Showing 14 items matching "gona"
-
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesSlide, Dorothy Wickham, Community hut at Gona near Bune, Papua New Guinea, 1958
This photograph was taken around 1958.Scanned from a coloured slideView from this sidepapua new guinea, papuan hut, gona, bune -
 Monbulk RSL Sub Branch
Monbulk RSL Sub BranchBook, Allen and Unwin, A bastard of a place : the Australians in Papua : Kokoda, Milne Bay, Gona, Buna, Sanananda, 2004
In 1942 and early 1943 Papua New Guinea was 'a bastard of a place' to fight a war. This book gives us the final, all-encompassing story of the five battles that changed Australia forever. The compelling narrative resonates with the voices of both the well-trained AIF volunteer, and the young Militia conscript who triumphed together. The author interviewed hundreds of these soldiers and himself travelled the treacherous terrain and bloody battlegrounds where so many of their mates perished, and reveals the inside story of how Generals MacArthur and Blamey sacrificed many of the senior Australian field commanders as scapegoats to protect their own positions. A Bastard of a Place restores Milne Bay, Gona, Buna and Sanananda to their rightful place beside Kokoda to what they should collectively be for all Australians - sacred ground.Index, bibliography, notes, ill, maps, p.691.non-fictionIn 1942 and early 1943 Papua New Guinea was 'a bastard of a place' to fight a war. This book gives us the final, all-encompassing story of the five battles that changed Australia forever. The compelling narrative resonates with the voices of both the well-trained AIF volunteer, and the young Militia conscript who triumphed together. The author interviewed hundreds of these soldiers and himself travelled the treacherous terrain and bloody battlegrounds where so many of their mates perished, and reveals the inside story of how Generals MacArthur and Blamey sacrificed many of the senior Australian field commanders as scapegoats to protect their own positions. A Bastard of a Place restores Milne Bay, Gona, Buna and Sanananda to their rightful place beside Kokoda to what they should collectively be for all Australians - sacred ground.world war 1939 – 1945 – campaigns – new guinea, world war 1939 – 1945 – campaigns – kokoda -
 Tramways/East Melbourne RSL Sub Branch - RSL Victoria Listing id: 27511
Tramways/East Melbourne RSL Sub Branch - RSL Victoria Listing id: 27511Book, Lex Mc AULAY et al, TO THE BITTER END (The Japanese Defeat At Buna & Gona 1942-43), 1993
940.5425, historical -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumPhotograph (Item) - Assorted Aerial Photos Of Lae, Rabaul, Horn Island, Kahili, Buna, Gona , Ballale Island
-
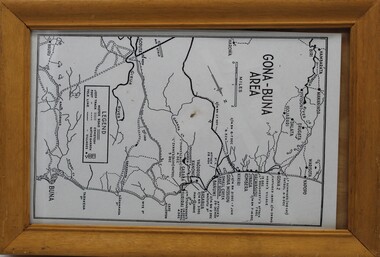 Ringwood RSL Sub-Branch
Ringwood RSL Sub-BranchWork on paper - Gona-Buna Area
Gona-Buna Area -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumAlbum - ALBUM WW2, PHOTOGRAPH, 1942 - 1945
Collection of Frank Herbert HORN QX16945, 7th Division Postal Unit. Area of Service, Middle East & South Pacific.Blue cardboard covered photo album containing 30 photos taken during WWII in Gona, Papua New Guinea.album, photographs -
 Doncaster RSL Sub Branch
Doncaster RSL Sub BranchWar In New Guinea, The F.G. Johnstone Publishing Company Sydney, War In New Guinea, Mid 1940s
One phase of the Papuan campaign as seen by the camera of George Silk a department of Information photographer, 194240 Page Pamphlet with black and white photograph on front cover of Cpl. F.R.Smith of Queensland, with his tommy gun near Gona Front line.Official War Photographs of the Battle for Australia -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumBook - BOOK, 39TH BATTALION, Carl Johnson, "Mud Revisited Over Blood"
Stories from the 39th Battalion 1941-43, Kokoda to Gona. 70th Anniversary Edition of the Kokoda Track operations, WWII.Hard cover book with dust cover (dust cover same as book). Hard cover - cardboard with dark green glossy coloured background. White and gold print on front, spine and back. Front - illustrated black and green toned photograph of 2 soldiers in uniform in jungle. Back - black and white photograph of 7 soldiers. Brown over red oval colour patch front and back. Front and back flyleaf and end papers illustrated dark green and white maps. 320 pages, cut, plain, white. Illustrated black and white photographs, portraits, documents and maps.Opposite Title Page - printed donation label - "Donated by 39th Australian Infantry Battalion (1941 - 43) Association Inc. www.39battalion.com” books, military, history, wwii -
 Australian Army Museum of Western Australia
Australian Army Museum of Western AustraliaQueen's Colour - 16th Battalion (The Cameron Highlanders of Western Australia)
With the re-activation of the Citizen Military Forces (CMF) following the Second World War, the 16th/28th Infantry Battalion (The Cameron Highlanders of Western Australia) was raised in 1948 to carry on the identity and traditions of the pre-war 16th and 28th Battalions respectively. The King's and Regimental Colours formerly held by these two battalions were passed on to the new battalion who paraded them in rotation on ceremonial occasions It was decided in 1950 that a new set of Colours would be presented to 16th Battalion. For reasons that still remain unclear, these were manufactured under local arrangement by "cannibalising" the original 1933 set of colours and transferring the devices and battle honours (in the case of the Regimental Colour) to the new Colours. (Reported by Western Command to the Adjutant General -reference file A 107/1/11 dated 30 April 1952). These new colours were presented by Major-General JS Whitelaw, CB, CBE at a parade of the 16th/28th Infantry Battalion held on the Esplanade, Perth, 26 August 1951. (For details of Colours previously presented to 16th Battalion see separate section below). 16th/28th Infantry Battalion became unlinked in March 1952 with both 16th and 28th becoming independent battalions within their own right. With the accession of HM Queen Elizabeth II to the throne in 1953, all Colours that had originally been presented as King's Colours, and were still carried by units on the current Order of Battle, were automatically deemed to be Queen's Colours. Under major reorganisation of the CMF in 1960, all individual infantry battalions that existed at the time within each State were amalgamated to form State regiments, taking effect from 1 July 1960. Thus from that date the 11/44th, 16th and 28th Infantry Battalions were amalgamated to form The Royal Western Australia Regiment. In September 1960, at a ceremonial parade held at Northam Camp, the Colours carried by all former battalions were handed over for safe keeping by the new regiment. Battle Honours for the Second World War were promulgated under Australian Army Order 135/1961 and the 10 selected honours approved for emblazoning on the Queen's Colour were subsequently added in 1962 These former colours were subsequently laid up in the undercroft at the State War Memorial, King's Park on 29 November 1964. These were transferred to the Army Museum of WA in 1988 as part of the Bicentenary Colours Project Previous Colours presented to 16th Battalion The designation "16th" was allocated to several different infantry battalions that had been raised at different stages during changes to organisational structure of the Citizen Forces during the 1920's and 1930's. The original King's Colour awarded for service of 16th Battalion (AIF) and received in 1920 by the Citizen Force unit 2nd Battalion, 16th Infantry Regiment was later passed on to 16th Battalion (The Goldfields Regiment) which had been raised in the Kalgoorlie area in 1921. This unit became inactive and this Colour was later laid up in the Kalgoorlie Council Chambers. In order to maintain the identity of 16th Battalion as a Citizen Force unit, in 1930 11th Battalion (The Perth Regiment) was reformed as a linked battalion under the designation 11th/16th Battalion. As the 11th Battalion had already received its set of colours in the 1920's, it was decided that a set of King's and Regimental Colours be presented for 16th Battalion. These were presented by HE the Lieutenant-Governor Sir James Mitchell, KCMG at a parade of 11th/16th Battalion held at Perth Oval on 15 October 1933. The colours were consecrated by the Chaplain General, Archbishop COL Riley, OBE, VD, DD. In 1936 16th Battalion was re-established as a separate battalion within its own right, being formed as 16th Battalion (The Cameron Highlanders of Western Australia). The colours presented in 1933 were passed on to this new battalion and were also initially carried by the post-World War Two unit 16th/28th Infantry Battalion (The Cameron Highlanders of Western Australia) as already mentioned. Union flag with gold fringe. In the centre the Arabic numeral "16" on a red background within a circle inscribed "SIXTEENTH BATTALION", surmounted by the Crown. Emblazoned on the colour are the following Second World War Battle Honours:- NORTH AFICA 1941, SYRIAN FRONTIER, THE LITANI, SIDON, WADI ZEINI, DAMOUR, KOKODA TRAIL, BUNA-GONA, LIBERATION OF AUSTRALIAN NEW GUINEA, BORNEO -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - PHOTOGRAPHS WW2, 1) 1941; .2 - .39) 1940-45
.1) 19.1.41 To Gladys with best wishes from Viv. Later someone has written VX15538 VRG THOMAS D Coy 2/14 Battalion Vivian Raymond George Thomas enlisted in the 2nd AIF on 17.5.1940 age 28 years. He is listed as KIA at Gona New Guinea on 28.11.1942 while serving in the 2/14th Batt with the rank of Cpl and is buried in the Bomana War Cemetery Port Moresby..1) Post card in the form of a 'One Palestine Pound' with inset photo of an Australian Soldier VRG THOMAS. Colour in sepia tones. .2) Photograph copy enlarged from .3) showing German graves. Sepia colour. .3) - .39) Series of original photographs in black & white, sepia re war in North Africa, pyramids, towns, cities. Several are in the islands.photography-photographs, military history - army, documents - postcards -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncDocument (Item) - Article, The Eltham Roll of Honour: Second World War, 9 Aug 2020
Information regarding the circumstances of the eleven men of the Shire of Eltham who died serving their country in the Second World War and for whom the Eltham War Memorial was dedicated. Their names are listed on the Eltham Roll of Honour in order of rank. The image portrayed shows the eleven men (left to right, top to bottom) by date of fatality: CASTLEDINE, George Ernest, Spr., VX10044 (KIA 18 Apr 1941, Greece) GAHAN, Studley Manston, Capt., VX48379 (KIA 17 May 1941, Tobruk, Libya) RUTTER, David, Flying Off., 833 (400833) (KIA 9 Dec 1941, Bir El Gubbi, Libya) CLERKE, Alfred Charles, Cpl., VX23112 (KIA 2 Feb 1942, Laha, Ambon Island) DUNLOP, Cuthbert Douglas, Sgt., VX15252 (KIA 22 Nov 1942, Gona, New Guinea) INGRAM, Lester Neil, Flt. Sgt., 410236 (DOD 22 Apr 1943, Longworth, England) McLEAN, Stanley, Flt. Sgt., 419844 (KIA 7 Oct 1944, Emmerich, Germany) FELDBAUER, Theodore, Sgt., VX51733 (DOD 27 Mar 1945, Borneo) RUTTER, Donald Hemphill, Flt. Lt., 410262 (KIA 5 Apr 1945, Varrelbusch, Germany) FIELD, Kevin Francis, Pte., VX144763 (KIA 28 Jun 1945, Bougainville, PNG) BUTHERWAY, Jack Herbert, Pte, VX37645 (DOD 8 Jul 1945, Borneo)eltham war memorial, roll of honour, second world war, eltham, eltham roll of honour, shire of eltham, 2/4 field workshop, 22 independent brigade group ordnance workshop, a.i.f., australian army ordnance corps, australian corps of electrical and mechanical engineers, changi, falkiner street, florence mary butherway, jack herbert butherway, prisoner of war (pow), ranau number 1 jungle camp, sandakan death march, singapore, thomas james butherway, vx37645, 2/2 field company, 6th division, abington, annie castledine, arthur frederick castledine, george ernest castledine, greece, jean simonson, lower plenty, old eltham road, royal australian engineers, vx10044 sapper g. e. castledine, 2/23 bn, derril, gahan house, main road, rats of tobruk, studley manston gahan, tobruk, vx48379, 3 squadron r.a.a.f., aboukir, alamein memorial, beulah alice (simpson) rutter, bir el gubbi, broken hill aero club, david rutter, egypt, hubert rutter, libya, yarra braes, 2/21 bn, 23rd australian infrantry brigade, 8th division, alfred charles clerke, ambon island, battle of ambon, bidgeland park estate, inga caroline (nicholls) clerke, inga mary nicholls, laha airfield, nora ann clerke, rose matilda clerke, vx23112, william charles clerke, 2/14 bn, 2/16 bn, 21st brigade, 7th division, cuthbert douglas dunlop, gona, gona war cemetery, henry street, janet dunlop, kokoda track, new guinea, palestine, papua new guinea, port moresby (bomana) war cemetery, reuben cuthbert dunlop, syria, vx15252, 10 operational training unit, 410236, ada (key) ingram, berkshire, bomber command, england, group no. 91, john ingram, lester neil ingram, longworth, n.1374, r.a.a.f., r.a.f., r.a.f. abington, research (vic.), whitley v bomber, 419844, 514 bomber squadron, emmerich, germany, gordon stanley mclean, ji-g2, kleve, lancaster lm735, lucy mclean, mount pleasant road, r.a.f. waterbeach, reichswald forest war cemetery, stanley mclean, 2/10 ordnance workshops, albert feldbauer, eltham cricket association, eltham girls club, frank street, henry feldbauer, jessie margarette feldbauer, june feldbauer, ken ingram, margaret (feldbauer) ingram, montmorency imperials, research cricket club, research state school, sandakan number 1 camp, sandakan number 2 camp, theodore albert feldbauer, valerie (feldbauer) waller, violet amelda (teagle) feldbauer, vx51733, 247 ‘china-british’ squadron, caithness, cloppenburg, donlad hemphill rutter, essen, gloucester, hanover war cemetery, hanover-limmer british military cemetery, holten-lochem, oldenburg, r.a.f. castletown, r.a.f. station lealing, stoppenburg, typhoon ib jp443, typhoon ib sw526, 15th australian infantry brigade, 1940 cup, 3rd division, 57th/60th bn, best and fairest, bougainville island, buin road, mary field, mayona road, mivo river, mobiai river, montmorency, vx144763, william field -
 Lara RSL Sub Branch
Lara RSL Sub BranchBook, Australia in the War of 1939 - 1945 ARMY South-West Pacific Area First Year - Kokoda to Wau. Author Dudley McCarthy, First Published in 1959
WWII Kokoda to Way Australia at War 1939-1945 List of events ARMY Historical Record of Kokoda to Way.Australia in the War of 1939-1945 - South-West Pacific Area First Year - Kokoda to War Maps, Illustrations and PhotographsAustralian War Memorialkokoda, milne bay, kanga force, ioribaiwa, eora creek, buna, gona, sanananda track, wau, blamey, general mac arthur, minister forde, owen stanley's, ower's corner, native carriers fuzzy wuzzies -
 Waverley RSL Sub Branch
Waverley RSL Sub BranchMedal set Framed
During WWII the Batallion fought in Syria, New Guinea,Borneo and Darwin. Pte. Eric Wild D.O.B. 30/09/1909 enlisted in Windosr Vic. 27/05 1940. and served with the 16RWAR. until his discharge 27/10/1944, at which time he had been assigned to 2/2 Army Fld. Wshops. He saw service in Africa and the Pacific 16 RWAR Campaign WWII North Africa 1941, Syria, Syrian Frontier, The Litani, Sidon, Wadi Zeini, Damour, South West Pacific 1942 - 1945, Kokoda Trail, Isurava, Eora Creek, Templetons Crossing, Efogi-Menari, Ioribaiwa, Buna-Gona, Gona, Liberation of Australian New Guinea, Ramu Valley, Shaggy Ridge, Borneo, Balikpapan, WaitavoloMedal set 1939-45 star, Africa star,Pacific Star,Defence Medal,War Medal 1939-45 and Australian Service Medal 1939-45.Also patches for 16 RWAR Awarded to Wild, Eric Vincent VX 17865 2/2 Field Workshop16 rawr, wild eric vincent -
 Australian Commando Association - Victoria
Australian Commando Association - VictoriaBook, The Private War of the Spotters: A history of the New Guinea Air Warning Wireless Company, February 1942-April 1945
The history of the New Guinea Air Warning Wireless Company. This reprinted version contains a map of the dispositions of Spotting Stations August 1943, additional MID awards listed and some additions to the nominal roll. The New Guinea Air Warning Wireless Company was formed in Port Moresby in late January 1942 and was granted “Separate Independent Establishment” status in October 1943. The company’s “founding father” was Major Don Small, who had witnessed Japanese air raids on Rabaul and realised that having lacked an effective early-warning system around New Britain meant that the defenders were taken by surprise. At the time, gaps had also appeared in the coast-watching communications network because the territory administration ordered the withdrawal of civilian wireless operators when Japan entered the war. The first influx of men into the company consisted largely of volunteers from the 39th Infantry Battalion, which was stationed at Port Moresby. Initial training was rudimentary, hasty, and was sometimes even carried out on en route to a new station. The first party of company personnel, or “spotters”, left Port Moresby as early as 1 February 1942, bound for the strategically important Samarai area, at the tip of Papua. In the first month of the company’s existence 16 spotter stations were established on the coast of Papua and in the mountains around Port Moresby. At the end of 1942 there were 61 operational stations being run by 180 men. The company’s high-water mark was in late 1944, by which time over 150 stations had been set up in Papua and New Guinea behind enemy lines. On 3 February 1942 the company issued its first air warning in Papua, when spotters at Tufi saw Japanese aircraft about to attack Port Moresby for the first time. The following month the company was responsible for the first Japanese killed in action in Papua by Australian ground forces, when spotters from Gona engaged the crew of a downed Japanese bomber. And in July 1942 the station at Buna signalled Port Moresby with news of the Japanese landings in Papua, marking the beginning of the Kokoda campaign. The dangers involved in the company’s work had also been made clear by this time. In July 1942 a party of spotters attempting to set up a station at Misima Island, off Milne Bay, was intercepted by a Japanese destroyer, resulting in the company’s first operational losses. Anticipating the direction of the campaign as a whole, the company’s focus moved north and north-west over the three years of its existence. In May 1942 a network was set up in the Wau area in association with the activities of Kanga Force. As part of the Wau network, spotter Ross Kirkwood audaciously constructed an observation post overlooking the Japanese airstrip at Salamaua. Kirkwood’s position was photographed by Damian Parer on the understanding that the pictures would not be published. They nevertheless appeared in a Sydney newspaper. The day after the publication of the photographs the observation post was attacked by the Japanese and Kirkwood was lucky to escape. In June 1944 the company’s headquarters were moved to Nadzab. By that time, spotter stations existed behind Japanese lines, as far north as Hollandia, and the company began to train Americans to perform similar work in the Philippines. In early 1945 the company moved to Balcombe, Victoria, where its members were posted to other units of the Australian Corps of Signals.gray plasticnon-fictionThe history of the New Guinea Air Warning Wireless Company. This reprinted version contains a map of the dispositions of Spotting Stations August 1943, additional MID awards listed and some additions to the nominal roll. The New Guinea Air Warning Wireless Company was formed in Port Moresby in late January 1942 and was granted “Separate Independent Establishment” status in October 1943. The company’s “founding father” was Major Don Small, who had witnessed Japanese air raids on Rabaul and realised that having lacked an effective early-warning system around New Britain meant that the defenders were taken by surprise. At the time, gaps had also appeared in the coast-watching communications network because the territory administration ordered the withdrawal of civilian wireless operators when Japan entered the war. The first influx of men into the company consisted largely of volunteers from the 39th Infantry Battalion, which was stationed at Port Moresby. Initial training was rudimentary, hasty, and was sometimes even carried out on en route to a new station. The first party of company personnel, or “spotters”, left Port Moresby as early as 1 February 1942, bound for the strategically important Samarai area, at the tip of Papua. In the first month of the company’s existence 16 spotter stations were established on the coast of Papua and in the mountains around Port Moresby. At the end of 1942 there were 61 operational stations being run by 180 men. The company’s high-water mark was in late 1944, by which time over 150 stations had been set up in Papua and New Guinea behind enemy lines. On 3 February 1942 the company issued its first air warning in Papua, when spotters at Tufi saw Japanese aircraft about to attack Port Moresby for the first time. The following month the company was responsible for the first Japanese killed in action in Papua by Australian ground forces, when spotters from Gona engaged the crew of a downed Japanese bomber. And in July 1942 the station at Buna signalled Port Moresby with news of the Japanese landings in Papua, marking the beginning of the Kokoda campaign. The dangers involved in the company’s work had also been made clear by this time. In July 1942 a party of spotters attempting to set up a station at Misima Island, off Milne Bay, was intercepted by a Japanese destroyer, resulting in the company’s first operational losses. Anticipating the direction of the campaign as a whole, the company’s focus moved north and north-west over the three years of its existence. In May 1942 a network was set up in the Wau area in association with the activities of Kanga Force. As part of the Wau network, spotter Ross Kirkwood audaciously constructed an observation post overlooking the Japanese airstrip at Salamaua. Kirkwood’s position was photographed by Damian Parer on the understanding that the pictures would not be published. They nevertheless appeared in a Sydney newspaper. The day after the publication of the photographs the observation post was attacked by the Japanese and Kirkwood was lucky to escape. In June 1944 the company’s headquarters were moved to Nadzab. By that time, spotter stations existed behind Japanese lines, as far north as Hollandia, and the company began to train Americans to perform similar work in the Philippines. In early 1945 the company moved to Balcombe, Victoria, where its members were posted to other units of the Australian Corps of Signals.world war ii, special operations, new guinea, new guinea air warning wireless company
