Showing 62 items matching "19th century mining"
-
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Miners candle holder, Late 19th century
... 19th century mining... and district went to the gold mining districts in the 19th century... and district went to the gold mining districts in the 19th century ...This candle holder has a sharpened point to push or hammer into soft rock and a hook to hang on a ledge or piece of rock. It is intended to be used in a mine and many residents of Warrnambool and district went to the gold mining districts in the 19th century. But it could have been used in the Warrnambool district if a small night light was required in one of the many local quarries or even in the search for coal deposits in the region. It could also have been used in a household.This miner’s candle holder has no known local provenance but it is retained as an interesting example of a candle holder used in the past.This is a thin piece of metal tapering to a point at one end and curving around in a loop at the other end to make a handle. Along the straight metal piece is attached a curved metal hook. At the end of the loop is an open-ended circular piece with a serrated top. The circular piece has a rectangular-shaped end piece which enables the hole in the curved piece to be pushed out or pulled in to make the hole smaller or bigger. The metal is much rusted. 19th century mining, history of warrnambool -
 Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and Archives
Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and ArchivesBook, Richard Osburne, The history of Warrnambool, capital of the western ports of Victoria, from 1847 (when the first government land sales took place) up to the end of 1886, 1980
... and protectionism. settlement and contacts - 19th century. mining industry ...The history of Warrnambool, capital of the western ports of Victoria, from 1847 (when the first government land sales took place) up to the end of 1886 / by Richard Osburne Other Authors, Fraser, Malcolm, 1930-2015, (author of introduction, etc.) Tylee Memorial Collection368 pages, unnumbered and folded leaves of plates : illustrations (some colour), maps, portraits, plans ; 19 cmnon-fictionThe history of Warrnambool, capital of the western ports of Victoria, from 1847 (when the first government land sales took place) up to the end of 1886 / by Richard Osburne Other Authors, Fraser, Malcolm, 1930-2015, (author of introduction, etc.) Tylee Memorial Collectionvictoria. warrnambool, 1847-1886. facsimiles, government policy - initial period and protectionism., settlement and contacts - 19th century., mining industry - gold., race relations - violent - massacres, religions - christianity - missions., warrnambool (vic.) -- history., framlingham / purnim (w vic sj54-11), demography - census data, book -
 Ballarat Diocesan Historical Commission
Ballarat Diocesan Historical CommissionCandle holder, 7 branch candle holder (one of a pair)
... This pair of 19th century candleholders were presented... richest 19th century gold-mining entrepeneurs. J.A.Chalk ...This pair of 19th century candleholders were presented to Nazareth House Ballarat by J.A.Chalk one of Ballarat's richest 19th century gold-mining entrepeneurs. J.A.Chalk was a partner in the Madam Berry Mines together with Martin Loughlin and William Bailey and was Manager of the Buninyong Estate Co., the Band and Barton Co., the Sebastopol Plateau Co., and the Prince of Wales and Bonshaw Co. mines in 1887. Chalk was a Quaker and benefactor to many Ballarat institutions. He arranged for the Council Chambers to be made available for meetings of the Society of Friends (Quakers) in the mid 19th century.One of a pair of large 19th century ornamented candle holders for use in the Chapel at Nazareth House Ballarat presented by 19th century Ballarat philanthropist and gold-mining magnate.The candleholders are in two separate sections the heavy lead-filled brass base with demountable seven-branched candleholders surmounting the base. The lower portion or base form a single candlestick when the branched top section is removed. The branches are decorated with styalised rose petals and the tops of each base decorated with rims of neo-gothic coronas.Presented with King Regards By J.A.Chalk Ballarat.candleholders, candlesticks, nazareth house, ballarat. j.a.chalk, madam berry mines, goldmining, entrepenauer, buninyong, sebastopol, prince of wales, bonshaw co, quaker, society of friends. -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
... mining, or quartz reef mining, was common in 19th Century... mining, or quartz reef mining, was common in 19th Century ...This photograph depicts a reef mine in Beechworth. Reef mining, or quartz reef mining, was common in 19th Century Victoria. This gold mining technique requires mine shafts to be sunk into underground quartz reefs, with horizontal tunnels dug from the original shaft at differing levels to find the gold-bearing rock. The quartz would then be hoisted to the surface, which would then be pounded to access the gold in its metallic state. Gold was discovered in Beechworth in February 1852, at Spring Creek. Within 11 months of that discovery, over 8000 hopeful prospectors quickly descended on this region, transforming it into a thriving, wealthy township. Reef mining and hydraulic sluicing were gold mining techniques used in this region in the 19th and early 20th centuries. This photograph interestingly contains dogs alongside the miners. While dogs have been recorded as deterrents to thieves in the Victorian goldfields, these dogs appear as companions to these men.The search for gold is ingrained into the history of Victoria and therefore, images like this one can reveal important information for society and technology for the date when the photograph was taken. It also shows a location where reef mining was undertaken which provides insight into the impact on the environment at a time when it was done. Although quartz is one of the most common minerals found in the earth's crust, it does not always contain gold. Those reefs that do are rare and highly sought after by prospectors. The Beechworth Burke Museum has additional images relating to gold mining which can be analysed and studied alongside images like this one.Sepia coloured rectangular photograph printed on gloss photographic paper. Obverse: Reverse: United Shire of Beechworth/ Shire Secretary/ Reef Mining, Beechworth./ 6167.abeechworth, burke museum, gold, gold mining, gold rush, victorian gold rush, reef mining, quartz, companion dog, horse and cart -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Photograph - Reproduction
... in Beechworth. Reef mining, or quartz reef mining, was common in 19th... in Beechworth. Reef mining, or quartz reef mining, was common in 19th ...This reproduced photograph depicts a reef mine in Beechworth. Reef mining, or quartz reef mining, was common in 19th Century Victoria. This gold mining technique requires mine shafts to be sunk into underground quartz reefs, with horizontal tunnels dug from the original shaft at differing levels to find the gold-bearing rock. The quartz would then be hoisted to the surface, which would then be pounded to access the gold in its metallic state. Gold was discovered in Beechworth in February 1852, at Spring Creek. 8000 hopeful prospectors quickly descended on this region within the year, transforming it into a thriving, wealthy township. Reef mining and hydraulic sluicing were gold mining techniques used in this region in the 19th and early 20th centuries. This reproduction photograph interestingly contains dogs alongside the miners. While dogs have been recorded as deterrents to thieves in the Victorian goldfields, these dogs appear as companions to these men.The search for gold is ingrained into the history of Victoria and therefore, images like this one can reveal important information for society and technology for the date when the photograph was taken. It also shows a location where reef mining was undertaken which provides insight into the impact on the environment at a time when it was done. The Beechworth Burke Museum has additional images relating to gold mining which can be analysed and studied alongside images like this one.Black and white rectangular reproduction photograph on gloss photographic paper. Obverse: Reverse: L is miners 26%/ 10 x 8/ 6167.bbeechworth, burke museum, gold, gold mining, gold rush, victorian gold rush, reef mining, quartz, companion dog, horse and cart -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, est. 1860-1875
In 1875, the Rocky Mountain Extended Gold Sluicing Company Ltd was created, utilising the previous Rocky Mountain claim for the area near Lake Sambell. The company employed A.L Martin to survey an area for a tunnel underneath Beechworth and Johnson Stephens to dig it. The tunnel was built at a rate of 40 feet a month and eventually measured 800 metres. The tunnel was a true accomplishment both in the present and during the 19th century. It was considered to be a marvelous engineering feat. Beechworth is renowned for its hydraulic sluice method of mining. This involved soil being exposed to torrents of water from high-pressure hoses. From 1876 until its closure in 1921, the mine produced an astounding 47,926 ozs of gold. Companies like this were the source of income for many Chinese gold-diggers who sought to make their fortune on the goldfields of Beechworth. During the height of the rush, the town had around 7,000 Chinese inhabitants living on the outskirts of town as they were not permitted to live within Beechworth itself.The search for gold is ingrained into the history of Victoria and therefore, images like this one which portrays an open-cut sluicing site can reveal important information for society and technology for the date when the photograph was taken. This image is of important historical significance for its ability to convey information about sluicing and the methods used to find gold in 1910. It also shows a location where sluicing was undertaken which provides insight into the impact of sluicing on the environment at a time when it was done. This image of the Rocky Mountain mine is historically significant as the mining complex is now non-existent, with the only remains being the tunnel built in 1880 by the company, which was considered one of the greatest engineering feats of the time. The image also provides a first-hand look into the social and cultural networks at play during the 19th century with racial segregation of the Chinese at the 'Chinese Camp', as well as an insight into Beechworth's origins during the Gold Rush.A sepia rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper as a postcardReverse: Historic Beechworth / 7792.1 / ROCKY MOUNTAIN MINE / Viewed from the “Chinese Camp”, shown partly in the foreground, we see the central plant of the famous Rocky Mountain Mining Company. This extensive complex, of which nothing remains, was situated between Silver Creek and the present Lake Sambell area. The company was responsible for a tunnel cut through solid bedrock underneath the town of Beechworth and surfacing near the keystone bridge on the Wangaratta side. Completed in 1880 it was declared to be one of the greatest engineering feats in Australia. The tunnel is still basically intact today. / Series by Wooragee Graphics: Historic Beechworth. / COPYRIGHT BURKE MUSEUM / No.72 beechworth, rocky mountain mine, sluicing, gold rush, mining, gold -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, Estimate 1999
This photograph was taken in 1999 at 'The Harvest' exhibition at the Burke Museum for members of Baking Industry Victoria. The grain mill, manufactured by B.M. Purshouse in Wolverhampton, England, was of special interest.This photograph is of primary social significance to the Beechworth community because it depicts a 19th-century grain mill, manufactured by B.M. Purshouse in Wolverhampton, England, which was probably used at flour mills in the Ovens District, such as that at Tarrawingee, which opened in 1866. The purchase of agricultural machinery such as the grain mill accompanied the expansion of agriculture, including grain growing, in the Ovens District following the gold mining prosperity of the 1850s. This photograph may be of interest to researchers who wish to observe an image of the Purshouse grain mill.Colour rectangular photograph printed on matte AGFA photographic paper.Obverse: THE HARVEST / THE HARVEST Reverse: 2854beechworth, burke museum, promoting settlement, living in country towns, making regional centres, preserving traditions and commemorating, farming and agriculture, exhibitions, burke museum exhibitions, building local economies, transforming land, victorian agricultural history, marketing and promoting agricultural products, the harvest exhibition, harvests, victorian gold rush towns, grain mill, bm purshouse, crops and grain, baking industry victoria -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Stereoscopic Photograph, Unknown c1875
Depicted in the photograph is Newtown Bridge or the Newtown Falls Bridge, in Beechworth, Victoria. Noted for its location, detailed craftsmanship and stonemasonry by Scottish stonemasons the Newtown Bridge was built in the 19th century provincial town of Beechworth (completed in 1875). The bridge was built over Spring Creek, spanning 6.3 meters wide and 24.8 meters tall. Beechworth held a distinct role in the administrative and commercial management of Victoria's north-eastern goldfields, with many objects and structures still well preserved from the towns establishment. The bridge indicates the growth of the town, replacing a previous timber structure as well as its association to the mining activity in the area and the rapid increase in Australia's economy that led to investment and development of roads and railways. The local granite used in the construction of the single arch Newtown Bridge makes the bridge and other buildings made with the granite unique to the area, the honey-toned material distinct to Beechworth. This photograph is historically significant as it provides insight into the industrial development of Beechworth and the surrounding area, contributed to by the goldfields. The photograph further captures the representation of vernacular engineering traditions and Scottish stonemasonry.Two sepia-toned rectangular photographs featuring a bridge in the background printed on matte photographic paper mounted on card.Reverse: 97.2324/ Newtown Bridge/ Beechworthbridge, newtown beechworth, newtown bridge, newtown, beechworth, beechworth falls bridge, beechworth mining district, spring creek, -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Photograph - Reproduction
The photograph is a reproduction of a postcard from the Rocky Mountain Mining Company. In 1875, the Rocky Mountain Extended Gold Sluicing Company Ltd was created, utilising the previous Rocky Mountain claim for the area near Lake Sambell. The company employed A.L Martin to survey an area for a tunnel underneath Beechworth and Johnson Stephens to dig it. The tunnel was built at a rate of 40 feet a month and eventually measured 800 metres. The tunnel was a true accomplishment both in the present and during the 19th century. It was considered to be a marvelous engineering feat. Beechworth is renowned for its hydraulic sluice method of mining. This involved soil being exposed to torrents of water from high-pressure hoses. From 1876 until its closure in 1921, the mine produced an astounding 47,926 ozs of gold. Companies like this were the source of income for many Chinese gold-diggers who sought to make their fortune on the goldfields of Beechworth. During the height of the rush, the town had around 7,000 Chinese inhabitants living on the outskirts of town as they were not permitted to live within Beechworth itself.This image of the Rocky Mountain mine is historically significant as the mining complex is now non-existent, with the only remains being the tunnel built in 1880 by the company, which was considered one of the greatest engineering feats of the time. The image also provides a first-hand look into the social and cultural networks at play during the 19th century with racial segregation of the Chinese at the 'Chinese Camp', as well as an insight into Beechworth's origins during the Gold Rush.Black and white rectangular reproduced photograph printed on paperbeechworth, rocky mountain mine, sluicing, gold rush, mining, gold -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, c1960
The photographs in this set depict views across the water at Lake Sambell. The images date from approximately 1960. The present day park and reserve occupies the site of the former Rocky Mountain Mining Company, an open-cut sluice mine that began operations in the mid-19th Century and operated until the early 1900s, through the peak of Victoria’s Gold Rush. It was converted into a park and leisure area in the 1920s. Lake Sambell was formally opened to the public on Friday 5th October 1928 and was opened by the Victorian Government’s Minister of Lands, Mr Bailey, as part of initiatives to boost the economies and development of country towns. The lake was named after Mr L.H. Sambell, a shire engineer and secretary of the Forward Beechworth Committee who was involved in promoting the transformation of the mining site and promoting plantation forestry and tourism as alternative industries. £300 to begin the process was provided by Mr J. McConvill, a former resident of Beechworth, who is remembered in a street name adjacent to the lake. Residents of Beechworth have worked to raise funds to improve the Lake Sambell reserve several times, such as efforts in the 1930s and 1940s to raise the banks several feet to deepen the water for swimming purposes. Fundraising campaigns include the ‘Ugly Man’ competition conducted on behalf of the Wallace Park-Lake Sambell Development Scheme. The latter competition was run by the Fire Brigade Bend’s team as part of a larger competition called the ‘Mile of Pennies’; it was won by Mr Len Knight of Beechworth’s Commercial Hotel. The ‘Mile of Pennies’ was conducted at a Carnival held on New Year’s Eve, 1947. It was proposed by the Beechworth and District Progress Association. As well as improving swimming facilities, funds were raised to install a caravan park facility near the lake. Funds were also donated by commercial entities, such as £250 received from Zwar Bros. Pty Ltd.The photographs are significant as they show the level of development in Beechworth in the middle of the Twentieth Century. Four sepia and black and white rectangular photographs printed on matte photographic paper. 3469.1: Obverse: nil Reverse: 3469-1 3469.2: Obverse: nil Reverse: 3469-2 3469.3: Obverse: nil Reverse: 3469-3 3469.4: Obverse: nil Reverse: 3469-4beechworth, beechworth lake, lake sambell, lake, beechworth and district progress association, forward beechworth committee, ugly man, mile of pennies, wallace park lake sambell development scheme, wallace park-lake sambell development scheme, zwar bros, zwar, l.h. sambell, j. mcconvill, minister of lands, commercial hotel, len knight, rocky mountain mining company, rocky mountain mining co, gold rush, redevelopment, transformation, community fundraising -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Cassiterite
This specimen is Cassiterite in Quartz. Cassiterite is a tin oxide metal that forms in thin crystals which can have a beautiful lustre. Quartz is made of silicon dioxide, also known as silica, and is one of the most common minerals on earth. Cassiterite has been a fundamental source of tin ore for humans throughout history, including today. Tin is an important metal that has a wide variety of human uses in different areas, from dying fabric, to making mirrors, and their most well-known use ‘tin’ cans. Tin cans are primarily made of steel and are coated with tin in order to take advantage of tin’s property of being non-corroding. This is a massive step in the history of food preservation. Tinned food first reached Australia in 1815 with early settlers, and it began to be manufactured here in the 1840s. It was incredibly popular, and was a highly exported product, which would be a contributing factor to the ‘tin mining boom’ of the early 1880s. This specimen was collected at Jingellic, New South Wales, in about 1852. Although the Goldfields of the 1800s are much more well-known, tin mines existed alongside the gold mines which began in the mid 19th century and extended almost one hundred years, to the mid 20th century. Specimens like this would have been used as evidence to justify tin mining operations in the region as an investment. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study. The Geological Survey of Victoria was headed by British geologist, Alfred Richard Cecil Selwyn (1824-1902), who was responsible for issuing over 60 geological maps during his 17 years as director. These maps were all hand-drawn and coloured and became the benchmark for accuracy for geological mapping. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study. A fist-sized solid geological specimen made on one half of tin oxide, which is dark grey, and on the other side of silica, which is brown and cream.burke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyspecimen bottle, circa 19th, early 20th century
... in the Orbost district began in the last half of the 19th century ...On loan from John Mundy family. Searching for gold in the Orbost district began in the last half of the 19th century and continued until circa 1930s. The original Mundy family moved to a land "selection" at Betebolong in the early 1880's from Buchan. This item is reflective of the late 19th -early 20th century gold mining era in East Gippsland.A small square bottle with a push-in cork stopper. This bottle contains specks of gold or gold dust. mining-gold -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photograph, 1897
... . This is a pictorial record of gold mining in East Gippsland in the late 19th ...The photo shows miners looking for gold at Dead Horse Creek at Club Terrace. The subjects are unknown.This is a pictorial record of gold mining in East Gippsland in the late 19th century.A yellowed black / white photograph on grey buff card. It is of seven men in the bush mining for gold.on back - "Dead Horse Creek - Club Terrace, 1897"gold-mining gold-panning-club-terrace dead-horse-creek-gold -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photograph, 1895 - 1905
... mining in East Gippsland during the late 19th - early 20th ...This photograph shows the Battery Goldmine at Club Terrace from 1896 - 1905. Gold was found at Club Terrace in 1896. One of the best finds at Club Terrace was the 'Ace of Clubs' mine which was later sold to the Mallina Gold Mining Company. Syd Cadwallader was appointed manager of the company. The gold was smelted and brought to Orbost on horseback. The only protection against thieves was a revolver and riding crop, which the manager always carried. The 'Ace of Clubs' was eventually closed as the company was unable to cope with the rising water problem. (information Newsletter February 2011 - John Phillips)This is a pictorial record of gold mining in East Gippsland during the late 19th - early 20th century.A black / white photograph of a mine site with timber mine constructions spread around. There is a river in the foreground. Some wooden buildings can be seen in the background.gold-mining-battery-mine club-terrace -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
This photograph dating between the 1850s and early 1900s depicts an open cut sluicing site located in Allan's Flat looking upon the open cut from Staghorn Flat Number 1. Sluicing was undertaken in the area from 1850 to 1904. The image depicts a location mined by Yackandandah Sluicing Co. It portrays and open space with pipes laying on the ground and connected to pipes leaving the barge. These pipes were used to wash and seperate the qaurtz. There are two small buildings on high ground over looking the barge. Yackandandah Sluicing Co. was created by J.A. Wallace in the 1880s. The Yackandandah Sluicing Co. operated from the mid-1880s to the early 1900s, when resources eventually ran out. Open cut sluicing involved the use of high-powered hoses which used the centrifugal sand pump system (known as hydraulic sluicing) which broke down the soil which was then processed for quartz, gold and other materials. After the resources where drained, Wallace reaped the benefits of his mining business. Allan's Flat is located on the Yackandandah Creek, and is 10km north-east of Yackandandah and 20km south of Wodonga in Victoria's regional north-east. Allan's Flat was initially used to mine gold through alluvial methods, however that came to an end with little results. The mining business was then revived by J.A. Wallace with the introduction of hydraulic sluicing.The search for gold is ingrained into the history of Victoria and therefore, images like this one which portray an open cut sluicing site can reveal important information for society and technology for the date when the photograph was taken. This image is of important historical significance for its ability to convey information about sluicing and the methods used to find gold and other minerals in the lat 19th Century. It also shows a location where sluicing was undertook which provides insight into the impact of sluicing on the environment at a time when it was done. This image is important for current research into the history of Allan's Flat, a small regional location near Yackandandah in Victoria's North East. Therefore, this image has the capacity to be beneficial for research into society and the motivations of those living and working in this region during this period and therefore, has social significance. The Beechworth Burke Museum has additional images relating to gold sluicing and Allan's Flat which can be analysed and studied alongside images like this one.Sepia coloured retangular photograph printed on gloss photographic paper mounted on board.Revers: Sluicing at Allan's Fortallan's flat, north east gold, sluicing, gold sluicing, hydraulic sluicing, mining, gold and quartz mine, beechworth, burke museum, yackandandah -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photograph, 1896 - 1905
... mining in East Gippsland during the late 19th - early 20th ...This photograph shows the Battery Goldmine at Club Terrace from 1896 - 1905. Gold was found at Club Terrace in 1896. One of the best finds at Club Terrace was the 'Ace of Clubs' mine which was later sold to the Mallina Gold Mining Company. Syd Cadwallader was appointed manager of the company. The gold was smelted and brought to Orbost on horseback. The only protection against thieves was a revolver and riding crop, which the manager always carried. The 'Ace of Clubs' was eventually closed as the company was unable to cope with the rising water problem. (information Newsletter February 2011 - John Phillips) This is a pictorial record of gold mining in East Gippsland during the late 19th - early 20th century.A black / white photograph of an operational mine with scaffolding and bridges. There are several men standing in front.mining-club-terrace mallina-mine battery-mines gold-mining-east-ippsland -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Letter, Power of Attorney Augustus Bostock, 1888
Augustus Bostock was the 9th child of Robert & Rachael Bostock of Vaucluse Epping Forest, Van Diemen’s Land. He was only 4 years old when his mother died. He was inspired by his father to seek his fortune in the Western District of Victoria. He arrived around 1850. He married Margaret Aitkin in July 1865. Augustus owned several properties in the district and leased others. He sat on the court of Warrnambool, Mortlake or Hexham as required. He resided at Marramook in Hawkesdale and later moved to Vaucluse in Hopetoun Road Warrnambool, where he died in 1920 at the age of 87. He was involved in many aspects of life in the Western District, racing, cricket, and social activities to name a few. This document relates specifically to power of Attorney in relation to the Croydon goldfields in Northern Queensland which operated in the latter part of the 19th century. By 1907 it was failing although there were attempts to revive it in the 1920’s. Patrick O’Neil authorized as the agent for Augustus Bostock was a confidential mining agent for Sandhurst mines one of the larger mining companies at that period of Australian history.This is one of a number of documents which relate to the Bostock family who were one of the most important pioneering families of the Western District. They owned and leased various properties around Warrnambool and were involved in many aspects of social and business life. This letter records one of Augustus Bostock’s many interests, being for the Croydon goldmine which is situated on the Gulf of Carpentaria.White lined paper handwritten in black ink. Coomete, Hexham, Victoria printed at top right hand corner.Signed Augustus Bostock.warrnambool, augustus bostock, croydon goldmines, sandhurst mines, 1888, goldmining, patrick o’neil, -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Federation University Australia: Celebrating 150 Years, 2020
Blue covered book celebraring 150 years since the establishment of the Ballarat School of Mines in Ballarat. Many illustrations from the Federation Univsity Historical Collection. non-fictionfederation university, history, anniversary, sesquicentenary, terry moran, duncan bentley, cameron pegg, carolyn simm, clare gervasoni, margot burke -
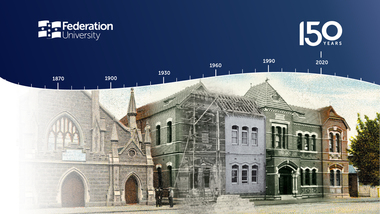 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionArtwork, other, Federation University Australia: Celebrating 150 Years Screen Background, 2020
Since the establishment of the School of Mines Ballarat (SMB) in 1870, Federation University Australia has emerged in multiple forms, and under multiple names, to educate generations of engineers, nurses, and teachers – and in more recent years, games designers, sports and exercise scientists, craft beer brewers, and other professional occupations inconceivable to the University’s founders in the late 19th century. Today, our footprint stretches around the world, thanks to key partnerships established domestically, and with institutions in China, Malaysia, and India. But the story starts with a meeting of the Ballarat Mining Board, in 1869, and a pressing need for innovation.A number of screen backgrounds used during 2020, the 150th anniversary of the Ballarat School of Mines. The anniversary took place in the middle of lockdowns associated with Covid19, making screen backgrounds important.non-fictionfederation university, anniversary, sesquicentenary, 150th anniversary, covid19 -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyMiners Pick - short
Formerly KV 071. It was used to break up rock and ore, making it easier to extract valuable minerals. The pointed end of the pick axe was used to chip away rock, while the flat end was used to strike the rock for breaking it apart. This one has a short handle. Miners picks were commonly used in the the 19th and early 20th centuries for extracting gold from underground mine tunnels.Used in the Kiewa Valley where prospecting for gold occurred.Formerly KV 071. Cast iron symmetrical pick tool on cast iron with a wooden handle. It has a pointed end and a flat end. It is 12 inches long.gold mining, miners' pick axe, hand tool -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical SocietyCertificate - share, 30/10/1940
Share certificate issued by New Gippsland Boulder Mine - operating at Errinundra and receipt for Herbert, Eric W. Receipt is for amount of four pounds - signed by Bird, W. Prospectus was printed in 1934 at office of Snowy River Mail - 4 page booklet. Gold, copper and silver were the target minerals.The crusher from the Boulder Mine is now at the Slab Hut in Orbost. The first Gippsland Boulder Co.,was at Boulder Creek – 13 miles north of Club Terrace, within 2 miles of Errinundra River. The company registered in January 1898 and commenced crushing in September with a 10-head battery. In the first nine months’ yields totalled 1,418 oz from 972 tons.There was a tramway between the mine workings and the battery.The crusher from the Boulder Mine is now at the Slab Hut in Orbost. This document is a reference for gold mining and exploration in the Far East Gippsland area. The Herbert family has reside in Orbost since the late 19th century.Copy of New Gippsland Boulder Mine share certificate and receipt. Framed in small black wooden frame.certificate-share-new-gippsland-boulder-mine mineralogy mining boulder-creek -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photograph, late nineteenth - early 20th century
Gold was found at Club Terrace in 1896. One of the best finds at Club Terrace was the 'Ace of Clubs' mine which was later sold to the Mallina Gold Mining Company. Syd Cadwallader was appointed manager of the company. The gold was smelted and brought to Orbost on horseback. The only protection against thieves was a revolver and riding crop, which the manager always carried. The 'Ace of Clubs' was eventually closed as the company was unable to cope with the rising water problem. (information Newsletter February 2011 - John Phillips)This is a pictorial record of mining methods in East Gippsland in the late 19th century to early 20th century.A black / white photograph of a mine. It is in a bush setting. Men are standing in front of timber mine constructions. Some wooden buildings can be seen behind the structureson back - "Cadwallader's Malina Mine"mining-gold mining-east-gippsland cadwallader-malina-mine gold-mining-battery -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societychoker
Jet came into common usage in the 19th century when a small town in England, Whitby, began mining jet to make mourning jewellery. When Queen Victoria declared that her court wear mourning attire for the three years after the death of Albert,and that only jet jewelry was to be worn at court for the first year jet jewellery was widely worn. In the Victorian era, there was a wide variety of materials used to mimic Whitby Jet for mourning jewelry. This item is an example of typical mourning style jewelry which became popular as a universal form of adornmentA black jet bead choker with fasteners at the ends.jewellery choker jet -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionProgramme, Programme for the Official Opening of the Mt Helen Campus, 10/1970
The first building at the Mt Helen Campus was opened in October 1970. Students first starting using the campus in the same year. The programme includes the following historical information: "On 26th October, 1870, Sir Redmond Barry officially opened the first venture into formal technical education in Australia - the Ballarat School of Mines. Over the preceding year a small group of Ballarat citizens interested in mining had conceived and brought into being the idea of creating such a school. They leased a derelict Court House next to the Ballarat Gaol in Lydiard St., at a nominal rental for15 years, and started classes with 4 students and an honorary lecturer. The School developed its courses beyond the initially intended range of studies related to mining, increased in enrolments, took over neighbouring properties and buildings and developed three levels of education - tertiary, trade and secondary. From the latter part of the 19th Century, even though remaining under the control of its own autonomous Council, it developed close links with the State Education Department. From the earliest times the School achieved widespread recognition and a particularly high reputation, and its graduates spread across Australia and the world. For several years it was affiliated with Melbourne University. In the last decade its scope has been further broadened by the introduction of new tertiary courses. During 1965 the State Government created the Victoria Institute of Colleges - a non-teaching body empowered to award degrees and directed towards the task of co-ordinating and developing tertiary education in Victorian in institutions other than universities. the tertiary division of the School became affiliated with the V.I.C. at the end of that same year. Subsequently the Council of the School decided that, whilst retaining for the whole establishment the time honoured title - The School of Mines and Industries, Ballarat - it should more distinctly sub-title the three divisions. the tertiary division then became known as the Ballarat Institute of Advanced Education. On receipt of substantial Commonwealth-State Grants, made to it as a college of advanced education, the Council was enabled at the start of 1967, to purchase for the Institute the 20 acre campus at Mt Helen. A master plan has been produced to develop this beautiful and spacious site as a tertiary institution enrolling, in due course, some 3000 full time students. the first sod was turned, to initiate this development, by the then Governor General of Australia, The Right Honourable Lord Casey, on 19th October, 1967. The first building group, now completed and occupied, has involved an expenditure approaching $1,000,000. It contains the departments of Mechanical, Civil and Mining Engineering, Metallurgy and Geology. it also contains the Computer Centre, a temporary Library and temporary student amenities. Over the next two years a further four buildings, costing about $2,500,000, will be erected, and a further major portion of the Institute will move to Mt Helen. these buildings, in addition to one for direct teaching work, will include a Library, a Union and the first stage of a Hall of Residence."White, folded, paper programme printed on the occasion of the official opening of the Ballarat Institute of Advanced Education (BIAE) Mount Helen Campus on the occasion of the centenary of the Ballarat School of Minesuniversity of ballarat, ballarat school of mines, biae, mount helen, mt helen campus, mb john, jack barker, e.j. barker, rolly parfenovics, parfenovics, nigel bown, campus. victorian institute of colleges, m.b. john -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Machinery for Metalliferous Mines, 1894, 1894
... of the machinery used in late 19th century metal mining in the UK ...The 1st edition of this famous work, giving an excellent account of the machinery used in late 19th century metal mining in the UK and overseas is very rare. It covers a wide range of equipment - pumps, steam engines, drills, winding engines, stamps & concentration mills, aerial ropeways, tramways and early uses of electricity etc. Brown hard cloth covered book. xvi 564 pages with additional advertisements, with over 300 illustrations and drawings, some fold out. Chapters include Water as a motive power, Wind engines and ventilating machinery, Steam boilers/engines and oil engines, hoisting machinery, draining of Mines, pumping engines, rock drilling machinery, boring machinery, concentration machinery, sizing and classifications trommels, joggers and jigging, fine concentration, milling of gold ores, milling of silver ores, amalgamation plates and machinery, dry and roasting machinery, chlorination and cyandide processes for the extraction of gold, electricity as a motive power for mining, electric lighting and blasting, aerial wire ropeways, transport by rail and road. There a a number of lovely line illustrations in the book including: Poncelot's undershot waterwheel; Fromont furnace;Victor turbine; Pelton waterwheel; Root's positive blower;Cross section and front elevation of Lancashire boiler; Robey's Compound Mill Engine; Portable Winding Plant; Iron Pit Head Gear ; Loading Arrangement in an Incline Shaft; kibble; Worthington Pump; California Pump; Scram's Air Compressor; Rock drill Bits; Special Sharpening tools; Boring tools;Rotating Picking table; Ore Feeder; roller crusher; stamp battery; round buddle; slime table; vanner; amalgamating plant; belt elevator;roasting furnace;splicing wire rope; capel; tipping waggon;mining, cornish pump, linkenbach table, water wheel, ventilation, oil engine, california, america, water, steam boilers, steam engines, oil engines, pumpimg, rock drilling, boring, jiggers, milling, silver, gold, drying and roasting, chlorination, cyaniding, lead, zinc, copper, electricity, electric lighting, wire ropes, transport, wind engine, poppet head -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Chemical Storage Jug, Wilhelm & Marie Wischer, 1895-1920
Wilhelm and Marie Wischer were the founding couple of the successful Wischer phosphate and chemical works at Yarraville, Melbourne. They had emigrated from Magdeburg in Germany in the late 19th century and had undertaken the journey to Australia over three months. During this voyage, several passengers had died and a number of babies had been born. The travellers had endured storms, injuries, broken equipment, and numerous other privations. The couple had lived in the suburb of Hawthorn and their family history is documented in a book by John Wischer. The link is in references this document from "Kainos Books" and makes for fascinating reading as it reveals an account of life in Melbourne during the late 19th and early 20th century. The book also gives an account of the Wischer phosphate mining activities on Ocean Island in 1904, Wischer & Co. eventually merged with Mt. Lyell Chemical works.An item giving a snapshot of early industrial life in Melbourne during the late 19th century with also an interesting story of early migration to Australia. The item also makes us aware of the privations early migrants had in trying to establish a life in a new country and how the Wischer family overcame these challenges to establish a very successful business.Jug, clay large with handle glazed screw on stopper. Sulphur Acid Wischer Chemical Company Yarraville printed on side, also a number 5 on the screw lidflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Tool - MERCURY BUCKET
... mining in 19th century Victoria. Peter Davies1... in 19th century Victoria. Peter Davies1 Susan Lawrence and Jodi ...Cast iron mercury bucket, used to hold mercury, potentially in the process of recovering minute pieces of gold mixed in soil and sediments. See research page for description of one process of using mercury to extract gold.gold mines, mining equipment, mercury bucket, miners used mercury in a number of ways to amalgamate gold, with each mill or battery operator having their preferred method depending on the nature of the ore. by the late 1850s the most common way of crushing goldbearing quartz ores or consolidated alluvial cements was in a stamp battery. the battery featured heavy iron stamp heads held in a frame, with each head often weighing up to 500 pounds (226 kg) or more (see msv 1880, page 45) (birrell 2005). stamp heads were lifted and dropped by a rotating overhead cam shaft driven by a steam engine or water wheel. ore was fed into a large cast-iron battery box, mixed with a steady stream of water, and pulverised by the stamp heads. in some batteries, mercury was placed in the base of the boxes to amalgamate with freed gold. the violent agitation of the mercury in the mortar box, however, could cause the mercury to break into myriad tiny globules that were carried away by the water with the tailings, thus losing a certain amount of gold in the process (thompson 1867; ritchie & hooker 1997). the water and sand slurry was splashed by the falling stamps from the box through fine mesh screens and onto inclined wooden tables below the mortar box (figure 2). the tables were covered with copper sheets or plates coated with mercury, which caught and amalgamated with a portion of the gold. the grey putty-like amalgam was periodically scraped off the sheets and retorted in a furnace to collect the gold and recover the mercury for reuse. mercury was inevitably lost from the plates, while poor maintenance resulted in further losses of gold and mercury in the tailings. mercury use and loss from gold mining in 19th century victoria. peter davies1, susan lawrence, and jodi turnbull, department of archaeology and history, la trobe university. -
 Myrtleford and District Historical Society
Myrtleford and District Historical SocietyMemorial Plaque, Memorial Plaque Factory, "Dead Man's Penny", Circa 1921
The "Dead Man's Penny" of Private George Matthews (24/1744) is a district link to the First World War. George enlisted with the Otago Regiment, New Zealand Expeditionary Force as a rifleman. Born in 1891, he was a former pupil of Myrtleford State School 955 and was one of four first cousins killed in action and recorded in a memorial window and honour board at the Uniting (formerly Methodist) Church, the Soldier's Memorial Square and on the State School Honour Board. George's parents, John and Mary Matthews,received the plaque in a pack, together with a letter and commemorative scroll from King George V. George Matthews is buried at the Caterpillar Valley (N.Z.) Memorial, France, having died on October 1, 1916, aged 25. The memorial plaque links local family tragedy to world conflict. It represents the impact of such events must have had on small town communities. George Matthews' enlistment in New Zealand is an indicator of the migratory nature of men involved in gold mining after the decline of the industry in Victoria and New South Wales in the late 19th centuryA World War 1 memorial plaque issued to next-of-kin of all British and Empire service personnel who died as a result of the war. They were round and cast in bronze, hence their similarity to the much smaller penny coin. The plaque includes an image of Britannia, holding a trident and standing with a lion. Britannia holds an oak leaf above the deceased's name, which is recorded without rank. Two dolphins swim around Britannia, symbolizing sea power, and at the base a second lion is tearing apart the German eagle. Around the picture a legend reads: "He died for freedom and Honour"Name engraved: GEORGE MATTHEWSmemorial plaque dead man's penny george matthews -
 Myrtleford and District Historical Society
Myrtleford and District Historical SocietyGold Mining Sign
This sign was required to be displayed in the vicinity of gold mining sites. Myrtleford district was known to have had 100 sites within a ten mile radius of the town; the sign was recovered by Charlie McFadyen, a local prospector and fossicker, of some 60 yearsThe sign relates to local gold mining activity, a key source of wealth and employment from 1854 to the late 19th century. Such signs continued to be in use during the period between World War 1 and 2,including the period of the Great Depression.Tin rectangular mining sign embossed with a warningInscription: "THIS LAND IS AURIFEROUS AND SUBJECT TO MINING CONDITIONS"auriferous mining -
 Buninyong & District Historical Society
Buninyong & District Historical SocietyPhotograph - Colour photograph, Framed copy of Award to Cornelius Westh from the Royal Humane Society of Australasia, 1940's
Cornelius Westh was presented with this award for attempting to rescue John James who was buried by a fall of earth in the Imperial Mine Hiscocks on 23 June 1891Record of an attempted mine rescue in the late 19th century by a prominent local citizenColoured, framed copy of an award presented to Cornelius Westh by the Royal Humane Society of AustralasiaGift of Christine Westh to Buninyong and District Historical Society February 1995mining, hiscocks, rescue, award, westh
