Showing 49 items matching "forging"
-
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyNewspaper Clipping, Diamond Valley Leader, Forging paths for soldiers ; and, Appeal keeps the volunteers busy, 19/04/2017
2 articles: A former serviceman is driven to help war veterans find work reports and, Appeal keeps volunteers busy. Local RSLs raise funds in the lead up to ANZAC Day.News article 2 pages, black text, colour image.soldiers, war veterans, anzac day -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumBooklet - CAC Commonwealth Aircraft Corporation, Notes on Forging Design Avon Sabre
-
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumDocument, Still Forging Ahead, 1987
Life story of Ralph Newnham, Blacksmith, Tatura. Aged 82 years. Photos of his workshop from the Sun Nov. 12, 1987Black and white newspaper article on Ralph Newnham, Blacksmith, Tatura (2 copies)newnham r, blacksmith, the sun, bamber, s, chivers i, tatura, documents, history, local, newspapers -
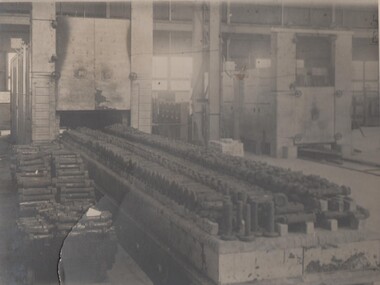 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - BENDIGO ORDINANCE FACTORY COLLECTION: UPSET FORGINGS ON ELECTRIC BOGIE HEARTH FURNACE FOR NORMALIZING
Photo titled 'Upset Forgings on Electric Bogie Hearth Furnace for Normalizing' Undated B&W print mounted on stiff cardboard -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionTool, Blacksmith Tongs
Probably used in Ballarat School of Mines blacksmithing classesMetal stricker's Forging and Blacksmith tongs. Strong metal jaws to hold and move metal during processing. Hook at end on one handle to assist control. ballarat school of mines, blacksmith, forge -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumBook, M T RICHARDSON, PRACTICAL BLACKSMITHING, 1905-1909
A COLLECTION OF ARTICLES CONTRIBUTED AT DIFFERENT TIMES BY SKILLED WORKMENT TO THE COLUMNS OF "THE BLACKSMITH AND WHEELWRIGHT: AND COVERING NEARLY THE WHOLE RANGE OF BLACKSMITHING FROM THE SIMPLEST OJOB OF WORK TO SOME OF THE MOST COMPLEX FORGINGS.1 VOLUME 1 BOOK WITH HANDSEWN BLACK FABRIC COVER .2 VOLUME 2 BOOK WITH HANDSEWN BLACK FABRIC COVER .3 VOLUME 3 BOOK WITH TAN FABRIC COVER IMAGE OF AN ANVIL AND TITLE OF THE BOOK IN BLACK PRINT .4 VOLUME 4 BOOK WITH TAN FABRIC COVER IMAGE OF AN ANVIL AND TITLE OF THE BOOK IN BLACK PRINTA COLLECTION OF ARTICLES CONTRIBUTED AT DIFFERENT TIMES BY SKILLED WORKMENT TO THE COLUMNS OF "THE BLACKSMITH AND WHEELWRIGHT: AND COVERING NEARLY THE WHOLE RANGE OF BLACKSMITHING FROM THE SIMPLEST OJOB OF WORK TO SOME OF THE MOST COMPLEX FORGINGSblacksmithing, forging -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayMachine - Steam Hammer, G James, 1841
Steam hammers, invented by Englishman John Naysmith in 1841, made possible the forging of heavy iron bars and greatly reduced the physical labour required in forging. The hammers could vary in capacity (drop-force) from 400 pounds [lbs.] (181 kg) to 400 Tons (406.3 tonnes) and were once a part of most major engineering works. The Victorian Railways, from where the Museum exhibit came, used many hammers of varying sizes, their largest being at Newport Workshops measuring 30 feet (9.1 metres) high by 15 feet (4.6 metres) wide. Steam Hammers have made forging of heavy iron bars possible and has greatly reduced the physical labour required in forging. Historic - Victorian Railways - Industrial Steam Hammer Large metal mechanical steam hammer. made of iron & wrought ironC James Maker Melbournelarge, mechanical, steam, hammer -
 Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.
Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.Information folder - Federation, 2001 (approx)
Folder containing items pertaining to Federation. Contents:-/Trifold pamphlet "Forging The Nation, Melbourne Museum/Fact sheet "Historical links between Federation and Knox and the surrounding region", attached to a "With compliments" note from Dandenong Ranges Music Council.federation of australia -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyNewspaper, Scrapbook Clipping, Library Collection, Ringwood, Victoria, `
``Newspaper clipping from "The Mail" 28-9-93, P 3. NEWS watch. "Basketball stadium comes a step closer" by Jodie Haythorne Ringwood Basketball Association and Ringwood Council are forging ahead with plans for the municipality's first big basketball complex. The council has allocated $400,000 in its 1993-1994 budget towards the $1.3 million project.` -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyTool - Blacksmith Tongs, Unknown
A pair of small vintage handmade blacksmith tongs with two handles called reins, which are riveted together to form a hinge joint for the flat edged tongs. The blacksmith opens and closes the tongs using the handles. They are made of flat mild steel. They were used for holding steel in position and turning it over during forging operations.blacksmithing tools, forging tools, metalworking tools, furnace tongs, tools -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyTool - Blacksmith Tongs, Unknown
A pair of long handled vintage handmade blacksmith tongs with two handles called reins, which are riveted together to form a hinge joint for the flat edged tongs. The blacksmith opens and closes the tongs using the handles. They are made of flat mild steel. They were used for holding steel in position and turning it over during forging operations.blacksmithing tools, forging tools, metalworking tools, furnace tongs, tools -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyTool - Blacksmith Tongs, Unknown
A pair of vintage handmade blacksmith tongs with two handles called reins, which are riveted together to form a hinge joint for the long 90 degree right angled flat edged tongs. The blacksmith opens and closes the tongs using the handles. They are made of flat mild steel. They were used for holding steel in position and turning it over during forging operations.blacksmithing tools, forging tools, metalworking tools, furnace tools, tools -
 Nillumbik Shire Council
Nillumbik Shire CouncilSculpture: Matcham SKIPPER, George Dreyfus Composer, 1987
Eltham was a creative hub during the twentieth century, attracting innovative visual artists, architects, writers and film makers to collaborate, forging lifelong friendships and artistic legacies. Skipper produced this bronze sculpture of friend, Composer George Dreyfus for the then Shire of Eltham Art Award. Matcham Skipper (b.1921 NZ - d. 2011 Melb.) was a renowned local sculptor, jeweller and builder and an accomplished teacher, designer, ironworker, and photographer. His work is held by many museums and public collections in Australia and overseas. He was a long term resident of Montsalvat in Eltham with his family deeply involved in the building and evolution of this artists colony, which was the vision of architect and painter Justus Jorgensen. George Dreyfus (b.1928 Germany - arrived 1939 Aus) is an Australian contemporary classical, film and television composer. He has composed numerous film and television scores, including Tim Burstall's 'The Adventures of Sebastian the Fox' (1963), 'A Steam Train Passes' (1974), 'Rush' (1974), 'Dimboola' (1979) and 'The Fringe Dwellers' (1986). It was the score for 'Rush' which brought him wider recognition. He has written four operas, two symphonies, chamber music and film scores spanning five decades. Dreyfus is well known for having worked with the late director, writer and producer Tim Burstall, a key figure in Australian postwar cinema and local who lived in Eltham. Burstall was instrumental in rebuilding the Australian film industry in the 60s, creating groundbreaking Australian films including 'Stork' and 'Alvin Purple'. Figurative bronze bust of well known Australian composer George Dreyfus. He is wearing a shirt underneath a sweater. His left arm/hand is placed over his chest. His eyes are half closed as if immersed in the music. A green patina can be seen in areas on the sculpture. Signature and date cast (incised with tool) onto the back shoulder blade: 'MATCHAM SKIPPER 1987'ek prac 2015, montsalvat, eltham, george dreyfus, matcham skipper, bronze, bust, tim burstall, sculpture, rush -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Article - JOHN WILLIAMS COLLECTION: NEWSPAPER ARTICLE FORGING A SOLID CRAFT, 2003
JOHN WILLIAMS COLLECTION: NEWSPAPER ARTICLE FORGING A SOLID CRAFT Newspaper Article Bendigo Advertiser Thursday May 29, 2003 Photo and article of Tom Morton and his replica Ned Kelly armour. Tom, a pupil at Quarry Hill Primary School yesterday submitted his latest piece of homework to grade 5-6 teacher John Williams. The article descrives how Tom went about it. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAnvil
This anvil was once the property of Warrnambool Ports and Harbours. It is associated with the shipping trade and wold have been used by a blacksmith or tinsmith for forging and shaping metal. According to Pliny, the anvil is supposed to be invented by Cinyra of Cyprus, but it was probably much older. There has been very little change in the basic design of the anvil since Greek and Roman times. This anvil is significant for its association with the local government body of Warrnambool Ports and Harbours, which is of local historic significance. It is also significant for its association with blacksmiths and tinsmiths, which are rare trades today.Anvil, small, for use by blacksmiths and tinsmiths.It was once the property of the Warrnambool Ports and Harbours.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, anvil, blacksmiths, tinsmith, tools, trades, warrnambool ports and harbours -
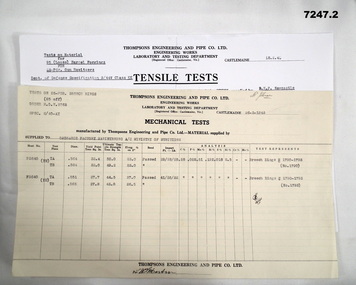 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumDocument - MECHANICAL TEST RESULTS, Thompson's Engineering and Pipe Works, 26 Mar 1943
By referring to Cat No 7237.2 will bring all items associated with Thompsons.1. Single sheet of paper. From Thompson's Engineering & Pipe Co Ltd to Ordnance Factory Maribyrnong. A/c Ministry of Munitions. Titled - mechanical tests - Test on 25 PDR Breech rings. Rings NR (1790-1793). Dated 26 March 1943. 2. Tensile tests on material for 95 (loose) Barrel forgings for 25 PDR Gun Howitzers. From Thompson's to Commonwealth of Australia - Ministry of Munitions. Barrel 14236/1 (Y2) - Barrel 635/3 - Dated 18 Feb 1942.1. Top has name "Mr. Johnson" written. In the middle is an unidentifiable signature dated 26-3-1943. Bottom has (??) Martin. 2. At bottom signed off by (??) Martin.25 pdr, thompson's castlemaine, ordnance factory maribyrnong. -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionArticle - Article - Women, Ballarat Teachers' College: Women of Note; Isobel Dowling, Educator, d.2013
Isobel Dowling began her career in tertiary education in Ballarat at the Teachers' College. This merged with the Ballarat College of Advanced Education in 1976. More name changes and she finished her career as a lecturer in Sociology and Politics at the University of Ballarat. One of her students was Steve Bracks who became Premier of Victoria. One of her greatest achievements involved pioneering work towards forging a career in higher education for women. An inaugural listing on "Ballarat's Great Women Honour Roll' in 2008, Isobel Dowling died in 2013.isobel dowling, women of note, tertiary educator, ballarat teachers' college, ballarat college of advanced education, university of ballarat, sociology and politics, steve bracks, premier of victoria, career in higher education for women, honour roll in 2008 -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesPhotograph, 'Schutt and Barrie Flour Mill employees, Geelong Road West Footscray, Unknown
FORGING AHEAD City of Footscray City of Braybrook Incorporated 1959 Chaff Milling Section Interior photograph: Caption: Chaff baggers in operation Accompanying Text Schutt & Barrie Pty. Ltd. commenced operations in 1913 [Schutt]at Spotswood, but two years later a transfer was made to the present site at the corner of Geelong and Williamstown Road Footscray. The output for years past has been 100 tons of chaff a day- the largest of any mill of its kind in Australia. The firm’s “Green String” is widely known.Schutt & Barrie workmen with John Ralph Schutt and C E Barrie.local identities, agriculture -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomPrincess Mary Gift Tin, 1914
In November 1914, an advertisement was placed in the national press inviting monetary contributions to a 'Sailors & Soldiers Christmas Fund' which had been created by Princess Mary, the seventeen year old daughter of King George V and Queen Mary. The purpose was to provide everyone wearing the King's uniform and serving overseas on Christmas Day 1914 with a 'gift from the nation'. The response was truly overwhelming, and it was decided to spend the money on an embossed brass box, based on a design by Messrs Adshead and Ramsey. The contents varied considerably; officers and men on active service afloat or at the front received a box containing a combination of pipe, lighter, 1 oz of tobacco and twenty cigarettes in distinctive yellow monogrammed wrappers. Non-smokers and boys received a bullet pencil and a packet of sweets instead. Indian troops often got sweets and spices, and nurses were treated to chocolate. Many of these items were despatched separately from the tins themselves, as once the standard issue of tobacco and cigarettes was placed in the tin there was little room for much else apart from the greeting card All boxes, irrespective of recipient, contained a Christmas card and a picture of the Princess. Those which were not distributed until after Christmas were sent out with a card wishing the recipient a 'victorious new year'. The wounded on leave or in hospital, nurses, and the widows or parents of those killed were also entitled to the gift. Prisoners of war at the time had theirs reserved until they were repatriated. Great efforts were made to distribute the gifts in time for Christmas, and huge demands were made on an already stretched postal service. More than 355,000 were successfully delivered by the deadline. As time pressed on, a shortage of brass meant that many entitled personnel did not receive their gift until as late as the summer of 1916, and in January 1919 it was reported that 'considerable' numbers had still not been distributed. Orders for brass strip were placed with the USA, who were not yet involved in the war, and a large consignment was lost with the ship 'Lusitania'. As so much brass was being consumed in the production of weapons and munitions, the quality of the boxes which were manufactured late on was poor, being of a plated inferior alloy, when compared with the earlier pure brass examples. When the fund finally closed in 1920, almost £200,000 had been donated for the provision of more than two and a half million boxes with contents. The 'tin' is approximately 5" long by 3¼" wide by 1¼" deep with a double-skinned, hinged, lid. The surface of the lid depicts the head of Princess Mary in the centre, surrounded by a laurel wreath and flanked on either side by the 'M' monogram. At the top, a decorative cartouche contains the words 'Imperium Britannicum' with a sword and scabbard either side. On the lower edge, another cartouche contains the words 'Christmas 1914', which is flanked by the bows of battleships forging through a heavy sea. In the corners, small roundels house the names of the Allies: Belgium, Japan, Montenegro and Servia; France and Russia are at the edges, each superimposed on three furled flags or standards. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Balance Spring Scale, Peck, Stow & Wilcox, 1890-1910
Peck, Stow & Wilcox was founded in 1870 by the merger of three different industrial tool manufacturers specializing in tin-processing equipment. Their factory complex was at 217 Centre Street in Southington, Connecticut. The company grew rapidly, and was by 1890 producing a diversified array of tools. It was also the town's largest employer. The plant was substantially enlarged in 1912, which is the period when most of the buildings surviving in 1989 were built. By that time, the complex was operated by Ideal Forging. That company went bankrupt in 2003, and the plant was acquired by real estate developers not long afterwards. Demolition of the premises took place in 2015, after hazardous materials were removed from the site.A large American company that exported it’s goods all over the world and was a major producer of balance scales. The company no longer in existence and its products are now regarded as collectors items. The subject item in the Flagstaff Hill collection is significant as the pocket spring balance scale is one of the earliest produced.Spring Balance Scale Weighs 0 to 25LBS.Stamped PS&W. Has a five pointed star stamped on front.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, spring balance scales, peck stow & wilcox, pocket balance scale, weighing scales -
 Victorian Interpretive Projects Inc.
Victorian Interpretive Projects Inc.Photograph - colour, Clare Gervasoni, Furphy Water Cart, 2014, 01/11/2014
The water cart was in itself a complete invention of John Furphy and was first made in the 1880's. At the time no similar article was used in Australia. Few houses of the time were designed to collect rain water from the roof and hence, water needed to be collected elsewhere and transported for stock and domestic use. The method of carting water was then confined to horse drawn drays or sleds with mounted wooden barrels or casks. At the same time the growing demand for agricultural implements, led to the establishment of a foundry with a furnace to cast components rather than the time consuming task of forging. This became the catalyst for the efficient production of the robust and mobile water carrier known then, and now, as the Furphy Farm Water Cart.Four colour photographs showing a tank made by Furphy and Sons, Shepparton.furphy, shepparton, water storage -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncFunctional object - Foot Bellows, Fletcher Russell & Co. Ltd, c1895
FLETCHER RUSSELL & CO. LTD/ WARRINGTON MANCHESTER & LONDON Thomas Fletcher (1840-1903) had established a gas appliance manufactory in Thynne Street, Warrington by the 1880s. By 1895 the company had become Fletcher Russell and Co Gas Engineers, his firm having merged with Alexander and William Russell of Pendleton Iron Works. In 1950, the firm merged into Radiation Ltd which was later acquired by 'TI New World. In the early 1880s Thomas Fletcher was a registered dentist who went on to found a dental apparatus manufacturing business. He later diversified into producing equipment for blacksmiths, foundries, forging and other sectors. The company had grown to 900 employees in 1914. These foot-operated bellows were for pumping gas to keep the patient relaxed while the dentist worked on their teeth. They were later modified for a variety of uses where a continual flow of air was needed.These bellows are representative of a range of devices developed in the late 19th Century to assist in manufacturing. They were donated to our collection by a Wodonga resident.A set of foot bellows made from timber, metal and leather. The bellows were activated by pressing up and down on the metal step-shaped lever at the front. The air outlet on one side would have a hose attached to it to direct the air current to wherever it was needed. The bellows are made from leather. The manufacturers mark is attached to the top within a metal circle.On top of Bellows in a circle: "FLETCHER RUSSELL & CO./ WARRINGTON/ MANCHESTER / LONDON"foot bellows, fletcher russell & co. ltd. -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyInk Well Desk Set, circa mid to late 1900's
The "nib" pen was the preferred scribe method up until the "fountain" pen was produced (1940's), both could use specific inks that had longer life periods on paper surfaces. Ink wells such as those incorporated in this desk set allowed the user to select the colour and "type of ink" required. The nib pen was the only writing pen that could tolerate "Iron gall" ink. Legal documents were at the start of the mid 1980's required by law(in Australia) to be signed by "well" filled pens. The inks used were either "indian" or "iron/oak gall" because their infusion into paper could not be erased and they had a longer "paper" life and were harder to forge. Bottled ink was superior to that supplied in fountain pens or "biro pens" because the user's choice to a greater range of inks covered a variety of scenarios. Forging a nib signature is extremely hard compared to that of a "biro pen" because a nib settles in to the users particular style of pen movement and arm pressure.This desk writing set was typical of those used by administrators, businesses or quasi legal sectors within the Kiewa Valley, before the lifting of the ban on the use of biros "to sign" legal documents. Fountain pens were used extensively before cheaper biros (throw away) writing implements (1940's) came into the market place.This glass ink well desk set has two circular ink wells connected to their respective nib holders. The nib holders are smaller circular receptacles and feed off the larger ink reservoirs. Between the two larger ink wells is a shallow bottomed elongated "oval" sphere able to contain "slide on" clips, two pronged fasteners (require a hole to be punched in papers) or small "bulldog" clips. At the front edge is an elongated and grooved (two) place for writing nibs. The grooves keep each nib or fountain pen separated.The glass structure is made from clear glass and only the outside "boxed" walls of the desk set make contact with the desk surface. The ink wells can also securely accommodate small bottles of ink. This would have been the case for refillable fountain pens.stationery, fountain pens, nib pens, ink receptors, glass ink wells -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPamphlet, British Engineering Standards Association, British Standards Institution, 1959 - 1960
Set of 6 technical data sheets, published by the British Standards Institution in 1959 / 1960 providing information about the standards for various railway products in a summary sheet form. Each sheet has been folded into 8 with the title and other sheets on the outside when folded. .1 - Sheet 3A - Flat Bottom Railway Rails, fishplates and Steel sleepers - PD 3876 - August 1960. .2 - Sheet 3B - Axles, Tyres, Solid Rolled Steel Wheels and disc wheel centres - PD3277 - December 1959 .3 - Sheet 3C - Steel billets, blooms, bars and forgings for railway rolling stock - PD 3361 - April 1959 .4 - Sheet 3D - Steel slabs, plates, sections, bars and rivets for loco boilers, locomotives, carriages and wagons - PD 3387, May 1959. .5 - Sheet 3E - Laminated springs and spring steels - PD 3365 April 1959 .6 - Sheet 3F - Helical and Volute Springs and Spring Steelstrams, tramways, steel, wheels, springs, specification, materials -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Flat Iron, circa 1900
Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top. An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today. Iron; small flat domestic iron.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, iron, flat iron, domestic iron, laundery, ironing equipment, sad iron -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Clothes Iron, last quarter of the 19th century
Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today.Clothes Iron, wedge shaped, cast iron painted black with cylindrical handle small funnel through centre of handle.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry equipment, sad iron, domestic object -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Clothes Iron, last quarter of the 19th century
Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today.Clothes Iron, wedge shaped, cast iron painted black with cylindrical handle small funnel through centre of handle.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry equipment, sad iron, domestic object -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Clothes Iron, last quarter of the 19th century
Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today.Clothes Iron, wedge shaped, cast iron painted black with cylindrical handle small funnel through centre of handle.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry equipment, sad iron, domestic object -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Flat Iron, 1890-1935
Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today. Flat iron cast iron with traces of original black finish on handle. Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry, clothes ironing, sad iron, tailors goose -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Flat Iron, 1890-1935
Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today. Flat iron cast iron with stand None item too badly corrodedflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry, clothes ironing, sad iron, tailors goose
