Showing 28 items matching "build a boat"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, Build A Boat
... Build A Boat...Build A Boat...Build A Boat Publisher: Popular Mechanics Company Date... A Boat Build A Boat Publisher: Popular Mechanics Company Date ...Build A Boat Publisher: Popular Mechanics Company Date: 1941warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, great ocean road, book, warrnambool library, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, warrnambool children’s library, build a boat -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyLetter - Office of Lands & Survey re permission to build a boat on Sandridge Beach, Secretary for Lands, 22 Jun 1876
... Office of Lands & Survey re permission to build a boat on... & Survey, 22 June 1876. Re permission to lease land to build a boat... June 1876. Re permission to lease land to build a boat ...Photo\copies of letter and small map from Office of Lands & Survey, 22 June 1876. Re permission to lease land to build a boat on Sandridge Beach. Original letter sent to J.C. Lowrie of Stokes Street. Various copies stapled together.local government - borough of sandridge, j c lowrie, sandridge beach -
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyCoxed Pair race boat, Richmond Boat Sheds, The Queen of Hearts, 1936
... Clinker build racing row boat... regatta boats on stern VRA No. 176 Clinker build racing row boat ...First used Boxing day 1936 at Nagambie, Launched by Mrs S.G. Williams wife of the Shire President. The champaign bottle failed to break and a hammer was required. The first race was rowed by H. Gayer (bow) W. Bourke (stroke), Ted Forbes (cox) winning maiden pairs and the same crew won lightweight pairs at Lake Moodemere 1st Jan 1937. The boat was then purchased with funds raised in a queen competition held in Rutherglen and contested by 3 queens, Elise Frances, Emma Howard and Peggy Bourke (the winner and she went on to marry the bow H. Gayer). The Queen of Hearts went to the Air Force at Tocumwal during the WWIIClinker build racing row boaton stern VRA No. 176rowing, regatta, boats -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageVehicle - Vessel, Dinghy, Proudfoot's Boat, c. 1885
... This boat or dinghy is one of a few remaining boats made...This boat or dinghy is one of a few remaining boats made ...This boat or dinghy is one of a few remaining boats made for Proudfoot’s Boathouse, 2 Simpson Street Warrnambool, on the Hopkins River, in about 1885. It was one of many rowing, fishing, sailing and picnic boats that were available to hire. Proudfoot’s Boathouse, a beautiful Victorian Period building, was designed, built and established by Thomas Proudfoot. He applied to build a boat jetty in 1885. He died in 1900 and his wife Catherine took over, running it for many years. Later her son Bruce and after that her granddaughter Ena Hunt and her husband took over; it remained in the family until 1979. Proudfoot’s was a very popular tourist destination for visitors coming from Melbourne to fish and row and enjoy afternoon tea. The buildings, including the ‘U’ shaped jetty and tearooms, were restored and modified in the 1990s by the Warrnambool Sports Club, under the control of the Warrnambool City Council. The dinghy was brought to Flagstaff Hill in about 1992 and restored to its original condition and painted in traditional paint colours of orange with dark green gunnel and black and gold pinstripes. Since that time it has been painted by Flagstaff Hill's boatbuilder.This dinghy, Proudfoot’s Boat, is significant for its association with Proudfoot’s Boathouse, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register, VHR H0620. “Proudfoot's Boathouse on the Hopkins River near Warrnambool is an outstanding example of a late-19th century boathouse complex with associated residences and jetties. Thomas Proudfoot first applied for a jetty licence in 1885 with a view to establishing a boating business on the Hopkins River. The early single-storey sections are thought to date from this period. The two storey second stage probably dates from 1893 when additions were constructed. The entire complex was designed and built by Proudfoot himself. The business remained in the Proudfoot family until 1979. The buildings were modified in the 1990s in the process of creating a sporting club on the site. Proudfoot's Boathouse is of architectural, historical and social significance to the State of Victoria. Proudfoot's Boathouse is of architectural significance as perhaps the finest example of a 19th-century boathouse in Victoria. Although recent modifications have reduced the intactness of the buildings, many original features remain. The beautifully ornamented buildings still provide an attractive instance of 19th-century leisure facility architecture. Proudfoot's Boathouse is of historical significance as an example of late-Victorian recreational and tourist facilities. Boathouses were popular 19th-century tourist and recreational attractions, providing refined and healthy activity. This boathouse shows the early realisation of the tourism and leisure potential of seaside towns such as Warrnambool, a potential that has become increasingly important as port uses have ceased and other industries have been subjected to financial pressure. Proudfoot's Boathouse is of social significance because it illustrates the continuity of the attraction of this kind of leisure facility. Although the glory days of the boathouse were in the 19th century, those that survive continue to be well patronised. Proudfoot's Boathouse has been an important recreational facility and attraction for tourists flocking to the Hopkins River, one of the State's most popular boating and fishing resorts, since 1885.” (Statement of Significance is from the Victorian Heritage Register)Wooden vessel or boat, called a dinghy, known as Proudfoot’s Boat. Paint work is orange with dark green gunnel and black stripe. The rowboat is propelled by oars and has two pair of thole set into the gunnel (gunwale) to hold the oars in place and to serve as a fulcrum when rowing. The boat is dated around 1885. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, small marine vessel, dinghy, proudfoot's boat, proudfoot's boathouse, picnic boat, orange and black boat -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaJournal (item) - Periodicals-Annual, Shiplovers' Society of Victoria, The Annual Dog Watch
... Father Tremblay Builds a Boat - Captain F. K. Klebingat - 48.... Cowling - 35 Some Time - C. L. Lewis - 47 Father Tremblay Builds ...This journal provides the reader with glimpses of the adventures and hardships of a seaman's life. Many of the stories are of sailing ships.Contributes to our knowledge of the importance of shipping and places on record those stories of the sea which would otherwise be lost.Contents Foreword - Commodore Rodney Rhoades, D.S.C., R.A.N. (Ret.) - 9 Editorial - "Restoration and Replicas" - S. A. E. Strom - 11 "Polly Woodside" Remains Afloat - Dr. E. Graeme Robertson - 17 Gleams Through the Darkness - N. S. Smith - 23 Captain W. E. Smith - Captain E. Molyneux - 33 Nearly Sixty Years Ago - Captain W. J. Cowling - 35 Some Time - C. L. Lewis - 47 Father Tremblay Builds a Boat - Captain F. K. Klebingat - 48 A Memory of White Russia - F. L. Ogle - 56 The First of Port Phillip Pilots - Darren Baillieu - 58 Captain Robert Pattman of the "Loch Torridon" - Captain W. R. Chaplin - 72 With "Antiope" in the Northern Waters - Captain A. R. Nancarrow - 77 Rottnest Island - B. D. Goldfinch - 82 "Port Nicholson" to the Rescue - J. R. Brazier - 87 Glossary - - 91 Lights on the Hill - C. E. Bonwick - 93 Murray River Shipping - Ross Holloway - 94 What's in a Name - - 103 That was the Trouble - Dr. Stanislaw Bernatt - 110 "Eight Bells" - H. F. Watson - 111 Musings of an Old Sailor - Captain J. W. Carr - 112 A Voyage on the SS "Orange Branch" - I. L. Barton - 114 Book Reviews - - 129sailing ships, steamships, shipping, seafaring life, shiplovers' society of victoria, dog watch, herzogin cecile -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard - Historical, Warrnambool, Proudfoot’s Boat House, Hopkins River, Warrnambool, Early 20th century
... and established by Thomas Proudfoot. He applied to build a boat jetty... and established by Thomas Proudfoot. He applied to build a boat jetty ...The nine postcards in this set were donated together and date to the early 1900s. All but one postcard in this set shows images of Warrnambool, in the Western District of Victoria; the other has a London image. The postcards were all printed in Great Britain according to that country’s postal regulations. All cards have titles on the front printed in red. The majority of the images on the cards are attributed to photographer Joseph Jordan and belong to the Jordan Series. The back of these cards has an outline for a postage stamp, a vertical dividing line and a heading on each side of the line to separate the Correspondence from the Address. Postcards or ‘correspondence cards’ appeared in Britain in 1894. They were plain cards with a space for the message on one side and an address on the other; regulations didn’t allow anything but the address to be written on the ‘address’ side. In 1902 the British regulations then allowed a picture to be printed on the front and the address on the back, so messages had to be written on the picture side. Soon, the regulations changed and the back was divided for a message and the address. Proudfoots Boat House – Proudfoot’s Boathouse is at 2 Simpson Street Warrnambool, on the banks of the Hopkins River. In the 1880s it was a venue for hiring boats for rowing, fishing, sailing and picnics. It was a popular destination for tourists coming from Melbourne for a day or weekend outing. The beautiful historic Victorian period building was designed, built and established by Thomas Proudfoot. He applied to build a boat jetty in 1885. He died in 1900 and his wife Catherine took over, running it for many years. Later her son Bruce and after that her granddaughter Ena Hunt and her husband took over; it remained in the family until 1979. The buildings, including the ‘U’ shaped jetty and tearooms, were restored and modified in the 1990s by the Warrnambool Sports Club, under the control of the Warrnambool City Council. Joseph Jordan - Joseph Jordan was born in 1841 in Leicester England. When he was 16 he joined the 7th Queen's Own Hussars and was sent to India at the outbreak of the mutiny. He took part in the relief of Lucknow and remained in India for eleven years. It was during this time, he became interested in photography. He was posted to New Zealand and later came to Victoria, becoming a sergeant major of the Mounted Rifles. In the mid-1880s he came to the Western district where he was responsible for establishing units of the Mounted Rifles in various country towns such as Dunkeld, Mortlake, Panmure, Bushfield, Koroit etc. He resigned from the army in 1889 and set up a professional photography studio in Liebig Street, Warrnambool. He became very well known in the Western District for family photographs, official photographs of local councillors and groups as well as views of local scenery. In 1891 he photographed the wrecked barque ‘Fiji’ at ‘Wrecks Beach’ near Princetown. His business was taken over by his son Arthur around 1917. Joseph was a keen rifle shot and in 1924 he donated the "Jordan Shield" as a prize to the Victorian Rifle Association. He was made a "Life Honorary Member" of the Warrnambool Returned Soldiers League and in 1933 he was recognised as being the oldest living soldier in Victoria. Joseph died in 1935 aged 95.This card is the only one of the nine cards with the location of Warrnambool added to the name 'Joseph Series'. It is also the only one that has text within the outline for the postage stamp. The font used for the test of the headings is slightly different to the other cards. Joseph Jordan is a significant figure in Warrnambool history as he helped to establish early units of the Mounted Rifles (G Company) in local towns during the late 1880's and later, photographed local scenes, groups and citizens of early Warrnambool. This postcard of Proudfoot's Boathouse is of historical significance for is connection with Proudfood’s Boathouse. Proudfoot’s Boathouse is an example of late-Victorian recreational and tourist facilities. Boathouses were popular 19th-century tourist and recreational attractions, providing refined and healthy activity. This boathouse shows the early realisation of the tourism and leisure potential of seaside towns such as Warrnambool, a potential that has become increasingly important as port uses have ceased and other industries have been subjected to financial pressure. Proudfoot's Boathouse is of social significance because it illustrates the continuity of the attraction of this kind of leisure facility. Although the glory days of boathouses were in the 19th century, those that survive continue to be well patronised. Proudfoot's Boathouse has been an important recreational facility and attraction for tourists flocking to the Hopkins River, one of the State's most popular boating and fishing resorts, since 1885.” (Statement of Significance is from the Victorian Heritage Register)Postcard, one of nine, landscape orientation. Coloured photograph print within an oval border and mauve-toned shading. Cameo Image of figures in three rowing boats on still water beside a building with three gable roofs and decorative verandas. Other boats are moored at the landing in front of the building. The roofs each have a tall pole at the front. There is a park right of the building that also has a landing. In the background is a grassed slope and the sea. Reverse has printed inscriptions and an outline for a postage stamp. There is no correspondence written on the card. The card is one of the Jordan Series by Joseph Jordan, printed in Great Britain in the early 1900s. Front, in red: “PROUDFOOT’S BOAT HOUSE / HOPKINS RIVER, WARRNAMBOOL” Reverse in black: “Jordan Series Warrnambool” “POST CARD” “Printed in Great Britain” “This space may be used for Communication” “The Address to be written here” Within the stamp outline: “3 / BRITISH / MANUFACTURE"flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, maritime museum, warrnambool, great ocean road, warrnambool and district, warrnambool scenes, local scenes, views of warrnambool, joseph jordan, jordan series, jordan photography, postcard, souvenir, correspondence, cameo postcard, landscape, proudfoots boat house, boat house, proudfoots, hopkins river, boats for hire, row boats, recreation -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Granite
Gabo Island sits off the coast of East Gippsland in Victoria, with cliffs of granite in a relatively unique red/pink colour. Early attempts to build a lighthouse on the island were abandoned due to poor foundations, but when a ship ran aground on the nearby Tullaberga Island in 1853 and led to the death of 37 people, efforts were reignited. Construction of a new lighthouse was completed by 1858, using Gabo Island granite. The lighthouse is Australia's second tallest in Australia and continues to play an important role in guiding boats around the coast as they journey between Melbourne and Sydney. The distinct pink colour from the granite means the lighthouse continues to be a defining feature of the island. Gabo Island granite was also used to construct the Treasury Building at 117 Macquarie Street in Sydney, now the Intercontinental Hotel.Granite in the pink colour of this specimen is relatively rare. The connection to the lighthouse on Gabo Island also gives the specimen historic significance and social significance regarding the maritime history of Victoria. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid palm-sized mineral, coloured by flecks of pink, red, and grey. Granite is formed by the slow crystallisation of magma below the earth's surface. It is typically composed of a mix of quartz, feldspar, and other minerals, though syenitic granite like this sample has a smaller amount of quartz than typical granite. This different mineral composition leads to the more distinct pink and red colouring.First sticker: [torn]logical survey / R........ S........ / Loc Gabo Island / 1/4 Sheet / Second Sticker: 15 Third Sticker: Syenitic Graniteburke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, beechworth museum, geological, geological specimen, mineralogy, gabo island, gabo island lighthouse, lighthouse, granite, coast, coastal, granite specimen, victoria, coastal cliffs -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photograph, Green, O. S, April 1897
This photograph shows the Richardson family having a picnic on the verandah of Captain McNeil' house at Marlo - April 1897. Snowy River Shipping Company formed in 1880. They were soon shipping produce (mainly vegetables) from the area to Melbourne. The Snowy River Shipping Company was formed by Mr Henry James during the 1880s, with Captain McNeil as master. Captain Hegarty was the shipping agent at Marlo. Towing a line of small barges these paddle steamers plied their trade between the port of Marlo, and the farms along the river banks, churning their way almost twenty miles upstream to a landing beside what is now Frank Richardson’s property. On these trips, the barges carried mail and supplies to the townspeople and farmers, loading their produce, mostly maize, on the return trip to the coast. The coming of the railway in 1915 spelt the end for the little river boats. ( ref. F. W. RODWELL in the “Snowy Review”) Frank Richardson 1877-1950 was a sawmiller at Tabbara and helped build and run paddle steamer "Curlip"as engineer. Captain McNeil was an always cheerful Marlo identity and local children had many times sailing with him on the river. Captain McNeil with tug went out through the entrance and brought in the schooners.This item is associated with the Richardson family, early settlers of the Orbost district.A black / white photograph of a group of people having afternoon tea on the end of a verandah of a wooden house. All are seated.on back - " The Richardson family picnic at Marlo"richardson-family-orbost-marlo mcneil-captain -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaPhotograph - Reproduction, Jay Miller, 6 June 2019
This photograph was published in the Geelong Advertiser on Friday 23 November 1906, page 4 with this article: "Owing to the generosity of an anonymous donor, the Victorian Missions to Seamen has been supplied with a long felt want in the shape of a modern motor launch to facilitate and render more efficient the work among the vessels in the Yarra and Hobson's Bay. The order for the construction of the boat, was placed with Mr. Chas. Blunt, of the Eastern Beach, and complimentary references were made to her graceful line- as she rode in light .trim after the launching on Wednesday afternoon. She is 31ft. long. Oft. beam, and has a depth of 3ft. The frame is of jarrah and ben* blackwood. and inch kauri planking has been used in building Iter. A neat deck-house with Oft. headroom is situat ed-umidsliip*. and a short mast is pro vided to carry the well-known blue flag of the -.fission. The launch motors will develop a speed of between nine and ten miles an hour: The finishing touches have yet to be given her. and she will afterwards be row«l to have her engines fitted in. -The launch will he ready for service for the busy wheat season com mencing at- the end of the year. The launching ceremony took place at 6 p.m. on Wednesday at the builder's yards, in the .presence of njarge gather ing of spectators. The Archdeacon of Geelong. the Rev. O. P. C'ros-.ley. ecu ducted a short dedication service, and the other clergymen who took part in the service were the Primate of Aus tralia. the Right Rev. Dr. Sauiuarcz Smith: the Rev. A. Giirney Goldsmith, the Missions chaplain: and the Rev. H. Kelly. The Bishop of Newcastle, Dr. Stretch, and the chaplain of the New castle Mission, the Rev. AYnddy. and Canon Nash were also present. The Primpte. addressing the gar boring as "My good friends of Geelong." said be had never been in sight of the hay before. bill had'gladly accepted the in vitation to say a few words in connec tion with the dedication of tiro launch. He had always been interested in mis sions of all sorts, as they ali as Christian men and women 110 doubt- were, and lie was particularly interested in Missions to Seamen, because in the Society at' borne, with which this Society was con nected, he had a son-in-law who was mission chaplain in the Medway. He therefore know something about a launch for the purpose of a mission like this, and also knew 'something about missions to seamen. In Sydney for some time past it had been doing good work—work which he was sure they would all feel was of the widest possible value. This year he was at the annual meeting of the Missions to Seamen in London presided over by the Bishop o-f Stcphney. -He (the Primate) at that meeting remarked that the Mission in it, value was personal, local and Im perial. It was of personal value to thee who came under the ministra tions of the church, and in the social as pect : it was local because where the Mission existed the feelings of the lo cality were thrown out. in sympathy with j tlie -Mission, and the people themselves thus benefited. It was also a matter of Imperial interest because it- was really i a world-wide Mission, inasmuch as the | sailors as they" went from one part of the world to another were in themselves j missionaries either for evil or for good, i Thev might he missionaries with a mcs i sago which might degrade and "work ail I evil influence amongst, men, and with i conduct which might reflect a reproach !' upon Christian profession. On the other hand, they might be Chrisian men endeavoring more and more to show the .example of the Christian life in the J midst of very big difficulties and tempta tions. • -Ho came to show liis sympathy with tlio appropriately-named '"'Southern Cross," and from what lie had boon told he believed she was a good boat, a good gift, and launched for a good purpose. They should be thankful that it was a good boat and .thankful because it was a good gift by an anonymous donor, whom he congratulated on doing such a useful thing." The idea of the launch ing ceremony was to ask the blessing of God because ".Except the Lord hless'the house their labor is hut lost'that build it." The Archdeacon expressed thanks to the Primate for attending the cere mony, and regretted that the Arch bishop was unable to attend. They dc- | sired that the boat- should always be as sociated with the.Church Congress 1906. I The opening hymn was "For those in j peril on the sea," followed hv Psalm I 107, "'They'that, go down to the sea in 1 Ships." Tlio prayers included an ap peal foiUDirine blessing on .the launch, and for tho preservation of those who may travel in her. ' Xlio Benediction was pronounced by the Primate, and the christening cere mony performed by Hiss Connibere. From the bow there was suspended a bottle of pure water covered with red, white and blue streamers and roses. Dashing the bottle in,fragments against the launch's bow. Miss Connibere named her the "Southern Cross." Cheers were given for the launch/and as she travell ed down the slip further cheers were given. She carried the Mission flag at tho masthead, and between Union Jacks at tho bow and stern, a long string of flags fluttered gaily* in the breeze. The collection was in aid of the Mis sions to Seamen and the Geelong Sailors' Rest.Reproduction of a photograph from a newspaper.Fujifilm / Quality Dry Photo papersouthern cross, motor boat, mission to seamen, seamen's mission, charles blunt, blunt boatbuilders, geelong -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Portland Lifeboat, n.d
Built in 1858 at the Port and Harbour Master's yard in Williamstown Victoria, the Portland Lifeboat was overseen by Harbour Master Charles Ferguson. It is understood to have been constructed from the same moulds used to build the Port Fairy Lifeboat, designed by William White, in 1857. Both boats are similar to the lifeboats designed in England by James Peake and adopted by the Royal National Lifeboat Institution (RNLI) in the UK. The Portland Lifeboat's 9.14 m (30 ft) long hull is double diagonally planked in New Zealand kauri, and many of the planks run from gunwale to gunwale in one piece under the inner keel section. Eucalyptus and oregon were used elsewhere and the local blacksmith made the iron work. The fastenings are copper. There are two flotation or buoyancy tanks at either end, with prominent whaleback style decking. Under the thwarts is a deck with scuppers so that the craft is both buoyant and self draining whenever large waves are taken aboard in rough conditions. The lifeboat was oar-powered with a sailing rig. The original rig was a lug mainsail, but this was replaced with a lug and headsail rig taken from a fishing boat in 1903. The lifeboat was manned by volunteer crews, mostly local fishermen from Portland. They maintained this service until 1915 when the boat was replaced with a new motorised craft. The lifeboat's most outstanding service was to the steamer ADMELLA in 1859 when the ship grounded on a reef off Cape Banks in South Australia, 150 km to the west of Portland. Survivors clung to the rigging in heavy seas for over a week and 89 people lost their lives in the shipwreck. Taken to the scene by the steamer LADY BIRD, the Portland Lifeboat was unable to assist until eight days after the ADMELLA's grounding when the seas abated enough for the lifeboat to manoeuvre close to the ship and rescue the last 19 survivors. Since its retirement in 1915 the lifeboat has been a memorial to those who manned it and those it rescued. For a long period it was on display in the Portland Gardens, first in the open and then under a canopy. In 2008 it was on display inside the Portland Maritime Discovery Centre, still in original condition complete with the rig from 1915. It is one of the oldest vessels of its type in Australia, and the world.Portland LifeboatPhotograph showing the Portland Lifeboatphotography, portland lifeboat, admella -
 Geelong RSL Sub Branch
Geelong RSL Sub BranchPhotographs - Ships, HMAS Quickmatch, HMAS Quiberon, Air Sea Rescue Vessel, Early 20th century
HMAS Quickmatch was a Q Class destroyer built for the Royal Navy and was commissioned to RAN in September 1942. HMAS Quiberon was a Q Class destroyer build for the Royal Navy and was commissioned to RAN in July 1942. Air Sea Rescue Boats, after their order were delivered to Sydney in June/July 1944. HMAS Quickmatch was used as a Convoy Escort during WW2. HMAS Quiberon was used as a Convoy Escort during WW2. Air Sea Rescue Boats were mostly stationed in northern Australian waters or in New Guinea during WW2. Three black and White Photographs of Ships on photo paper. Ships - HMAS Quickmatch, HMAS Quibero, Air Sea Rescue Vessel.Hand written on the back of the photo 1. HMAS Quickmatch, HMAS Quiberon, Air Sea Rescue. -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societycheque, 1880's
Snowy River Shipping Company formed in 1880. They were soon shipping produce (mainly vegetables) from the area to Melbourne. The Snowy River Shipping Company was formed by Mr Henry James during the 1880s, with Captain McNeil as master. Captain Hegarty was the shipping agent at Marlo. Towing a line of small barges these paddle steamers plied their trade between the port of Marlo, and the farms along the river banks, churning their way almost twenty miles upstream to a landing beside what is now Frank Richardson’s property. On these trips, the barges carried mail and supplies to the townspeople and farmers, loading their produce, mostly maize, on the return trip to the coast. The coming of the railway in 1915 spelt the end for the little river boats. ( ref. F. W. RODWELL in the “Snowy Review”) Frank Richardson 1877-1950 was a sawmiller at Tabbara and helped build and run paddle steamer "Curlip"as engineer.This item is associated with an early transport business of the local district. The Snowy River once had its own paddle steamers. This item is reminiscent of that time.A light blue and white blank cheque for the Snowy River Shipping Company. The cheque is for The National Bank of Australasia and is numbered 01,491 in bold black print. It has a one penny stamp duty imprint.snowy-river-shipping-company james-harry -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageOar, early 20th century
This oar is from the Lifeboat Warrnambool, which is on sit at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The construction of the lifeboat ‘Warrnambool’ began 15th September 1909 and was completed almost 12 months later, 1st September 1910. It was built at the Government Dockyard in Williamstown, Victoria, along the lines designed by the Great Britain’s Royal Lifeboat Institution, and included whaleback decks fore and aft, mast and centreboard, and rudder and tiller hung from the sternpost. It could be propelled by both sail and oar. At that time Captain Ferguson was Chief Harbour Master and Mr Beagley was foreman boat builder. Mr Beagley built the lifeboat with his fellow workmen. The boat was described as “… a fine piece of workmanship and does credit to her builders and designers…” It had all the latest improvements in shape, disposition of weight and watertight compartments, and it had space for a large number of people in addition to the crew. It appears that 'H Meiers' whose signature was on the plaque that was found concealed in the hull, was involved with the building of the lifeboat. His signature and the dates of the start and finish of the boat’s construction are pencilled on the raw timber 'plaque' found in the hull in the early 1990’s when the lifeboat was being restored. It is interesting that the ‘Melbourne Directory’ of 1911, published by Sands and MacDougal, lists McAuley and Meiers, boat builders, Nelson Place foreshore, between Pasco and Parker Streets, Williamstown, (Victorian Heritage Database, ‘Contextual History, Maritime Facilities’), It is quite possibly the business of the person whose name is inscribed on the lifeboat plaque. Flagstaff Hill’s documentation also mentions that the keel was laid at ‘Harry Myers, boat builders, Williamstown, Melbourne’ – the name ‘Myers’ can also be spelled ‘Meiers’, which could be the same person as the Meiers in “McAuley and Meiers” (as mentioned in genealogy lines of Myers). The new lifeboat, to be named ‘Warrnambool’ was brought to town by train and launched at the breakwater on 1st March 1911 using the Titan crane (the old lifeboat built in 1858, was then returned to Melbourne in 1911). This new lifeboat was stationed at Warrnambool in a shed located at the base of the Breakwater, adjacent to the slipway. A winch was used to bring it in and out of the water. The lifeboat ‘Warrnambool’ was similar in size to the old lifeboat but far superior in design, build and sea-going qualities such as greater manoeuvrability. The ‘self-righting, self-draining’ design was “practically non-capsizeable” and even if the boat overturned it would right itself to an even keel and the water would drain away. The hull was built of New Zealand Kauri, using double diagonal planking, laid in two layers at right angles, with a layer of canvas and red lead paint between the timbers to help seal the planking. It has “… plenty of freeboard, high watertight spaces between the deck and bottom… through which pipes lead…” The backbone timbers were made of Jarrah. The lifeboat Warrnambool was one of several rescue boats used at Port Fairy and Warrnambool in early 1900's. In late 1914 the Warrnambool lifeboat and crew were used to help find what was left of the tragic wreckage of the Antares, and were able to discover the body of one of the crewmen, which they brought back to Warrnambool. Between 1951 and 1954 the lifeboat was manned under the guidance of Captain Carrington. He held lifeboat practice each month on a Sunday morning, to comply with the Ports and Harbour’s request that lifeboats be manned by a strong and competent crew, ready for action in case of emergency. In the early 1960’s it ended its service as a lifeboat and was used in Port Fairy as a barge to help dredge the Moyne River, bolted to the Port Fairy lifeboat. Flagstaff Hill obtained the Warrnambool in 1975. In 1984 it was on display at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. On 23rd May 1990 she was lifted from the water and placed in a cradle for restoration. The name ‘WARRNAMBOOL could be seen faintly on the lifeboat before it was restored. It was during the restoration that Flagstaff Hill's boat builder discovered the 'plaque' inside the hull. A copy of the blueprint plans has the name “V.E.E. Gotch” printed on it. His advertisement in Footscray’s ‘Independent’ newspaper of Saturday 11th May 1901 states he is “Principal and Skilled member (Naval Architect) to the Court of Marine Inquiry of Victoria and holds classes for naval architectural drawing and arithmetic.” The oar is significant for its association with the lifeboat WARRNAMBOOL, which is significant for its half century service to the local community as a lifesaving vessel. She was also used to help retrieve the body of a shipwrecked crew member of the ANTARES. Large wooden oar, shaped two handgrip with tapering shaft to large flattened blade, (2) copper reinforcing strips on blade. Sweep oar is from the Lifeboat Warrnambool. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, oar, lifeboat warrnambool, sweep oar -
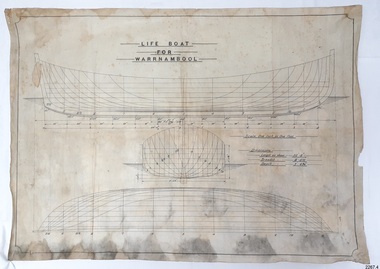 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePlan - Vessel Line Drawing, Life Boat for Warrnambool, ca. 1900-1909
The plans were used for the construction of the lifeboat ‘Warrnambool’, which began 15th September 1909 and was completed almost 12 months later 1st September 1910. It was built at the Government Dockyard in Williamstown, Victoria, along the lines designed by Great Britain’s Royal Lifeboat Institution, and included whaleback decks fore and aft, mast and centreboard, and rudder and tiller hung from the sternpost. It could be propelled by both sail and oar. At that time Captain Ferguson was Chief Harbour Master and Mr Beagley was the foreman boat builder. Mr Beagley built the lifeboat with his fellow workmen. The boat was described as “… a fine piece of workmanship and does credit to her builders and designers…” It had all the latest improvements in shape, disposition of weight and watertight compartments, and it had space for a large number of people in addition to the crew. It appears that 'H Meiers' whose signature was on the plaque that was found concealed in the hull, was involved with the building of the lifeboat. His signature and the dates of the start and finish of the boat’s construction are pencilled on the raw timber 'plaque' found in the hull in the early 1990s when the lifeboat was being restored. It is interesting that the ‘Melbourne Directory’ of 1911, published by Sands and MacDougal, lists McAuley and Meiers, boat builders, Nelson Place foreshore, between Pasco and Parker Streets, Williamstown, (Victorian Heritage Database, ‘Contextual History, Maritime Facilities’), It is quite possibly the business of the person whose name is inscribed on the lifeboat plaque. Flagstaff Hill’s documentation also mentions that the keel was laid at ‘Harry Myers, boat builders, Williamstown, Melbourne’ – the name ‘Myers’ can also be spelled ‘Meiers’, which could be the same person as the Meiers in “McAuley and Meiers” (as mentioned in genealogy lines of Myers). The new lifeboat, to be named ‘Warrnambool’ was brought to town by train and launched at the breakwater on 1st March 1911 using the Titan crane (the old lifeboat built in 1858, was then returned to Melbourne in 1911). This new lifeboat was stationed at Warrnambool in a shed located at the base of the Breakwater, adjacent to the slipway. A winch was used to bring it in and out of the water. The lifeboat ‘Warrnambool’ was similar in size to the old lifeboat but far superior in design, build and sea-going qualities such as greater manoeuvrability. The ‘self-righting, self-draining design was “practically non-capsizeable” and even if the boat overturned it would right itself to an even keel and the water would drain away. The hull was built of New Zealand Kauri, using double diagonal planking, laid in two layers at right angles, with a layer of canvas and red lead paint between the timbers to help seal the planking. It has “… plenty of freeboard area, high watertight spaces between the deck and bottom… through which pipes lead…” The backbone timbers were made of Jarrah. The lifeboat Warrnambool was one of several rescue boats used at Port Fairy and Warrnambool in the early 1900s. In late 1914 the Warrnambool lifeboat and crew were used to help find what was left of the tragic wreckage of the Antares and were able to discover the body of one of the crewmen, which they brought back to Warrnambool. Between 1951 and 1954 the lifeboat was manned under the guidance of Captain Carrington. He held lifeboat practice each month on a Sunday morning, to comply with the Ports and Harbour’s request that lifeboats be manned by a strong and competent crew, ready for action in case of emergency. In the early 1960’s it ended its service as a lifeboat and was used in Port Fairy as a barge to help dredge the Moyne River, bolted to the Port Fairy lifeboat. Flagstaff Hill obtained the Warrnambool in 1975. In 1984 it was on display at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. On 23rd May 1990, she was lifted from the water and placed in a cradle for restoration. The name ‘WARRNAMBOOL could be seen faintly on the lifeboat before it was restored. It was during the restoration that Flagstaff Hill's boat builder discovered the 'plaque' inside the hull. A copy of the blueprint plans has the name “V.E.E. Gotch” printed on it. His advertisement in Footscray’s ‘Independent’ newspaper of Saturday 11th May 1901 states he is “Principal and Skilled member (Naval Architect) to the Court of Marine Inquiry of Victoria and holds classes for naval architectural drawing and arithmetic.” The line drawing is significant for its connection with the lifeboat WARRNAMBOOL. The lifeboat is very significant to local and state history for its use in the lifesaving rescues of seafarers, particularly in Lady Bay. It was part of the local rescue equipment. It gave a half-century of service to the local community as a lifesaving vessel, including its involvement in retrieving the body of a shipwrecked crew member of the ANTARES. Line drawing in black ink and pencil on rectangular parchment or waxed linen. Drawing has diagrams of three profiles of a vessel, with measurements and connecting pencil lines on the left quarter. The plan is for the lifeboat named “Warrnambool”, which was built in Melbourne and completed in 1910. Old blue copies of the Lifeboat plan are archived also.“LIFE BOAT / FOR / WARRNAMBOOL” “Scale, One Inch to One Foot” “ “Length as shown 30’ – 8” “ “Breadth “ “ 8’ – 6 ½ “ “ “Depth “ “ 3’ – 4 ¾” “flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, lifeboat, warrnambool lifeboat, boat plans, lifeboat plans, boat construction, boat building, line drawing, plan for lifeboat, life boat, life boat 'warrnambool', clinker design, 1910 lifeboat, life saving equipment, shipbuilding -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageRowlock, early 20th century
Rowlock from the Lifeboat Warrnambool, which is on site at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The construction of the lifeboat ‘Warrnambool’ began 15th September 1909 and was completed almost 12 months later, 1st September 1910. It was built at the Government Dockyard in Williamstown, Victoria, along the lines designed by the Great Britain’s Royal Lifeboat Institution, and included whaleback decks fore and aft, mast and centreboard, and rudder and tiller hung from the sternpost. It could be propelled by both sail and oar. At that time Captain Ferguson was Chief Harbour Master and Mr Beagley was foreman boat builder. Mr Beagley built the lifeboat with his fellow workmen. The boat was described as “… a fine piece of workmanship and does credit to her builders and designers…” It had all the latest improvements in shape, disposition of weight and watertight compartments, and it had space for a large number of people in addition to the crew. It appears that 'H Meiers' whose signature was on the plaque that was found concealed in the hull, was involved with the building of the lifeboat. His signature and the dates of the start and finish of the boat’s construction are pencilled on the raw timber 'plaque' found in the hull in the early 1990’s when the lifeboat was being restored. It is interesting that the ‘Melbourne Directory’ of 1911, published by Sands and MacDougal, lists McAuley and Meiers, boat builders, Nelson Place foreshore, between Pasco and Parker Streets, Williamstown, (Victorian Heritage Database, ‘Contextual History, Maritime Facilities’), It is quite possibly the business of the person whose name is inscribed on the lifeboat plaque. Flagstaff Hill’s documentation also mentions that the keel was laid at ‘Harry Myers, boat builders, Williamstown, Melbourne’ – the name ‘Myers’ can also be spelled ‘Meiers’, which could be the same person as the Meiers in “McAuley and Meiers” (as mentioned in genealogy lines of Myers). The new lifeboat, to be named ‘Warrnambool’ was brought to town by train and launched at the breakwater on 1st March 1911 using the Titan crane (the old lifeboat built in 1858, was then returned to Melbourne in 1911). This new lifeboat was stationed at Warrnambool in a shed located at the base of the Breakwater, adjacent to the slipway. A winch was used to bring it in and out of the water. The lifeboat ‘Warrnambool’ was similar in size to the old lifeboat but far superior in design, build and sea-going qualities such as greater manoeuvrability. The ‘self-righting, self-draining’ design was “practically non-capsizeable” and even if the boat overturned it would right itself to an even keel and the water would drain away. The hull was built of New Zealand Kauri, using double diagonal planking, laid in two layers at right angles, with a layer of canvas and red lead paint between the timbers to help seal the planking. It has “… plenty of freeboard, high watertight spaces between the deck and bottom… through which pipes lead…” The backbone timbers were made of Jarrah. The lifeboat Warrnambool was one of several rescue boats used at Port Fairy and Warrnambool in early 1900's. In late 1914 the Warrnambool lifeboat and crew were used to help find what was left of the tragic wreckage of the Antares, and were able to discover the body of one of the crewmen, which they brought back to Warrnambool. Between 1951 and 1954 the lifeboat was manned under the guidance of Captain Carrington. He held lifeboat practice each month on a Sunday morning, to comply with the Ports and Harbour’s request that lifeboats be manned by a strong and competent crew, ready for action in case of emergency. In the early 1960’s it ended its service as a lifeboat and was used in Port Fairy as a barge to help dredge the Moyne River, bolted to the Port Fairy lifeboat. Flagstaff Hill obtained the Warrnambool in 1975. In 1984 it was on display at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. On 23rd May 1990 she was lifted from the water and placed in a cradle for restoration. The name ‘WARRNAMBOOL could be seen faintly on the lifeboat before it was restored. It was during the restoration that Flagstaff Hill's boat builder discovered the 'plaque' inside the hull. A copy of the blueprint plans has the name “V.E.E. Gotch” printed on it. His advertisement in Footscray’s ‘Independent’ newspaper of Saturday 11th May 1901 states he is “Principal and Skilled member (Naval Architect) to the Court of Marine Inquiry of Victoria and holds classes for naval architectural drawing and arithmetic.” The rowlock is significant for its association with the lifeboat WARRNAMBOOL, which is significant for its half century service to the local community as a lifesaving vessel. She was also used to help retrieve the body of a shipwrecked crew member of the ANTARES. Rowlock, iron, upper ends scroll over, from the Lifeboat Warrnambool.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, life boat, life saving vessel, 1910 vessel, port fairy, boat builder plaque, rescue boat, beagley, government dockyard, williamstown, v.e.e. gotch, royal lifeboat institution, captain ferguson, non-capsizeable lifeboat, self-righting lifeboat, antares shipwreck, double diagonal planking, captain carrington, rowlock, lifeboat rowlock, lifeboat warrnambool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageVehicle - Vessel, Lifeboat Warrnambool, 01/09/1910
The construction of the lifeboat ‘Warrnambool’ began 15th September 1909 and was completed almost 12 months later, 1st September 1910. It was built at the Government Dockyard in Williamstown, Victoria, along the lines designed by the Great Britain’s Royal Lifeboat Institution, and included whaleback decks fore and aft, mast and centreboard, and rudder and tiller hung from the sternpost. It could be propelled by both sail and oar. At that time Captain Ferguson was Chief Harbour Master and Mr Beagley was foreman boat builder when he and his fellow workmen built the boat. The boat was described as “… a fine piece of workmanship and does credit to her builders and designers…” It had all the latest improvements in shape, disposition of weight and watertight compartments, and it had space for a large number of people in addition to the crew. It appears that 'H Meiers' whose signature, along with building dates, is pencilled on a concealed timber 'plaque' in the hull, was involved with the building of the lifeboat. It is interesting that the ‘Melbourne Directory’ of 1911, published by Sands and MacDougal, lists McAuley and Meiers, boat builders, Nelson Place foreshore, between Pasco and Parker Streets, Williamstown, (Victorian Heritage Database, ‘Contextual History, Maritime Facilities’), It is probably the company of the person whose name is inscribed on the lifeboat plaque. Flagstaff Hill’s documentation also mentions that the keel was laid at ‘Harry Myers, boat builders, Williamstown, Melbourne’ – the name ‘Myers’ can also be spelled ‘Meiers’, which could be the same person as the Meiers in “McAuley and Meiers” (as mentioned in genealogy lines of Myers). The new lifeboat, to be named ‘Warrnambool’ was brought to town by train and launched at the breakwater on 1st March 1911 using the Titan crane (the old lifeboat built in 1858, was then returned to Melbourne in 1911). This new lifeboat was stationed at Warrnambool in a shed located at the base of the Breakwater, adjacent to the slipway. A winch was used to bring it in and out of the water. The lifeboat ‘Warrnambool’ was similar in size to the old lifeboat but far superior in design, build and sea-going qualities such as greater manoeuvrability. The ‘self-righting, self-draining’ design was “practically non-capsizeable” and even if the boat overturned it would right itself to an even keel and the water would drain away. The hull was built of New Zealand Kauri, using double diagonal planking, laid in two layers at right angles, with a layer of canvas and red lead paint between the timbers to help seal the planking. It has “… plenty of freeboard, high watertight spaces between the deck and bottom… through which pipes lead…” The backbone timbers were made of Jarrah. The lifeboat Warrnambool was one of several rescue boats used at Port Fairy and Warrnambool in early 1900's. In late 1914 the Warrnambool lifeboat and crew were used to help find what was left of the tragic wreckage of the Antares, and were able to discover the body of one of the crewmen, which they brought back to Warrnambool. Between 1951 and 1954 the lifeboat was manned under the guidance of Captain Carrington. He held lifeboat practice each month on a Sunday morning, to comply with the Ports and Harbour’s request that lifeboats be manned by a strong and competent crew, ready for action in case of emergency. In the early 1960’s it ended its service as a lifeboat and was used in Port Fairy as a barge to help dredge the Moyne River, bolted to the Port Fairy lifeboat. Flagstaff Hill obtained the Warrnambool in 1975. In 1984 it was on display at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. On 23rd May 1990 she was lifted from the water and placed in a cradle for restoration. The name ‘WARRNAMBOOL could be seen faintly on the lifeboat before it was restored. It was during the restoration that Flagstaff Hill's boat builder discovered the 'plaque' inside the hull. A copy of the blueprint plans has the name “V.E.E. Gotch” printed on it. His advertisement in Footscray’s ‘Independent’ newspaper of Saturday 11th May 1901 states he is “Principal and Skilled member (Naval Architect) to the Court of Marine Inquiry of Victoria and holds classes for naval architectural drawing and arithmetic.”The lifeboat WARRNAMBOOL is significant for its half century service to the local community as a lifesaving vessel. She was also used to help retrieve the body of a shipwrecked crew member of the ANTARES. Lifeboat "Warrnambool", a wooden, clinker hull, 'self-righting, self-draining design, single mast, pivoting centreboard. Complete with sail and yardarm. A 'plaque' was found inside the hull of the lifeboat, made of untreated wood, disc-shaped with one straight edge (Diam 15.5cm), inscribed by one of the boat builders in pencil script "Life Boat Start building / 15/9/09 - complete 1/9/10 / (signature looks like H Meiers) / Boat Builder)."'Plaque' inside body of boat is inscribed in pencil, script writing "Life Boat Start building / 15/9/09 - complete 1/9/10 / (signature looks like H Meiels) / Boat Builder)." flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, lifeboat, life boat, vessel, life saving, 1910 vessel, port fairy, boat builder plaque, rescue boat, beagley, williamstown, government dockyard, v.e.e. gotch, royal lifeboat institution, captain ferguson, meiers, nelson place, non-capsizeable, self-righting, titan crane, double diagonal planking, captain carrington, barge, antares, self righting, crew of twelve, capacity of 30 survivors -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Toolbox, Laurie Dilks, shipwright, Mid-to-late 20th century
Caulking is a process used by shipwrights and other tradespeople to seal the gaps and cracks in boats and ships, buildings and plumbing fittings. It prevents water, air and pests from entering the through the gaps. The shipwright’s caulking box and a display of shipwright's tools are connected to the maritime history of Victoria through their past owner, user and donor, Laurie Dilks. Laurie began his career as a shipwright in the mid-1900s, following in the wake of the skilled carpenters who have over many centuries used their craft to build and maintain marine vessels and their fittings. Laurie worked for Ports and Harbours, Melbourne, for over 50 years, beginning in the early 1960s. He and a fellow shipwright inscribed their names on a wheelhouse they built in 1965; the inscription was discovered many decades later during a repair of the plumbing. Many decades later Laurie worked on the Yarra River moving barges up and down the river and was fondly given the title ‘Riverboat Man’ His interest in maritime history led him to volunteer with the Maritime Trust of Australia’s project to restore and preserve the historic WWII 1942 Corvette, the minesweeper HMAS Castlemaine, which is a sister ship to the HMAS Warrnambool J202.The shipwright’s caulking box containing caulking tools is an example of the equipment used by shipwrights in the early to mid-20th centuries. This box is connected to the maritime history of Victoria through its past owner, user and donor, Laurie Dilks. Laurie began his career as a shipwright at Ports and Harbours in Melbourne in the mid-1900s, following in the wake of the skilled carpenters who have over many centuries used their craft to build and maintain marine vessels and their fittings.Shipwright's caulking box, green wooden exterior with green and cream interior. Box has a Perspex face. A rope handle, knotted on each end, extends from one side to the other. A white rectangular plaque with rounded corners is screwed to the top and has yellow and black printed text. The donor was shipwright Laurie Dilks.Printed on plaque "SHIPWRIGHTS / CAULKING BOX / DONATED BY LAURIE DILKS [SHIPWRIGHT]'"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, caulking tools, caulking equipment, caulking box, shipwright's tools, laurie kilks, ports and harbours -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaBanner
The letters of the completed banner were made by different churches within in the presbytery and spelled a sentence, presumably "BUILD YOUR CHURCH LORD!" Orbost was one of the churches that had the finished banner on display. One of 24 small banners with tabs at the top of each for hanging on a rod. 19 have large blue letters appliqued on them. Twenty two of the banners are roughly square and two are smaller and oblong. Three have no letters and are used as spacers in the four word sentence that the letters make. The banners are decorated with rural and coastal images. BN068.4 "L" with a pelican, fishing boat with a net, shells and sand "L"uniting church adult fellowship -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaBanner - Banners
The letters of the completed banner were made by different churches within in the presbytery and spelled a sentence, presumably "BUILD YOUR CHURCH LORD!" Orbost was one of the churches that had the finished banner on display. 24 small banners with tabs at the top of each for hanging on a rod. 19 have large blue letters appliqued on them. Twenty two of the banners are roughly square and two are smaller and oblong. Three have no letters and are used as spacers in the four word sentence that the letters make. The banners are decorated with rural and coastal images. BN068.14 "C" with appliqued boat, sky and sun "C"uniting church adult fellowship -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyPostcard, Penny Royal Gunpowder Mills Postcard
The place shown on the photo still has an important relevance for the local history in Launcestown Tasmania. This place represents one of the most relevant touristic places of Tasmania and brings to the local government a very good amount of income for local developments and self management of the place. The date of this postcard is unknown but probably around 1980 as this place apparently was opened by 1979. The connection to Legacy is unknown but other postcards were sent to the Comradeship Committee when Legatees travelled.Comradeship Committee often received postcards from Legatees when they were away on holidays.Glossy postcard, with serrated edges, showing a photo of the Penny Royal Gunpowder Mills.Handwritten text: 'They have the small cannons on the boat - noisy and scared Alison but quite effective really. The whole complex is build in an old quarry', in black pen. Back side: Printed in paper, PENNY ROYAL GUNPOWDER MILLS / The 10 Gun Sloop-of-War 'Sandpiper' sails to prove its gun and powder in battle against those on Fort Island. / Douglas Souvenir Distributors [Logo] / DS 118, Colour Photography and Copyright by Robert Schorn. Printed in Australia. / I LIKE TO BE SEEN - PLEASE don't send me in an ENVELOPE. / Published by Douglas Souvenir Distributors - Tasmania (004) 312806tasmania, souvenir -
 Bayside Gallery - Bayside City Council Art & Heritage Collection
Bayside Gallery - Bayside City Council Art & Heritage CollectionPainting - acrylic on canvas, Mike Green, Keefers, 1976
In the early 1900s, Melbourne builder Charles Keefer was hired by the Moorabbin Council to build the municipal baths at Beaumaris. In 1903, Keefer took over the Beaumaris Boat House and enlarged it to form Keefer's Boat Shed where day trippers and holiday makers could hire boats and venture out into the bay. Although rebuilt following the devastating storms in 1934, Keefer’s Boat Shed was completely destroyed by fire in 1984.Realismkeefer's, boatshed, bayside, coast, beaumaris, fence, water, bay, charles keefer, pier, mike green -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPhotograph - Lakes Entrance, 1997
Date made 7 July 1997Colour photograph being an aerial view of the western end of Cunninghame Arm, showing the entrance between the hummocks, Bullock Island, entrance to North Arm, Snake Island surrounded by sand build-up. Lakes Entrance Victoriatopography, waterways, aerial photograph, boats and boating, township, islands -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Gold Cross, Bef. 01-06-1878
The gold cross was discovered by Victorian scuba diver Julie Wilkins, who had already experienced more than 500 dives in Australia and overseas. She was holidaying in Peterborough, Victoria, and looking forward to discovering more about the famous Loch Ard ship, wrecked in June 1878 at Mutton Bird Island. The fast Glasgow-built clipper ship was only five years old when the tragedy occurred. There were 54 people on board the vessel and only two survived Julie's holiday photograph of Boat Bay reminds her of her most memorable dive. Submerged in the calm, flat sea, she was carefully scanning around the remains of the old wreck when, to her amazement, a gold coin and a small gold cross suddenly came up towards her. She excitedly cupped them in her hands, then stowed the treasures safely in her wetsuit and continued her dive. She soon discovered a group of brass carriage clock parts and some bottles of champagne. It was a day full of surprises. The items were easily recognisable, without any build-up of encrustations or concretion. Julie secretly enjoyed her treasures for twenty-four years then packed them up for the early morning train trip to Warrnambool. After a short walk to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village, her photograph was taken as she handed over her precious find. She told her story to a local newspaper reporter, lunched a café in town then took the late afternoon train home. Her generous donation is now part of a vast collection of Loch Ard shipwreck artefacts, including the gold watch and the Minton Majolica model peacock. The small decorative cross dates back to on or before 1878, when the Loch Ard had set sail. The loop and ring have been added, perhaps as a pendant, pocket watch accessory or similar purpose. It may have been worn for ‘good luck’ or a ‘blessing’ on the long journey to Australia, where ships had to carefully navigate the treacherous Bass’s Strait before arriving at their destination of Melbourne. Sadly, many met their fate on that short stretch of ocean aptly named the Shipwreck Coast. The cross is very recognisable even though it was exposed to the wrecking of the ship, its consequent movement, and the sea's turbulence. Its scratched, pitted and worn condition, and the damage near the loop, is part of its story. The red-brown-black discolouration is similar to that found on other gold coins, sometimes called the ‘corrosion phenomena’. Studies suggest the possible cause is contaminants in the minting process reacting to the coins’ environment. Three edges of the cross have slightly raised narrow ridges of gold which could have been cause by the gold being cast liquid gold into a mould.This gold cross pendant is significant as a symbol of Christianity, a sign of hope and safety, and a sample of the religious following on board the Loch Ard, although not everyone wears a cross for this reason. This cross is a sample of jewellery owned by people migrating to Australia in the late 19th century. The cross and the guinea recovered together from the wreck of the Loch Ard are made of gold and help interpret the financial status of some of those on board.Gold cross; yellow gold with decorative hand engraved foliage design on the front, fitted loop and ring on top. The simple Latin or Roman variation of the cross, with an elongated vertical arm, has no figure on it and the reverse has no decoration. The right, left and base edges have sections of narrow, long slightly raised ridges. The top edge has remnants of red-black colour. Victorian era cross, ca. 1878. The cross was recovered from the wreck of the ship Loch Ard.Engraved foliage design. Slightly raised long ridges on sides and base edges. flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, gold cross, religious cross, religious trinket, religious jewellery, engraved cross, cross pendant, cross with ring, victorian era, 1878, antique cross, crucifix, religious symbol, christian symbol, christian jewellery, contamination phenomena, gold corrosion, good luck, lucky charm, blessing, pendant, loch ard, wreck of the loch ard, mutton bird island, peterborough, scuba diver, 1980s, shipwreck artefact, relic, latin cross, roman cross, pectoral cross, julie wilkins -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Clock Parts, Bef. 01-06-1878
The clock parts were discovered in 1980 by Julie Wilkins, a Victorian scuba diver who had already experienced more than 500 dives in Australia and overseas. She was holidaying in Peterborough, Victoria, and looking forward to discovering more about the famous Loch Ard ship, wrecked in June 1878 at Mutton Bird Island. The fast Glasgow-built clipper ship was only five years old when the tragedy occurred. There were 54 people on board the vessel and only two survived Julie's holiday photograph of Boat Bay reminds her of her most memorable dive. Submerged in the calm, flat sea, she was carefully scanning around the remains of the old wreck when, to her amazement, a gold coin and a small gold cross suddenly came up towards her. She excitedly cupped them in her hands and then stowed the treasures safely in her wetsuit and continued her dive. She soon discovered a group of brass carriage clock parts and some bottles of champagne. It was a day full of surprises. The items were easily recognisable, without any build-up of encrustations or concretion. Julie secretly enjoyed her treasures for twenty-four years then packed them up for the early morning train trip to Warrnambool. After a short walk to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village, her photograph was taken as she handed over her precious find. She told her story to a local newspaper reporter, lunched a café in town then took the late afternoon train home. Her generous donation is now part of a vast collection of Loch Ard shipwreck artefacts, including the gold watch and the Minton Majolica model peacock. This group of brass clockwork parts is incomplete. The pieces were in the ocean for over 100 years before Julie recovered them from the Loch Ard wreck. Their size would suit the works of a carriage clock, with a mainspring and weight to power the clock movement, a pendulum to measure the clock's speed, arbours, posts, pillars and at least one other plate. They would have been mounted inside a protective case with a small door to easily access the clock face for setting the time and accessing the key's winding hole. The clock cases were usually made from decorative gilt brass with a glass front and a carrying handle. The parts include a weighted second hand with a decorative four-pronged finish at one end, a rounded weight at the other, and a hole for attaching it to the clock face. The gear teeth profiles are ‘cycloidal’, an arch shape with vertical sides, which is common for antique clocks. Modern clockworks have ‘involute’ teeth with sloping sides and a squared-off top. The brass carriage clock parts are an example of a mechanical clock produced in the 1870s. The clock's design is a part of the chain of technological improvements in methods for timekeeping. Its cycloidal gear teeth were the forerunner of the more modern involute gears. The group of clock parts includes a weighted hand or arm for signifying the seconds. This feature was uncommon in portable Victorian-era clocks. The clock parts are also significant for their association with the ill-fated sailing ship Loch Ard, wrecked in 1878. The travelling clock or officer’s clock may have been part of the cargo destined for the 1880 Melbourne Exhibition, or the personal possession of one of the people on board the vessel. Brass clockwork parts from a mechanical clock, sixteen pieces. Parts comprise a plate, large gears or wheels, small pinions or wheels with fine teeth, wheels with cogs, and a weighted second hand. The parts were from a carriage clock ca. 1878. They were recovered from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, loch ard, wreck of the loch ard, 1878, mutton bird island, peterborough, scuba diver, 1980s, shipwreck artefact, relic, clock, mechanical, clock parts, time, timekeeper, horology, chronometry, cogs, time keeping device, scientific instrument, chronometer, john harrison, longitude, carriage clock, coach clock, portable clock, travelling clock, travel clock, traveller’s clock, officer’s clock, weighted second hand, victorian era, cycloidal gear teeth, brass clock, julie wilkins -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Guinea Coin, The Royal Mint, 1793 George III Spade Guinea, 1793
The coin was discovered by Julie Wilkins, a Victorian scuba diver who had already experienced more than 500 dives in Australia and overseas. She was holidaying in Peterborough, Victoria, and looking forward to discovering more about the famous Loch Ard ship, wrecked in June 1878 at Mutton Bird Island. The fast Glasgow-built clipper ship was only five years old when the tragedy occurred. There were 54 people on board the vessel and only two survived Julie's holiday photograph of Boat Bay reminds her of her most memorable dive. Submerged in the calm, flat sea, she was carefully scanning around the remains of the old wreck when, to her amazement, a gold coin and a small gold cross suddenly came up towards her. She excitedly cupped them in her hands, then stowed the treasures safely in her wetsuit and continued her dive. She soon discovered a group of brass carriage clock parts and some bottles of champagne. It was a day full of surprises. The items were easily recognisable, without any build-up of encrustations or concretion. Julie secretly enjoyed her treasures for twenty-four years then packed them up for the early morning train trip to Warrnambool. After a short walk to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village, her photograph was taken as she handed over her precious find. She told her story to a local newspaper reporter, lunched a café in town then took the late afternoon train home. Her generous donation is now part of a vast collection of Loch Ard shipwreck artefacts, including the gold watch and the Minton Majolica model peacock. The coin is a British 1793 George III Gold Spade Guinea. It was already 83 years old when the Loch Ard had set sail. The loop and ring have been added, perhaps as a pendant, pocket watch accessory or similar purpose. It may have been worn for ‘good luck’ on the long journey to Australia, where ships had to carefully navigate the treacherous Bass’s Strait before arriving at their destination of Melbourne. Sadly, many met their fate on that short stretch of ocean aptly named the Shipwreck Coast. The coin is very recognisable even though it was exposed to the wrecking of the ship, its consequent movement, and the sea's turbulence. Its bent, scratched, buckled, split, dinted and worn condition is part of its story. The red-brown-black discolouration is similar to that found on other gold coins, sometimes called the ‘corrosion phenomena’. Studies suggest the possible cause is contaminants in the minting process reacting to the coins’ environment. The GEORGE III GOLD SPADE GUINEA: - The British Guinea was introduced in 1663 and was circulated until 1814. It was made of 22 carat gold, was 25 to 26 cm in diameter and weighed 8.35 grams. It had a value of 21 British shillings. The guinea coin ceased circulation after 1816 and was replaced by the one-pound note. However, the term ‘guinea’ continued to represent 21 shillings. King George (1738-1820) had six gold guinea designs minted during his reign from 1760 and 1820. Each of the six had different obverse portraits, all facing the right. There were three different reverse sides. The Spade Guinea was the fifth issue of the coin, introduced in 1787 and produced until 1799. The reverse shows a royal crown over a flat-topped shield with the Royal Arms of Great Britain, used in Scotland between 1714 and 1800. The shield images are, from left to right, top to bottom, the Arms of England and Scotland, the Arms of France, the Arms of Ireland, and the Arms of the House of Hanover. The Gold Guinea is also part of Australia’s history. It was the first coin mentioned in the announcement of Governor King of New South Wales his Australian Proclamation of a limited variety and denomination of coins accepted for use in the Australian Colony. The historic and decorative George III Spade Guinea has been reproduced for special collections of coins. However, replicas and imitations have also been made as souvenirs for tourists, as gaming tokens and chips for gamblers, and as ‘fake’ coins for profit. These coins differ in many ways; they may be only half the weight of the genuine coin. Often have a small stamp on the obverse with “COPY” or the manufacturer’s name or initials. Some have scalloped edges, some have dates that are different to the original dates of issue, and some even have text in Latin that translates as something very different to the original coin.The King George III Guinea was only produced from 1663 to 1814 and was the first English coin to be mechanically minted. The coin is the fifth edition of the King George III Guinea, the Spade Guinea, was only produced between 1787 and 1799. It is the only edition with this portrait of King George and the only one with the Royal Coat of Arms of Great Britain in Scotland on the reverse side. This edition was also the last guinea in circulation, because the sixth edition was reserved as the Military guinea. This edition of the Guinea is unique; This coin is the only guinea in our collection. It was minted in 1793, so it is now over 230 years old. The Gold Guinea is part of Australia’s history; it was the first coin in the list of coins for use in the Australian Colonies, mentioned by Governor King of New South Wales in his Australian Proclamation speech of 1800. The George III Spade Guinea was included in the Limited Edition Sherwood 12 Coin Collection of Notable Coinage of Australia. This coin is the only known guinea coin recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard. It was already 85 years old when the ship was wrecked.Gold coin; British. 1793, King George III of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1760-1820), Spade Guinea. Yellow gold coin with gold metal loop mount and a gold ring through the loop. The design is the fifth issue of the George III Gold Guinea. The obverse relief is a portrait of George III facing right. Reverse relief is a crown above the Coats of Arms (1801-1816) of flat top spade-shaped shield divided into four quadrants that depict crowned lions, fleur de lies, a harp. These images are identified as, from left to right, top to bottom, England and Scotland, France, Ireland and Hanover. Inscriptions are minted around the rims of each side. The coin is dated 1793. Its surface has dark areas on both sides and the reed edge and surfaces are well worn. The loop mount is bent and the ring is buckled. The coin was recovered from the wreck of the ship Loch Ard.Obverse text; 'GEORGIVS III DEI GRATIA' (translates to George the Third, by the Grace of God) Obverse relief; (King George III bust, facing right, laurel wreath on head) Reverse text; 'M.B.E.ET.H.REX.F. D.B.ET.L.D. S.R.I.A.T.ET.E' '1793' (translates to: King of Great Britain, France and Ireland, Defender of the Faith, Duke of Brunswick and Lüneburg, Arch-Treasurer and Elector of the Holy Roman Empire) Reverse relief; a spade-shaped image i.e. (Crown with fleer de lies, above Shield with crowned lions in different postures, a harp, and other details)flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, royal mint, british coin, currency, guinea, military guinea, australian currency, british guinea, gold coin, spade guinea, king george iii, george iii, fifth portrait, arms of england and scotland, arms of france, arms of ireland, arms of the house of hanover, coins, gold coins, gold medallion, georgian era, 1793, numismatics, contamination phenomena, gold corrosion, good luck, lucky charm, pendant, lucky coin, trade, loch ard, wreck of the loch ard, 1878, mutton bird island, peterborough, scuba diver, 1980s, guinea coin, gold guinea, shipwreck artefact, relic, julie wilkins -
 Merri-bek City Council
Merri-bek City CouncilWork on paper - Charcoal and pages from Aboriginal Words and Place Names, Jenna Lee, Without us, 2022
Jenna Lee dissects and reconstructs colonial 'Indigenous dictionaries' and embeds the works with new cultural meaning. Long obsessed with the duality of the destructive and healing properties that fire can yield, this element has been applied to the paper in the forms of burning and mark-making. In Without Us, Lee uses charcoal to conceal the text on the page, viewing this process as a ritualistic act of reclaiming and honouring Indigenous heritage while challenging the oppressive legacies of colonialism. Lee explains in Art Guide (2022), ‘These books in particular [used to create the proposed works] are Aboriginal language dictionaries—but there’s no such thing as “Aboriginal language”. There are hundreds of languages. The dictionary just presents words, with no reference to where they came from. It was specifically published by collating compendiums from the 1920s, 30s and 40s, with the purpose to give [non-Indigenous] people pleasant sounding Aboriginal words to name children, houses and boats. And yet the first things that were taken from us was our language, children, land and water. And the reason our words were so widely written down was because [white Australians] were trying to eradicate us. They thought we were going extinct. The deeper you get into it, the darker it gets. But the purpose of my work is to take those horrible things and cast them as something beautiful.’Framed artwork -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageVehicle - Vessel, Surf Boat, 1949
In 1952 the subject surf boat crewed by Geoff Scott, Ron Blackney, Wes McLaren, Jim Tibb, and Stan Stephens, won the Victorian Surf Boat Championships. When the club had finished with the boat Mr. Harold Stephenson paid one shilling and it eventually found its way into a garage where it remained for over 20 years before being donated to Flagstaff Hill. This boat is regarded as a unique example of craftsmanship, closely resembling Bay whaleboats used around the Warrnambool area in the 1800s. This timber caravel surf boat was named “Aeroplane Jelly” and was built by N & E Towns a Newcastle boat builder in 1949 Aeroplane Jellies and David Jones as sponsors of the Sydney Surf Carnival of 1950/1951 donated jointly the vessel. George Towns started his boat-building business in 1869 on Dempsey Island on the Hunter River, NSW. George's sons took over the business as N & E Towns (Norman and Eldrid) and continued until the early 1950s. The business made a variety of small craft including fishing boats, launches, and flood boats. In 1928 they built their first surf boat it took about six weeks to build with cedar planks and hardwood frames. After World War II surf boats became their main focus and they became well known for the lighter and faster designs. Many “Towns built” craft have won events at state and national surf championships. They were renowned Boat Builders producing a much lighter and faster running boat than anything previously made, with a buoyant type bow design giving it the lift necessary to get out and through heavy surf. while its sleek lines from amidships aft provided very fast running qualities. Either side of its bows, it bore the bright silver aircraft transfer of the Aeroplane Jellies Company. After a surf competition at Narrabeen NSW, the competing Warrnambool surf lifesaving team returned home to Warrnambool their club committee decided to purchase the "Aeroplane Jellies" Surf boat if and when it became available as the team had been so impressed with the boat. On 30 October 1951 a cheque for £207-2/6' was raised, £180 for the boat, balance for oars. Transport was arranged and the boat was delivered in November 1951. When the "Aeroplane Jellies" competition days were over in the early 1960's due largely to changing surf boat design, Warrnambool Club's Secretary, Mr. Harold Stephenson, sought permission from the Committee to purchase the boat for the nominal sum of one shilling thus preserving the vessel for posterity. The boat had been stored for many years at the Nullawarre Bakery where it remained until Mr. Stephenson died in 1985. After Mr. Stephenson's passing his family donated the vessel to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in 1986.A very rare example of a surf lifesaving boat that for its time was a unique creation that revolutionised small vessel design in Australia. It was made by a renowned maker that today unfortunately many of his examples of boats he made, especially surf life-saving boats no longer exist making the Flagstaff Hill boat very significant to not only surf lifesaving history but to the part it played in our social life for all those who went to the beaches in 1960s Australia.Surf boat named "Aeroplane Jellies". Timber, double ender carvel, built in 1949 by N & E Towns, Newcastle, NSW. Only a few are in existence. She was a trophy prize at Sydney Surf Carnival 1950/1951, donated by Aeroplane Jellies and David Jones Dept. Store, Sydney. The boat was won by South Narrabeen Surf Club. Warrnambool Surf Club purchased her on 30/10/1951 for £207-2/6, and she was sold to Harold Stephenson in early 1960's for 1 shilling. Donated to Flagstaff Hill by the family of Harold Stephenson around 1985-1986. The name Aeroplane Jellies was lettered in gold across the boat's coaming and there is a remnant of some of the gold lettering still there.warrnambool, flagstaff hillflagstaff hill maritime museum, great ocean road, ememgency, historic boat, surf boat, n & e towns, carvel, vintage boat, double ender boat, lifesaving boat, geoff scott, south narrabeen surf club, warrnambool surf life saving club, lifeboat -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPhotograph - North Arm Bridge, road to Bullock Island, build up of sand spit later site for Fishing Club and boat ramp, Lakes Entrance Victoria, G W Holding, 1/04/1979 12:00:00 AM
North Arm Bridge, road to Bullock Island, build up of sand spit later site for Fishing Club and boat ramp, Lakes Entrance Victoria. Taken during the King of the Straits eventColour photograph taken from Kalimna Heights showing North Arm Bridge, road to Bullock Island, build up of sand spit later site for Fishing Club and boat ramp, Lakes Entrance Victoria waterways, islands, bridges
