Showing 3801 items matching " vehicle"
-
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncCertificate - Certificate of Marriage, Henry de Castres Kellett & Joan Harrison, 1880, 09/11/1880
Sir Henry de Castres Kellett (1851-1924) the son of a hereditary baronet, was born at Mt Gambier, South Australia in 1851. His English title had been created in Ireland in 1801, but the family was originally Norman with the later branches living in England and Ireland. Sir Henry Kellett assumed the title in 1906. Henry Kellett was a prominent Kew retailer, continuing his father’s newspaper and stationery business in Bulleen Road (now High Street). At various stages, he also acted as an insurance, postal and real estate agent. He lived in Walpole Street and later at Lota Begg (now demolished) in Westbrook Street, East Kew. In 1884, Henry Kellett was elected to the Kew Borough Council and served for 40 years; a remarkable example of public service. He was elected Mayor for a single term in 1888-9. Sir Henry de Castres Kellett died in St George’s Hospital in 1924 following a tragic car accident in Cotham Road, Kew while on Council business. The vehicle, in which he was travelling with fellow councillors and the Town Clerk, collided with a tram. Sir Henry Kellett is commemorated in the naming of Kellett Reserve and Kellett Grove.Original Marriage Certificate of Henry de Castres Kellet and Joan Harrosn, in Richmond on 9 November 1880mayors of kew (vic), sir henry de castres kellett -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncLetter - Letter of Condolence, Lady Kellett, Lota Begg, Westbrook Street, Kew, 1924
Sir Henry de Castres Kellett (1851-1924) the son of a hereditary baronet, was born at Mt Gambier, South Australia in 1851. His English title had been created in Ireland in 1801, but the family was originally Norman with the later branches living in England and Ireland. Sir Henry Kellett assumed the title in 1906. Henry Kellett was a prominent Kew retailer, continuing his father’s newspaper and stationery business in Bulleen Road (now High Street). At various stages, he also acted as an insurance, postal and real estate agent. He lived in Walpole Street and later at Lota Begg (now demolished) in Westbrook Street, East Kew. In 1884, Henry Kellett was elected to the Kew Borough Council and served for 40 years; a remarkable example of public service. He was elected Mayor for a single term in 1888-9. Sir Henry de Castres Kellett died in St George’s Hospital in 1924 following a tragic car accident in Cotham Road, Kew while on Council business. The vehicle, in which he was travelling with fellow councillors and the Town Clerk, collided with a tram. Sir Henry Kellett is commemorated in the naming of Kellett Reserve and Kellett Grove.Original official document from a noted event in Kew's historyOne page undated, handwritten letter of condolence to Lady Kellett on her husband's accidental death in 1924 while serving as a Kew Councillor. The latter is signed by his fellow councillors, the Mayor and the Town Clerkmayors of kew (vic), sir henry de castres kellett -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncDrawing - Visual Vignettes, Sir Henry de Castres Kellett & Arthur Wills / by Arthur Wills, 1920
Sir Henry de Castres Kellett (1851-1924) the son of a hereditary baronet, was born at Mt Gambier, South Australia in 1851. His English title had been created in Ireland in 1801, but the family was originally Norman with the later branches living in England and Ireland. Sir Henry Kellett assumed the title in 1906. Henry Kellett was a prominent Kew retailer, continuing his father’s newspaper and stationery business in Bulleen Road (now High Street). At various stages, he also acted as an insurance, postal and real estate agent. He lived in Walpole Street and later at Lota Begg (now demolished) in Westbrook Street, East Kew. In 1884, Henry Kellett was elected to the Kew Borough Council and served for 40 years; a remarkable example of public service. He was elected Mayor for a single term in 1888-9. Sir Henry de Castres Kellett died in St George’s Hospital in 1924 following a tragic car accident in Cotham Road, Kew while on Council business. The vehicle, in which he was travelling with fellow councillors and the Town Clerk, collided with a tram. Sir Henry Kellett is commemorated in the naming of Kellett Reserve and Kellett Grove.Original artwork by Arthur Wills, descendent of a noted pioneer family, and former mayor of Kew.Two sided illustrated humorous vignettes featuring two noted Kew citizens: Henry de Castres Kellet and Arthur Wills. The latter is the illustrator. The item was illustrated in 1920.mayors of kew (vic), sir henry de castres kellett, arthur wills, willsmere, wills family -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncNewspaper - Newspaper Article, Late Sir Henry Kellett, 1924, 1924
Sir Henry de Castres Kellett (1851-1924) the son of a hereditary baronet, was born at Mt Gambier, South Australia in 1851. His English title had been created in Ireland in 1801, but the family was originally Norman with the later branches living in England and Ireland. Sir Henry Kellett assumed the title in 1906. Henry Kellett was a prominent Kew retailer, continuing his father’s newspaper and stationery business in Bulleen Road (now High Street). At various stages, he also acted as an insurance, postal and real estate agent. He lived in Walpole Street and later at Lota Begg (now demolished) in Westbrook Street, East Kew. In 1884, Henry Kellett was elected to the Kew Borough Council and served for 40 years; a remarkable example of public service. He was elected Mayor for a single term in 1888-9. Sir Henry de Castres Kellett died in St George’s Hospital in 1924 following a tragic car accident in Cotham Road, Kew while on Council business. The vehicle, in which he was travelling with fellow councillors and the Town Clerk, collided with a tram. Sir Henry Kellett is commemorated in the naming of Kellett Reserve and Kellett Grove.Newspaper report from 1924, providing an obituary of Sir Henry de Castres Kellettmayors of kew (vic), sir henry de castres kellett -
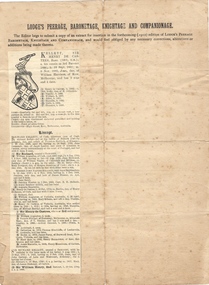 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncDocument, Lodge's Peerage, Baronetage, Knightage and Companionage - KELLETT, Sir Henry de Castres Bart
Sir Henry de Castres Kellett (1851-1924) the son of a hereditary baronet, was born at Mt Gambier, South Australia in 1851. His English title had been created in Ireland in 1801, but the family was originally Norman with the later branches living in England and Ireland. Sir Henry Kellett assumed the title in 1906. Henry Kellett was a prominent Kew retailer, continuing his father’s newspaper and stationery business in Bulleen Road (now High Street). At various stages, he also acted as an insurance, postal and real estate agent. He lived in Walpole Street and later at Lota Begg (now demolished) in Westbrook Street, East Kew. In 1884, Henry Kellett was elected to the Kew Borough Council and served for 40 years; a remarkable example of public service. He was elected Mayor for a single term in 1888-9. Sir Henry de Castres Kellett died in St George’s Hospital in 1924 following a tragic car accident in Cotham Road, Kew while on Council business. The vehicle, in which he was travelling with fellow councillors and the Town Clerk, collided with a tram. Sir Henry Kellett is commemorated in the naming of Kellett Reserve and Kellett Grove.Printed extract from Lodge's Peerage, Baronetage, Knightage and Companionage listing KELLETT, Sir Henry de Castres Bart.mayors of kew (vic), sir henry de castres kellett -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Carte de Visite, Captain RJ Napier Kellett, Undated
Sir Henry de Castres Kellett (1851-1924) the son of a hereditary baronet, was born at Mt Gambier, South Australia in 1851. His English title had been created in Ireland in 1801, but the family was originally Norman with the later branches living in England and Ireland. Sir Henry Kellett assumed the title in 1906. Henry Kellett was a prominent Kew retailer, continuing his father’s newspaper and stationery business in Bulleen Road (now High Street). At various stages, he also acted as an insurance, postal and real estate agent. He lived in Walpole Street and later at Lota Begg (now demolished) in Westbrook Street, East Kew. In 1884, Henry Kellett was elected to the Kew Borough Council and served for 40 years; a remarkable example of public service. He was elected Mayor for a single term in 1888-9. Sir Henry de Castres Kellett died in St George’s Hospital in 1924 following a tragic car accident in Cotham Road, Kew while on Council business. The vehicle, in which he was travelling with fellow councillors and the Town Clerk, collided with a tram. Sir Henry Kellett is commemorated in the naming of Kellett Reserve and Kellett Grove.Rare portrait of a Kellett ancestorCarte de Visite of Captain RJ Napier Kellett, an ancestor of Sir Henry de Castres Kellett.CAPN RK NAPIER KELLETT / RIFLE BRIGADE / WATERLOO MEDAL / CAPN ROYAL 42ND HIGHLANDERS THOS NORTH PHOTOGRAPHER / 71 GRAFTON STREET DUBLIN sir henry de castres kellett, cape rj napier kellett, battle of waterloo -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncNewspaper - Newspaper Article, Sir Henry de Castres Kellett - Burial Report, 1924
Sir Henry de Castres Kellett (1851-1924) the son of a hereditary baronet, was born at Mt Gambier, South Australia in 1851. His English title had been created in Ireland in 1801, but the family was originally Norman with the later branches living in England and Ireland. Sir Henry Kellett assumed the title in 1906. Henry Kellett was a prominent Kew retailer, continuing his father’s newspaper and stationery business in Bulleen Road (now High Street). At various stages, he also acted as an insurance, postal and real estate agent. He lived in Walpole Street and later at Lota Begg (now demolished) in Westbrook Street, East Kew. In 1884, Henry Kellett was elected to the Kew Borough Council and served for 40 years; a remarkable example of public service. He was elected Mayor for a single term in 1888-9. Sir Henry de Castres Kellett died in St George’s Hospital in 1924 following a tragic car accident in Cotham Road, Kew while on Council business. The vehicle, in which he was travelling with fellow councillors and the Town Clerk, collided with a tram. Sir Henry Kellett is commemorated in the naming of Kellett Reserve and Kellett Grove.Newspaper report from 1924 of the funeral of Sir Henry de Castres Kellett at Boroondara General Cemeterysir henry de castres kellett -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncNewspaper - Newspaper Article, The Kellett Baronetcy, 1906, 1906
Sir Henry de Castres Kellett (1851-1924) the son of a hereditary baronet, was born at Mt Gambier, South Australia in 1851. His English title had been created in Ireland in 1801, but the family was originally Norman with the later branches living in England and Ireland. Sir Henry Kellett assumed the title in 1906. Henry Kellett was a prominent Kew retailer, continuing his father’s newspaper and stationery business in Bulleen Road (now High Street). At various stages, he also acted as an insurance, postal and real estate agent. He lived in Walpole Street and later at Lota Begg (now demolished) in Westbrook Street, East Kew. In 1884, Henry Kellett was elected to the Kew Borough Council and served for 40 years; a remarkable example of public service. He was elected Mayor for a single term in 1888-9. Sir Henry de Castres Kellett died in St George’s Hospital in 1924 following a tragic car accident in Cotham Road, Kew while on Council business. The vehicle, in which he was travelling with fellow councillors and the Town Clerk, collided with a tram. Sir Henry Kellett is commemorated in the naming of Kellett Reserve and Kellett Grove.Letter to the Editor by Sir Henry de Castres Kellett regarding his Baronetcysir henry de castres kellett, kellett baronetcy -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncNewspaper - Newspaper Article, Cr Henry Kellett, Mayor of Kew, 1888
Sir Henry de Castres Kellett (1851-1924) the son of a hereditary baronet, was born at Mt Gambier, South Australia in 1851. His English title had been created in Ireland in 1801, but the family was originally Norman with the later branches living in England and Ireland. Sir Henry Kellett assumed the title in 1906. Henry Kellett was a prominent Kew retailer, continuing his father’s newspaper and stationery business in Bulleen Road (now High Street). At various stages, he also acted as an insurance, postal and real estate agent. He lived in Walpole Street and later at Lota Begg (now demolished) in Westbrook Street, East Kew. In 1884, Henry Kellett was elected to the Kew Borough Council and served for 40 years; a remarkable example of public service. He was elected Mayor for a single term in 1888-9. Sir Henry de Castres Kellett died in St George’s Hospital in 1924 following a tragic car accident in Cotham Road, Kew while on Council business. The vehicle, in which he was travelling with fellow councillors and the Town Clerk, collided with a tram. Sir Henry Kellett is commemorated in the naming of Kellett Reserve and Kellett Grove.Illustrated newspaper article from 1888, describing the elevation to the position of mayor of Kew by Cr Henry KellettHERALD 29/8/88sir henry de castres kellett, mayors of kew -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncNewspaper - Newspaper Article, Missed Death by Half a Second - Councillors in Car Smash, 1924, 1924
Sir Henry de Castres Kellett (1851-1924) the son of a hereditary baronet, was born at Mt Gambier, South Australia in 1851. His English title had been created in Ireland in 1801, but the family was originally Norman with the later branches living in England and Ireland. Sir Henry Kellett assumed the title in 1906. Henry Kellett was a prominent Kew retailer, continuing his father’s newspaper and stationery business in Bulleen Road (now High Street). At various stages, he also acted as an insurance, postal and real estate agent. He lived in Walpole Street and later at Lota Begg (now demolished) in Westbrook Street, East Kew. In 1884, Henry Kellett was elected to the Kew Borough Council and served for 40 years; a remarkable example of public service. He was elected Mayor for a single term in 1888-9. Sir Henry de Castres Kellett died in St George’s Hospital in 1924 following a tragic car accident in Cotham Road, Kew while on Council business. The vehicle, in which he was travelling with fellow councillors and the Town Clerk, collided with a tram. Sir Henry Kellett is commemorated in the naming of Kellett Reserve and Kellett Grove.Illustrated newspaper article from 1924, describing the death of Cr Henry Kellettsir henry de castres kellett -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Mylon Centre, Wodonga
In 1906 Patrick Mylon started a passenger transport service in the Albury-Wodonga border area with horses and cabs. His son Jack went into business in the late 1920s, and his grandson Bernie joined the firm early in 1970. When Patrick started with the horses and cabs, each cab carried eight passengers and he always had two horses per cab. As the business expanded, Mylons used a range of buses and coaches including Reo, Chev and Bedford vehicles. Mylon Travel Centre opened at 152 High Street, Wodonga on 21 November 1992. It allowed Mylons to extend their service for holidaymakers. Mylon’s staff can help will all holiday needs, including answering questions about destinations as well as booking tours, accommodation, concert seats and express coach bookings. The new Centre had a computerised resto ervation system with direct link-up for world-wide reservations, During more than 100 years of service to the Wodonga region and beyond, Mylon Motorways received many awards for Excellence and tourism. On July 2, 2008 the company, including its 31 buses and 45 staff members were transferred to the Dyson Group.This building was part of a major local company which serviced Wodonga for over 100 years.A colour photo depicting the front of a building and roadway.Above building: MYLON TRAVEL / MYLON CENTREmylon motorways, mylon travel centre, wodonga businesses -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyPhotograph, Back to Caulfield 1995, 1995
For many years Legacy had a "Back to Caulfield Race Day" for Legatees, widows and their families. 1995 was the 50th anniversary of the end of World War 2 and the race day was part of the "Australia Remembers" commemorations. Also a Legacy 'Lone Pine' was planted. The article in the Answer says: "Over 800 members of the Legacy family (past and present) reunite at the "Australia Remembers" Back to Caulfield Commemorative Race Day held on August 12th. It was a special day which incorporated a wide range of activities, including a display of military vehicles, a flyover, a parachute jump by the Red Berets, military bands, and displays of memorabilia when the racecourse was used as an army camp. An official ceremony also included the presentation of a Legacy 'Lone Pine' (a descendant of the Gallipoli 'Lone Pine') by the President of the Melbourne Legacy, Legatee David Millie, which was very warmly received by the Chairman of the V.A.T.C., Mr Peter Lawrence. These photos show President David Millie and Legacy widow Rosie Ellis (Bell) and a close up of her Junior Legacy badge, perhaps she had originally been an Junior Legatee. He is shown pointing her badge out to other people gathered around. See also photos at 01003 and 01091, 01092 and 01093.This is a good image of a Junior Legacy badge. Legacy retains a tie with Caulfield racecourse as it was once an army camp and staging post of young men going overseas to war and now it is the site of a lone pine. The annual gathering at Caulfield racecourse was an event that gets the Legacy family together.Colour photo x 4 of a Junior Legacy badge and an event at Caulfield racecourse, and an article in The Answer.Printed on the back film number 788, various frame numbers.answer, events -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - Demonstration of TI4100 GPS Receiver, Royal Australian Survey Corps, c1988
This is a set of four photographs of WO2 Graham Ragless from the Royal Australian Survey Corps demonstrating the operation of Global Positioning System equipment in c1988. The photos were probably taken at the School of Military Survey (SMS), Bonegilla, VIC. Texas Instruments TI4100 portable Global Positioning System (GPS) geodetic receivers were introduced from 1986–1988. The GPS receivers and Ferranti FILS3 helicopter and vehicle mounted Inertial Positioning System (IPS) replaced the TRANSIT satellite receivers. The equipment was deployed to establish the baseline for a GPS controlled air camera and photogrammetric system to significantly reduce the requirement for ground survey to accurately control air photography for topographic mapping. Personnel from the four field survey squadrons at this time were trained at the SMS to operate the TI4100 receivers. Field survey operations using GPS and IPS equipment followed in the late 1980s. This technology is described in more detail in the RA Svy booklet titled An Introduction to Topographic Mapping. See record ID - 6010. WO2 Graham Ragless progressed to the rank of WO1 and was appointed as RSM of the Army Survey Regiment from 1990 to 1992. Refer to item 6186.2P for more photographs of WO2 Graham Ragless demonstrating the TI4100.This is a set of four photographs of a technician from the Royal Australian Survey Corps demonstrating the operation of Global Positioning System equipment in c1988. Colour photos are on 35mm slide film and were scanned at 96 dpi. .1) to .4) - Photo, colour, c1988, WO2 Graham Ragless demonstrating the operation of a TI4100 GPS receiverThere are no annotations.royal australian survey corps, rasvy, army survey regiment, army svy regt, fortuna, asr, surveying -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - Demonstration of TI4100 GPS Receiver, Royal Australian Survey Corps, c1988
This is a set of two photographs of WO2 Graham Ragless from the Royal Australian Survey Corps demonstrating the operation of Global Positioning System equipment in c1988. The photos were probably taken at the School of Military Survey (SMS), Bonegilla, VIC. Texas Instruments TI4100 portable Global Positioning System (GPS) geodetic receivers were introduced from 1986–1988. The GPS receivers and Ferranti FILS3 helicopter and vehicle mounted Inertial Positioning System (IPS) replaced the TRANSIT satellite receivers. The equipment was deployed to establish the baseline for a GPS controlled air camera and photogrammetric system to significantly reduce the requirement for ground survey to accurately control air photography for topographic mapping. Personnel from the four field survey squadrons at this time were trained at the SMS to operate the TI4100 receivers. Field survey operations using GPS and IPS equipment followed in the late 1980s. This technology is described in more detail in the RA Svy booklet titled An Introduction to Topographic Mapping. See record ID - 6010. WO2 Graham Ragless progressed to the rank of WO1 and was appointed as RSM of the Army Survey Regiment from 1990 to 1992. Refer to item 6226.4P for more photographs of WO2 Graham Ragless demonstrating the TI4100.This is a set of two photographs of a technician from the Royal Australian Survey Corps demonstrating the operation of Global Positioning System equipment in c1988. Colour photos are on 35mm slide film and were scanned at 96 dpi. .1) and .2) - Photo, colour, c1988, WO2 Graham Ragless demonstrating the operation of a TI4100 GPS receiverThere are no annotations.royal australian survey corps, rasvy, army survey regiment, army svy regt, fortuna, asr, surveying -
 Falls Creek Historical Society
Falls Creek Historical SocietyPhotograph - Veruschka at Koki, Falls Creek, 1969
These items are from the private collection of George Shirling of Red Onion, Falls Creek. Veruschka von Lehndorff, known simply as Veruschka, was a German aristocrat and fashion model. In 1969 The Australian Ski Year Book included the following report on her visit to Falls Creek. "George Shirling and Michael Blackwell pulled off quite a coup for Ko-Ki when they played host to the world's top model, Veruschka, Countess von Lehndorff, last July. Veruschka, all blonde six feet of her, and her photographer-manager, Franco Rubartelli, chose Falls Creek as the location for a series of photographs featuring new-season's ski wear. The model, whose reputed fee is $800 to $1,000 a day for advertising shots was on assignment for Vogue International, and the article was to appear during the early part of the Northern Winter. Veruschka and her manager spent 10 days at Falls Creek, during which they photographed $8,000 worth of the best high-fashion ski wear and experimental ski equipment, especially air freighted from the USA". In this photo she is riding on the snowmobile from Koki Alpine Lodge. The Koki smiling face logo can be seen on the front of the vehicle.This item is significant because Veruschka's visit to Falls Creek brought it international attention.A colour photo of Veruschka riding the Koki Snowmobile at Falls Creek.koki alpine lodge, george shirling, veruschka -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Black & White Photograph/s, late 1920's
Yields information about a vehicle the Electric Supply Co of Victoria used to provide additional services in Ballarat in the face of bus competition. See page 59 of Golden City and its Tramways for further information.Black and white photograph contained within Reg. Item 2488, page 55, of ESCo or Ballarat Tramways motor bus, with the destination of Mt. Pleasant on the side. Driver W. Irwin? Handwritten caption by H.P. James. Note Item Not formally Numbered. Image btm2507i2 shows position on page relative to items 2507 to 2512. For a copy photograph of this image, see Reg Item 3813. High Res Images added 15/3/2011. Digital scan of a negative in the Wal Jack Collection added 21/4/2019 as image btm2510i4Handwritten in Pencil under the photograph is "Here is an interesting picture. Note the driver he is W. Irwin who gave me these pictures for which I am very grateful. The bus petrol engine International type was formerly in the possession of, one, Cruickshanks, an independent driver with a permit from the council to run between The Point of Pictures?, Ness St, Mt Pleasant via Bond St, Peel St. to City but the Electric Supply Coy purchased the vehicle and ran it from 1927 to 1929 (unpayable). The most use it was put to was on Mt Pleasant, but it ran also to High School as replacement for trams on Sebas if an electric tram was derailed. Perhaps the most unique trips it ever made was between Forest St. Wendouree to the Aerodrome, 1929, on the occasions of any ?? flight. Again Mr Irwin was the driver (& made two trips)"tramways, trams, esco, motor buses, mt pleasant, cruickshanks -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - VIEWS OF BENDIGO: EAGLEHAWK HIGH STREET TOWARDS TOWN HALL, 1875
Sepia photograph. View looking north along High Street, Eaglehawk towards the Eaglehawk Town Hall and Virginia Hill behind. On either side of the street are double and single storied businesses. Wooden slatted tree guards, triangular configuration are close to the road gutter. Some horse-drawn vehicles are on the right side of the street. On Virginia Hill a mine and crushing battery building and chimney along with a few eucalypts can be seen. Inscriptions: Views of Bendigo No. 49', 'Township of Eaglehawk', 'NJ Caire photo Sandhurst', 'Casey & Wenborn's print', Forbes & Holmes Agents'. In grey lead on back of mount 'Mrs Brown, Barnard Street, Bendigo', Stamped 'Royal Historical Society of Victoria, Bendigo Branch'. In image 'Victoria Hotel, Sam Watson?', 'Saddler', 'Exchange Hotel'. History: in grey lead pencil, Mrs Brown, Barnard Street, Bendigo. Three col. Stamped 'Royal Historical Society of Victoria, Bendigo Branch', in ballpoint pen 1959, 71. (Two copies) Nicholas CaireNicholas J Caireplace, streetscape, high street, eaglehawk, the photographic mount -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPostcard, Nu-color-vue or Nucolorvue Productions, Sturt St at night, late 1960's or early 1970's
Demonstrates post card making by a major postcard manufacture, late 1960's and yields information about Sturt St at night.Colour postcard with serrated edges of a Ballarat bogie tram at dusk in Sturt St, parked in City Loop. with Town Hall in background. Tram has destination of "CITY". Photo includes illuminated Paterson, T&G, Myer and the Vegas theatre signs. Has many parked cars in Sturt St, with red lines from the tail lights of vehicles moving on image. On rear , printed in dark green ink is the card details etc. "Ballarat, Victoria, Sturt St, Ballarat at dusk looking to the Town Hall." Nucolorvue card, BT 69. 2nd copy - in good order. See also Reg. Item 1176 for colour slide of this view. 960 copy 1 - made by enlarging postcard to an A4 print by colour photocopying and laminated for display purposes. Made July 2000 for the Trams at Night exhibition in the depot. Made by W.Doubleday. Has four Velcro dots on rear. Overall size 208H x 296W. Stored in same box at rear of large photos area in an A4 plastic folder. trams, tramways, ballarat, town hall, sturt st., tram 8 -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Leaf from a photo album, 1920s
Leaf from a photo album containing 4 black and white photographs pasted onto sheet of brown/grey cardboard with two punch holes at one end. Photos taken early 1920's or just after construction of the Memorial Arch. Photo 1 - "Ballarat" handwritten in pencil at top - Town Hall from the North West taken from a building near Doveton St. Has a Sebastopol tram west bound in Sturt St. passing Town Hall. Photo 2 - "Sturt Street Ballarat" handwritten in pencil at base - Sturt St. Ballarat looking east from most likely the Ballarat City fire station lookout tower. Has a Sebastopol tram travelling eastbound in the photograph. Town Hall in background. No motor vehicles in photograph. Photo 3 - "Memorial Arch, Ballarat" handwritten in pencil at top - photo of the new Memorial Arch at the start of the Avenue of Honour. Photo 4 - "Eureka Stockade, Ballarat" - photo of the Eureka Stockade monument the park.trams, tramways, ballarat, sturt st, memorial arch - avenue of honour, eureka -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - B&W print of donated negative - set of 4, State Electricity Commission of Victoria (SECV), late 1930's
Yields information about an accident or collision between a tramcar and a vehicle late 1930's. Gives information about the damage to the tramcar and livery detailsSet of four Black and white photo prints from collected negative of Ballarat (SEC) No. 27 photographed in the depot yard after a collision with motor vehicle or possibly another tram, as the damage is at the roof line, where the two trams tend to hit before hitting at the bumper bar level. Thought to be late 1930's. 1367.1 - general view of the end cab showing the damage to the roof level, destination box and beading. 1367.2 - close up of the damage from one side. 1367.3 - side on view showing how the driver's windows have been pushed back. 1367.4 - close up of the damage from the opposite side to that of 1367.2 Copy 2 - of all above photos - large format prints (253H x 203W) - added 30/7/2007, ex Alan Bradley holding of prints, received 5/2007. See also Reg Item 3905 for a mounted set of these photographs along with that of Reg Item. 1364. .Negatives rescanned 17/5/2020 and image updated.tramways, trams, accidents, collision, damage, tram 27 -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPostcard, ESCo tram just past the intersection of Doveton St. and Sturt St
Photographically printed black and white postcard with an impressed image of an ESCo tram just past the intersection of Doveton St. and Sturt St. travelling east along the north side of Sturt. Street towing a heavily laden horse tram as a trailer. Photo appears to be taken soon after opening of the electric trams, as the tram does not have any destination box above the driver. Possibly summer 1905/1906. Numerous people in the street, some horse drawn vehicles in the photograph. Shows buildings along the south side of Sturt St. and part of the verandah of the building at the NE corner of Doveton St. For a list and description of the same base image see Archives file - "Notes on ESCo Tram towing a heavily loaded trailer" On rear is places for correspondences stamp, address. Addressed to Miss E. Freeman, in Dunedin NZ, with a hand written message. Posted in Melbourne on 28/10/1908. Titled "Sturt Street, Ballarat" along bottom edge with "47" in bottom left hand corner of image.. trams, tramways, sturt st, postcards, esco, doveton st -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPostcard, Kodak, ESCo crossbench tram No. 19
Printed black and white photographic postcard of Ballarat ESCo crossbench tram No. 19 at the intersection of Armstrong and Sturt St. travelling east along the north side of Sturt Street. Photo appears to be taken in the early days of tram operation - small destination box. Has the Ballarat Town Hall, the National Mutual Life building, Snows and other buildings on the south side of Sturt. St. Has a number of horse drawn vehicles in the image as well. Titled "Sturt Street, Ballarat" in bottom right hand corner". On rear of postcard, printed is the words "Post Card", areas for "Correspondence" and "Address Only" and in stamp area in a square "Kodak Australia" twice. Handwritten on the card is "With Best Wishes for a Happy New Year to all Rostella / W. Lovett". Images .1 - shows postcard, .2 - close up, of No. 19, note Inspector along side tram, the stance of the motorman/driver, and conductor on the rear platform of the tram. Appears to have a destination of "Gardens ?" .3 - rear of postcard Handwritten letter on card.trams, tramways, esco, sturt st, postcards, armstrong st -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPostcard, E.W. Cole Arcade, Ballarat Horse tram arriving at the Grenville St. terminus, c1900
Demonstrates aspects of working of Ballarat tramways, with a passenger stepping off a moving horse tram at Grenville St. Has a strong association with the sender and receiver, giving family/friends movements. Hand painted card.Printed black and white postcard with hand painted light blue sky background of Ballarat Horse tram arriving at the Grenville St. terminus, at the bottom end of Sturt St terminus with a person stepping off the tramcar. Has buildings on both sides of Sturt St. in photograph, and one other horse drawn vehicle. Also Suttons and Richards & Co. buildings in photo. See Reg. Item 1539 for photographic image of the postcard and 2762, and 3298. Titled "Sturt Street, Ballarat" in bottom left hand corner". On rear of postcard, printed is the words "Post Card", areas for "This space may be used for correspondence" and "The Address to be written here" and in stamp area in a square "Penny Stamp here". On the left hand side of the card "Cole's Sunny Australia 96 Views", E.W. Cole Book Arcade Melbourne, Sydney and Adelaide. See also Reg Item 2762 for another postcard using the same photograph and Reg Item 3298 for another version with some writing on the card.On front of card in black ink "April 18 1906" and "William St" On rear stamped "Melbourne, 17.4.06", 1d stamp and addressed to Mrs. Keast, Cumberland, Waymouth St Adelaide. and a message about family members/friends travelling. On top edge stamp "E.G.Butland"trams, tramways, sturt st, postcards, horse tram, grenville st, tram 35 -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Report, The Met, "The Met Student Training Card", Jan. 1994 to Feb. 1995
Set of 9 "The Met Student Training Cards" - comprising a brown envelope with student name and other details, containing a manila folded card containing a record or practical training - dates, routes, table, vehicle type, trained in, progress to date, comments and trainer name. Gives the name of the student and the trainer and type of training. All commenced their training at Hawthorn during Jan. 1994 to Feb. 1995. All from South Melbourne depot. .1 - Mohamed Farah - Conductor - trainer - Roberto D'Andrea .2 - Sameh Ghobrial - Conductor - trainers Margaret Drew and Zorzi .3 - S. Adikari Tram driver - trainer - T. Fenwick .4 - Jennifer Stebbing - conductor - trainer Monk .5 - Arsenio Granada - conductor - trainer McGill .6 - Ralph Bosworth - conductor - trainer Zorzi .7 - N. Pamulo - conductor - trainer Monk .8 - Marie Murage - tram driver - trainer - Phillips .9 - Pugh - tram driver - trainer - Robertsontrams, tramways, centenary, yarra trams, 100 years of electric trams, melbourne, depots, marketing -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumFunctional object - Run Number Plate, Metropolitan Transit Authority (MTA), AVM types, mid to late 1980's
Set of 3 run number plates used for the vehicle identification system used in the AVM. Item was pushed into a slot of a reader which then recognised the identification through the series of holes on the left hand side. Fitted with metal strips, riveted on, to enable the card to be slotted into the holder by the crew member and then withdrawn when not required. Understood that the tram carried one of these at one end and then another without the holes at the other end. Number has been engraved into the plastic sheet and then painted in black. Used to identify the depot and "run number" or timetable that the tram was running on, two in each tram, to enable monitoring by inspectors and crews. System introduced by the MTA during the second half of the 1980's. .1 - E25 (see also 6020 for another version used for transporting trams to and from Preston Workshops) .2 - B21 .3 - D37 Essendon Depot E25 added 21/6/2017 from donation of Neil Elphic. See Reg Item 4660 for V21.trams, tramways, mta, avm, timetables, buses, trams, inspectors, essendon depot, brunswick depot, doncaster depot -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Folder with papers, Goninan & Co, "Goninan Quality", Nov. 1995
Folder - presentation white card - with printed gold front with large round tab on the right hand side, with the words "Goninan Quality" on the cover. Inside are papers: 1. Welcoming the members of the Australian Electric Traction Association - AETA - for a tour of the Preston Light Rail Facility on Friday 10 November 1995, including a very prelim sketch of a Hong Kong light rail vehicle, newspaper cuttings about overseas contracts for the Hong Kong - Kowloon Canton Railway. Includes notes on Howard Smith Company, the owner of Goninan at the time. 2 - Copy of Goninan News - No. 78, July / August 1995 - all locomotives. 3 - Pamphlet on Goninan - activities, Victoria operations - Double Deck train for Melbourne, Sprinter Rail Cars, City Circle Trams and Driver Only trams. Gives contact details. 4 - Press Release - about Goninan & Co being successful for the building of up to 120 locos for the National Rail Corporation - dated Thursday 5/10/1995.trams, tramways, goninan & co., light rail, hong kong, preston workshops, aeta, tours -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPostcard, Biscay Greetings, Bourke St. Melbourne from Parliament house with MMTB Z8, mid 1970's
Colour postcard with of Bourke St. Melbourne from Parliament house with MMTB Z8 and about 6 W7's in photo, along with many motor vehicles. Also shown are the Safety Zones and stops. In image are buildings along either side of Bourke St., featuring the sign of the Salvation Army City Temple in the top left hand corner, Mittys, and a Kwikasair van by the outbound safety zone. Tram Z8 has destination of "CITY - SPENCER ST." and showing route 89. Mid 1970's. Card has a caption underneath the photo - "Melbourne's Trams in Bourke St, Victoria" Back has space for name and address, stamp and a message and details of the postcard. Produced by Biscay Greetings, possibly mid to late 1980's. Card No. 2AUS 58 .1 - as above but without the caption on the bottom of the photograph. Biscay postcard No. 98, with a caption on the rear that it was a "New Z class tram". .2 - another version with caption and different wording on rear - has number 2AUS58.trams, tramways, postcards, bourke st, route 89, z class, w7 class, tram 8 -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumFunctional object - Badge/s, PTU - AA Products Sydney, 1980's to mid 1990's?
.1 - Set of 9 Tramway Union badges and other badges pinned to a piece of heavy blue cloth with sewn edges comprising 5 Public Transport Union (PTU) badges, three Australian Tramway and Motor Omnibus Employees Association (ATMOEA) badges, three The Met number lapel badges (Nos. 1121, 2416 and 3817), one RSL tie clip and one tie clip with a wheel inside a black background, with a "LEGA" .2 - AMTOEA badge in a plastic bag as would have been received by the member - brass back with pin clip on rear with blue surround and red around the state name. .3 - PTU badge in a plastic bag, brass, with clip missing, black surround, with red vehicles, green map of Australia and yellow around the map. Has a staple in the plastic bag. http://www.rtbu.org.au/a_short_history accessed 2/12/2019, notes that the PTU formed in 1993 and renamed RTBU in 1998 to reflect the impact of privatisation.trams, tramways, badges, unions, ptu, atmoea, rtbu -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPrint - Framed Print, Glen Waverley Picture Framing, 1970's?
Framed, glazed, black and white photograph of the intersection of Flinders and Swanston St Melbourne, looking towards Flinders St railway station. Timber frame, painted brown and gold, with brown paper lining on rear. Has brown string stapled at rear on both sides for hanging. In the central bottom of the rear is "Glen Waverley Picture Framing, sticker, 698 High St Road, Glen Waverley with a 7 digit phone number. Photo c1926?? features a very busy intersection cable trams (No. 17 west bound in Flinders, tram 160 north bound in Swanston, two W class trams, other cable trams, many motor cars, horse drawn vehicles, cyclist and pedestrians. Note the standing zone in Flinders St. In photo are Young and Jacksons Hotel, Bacchus Marsh Concentrated Milk table cream, and numerous signs on the railway station. See Reg Item 5272 for the photo on a Greetings Card and 5217 for a photographic print.on rear top "Donated to Hawthorn Tram Museum Feb 1912 Ron Scholten" in ink.trams, tramways, flinders st station, swanston st, flinders st, melbourne, cable trams -
 Lara RSL Sub Branch
Lara RSL Sub BranchPhoto, Harry Grove
This photo is from 1917 and is of Private Harry Groves (standing) with his cousin Arthur Whitter (seated). Private Groves was the Uncle of Ron Ellis, who was a Lara Sub-Branch member. Cpl. Ronald Warren Ellis, EM (VX502517) was born in Brunswick in 1927. His family moved to Lara when he was young, and his schooling took place at the Lara State School. After finishing his education, Ron took up employment at Sims Coopers in Corio. Ron was enlisted in the second AIF at Melbourne, and posted to the 3rd Recruit Training Battalion at Greta west of Newcastle, NSW. After 3 months training, he was sent to the Service Corps Training Centre for driver and maintenance training in Ingleburn, south of Sydney. When this course was completed, Ron was posted to the Australian Army Service Corps as a driver motor vehicle with the 2nd AIF. Rons service with the AIF lasted 425 days, when he was then transferred to the Interim Army for a further 309 days. The duration of his service was in NSW. Ron was discharged from the Army in Melbourne on the 4th of May 1948. In 1957, Ron enlisted in the CMF and served with 22nd Construction Squadron for 17 years with the last 5 as a Corporal, and was awarded the Efficiency Medal for long service and good conduct. This photo represents the connection that Lara RSL members and their family members have to the conflicts that Australia has been involved in over time. Photograph of Harry Grove (standing) with his cousin Arthur Witter (seated) - France 1917. The black and white photo is framed within a wooden frame, and above it is a piece of paper with details about the photo written in red texta. The photo is black and white, and in the bottom right corner in pencil is written: Sincerely Yours, Arthur. The remainder of the text extends under the frame, but looks as though it says: Arthur, France. world war 1, ww1, wwi, photo, family, private, corporal
