, market gardeners, sewing, craftwork, clothing, moorabbin, brighton, bentleigh, fireplaces, stoves -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Domestic object - Kitchen equipment, sad iron, c1880
Sad-irons or "solid" irons were made by blacksmiths and used to smooth out material by pressing the hot iron over it. A piece of sheet -iron was placed over the kitchen fire and the irons placed on it could be heated whilst remaining clean of ash.. The women used 2 irons - one heating while the other was used. Thick cloth or gloves protected their hands from the hot irons. The handle was removed from the cool iron and re- attached to remove the hot iron from the fire. The cool iron was replaced on the fire or stove to heat again. These irons were cleaned with steel wool to prevent them marking the material. If the iron was too hot the material would scorch. Most homes set aside one day for ironing and some large households had an ironing room with a special stove designed to heat irons. However, most women had to work with a heavy, hot iron close to the fireplace even in summer.These sad irons remind us of the difficult circumstances experienced in their daily routines by the pioneers and early settlers of Moorabbin Shire. The family of Miss M Curtis were early settlers in Moorabbin Shire. Sad-iron, domestic, flat, cast iron, Silvester's Patent, No 6, Salter, England, c. 1890-1900s A sad iron made from cast iron was heated over a fire or on a stove and used for pressing clothing and table wareSILVESTER'S/ PATENT/ SALTERS / No 6 with the pretzel & a arrow going through the centresad iron, kitchen equipment, pioneers, early settlers, market gardeners, sewing, craftwork, clothing, moorabbin, brighton, bentleigh, fireplaces, stoves -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Domestic object - Kitchen Equipment, flat iron with trivet stand, c1880
Sad-irons or "solid" irons were made by blacksmiths and used to smooth out material by pressing the hot iron over it. A piece of sheet -iron was placed over the kitchen fire and the irons placed on it could be heated whilst remaining clean of ash.. The women used 2 irons - one heating while the other was used. Thick cloth or gloves protected their hands from the hot irons. The handle was removed from the cool iron and re- attached to remove the hot iron from the fire. The cool iron was replaced on the fire or stove to heat again. These irons were cleaned with steel wool to prevent them marking the material. If the iron was too hot the material would scorch. Most homes set aside one day for ironing and some large households had an ironing room with a special stove designed to heat irons. However, most women had to work with a heavy, hot iron close to the fireplace even in summer. These sad irons remind us of the difficult circumstances experienced in their daily routines by the pioneers and early settlers of Moorabbin Shire The family of Miss M Curtis were early settlers in Moorabbin Shire. A) A heavy cast iron, flat iron with B) horseshoe shaped trivet stand c1880 The trivet can be attached to a table by an adjustable clamp.A) 5 on tip of ironsad iron, kitchen equipment, pioneers, early settlers, market gardeners, sewing, craftwork, clothing, moorabbin, brighton, bentleigh, fireplaces, stoves -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Domestic object - Kitchen Equipment, sad iron with lifter, c1900
Sad-irons or "solid" irons were made by blacksmiths and used to smooth out material by pressing the hot iron over it. A piece of sheet -iron was placed over the kitchen fire and the irons placed on it could be heated whilst remaining clean of ash.. The women used 2 irons - one heating while the other was used. Thick cloth or gloves protected their hands from the hot irons. The handle was removed from the cool iron and using the lifter the cool iron was replaced on the fire or stove to heat again. These irons were cleaned with steel wool to prevent them marking the material. If the iron was too hot the material would scorch. Most homes set aside one day for ironing and some large households had an ironing room with a special stove designed to heat irons. However, most women had to work with a heavy, hot iron close to the fireplace even in summer.These sad irons remind us of the difficult circumstances experienced in their daily routines by the pioneers and early settlers of Moorabbin Shire. The Curtis family were early settlers in Moorabbin ShireA) This heavy sad iron, made from cast iron, was heated over a fire or on a stove and used for pressing clothing and haberdashery. B) The separate tapered handle was used to lift the hot iron from the fire and when a "Potts" Handle was attached the ironing commenced. sad iron, kitchen equipment, fireplaces, stoves, pioneers, early settlers, market gardeners, sewing, craftwork, clothing, moorabbin, brighton, bentleigh -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumDocument - Correspondence, B. Prentice, 1973
1230.1 - copy of letter sent to Neville Gower from Bob Prentice enclosing a number of documents regarding submissions and other associated documents pertaining to the operation of Bendigo's trams by the Bendigo trust. Sent on the 1st March 1973. Typed onto light blue paper. 1230.2 - 14 page photocopy (Foolscap size on heat sensitive paper) of the submission prepared by the Bendigo trust - detailing the history of trams in Bendigo, types of trams in Bendigo, selection of the route, equipment and plant required, planned development, list of trams in Bendigo, their condition and financial statements of the Bendigo Trust 1972. 1230.3 - 14 pages photocopy (Foolscap size on heat sensitive paper) Appendix II - submission details projected passengers, operational details and proposals, estimated revenue, Philosophy of operation, trams required, operating budgets, how the service could be operated - internal combustion engines, batteries, stationary engine and generator or converter station and costs associated with the options. If item to be researched, copy on more stable photocopy paper to be provided.tram, trams, bendigo, bendigo trust, tourist trams, power supply -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Report, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), "Comparison between service requirements using two bogie trams and a mixed fleet of three bogie articulated trams and two bogie trams.", Sep. 1965
.1 - Report Foolscap 6 typed pages, multiple diagrams and tables (some on heat sensitive paper) with card covers, with red binding strips, titled "Comparison between service requirements using two bogie trams and a mixed fleet of three bogie articulated trams and two bogie trams for Kew Depot routes", dated June 1965. Includes diagrams of passengers each hour for multiple stops. Concludes that crew and tram savings would be in excess of 20%. Report - Foolscap 6 typed pages, multiple diagrams and tables (some on heat sensitive paper) with card covers, with red binding strips, titled "East Preston depot routes - comparison between service requirements using two bogie trams and a mixed fleet of three bogie articulated trams and two bogie trams" Dated September 1965. Includes diagrams of passengers each hour for multiple stops. Concludes that for the East Preston route, a 20% saving in crews. Brunswick route would not applicable.In top left hand corner "Lees" in penciltrams, tramways, mmtb, tramways, speed of services, articulated trams, surveys, east preston depot, kew depot -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societypreserving jar, 1915 - 1975
This preserving jar was used in the first half of the 20th century to preserve cooked food - pickles. Preserving home produce in bottles is a method that applies heat to food in a closed glass home canning jar to stop the natural spoilage that would otherwise take place. It removes air from the jar to create a seal. he bottling process forms an air tight seal between the bottle and the lid. Residents of Orbost have long been self sufficient growing their own fruit and vegetables with earlier market gardeners They preserved their produce for use all year. Fowlers Vacola preserving kits were common in most kitchens.A brown glass Fowler's Vacola preserving jar filled with pickles. It is a No. 27 bottle with a size 3 metal clip. It has an 850ml capacity. The lid has metal tension clips which are secured during the canning process and are removed once a vacuum seal has formed. The lid is tin-plated with a lacquer coating, double-coated on the underside.On lid Fowlers Vacola Size 3 Top of jar- embossed with the words Fowlers Vacola food-preservation fowlers-vacola container-glass -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionBedford M Series fire tanker
Ash Wednesday Veteran This Bedford M Series tanker spent its working days at the Forests Commission depot at Gembrook, and among its many forays, fought the deadly Ash Wednesday bushfires at nearby Upper Beaconsfield and Cockatoo on 16 February 1983. Earlier in 1975, the M Series tankers underwent a design change at the Altona North workshops, replacing the cylindrical water tank with a “V” bottom 4090 litre water tank that sat low between the chassis rails to reduce its centre of gravity. Aluminium heat shields were also added to protect the pump operators on the back. While generally considered "bulletproof" the petrol fuel lines on this particular model were very prone to vaporise in the heat causing the motor to stall, often at the most dangerous moment.... in this case frightening the hell out of its driver, affable knockabout bloke, and firefighting legend Lex Wade. Some jokingly said this design quirk was an inbuilt safety feature to stop crews getting too close to the fire in the first place. The Gembrook tanker was later sent into the workshop and all its brake and fuel lines fitted with heat resistant lagging. Fortunately, this remarkable bushfire survivor was rescued from the scrap heap by Lex and fire equipment wizard Barry Marsden upon its retirement from a loyal and lengthy service. After a lick of fresh paint and most of its battle scars "buffed out", this time-honoured veteran now takes pride of place at the Altona North workshop.Bedford M series fire tankerMZF 347fire pump, fire tanker, forests commission victoria (fcv) -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumBook, Tasmania Transport Museum, "Proceedings of the 13th Conference of the Australasian Tramway Museums, Hobart - Tasmania August September 1996", 2000
122 page A4 size book with white heat bound clear plastic front cover and glossy white heavy paper rear cover. Details the Proceedings of the 13th Conference of the Australasian Tramway Museums (COTMA), Hobart Tasmania, 31 August to 7th September 1996. Produced by the Tasmanian Transport Museum Inc. Includes a list of contents -page 3 and list of delegates - page 4. For full pdf file - see COTMA website, conference pages.BTM received Stamp on inside front cover, dated 14 April 2000 and item number 9149.trams, tramways, cotma, conferences, tasmania transport museum -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Victorian Canoe Club, Steaming gear, 1920-30
Canoeing on the River Yarra at Melbourne was an important and widespread recreational pursuit for Melbournians, especially in the first half of the twentieth century. The Victorian Canoe Club was formed in 1912 at a meeting in Melbourne and its first committee elected in the same year. Records indicate that the Club continued into at least the 1950s .The album has historic and social significance as a record of recreational activities (as well as canoe making) in the early years of the twentieth century. It has local significance as the site of the headquarters of the Club was in Studley park. A number of photographs in the album provide vistas of Kew on the Yarra that are otherwise unavailable.One of 24 labelled photos in part album, originating from the Victorian Canoe Club, which had its headquarters in Studley Park, Kew. The album includes a photographic record of canoe construction and also locations in Studley Park and Kew where the canoes were used. The subject of this photograph is identified as 'Steaming gear' which was the equipment used in a backyard to heat and soften the wood used to make a canoe so that it would be pliable and could respond to a mould."Steaming gear"victorian canoe club, canoe making, river yarra, burke road, mornington, studley park, kew, steaming gear, canoe construction
