Showing 33 items matching "detention"
-
 Lara RSL Sub Branch
Lara RSL Sub BranchCard, UN Disarmament, Apprehension and Detention Card
The United Nations Transitional Administration in East Timor (UNTAET) provided an interim civil administration and a peacekeeping mission in the territory of East Timor, from its establishment on 25 October 1999,[1] until its independence on 20 May 2002, following the outcome of the East Timor Special Autonomy Referendum. This card instructs personnel the correct procedure for the disarmament, apprehension and detention.A green UN Disarmament, Apprehension and Detention Card that has writing on both sides. Used by United Nation Forces in East Timor.military, army, timor, east timor, united nations, un, card, laminated, untaet, untaet pkf, pkf, green card, disarmament, apprehension, detention -
 Beechworth RSL Sub-Branch
Beechworth RSL Sub-BranchCard - Card, Guidance on the Use of Force, UNTAET PKF-INDIVIDUAL GUIDANCE ON DISARMAMENT, APPREHENSION AND DETENTION, 1999-2002
This card provided rules of engagement for Australian soldiers deployed to East Timor as part of UNTAET (United Nations Transitional Administration), an integrated, multi-dimensional peacekeeping operation fully responsible for the administration of East Timor during its transition to independence. UNTAET was the UN mission in East Timor, following its independence from Indonesia in 1999. The mission provided interim civil administration and a peacekeeping functions from 1999 until it was superseded by The United Nations Mission of Support in East Timor (UNMISET) following East Timorese elections in 2002. This information card was carried by all peacekeeping duty that could be referred to should it be requiredSmall green laminated card and rounded corners. Has text on both sides.UNTAET PKF-INDIVIDUAL GUIDANCE ON DISARMAMENT, APPREHENSION AND DETENTIONbeechworth, un, east timor, timor leste, peacekeeping -
 Beechworth RSL Sub-Branch
Beechworth RSL Sub-BranchCard, Rules of Engagement, UNTAET PKF-INDIVIDUAL GUIDANCE ON DISARMAMENT, APPREHENSION AND DETENTION, 1999-2002
This card provided rules of engagement for Australian soldiers deployed to East Timor as part of UNTAET (United Nations Transitional Administration), an integrated, multi-dimensional peacekeeping operation fully responsible for the administration of East Timor during its transition to independence. UNTAET was the UN mission in East Timor, following its independence from Indonesia in 1999. The mission provided interim civil administration and a peacekeeping functions from 1999 until it was superseded by The United Nations Mission of Support in East Timor (UNMISET) following East Timorese elections in 2002. Small blue card with a gloss surface and rounded corners. Has text on both sides.UNTAET PKF-INDIVIDUAL GUIDANCE ON DISARMAMENT, APPREHENSION AND DETENTIONbeechworth, un, east timor, timor leste, peacekeeping -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Photograph, Gibbons, Denis, Detention Barrack
Denis Gibbons (1937 – 2011) Trained with the Australian Army, before travelling to Vietnam in January 1966, Denis stayed with the 1st Australian Task Force in Nui Dat working as a photographer. For almost five years Gibbons toured with nine Australian infantry battalions, posting compelling war images from within many combat zones before being flown out in late November 1970 after sustaining injuries. The images held within the National Vietnam Veterans Museum make up the Gibbons Collection. A black and white photograph of the Australian Forces Vietnam detention barack located at 1st Australian Logistic Support Base, Vung Tau. It was here that those diggers who wer responsible for the more serious breaches of good order and military discipline were sent.photograph, 1st alsg base, military police, vung tau, detention barrack, gibbons collection catalogue, diggers, military discipline, denis gibbons -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumDocument, All Locked Up And Nowhere To Go, c.2000
Written as a thesis for a tertiary qualification.Black plastic multi ring folder with clear plastic front. A comparative study of children in wartime internment camps and present day immigration detention centres in Australia. 74 pages of double spaced tying. Story and photographs.All Locked up and Nowhere to Go A comparative study of children in wartime internment camps and present day immigration detention centres in Australia by Claire Thomasinternment of children, claire thomas, all locked up and nowhere to go -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - STRAUCH COLLECTION: TRIAL BAY GAOL
Trial Bay opened in 1886 after 13 years construction. It was designed for prisoners who were low risk and nearing the end of their sentences. From here they would participate in Public Works projects. It was named Trial Bay after the brig "Trial" sank there. This ship had been commandeered by convicts in Port Jackson and forced to sail north. Between 1915 and 1918 the prison became a detention centre for German citizens.Trial Bay Gaol, Public Works Prison and Wartime Detention Camp, a Macleay River Historical Society publication Kempsey, New South Wales, small booklet with black and white photographs.Marie h Neilhistory, australian, prisons, australia-history-nsw-prisons -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - BADHAM COLLECTION: VICTORIAN RAILWAYS -ROLLING STOCK BRANCH FORM R.S. 12A
Victorian Railways Rolling Stock Branch form R.S. 12a - 'Driver's report of casualties, irregularities, detention to trains, small paper form faded.document, memo, railway, victorian railways -rolling stock branch form r.s. 12a - 'driver's report of casulalties , irregularities , detention to trains -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Photograph, Gibbons, Denis, Prison Cell
Denis Gibbons (1937 – 2011) Trained with the Australian Army, before travelling to Vietnam in January 1966, Denis stayed with the 1st Australian Task Force in Nui Dat working as a photographer. For almost five years Gibbons toured with nine Australian infantry battalions, posting compelling war images from within many combat zones before being flown out in late November 1970 after sustaining injuries. The images held within the National Vietnam Veterans Museum make up the Gibbons Collection. A black and white photograph of the regimentation, discipline and order required of a prisoner, in his cell, when confined to Australian Forces Vietnam Detention Barack located at the First Australian Logistic Support Base, Vung Tauphotograph, detention barrack, 1st alsg base, vung tau, military police, gibbons collection catalogue, prisoners, australian forces vietnam detention barack, denis gibbons -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyNewspaper Clipping, Diamond Valley Leader, Asylum seekers open up, 21/06/2017
A former asylum seeker who spent time in detention will speak about his experience at a special Refugee Week event in Montmorency.News article 1 page, black text, colour image.montmorency, refugee week, asylum seeker -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyNewspaper Clipping, Diamond Valley News, Protest on State centre, 1973_11c
The Institute of Social Welfare, Watsonia operated on the Loyola Seminary campus 1973-74, which was purchased by the Probation and Training Division to run certificate courses for social workers and others. There was a proposal to establish a periodic detention centre on the site in November 1973, against which there were protests by local residents.News article, text only. Word document with research notes on item.institute of social welfare, watsonia, loyola college -
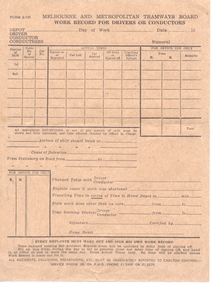 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Form/s, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), "Work Record for Drivers or Conductors", 1950's?
Printed form on brown paper, titled "Work Record for Drivers or Conductors" provides the various information for crews to fill in depot, day of week, person, shifts details actual times, detention times and other information to enable the calculation of pays etc. Has notes on the bottom of the sheet regarding completing the form and Carlton Control contact details. Form No. 3/133, not formally dated.trams, tramways, conductors, depots, crews, drivers, payroll -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumFolder, 1940s
Forms regarding Joachim Stahr, an internee aboard the Dunera.Documents contained in folder marked "S" in sheet protectors. Contains: Form of Application for Residence Order for Detention of Enemy Alien Report on Internees Internees - Service and Casualty Form Medical Examination Mobilisation Attestation Form Service and Casualty Form Employment Company Form Determination of Demobilisation Priority Application for Admission of Relative or Friend to Australia Report on Internee Internee - Service and Casualty Form Email correspondencejoachim stahr, dunera, ww2 internee -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumBook, Hidden Lives: war, internment and Australia's Italians, 2018
Tells the stories of those immigrants who experienced detention during World War 2 as enemy aliens in these allied nations. Some Italian families whose husbands were arrested as "security risks" were sent to internment camps such as Loveday S.A hundreds of miles away leaving their wives and families to cope alone during W.W.2Cover has colours of the Italian flag, green, white and red. Across the centre of the flag is a photo of Italian internees arriving at a camp.For our surrogate mother, Lurline Knee. Thank you for bringing the Tatura story to us. beast wishes from Claudia (Marsella) Barker may 2018.world war two, italian internees -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyNewsletter, Greenhills and North Greensborough Progress Association, Community News: official journal of the Greenhills and Nth. Greensborough Progress Association.1st November,1974. Edition No. 7/74, 01/11/1974
This edition includes a report on the Progress Association's September 1974 meeting, Councillor's report, Yandell rally cross, Loyola Detention Centre ??, Open letter to the Shire Engineer, From the Council Chamber, Meet the natives, School and kinder news, Letter to the Editor, Planning prospects, For the environmentalists. A digital copy of this Newsletter is available from Greensborough Historical Society.Newsletter, 24 p., illus.greenhills and north greensborough progress association, greenhills -
 Ballarat Clarendon College
Ballarat Clarendon CollegeReport card, 1929
This Form IVA & Romove third term (end of year) report was issued for Jean Wilson in December 1929 and signed by CPLC Principal, Lucy Shaw. The report details subjects studied and gives student percentage, class average, cohort total, position in class, personal comment and examination/term marks. Other management of earning indicators include conduct, homework, detentions and attendance. This report has social significance because it gives indication of educational standards and expectations of the era. Light card, folded in half; Clarendon presbyterian ladies College crest, motto and name on front page; Report on centre pages; back page blankjean wilson, 1929 -
 Merri-bek City Council
Merri-bek City CouncilArchival pigment print, Hoda Afshar, Behrouz Boochani – Manus Island No.2, 2018
Hoda Afshar's 2018 body of work, "Remain," offers a forthright and unapologetic political commentary on Australia's border protection policy, shedding light on its impact on human rights. This collection comprises a film and a series of photographic portraits that chronicle the stories of stateless men who chose to stay on Manus Island, Papua New Guinea, even after the closure of the immigration detention centre in October 2017. In the accompanying film, the experiences of these men are conveyed through episodic fragments, narrated with a mix of lyrical and brutal voiceovers. Some express themselves through poetry, others through song, while some recall the riots and suicides. Set against the backdrop of a picturesque landscape featuring lush foliage and crystal-clear water—a stark contrast to the harsh realities described—the emotional impact of the work is intensified. It creates a simultaneous sense of beauty and horror. The photographic portraits of the same individuals are equally compelling. Positioned prominently against a dark backdrop, these subjects assert their presence, emphasizing their right to be seen. The deliberate simplicity of these portraits serves as a powerful political statement, countering the invisibility imposed by the act of detention. Afshar metaphorically acknowledges the struggles faced by these men, depicting them contending with the elements—fire, water, and earth—yet never questioning their inherent humanity. Here we see Behrouz Boochani, the Kurdish Iranian writer whose memoir ‘No Friend but the Mountains: Writing from the Manus Prison’ won the Victorian Premier’s Prize for Literature and the Prize for Non-Fiction in 2019. Boochani was held in detention on Manus Island from 2013 until the centre’s closure in 2017 and was forced to remain on the island in a stateless condition. -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumDocument - Rule Book, City of Ballaarat, "City of Ballaarat - Regulation No. 13", 1882
Rule book or printed set of Regulation contained within Reg. Item 2526, page 16, titled "City of Ballaarat - Regulation No. 13". Booklet comprises eight pages, pinned and glued into the book. Details the regulations prepared to regulate the operations and parking of Hackney Carriages and Borough Stage Coaches. Details carriage stage coach stands locations and parking rules around Ballarat, Sebastopol, Stands for Omnibuses, and Fares for Hackney Carriages, by distance, detention and by time. Passed by the Council of City of Ballaarat 30/1/1882 and Gazetted in the Victorian Govt. Gazette, page 290 on 3/2/1882. Note Item Not formally Numbered.trams, tramways, ballarat, hackney carriages, regulations, fares -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionWork on paper - Artwork - Printmaking, 'Untitled', by Ludwig Hirshfeld-Mack, 1959
Ludwig HIRSCHFELD-MACK (1893-1965) Born 11 July 1893, Frankfurt am Main, Germany In 1940 Hirschfeld-Mack was deported to Australia from England as an enemy alien in the Dunera. He was interned at Hay and Orange, New South Wales, and at Tatura, Victoria. There he made a number of woodcuts that illustrated life under detention. Released in 1942 through the sponsorship of (Sir) James Darling, headmaster of Geelong Church of England Grammar School, Hirschfeld-Mack was appointed its art master. He promoted his pupils' self-knowledge, introduced them to avant-garde painting techniques, and encouraged wood-carving, weaving, musical instrument-making, leatherwork and other crafts. (http://adb.anu.edu.au/biography/hirschfeld-mack-ludwig-10510, accessed 29 June 2016) He died on 7 January 1965 at Allambie Heights, Sydney Framed abstract paintingSigned in pencil lower left hand side 'L.H.Mack 1959'art, artists, mack, hirschfeld-mack, ludwig hirschfeld-mack, ludwig hirshfeld-mack, printmaking, monoprint, bauhaus -
 St Kilda Historical Society
St Kilda Historical SocietyPhotograph, Edith Cavell statue, St Kilda Botanical Gardens - images collection
Edith Cavell was born in England in 1865 and trained as a nurse in the late 1890s. She was also an accomplished linguist, musician and artist. In 1907 she was assisted in establishing a modern nursing system at the Berkendael Medical Institute in Brussels. At the outbreak of World War One she was left in charge of the hospital and what is now known as the Red Cross. During that time she assisted more than 200 Belgian, British and French soldiers who had been separated from their armies, or who had escaped German detention. In 1915, she was accused of conspiring to help prisoners escape, and was tried by a military court in Brussels. She was convicted and sentenced to death, along with four others. Cavell was executed by firing squad on 12 October 1915; she was still wearing her nurse’s uniform. Her body was returned to England in 1919, where a full military service was conducted at Westminster Abbey.colour photograph unmountedBase of the bust: Edith Cavell 1865-1915 Plaque on the plinth: Restored and located in the St Kilda Botanical Gardens in recognition of his mayoral year 1985-86. John Callanan, JP, Mayor. St Kilda Garden Festival 26th October 1986st kilda, st kilda botanical gardens, plaques, edith cavell, world war i -
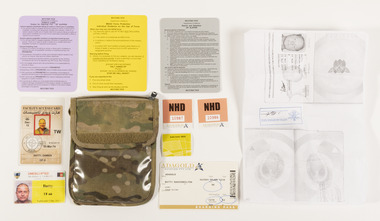 Beechworth RSL Sub-Branch
Beechworth RSL Sub-BranchField Notebook Holder Contents, c2012
Contents belonged to Major Damien Batty whilst serving with the United Nations Forces in Afghanistan. Major Damien Batty served in Afghanistan in 2011-2012 with the Bravo Commando Company Group, 2nd Commando Regiment in Uruzgan. The Commandos took part in 20 rotations with the Special Operations Task Group (SOTG) between 2007 and 2012. During this time they undertook significant combat operations, and were awarded for its actions, the regiment was collectively awarded the Unit Citation for Gallantry and the Meritorious Unit Citation.Contents from the Field Notebook Holder, (see 0096.1) belonging to Major Damien Batty whilst serving with the United Nations in Afghanistan. Located in the clear plastic compartment of the Field Note Holder: 0096.02 - Authority card in colour featuring a photograph of Major Damien Batty. 0096.03 - Facility access card in colour featuring a photograph of Major Damien Batty. Located in the folded compartment of the Field Note Holder: 0096.04 - White boarding pass with colour text 0096.05 - Peach sticker with black text 0096.06 - Peach sticker with black text 0096.07 - Green sticker with black text 0096.08 - White A4 sized paper copy of passport with certification stamp 0096.09 - Small grey Rules of Engagement card with a gloss surface and rounded corners. Has text on both sides 0096.10 - Small yellow Rules of Engagement card with a gloss surface and rounded corners. Has text on both sides 0096.11 - Small purple Rules of Engagement card with a gloss surface and rounded corners. Has text on both sides 0096.12 - White piece of paper torn from a spinal notebook with written text in blue and red ink. (Not pictured) 0096.02 - UNESCORTED / WEAPONS AUTHORISED / CELL PHONE ALLOWED / BATTY / TF-66 / VALID UNTIL 5 DECEMBER 2012. 0096.03 - 03-MAR-74 / BATTY DAMIEN / OF-3 Back 0096.04 - ADAGOLD / AVIATION PTY LTD / FROM SYDNEY / TO MIHAD MILITARY / DATE 05 JUN /1310 / 0096.05 - NHD / 10987 /ADAGOLD / AVIATION PTY LTD / 0096.06 - NHD / 10986 / ADAGOLD / AVIATION PTY LTD / 0096.07 - QUALITY CONTROL / 0096.08 - DAMIEN BATTY / 0096.09 - RESTRICTED / DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE / SEARCH AND DETENTION / OP SLIPPER / (AFGHANISTAN ONLY) / DEC 2010 / 0096.10 - RESTRICTED / DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE / MEAO FORCE PROTECTION / INDIVIDUAL GUIDANCE ON THE USE OF FORCE / APR 2009 / 0096.11 - RESTRICTED / DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE / PURPLE CARD / ORDERS FOR OPERATING FIRE / OP SLIPPER / contents, field notebook holder, identification, united nations -
 Sunshine and District Historical Society Incorporated
Sunshine and District Historical Society IncorporatedUniform - School Uniform, SUNSHINE HIGH SCHOOL, Late 20th century
Sunshine High School existed in its own right from 1955 to 1991. During the early years the wearing of 'correct' uniforms was strictly enforced. Girls had to wear hats and boys had to wear caps as part of the uniform when outside the school grounds, or else they risked detention if caught without head wear by a Prefect. The boys therefore always had a rolled up cap in the back pocket to quickly slip on whenever there was danger of being nabbed by a Prefect. The girls had a winter uniform, which included thick beige stockings and a maroon blazer, and a summer frock in which they could be relatively cool during hot days. The boys had to wear their double breasted grey suits all year, with a jumper under the jacket in cold weather. The boys were supposedly being groomed as gentlemen, and so even during hot conditions were not allowed to remove their suit jackets in the class room. On about two very hot afternoons a year, the headmaster removed his jacket and so allowed the boys to do likewise. With single breasted suits becoming fashionable, it became difficult to find double breasted grey suits in the wide range of sizes required by students. In about late 1960 or early 1961 the uniform rules for boys were changed to enable them to wear single breasted grey suits. They still however were not allowed to remove their jackets in class on hot days. Over the years the rules for the wearing of uniforms were relaxed and in the late 1970's students were wearing either uniforms, or parts of uniforms, or their normal clothing. The wearing of uniforms at Sunshine High School eventually died out well before the School vacated the buildings on Ballarat Road, and amalgamated with other local secondary schools to form the Sunshine College.The three items of clothing, although not a complete uniform set, serve as a reminder of the summer and winter uniforms, as well as the colours, that were worn by the girls at Sunshine High School during the early years. The jumper is identical in appearance to that worn by the boys and so it is not difficult to imagine how a male Sunshine High School student would look like with a grey suit and that type of jumper.THREE ITEMS of girls uniform from the no longer existing SUNSHINE HIGH SCHOOL are individually displayed here. The items being: (1) Beige with maroon print cotton summer frock. (2) Maroon polyester/wool winter tunic. (3) Maroon V-necked wool/nylon jumper with light blue and gold coloured stripes around the cuffs and the neck.Ecole brand winter tunic. Buxwear brand summer frock of Style S289. M.G.Magree brand jumper.sunshine high school, uniform, frock, tunic, jumper, girls school uniform, maroon uniform -
 Ruyton Girls' School
Ruyton Girls' SchoolPhotograph, Ruyton Girls' School, 1951
Depicted are four students who were the 1951 House Captains at Ruyton Girls' School. The photo is an official school portrait, taken outdoors in front of Henty House (formerly Tarring). In the background, we can see two bicycles. The girls are dressed in their school uniforms, comprising a knee-length check-print skirt, dark jumper, light-coloured collared buttoned blouse with a dark tie, wool blazer, stockings, and dark-coloured lace-up shoes. Two of the girls are standing, while the other two are seated on a small concrete plinth. The students have been identified, from left to right, as A. Dickinson (Lascelles), C. Kent (Anderson, H. Cole (Bromby), and E. Duff (Daniell). Student leadership commenced at Ruyton Girls' School in 1906 with the introduction of the prefect system. Prefects had numerous responsibilities—gate duty, grounds duty, classroom marking, assembly door watch, uniform monitoring, and even supervising student detention. In 1947, a dedicated Prefects Room was erected on the east side of the Ruyton Girls' School Assembly Room in Henty House. The prefects system was revised in 1968 with a new leadership structure: there would be a permanent School Captain, Vice Captain and School Sports Captain; six permanent prefects would be elected, and the rest of the Matriculation class would form committees. These included Library, Social Services, S.C.M., Editorial, and Music. In this way, it was thought "that each Matric girl would have a certain amount of responsibility." With this revised structure came a brand new Prefects' Study, located in a former classroom next to the Domestic Science building. Each prefect was allocated one book locker, one clothing locker, "a small share in the heater", plus a new shared lounge. The prefect system was updated again in 1974. All sixth formers would become prefects, or "school officials." This saw the sixth form divided into two halves: one group would be prefects for the first half of the year, then the second group would take the reigns in the latter half of the year. In October 2023, Ruyton announced a new collaborative leadership structure for captains, prefects and house leaders, which would see two students in each leadership role.The record has strong historic significance as it gives insight into the House system at Ruyton Girls' School. In the early 1920s, Ruyton was settling into its new home at Selbourne Road, Kew. At the time, students were arranged by their form (or year level) for lessons and other school activities. A collection of eight emblems and mottoes for each form group was published in the Ruytonian December 1922, although the genesis of each were left unexplained. With enrolments continually growing, Principal Miss Hilda Daniell felt a new basis of organisation would benefit students, giving them a broader outlook and something bigger to work for. She took inspiration from tradition and implemented a House system. The House system was adopted at Ruyton in September 1924 to "provide a new kind of co-operation and competition among the girls, especially in Sport." There were four houses, three of which were named after early Principals: Anderson, Bromby and Lascelles. There was also the School House, initially for boarders only. Some time after the publication of the Ruytonian in April 1928, the School House was renamed Daniell House, and had opened up to day girls. The account published by the newly formed Daniell House in the Ruytonian December 1928 reads, "we are rather bashful in presenting this account of our doings, for we are conscious of our newness. Our house has now the honour of being known as Daniell House." Four of the original eight form emblems were adopted by the new Houses, while the others were discarded. According to former teacher and author of the centenary history of Ruyton, Ms Majorie Theobald, the House system "gave a new focus for all competitive sport, which had previously been organised on a rather inequitable basis." The colours chosen for the Houses were cherry red for Anderson, royal blue for Bromby, gold for Lascelles, and pale blue for School (later Daniell). New students starting at Ruyton from Prep onwards are allocated to one of the Houses with consideration to family connections and balance of numbers. The record's significance is further enhanced by its strong provenance, having been produced by Ruyton Girls' School and donated to the Archives by a familial connection of a former notable student.Black and white rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper.Reverse: Caroline Kent / Mary Murray. / 11.12.51. / Ann Dickinson / RGS011/1951/0003ruyton girls' school, ruyton, students, school, senior school, girls school, kew, melbourne, school uniform, prefects, photograph, henry henty, henty house, marion henty, tarring -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Burning of an Effigy of Pauline Hanson, 03 December 2016, 03/12/2016
Media Release 29 January 2016 Advocate of Racism to burn at Eureka Dawn A cardboard effigy of Senator Pauline Hanson, will burn at the Ballarat Eureka Stockade Memorial next Eureka Dawn 3 December. For eight years now effigy burning has become an integral and flamboyant part of the annual 3 December Eureka remembrance, part of the Reclaim the Radical Spirit of the Eureka Rebellion program organised by Dr Joe Toscano, medical practitioner, broadcaster on Melbourne community radio 3CR and Australia's best known anarchist. Colour photographs of the burning of a cardboard effigy of Pauline Hanson at dawn on Eureka Day, 03 December 2016. Pauline Hanson was chosen as the effigy to be burnt by the Anarchist Media Alliance at Eureka Dawn because she was an advocate of racism. eureka stockade, anniversary, joe toscano, reclaim the radical spirit of the eureka rebellion, graeme dunstam, pauline hanson, effigy burning, pauline hanson effigy -
 Ruyton Girls' School
Ruyton Girls' SchoolPhotograph, Ruyton Girls' School, 1951
Depicted are nine Ruyton Girls' School prefects for the 1951 school year. The image is a formal school portrait taken outdoors on school grounds outside of Henty House (formerly Tarring). In the background, we can see three bicycles with cane baskets. The students are all dressed in knee-length check skirts, a dark jumper, light-coloured collared button-up blouse with a dark tie, wool blazers, and dark coloured shoes. Four girls are standing in the back row, and five are positioned in the front row. Students in the back row have been identified from left to right as M. Murray, B. Addison, T. Abson and H. Cole; in the front row, from left to right we can see S. Backhouse, J. Wigg (Vice Captain), F. Jacobs (Captain), E. Duff, and A. Dickinson. The same photograph appears in the Ruytonian 1951. Student leadership commenced at Ruyton Girls' School in 1906 with the introduction of the prefect system. Prefects had numerous responsibilities—gate duty, grounds duty, classroom marking, assembly door watch, uniform monitoring, and even supervising student detention. In 1947, a dedicated Prefects Room was erected on the east side of the Ruyton Girls' School Assembly Room in Henty House. The prefects system was revised in 1968 with a new leadership structure: there would be a permanent School Captain, Vice Captain and School Sports Captain; six permanent prefects would be elected, and the rest of the Matriculation class would form committees. These included Library, Social Services, S.C.M., Editorial, and Music. In this way, it was thought "that each Matric girl would have a certain amount of responsibility." With this revised structure came a brand new Prefects' Study, located in a former classroom next to the Domestic Science building. Each prefect was allocated one book locker, one clothing locker, "a small share in the heater", plus a new shared lounge. The prefect system was updated again in 1974. All sixth formers would become prefects, or "school officials." This saw the sixth form divided into two halves: one group would be prefects for the first half of the year, then the second group would take the reigns in the latter half of the year. In October 2023, Ruyton announced a new collaborative leadership structure for captains, prefects and house leaders, which would see two students in each leadership role.The record has strong historic significance as it depicts a former notable student, Helen Gordon (maiden name Cole), pictured third from the right in the front row. Helen started at Little Ruyton in Prep 1940 and finished Year 12 in 1952 as School Captain, Bromby Captain, Form Captain for Matric, Tennis Captain, Hockey Captain, Swimming Vice Captain, and an award for Best All-Round Girl. She also played baseball for Victoria. After finishing school, Helen went on to graduate from the University of Melbourne as a physiotherapist in 1956. Her first position at age 19 involved setting up clinics with the Victorian Health Department Poliomyelitis Rural division. Helen’s strong ties to Ruyton continued when she held the position of President of the Old Ruytonians’ Association from the start of 1966 to the end of 1967. In 2019, Helen received an Order of Australia Medal for service to community health as a physiotherapist. She was also the recipient of the 2022 Victorian Senior Achiever Award at Parliament House. Helen passed away in July 2023 at age 88. The record's significance is further enhanced by its strong provenance, having been produced by Ruyton Girls' School and donated to the Archives by a familial connection.Black and white rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper.Reverse: Felicity Jacobs / Judi Olsen / Ann Dickinson / Bev. Addison / RGS011/1951/0004 /ruyton girls' school, ruyton, students, school, senior school, girls school, kew, melbourne, school uniform, prefects, photograph, henry henty, henty house, marion henty, tarring -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Colour, Jarrod Watt, Hong Kong Street Flyer by an unknown artist, 2019, 06/2019
Carrie Lam, Hong Kong’s chief executive, had plenty of political support in the territory’s pro-Beijing legislature to pass a bill that would allow extraditions to mainland China. The legislators were set to begin discussing the bill in early June, and intended to vote on it just weeks later. A series of protests took place, and after a June 16 protest saw the largest turnout yet, Ms. Lam made a major concession: She postponed the bill, at least temporarily. It was an undeniable victory for the protesters — but it did little to quell the unrest. Since the bill could later be reintroduced, protesters felt they remained in danger. The police tactics to break up the demonstrations on June 12, including the use of more than 150 tear gas canisters to push protesters far away from the government office, created a new set of demands from the protesters. Now, instead of just calling for the withdrawal of the bill and Ms. Lam’s resignation, they said they wouldn’t be content unless there was an independent investigation of officers’ conduct. They also wanted the release of protesters arrested on June 12, and for the government to rescind its description of the demonstrations as a “riot,” a designation that carries legal significance. None of that has happened. Many analysts say Ms. Lam is unlikely to step down, nor would Beijing accept her resignation if she offered it. She has more wiggle room on the other demands, but has not indicated any willingness to budge. The Hong Kong Protests are a leaderless, digital movement.There is no single leader or group deciding on or steering the strategy, tactics and goals of the movement. Instead, protesters have used forums and messaging apps to decide next steps. Anyone can suggest a course of action, and others then vote on whether they support it. The most popular ideas rise to the top, and then people rally to make them happen. At its best, this structure has empowered many people to participate and have their voices heard. Protesters say it keeps them all safe by not allowing the government to target specific leaders. Their success in halting the extradition bill, which was shelved by the territory’s chief executive, speaks to the movement’s power. Despite the lack of a clear leader, protesters have shown extensive coordination at the demonstrations, having planned the specifics online beforehand. Supply stations are set up to distribute water, snacks, gloves, umbrellas and shields made of cardboard. Volunteer first aid workers wear brightly colored vests. People form assembly lines to pass supplies across long distances, with protesters communicating what they need through a series of predetermined hand signals. Anyone walking in dangerous areas without a helmet or a mask is quickly offered one. No individual can speak on behalf of the protesters, which makes negotiations difficult, if not impossible. (https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/02/world/asia/hong-kong-protest-explained.html, accessed 07/07/2019) Hong Kong’s amended extradition law would allow the extradition of suspects to mainland China for the first time. Supporters say the amendments are key to ensuring the city does not become a criminal refuge, but critics worry Beijing will use the law to extradite political opponents and others to China where their legal protections cannot be guaranteed. The government claims the push to change the law, which would also apply to Taiwan and Macau, stems from the killing last year of a Hong Kong woman while she was in Taiwan with her boyfriend. Authorities in Taiwan suspect the woman’s boyfriend, who remains in Hong Kong, but cannot try him because no extradition agreement is in place. Under the amended law, those accused of offences punishable by seven years or more in prison could be extradited. The new legislation would give Hong Kong’s leader, known as the chief executive, authority to approve extradition requests, after review by the courts. Hong Kong’s legislature, the legislative council, would not have any oversight over the extradition process. Many Hong Kongers fear the proposed extradition law will be used by authorities to target political enemies. They worry the new legislation spells the end of the “one country, two systems” policy, eroding the civil rights enjoyed by Hong Kong residents since the handover of sovereignty from the UK to China in 1997. Many attending the protests on Sunday said they could not trust China as it had often used non-political crimes to target government critics, and said they also feared Hong Kong officials would not be able to reject Beijing’s requests. Legal professionals have also expressed concern over the rights of those sent across the border to be tried. The conviction rate in Chinese courts is as high as 99%. Arbitrary detentions, torture and denial of legal representation of one’s choosing are also common. Many in the protests on Sunday 09 June 2019 said they felt overwhelmed by a sense of helplessness in the face of mainland China’s increasing political, economic and cultural influence in Hong Kong. Hong Kong’s top political leader is not elected by ordinary voters but by a 1,200-strong election committee accountable to Beijing. Half of its legislature are chosen through indirect electoral systems that favour pro-Beijing figures. Many Hong Kongers also cited the jailing of leaders and activists from the 2014 Occupy Central movement– a 79-day mass civil disobedience movement – as well as the disqualification of young localist lawmakers as signs of the erosion of civil freedoms. Resentment towards China has been intensified by soaring property prices – with increasing numbers of mainland Chinese buying properties in the city – as well as the government’s “patriotic education” drive, and the large numbers of mainland tourists who flock to Hong Kong. Many Hong Kongers are also concerned about China’s growing control over the city’s news media, as they increasingly self-censor and follow Beijing’s tacit orders. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/jun/10/what-are-the-hong-kong-protests-about-explainerPhotograph of a street art poster taken on the streets of Hong Kong during the protests against legislation to allow Hong Kong suspects to be extradited to mainland Chinese carrie lam, hong kong protests, extraditions, poster art, posters -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Colour, Jarrod Watt, A thousand protestors surround Hong Kong's main police headquarters on Arsenal Street in Wan Chai on June 26th 2019, 21/06/2019
Carrie Lam, Hong Kong’s chief executive, had plenty of political support in the territory’s pro-Beijing legislature to pass a bill that would allow extraditions to mainland China. The legislators were set to begin discussing the bill in early June, and intended to vote on it just weeks later. A series of protests took place, and after a June 16 protest saw the largest turnout yet, Ms. Lam made a major concession: She postponed the bill, at least temporarily. It was an undeniable victory for the protesters — but it did little to quell the unrest. Since the bill could later be reintroduced, protesters felt they remained in danger. The police tactics to break up the demonstrations on June 12, including the use of more than 150 tear gas canisters to push protesters far away from the government office, created a new set of demands from the protesters. Now, instead of just calling for the withdrawal of the bill and Ms. Lam’s resignation, they said they wouldn’t be content unless there was an independent investigation of officers’ conduct. They also wanted the release of protesters arrested on June 12, and for the government to rescind its description of the demonstrations as a “riot,” a designation that carries legal significance. None of that has happened. Many analysts say Ms. Lam is unlikely to step down, nor would Beijing accept her resignation if she offered it. She has more wiggle room on the other demands, but has not indicated any willingness to budge. The Hong Kong Protests are a leaderless, digital movement.There is no single leader or group deciding on or steering the strategy, tactics and goals of the movement. Instead, protesters have used forums and messaging apps to decide next steps. Anyone can suggest a course of action, and others then vote on whether they support it. The most popular ideas rise to the top, and then people rally to make them happen. At its best, this structure has empowered many people to participate and have their voices heard. Protesters say it keeps them all safe by not allowing the government to target specific leaders. Their success in halting the extradition bill, which was shelved by the territory’s chief executive, speaks to the movement’s power. Despite the lack of a clear leader, protesters have shown extensive coordination at the demonstrations, having planned the specifics online beforehand. Supply stations are set up to distribute water, snacks, gloves, umbrellas and shields made of cardboard. Volunteer first aid workers wear brightly colored vests. People form assembly lines to pass supplies across long distances, with protesters communicating what they need through a series of predetermined hand signals. Anyone walking in dangerous areas without a helmet or a mask is quickly offered one. No individual can speak on behalf of the protesters, which makes negotiations difficult, if not impossible. (https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/02/world/asia/hong-kong-protest-explained.html, accessed 07/07/2019) Hong Kong’s amended extradition law would allow the extradition of suspects to mainland China for the first time. Supporters say the amendments are key to ensuring the city does not become a criminal refuge, but critics worry Beijing will use the law to extradite political opponents and others to China where their legal protections cannot be guaranteed. The government claims the push to change the law, which would also apply to Taiwan and Macau, stems from the killing last year of a Hong Kong woman while she was in Taiwan with her boyfriend. Authorities in Taiwan suspect the woman’s boyfriend, who remains in Hong Kong, but cannot try him because no extradition agreement is in place. Under the amended law, those accused of offences punishable by seven years or more in prison could be extradited. The new legislation would give Hong Kong’s leader, known as the chief executive, authority to approve extradition requests, after review by the courts. Hong Kong’s legislature, the legislative council, would not have any oversight over the extradition process. Many Hong Kongers fear the proposed extradition law will be used by authorities to target political enemies. They worry the new legislation spells the end of the “one country, two systems” policy, eroding the civil rights enjoyed by Hong Kong residents since the handover of sovereignty from the UK to China in 1997. Many attending the protests on Sunday said they could not trust China as it had often used non-political crimes to target government critics, and said they also feared Hong Kong officials would not be able to reject Beijing’s requests. Legal professionals have also expressed concern over the rights of those sent across the border to be tried. The conviction rate in Chinese courts is as high as 99%. Arbitrary detentions, torture and denial of legal representation of one’s choosing are also common. Many in the protests on Sunday 09 June 2019 said they felt overwhelmed by a sense of helplessness in the face of mainland China’s increasing political, economic and cultural influence in Hong Kong. Hong Kong’s top political leader is not elected by ordinary voters but by a 1,200-strong election committee accountable to Beijing. Half of its legislature are chosen through indirect electoral systems that favour pro-Beijing figures. Many Hong Kongers also cited the jailing of leaders and activists from the 2014 Occupy Central movement– a 79-day mass civil disobedience movement – as well as the disqualification of young localist lawmakers as signs of the erosion of civil freedoms. Resentment towards China has been intensified by soaring property prices – with increasing numbers of mainland Chinese buying properties in the city – as well as the government’s “patriotic education” drive, and the large numbers of mainland tourists who flock to Hong Kong. Many Hong Kongers are also concerned about China’s growing control over the city’s news media, as they increasingly self-censor and follow Beijing’s tacit orders. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/jun/10/what-are-the-hong-kong-protests-about-explainerMore than a thousand protestors surround Hong Kong's main police headquarters on Arsenal Street in Wan Chai on June 26th following a peaceful rally at Edinburgh Place in Central. Doors to the complex were barricaded by protestors, who left after a six hour siege in protest at police violence at a prtest held earlier on 12 June 2019. Protesters ended a six-hour siege of Hong Kong’s police headquarters – their second in a week over the now-suspended extradition bill – early on Thursday morning. More than 1,000 were involved at the height of the protest, which began after 10pm on Wednesday. Around 100 were left at the end and dispersed without a fight when officers with riot shields emerged from the building in Wan Chai at 4am on Thursday. After a peaceful rally attended by thousands earlier at Edinburgh Place in the Central business district, hundreds descended on Arsenal Street, blocking the junction with Lockhart Road to all traffic and sealing the entrances to the police base. (https://www.scmp.com/news/hong-kong/politics/article/3016238/hong-kong-police-under-siege-again-protesters-surround )carrie lam, hong kong protests, extraditions, protest, protestors -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Jarrod Watt, Seven police officers stand guard in front of Hong Kong's main police headquarters on Arsenal Street in Wan Chai, 2019, 21/06/2019
Carrie Lam, Hong Kong’s chief executive, had plenty of political support in the territory’s pro-Beijing legislature to pass a bill that would allow extraditions to mainland China. The legislators were set to begin discussing the bill in early June, and intended to vote on it just weeks later. A series of protests took place, and after a June 16 protest saw the largest turnout yet, Ms. Lam made a major concession: She postponed the bill, at least temporarily. It was an undeniable victory for the protesters — but it did little to quell the unrest. Since the bill could later be reintroduced, protesters felt they remained in danger. The police tactics to break up the demonstrations on June 12, including the use of more than 150 tear gas canisters to push protesters far away from the government office, created a new set of demands from the protesters. Now, instead of just calling for the withdrawal of the bill and Ms. Lam’s resignation, they said they wouldn’t be content unless there was an independent investigation of officers’ conduct. They also wanted the release of protesters arrested on June 12, and for the government to rescind its description of the demonstrations as a “riot,” a designation that carries legal significance. None of that has happened. Many analysts say Ms. Lam is unlikely to step down, nor would Beijing accept her resignation if she offered it. She has more wiggle room on the other demands, but has not indicated any willingness to budge. The Hong Kong Protests are a leaderless, digital movement.There is no single leader or group deciding on or steering the strategy, tactics and goals of the movement. Instead, protesters have used forums and messaging apps to decide next steps. Anyone can suggest a course of action, and others then vote on whether they support it. The most popular ideas rise to the top, and then people rally to make them happen. At its best, this structure has empowered many people to participate and have their voices heard. Protesters say it keeps them all safe by not allowing the government to target specific leaders. Their success in halting the extradition bill, which was shelved by the territory’s chief executive, speaks to the movement’s power. Despite the lack of a clear leader, protesters have shown extensive coordination at the demonstrations, having planned the specifics online beforehand. Supply stations are set up to distribute water, snacks, gloves, umbrellas and shields made of cardboard. Volunteer first aid workers wear brightly colored vests. People form assembly lines to pass supplies across long distances, with protesters communicating what they need through a series of predetermined hand signals. Anyone walking in dangerous areas without a helmet or a mask is quickly offered one. No individual can speak on behalf of the protesters, which makes negotiations difficult, if not impossible. (https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/02/world/asia/hong-kong-protest-explained.html, accessed 07/07/2019) Hong Kong’s amended extradition law would allow the extradition of suspects to mainland China for the first time. Supporters say the amendments are key to ensuring the city does not become a criminal refuge, but critics worry Beijing will use the law to extradite political opponents and others to China where their legal protections cannot be guaranteed. The government claims the push to change the law, which would also apply to Taiwan and Macau, stems from the killing last year of a Hong Kong woman while she was in Taiwan with her boyfriend. Authorities in Taiwan suspect the woman’s boyfriend, who remains in Hong Kong, but cannot try him because no extradition agreement is in place. Under the amended law, those accused of offences punishable by seven years or more in prison could be extradited. The new legislation would give Hong Kong’s leader, known as the chief executive, authority to approve extradition requests, after review by the courts. Hong Kong’s legislature, the legislative council, would not have any oversight over the extradition process. Many Hong Kongers fear the proposed extradition law will be used by authorities to target political enemies. They worry the new legislation spells the end of the “one country, two systems” policy, eroding the civil rights enjoyed by Hong Kong residents since the handover of sovereignty from the UK to China in 1997. Many attending the protests on Sunday said they could not trust China as it had often used non-political crimes to target government critics, and said they also feared Hong Kong officials would not be able to reject Beijing’s requests. Legal professionals have also expressed concern over the rights of those sent across the border to be tried. The conviction rate in Chinese courts is as high as 99%. Arbitrary detentions, torture and denial of legal representation of one’s choosing are also common. Many in the protests on Sunday 09 June 2019 said they felt overwhelmed by a sense of helplessness in the face of mainland China’s increasing political, economic and cultural influence in Hong Kong. Hong Kong’s top political leader is not elected by ordinary voters but by a 1,200-strong election committee accountable to Beijing. Half of its legislature are chosen through indirect electoral systems that favour pro-Beijing figures. Many Hong Kongers also cited the jailing of leaders and activists from the 2014 Occupy Central movement– a 79-day mass civil disobedience movement – as well as the disqualification of young localist lawmakers as signs of the erosion of civil freedoms. Resentment towards China has been intensified by soaring property prices – with increasing numbers of mainland Chinese buying properties in the city – as well as the government’s “patriotic education” drive, and the large numbers of mainland tourists who flock to Hong Kong. Many Hong Kongers are also concerned about China’s growing control over the city’s news media, as they increasingly self-censor and follow Beijing’s tacit orders. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/jun/10/what-are-the-hong-kong-protests-about-explainerSeven police officers stand guard in front of Hong Kong's main police headquarters on Arsenal Street in Wan Chai as an estimated one thousand protestors surround on 26 June 2019. Protestors take turns to step up and hurl abuse at the officers, in a protest lasting 6 hours before peacefully dispersing. The protesters chanted 'Release the martyrs' and 'Stop police violence' in reference to violent clashes with police in the days previous. ( https://www.scmp.com/news/hong-kong/politics/article/3016238/hong-kong-police-under-siege-again-protesters-surround)carrie lam, hong kong protests, extraditions, protest, protestors, police, wan chai -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Colour, Jarrod Watt, Crowds Gather on June 16 on the Streets of Causeway Bay, 2019, 17/06/2019
Carrie Lam, Hong Kong’s chief executive, had plenty of political support in the territory’s pro-Beijing legislature to pass a bill that would allow extraditions to mainland China. The legislators were set to begin discussing the bill in early June, and intended to vote on it just weeks later. A series of protests took place, and after a June 16 protest saw the largest turnout yet, Ms. Lam made a major concession: She postponed the bill, at least temporarily. It was an undeniable victory for the protesters — but it did little to quell the unrest. Since the bill could later be reintroduced, protesters felt they remained in danger. The police tactics to break up the demonstrations on June 12, including the use of more than 150 tear gas canisters to push protesters far away from the government office, created a new set of demands from the protesters. Now, instead of just calling for the withdrawal of the bill and Ms. Lam’s resignation, they said they wouldn’t be content unless there was an independent investigation of officers’ conduct. They also wanted the release of protesters arrested on June 12, and for the government to rescind its description of the demonstrations as a “riot,” a designation that carries legal significance. None of that has happened. Many analysts say Ms. Lam is unlikely to step down, nor would Beijing accept her resignation if she offered it. She has more wiggle room on the other demands, but has not indicated any willingness to budge. The Hong Kong Protests are a leaderless, digital movement.There is no single leader or group deciding on or steering the strategy, tactics and goals of the movement. Instead, protesters have used forums and messaging apps to decide next steps. Anyone can suggest a course of action, and others then vote on whether they support it. The most popular ideas rise to the top, and then people rally to make them happen. At its best, this structure has empowered many people to participate and have their voices heard. Protesters say it keeps them all safe by not allowing the government to target specific leaders. Their success in halting the extradition bill, which was shelved by the territory’s chief executive, speaks to the movement’s power. Despite the lack of a clear leader, protesters have shown extensive coordination at the demonstrations, having planned the specifics online beforehand. Supply stations are set up to distribute water, snacks, gloves, umbrellas and shields made of cardboard. Volunteer first aid workers wear brightly colored vests. People form assembly lines to pass supplies across long distances, with protesters communicating what they need through a series of predetermined hand signals. Anyone walking in dangerous areas without a helmet or a mask is quickly offered one. No individual can speak on behalf of the protesters, which makes negotiations difficult, if not impossible. (https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/02/world/asia/hong-kong-protest-explained.html, accessed 07/07/2019) Hong Kong’s amended extradition law would allow the extradition of suspects to mainland China for the first time. Supporters say the amendments are key to ensuring the city does not become a criminal refuge, but critics worry Beijing will use the law to extradite political opponents and others to China where their legal protections cannot be guaranteed. The government claims the push to change the law, which would also apply to Taiwan and Macau, stems from the killing last year of a Hong Kong woman while she was in Taiwan with her boyfriend. Authorities in Taiwan suspect the woman’s boyfriend, who remains in Hong Kong, but cannot try him because no extradition agreement is in place. Under the amended law, those accused of offences punishable by seven years or more in prison could be extradited. The new legislation would give Hong Kong’s leader, known as the chief executive, authority to approve extradition requests, after review by the courts. Hong Kong’s legislature, the legislative council, would not have any oversight over the extradition process. Many Hong Kongers fear the proposed extradition law will be used by authorities to target political enemies. They worry the new legislation spells the end of the “one country, two systems” policy, eroding the civil rights enjoyed by Hong Kong residents since the handover of sovereignty from the UK to China in 1997. Many attending the protests on Sunday said they could not trust China as it had often used non-political crimes to target government critics, and said they also feared Hong Kong officials would not be able to reject Beijing’s requests. Legal professionals have also expressed concern over the rights of those sent across the border to be tried. The conviction rate in Chinese courts is as high as 99%. Arbitrary detentions, torture and denial of legal representation of one’s choosing are also common. Many in the protests on Sunday 09 June 2019 said they felt overwhelmed by a sense of helplessness in the face of mainland China’s increasing political, economic and cultural influence in Hong Kong. Hong Kong’s top political leader is not elected by ordinary voters but by a 1,200-strong election committee accountable to Beijing. Half of its legislature are chosen through indirect electoral systems that favour pro-Beijing figures. Many Hong Kongers also cited the jailing of leaders and activists from the 2014 Occupy Central movement– a 79-day mass civil disobedience movement – as well as the disqualification of young localist lawmakers as signs of the erosion of civil freedoms. Resentment towards China has been intensified by soaring property prices – with increasing numbers of mainland Chinese buying properties in the city – as well as the government’s “patriotic education” drive, and the large numbers of mainland tourists who flock to Hong Kong. Many Hong Kongers are also concerned about China’s growing control over the city’s news media, as they increasingly self-censor and follow Beijing’s tacit orders. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/jun/10/what-are-the-hong-kong-protests-about-explainerPhotograph crowds gathering on June 16 on the streets of Causeway Bay before an estimated 2 million people take part in march protesting the government's push for extradition laws to China and demanding an apology from the chief executrive Carrie Lam. Nearly 2 million’ people take to streets, forcing public apology from Hong Kong leader Carrie Lam as suspension of controversial extradition bill fails to appease protesters. (https://www.scmp.com/news/hong-kong/politics/article/3014737/nearly-2-million-people-take-streets-forcing-public-apology )carrie lam, hong kong protests, extraditions, protest, protestors -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Jarrod Watt, Street Protests in Hong Kong against proposed extradition laws, 2019, 17/06/2019
Carrie Lam, Hong Kong’s chief executive, had plenty of political support in the territory’s pro-Beijing legislature to pass a bill that would allow extraditions to mainland China. The legislators were set to begin discussing the bill in early June, and intended to vote on it just weeks later. A series of protests took place, and after a June 16 protest saw the largest turnout yet, Ms. Lam made a major concession: She postponed the bill, at least temporarily. It was an undeniable victory for the protesters — but it did little to quell the unrest. Since the bill could later be reintroduced, protesters felt they remained in danger. The police tactics to break up the demonstrations on June 12, including the use of more than 150 tear gas canisters to push protesters far away from the government office, created a new set of demands from the protesters. Now, instead of just calling for the withdrawal of the bill and Ms. Lam’s resignation, they said they wouldn’t be content unless there was an independent investigation of officers’ conduct. They also wanted the release of protesters arrested on June 12, and for the government to rescind its description of the demonstrations as a “riot,” a designation that carries legal significance. None of that has happened. Many analysts say Ms. Lam is unlikely to step down, nor would Beijing accept her resignation if she offered it. She has more wiggle room on the other demands, but has not indicated any willingness to budge. The Hong Kong Protests are a leaderless, digital movement.There is no single leader or group deciding on or steering the strategy, tactics and goals of the movement. Instead, protesters have used forums and messaging apps to decide next steps. Anyone can suggest a course of action, and others then vote on whether they support it. The most popular ideas rise to the top, and then people rally to make them happen. At its best, this structure has empowered many people to participate and have their voices heard. Protesters say it keeps them all safe by not allowing the government to target specific leaders. Their success in halting the extradition bill, which was shelved by the territory’s chief executive, speaks to the movement’s power. Despite the lack of a clear leader, protesters have shown extensive coordination at the demonstrations, having planned the specifics online beforehand. Supply stations are set up to distribute water, snacks, gloves, umbrellas and shields made of cardboard. Volunteer first aid workers wear brightly colored vests. People form assembly lines to pass supplies across long distances, with protesters communicating what they need through a series of predetermined hand signals. Anyone walking in dangerous areas without a helmet or a mask is quickly offered one. No individual can speak on behalf of the protesters, which makes negotiations difficult, if not impossible. (https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/02/world/asia/hong-kong-protest-explained.html, accessed 07/07/2019) Hong Kong’s amended extradition law would allow the extradition of suspects to mainland China for the first time. Supporters say the amendments are key to ensuring the city does not become a criminal refuge, but critics worry Beijing will use the law to extradite political opponents and others to China where their legal protections cannot be guaranteed. The government claims the push to change the law, which would also apply to Taiwan and Macau, stems from the killing last year of a Hong Kong woman while she was in Taiwan with her boyfriend. Authorities in Taiwan suspect the woman’s boyfriend, who remains in Hong Kong, but cannot try him because no extradition agreement is in place. Under the amended law, those accused of offences punishable by seven years or more in prison could be extradited. The new legislation would give Hong Kong’s leader, known as the chief executive, authority to approve extradition requests, after review by the courts. Hong Kong’s legislature, the legislative council, would not have any oversight over the extradition process. Many Hong Kongers fear the proposed extradition law will be used by authorities to target political enemies. They worry the new legislation spells the end of the “one country, two systems” policy, eroding the civil rights enjoyed by Hong Kong residents since the handover of sovereignty from the UK to China in 1997. Many attending the protests on Sunday said they could not trust China as it had often used non-political crimes to target government critics, and said they also feared Hong Kong officials would not be able to reject Beijing’s requests. Legal professionals have also expressed concern over the rights of those sent across the border to be tried. The conviction rate in Chinese courts is as high as 99%. Arbitrary detentions, torture and denial of legal representation of one’s choosing are also common. Many in the protests on Sunday 09 June 2019 said they felt overwhelmed by a sense of helplessness in the face of mainland China’s increasing political, economic and cultural influence in Hong Kong. Hong Kong’s top political leader is not elected by ordinary voters but by a 1,200-strong election committee accountable to Beijing. Half of its legislature are chosen through indirect electoral systems that favour pro-Beijing figures. Many Hong Kongers also cited the jailing of leaders and activists from the 2014 Occupy Central movement– a 79-day mass civil disobedience movement – as well as the disqualification of young localist lawmakers as signs of the erosion of civil freedoms. Resentment towards China has been intensified by soaring property prices – with increasing numbers of mainland Chinese buying properties in the city – as well as the government’s “patriotic education” drive, and the large numbers of mainland tourists who flock to Hong Kong. Many Hong Kongers are also concerned about China’s growing control over the city’s news media, as they increasingly self-censor and follow Beijing’s tacit orders. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/jun/10/what-are-the-hong-kong-protests-about-explainerPhotograph of a crowd or protestors against proposed extradition laws gathering on the streets of Causeway Bay, Hong Kong, leading down to the gathering area. carrie lam, hong kong protests, extraditions, protest, protestors -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Colour, Jarrod Watt, Street Protests in Hong Kong against proposed extradition laws, 2019, 17/06/2019
Carrie Lam, Hong Kong’s chief executive, had plenty of political support in the territory’s pro-Beijing legislature to pass a bill that would allow extraditions to mainland China. The legislators were set to begin discussing the bill in early June, and intended to vote on it just weeks later. A series of protests took place, and after a June 16 protest saw the largest turnout yet, Ms. Lam made a major concession: She postponed the bill, at least temporarily. It was an undeniable victory for the protesters — but it did little to quell the unrest. Since the bill could later be reintroduced, protesters felt they remained in danger. The police tactics to break up the demonstrations on June 12, including the use of more than 150 tear gas canisters to push protesters far away from the government office, created a new set of demands from the protesters. Now, instead of just calling for the withdrawal of the bill and Ms. Lam’s resignation, they said they wouldn’t be content unless there was an independent investigation of officers’ conduct. They also wanted the release of protesters arrested on June 12, and for the government to rescind its description of the demonstrations as a “riot,” a designation that carries legal significance. None of that has happened. Many analysts say Ms. Lam is unlikely to step down, nor would Beijing accept her resignation if she offered it. She has more wiggle room on the other demands, but has not indicated any willingness to budge. The Hong Kong Protests are a leaderless, digital movement.There is no single leader or group deciding on or steering the strategy, tactics and goals of the movement. Instead, protesters have used forums and messaging apps to decide next steps. Anyone can suggest a course of action, and others then vote on whether they support it. The most popular ideas rise to the top, and then people rally to make them happen. At its best, this structure has empowered many people to participate and have their voices heard. Protesters say it keeps them all safe by not allowing the government to target specific leaders. Their success in halting the extradition bill, which was shelved by the territory’s chief executive, speaks to the movement’s power. Despite the lack of a clear leader, protesters have shown extensive coordination at the demonstrations, having planned the specifics online beforehand. Supply stations are set up to distribute water, snacks, gloves, umbrellas and shields made of cardboard. Volunteer first aid workers wear brightly colored vests. People form assembly lines to pass supplies across long distances, with protesters communicating what they need through a series of predetermined hand signals. Anyone walking in dangerous areas without a helmet or a mask is quickly offered one. No individual can speak on behalf of the protesters, which makes negotiations difficult, if not impossible. (https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/02/world/asia/hong-kong-protest-explained.html, accessed 07/07/2019) Hong Kong’s amended extradition law would allow the extradition of suspects to mainland China for the first time. Supporters say the amendments are key to ensuring the city does not become a criminal refuge, but critics worry Beijing will use the law to extradite political opponents and others to China where their legal protections cannot be guaranteed. The government claims the push to change the law, which would also apply to Taiwan and Macau, stems from the killing last year of a Hong Kong woman while she was in Taiwan with her boyfriend. Authorities in Taiwan suspect the woman’s boyfriend, who remains in Hong Kong, but cannot try him because no extradition agreement is in place. Under the amended law, those accused of offences punishable by seven years or more in prison could be extradited. The new legislation would give Hong Kong’s leader, known as the chief executive, authority to approve extradition requests, after review by the courts. Hong Kong’s legislature, the legislative council, would not have any oversight over the extradition process. Many Hong Kongers fear the proposed extradition law will be used by authorities to target political enemies. They worry the new legislation spells the end of the “one country, two systems” policy, eroding the civil rights enjoyed by Hong Kong residents since the handover of sovereignty from the UK to China in 1997. Many attending the protests on Sunday said they could not trust China as it had often used non-political crimes to target government critics, and said they also feared Hong Kong officials would not be able to reject Beijing’s requests. Legal professionals have also expressed concern over the rights of those sent across the border to be tried. The conviction rate in Chinese courts is as high as 99%. Arbitrary detentions, torture and denial of legal representation of one’s choosing are also common. Many in the protests on Sunday 09 June 2019 said they felt overwhelmed by a sense of helplessness in the face of mainland China’s increasing political, economic and cultural influence in Hong Kong. Hong Kong’s top political leader is not elected by ordinary voters but by a 1,200-strong election committee accountable to Beijing. Half of its legislature are chosen through indirect electoral systems that favour pro-Beijing figures. Many Hong Kongers also cited the jailing of leaders and activists from the 2014 Occupy Central movement– a 79-day mass civil disobedience movement – as well as the disqualification of young localist lawmakers as signs of the erosion of civil freedoms. Resentment towards China has been intensified by soaring property prices – with increasing numbers of mainland Chinese buying properties in the city – as well as the government’s “patriotic education” drive, and the large numbers of mainland tourists who flock to Hong Kong. Many Hong Kongers are also concerned about China’s growing control over the city’s news media, as they increasingly self-censor and follow Beijing’s tacit orders. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/jun/10/what-are-the-hong-kong-protests-about-explainerPhotograph of a crowd on the streets of Hong Kong to protest against proposed extradition laws, heading towards Admiralty. carrie lam, hong kong protests, extraditions, protest, protestors, admiralty
