Showing 275 items matching "cone"
-
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPhotograph, Mrs. John Cone. Ringwood, c1950's
Black and white photographWritten on back of photograph, "Mrs. John Cone". Mrs Cone was the wife of Dr J.C.P. Cone who practiced in Dr Hewitt's Surgery in Warrandyte Road. -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionDrawing - Artwork - Drawing, [Cone] by Marcus Wills, 1989
Marcus WILLS (1972 - ) Born Kaniva, Victoria Marcus Wills is a figurative realist painter who completed an Advanced Certificate of Art and Design between 1989 and 1991 at the Wimmera Community College of TAFE (now Federation University Australia's Horsham Campus). He graduated from the Victorian College of the Arts in 1995. he won the second Brett Whiteley Travelling Art Scholarship in 1999. In 2006 Marcus Wills won the Archibald Prize for his painting of 'The Paul Juraszek Monolith', based on an engraving by Marcus Gheeraerts the Elder.Framed drawing of a cone. art, artwork, marcus wills, drawing, horsham campus, wimmera campus, alumni, horsham campus art collection, horsham available -
 The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical Collection
The 5th/6th Battalion Royal Victoria Regiment Historical CollectionWeapon - Explosive Ordnance-Inert, Nose cone
Green/ olive nose cone, hollow, with rusted screw thread at base and metal coloured tip. FFE409 6-02 5/6-16 -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Heather Cone at Eltham Railway Station, c.1949
Note: Between April 1923 and August 1926, electric trains from Melbourne terminated at Eltham. A connecting steam train ran between Eltham and Hurstbridge. Pages from a scrapbook belonging to Heather Jenkins (nee Cone) who lived as a child in the Police Residence at 728 Main Road, Eltham from 1911 to the early 1920s. (Reported in Newsletter No. 98, Sept. 1994) Heather McKnight Cone born Eltham 1911 (Vic. 19538/1911), daughter of John Thomas Cone (b1859) and Charlotte Helena McKnight Cone (nee Black, schoolteacher b1875) who were married in 1906 (Vic7936/1906). It was John’s second marriage, his first wife, Mary Jane Lannin (b1865) died in 1899. Constable John Thomas Cone, Badge #3935 served at Eltham Police Station 1 May 1911 to 9 July 1922. He died at Eltham in October 1922 and was buried October 6 at Melbourne General Cemetery. The procession commenced from his home in Main Road, Eltham. Cone was succeeded by Constable William Charles Sergeant Badge #4625 who served from 1 August 1922 to 1 March 1927 Electoral Roll Records Eltham Police Residence, Main Road 1911-1922, Cnst. John Thomas Cone and Charlotte Helena Cone and daughter Heather McKnight Cone (b1911) Eltham, John Street 1925-1934, James Gardiner Jenkins, Railway employee Eltham (Main Road?) 1924: Charlotte Helena Cone, home duties Malvern, 229 Glenferrie Rd Charlotte Helena Cone, Registrar of Births 1934 Heather McKnight Cone, Clerk, 1934 James Gardiner Jenkins, Railway employee 1935-1936 Glen Iris, 13 Ashburton Rd Charlotte Helena Cone, Home duties 1936-1946 Heather McKnight Cone, Clerk 1936-1954 Heather McKnight Jenkins, Receptionist 1963-1972 James Gardiner Jenkins, Railway employee 1936-1972 From records and family trees (Ancestry.com) James Gardiner Jenkins was born in 1892 in Whittlesea. He served in the AIF in WW1. According to Electoral Roll records, Jim was employed with the railways at Eltham, living in John Street. It was probably around then that he met and married Fanny Davidson Carrucan. They were married in 1925 (Vic 7206/1925). Fanny died 1929 at age 30. At the time of Fanny’s death in 1929, Jim Jenkins was 37, Charlotte Cone was 54 and Heather Cone 18. Some time between 1924 and 1934 but most probably closer to 1934, Charlotte and daughter Heather left Eltham and were living at 229 Glenferrie Road, Malvern. By 1935 Jim Jenkins was living with them. By 1936 all three moved to 13 Ashburton Road, Glen Iris where it appears they may have lived out their lives. Charlotte died in 1952, and Heather was still living under her maiden name in 1954 but by 1963 was recorded as Heather Jenkins. Jim is last found in the Electoral Rolls for 1972; he died in 1975. Heather died in 2010. JENKINS. - Heather. Passed away peacefully at Cabrini Ashwood on Oct. 24, 2010 Reunited with Jim and Jonathon No Funeral at her request [Herald Sun 26/10/2010] Sources: • VIC BDM • Electoral Roll Records via Ancestry.com • Family Notices (1922, October 6). The Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 - 1954), p. 16. Retrieved July 30, 2025, from http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article205053816 • Police Honour Roll Eltham Police Station Heather Jenkins was the daughter of Constable John Thomas Cone, Badge #3935 served at Eltham Police Station 1 May 1911 to 9 July 1922.Glued on a brown paper scrapbook page (torn from scrapbook) with 8 black and white/sepia photos of varying sizes, 1 newspaper clipping and one greeting card with printed sketch and handwritten captions in ink. On back of page is 1 black and white photo and a large newspaper clipping.eltham railway station, heather jenkins (nee cone) -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Probably Heather Cone in a 1946 Morris 10, c.1946
Pages from a scrapbook belonging to Heather Jenkins (nee Cone) who lived as a child in the Police Residence at 728 Main Road, Eltham in the 1920s.Heather Jenkins was the daughter of Constable John Thomas Cone, Badge #3935 served at Eltham Police Station 1 May 1911 to 9 July 1922.Glued on a brown paper scrapbook page (torn from scrapbook) with 8 black and white/sepia photos of varying sizes, 1 newspaper clipping and one greeting card with printed sketch and handwritten captions in ink. On back of page is 1 black and white photo and a large newspaper clipping.eltham, 1946 morris 10, car, heather jenkins (nee cone) -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Black and White Print, Weapons Research Establishment (WRE), Nose Cone - Skylark Rocket, 17 June, 1960
On reverse: Nose Cone - Skylark Rocket Also stamped in blue ink: Phone: Ex. 253 STILL PHOTO SECTION W.R.E. SALISBURY, S.A. Neg. No. E1532A (in pencil) Date: 17.6.60 (in pencil) Subject: Skylark Nose. (in pencil) Classification: RESTRICTED (over stamped) 9 Feb 1961 (over stamped)alan gardiner collection, space industry, 1960-06-17, rocket, salisbury, skylark rocket, south australia, weapons research establishment (wre), woomera, 1960 -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Black and White Print, Weapons Research Establishment (WRE), Nose Cone - Skylark Rocket, 17 June, 1960
On reverse: Nose Cone - Skylark Rocket Also stamped in blue ink: Phone: Ex. 253 STILL PHOTO SECTION W.R.E. SALISBURY, S.A. Neg. No. E1532B (in pencil) Date: 17.6.60 (in pencil) Subject: Skylark Nose. (in pencil) Classification: RESTRICTED (over stamped) 9 Feb 1961 (over stamped)alan gardiner collection, space industry, 1960-06-17, rocket, salisbury, skylark rocket, south australia, weapons research establishment (wre), woomera, 1960 -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Black and White Print, Weapons Research Establishment (WRE), Nose Cone - W.R.E. Skylark Rocket, 17 June, 1960
On reverse: Nose Cone - W.R.E. Skylark Rocket Also stamped in blue ink: Phone: Ex. 253 STILL PHOTO SECTION W.R.E. SALISBURY, S.A. Neg. No. E1532 (in pencil) Date: 17.6.60 (in pencil) Subject: Skylark Nose. (in pencil) Classification: RESTRICTED (over stamped) 9 Feb 1961 (over stamped)alan gardiner collection, space industry, 1960-06-17, rocket, salisbury, skylark rocket, south australia, weapons research establishment (wre), woomera, 1960 -
 Mentone Grammar School
Mentone Grammar SchoolArchive, Memorial Cone from the original Lone Pine, Gallipoli, 1916
Memorial cone from the original 'Lone Pine' at Gallipoli, presented to Headmaster Neville Clarke by B Company, Mentone Grammar Cadet Unit, 15th August 1995 in memory of those who served. The Battle of Lone Pine was fought between Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZAC) and Ottoman Empire forces during the Gallipoli Campaign of the First World War, between 6 and 10 August 1915. The battle was part of a diversionary attack to draw Ottoman attention away from the main assaults being conducted by British, Indian and New Zealand troops around Sari Bair, Chunuk Bair and Hill 971, which became known as the August Offensive. -
 Upper Yarra Museum
Upper Yarra MuseumWooden Cone shape
Green wooden cone shaped teaching tool used at Powelltown Primary SchoolConecone wooden teaching aid tool powelltown primary school shape -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDrawing (item) - Dassault Nose Cone Drawings and Stage Ops
-
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (item) - Mirage Cyrano Nose Cone M800545
-
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesArticle, J.A. Plumridge, Cone-bearing trees, 1955
Reprint of article by J.A. Plumridge from Journal of the Department of Agriculture, 2 copiesj.a. plumridge, department of agriculture, journal -
 Queen's College
Queen's CollegeFunerary cone, New Kingdom, 18th Dynasty, 1550 - 1295 BCE
This item is part of the Dodgson Collection, which was bequeathed to Queen's College in 1892 by the Rev. James Dodgson. The collection was created by Aquila Dodgson, brother of James. Aquila Dodgson was a friend of the English Egyptologist Flinders Petrie, and it was through this friendship the Aquila was able to acquire ancient Egyptian artefacts. A detailed study of the collection was made by Christine Elias "Discovering Egypt: Egyptian Antiquities at the University of Melbourne", M.A. thesis 2010.Two ovals of hieroglyphs with remains of a red/brown paint on face of cone and round edge. Small paper label inscribed with 'A6' attached to cone.funerary cone, james dodgson, aquila dodgson, flinders petrie -
 Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of Melbourne
Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of MelbournePlant specimen - Genus Picea. Family Pinaceae. The spruces. Genus Larix. Family Pinaceae. The Larches, Display sheet. Spruce and Larch seed cones from international sources glued to sheet and identified
Seed cones mounted on a paper boardDisplay sheet. Spruce and larch seed cones from international sources glued to sheet and identified. -
 Queen's College
Queen's CollegeFunerary cone, New Kingdom, 18th Dynasty, 1550 - 1295 BCE
This item is part of the Dodgson Collection, which was bequeathed to Queen's College in 1892 by the Rev. James Dodgson. The collection was created by Aquila Dodgson, brother of James. Aquila Dodgson was a friend of the English Egyptologist Flinders Petrie, and it was through this friendship the Aquila was able to acquire ancient Egyptian artefacts. A detailed study of the collection was made by Christine Elias "Discovering Egypt: Egyptian Antiquities at the University of Melbourne", M.A. thesis 2010.Three columns of hieroglyphs and remains of a red/brown paint on the face of the cone and on body, end broken off. Small paper label inscribed with 'A6' attached to cone.funerary cone, james dodgson, aquila dodgson, flinders petrie -
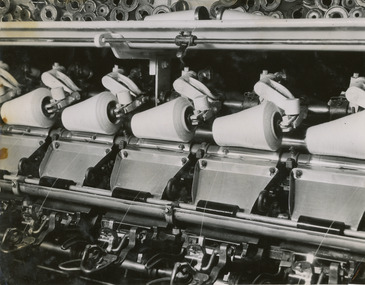 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumPhotograph - Cone Winding, 1960s
One of fifty one photographs originally in a photo album found in the National Wool Museum’s office. The album was water damaged and the images were removed for conservation. The images follow the process of wool. Beginning in a sheep paddock and finishing as a folded fabric. It includes all the steps in between in this process, including shearing, transporting, selling, washing and the many different steps in the process of turning a single thread of wool into fabric.Black and white image showing detail of a cone winding machine.AUSTRALIAN NATIONAL PUBLICITY / ASSOCIATION / FLINDERS STREET RAILWAY BUILDING, / MELBOURNE AUSTRALIA / W20 / W20. Cone Winding.wool industry, working life, women, boonoke station, farming, sheep farming, agriculture, sheep stations, transport, wool processing, shearing, textile industry, wool -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumPhotograph - Cone Roving, 1960s
One of fifty one photographs originally in a photo album found in the National Wool Museum’s office. The album was water damaged and the images were removed for conservation. The images follow the process of wool. Beginning in a sheep paddock and finishing as a folded fabric. It includes all the steps in between in this process, including shearing, transporting, selling, washing and the many different steps in the process of turning a single thread of wool into fabric.Black and white image showing two women working at a cone roving machine.AUSTRALIAN NATIONAL PUBLICITY / ASSOCIATION / FLINDERS STREET RAILWAY BUILDING, / MELBOURNE AUSTRALIA / W22 / W22. Cone Roving.wool industry, working life, women, boonoke station, farming, sheep farming, agriculture, sheep stations, transport, wool processing, shearing, textile industry, wool -
 Warrnambool RSL Sub Branch
Warrnambool RSL Sub BranchBomb Tail firing cap, Around late 1938 to 1945
A cone shape at the base section with a cylinder section on the top half made of brass and is screwed onto the rear section of and Arial Bomb. There are 2 leavers either side of the cylinder section which open out after the bomb has been dropped from a plane ,this helps slow the bombs decent and with a brass propeller at the very top of the devise helps to activate the firing pin and arming the bombThere are a number of Japaness markings on the cone section with some numbersww2 japaness bomb arming mechanisum -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumCone
Designed for nce only use. Used for holding the yarn during yarn dyeing. The process was called "pressure dyeing" for a small amount of yarn. Doesn't create an even dye effect.Wangaratta Woollen Millsweaving mills, wangaratta woollen mills -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyPhotograph - Photo, Legacy Lone Pines, 1989
Photos of President Chas Wilks collecting pine cones from the Lone Pine descendant at the Shrine of Remembrance, the 24th Battalion tree. The cones dropped to the ground and school children are seen collecting them. Legacy has run a programme since the 1970s of propagating saplings taken from seeds of pine descended from a pine tree from Gallipoli and giving them to various clubs, schools and town councils. The photo appeared in the President's Highlights report in 1989. The caption says '1,000 seedlings from the historic Lone Pine tree near the Shrine of Remembrance will be propagated on behalf of Melbourne Legacy by the Department of Conservation Forests and Lands. Melbourne President Legatee Chas Wilks, along with the Minister for CFL, Ms Kay Setches and pupils from South Yarra Primary School helped to collect the seeds. The trees, once grown will be distributed to schools by Melbourne Legacy. Also see item at 01334 in 1993 when President Woodward was giving out saplings, it was three years later was when the saplings grown from these seeds were distributed. Legacy is helping to keep the memory of the Gallipoli "Lone Pine" alive - its spirit living on today. Presentations are made to schools, ex-service organisations and interested bodies by Legacy Clubs in the hope that they will be cherished as a symbol of nationhood and of its just pride, devotion, courage, selflessness and sense of service to others.A record of the way Legacy was propagating Lone Pine saplings for schools and organisations. The Lone Pine programme show the type of work done by Legatees to keep the memory of Gallipoli and fallen comrades alive.Colour photo x 4 of President Chas Wilks in a crane collecting pine cones at the Shrine and children collecting the cones.Handwritten '10' in a circle in blue pen.tree planting, lone pine -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumSign
Used to advertise vacant job positions at the entrance to Foster Valley Mill.Cone Rover -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumSign
Used to advertise vacant job positions at the entrance to Foster Valley Mill.Cone Drawing -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumWeapon - NOSE CAPS, ARTILLERY, c.WWI
These are WW1 graduated nose caps. Shell nose caps, brass, steel & aluminium with graduated markings. .1) Cone shaped nose cap. .2) Broken ring section, brass stem rounded nose cap..1) Graduated markings “0-22” stamped on cone: “146 287 V RAL T” .2) Graduated markings “K-70”, stamped on cap: “Dopp 2. 96. n/A, K514 (3 below 5)”arms - ammunition, military history - souvenirs, metalcraft- brassware, metalcraft - aluminium, passchendaele barracks trust -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Photograph
Coloured photo of the front view of a Caribou aircraft. The pilot & co-pilot are clearly visible in the cockpit. The photo is mounted on a timber board.73 on the Nose cone.caribou -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Cone, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A woven cane cone, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre and two crossed metal bars at the base. The central rod has a loop at the top and passes through the bars at the base, finishing in a metal loop. The rod has swivels at each end.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, marine navigation, marine communications, communication signal, lifesaving, ship at sea, day shape, masthead signal, day signal, day mark signals, marine technology, safety equipment, navigation equipment, marine day shape, day marker, cane day shape, signal cone, day signal cone, cone signal, cone day shape, distant signal, flagstaff signal, signal station, communications, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Cone, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A woven cane cone, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre and two crossed metal bars at the base. The central rod has a loop at the top and passes through the bars at the base, finishing in a metal loop. The rod has swivels at each end.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, marine navigation, marine communications, communication signal, lifesaving, ship at sea, day shape, masthead signal, day signal, day mark signals, marine technology, safety equipment, navigation equipment, marine day shape, day marker, cane day shape, signal cone, day signal cone, cone signal, cone day shape, distant signal, flagstaff signal, signal station, communications, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897 -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesSlide - Glass slide, 1891-1905
Glass slide of cones on branch.4trees, cones -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Vehicle, Lockhead C130A Hercules Forward Fuselage A92-214, Abt. 1950's
The C-130 Hercules during the Vietnam War performed airlifts, airdrops for which is was designed. C-130 could disgorge large quantities of cargo and supplies on pallets, either by parachute from altitude or simply pulled out the back dropped with the help of drag chutes and buzz job heights. The Fuselage is the only part of the C130A Hercules that is on display. The number, 14 is located above the nose cone.c-130 hercules, c-130 hercules forward fuselage, military transport -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncPhotograph, On the Binder, c 1930's
Mick Wlash's Father on the binder taken during the 1930's.Copy of a B/W Photograph showing a Man and a Youg Girl on a machine being towed by horses'35" on a white sticker on the lower left conerfarming
