Showing 15 items matching "1820s"
-
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book, Mechanics Institute, 2015
This book contains information on all known Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. Mechanics’ Institutes were organizations formed originally to improve the education of working men and to instruct them in their various trades. The first Institutes were established in London and Manchester in the 1820s and in Australia the first Institutes were set up in New South Wales and Tasmania in the late 1820s, with the first one in Melbourne in 1839. Mechanics’ Institutes were set up in Victorian country towns, in many cases, soon after the settlements were founded. This book is of some importance as a reference book as it gives information on all known Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria and there were many in the Warrnambool region. The Mechanics’ Institutes were important centres for local adult education and recreation. The book will therefore be of great use to readers of local history and researchers. This is a hard cover book of 704 pages. It has many photographs, mostly black and white, and other images related to Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria. It has a Contents page, Foreword, Dedications, a story entitled ‘Dingo Flat’, Preface, Introduction, Acknowledgements and articles on hundreds of Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria, whether closed or still existing. The front cover has two black and white photographs and the title and the back cover has images from two Mechanics’ Institutes. The authors are Pam Baragwanath and Ken James.Front Cover: ‘These Walls Speak Volumes’, ‘A History of Mechanics’ Institutes in Victoria, ‘Pam Baragwanath and Ken James’mechanics’ institutes in victoria -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncClothing, Paisley Shawl, 20th Century
Imitation Kashmiri shawls were produced in large numbers in Europe in the second half of the 19th and also in the 20th centuries. The first mechanised production of such shawls was made possible by the invention of the Jacquard loom in France in the 1820s. Machine woven paisley shawl, based on traditional hand-woven Kashmiri designs. paisley shawl, shawls -
 Brighton Historical Society
Brighton Historical SocietyClothing - Dress, Day dress, circa 1820
This dress, which was made around 1820, was passed down through five generations of a single family before its donation to Brighton Historical Society in 2007. It originally belonged to a great-grandmother of Margaret Reynolds (1881-1958) of Hertfordshire, England, who herself came into possession of the dress around the early twentieth century. Having no daughters of her own, in 1945 the 64-year-old Margaret sent the dress as a Christmas gift to her niece, Margaret Willoughby Reynolds (1907-1996). In the letter accompanying the parcel, donated to the Society with the dress, the elder Margaret writes that she loves the dress very much but has now outgrown it. She makes reference to her own mother Mary Reynolds (nee Lloyd)'s pleasure at seeing the dress worn, indicating that it may originally have belonged to one of Mary's grandparents. She had two requests of her niece: first, that the younger Margaret wear the dress on Christmas Eve as a treat for her Mary (the letter includes styling advice on how the dress should be worn and accessorised), and second, that she one day pass the dress on to her own daughter or niece. In March 1968, the younger Margaret gifted the dress to her Australian-born niece, Dorothy May England (nee Reynolds, 1924-2013), along with a letter of her own. Dorothy, a Bayside resident, donated the dress and both letters to the Society in 2007. The letters paint a picture of the significance of the dress within the Reynolds family and its journey from England to Australia.A white, mauve, purple, red, and green paisley / floral printed cotton day dress from circa 1820. The day dress features a wide scooped neckline, with a dropped shoulder line. At the head of the sleeve is has three lines of gathering creating a narrow arm hole around the shoulder, flaring out into a leg of mutton sleeve. The sleeve finishes neatly at the wrist with a cuff that secures with two brass hook and eye closures. The dress bodice is open at the centre front and secures with six hook and eye closures to the empire line waist. Over the breast on either side of the opening are six diagonal pleats, pressed and secured facing towards the neck. This pleated detail is on a facing that extends from shoulder to shoulder and finishes with a bound edge. The remainder of the front bodice is plain and secures to the skirt at the empire waistline. The skirt pleats onto a binding, wrapping around the torso and securing to the bodice with eight hook closures. At approximately knee, height the skirt has an additional gathered flounce with the dress finishing at approximately ankle length. From the back, the bodice is plain and the skirt is gathered and sewn to the bodice at Empire line. Alterations to the garment have been made with the addition of hooks and eyes. The garment is generally in good condition although the skirt at the front shows evidence of damage and subsequent repair.day dress, 1820s, migration, dorothy may england, margaret willoughby reynolds, margaret reynolds -
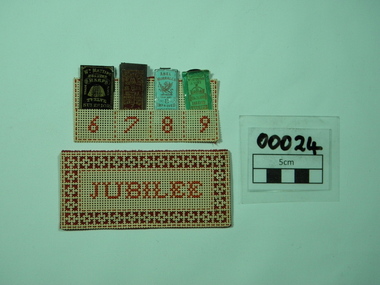 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Functional object - Sewing Equipment, needles
In the 1820s perforated cardboard first became available. Then, with the invention of the printing press, designs such as sentimental or religious mottos were pre-printed on the card and a Victorian craze began as it provided a simpler and cheaper method of embroidering for the masses compared to the previously far more expensive linen embroidery. Over the following decades embroidering of punched-card grew enormously in popularity and a variety of articles from Christmas decorations to birthday cards, and in this case a Neele case to celebrate Queen Victoria's golden Jubilee in 1887. The pioneer settlers and market gardeners of Moorabbin Shire had to be self reliant and made their own clothing and utensils. This is one of many items used to exhibit the skill and craftsmanship of the women in these families. Small cream coloured Punched-Cardboard needle case,with red satin lining and red cross-stitch decoration. The case contains four paper packets each containing sewing needles of a different gauge. Each packet of needles is 3 1/2 cms long and 1 cm wide. The size of the needles In red cot tonCross stitch on one side of the card needle case the word "NEEDLES" is embroidered, and on the other side the word "JUBILEE". Inside the needle case is four packets of different sized needles, by Wm Mattins1887, queen victorias golden jubilee, victorian punched card work, hand embroidery, different packets, different gauge sharp needles, wm shrimpton and sons, william mattins, abel morrals, copestakes, cross stitch -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotographs x 2- D Reids home at Mill Park 1973, 2/12/1973
David Reid (1820-1906) was a pastoralists and politician. He left school at 16 and after meeting the overlander John Gardiner he decided to look for land south of the Murray River. Equipped by his father with some 500 head of cattle, 2 bullock wagons and teams and 6 assigned servants, he reached the Ovens River on 8 September 1838. David settled at Currargarmonge, near Wangaratta. At the end of 1843 he took up land near Yackandandah. In 1847 he took up a section of the family run of which Woorajay (Wooragee) formed a part. He built the first water driven flour-mill in the district on his Yackandandah run in 1845; his woolclip of 1848 was one of the first to be handled by R. Goldsbrough and was claimed to come from sheep descended from stock imported in the 1820s from George III's flock. Going into politics, he held the Legislative Assembly seat of Murray from October 1859 to May 1862. David Reid was a highly regarded grazier and local politician who was significantly involved in settlement around the Yackandandah area. Photo demonstrates ongoing interest in the local history of the area and its early residents2 colour photographs mounted together on buff card 1. Man and 2 children (unidentified) standing outside the remains of the Reid home. 2 Dec, 1973 2. Group of unidentified people on a tour of the old homestead of D. Reid. 2 Dec, 19731. Handwritten in black ink under photo 'D. Reid's home 1845. At Mill Park. 2 Dec 1973 2. Handwritten in blue ink under photo 'Snapshots Clare Roper"clare roper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLeisure object - Tobacco Pipe, Early 20th century
People in ancient civilisations smoked pipes during various healing and religious ceremonies. By the end of the 15th century, after tobacco was discovered in America, smoking had become a common pastime for everyday people. From that time, tobacco pipes were fashioned from many materials ranging from gold and silver to corn cobs and clay. A popular material was meerschaum, an expensive, soft, white stone from Turkey. In the 1820s, French craftsmen carved pipes out of the wood from the growth on the root of a Mediterranean White Heath. This material became increasingly popular due to its durable, heat-resistant qualities. The growth was called ‘bruyere’, now anglicised to ‘briar’ wood. Bakelite was the first plastic made from synthetic components. It was developed by Leo Baekeland of New York in 1907. The material was heat-resistant and could be moulded into any shape and hardened to keep its shape. This invention greatly impacted the industrial world and the products available to the domestic market, making more objects available at reduced cost.This smoker's tobacco pipe symbolises one of the leisure activities of the early 20th century that has continued into modern times. The shape and materials of the pipe represent a point in time in the evolution of tobacco pipes, including the revolutionary impact that the 1900s invention of Bakelite had on objects available in the domestic and industrial markets.Smoker's tobacco pipe; a round brown wooden pipe bowl joined to a dark brown mouthpiece. The French pipe's bowl is made from briar wood, and its mouthpiece is Bakelite. There is an inscription on the pipe."French Briar Pipe"warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, smoker's pipe, tobacco pipe, briar wood pipe, wooden pipe, smoking, french pipe, bakelite, smoker's equipment -
 Lara RSL Sub Branch
Lara RSL Sub BranchThe Evolution of the Rising Sun Badge of the Australian Army, Captain D'arcy.2004, 2004
The origins of the rising sun badge are disputed. Rising sun designs had appeared on early Australian colonial coins and military insignia decades before the federation of the Australian colonies in 1901, and may have represented the image of Australia as 'a young nation' and a 'new Britannia'.[2] As early as the 1820s, the symbol of a 'rising sun' was used by various progressive organisations, loosely characterised under the banner "Advance Australia". The rising sun crest used in the New South Wales colonial and State crests was taken from the crest used on the first Advance Australia Arms, circa 1821, and consistently since then.[3] The oldest known example is the 'Advance Australia' coat of arms. The 'Advance Australia Arms' (named because of the motto inscription) became widely used in New South Wales and the neighbouring colonies by private corporations and individuals. Although they never had any official status, they formed the basis for several official coats of arms, including the New South Wales coat of arms. The representation below was reputedly painted for Thomas Silk, the son of the captain of the Prince of Orange, a convict ship that visited Sydney in 1821. The symbol struck a chord with the pre-federation population and many examples still exist on colonial architecture.[4] Proudly worn by soldiers of the 1st and 2nd Australian Imperial Force in both World Wars, the 'Rising Sun' badge has become an integral part of the digger tradition. The distinctive shape of the badge, worn on the upturned side of a slouch hat, is commonly identified with the spirit of Anzac.Glass covered Rectangular Picture Frame showing the Evolution of the Rising Sun Badge of the Australian Army.Gives a brief rundown on the Evolution of Rising Sun Badge with 12 examples and explanatory notes -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Scale, George Salter & Co, ca. 1886
There were at least three 1880s vessels named Lady Loch, all built in Victoria; a river launch (ca 1884 to ca 1916, originally named Lady of the Lake), a steamer ferry (1884 to 1920s), and a government lighthouse tender steamer HMV Lady Loch (1886 to 1962). The spring balance scale was part of the equipment on the HMV Lady Loch. The scale was made by the renowned company Salter Weighing Machines in the United Kingdom, to Silvester's patent design. Salter Weighing Machines, Britain, began making spring scales in the 1820s. In 1908 Salter opened up an Australian branch named Salter Scales Pty. Ltd. The scale is marked HMV SS Lady Loch. It would be suspended by its top ring, a basket or other container is hung from the hook, and the items inside the basket are then pulled downwards on the hook, which stretches the springs inside the works. The pulling action moves a rack and gears a calculated distance and the gears turn the pointer on the dial to indicate the weight of the goods. This scale measures up to 200 pounds capacity. The HMV SS Lady Loch was an iron steamship built in Footscray, Melbourne, by Campbell, Sloss and McCain in 1886 for the colonial Victorian government’s Department of Trade and Customs. It was armed with a 6-inch gun and two 1-inch Nordenfelt guns. The Sydney Morning Herald of 27th January 1888 describes the vessel in detail. It even comments on the interior of the Saloon “The wood work … is on a very elaborate scale and is exceedingly neat …”. The HMV Lady Loch performed Customs duties and serviced the lighthouses along the coast. The scale could have measured goods for the Customs Tax, or for measuring out supplies for the lighthouse keepers. The vessel was named after Lady Elizabeth Loch, wife of Sir Henry Loch, Governor of Victoria from 1884 to 1889. In 1932 Lady Loch was converted to a hulk and used in Brisbane, and finally scuttled in 1962 at Moreton Bay, Queensland.The scale has importance due to its connection to the 1886 HMV Lady Loch, a vessel of great significance to Melbourne’s shipbuilding industry. It was the largest auxiliary vessel in the Victorian Colonial Government’s fleet and the first prominent vessel launched by Melbourne’s shipbuilding industry. The scale is also important for its connection with the colonial navy's Custom's work, as the scale was available to weigh goods that could attract taxes and deal out goods for distribution to lighthouse keepers. The HMV Lady Loch was also important part of Victoria's maritime history for its communication and support of the lighthouse keeper's along the coast of Victoria.Scale; Salter's spring balance mechanical hanging scale, brass and iron. Equally spaced marks around the circular dial have values from 0 to 200 in increments of 10, each increment is also divided into 10. An iron ring is attached to a fitted loop on the top of the scale, and an iron hook is attached to the fitted loop onthe bottom of the scale. A moving pointer attached to the centre of the dial has a calibration screw joined to its base. Four screws fix the brass face to the works at the back. There are stamped and embossed inscriptions. Made by Salter in Britain, to Silvester's Patent design. The scale was once equipment carried abourd the steamship HMV SS Lady Loch. Stamped: "SALTER'S / SPRING BALANCE" "SILVESTOR'S / PATENT" Embossed in script: "HMV SS / Lady Loch"warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, scale, salter, spring balance, silvester's patent, lady loch, steamship, hmv, colonial navy, victoria, lady elizabeth loch, custom's vessel, lighthouse tender, 1886, government vessel, victorian government, measuring instrument, weight, weighing instrument, mechanical scale, hanging scale, hmv lady loch, weights and measures, silvestor's patent, george salter & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePen Nibs, 1920's
The two cards of nibs are retail display cards of the dip pen nibs that William Mitchell Calligraphy produced, dating back to around the 1920’s, which was the time of the Great Exhibition in the UK. At that time dip pens with steel nibs were the main writing instruments. British Pens Ltd. had recently formed as a company and its subsidiaries included the the company William Mitchell, which is why British Pens Ltd. is named on the cards as well. One card (1) has the Round Hand nib, which is widely used today for calligraphy scripts. The other card (2) has the Script nib that has round upturned points for monocline or unshaded lettering that is also used for calligraphy. The nibs also have a detachable reservoir. The pen nibs are shaped to fit into a slot in the base of a wooden or Bakelite pen holder. The hole at the front of the nib is for collecting ink from a well, which is then stored in a reservoir at the back of the nib. The nibsare stamped with their nib size and Pedigree (what type of nib it is) and maker’s details. William Mitchell Calligraphy still makes these nibs today with a slightly difference finish. (ref: Sales and Marketing Director of William Mitchell Calligraphy in 2016). HISTORY of the Ink Pen Quills and ink were common writing tools until the early 19th century when the pen trade began mass producing steel nibs and pens. The steel nibs each have a hole in the middle that acts like a well for the ink. When the nib is dipped into the ink well the writer needs to ensure that it is dipped to only just past that well. India Ink was one of the most popular inks used with the nib pens, notable for its satin-like smooth flow. This ink is composed of a particularly fine carbon mixed with water; it can also be obtained as a dry stick that is then crushed and mixed with water as required. The Jewellery Quarter of Birmingham had the largest concentration of independent jewellers in Europe. Birmingham became the centre of the world’s pen trade for many years -, during the 1800’s over 100 factories, employing 1000s of skilled workers, manufactured the ‘Birmingham Pen’. ABOUT WILLIAM MITCHELL CALLIGRAPHY LTD.* (*The following text is quoted from the William Mitchell Calligraphy website) British based William Mitchell Calligraphy has been designing and manufacturing exceptional pens for almost 200 years. The William Mitchell heritage in making pen nibs began whilst working with his brother John Mitchell in the early 1820s. William Mitchell established his own business in 1825 to become one of the leading nib manufacturers and famous for lettering pens. Almost 100 years later William Mitchell merged with Hinks, Wells & Co, another pen manufacturer, to form British Pens, employing around 1000 people in the Bearwood Road area of Birmingham. During the early 1960s British Pens acquired the pen business of other pen manufacturers Perry & Co and John Mitchell, once again reuniting the two brothers. Joseph Gillott, who were famous for their artist drawing and mapping nibs, amalgamated with British pens in 1969. William Mitchell and Joseph Gillott established in Birmingham during the early part of the nineteenth century and [their products] are still proudly made here. British Pens were subsequently purchased by its current owner Byron Head, the owner of William Mitchell (Sinkers) in 1982, and was subsequently renamed William Mitchell (calligraphy) Ltd. Established in 1827 Joseph Gillott was one of the pioneers of mass steel pen nib manufacturing. The company was particularly strong in the American market, prompting Elihu Burrit, the American consul, to write “In ten thousand school houses across the American continent between two oceans, a million children are as familiarly acquainted with Joseph Gillott as with Noah Webster” (The compiler of the famous American dictionary). The company consequently received visits from many notable Americans, including president Ulysses S Grant. The early 19th century invention and mass production of pen nibs such these in our collection had a large impact on education and literacy because the nibs could be produced in great numbers and affordable prices.Pen nibs; 2 cards of steel dip pen nibs from the 1920’s. The steel nibs are attached to cards by 2 rows of entwined cotton cord. Reverse sides of cards have some hand written marks. Manufacturer; William Mitchell, Birmingham, England. Card issued by British Pens Ltd. Nibs have shaped ends, a hole in the centre with a well on the underside, and the tops are shaped approximately quarter circle. Inscriptions are pressed into each nib. The script pens have detachable reservoirs made of a metal different to the nib. (Card 1) Round Hand Pens, 11 nibs remain from card of 12. Printed on card “Round Hand Pens for Beautiful Writing, Twelve degrees of point, Square points. William Mitchell, Birmingham, England. This card is issued by British Pens Ltd. MADE IN ENGLAND” Also printed on top left of card is a pen drawing of a person writing at a desk, background of decorative 3-paned window in brick wall. (Card 2) Script Pens; 11 nibs remain from card of 12. “Script pens fitted with detachable reservoir. William Mitchell, Birmingham, England. This card is issued by British Pens Ltd. MADE IN ENGLAND” Also printed on top right of card is a pen drawing of a person writing at a desk, background of decorative 3-paned window in brick wall. On Card 1, - each nib is stamped with its size, and “Wm MITCHELLS / PEDIGREE / ROUND HAND / ENGLAND” - hand written on front bottom of card in ball point pen “Lettering 5 times size of nib” - hand drawn on back of card in red and blue ball point pen are scribbled lines On Card 2 - each nib is stamped with its size, and “WILLIAM / MITCHELLS / SCRIPT PEN / ENGLAND” - a black circle corresponding to the nib is printed on the card above each nib. - hand written on back of card in black felt tip pen are numerals - hand drawn on back, 4 parallel lines in red ball point pen with the numbers “10” between 2 of the lines flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, william mitchell calligraphy ltd, british pens ltd., pen nib, writing implement, dip pen, round hand nib, script nib, birmingham manufacturer, communication in writing, mass produced pen nibs -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Lamp Light, late 19th - early-20th century
This gas lamp light and stand came from the original manufacturer in Melbourne. Gas street lights such as this one were used in Melbourne from the mid-19th century. The lights enabled safer after-dark travel for pedestrians and vehicles and were a deterrent to crime. A lamp lighter was employed to keep the lamps lit, sometimes with little success due to weather conditions and the pranks of youths. WARRNAMBOOL Gasworks In Warrnambool prior to 1874 there were about twenty rare, individually lit street lights in Warrnambool, each with its own supply of kerosene. These lamps were in the central business area of Timor, Koroit and Liebig Streets. The Warrnambool Gas Company Ltd. was registered as an incorporated company in 1873. It was a private, locally owned business. It was located at 209-215 Merri Street, Warrnambool, on the land, which is just west of the later-built railway station. The first managers of the Gas Company lived in a substantial stone house on site, but later the managers lived in a residence in Henna Street between Merri and Timor Streets. The original home, which still stands, became a residence for the Railway Station Master from about 1890. In August 1874 the construction of the gasworks was complete and at the end of that month gas was supplied to all of the existing lamps in Warrnambool for the first time. The Warrnambool Gas Company wound up in 1880-1881 and was purchased by the Warrnambool Borough Council with money raised by a loan – the Borough’s first ‘loan transaction’. The Council established a piped network to supply gas to other street connections. The gasworks were privatised and upgraded in 1952. In 1972 the town supply was converted to liquid petroleum gas and by the early 1980s the gasworks were closed down. In 1986 Warrnambool was supplied with natural gas from a site near Port Campbell. The Warrnambool gasworks supplied all street and shop lighting and most domestic lighting until 1923 when electricity was available for lighting. Bromfield Street in Warrnambool was named after the director of the gasworks, James Astley Bromfield (1823-1903). He arrived in Warrnambool from Worcestershire, England, in 1852 and was very active in the local council and community. Cockman Street was named after the first secretary of the gasworks in 1874, Walter Cockman (c.1821-1892). He was a Mayor and businessman. The second Manager, Luther Rodgers, worked for the gas company for about twenty years and both Rodger Place and Rodgers Road in Warrnambool have been named after him. LAMP LIGHTS IN MELBOURNE In the 1820s Melbourne's innkeepers were legally required to have a lamp light outside their premises from sunset to sunrise. This was the first instance of street lamps being used in Melbourne. In 1847 the first oil lamp was used in the city. In 1849 a gas lamp was installed on the Swanston Street Bridge and much of the city had oil lamps installed by then. In August 1857 the installation of street gas lamps began in Melbourne. They were welcomed for the much brighter illumination they gave. By 1860 there were 414 lamp pillars. The phrase was quoted often - "A light was as good as a policeman". The first gas burners used for street lighting were called 'fishtail' gas burners. These were replaced in the early 1900s by gas mantles. The City of Melbourne Gas Coke Company was formed in 1850 but due to the Gold Rush the manufacture and distribution of the gas supply was delayed until January 1856. By the 1890s the gas supplying the lights was supplied by three companies in Melbourne. In 1879 a football match was played at the MCG under electric lighting and gradually electric arc lights were installed inside and outside buildings in the city. Lamp lights such as the one in Flagstaff Hill’s collection were no longer needed. (References: John Lindsay re Lamp Light history 2019-01-29, Former Warrnambool Gas Company Limited, Victorian Heritage Database Report, Heritage Number 149746 https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/149746/download-report ) The lamp light is representative of the lamps used in Melbourne from the mid-nineteenth century to light the streets at night and make Melbourne a safer city. The lamp is also representative of the gas street lighting in Warrnambool from the mid-1870s-1920s.Lamp light or gas light. Street light, one of the last gas street lights removed from Melbourne. (Reconditioned by Friends of Flagstaff Hill, 2013)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, lamp light, gas light, gas lamp, street lamp, street light, gas street light, melbourne street lighting, warrnambool street lighting, melbourne gas street light, warrnambool gas company, warrnambool gasworks, james bromfield, walter cockman, luther rodgers, city of melbourne gas coke company -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageNibs & box, late 19th to early 20th century
Box of dip pen nibs made by William Mitchell Calligraphy dating back to late 19th or early 20th century when dip pens with steel nibs were the main writing instruments. The pen nibs are shaped to fit into a slot in the base of a wooden or Bakelite pen holder. The hole at the front of the nib is for collecting ink from a well, which is then stored in a reservoir at the back of the nib. The nibs are stamped with their nib size and Pedigree (what type of nib it is) and maker’s details. William Mitchell Calligraphy still makes these nibs today with a slightly difference finish. (ref: Sales and Marketing Director of William Mitchell Calligraphy in 2016). HISTORY of the Ink Pen Quills and ink were common writing tools until the early 19th century when the pen trade began mass producing steel nibs and pens. The steel nibs each have a hole in the middle that acts like a well for the ink. When the nib is dipped into the ink well the writer needs to ensure that it is dipped to only just past that well. India Ink was one of the most popular inks used with the nib pens, notable for its satin-like smooth flow. This ink is composed of a particularly fine carbon mixed with water; it can also be obtained as a dry stick that is then crushed and mixed with water as required. The Jewellery Quarter of Birmingham had the largest concentration of independent jewellers in Europe. Birmingham became the centre of the world’s pen trade for many years -, during the 1800’s over 100 factories, employing 1000s of skilled workers, manufactured the ‘Birmingham Pen’. ABOUT WILLIAM MITCHELL CALLIGRAPHY LTD.* (*The following text is quoted from the William Mitchell Calligraphy website) British based William Mitchell Calligraphy has been designing and manufacturing exceptional pens for almost 200 years. The William Mitchell heritage in making pen nibs began whilst working with his brother John Mitchell in the early 1820s. William Mitchell established his own business in 1825 to become one of the leading nib manufacturers and famous for lettering pens. Almost 100 years later William Mitchell merged with Hinks, Wells & Co, another pen manufacturer, to form British Pens, employing around 1000 people in the Bearwood Road area of Birmingham. During the early 1960s British Pens acquired the pen business of other pen manufacturers Perry & Co and John Mitchell, once again reuniting the two brothers. Joseph Gillott, who were famous for their artist drawing and mapping nibs, amalgamated with British pens in 1969. William Mitchell and Joseph Gillott established in Birmingham during the early part of the nineteenth century and [their products] are still proudly made here. British Pens were subsequently purchased by its current owner Byron Head, the owner of William Mitchell (Sinkers) in 1982, and was subsequently renamed William Mitchell (calligraphy) Ltd. Established in 1827 Joseph Gillott was one of the pioneers of mass steel pen nib manufacturing. The company was particularly strong in the American market, prompting Elihu Burrit, the American consul, to write “In ten thousand school houses across the American continent between two oceans, a million children are as familiarly acquainted with Joseph Gillott as with Noah Webster” (The compiler of the famous American dictionary). The company consequently received visits from many notable Americans, including president Ulysses S Grant. Email on file, from Mike Chappell, Sales and Marketing Manager, William Mitchell Calligraphy, “20161122 - William Mitchell re pen nibs” How to use a dip pen to create modern calligraphy, https://thepostmansknock.com/how-to-use-a-dip-pen-to-create-modern-calligraphy/ India Ink, Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/India_ink birmingham Pen Trade, Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Birmingham_pen_trade The Pen Museum, http://penmuseum.org.uk/ The early 19th century invention and later mass production of pen nibs such these in our collection had a large impact on education and literacy because the nibs could be produced in great numbers and affordable prices.Box of patent Mitchell nibs containing 48 "Pedigree" nibs. Box depicts picture of William Mitchell on lid, and picture of nib pen on lid and side. Made in Birmingham, England. Nib “0505 Wm MITCHELLS PEDIGREE ENGLAND” Box “PEDIGREE / MAINFOLD SLIP”, “WILLIAM MITCHELL / BIRM - - - - - - LOND” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, william mitchell calligraphy ltd, pen nib, writing implement, writing accessories, dip pen, birmingham manufacturer, communication in writing, mass produced pen nibs -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesNewspaper, Lack of support may close hall, 1977
"The Mechanics Institute movement flourished in Victoria from 1839 to 1950. It was based on the development of Mechanics’ Institutes in Scotland and England from the 1820s, which were intended to educate and enlighten the working classes. The term ‘mechanic’ in those days meant an artisan, craftsman or working man, especially those who had moved from rural areas to work in new city factories during the Industrial Revolution. The early Institutes were usually equipped with a reading room, a library and a lecture room. Although enjoying mixed success in Britain, they contributed to the development of public education and library services. The movement was adopted more enthusiastically in the colonies. It began slowly in Victoria but its expansion after the gold rushes population influx was rapid, especially in rural areas. Every suburb and town wanted to have a Mechanics’ Institute. During the 1850s approximately forty Institutes were established, with even greater growth in the period 1860 to 1900. By 1900 there were 400 Institutes in Victoria. The establishment of a Mechanics’ Institute was often a great achievement for a local community, requiring organising committees to raise substantial funds for a building site (where this had not been granted by the Government), and the building. Once built, the committee then had to purchase books, provide a caretaker or librarian, and finance the ongoing use of and improvements to the building. ‘The history of many Institutes is a story of tremendous community effort, and often, financial difficulties’. In addition to being monuments to local enterprise and community life, the Mechanics’ Institutes played a vital role as an intellectual forum, and in contributing to an informed and participatory democracy in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. They provided journals and other reading matter on local, state, national and international issues, and hosted of lectures and held debates about wider issues such as Federation, colonial nationalism, defence, female suffrage, the price of land and labour. With the development of the school and technical education in the latter part of the nineteenth century, the need for community technical and adult education declined. As a result of the introduction of government library grants in 1867, many Mechanics’ Institutes incorporated a free library in their buildings to finance collection of their books. By 1884-85, there were 257 free libraries in Victoria. However, government support and library grants dropped off in the 1890s depression. Entertainment took on a greater role in the 1890s, with the introduction of moving pictures, billiards rooms, games rooms (chess), concerts and dances. The First World War had a devastating impact on many rural communities, and some Mechanics’ Institutes were no longer viable. On the other hand the early twentieth century was also a time of agricultural development, and many country towns were growing in this period. The 1930s depression further limited growth of many libraries and reduced grants substantially. In response many Mechanics’ Institutes were renamed, for example as memorial halls, in order to retain and attract more patrons (eg at nearby Sunbury). The diminishing role for Mechanics’ Institutes and the preference for larger and better appointed halls (with supper rooms, cloak rooms etc) resulted in demolition of some small Institutes. The advent of cars, radios, and television also provided other opportunities for recreation, learning and entertainment. The greater role of municipalities in providing library services also eroded the need for free libraries. While over 500 Mechanics’ Institutes or halls are extant, very few of these retain their original role as ‘diffusers of useful knowledge’. Most are still available for community purposes, as venues for meetings, socials, civic occasions etc, while others are employed as museums, shops and theatres. Most buildings are on Crown land, and managed by a delegated committee of management, who are responsible for raising revenue to maintain aging buildings. Many of those which were originally established on private land, such as Melton, have since reverted back to the Crown, and municipal Councils. The most common Mechanics Institute building form is the simple weatherboard gable building with iron roofs, notable for their ‘honest simplicity’ rather than as ‘monuments of the ancients’. At the other extreme there are some magnificent two storeyed brick and stucco structures with elaborate ornamentation (as was apparently envisaged by some in Melton in 1905-10)". The future of Melton Mechanic Institute Gazette articlelocal architecture -
 Mrs Aeneas Gunn Memorial Library
Mrs Aeneas Gunn Memorial LibraryBook, George Routledge and Sons, The mill on the floss, unknown
The classic tale of one young woman's quest for fulfillment in 1820s England, and the price she would pay for true freedom. Maggie Tulliver's entire life has been spent in the shadow of Dorlcote Mill on the River Floss with her beloved older brother, Tom. But when their father meets an untimely death, the siblings' singular bond is strained as Tom is forced to leave his studies and Maggie struggles to find a sense of belonging. Maggie's sharp intelligence and spirited nature have made her an oddity in the rural hamlet of St. Ogg's, where such unique qualities are perceived as unbecoming for a woman. Her need for recognition and love eventually drives her to defy her brother, who casts her out of his house to survive on her own. Forced to grieve the losses of both their father and each other, the siblings will have to find it in their hearts to forgive in order to reconcile before tragedy strikes again. Inspired by events in the life of the author, The Mill on the Floss is George Eliot's most heartfelt novel and one of her most compelling and moving worksp.765.fictionThe classic tale of one young woman's quest for fulfillment in 1820s England, and the price she would pay for true freedom. Maggie Tulliver's entire life has been spent in the shadow of Dorlcote Mill on the River Floss with her beloved older brother, Tom. But when their father meets an untimely death, the siblings' singular bond is strained as Tom is forced to leave his studies and Maggie struggles to find a sense of belonging. Maggie's sharp intelligence and spirited nature have made her an oddity in the rural hamlet of St. Ogg's, where such unique qualities are perceived as unbecoming for a woman. Her need for recognition and love eventually drives her to defy her brother, who casts her out of his house to survive on her own. Forced to grieve the losses of both their father and each other, the siblings will have to find it in their hearts to forgive in order to reconcile before tragedy strikes again. Inspired by events in the life of the author, The Mill on the Floss is George Eliot's most heartfelt novel and one of her most compelling and moving worksengland - fiction, romantic fiction -
 The Celtic Club
The Celtic ClubBook, Patrick O'Farrell, Letters from Irish Australia 1825-1929, 1984
Letters ranging from those of convicts writing to their wives in the 1820s, through accounts of the voyage out and pioneering life in mid-century, through love letters, to short stories and failure to master the land, to the remarkable family saga (1883-1929) which ends the book.Index, bib., p.218.non-fictionLetters ranging from those of convicts writing to their wives in the 1820s, through accounts of the voyage out and pioneering life in mid-century, through love letters, to short stories and failure to master the land, to the remarkable family saga (1883-1929) which ends the book. irish - australia - correspondence., australia- minorities- history. -
 Narre Warren and District Family History Group
Narre Warren and District Family History GroupCD, Patricia M Frei, Historical indexes of the Canberra/Queanbeyan district, 2006
Historical Indexes of the Canberra Queanbeyan District in 4 volumes Volume 1: Bungendore & Michelago NSW contains: 1. Registers of St. Mary's Church, Bungendore NSW: Baptisms 31 Dec 1882-23 Dec 1888 (extracts only) recorded at the back of the Queanbeyan Baptismal Register 1843-1877 2. Court Records, Bungendore NSW: Bench Books 29 Jul 1870-30 Nov 1891-Police & Summons Cases 3. St. Patrick's Church (Catholic), Michelago NSW: Baptisms 1891-1922; Marriages 20 Nov 1899-Oct 1936 & Oct 1937-1946 (selective entries only); Liber Defunctorum [Deaths & Burials] 1910-1973; Clergy List 1891-1972 4. Michelago memorials (St. Patrick's & St. Thomas's); Michelago cemetery register; Jerangle cemetery memorials 5. Court Records, Michelago NSW: Bench books: Police & Summons Cases 1875-1936 including Tickets of Leave; Free Reports; Passports; Applications for Conditional Pardons Volume 2: Council & Court Records, Queanbeyan NSW contains: 6. Selective notes from the: Minutes of meetings of Queanbeyan Municipal Council 1885-1926; Borough Council Record Book; Halloran & Co. vs Queanbeyan Municipal Council; Commons Trust Minute Book 1899-1916 7. Notes transcribed from the District Council Papers 1843-1847 8. Notes transcribed from the Yarrowlumla Shire Council Minutes Apr 1907-Feb 1950 9. Courthouse Records: Minutes of Proceedings in Court of Review, Queanbeyan (selective 1899-1903); Bailiffs Execution Book (selective entries 1897-1918) 10. Notes transcribed from the Bench of Magistrates Correspondence 1833-1851 11. Free Reports 1846-1847; Small Debts Register 1849-1864 (incl Return of Ticket of Leave Holders); Court of Requests-Judgement book Sep 1854- May 1859 (to Jan 1864) & Cash Book: Sep 1844-Aug 1846 12. Selective notes from the Court of Claims: Register of Cases from 1835 13. Publicans Licences 1841-1862 recorded in the Deposition Book from 1838 14. Bench Records-Queanbeyan 1838-1896 Volume 3: Land and Other Records contains: 15. Research notes from the: Queanbeyan Conditional Purchase Registers 1862-1872, 1874-1877; Selections made 1870-1879 under the Volunteers Regulation Act 1867; Conditional Purchase Registers, Queanbeyan 1862-1878; Dates of Birth-Juvenile Selectors 1872-1878 (selective) 16. Alienation of Lands 1812-1853 (selective Queanbeyan & district) incl. County Register 1829-1839 (King, St. Vincent, Murray Counties) 17. Land Selection 1869-1872, 1874-1876 (selective research notes on Queanbeyan & district) 18. Selective notes from the Royal Commission on the Site for a Federal Capital (site proposed at Queanbeyan: Wanniassa, Canberra, Lake George 1899-1902) 19. Teachers in Public Schools 1884 (selective Queanbeyan & district) 20. Notes transcribed from the Queanbeyan School of Arts Minute Book 21 Jul 1925-22 Jul 1935 21. Index to Obituaries & Personal Notices circa 1820s-2001 Volume 4: Parish Registers & Burial Records contains: 22. Deaths registered at Queanbeyan NSW 1856-1901 & Burials in outlying cemeteries 1856-1907 23. Queanbeyan NSW-Gemetery records transferred from denominational trustees 24. Supreme Crt of NSW-Probate Index 1800-1901 (extracts relating to the Queanbeyan district) 25. Supreme Crt of NSW-Wills & Administrations 1800-1901 (extracts only) 26. Cemetery transcriptions—Michelago, Riverside-Queanbeyan, Gundaroo, Upper Gundaroo, Barnsdale-Gundaroo, St.Thomas-Carwoola, Ss Peter & Paul—Hoskingtown (all NSW), Weetangerra, Hall, Tharwa (all ACT) 27. Anglican Church of St. John the Baptist, Canberra: baptisms 1845-1900; marriages 1845-1877; burials 1844-1915 (selective Gundaroo entries only) 28. Christ Church (Anglican), Queanbeyan (selective): baptisms 1838-1866; marriages 1838-1909, burials 1838-1880,1913-1917,1920-1968 29. St. Gregory's (Catholic), Queanbeyan: baptisms 1843-1920; marriages 1843-1857,1856-1898, 1881; burials 1844-1877,1937-1967 (selective) 30. Ministrations by RevT Hassall, Diocese of Goulburn: baptisms 1836; baptisms by T Hassall 1827-1834,1836; marr 1827-1833; burials 1827,1829 31. Fr. J.J. Therry's registers (Catholic baptisms, marriages & burials), Queanbeyan district 1820-1838 32. Anglican Church of St. Clement's, Yass NSW (Gundaroo entries only): baptisms 1839-1863; marriages 1839-1853; burials 1839-1875 33. Parish Registers, Gunning NSW, (Gundaroo entries only): baptisms 1839-1930; marriages 1840-1850; burials 1842-18554 optical discsnon-fictionHistorical Indexes of the Canberra Queanbeyan District in 4 volumes Volume 1: Bungendore & Michelago NSW contains: 1. Registers of St. Mary's Church, Bungendore NSW: Baptisms 31 Dec 1882-23 Dec 1888 (extracts only) recorded at the back of the Queanbeyan Baptismal Register 1843-1877 2. Court Records, Bungendore NSW: Bench Books 29 Jul 1870-30 Nov 1891-Police & Summons Cases 3. St. Patrick's Church (Catholic), Michelago NSW: Baptisms 1891-1922; Marriages 20 Nov 1899-Oct 1936 & Oct 1937-1946 (selective entries only); Liber Defunctorum [Deaths & Burials] 1910-1973; Clergy List 1891-1972 4. Michelago memorials (St. Patrick's & St. Thomas's); Michelago cemetery register; Jerangle cemetery memorials 5. Court Records, Michelago NSW: Bench books: Police & Summons Cases 1875-1936 including Tickets of Leave; Free Reports; Passports; Applications for Conditional Pardons Volume 2: Council & Court Records, Queanbeyan NSW contains: 6. Selective notes from the: Minutes of meetings of Queanbeyan Municipal Council 1885-1926; Borough Council Record Book; Halloran & Co. vs Queanbeyan Municipal Council; Commons Trust Minute Book 1899-1916 7. Notes transcribed from the District Council Papers 1843-1847 8. Notes transcribed from the Yarrowlumla Shire Council Minutes Apr 1907-Feb 1950 9. Courthouse Records: Minutes of Proceedings in Court of Review, Queanbeyan (selective 1899-1903); Bailiffs Execution Book (selective entries 1897-1918) 10. Notes transcribed from the Bench of Magistrates Correspondence 1833-1851 11. Free Reports 1846-1847; Small Debts Register 1849-1864 (incl Return of Ticket of Leave Holders); Court of Requests-Judgement book Sep 1854- May 1859 (to Jan 1864) & Cash Book: Sep 1844-Aug 1846 12. Selective notes from the Court of Claims: Register of Cases from 1835 13. Publicans Licences 1841-1862 recorded in the Deposition Book from 1838 14. Bench Records-Queanbeyan 1838-1896 Volume 3: Land and Other Records contains: 15. Research notes from the: Queanbeyan Conditional Purchase Registers 1862-1872, 1874-1877; Selections made 1870-1879 under the Volunteers Regulation Act 1867; Conditional Purchase Registers, Queanbeyan 1862-1878; Dates of Birth-Juvenile Selectors 1872-1878 (selective) 16. Alienation of Lands 1812-1853 (selective Queanbeyan & district) incl. County Register 1829-1839 (King, St. Vincent, Murray Counties) 17. Land Selection 1869-1872, 1874-1876 (selective research notes on Queanbeyan & district) 18. Selective notes from the Royal Commission on the Site for a Federal Capital (site proposed at Queanbeyan: Wanniassa, Canberra, Lake George 1899-1902) 19. Teachers in Public Schools 1884 (selective Queanbeyan & district) 20. Notes transcribed from the Queanbeyan School of Arts Minute Book 21 Jul 1925-22 Jul 1935 21. Index to Obituaries & Personal Notices circa 1820s-2001 Volume 4: Parish Registers & Burial Records contains: 22. Deaths registered at Queanbeyan NSW 1856-1901 & Burials in outlying cemeteries 1856-1907 23. Queanbeyan NSW-Gemetery records transferred from denominational trustees 24. Supreme Crt of NSW-Probate Index 1800-1901 (extracts relating to the Queanbeyan district) 25. Supreme Crt of NSW-Wills & Administrations 1800-1901 (extracts only) 26. Cemetery transcriptions—Michelago, Riverside-Queanbeyan, Gundaroo, Upper Gundaroo, Barnsdale-Gundaroo, St.Thomas-Carwoola, Ss Peter & Paul—Hoskingtown (all NSW), Weetangerra, Hall, Tharwa (all ACT) 27. Anglican Church of St. John the Baptist, Canberra: baptisms 1845-1900; marriages 1845-1877; burials 1844-1915 (selective Gundaroo entries only) 28. Christ Church (Anglican), Queanbeyan (selective): baptisms 1838-1866; marriages 1838-1909, burials 1838-1880,1913-1917,1920-1968 29. St. Gregory's (Catholic), Queanbeyan: baptisms 1843-1920; marriages 1843-1857,1856-1898, 1881; burials 1844-1877,1937-1967 (selective) 30. Ministrations by RevT Hassall, Diocese of Goulburn: baptisms 1836; baptisms by T Hassall 1827-1834,1836; marr 1827-1833; burials 1827,1829 31. Fr. J.J. Therry's registers (Catholic baptisms, marriages & burials), Queanbeyan district 1820-1838 32. Anglican Church of St. Clement's, Yass NSW (Gundaroo entries only): baptisms 1839-1863; marriages 1839-1853; burials 1839-1875 33. Parish Registers, Gunning NSW, (Gundaroo entries only): baptisms 1839-1930; marriages 1840-1850; burials 1842-1855queanbeyan nsw, canberra district (act), parish registers, burial records
