Showing 60 items matching "gynaecology"
-
 Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing History Collection
Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing History CollectionDocument - Lecture Notes - Alfred Hospital, Gynaecology notes for nurses (Alfred Hospital gynaecology lectures)
Alfred Hospital Gynaecology Nursing lecture notes [ca. 1973-1976] - belonged to Susan Kim Hollands (2/73). Kim has been an AHNL member for many years, is now an archive volunteer. Her career was at the Alfred until 1980, during which time she completed nursing training, staffing and a renal-respiratory intensive care course.Buff coloured manilla folder containing typed notes, purple stamp on front cover with staple marks from removed staples, handwritten annotationsnon-fictionAlfred Hospital Gynaecology Nursing lecture notes [ca. 1973-1976] - belonged to Susan Kim Hollands (2/73). Kim has been an AHNL member for many years, is now an archive volunteer. Her career was at the Alfred until 1980, during which time she completed nursing training, staffing and a renal-respiratory intensive care course. gynaecology, nurse lecture notes from 1970s, alfred hospital, nursing training -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Myoma Screw, Late 19th century
A myoma is a benign (non-cancerous) tumour in the muscle of the uterus. This myoma screw is used in surgery to remove such fibroids. It can be done abdominally or via the vagina. The fibroid is ‘screwed’ and clamped before removal. The myoma screw is almost crude in its simplicity. It has a straight shaft with an oval handle and a corkscrew head. This myoma screwwas donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The Myoma Screw is still in use today for the removal of fibroids. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Myoma screw, from W.R. Angus Collection. Doyen's, abdominal and gynaecological use. Coiled end, loop handle. Inscribed "LONDON" Inscribed 'HAVRICK(?) LONDON'flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, myoma screw, tumor, surgery, gynaecology, myoma, fibroids -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Cannula, Spackman's, c1969
Part of the laparoscopy equipment donated by Dr Geoff Bishop. Dr Geoffrey Bishop, whilst at the Department of O and G, University of Liverpool, UK, began laparoscopy in 1969. On returning to Australia, Bishop and Grimwade together with Mr Peter Paterson introduced gynaecological laparoscopy to Melbourne, practising at the Queen Victoria Memorial Hospital (QVMH), Melbourne in 1969. The College, through the Victorian State Committee of the Australian Council, RCOG, ran training courses in laparoscopy for local and interstate gynaecologists. These were conducted by Bishop, Grimwade and Paterson. They established protocols, with particular reference to safety, for the conduct of laparoscopy. Laparoscopy was used initially for diagnosis and for limited treatment using diathermy for conditions such as endometriosis. The real impetus came with the great upsurge of tubal sterilization in the early 1970s. Early techniques included diathermy and division of the Fallopian tubes using the Palmer forceps. [Dr Peter Renou, former honoury curator.]This Spackman's cannula was used by Dr Geoff Bishop during gynaecological laparscopioc surgery.He used this decice as a uterine elevator. Also, for testing tubal patency by inserting dye through it. Manufacturers stamp: ANAX.laparoscopy, tubal ligation, infertility investigation -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Cannula, infertility, c1969
Part of the laparoscopy equipment donated by Dr Geoff Bishop. Dr Geoffrey Bishop, whilst at the Department of O and G, University of Liverpool, UK, began laparoscopy in 1969. On returning to Australia, Bishop and Grimwade together with Mr Peter Paterson introduced gynaecological laparoscopy to Melbourne, practising at the Queen Victoria Memorial Hospital (QVMH), Melbourne in 1969. The College, through the Victorian State Committee of the Australian Council, RCOG, ran training courses in laparoscopy for local and interstate gynaecologists. These were conducted by Bishop, Grimwade and Paterson. They established protocols, with particular reference to safety, for the conduct of laparoscopy. Laparoscopy was used initially for diagnosis and for limited treatment using diathermy for conditions such as endometriosis. The real impetus came with the great upsurge of tubal sterilization in the early 1970s. Early techniques included diathermy and division of the Fallopian tubes using the Palmer forceps. [Dr Peter Renou, former honoury curator.]This cannula has two points for tubal attachments at one end. At yhe other end, a bell cap with a nossel.This was used by Dr Geoff Bishop during gynaecological laparscopioc surgery. This instrument is commonly used for suction. Also, for testing tubal patency by inserting dye through it. Manufacturers stamp: PRECIOUS.laparoscopy, tubal ligation, infertility investigation -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Medal - AOFOG Fellowship medal presented to Dame Ella Macknight, 1993
Ella Macknight was an Australian obstetrician and gynaecologist, who worked at the Queen Victoria Hospital, Melbourne. She was appointed as a Dame Commander of the Order of the British Empire on 1 January 1969 for services to medicine. (Wikipedia) Her name has been misspelled on the engraving on this medal.Silver coloured medal with gold coloured decoration on a blue ribbon. The medal is a physical representation of the AOFOG (Asia and Oceania Federation of Obstetrics and Gynaecology) logo, consisting of a translucent central blue circle (possibly made of glass) surrounded by eight abstract torso figures in alternating gold and silver colours. The base of the torso sits adjacent to the central blue circle, and depicts a figure with its arms raised straight up. The torso neighbour each other around the circumference of the central blue circle to form a circular pattern. The figure at the top of the medal has a silver torso and gold head, and these colours interchange from figure to figure (eg. the figure on either side has a gold torso and silver head). The medal is engraved with the text 'Dame Ella McKnight/FELLOW/OF/AOFOG/1993'. The ribbon has two velcro fastenings. The medal is in a protective case, the outside of which is lined with red velvet. Included in the case is a runsheet printed on paper for the ceremony in which Ella MacKnight was presented with this medal. The ceremony was held at PICC Plenary Hall on 14 November, 1993. The velvet case in stored inside a while, rectangular cardboard box, consisting of two parts - lid and base. Sticker attached to top of the cardboard box reads ' DAME ELLA MCKNIGHT/FELLOW/1993'.Dame Ella McKnight/FELLOW/OF/AOFOG/1993'obstetrics, gynaecology, awards -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Medal - British Medical Association President of Gynaecology and Obstetrics medal associated with Professor F.J. Browne, 1938
Francis James Browne died in Sydney 1963. He had a long career in obstetrics and gynaecology. Summary of appointments include: General Practice in Wales, Maternity Department of the Edinburgh Royal Infirmary, 1st director of obstetric unit, University College Hospital London. Retired and continued postgraduate teaching in London and NSW. Married to Grace Cuthbert, who was director of Maternal and Baby Welfare in NSW. A collection of objects found amongst Professor FJ Browne's papers were transferred from the Archives to the Museum collections in January 1994.A round metal badge with a green enamelled rim. There is a shield in the centre which is divided into three. In the left hand comer there is a flag, in the right hand comer the medical insignia, and at the bottom of the shield there is a sailing ship. The year 1938 is either side of a central white enamelled plug with the number "106" on it. Attached to the badge is a green grosgrain ribbon, to which is attached an oblong bar with a pin at the back. Inscriptions Around the edge of the badge: "THE BRITISH MEDICAL ASSOCIATION PLYMOUTH"; inscribed on the back of the badge: "BRUFORD, EASTBOURNE AND EXETER"; front lower right hand side ofbadge:"M & W"; front of bar: "PRESIDENT/ GYNAECOLOGY and OBSTETRICS"numismatics, browne fj, rcog -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Equipment - Sponge forceps used by Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson
This is one of a collection of items received from the practice of Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, FRCOG, Launceston, Tasmania.Stainless steel sponge forceps. Design of instrument resembles a pair of scissors. There are circular finger grips at one end, with a metal ratchet between them for locking the forceps in place. Each arm of the forceps ends in a serrated, round point. Text engraved near pin of forceps reads 'L.R.I./STAINLESS'.'L.R.I./STAINLESS'.gynaecology -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Instrument - Dührssen-style 8 bladed dilator, Unknown
Alfred Dührssen (23 March 1862 – 11 October 1933) was a German gynecologist and obstetrician born in Heide, Schleswig-Holstein, at the time part of Denmark. He studied medicine at the University of Marburg, as well as the Kaiser-Wilhelm-Akademie für das militärärztliche Bildungswesen (Kaiser-Wilhelm-Academy for Military Physicians). In 1886, he became an obstetrical assistant to Adolf Gusserow (1836-1906) in Berlin, and in 1888 he began work as a lecturer at the University of Berlin. In 1892 he opened a private clinic for obstetrics and gynecological diseases. Dührssen was a prominent figure in modern German gynecology, being remembered for his pioneer work in surgical practices such as vaginal Caesarean section (vaginalen Kaiserschnitt). He was an advocate of institutional births for all pregnancies, and proposed that pregnant women undergo screening processes to uncover possible difficulties prior to giving birth. (Wikipedia) Metal uterine dilator consisting of a handle, a short shaft, and eight prongs. The prongs each have a bump/curve in the prong towards the top, to allow them to bend around the shaft of the instrument and meet at their tips. There is a second 'bump' in the prongs just before the tips. The tip of each prong has five ridges to assist with grip. The handle of the device is a flat, rounded handle, which is turned to open the prongs and set them at various degrees of diameter. There is a gauge on the shaft of the instrument which ranges from 0-12, showing the current setting of the instrument. There is also a pin and T-shaped slot arrangement located just above the start of the prongs, which has been engraved '8' on the left hand side, and '1' on the right hand side. Each prong is also engraved with a number at the base of the prong, reading '1' to '8'. gynaecology -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Equipment - Kevorkian curette used by Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson
Used for endometrial biopsy. This is one of a collection of items received from the practice of Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, FRCOG, Launceston, Tasmania.Stainless steel curette. Thin metal instrument, consisting of a thicker handle section with a groove for finger grip attached to a slender metal shaft. The shaft ends in a hollowed, squared point. Writing engraved on handle of device reads 'martin GERMANY STAINLESS'. In white paper sterilisation bag bearing the handwritten text 'DR H/W' and KEVURKIAN (sic)/CURETTE''martin GERMANY STAINLESS'gynaecology -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Equipment - Punch forceps used by Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson
This is one of a collection of items received from the practice of Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, FRCOG, Launceston, Tasmania.Stainless steel punch forceps. There are two circular finger grips at one end, resembling a pair of scissors, attached to short arms that meet at a point. A long narrow shaft extends perpendicularly from this point, ending in a small, hinged, toothed grip. Writing engraved on one arm of forceps reads 'Stainless Germany'. Writing engraved on opposite side of forceps reads 'malyoung'.'Stainless Germany'; 'malyoung'gynaecology -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Equipment - Uterine sound used by Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson
This uterine sound is possibly made of aluminium, but this has not been confirmed.This is one of a collection of items received from the practice of Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, FRCOG, Launceston, Tasmania.Metal uterine sound. Instrument is a thin, tube-like piece of metal, which tapers and curves up into a blunt point at either end. The ends curve in opposite directions, forming a shape that resembles a tilde( ~).gynaecology -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Instrument - Unused Rocket vacuum aspiration catheters, Karman type, Rocket & Co, London
Two unused catheters in original packaging. One is 6mm width, the other is 8mm. Each catheter is a plastic tube, resembling a straw, open at one end and narrowing to a rounded point at the other. There are two openings in the tube just prior to the rounded point, staggered adjacently on either side of the tube, with a small overhanging notch at the top of each opening. Each catheter is sealed in sterile packaging, along with a note printed on yellow paper explaining their use. gynaecology -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Instrument - Set of ovum forceps
Set of metal ovum forceps. The instrument loosely resembles a pair of scissors, with two arms joined by a pin at the middle. Each arm is topped by a circular finger grip handle, and the top section of the arms, just below the handles, are bowed. The arms cross over each other both before and after the pin at centre. The end of each arm curves upwards and broadens into a hollow elongated teardrop shape, with the centre of each end cut out to form a teardrop shaped loop at the end of both arms.gynaecology -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Instrument - Set of Heywood-Smith ovum forceps
Metal surgical instrument resembling an elongated pair of scissors. Consists of two arms joined together with a pin at centre, each arm topped by a circular finger grip. Each arm ends in a shallow scoop with three rectangular slots running the majority of the length of a scoop. gynaecology -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Instrument - Ellinger-type uterine dilator, Medical Supply Depot
Metal surgical instrument. Consists of scissor like handles with circular finger grips atop two metal arms. There is a metal gauge extending between the handles approximately an inch below the finger grips which provides a measurement as to how far apart the tips of the instrument are at any given time. A curved metal plate is attached between the handles below the gauge which functions as a spring to give some resistance to the instrument. The arms are joined together by a pin at the centre. Metal plates attached to the underside of the lower part of the arms lock into place as the instrument is opened. Each arm narrows in the last two inches and ends in a round point, with the end points resembling the nose of a pair of pliers. The words 'MEDICAL SUPPLY DEPOT' are engraved on one arm of the instrument. The number '18' is engraved on the inside of both arms towards the tip.'MEDICAL SUPPLY DEPOT', '18'gynaecology -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Instrument - Set of curved uterine forceps
Surgical instrument. Resembles an elongated set of scissors. Consists of two arms, each topped by a circular finger grip. The arms are joined by a pin at centre. Each arm has an oval shaped hole through the arm just before it ends in a narrow, rounded point. The final section of each arm, from approximately 2cm before the tip, is hollowed out and concave. The edges of each arm around this concave section are corrugated for grip.gynaecology -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Instrument case with unidentified instruments
Donated by Miss Beatrice May Devlin, items that belonged to her paternal grandfather, Dr Henry William Devlin who graduated in Medicine from Dublin and worked at the Rotunda hospital, Dublin. He immigrated to Australia and was the first doctor to practise in Parkes NSW.Please refer to supplementary file filed under Accession number 1995001Instrument case, small, containing small silver knife, a small silver ladel with a sharp probe at one end, a tweezeer like instument and string with three hook attachments. Looks unused, not gynaecological, nasal?dr henry william devlin -
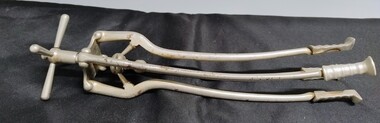
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Set of Braun's craniotomy forceps used by Box Hill Hospital labour ward, Allen & Hanburys, England
Carl Rudolph Braun (1823-1891) was the inventor of this instrument, as well as a type of decapitation hook. Braun was born and practiced in Austria, and followed Semmelweis as assistant to Klein at the Vienna Maternity Clinic in 1847, before becoming its head in 1856. Braud added a gynaecology section to the clinic in 1858, being convinced that obstetrics and gynaecology should be together. (Source: Baskett, Thomas. 'On the Shoulders of Giants: Eponyms and Names in Obstetrics and Gynaecology'). This device was included with a range of other obstetric instruments, mostly destructive instruments, given to RANZCOG from Box Hill Hospital labour ward in February- March 1998. The maternity service at Box Hill Hospital combined with St George's hospital in Kew to be known as Birralee Maternity Service. These instruments were collected by Julie Collette, Unit Manager, St George's Kew and given to RANZCOG Museum Curator, Susan Barnett.Craniotomy forceps, Braun's. Stainless steel forceps, with wingnut. Upper blade has open oval section and ridged grip section on the handle. Lower blade has serrated inner edge and ridged grip section on the handle. Wingnut is used for attaching the upper and lower blades of the forceps. Inscribed "B.H.H.L Ward" on forceps."B.H.H.L Ward"destructive instruments -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Equipment - Tenaculum forceps associated with Dr Felix Meyer
These forceps are a type of uterine forceps used for gynaecological procedures. This is one of a collection of items associated with Dr Felix Henry Meyer (1858-1937). Meyer was a very prominent early obstetrician and doctor, playing a part in the establishment of the role of the chair of obstetrics at the University of Melbourne in 1929. He was also a foundation member of the Royal Australian College of Surgeons.Set of metal scissor style forceps. Consists of two blades, joined with a pin, with a small ratchet for clamping below the finger grips/handles. The end of the forceps curves to one side, and each blade of the forceps ends with a hook. When the forceps are closed, the hooks on either blade join together to make a loop.surgery -
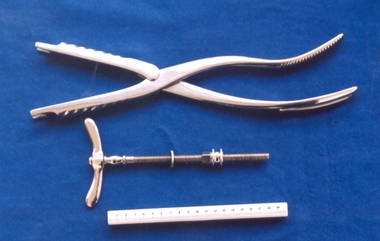
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Instrument - Preiss-style cervical dilator
Metal surgical instrument. Consists of four slightly curved arms approximately 25cm long, attached by pins to a central metal plate. A four pronged handle sits atop the metal plate, which operates a small jack that sits below the metal plate. The jack is attached to all four arms, and opens and closes the arms as the handle is turned. There is a gauge beneath the handle to provide a reading as to how open the arms are at any given time. A foot with a flat base in a quarter circle shape is attached to the bottom of each arm. When the arms are fully closed, the bases of the feet meet up to form a complete circle. The numbers, '1', '2', '3' and '4' are each engraved on one of the feet.gynaecology, obstetrics -
 Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing History Collection
Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing History CollectionBook - Illustrated textbook, Hilda M Gratton, Aids to gynaecological nursing, 1949
An historic textbook on gynaecological nursing for student nursesIllustrated textbook with red binding and black printnon-fictionAn historic textbook on gynaecological nursing for student nursesgynaecology, gynaecological nursing, nursing -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Vaginal irrigator associated with midwife Mary Howlett, c. 1866 - 1920
The vaginal syringe, also known as a female syringe, was introduced in the early 1900s and was in use until the late 1940s when it was replaced by the glass douche nozzle. (Thackray, 'Midwifery & Gynaecological Instruments, (M)463, p. 264.)Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920. She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them to the museum collection in 1993. Vaginal syringe with glass barrel and plunger and a cork bung. Fluid capacity of syringe 60-90 mls. Cotton thread is woven tightly around the end of the plunger. There are five holes in the end of the glass barrel.midwifery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Gynaecological examination chair associated with Dr Robert Zacharin, 1920
This chair belonged to Dr Zacharin from 1970 until he donated it to the College in 2009. Its origins prior to this time are uncertain.Gynaecological examination chair, metal painted white, with two detachable metal stirrups with a back panel, seat panel and leg panel. The leg panel can be adjusted upwards to make a table. The back panel has an upright and two reclining positions. The seat panel has a side mechanism that makes the panel tilt backwards, so that a patient can be positioned head downwards with legs upwardsobstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Framed photograph of Sir William Gilliatt, 1951
Sir William Gilliatt was born in 1884 in Lincolnshire. He was educated at Boston Grammar School and Wellingborough College, and began his medical career at the Middlesex Hospital in 1925. He became obstetric and gynaecological surgeon at King's College Hospital, a position he held until his retirement in 1946. Gilliatt was a foundation fellow of RCOG, U.K. and served on the Council from 1932 until his death in 1956. He was also the President of the RCOG from 1946 until 1949. Gilliatt was known to be an excellent clinical teacher and was gynaecologist to the Royal family for two decades. He wrote very little for the medical journals, but his influence on obstetric and gynaecological practice was considerable and his attention to detail was painstaking. He was killed in a motor accident on 27 November 1956.Framed black and white photograph. Photograph is a side-on portrait image of Sir WIlliam Gilliat, who is turning his head to face the camera slightly and is smiling. Photograph is signed 'William Gilliat/April 1951'. An inscription, likely to be the name of the photographer, appears in the bottom right-hand corner of the photograph. The frame is a simple gold coloured metal frame, with a rose decoration in each corner.William Gilliat/April 1951rcog -
 St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne Archives
St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne ArchivesCertificate - Nurse's Certificate, St Vincent's Hospital Training School Melbourne, awarded to May Mulcare in 1915
The first page of the folder contains the elaborate St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne Training School for Melbourne emblem. The second page certifies that May Mulcare has passed and is fully registered as a Trained Nurse following a three-year course in Medical, Surgical, Opthalmic and Gynaecological Nursing. It is signed by Andrew Brenan, MD. M.S and Mother Mary Berchmans Daly, Rectress.may mulcare, st vincent's hospital melbourne, mother mary berchmans daly, andrew brenan md, nurse training -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Printing block featuring image of the front of the Blair-Bell Medal, c. 1961, 1961
The Blair-Bell medal was awarded quinquennially for the advancement of science in gynaecology or obstetrics or both in the preceding five years. The image on this block was used in an article, "The Blair-Bell Award" in the Australian & New Zealand Journal O + G [1961]1:77 featuring Prof. F.J. Browne, winner of the Blair-Bell Medal, 28/10/60. Also used in obituary of Professor Browne.Metal printer's plate attached to a wooden block. Depicts the official recto medal image of the Blair-Bell medal, featuring a portrait of William Blair-Bell. blair-bell award, browne fj, printing -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Printers block featuring image of the back of the Blair-Bell Medal, c. 1961, 1961
The Blair-Bell medal was awarded quinquennially for the advancement of science in gynaecology or obstetrics or both in the preceding five years. The image on this block was used in an article, "The Blair-Bell Award" in the Australian & New Zealand Journal O + G [1961]1:77 featuring Prof. F.J. Browne, winner of the Blair-Bell Medal, 28/10/60. Also used in obituary of Professor Browne.Metal printer's plate attached to a wooden block. The image is the official verso medal image of the Blair-Bell medal, depicting a mother and child in Greco-Roman dress. The black of the block is covered in cream paper.blair-bell award, browne fj, printing -
 St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne Archives
St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne ArchivesCertificate - St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne Training School for Nurses' Certificate awarded to Marguerite Ousley, 1912
The first page of the folder contains the elaborate St Vincents Hospital Melbourne Training School for Nurse's emblem. The second page certifies that Marguerite Ousley has passed and is fully registered as a Trained Nurse following a three-year course of training in Medical, Surgical, Ophthalmic, Gynaecological Nursing. The Certificate is signed by AE Rowden White MD and M.Mary Berchmans Daly Mother Rectressmarguerite ousley, st vincents hospital melbourne, mother mary berchmans daly, nurse training, dr a e rowden white -
 St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne Archives
St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne ArchivesCertificate - St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne Training School for Nurses Certificate, awarded to Mary Freitag in 1910
The first page of the folder contains the elaborate St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne Training School emblem. The second page certifies that Mary Freitag has passed and is fully registered as a Trained Nurse following a three-year course in Medical, Surgical, Opthalmic and Gynaecological Nursing. It is signed by A E Rowden White MD Honorary Lecturer and Mother Mary Berchmans Daly, Rectress.St Vincents Hospital Melbourne Training School for Nurses.st. vincents hospital melbourne, mary freitag, nurse training -
 St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne Archives
St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne ArchivesCertificate, Nurses Certificate St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne awarded to Ethel Charles 1910
The first page of the folder contains the elaborate St Vincent's Hospital Melbourne Training School emblem. The second page certifies that Ethel Charles has passed and is fully registered as a Trained Nurse following a three-year course in Medical, Surgical, Opthalmic and Gynaecological Nursing. It is dated June 1910 and is signed John Murphy FRCS, Honorary Lecturer and Mary Berchmans Daly, Mother Rectress. st. vincents hospital melbourne, nurse training, ethel charles, john murphy frcs, mother mary berchmans daly
