Showing 37 items matching "geological formations"
-
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesBooklet - Photocopy, G.B. Pritchard, Old Yarrahistory as told by the …Geology of Burnley Heyington Tooronga, 1944
... geological formations..., 1944,3- 29pp and front cover. Describing the geological... of burnley geological formations geology victoria geology near ...Booklet by G.B. Pritchard, publ. F.W. Cheshire, Melbourne, 1944,3- 29pp and front cover. Describing the geological formations in the Burnley area. (Burnley, Heyington, Tooronga)g.b. pritchard, f.w. cheshire, geology of burnley, geological formations, geology victoria, geology near burnley victoria, old yarra history -
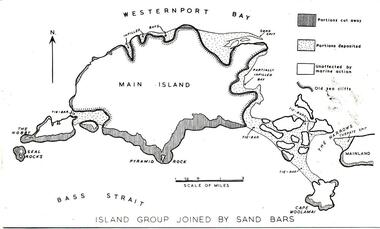 Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.
Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.Photograph
... in the geological formation... a late stage in the geological formation Photograph Bryant West ...One of a collection of over 400 photographs in an album commenced in 1960 and presented to the Phillip Island & Westernport Historical Society by the Shire of Phillip IslandPhotograph of a map of Phillip Island showing a late stage in the geological formationlocal history, photography, phillip island, black & white photograph, phillip island geology, map, map of phillip island, john jenner, bryant west -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - VICTORIA HILL - KEY TO SIGN POSTS ON AREA MAP
... and their associated equipment and geological formations. Initialled AR... equipment and geological formations. Initialled AR. Notes prepared ...Photocopied handwritten notes with typed copy of same, on Sign Posts on Victoria Hill.. Sign posts were for mines and their associated equipment and geological formations. Initialled AR. Notes prepared by Albert Richardson.document, victoria hill, key to sign posts on area map, north old chum shaft, ballerstedt's first open cut, rock formatins, lansell's big 180, 20 stampers crushing battery, foundations 'cleopatra needle' type chimney, victoria quartz mine, rae's open cut, quartz roasting, anticlinal arch, primitive tunnels, coloured rock formations, adit, oblique fault, spurry quartz veins, prospecting tunnels, floyd's small crushing battery, gt central victoria (midway) shaft -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncArchive (Sub-series) - Subject File, Kew Historical Society, Geology (Kew), 1958
... . These include a Parks Victoria brochure on the Geology of Yarra Bend... that includes information about the geological formation of the region ...Various partiesReference, Research, InformationSecondary Values (KHS Imposed Order)Subject file containing some secondary sources. These include a Parks Victoria brochure on the Geology of Yarra Bend Park and a printout of a web page about the Collingwood Children’s Farm that includes information about the geological formation of the region.kew historical society - archives, geology - kew (vic)kew historical society - archives, geology - kew (vic) -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - VICTORIA HILL - QUESTION 5 ON VICTORIA HILL
... on machinery, geological formations and earning from the mines..... Also contains notes on machinery, geological formations ...Handwritten notes and carbon copy titled Question 5. Notes refer to Victoria Hill being opened up by Theodore Ballerstedt and his son early in 1854. Theodore Ballerstedt left for Germany having sold his home, crushing battery and mine to Mr. Geo Lansell. He called the mine the '180'. Next mine north to the '180' was the Victoria Quartz. Also contains notes on machinery, geological formations and earning from the mines.document, gold, victoria hill, victoria hill, question 5 on victoria hill, theodore ballerstedt, mr geo lansell, fortuna villa, commonwealth survey regiment, the 180, ballerstedt's original open cut, bendigo south rotary club, john wybrandt, north old chum coy, victoria quartz, victoria reef quartz company, mr william rae, a roberts & sons united ironworks, australian mining standard special edition 1899, bendigo advertiser 10/2/1897, a harkness & coy, bendigo advertiser 30/6/1910 page 5, rae's open cut, e j dunn, bendigo saddle reefs, wittscheibe's 'jeweller's shop', roberts & frost, ashley noy & coy, grant & co, woodward & son, couth allen and co, taylor gould and co, crawshaw & co, roberts & co -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Prodromus of the Palaeontology of Victoria No iv, 1876 (exact)
... for the determination of the geological ages of the different geological... for the determination of the geological ages of the different geological ...This publication consists of many Decades which contain "figuers and descriptions of the fossil organic remains to be used for the determination of the geological ages of the different geological formations of the country." (p. 3). Frederick McCoy was born in Dublin, Ireland in 1817. He was a Professor of Natural Sciences, University of Melbourne 1854-1899. McCoy lectured in geology, zoology, chemistry, mineralogy, geography and botany. In 1858 He became the Director of the National Museum of Victoria and the President of the Royal Society of Victoria in 1864. In 1888, McCoy was awarded FRS for work in Palaeontology in Ireland, England and Australia. He died in his office while correcting examination papers in 1899A Paperback cover book. Decade IV. Title is written in black on front cover and on title page. At head of title: Geological Survey of Victoria. Illustrations, plates in b/w; 32 p. It includes figures and descriptions of Victorian Organic Remains and contents of Decades on the back cover of the book.australia palaeobotany, victoria palaeontology, geological survey of victoria, frederick mccoy, organic remains -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Prodromus of the Palaeontology of Victoria, 1877 (exact)
... for the determination of the geological ages of the different geological... for the determination of the geological ages of the different geological ...This publication consists of many Decades which contain "figuers and descriptions of the fossil organic remains to be used for the determination of the geological ages of the different geological formations of the country." (p. 3). Frederick McCoy was born in Dublin, Ireland in 1817. He was a Professor of Natural Sciences, University of Melbourne 1854-1899. McCoy lectured in geology, zoology, chemistry, mineralogy, geography and botany. In 1858 He became the Director of the National Museum of Victoria and the President of the Royal Society of Victoria in 1864. In 1888, McCoy was awarded FRS for work in Palaeontology in Ireland, England and Australia. He died in his office while correcting examination papers in 1899.A Paperback cover book. Decade v. Title is written in black on front cover and on title page. At head of title: Geological Survey of Victoria. Illustrations, plates in b/w; 41 p. It includes figures and descriptions of Victorian Organic Remains and contents of Decades on back cover.Stamped Ballarat East Public Library"australia palaeobotany, victoria palaeontology, geological survey of victoria, frederick mccoy, organic remains, ballarat east library, ballarat east public library -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, John Ferres, Government Printer, Prodromus of the Palaeontology of Victoria Decade vi, 1878 (exact)
... for the determination of the geological ages of the different geological... for the determination of the geological ages of the different geological ...This publication consists of many Decades which contain "figuers and descriptions of the fossil organic remains to be used for the determination of the geological ages of the different geological formations of the country." (p. 3). Frederick McCoy was born in Dublin, Ireland in 1817. He was a Professor of Natural Sciences, University of Melbourne 1854-1899. McCoy lectured in geology, zoology, chemistry, mineralogy, geography and botany. In 1858 He became the Director of the National Museum of Victoria and the President of the Royal Society of Victoria in 1864. In 1888, McCoy was awarded FRS for work in Palaeontology in Ireland, England and Australia. He died in his office while correcting examination papers in 1899.A Paperback cover book. Decade VI. Title is written in black on front cover and on title page. At head of title: Geological Survey of Victoria. Illustrations, plates in b/w; 42 p. It includes figures and descriptions of Victorian Organic Remains and contents of Decades at back of the book.australia palaeobotany, victoria palaeontology, geological survey of victoria, frederick mccoy, organic remains, john ferres -
 Sunbury Family History and Heritage Society Inc.
Sunbury Family History and Heritage Society Inc.Photograph, Bulla Primary School, Hanging Rock, 1995
... geological formations. Hanging Rock, also known as Mount Diogenes... and explored the rock for its interesting geological formations ...In 1995, the upper school students from Bulla Primary School attended a camp at Hanging Rock Reserve which is part of the Macedon Ranges. At this camp the students were shown basic rock climbing skills and explored the rock for its interesting geological formations. Hanging Rock, also known as Mount Diogenes, is the traditional land of the Dja Dja Wurrung, Woi Wurrung and Taungurung people. It is a mamelon formed when magma poured from a vent and congealed. There are interesting rock functions at the site such as the Colonnade, the Eagle and the UFO. The highest point on the rock is 718metres above sea level and 105 meters above the land at its base.Hanging Rock is an important geological and volcanic structure in the Macedon Ranges area and in central Victoria. A non-digital coloured photograph of three holiday cabins and a barbecue in a bushland setting. A red car is parked outside one of the cabins as well as two permanent picnic tables.hanging rock, mount diogenes, mamelons, volcanoes, school camps, bulla primary school -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Ilvaite
Ilvaite has acquired its name from Ilva (Latin for Elba) Island, Greece, where Ilvaite is most commonly found. The geological setting in which Ilvaite occurs is through contact with magnetite, zinc and copper ore deposits, along with contact metamorphic deposits and zeolite zones. llvaite crystallizes in the form of black prismatic crystals and columns . This specimen was retrieved from Broken hill, known as the world's richest and largest zinc-lead ore deposit. Because of Ilvaite's often unaesthetic crystal formations compared to other minerals, Ilvaite is uncommon in most rock collections, particularly specimens that are not well formed, such as this one. Ilvaite is also a member of the Sorosilicate subclass of the silicate minerals, which have an unusual basic unit of Si2O7, making Ilvaite a unique mineral. Given that Ilvaite is not commonly found in Australia, it marks a unique contribution to an Australian collection of minerals. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid hand-sized ferrous iron analogue mineral with of black with shades of beige Ilvaite is a brittle, opaque rock formation that has acquired its name from Ilva (Latin for Elba) Island, Greece, where Ilvaite is most commonly found. The geological setting in which Ilvaite occurs is through contact with magnetite, zinc and copper ore deposits, along with contact metamorphic deposits and zeolite zones. llvaite crystallizes in the form of black prismatic crystals and columns rock, mineral, ilvaite, ilvaite specimen -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Brown coal
This particular specimen was recovered from the Lal Lal Coal and Iron Mine in Victoria, 19km from Ballarat. Brown Coal was discovered here in 1857, just alongside the Geelong to Ballarat Railway line. This discovery of lignite (brown coal) was the first in Victoria, which would bring important benefits to the region and state, both of which had previously been reliant on coal imports. In the 1860s, iron ore was found just 5km from Lal Lal, and the area was converted into an Iron Ore Mine. The Lal Lal Iron Mining Company took over operations in 1874, who then peaked iron production in 1884. This mine continued operations until June 1884, when the blast furnace was extinguished and never recommenced. The blast furnace at Lal Lal is considered one of the most important and highly significant sites ion early industrial history in Australia, as it is the only remaining best furnace from the nineteenth century in the Southern Hemisphere. The furnace ruins are 17 metres high, and are clearly visible today on Iron Mine Road, Lal Lal, near the Bungal Dam. This specimen of Lignite (brown coal) is significant, as it was mined from the area where brown coal was first discovered in Victoria, leading to an important and controversial future of the mining and use of brown coal in this State. The Victorian Heritage Database has listed the Lal Lal Coal Mine with local significance, with their Statement of Significance stating: "The Lal Lal coal mine is historically significant as the site of the first discovery of lignite (brown coal) in Victoria, and one that promised important benefits to regional and state industries that were reliant on coal imports at the time. The significance of the stie is reduced by the poor state of preservation of the coal mining and processing fabric". This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A hand-sized light-weight, soft and combustable sedimentary rock specimen, that is dark brown in colour. The specimen has jagged edges, as though parts of the rock have crumbled away. Brown coal, or Lignite, is formed naturally from compressed peat, and is typically found in natural basins. The stages to the formation of coal ('coalification') begin with plant material and wood, which will decay if it is not subjected to deep burial or heating, and turn into Peat. Peat, when sufficiently compressed naturally, will turn into Brown Coal (Lignite), and finally into Black Coal (sub-bituminous, bituminous and anthracite). Each successive stage has a higher energy content and lower water content. It is brownish-black in colour. Brown Coal has a high moisture content, between 50 and 75 percent, and a low carbon content. Some Brown Coals may be stratified, with layers of plant matter, which means little coalification has occurred beyond the peat natural processing stage. When Brown Coal is submerged in dilute nitric acid or boiling potassium hydroxide solution, it reacts to produce a reddish solution, of which higher-ranked coals do not. When brown coal is pulverised and burned in boilers, the steam is used to drive turbines, which generates electricity. It is the lowest rank of coal, as when burned, it creates a relatively low heat content, which in turn does not create a great output of steam. burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, beechworth museum, geological, geological specimen, mineralogy, brown coal, brown coal specimen, lignite, lal lal, lal lal coal mine, lal lal iron mine, ballarat, blast furnace -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Ropy Lava
‘Ropy lava’ is known for its sculptural and layered qualities. It occurs in specific lava flows that are slow moving and slow cooling, allowing for unique formations to be created out of the motion. Ropy Lava is a flow that has a hardened crust with molten material underneath, the tension between these states is what creates its characteristic form. The brown/red hue of the stone is an indication of age, as it is oxidised iron deposits. This rock deposit is thought to be sourced from the area by Talbot, in western Victoria. This area has a rich mineral history and experienced the gold rush in the 1850's. The traditional owners of this area are the Dja Dja Wurrung people.This geological specimen shows the conditions in which the Australian landscape was created as well as provides an indication as to how these events occurred. It is representative of a common natural process that contextualises the formation of Australia with the formation of other landmasses. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.Hand sized specimen in brown/red hues42 / victoria, talbot, lava, ropy, ropy lava, mineral, geological specimen, geological, geological heritage, natural stone, natural history -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Brown Coal
Brown Coal is typically found as rocks. During formation the Brown Coal starts as peats, which is an acidic brown deposit resembling soil, and over time when subjected to pressure and heat these peats form the Coal. Brown Coal is the lowest rank of coal as it has a low carbon (energy) content, and a high moisture content. This high moisture content makes Brown Coal unsuitable for overseas exports. This particular specimen was recovered from the Yallourn Mine in Latrobe Valley, Victoria as part of the geological survey of Victoria being carried out by Alfred Selwyn. Otherwise known as the 'Yallourn Power Station', the Yallourn Mine is Australia's second largest mine. Yallourn Mine was first built in 1920, and since then it has been providing over 1 billion tonnes of Brown Coal to Australia every year. The Yallourn Mine is responsible for 22% of Victoria's electricity and 8% of Australia's electricity. As of 2021 the mine employs around 500 people. Due to ongoing maintenance issues and Australia's move to cleaner energy, the Yallourn Mine intends to shut down permanently as of 2028. Soon after gold was discovered in 1851, Victoria’s Governor La Trobe wrote to the Colonial Office in London, urging ‘the propriety of selecting and appointing as Mineral Surveyor for this Colony a gentleman possessed of the requisite qualifications and acquaintance with geological science and phenomena’. Alfred Selwyn was appointed geological surveyor in Australia in 1852 which began the Geological Survey of Victoria. In 1853-69 the Geological Survey issued under Selwyn's direction sixty-one geological maps and numerous reports; they were of such high standard that a writer in the Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society of London bracketed the survey with that of the United States of America as the best in the world. During his years spent in Australia, Selwyn collected numerous significant geological specimens, examples of which are held in collections such as the Burke Museum.Brown coal is considered to be an essential rock to Australia's energy consumption. Although plentiful in sources, Brown Coal is not able to be exported overseas due to its high moisture content. As Australia moves towards cleaner energy, Brown Coal is going become less used. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid hand-sized sedimentary rock that is a dark shade of brown.13 / BROWN COAL / Showing Woody structure / Locality: Yallourn, Vic. | Label probably / correct but / can't find reference / no. 13 to match in / registers. / C Willman / 15/4/21burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, beechworth museum, geological, geological specimen, mineralogy, yallourn, yallourn mine, victoria, coal, brown coal, brown coal specimen, alfred selwyn, geological survey of victoria, geological survey, yallourn power station -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Tourmaline in Quartz, Unknown
... leading to its formation. Geological Specimen geology Geology ...Tourmaline specimens are members of a crystalline silicate mineral group based on boron but influenced by elements including aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or potassium. Specimens present a wide variety of colours and forms according to the specific mix of these elements. Tourmalines are semi-precious gemstones with many applications, including commercial jewellery production. The word 'tourmaline' derives from the Sinhalese term for the carnelian or red-shaded specimens, "tōramalli". This specimen has been classified by geologists as 'Black Schoalou/Tourmaline in quartz'. Schoalou may equate to a common black-hued type of Tourmaline associated since around 1400 with mines in Saxony, Germany near a village called Schorl (today's Zchorlau). If this specimen is part of the 'Schorl' species of tourmaline it is a member of the most common group of Tourmalines, a divalent sodium ion influenced group accounting for 95% of specimens. On assessment, it was noted that the crossed lines (XIs) of this tourmaline have been fractured and rehealed by the quartz matrix in which the tourmaline rests. This item is significant as an example of its type of gemstone and the geological processes leading to its formation. A solid medium-sized piece of Black Schoalou/Tourmaline in a cream and peach coloured quartz matrix. Existing label: Black Schoalou / Tourmaline in / quartz. / Tourmalines XIs have / been fractured and / rehealed with / quartz / C. Willman / 15/4/21 /geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, indigo shire, north-east victoria, tourmaline, quartz, boron, crystals, minerals, gemstones, semi-precious, black schoalou, zchorlau, schorl -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Malachite, Unknown
Malachite is a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral. It has a chemical composition of Cu2(CO3)(OH)2. It often forms within limestone where a subsurface chemical environment favourable for the formation of carbonate minerals can occur. It is a substance that can be found in many different parts of the world including: Australia, USA, Russia and the Democratic Republic of Congo. Malachite has historically been used to produce copper, with mining of the mineral dating back over a period of four thousand years. Due to its beautiful green colourations, it is also commonly used for aesthetic purposes such as in the production of sculptures and jewellery. This particular specimen was collected from the town of Burra, South Australia as part of a geological survey undertaken during the nineteenth century. The locality (located on Ngadjuri Country) has a long history of mining, particularly in copper mining, as the area is rich in copper deposits. The first significant discovery of this was made in Burra (Burra Burra Mine) in 1845 and, at the time, the mine was the largest and richest of its kind in the world, producing nearly five percent of the total world copper output. This specimen is significant as it is considered to be a rare gemstone, as many of the original deposits for the stones are significantly depleted, leaving behind very few sources. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid palm-sized copper carbonate hydroxide mineral with patterns of green colourations Existing Label: MALACHITE / Locality: Burra / S. Aust. Other Label: Confirmed / as Malachite / C. Willman / 15/4/1 / + Bill Birch burke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen, malachite, gemstone, green gemstone, burra, burra burra mine, burra south australia, carbonate mineral, copper, copper mining, copper mining burra, carbonate hydroxide mineral, copper carbonate, malachite mining, malachite burra, monster mine -
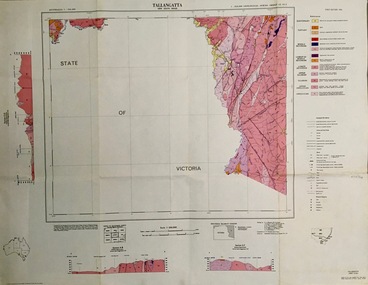 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMap - Geological, Tallangatta, New South Wales: 1:250,000 Geological Series, SJ 55-3, 1966, 1966
Compiled by the Geological Survey of N.S.W., Division of Regional Geology. Topographical base compiled from Snowy Mountains Hydro Electrical Authority, Department of Lands, County maps and Snowy Lease Map. Other sheet adjoin this map. There are 13 formation sections grouped into 9 - Quaternary, Tertiary, Middle Devonian, Lower to Middle Devonian, Lower Devonian, Upper Silurian, Silurian, Upper Ordovician and Ordovician.Large coloured map showing geological features, faults, bores, rivers and mineral deposits.Scale of map, longitude and latitude, river names. "Tallangatta 1:250,00" written in black pen.tallangatta, new south wales, geological survey, topographical base, snowy mountains hydro electrical authority, department of lands, snowy lease map, department of mines, quaternary, tertiary, middle devonian, lower to middle devonian, lower devonian, uper siluran, silurian, upper ordovician, ordovician -
 Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.
Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.Photograph
... & white photograph coastline geology rock formations John Jenner ...One of a collection of over 400 photographs in an album commenced in 1960 and presented to the Phillip Island & Westernport Historical Society by the Shire of Phillip IslandPhotograph of the basalt Jetty and geological feature near Surf Beachlocal history, photography, basalt jetty, surf beach, black & white photograph, coastline, geology, rock formations, john jenner, bryant west -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyBook, W. & A.K. Johnston, School atlas of physical geography: the elementary facts of geology; hydrography; meteorology and natural history by Alex Keith Johnston, 1871_
This atlas of physical geography has 20 plates illustrating maps and various rock formations.This volume illustrates a 19th century view of physical geography.51 pages, 20 plates, maps. Red hard cover with title in gold lettering.Inscribed on fly leaf with original owner's name (1890)physical geography, school books, atlases -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Princess Margaret Rose Caves, n.d
Coloured photograph showing stalactite and helictite formations in Princess Margaret Rose Caves.princess margaret rose caves, geology, tourism -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietySample Tubes
Part of Geological investigation into the characteristics of the rock formations and ground water.Water supply and infrastructure requires prior investigation before construction work can commence.Very small glass tubes (about 30) with cork toppers. Each tube is labelled. Resting on wool in a cardboard box with a lid. Stored in an old thick cardboard box with a very faint 'Harrietville ... Samples' on its lid.On the tubes - place and number "Harrietville / samples"geological samples, harrietville water -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societymagazine, List Print Nominees, The Buchan Experience, 1985
This magazine is a guide to the Buchan and Murrindal Caves of East Gippsland. From 1985 to 1993 Kent Henderson had published a number of full colour tourist-orientated books about limestone caves. This book is the second in the series. This one and a book on Jenolan Caves, in New South Wales, are the only two still in print.This item is a valuable research tool on the history of Buchan and in particular, The Buchan Caves.A soft cover, 64 pp stapled magazine with a glossy cover. On the cover is a coloured photograph of limestone stalagmite formations in a cave. The magazine contains coloured photographs and historical information about Buchan Caves.Inside on fly is "Mary Gilbert" hand-written in black felt tip.caves-victoria-buchan geology buchan -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Memoirs of the Geological Survey of Victoria No 14 The Ballarat Goldfields, 1923, 1923
William Baragwanath was educated at the Ballarat School of Mines, obtaining a Geology Certificate in 1911. After further study he went on the become Secretary for Mines, and Chief Mining Surveyor. Baragwanath was a Councillor of the Ballarat School of Mine from 1916 to 1950.Pink covered foolscap book of 257 pages and 32 maps and plans by William Baragwanath. Contents include topography, physiography, historical, geology, basalt, faults, dykes, minerals leads, alluvial mines, nuggets, structure of Ballarat West goldfields, structure of Ballarat East gold-field, quartz formation, indicators, defunct mines, existing mines, table of deepest shafts. Images include: section of the Ballarat Gold-Field, Dead HOrse Flat, lakes formed by Basalt Flows, Gong Gong Creek, Frenchman's Lead, Ballarat West Mines, LEases and positions of shafts (1857), puddling, White Horse Lead, Woah Hawp Canton, Ballarat Township mines, Sebastopol, syncline, Victoria United Line, First Chance Mine, Llanberris No 1 Mine, Saddle Reef, New Normanby Mine, Woah Hawp Canton Mine, South Star Mine, Sebastopol Plateau, south Woah Hawp Mine, Woah No. 2 Minegeology, geological survey no 14, ballarat, baragwanath, william baragwanath -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - black and white, Jamieson Valley: Broad alluvial flats of recent geological formation: Silurian and Devonian Ranges in background
... geological formation alluvial flats silurian devonian Photograph ...Photograph included in book "Victoria: Gold and Minerals" issued by Mines Department Victoria, 1935Photographvictoria, jamieson valley, geological formation, alluvial flats, silurian, devonian -
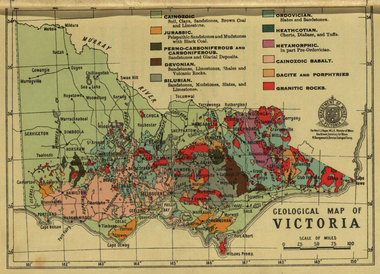 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - colour, William Baragwanath, Department of Mines: Geological map of Victoria, c1935
... key to land formations time periods jurassic geological map ...Photograph included in book "Victoria: Gold and Minerals" issued by Mines Department Victoria, 1935Photographmap, department of mines, victoria, key to land formations, time periods, jurassic, geological map -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Samuel Hughes F.G.S., CE, A Treatise on Waterworks for the Supply of Cities and Towns, 1882
... geological formation sewerage springs pumping machinery wells bores ...Light green embossed fabric bound hardcover book with gold title. 413 pages.N.F. Barret hand written on outer pagesgeological formation, sewerage, springs, pumping machinery, wells, bores, reservoirs, drainage, bagshot sand, filter beds, geology of england, cornish engines, waterworks -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument, SMB: Catalogue of a Collection of Rocks, Minerals, etc, 1883
This list of rocks, minerals, etc. from Victoria was complied and forwarded by the School of Mines, Ballarat, to the Calcutta International Exhibition. At the end of the exhibition the items were to be presented to the Geological Survey of India. One Hundred items are listed. Pages 4 and 5 also show diagrams relating to the land formations and sections. Places in Victoria are named indicating where items were found. List compiled by Professor Ferdinand Moritz Krause. He joined Ballarat School of Mines in 1880 and lectured in Mineralogy and Geology. He was also the Curator of the Ballarat School of Mines Museum.6 pages, handwrittenSignature of F M Krause Dated 30th August 1883ballarat school of mines, rocks, minerals, calcutta international exhibition, geology survey of india, victoria, professor ferdinand moritz krause, mineralogy, geology, curator, ballarat school of mines museum -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Map - MAP: VIRGINIA MINE GARDEN GULLY LINE OF REEF
Map of Virginia Mine on the Garden Gully line of reef, Eaglehawk, transverse section. Shaft, levels and Garden Gully anticlinal axial line drawn. Key shows types of formations - quartz, spurs, sandstone, slate, cleavage, lava. This map forms part of the Geological Survey of Victoria, Structure of Bendigo Goldfield report, No. 47, 1923. H.Herman, late Director of Geological Survey.Geological Survey Victoria, Geological Survey Office, Bendigo.bendigo, gold mining, virgina mine eaglehawk, eaglehawk, bendigo, gold mining, virginia mine, garden gully line of reef. -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumDocument, Geological Plan, Eildon Dam Site, 1945
To record details of geological aspects of EildonA series of maps illustrating rock formations etc., locations, boundaries and planswater/irrigation, documents, maps -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Anticline in the Hepburn Springs Reserve, 2019, 22/04/2019
Anticlines are folded rock formations that have an upwards convex shape. Anticlines can exist as a single fold or as a series of adjacent folds of alternating synclines and anticlines. The Hepburn Springs anticline is geologically associated with the west dipping fissures cutting across sandstone strata of the Hepburn Spring anticline.Colour photograph of an anticline at Hepburn Mineral Springs Reserve, in close proximity to the Sulphur Spring. hepburn springs, anticline, geology, hepburn mineral springs reserve, hepburn anticline, hepburn geology -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Galena (with quartz), unknown
Galena is the natural compound of lead and classed as a sulphide, it crystallises in a cubic pattern and its chemical formula is PbS. Galena is a primary source of both lead and silver. This specimen of Galena comes from Broken Hill. Broken Hill has one of the world’s largest and most significant deposit of ore for the production of lead. Mining of Galena at Broken Hill began with the staking of land by Charles Rasp in 1883. By the following year, in 1884, Rasp and six others had formed Broken Hill Mining Company. Broken Hill Mining Company eventually evolved into BHP group limited and is currently the largest mining company in the world and the largest company in Australia. There is archaeological evidence from artefacts discovered in Turkey that humans have been extracting lead from galena by the process of smelting since at least 6500 BCE. This specimen also has quartz on the top surface which is frequently discovered alongside Galena. This mineral specimen is of historic significance as a sample of Galena extracted from Broken Hill during the 19th century. Mining for Galena in Broken Hill begin in 1883 by Charles Rasp and evolved into the world’s largest mining company – BHP Group Limited. Broken Hill is one of the world’s most significant deposits of ore for the production of lead. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A flat, hand-sized, grey sulphide specimen that is the natural compound of lead with a quartz formation on the top surface. Existing Label: GALENA / (with quartz) / Locality: Broken Hill / N.S.W 120 x 70 x 29geological specimen, geology, geology collection, burke museum, beechworth, galena, galena quartz, quartz, charles rasp, broken hill mining company, bhp group limited, bhp, lead, ore, lead sulphide, sulphide, silver, broken hill
