Showing 167 items matching "high cliffs"
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument, Ken Clements, Peterborough Puzzles, 2009, 2009
... high cliffs... the grotto london bridge point hesse high cliffs the arch Cape Martyr ...Massacre Bay is located on Victoria's Great Ocean Road, and is in the centre of the Bay of Martyrs. The bay consists of 20 m high, red limestone bluffs. This paper by Ken Clements considers the origin of the term martyr in connection to this location, and where the Aboriginal massacre may have taken place. Thirteen page document by Ken Clements relating to Peterborough, Victoria. Contents include coastal features, local Aborigines, Bay of Martyrs, Massacre Bay, Massacre Hill, Buckley Creek Run, Pioneer Pastoralists, British Traversers, settlers, Peterborough, Maps, tourism, history method. Photographs by Laurie Moore.aborigines, bay of martyrs, massacre bay, massacre hill, buckley creek run, pioneer pastoralists, british traversers, settlers, peterborough, maps, tourism, history method, childers cove, barque children, murnane bay, sandy bay, dog trap bay, buckley creek, viviennes lookeout, stanhope bay, buttres bay, burnies beach, armstrong creek, flaxman hill, antares rock, lovers nook, crofts bay, clements, worm bay, halladale point, the well, wold dog cove, james irvine monument, curdies inlet, squirrel creek, wallaby creek, boggy creek, whiskey creek, pioneer beach, schomberg rock, young australia, spit, crown of thorns, newfield bay, the grotto, london bridge, point hesse, high cliffs, the arch, cape martyr, little massacre bay, aboriginal massacre, ken clements -
 Sunbury Family History and Heritage Society Inc.
Sunbury Family History and Heritage Society Inc.Photograph, 27 June 1934
... bridge spanning a river. There are high cliffs in the background.... a river. There are high cliffs in the background. Photograph ...This is a photograph of the bridge in the Bulla township which spans the Deep Creek, a tributary of the Maribyrnong River. It has been constructed from bluestone which is found across the volcanic western plains in Victoria. Kaolin was quarried from the cliff face in the background and was used in the making of bricks and pottery products manufactured at Northcote and Brunswick potteries.This is one of the many notable bluestone bridges which were built in the district in the nineteenth century.A black and white photograph of a valley with a five arched bridge spanning a river. There are high cliffs in the background.bulla township, deep creek, bridges -
 Sunbury Family History and Heritage Society Inc.
Sunbury Family History and Heritage Society Inc.Photograph, Johnson Cliff, C1937
... of a waterfall with water tumbling down the high cliff.... of a waterfall with water tumbling down the high cliff. Johnson Cliff ...The waterfall along the Jacksons Creek is sited at Johnsons Cliff which is near Craiglie and downstream from the town of Sunbury. A non- digital sepia photograph in post card format of a waterfall with water tumbling down the high cliff.JOHNSONS CLIFF SUNBURYwaterfalls, jacksons creek, johnsons cliff -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPostcard - Snowy River at Basin Ranch, Bulmer, 1930 c
... with two men in foreground pointing to high cliff across the river... with two men in foreground pointing to high cliff across the river ...Black and white postcard of Snowy River at Basin Ranch with two men in foreground pointing to high cliff across the river Gippsland VictoriaSnowy River at Basin Ranch H D Bulmer photowaterways, topography -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Souvenir - Heart shaped souvenir, 1870 - 1890
... from a ribbon. Printed with a scenic view of river and high... and high cliffs either side and a suspension bridge with figures ...Heart shaped wood and velveteen souvenir. May have hung from a ribbon. Printed with a scenic view of river and high cliffs either side and a suspension bridge with figures in foreground.View from suspension bridgedomestic items, ornaments / decorative -
 City of Kingston
City of KingstonPhotograph - Black and white, Percy Fairlam, c. 1910
... High cliffs required access to the beachfront to be made... Parkdale High cliffs required access to the beachfront to be made ...High cliffs required access to the beachfront to be made via a steep wooden staircase.Black and white image of the steep wooden staircase at Mentone Beach, leading down to the foreshore from the clifftops above. At the base of the staircase is a bicycle leaning against a foundation post.mentone, beach, staircase, access -
 Red Cliffs Military Museum
Red Cliffs Military MuseumFramed Photo, Barclay Memorial Sculpture, 1965 (exact)
... Barclay, which is located in Barclay Square, Red Cliffs... by Heather McClumpha,/ a student of Red Cliffs High School, 1965...., a student of Red Cliffs High School 1965. The phot is in an ornate ...Heather McClumpha is now Mrs. Newton HuntA framed photo of a Memorial Sculpture to honour Nathaniel Barclay, which is located in Barclay Square, Red Cliffs. The sculpture was designed by Heather McClumpha, a student of Red Cliffs High School 1965. The phot is in an ornate scrolled (scrolling made from plaster of paris) frame which is slightly damaged.Top: The Barclay Memorial/ Barclay Square. Under photo: To honour Cr. Nathaniel Barclay, DCM, MLA, J.P.,/ Designed by Heather McClumpha,/ a student of Red Cliffs High School, 1965.ww1, ww11, nathaniel, barclay, dcm, j p, mla -
 Halls Gap & Grampians Historical Society
Halls Gap & Grampians Historical SocietyPhotograph - Coloured
... have high, rock cliffs. In the foreground... with a further peak behind it. The front of the peaks have high, rock ...This is a photo of a painting by Nicholas Chevalier (1828-1902). The painting is "Mt Abrupt, Grampians", circa 1864, oil on canvas, 46.0 x 61.0 cm (held in a private collection, London).This is a photo of a painting. It shows a stylised view of a mountain with a further peak behind it. The front of the peaks have high, rock cliffs. In the foreground there is an aboriginal camp, including a shelter with two people sitting in it, two people and two dogs sitting outside on the grass and a camp fire between them and the hut.painting, landscape -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePostcard - Scenic, Warrnambool, Pillar Caves, near Warrnambool, 1902-1929
... image shows figures on the high, grass-topped cliff, one between... figures on the high, grass-topped cliff, one between the likeness ...The nine postcards in this set were donated together and date to the early 1900s. All but one postcard in this set shows images of Warrnambool, in the Western District of Victoria; the other has a London image. The postcards were all printed in Great Britain according to that country’s postal regulations. The fronts of all cards have titles printed in red. Most of the images on the cards are attributed to photographer Joseph Jordan and belong to the Jordan Series. The back of these cards has an outline for a postage stamp, a vertical dividing line and a heading on each side of the line to separate the Correspondence from the Address. Postcards or ‘correspondence cards’ appeared in Britain in 1894. They were plain cards with a space for the message on one side and an address on the other; regulations didn’t allow anything but the address to be written on the ‘address’ side. In 1902 the British regulations then allowed a picture to be printed on the front and the address on the back, so messages had to be written on the picture side. Soon, the regulations changed and the back was divided for a message and the address. Pliiar Caves, near Warrnambool – The formation at the front of the cave resembles the pillars of a porch, giving the cave its name. Local social media discussion locates the caves near Lake Gillear, east of Warrnambool. The area was popular with young lads as a place to explore and to go rabbiting. The caves in this area are home to colonies of bats and have been a source of bat feces or bat guano, which is an enriching additive to soil. The 19th century sailing ships in the Nitrogen or Guano trade collected large quantities of guano from caves and popular bird nesting locations to sell as a rich fertiliser, due to its high nitrogen and phosphorus properties. Joseph Jordan - Joseph Jordan was born in 1841 in Leicester England. When he was 16 he joined the 7th Queen's Own Hussars and was sent to India at the outbreak of the mutiny. He took part in the relief of Lucknow and remained in India for eleven years. It was during this time that he became interested in photography. He was posted to New Zealand and later came to Victoria, becoming a sergeant major of the Mounted Rifles. In the mid-1880s he came to the Western district where he was responsible for establishing units of the Mounted Rifles in various country towns such as Dunkeld, Mortlake, Panmure, Bushfield, Koroit etc. He resigned from the army in 1889 and set up a professional photography studio in Liebig Street, Warrnambool. He became very well known in the Western District for family photographs, official photographs of local councillors and groups as well as views of local scenery. In 1891 he photographed the wrecked barque ‘Fiji’ at ‘Wrecks Beach’ near Princetown. His business was taken over by his son Arthur around 1917. Joseph was a keen rifle shot and in 1924 he donated the "Jordan Shield" as a prize to the Victorian Rifle Association. He was made a "Life Honorary Member" of the Warrnambool Returned Soldiers League and in 1933 he was recognised as being the oldest living soldier in Victoria. Joseph died in 1935 aged 95.The image of the Pillar Caves rock formation with figures on it suggests that the location was a popular place to visit. The choice of subject for this postcard indicates the popularity of Warrnambool's natural environment as a tourist attraction at a time when ships called coastal traders brought passengers and cargo to the Port of Warrnambool from ports along Victoria's southwest coast. The presence of bats in local caves also connects the postcard to the 19th century Nitro Trade and Guano Trade, when bat guano was collected and sold for plant fertiliser around the world. Joseph Jordan is a significant figure in Warrnambool history as he helped to establish early units of the Mounted Rifles (G Company) in local towns during the late 1880's and later, photographed local scenes, groups and citizens of early Warrnambool.Postcard, one of nine, landscape orientation, coloured print within an oval border and mauve-toned shading. The cameo image shows figures on the high, grass-topped cliff, one between the likeness of pillars in the cave entry, and others walking on the rocks nearby. The background below is rough ground. There is no correspondence written on the card. The back has inscriptions and outlines for a postage stamp. Jordan Series, printed in Great Britain.Front, in red: “PILLAR CAVES, NEAR WARRNAMBOOL” Back in black: “Jordan Series” “POST CARD” “PRINTED IN GREAT BRITAIN” “For correspondence” “The Address only to be written here”flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, maritime museum, warrnambool, great ocean road, warrnambool and district, warrnambool scenes, local scenes, views of warrnambool, joseph jordan, jordan series, jordan photography, postcard, souvenir, correspondence, cameo postcard, landscape, rock formation, pillar caves, pillars cave, lake gillear, rebbiting, bats, guano, nitro trade, fertilizers -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photograph, late 19th century / early 20th century
... itself as " Under Vice-Regal Patronage. Situated on High Cliff... itself as " Under Vice-Regal Patronage. Situated on High Cliff ...The first settler to occupy the Marlo township area was James Stirling around the year 1875. He built a bark hut on the bluff that had two rooms, bark walls, earthen floors and a shingle roof. By 1884, this structure had expanded to a 9 roomed accommodation house and in 1886 became the Marlo Hotel when a liquor license was granted. The Governor-in-Council declared Marlo to be a township on 18 February 1889. During May 1889, the government surveyor, E.L. Bruce set out 19 sections of the new township, with the first sales of subdivided land occurring the following May. At this time, Stirling's Marlo Hotel was the unofficial hub for the community. It was a general store, accommodation house and the unofficial post office, with settlers taking turns in bringing the mail from Orbost or Cunningham. This continued until Aug 1942, and in 1969 was located in a house adjacent to the Marlo Hotel, before being transferred to the Marlo General Store in this year. The official Post Office List states the Marlo Post Office opened around 1902. in 1925, the "Marlo House" (a nine room accommodation guest house) was granted a liquor licence. The "Marlo House" became "The Marlo Hotel". The Marlo Hotel was popular with many Orbost and district settlers, who travelled to Marlo by horseback or buggy. In the early 20th century the hotel advertised itself as " Under Vice-Regal Patronage. Situated on High Cliff, fronting Ocean, Lakes and Snowy River. Those in search of Health, Rest and Sport should visit Marlo. Boating, Fishing, Shooting, Bathing, Golf. Comfort and Convenience at Marlo Hotel, near Orbost, East Gippsland. Nixon's Cars would meet the train at at Orbost. Fare---6s single, 12s return. Telephone No. 1, Marlo. S, P, STEWART, Proprietor." The Marlo Hotel, perched on the hill overlooking the estuaries and the entrance is a significant building in Marlo. Established in 1886, it has been operating for over 120 yearsAn original black / white photograph and a black / white copy of a party being held under trees on the lawn of the Marlo Hotel. It is a postcard with advertising of Marlo on the back.on back - "Where to spend your holiday - Marlo" on front - "Vice Regal Party at Hotel, Marlo"marlo-hotel -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Vessel, Sailing Ship, Original image recorded between 14 Nov 1908 and early Jan 1909
... off the coast. When high cliffs loomed up out of the darkness... off the coast. When high cliffs loomed up out of the darkness ...The photograph represents the original complete landscape (southerly) view of the FALLS OF HALLADALE shipwreck which occurred at 3 am on the 14th of November 1908. This image includes three groups of well-dressed Edwardian sightseers on the clifftop and a rocky headland. Subsequent reproductions of this well-known image have been cropped to a striking portrait view, emphasising the vertical line of the masts and sails of the sailing ship, and excluding the groups of sightseers on the adjoining headland. The small girl in the foreground and the loose topsail on the foremast are common to both the landscape and the cropped portrait images of this memorable scene. The photograph was taken at an early stage of the ship’s final days, somewhere between the date of her grounding in mid-November 1908 and early January 1909, when salvagers began dynamiting her masts to get to the cargo in her holds. The heavily laden FALLS OF HALLADALE was 102 days out of New York when the swell of the Southern Ocean lifted her onto the rocks near Peterborough. At the time she was sailing at six knots in a light breeze, her sails fully set and on an ENE tack. Mist over the land created an optical illusion of a distant horizon and the crew believed they were at least ten miles off the coast. When high cliffs loomed up out of the darkness it was too late in the light conditions to change tack or let go the anchors. Within minutes of running aground, her decks were awash and the holds filling with water. Captain Thomson and his 29 crew took to the boats, leaving the vessel stranded on the reef, looking awkwardly graceful in her predicament, firmly wedged between two parts of the reef and with all her square-rigged sails still set, FALLS OF HALLADALE provided a landmark visible for miles. Over the following two months, she attracted hundreds of sightseers, including contemporary photographers. A Court of Marine Inquiry at Melbourne on 30 November 1908 found Captain Thomson guilty of a gross act of misconduct ― in that he carelessly navigated the ship, neglecting to take proper soundings and failing to place the ship on the port tack before it was too late to do so. His Master’s Certificate of Competency was suspended for six months and he was ordered to pay £15/15/- toward the costs of the inquiry. It was an expensive outcome for the captain but his error provided many weeks of inexpensive entertainment for coastal residents and visitors to Peterborough. To judge from the standard of formal dress in this photograph, visiting the wreck was considered a special occasion as well as a popular one. Falls of Halladale: - The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co. they standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29The shipwreck of the FALLS OF HALLADALE is of state significance: Victorian Heritage Register No. S255. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Black and white photograph on cream-coloured backing card and in good condition. Description of Image: Quadrant 01, vessel with full set of sails perched on reef with stern submerged; Quadrant 02, predominantly clear sky over flat calm sea; Quadrant 03, two groups of standing sightseers on rocky promontory with three individuals approaching from far left foreground; Quadrant 04, fifteen well dressed sightseers seated on grassed cliff top including one child and six women. There is a deliberately obscured inscription in white ink along lower border or foreground of photograph.Letters in upper case and white contrast stretching across the grassed foreground of photograph have been smudged over by development process and are largely indecipherable. However rear of backing board of identical but reduced image Reg. No. 3207 bears pencilled words “Mrs Francis” and “Wreck of ‘Falls of Halladale’ Peterborough 1908”, which accords with what remains of the initial inscription.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, falls of halladale, shipwreck spectacle, shipwreck photograph, peterborough reef, edwardian sightseers, russell & co. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Light Bracket, Before 1878
... the high limestone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on Victoria’s south... 1878, the ship was wrecked against the high limestone cliffs ...This pressed brass artefact is a highly decorative side bracket for distancing a gas lamp flame from the internal wall of a building. It is hollow and made of light gauge metal, with an innovative aesthetic design, but no internal piping to transport gas. It was recovered from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. There are similar artefacts in the Flagstaff Hill collection. The LOCH ARD left Gravesend (London) on 2 March 1878, bound for Melbourne, with a crew of 37, 17 passengers, and a diverse and valuable cargo of manufactured goods, luxury items, and refined metal. Some of the cargo was destined for display at Melbourne’s first International Exhibition in 1880. At 3 am, 1 June 1878, the ship was wrecked against the high limestone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on Victoria’s south west coast near Port Campbell. Only two people survived the disaster — Tom Pearce, a male crew member, and Eva Carmichael, a female passenger. The cargo proved too difficult to salvage in the vessel’s exposed condition and was largely written off. The manifest of goods in the LOCH ARD’s holds included “Fittings gas (4 cases)”. The gas lighting of streets, public buildings, and the dwellings of wealthier private citizens was already well-advanced in the cities and major towns of the Australian colonies. In 1841 Sydney was the first to be gas-lit with 23 street lamps, 106 hotel lamps, and 200 private residences connected to the Darlinghurst “gasometer” by an underground network of metal pipes. “The dim days of oil and tallow are gone by!” pronounced one newspaper, flushed with civic pride. The 1850s Gold Rush promoted a similar attitude of confidence and affluence in the Colony of Victoria. In 1855 Melbourne was connected to its own system of subterranean gas pipes despite the same high rates of 25 shillings per 1000 cubic feet being charged, (reduced to 15 shillings in 1865 with cheaper sources of coal). By1858 Kyneton had its own gasworks to light the town (fuelled by eucalyptus leaves) and Geelong followed suit in 1860. Had the LOCH ARD reached its intended destination in 1878, it is probable that the 4 cases of brass gas light fittings on board would have found a ready market.The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance — Victorian Heritage Register S417. The gas light bracket is an example of lamp fittings and plumbing from the late 19th century.A pressed brass lighting bracket recovered from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. It would be used for attaching, but simultaneously offsetting, a gas nozzle to a wall. Highly decorative in an unusually ‘modern’ or ‘art-deco’ style, with sweeping curves dissected by angular geometric pattern, and supporting a short, vertical bar with a gas nozzle on top. It is constructed of light gauge metal, with splitting along seams, and some delicate tracery is missing. Outer surface has been polished, removing sediment, but greenish oxidation remains in dents and joins. warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck artefact, maritime museum, gas lamps, gas lighting, gas works, brass fittings, gas pipes, loch ard, 1878 shipwreck, victorian affluence, colonial gas lighting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Gas Fitting, Before 1878
... , 1 June 1878, the ship was wrecked against the high limestone... the high limestone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on Victoria’s south ...The artefact is a short cross-section of part of a functional part of a brass fitting that suspended a gas lamp, providing structural support, and internally, supplying the gas for its ignition. It combines elegant design with the elements required for safe and efficient delivery of gas. It was recovered from the LOCH ARD shipwreck site. There are similar artefacts in the Flagstaff Hill collection. The LOCH ARD left Gravesend (London) on 2 March 1878, bound for Melbourne, with a crew of 37, 17 passengers, and a diverse and valuable cargo of manufactured goods, luxury items, and refined metal. Some of the cargo was intended for Melbourne’s first International Exhibition to be held in 1880. At 3 am, 1 June 1878, the ship was wrecked against the high limestone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on Victoria’s south west coast near Port Campbell. Only two people survived the disaster — Tom Pearce, a male crew member, and Eva Carmichael, a female passenger. The cargo proved too difficult to salvage in the vessel’s exposed condition and was largely written off. The manifest of goods in the LOCH ARD’s holds included “Fittings gas (4 cases)”. The gas lighting of streets, public buildings, and the dwellings of wealthier private citizens, was already well advanced in the cities and major towns of the Australian colonies. In 1841 Sydney was the first to be gas lit with 23 street lamps, 106 hotel lamps, and 200 private residences connected to the Darlinghurst “gasometer” by an underground network of metal pipes. “The dim days of oil and tallow are gone by!” pronounced one newspaper, flushed with civic pride. The 1850s Gold Rush promoted a similar attitude of confidence and affluence in the Colony of Victoria. In 1855 Melbourne was connected to its own system of subterranean gas pipes despite the same high rates of 25 shillings per 1000 cubic feet being charged, (reduced to 15 shillings in 1865 with cheaper sources of coal). By1858 Kyneton had its own gasworks to light the town (fuelled by eucalyptus leaves) and Geelong followed suit in 1860. Had the LOCH ARD reached its intended destination in 1878, it is probable that the 4 cases of brass gas light fittings on board would have found a ready market.The gas fitting is significant for its association with the LOCH ARD shipwreck, which is of State significance and is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register S417. The fitting is an example of a late 19th-century plumbing and light fitting.A pressed brass gas light fitting, recovered from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The elegant and functional fitting extends from an ornate 8cm diameter ceiling flange, and comprises two short lengths of fluted column pipe with a brass joiner that are severed (cut off) at the end. Within this decorative outer layer of 3cm diameter is a full length brass tube liner, which is in turn protecting a narrow 0.75cm copper gas pipe that also runs full length. The artefact is generally unrestored with reddish/cream sandstone concretion, but is in good condition.warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck artefact, maritime museum, gas lamps, gas lighting, gas works, brass fittings, gas pipes, loch ard, 1878 shipwreck, victorian affluence, colonial gas lighting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Pipe Fitting, Before 1878
... . At 3 am, 1 June 1878, the ship was wrecked against the high... was wrecked against the high limestone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island ...This artefact is a functional, non-decorative fitting that essentially transports gas from a wall attachment to a lamp. It is a brass and copper gas lamp fitting, designed to direct and control the flow of gas from a flanged wall fitting to an exit nozzle that was lit. It was raised from the LOCH ARD shipwreck site by Flagstaff Hill divers in 1972. Related pieces can be found in the Maritime Village collection. The LOCH ARD left Gravesend (London) on 2 March 1878, bound for Melbourne, with a crew of 37, 17 passengers, and a diverse and valuable cargo of manufactured goods, luxury items, and refined metal; some of which was to be on show at Melbourne’s first International Exhibition in 1880. At 3 am, 1 June 1878, the ship was wrecked against the high limestone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on Victoria’s southwest coast near Port Campbell. Only two people survived the disaster — Tom Pearce, a male crew member, and Eva Carmichael, a female passenger. The cargo proved too difficult to salvage in the vessel’s exposed condition and was largely written off. The manifest of goods in the LOCH ARD’s holds included “Fittings gas (4 cases)”. The gas lighting of streets, public buildings, and the dwellings of wealthier private citizens were already well-advanced in the cities and major towns of the Australian colonies. In 1841 Sydney was the first to be gas-lit with 23 street lamps, 106 hotel lamps, and 200 private residences connected to the Darlinghurst “gasometer” by an underground network of metal pipes. “The dim days of oil and tallow are gone by!” pronounced one newspaper, flushed with civic pride. The 1850s Gold Rush promoted a similar attitude of confidence and affluence in the Colony of Victoria. In 1855 Melbourne was connected to its system of subterranean gas pipes despite the same high rates of 25 shillings per 1000 cubic feet being charged, (reduced to 15 shillings in 1865 with cheaper sources of coal). By1858 Kyneton had its gasworks to light the town (fuelled by eucalyptus leaves) and Geelong followed suit in 1860. Had the LOCH ARD reached its intended destination in 1878, the four cases of brass gas light fittings on board would probably have found a ready market.The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance — Victorian Heritage Register S417. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. This pipe is a gas lamp fitting. This extensively corroded fitting is made of brass and copper alloy. It comprises a 31 cm copper pipe of 1.5cm diameter which is connected to a 6.5cm diameter wall flange (via a flow tap and an adjustable swivel valve) at one end, and to a screw-in square coupling with a nozzle or gas jet at the other end. The copper pipe is dented and corroded and has three holes. The brass attachments are a more robust cast metal but the adjustable mechanisms are concreted into immobility by ocean sediment. No discernible maker’s marks. In unrestored but fair condition. The pipe with the fitting was recovered from the wreck of the LOCH ARD.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, gas lamps, gas lighting, gas works, brass fittings, gas pipes, loch ard, 1878 shipwreck, victorian affluence, colonial gas lighting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Optical, Binoculars, 1878 (estimated)
... into exhausted unconsciousness. Tom then scrambled to the top of the high... into exhausted unconsciousness. Tom then scrambled to the top of the high ...This pair of brass binoculars was presented to Tom Pearce in recognition of his heroic efforts at the wrecking of the Loch Ard and saving Eva Carmichael. They were presented to him by the Lady Mayoress of Sydney on 27th July 1878 on behalf of the colonists of New South Wales "In recognition of his gallant conduct on the occasion of the wreck of the Loch Ard". Tom (Thomas) Pearce was born in Ireland in 1859 and arrived in Melbourne two years later; he considered himself as Australian. Before sailing on the Loch Ard he had been at sea for three years as an apprentice sailor and had already experienced one shipwreck. Tom was on the deck of the Loch Ard with Captain Gibb throughout the night of May 31st 1878. It was mistakenly thought they were 150 miles (240 km) southwest of Cape Otway. By 2:00 am on June 1st, the wind was blowing "pretty fresh" but a thick haze remained and, when it eventually cleared, the land was so close the unsuccessful battle to save the Loch Ard began. After the ship struck Mutton Bird Island Tom and five others were sent to the lifeboats. Conditions were very dangerous as waves broke over the decks and they were all washed away. Tom found himself in the stormy waters and under a lifeboat, which had also been washed into the sea. After being swept into the gorge Tom left the boat and swam into shore; he was alone. Eva Carmichael, a passenger on the ship, had been snatched from her bed just before dawn and into the chaos, confusion and terror of the shipwreck, with rigging and rocks raining down. Thrown into the sea, she afterwards said: "God taught me to swim in my distressful plight, for I never swam before". Clinging to a spar, she was swept into the gorge and saw Tom Pearce walking along the beach. Upon hearing the cries of Eva, Tom swam out and with great difficulty brought her to the shore and placed her safely in a cave where he made a bed of grass and shrubs and gave her brandy to revive her. She sank into exhausted unconsciousness. Tom then scrambled to the top of the high cliff and after walking for some time he stumbled upon workers from Glenample Homestead. They rode back to the homestead for help but Tom insisted on returning to Eva. When Eva awoke she found herself alone, "cold, weak and terrified with the wild waves before me, and caves and cliffs around me" and upon hearing strange noises, which she imagined to be made by the local indigenous people, she hid. The noises were made by the rescue party from Glenample Homestead. After eventually discovering Eva they hauled her up the cliff in the darkness of night, “a work of great difficulty and danger” and took her to Glenample. Sadly, Tom and Eva were the only survivors of the 54 people on board the Loch Ard. Tom’s rewards for his bravery included the Gold Medal of the Humane Society, a gold watch and £1000 from the Victorian Government, a set of nautical instruments, (which included the binoculars) from the people of Sydney and £60 from the people of Warrnambool. He was also presented with a Bible by a “Friend of the Loyal Orange Institution of Victoria, Protestant Hall Melbourne” in August 1878. Coleman Jacobs composed the music "The Young Hero Schottische" and dedicated it, by permission, to Mr Thomas R. (Tom) Pearce. The sheet music was published in 1878 by Mr Roberts, professor of dancing and was on sale for 3/- (3 shillings) in aid of the "Loch Ard" fund. Tom Pearce went on to join the Loch Sunart on her return to England, only to be wrecked again off the Irish coast in January 1879. Tom left the Loch Line in 1883 and the following year married Edith Gurney Strasenbergh, the sister of his friend Robert who had died on the Loch Ard. They had three children, unfortunately, two of the male children were to die at sea. In 1895 Tom obtained his first command as Master of The Larne, a vessel with the Royal Mail Steam Packet Company. He remained with the company until he died in Southampton, England, on 14th December 1908. Tom Pearce never saw Eva Carmichael after he had fare welled her some 30 years before. Eveline Victoria Berta Carmichael was born in 1859 in Mountrath, Queens County, Ireland. After recovering from her ordeal in August 1878 Eva returned to Ireland and in 1884 married Thomas Achilles Townshend, a Civil Engineer. They had three sons, all of whom had successful military careers, and when Eva’s death notice appeared in the Melbourne Argus It read. "Townshend on 8th April 1934 aged 74 at her residence in Bedford, England, Evaline Victoria, widow of the late Thomas Archilles Townshend, C.E. of Co. Cork, Ireland. Mrs Townshend was the Eva Carmichael who, with the late Tom Pearce, were the only two survivors of the ship Loch Ard, which was wrecked near Port Campbell on June 1st 1878." The binoculars are significant for their association with the wreck of the Loch Ard and the only two surviving members of that wreck Tom Pearce and Eva Carmichael. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from Loch Ard is significant for being one of the largest. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The assemblage of items from the wreck is of historical significance in that they are associated with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history. Pair of brass marine binoculars in a wooden box On the left hand eye piece, on the underside, is an engraved inscription and another engraved word. On the right hand eye piece there is another small inscription and on the underside there is a small green mark. The binoculars have a pattern of embossed tiny circles on the outside. Some of the patterning is very shiny due to wear and rubbing, there is a brass ring on the underside of the binoculars for the attachment of a lanyard. The wooden box has a hinged lid and on the front of the box in the centre is a lock, and at either end are two hooks and eyes. The box is split across the top for about 3/4 of the length. Marking on the left underside reads, 'Presented on behalf of the Colonists of New South Wales By the Mayoress of Sydney on 27th. July 1878 to Mr Thomas B Pearce. In recognition of his gallant conduct on the occasion of the wreck of the "Loch Ard"'. Underneath this inscription is engraved 'Sydney'. On the other eye piece is engraved what looks like 'Mac Donnell & Co' binoculars, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, loch ard shipwreck, tom pearce, thomas r pearce, eva carmichael, mutton bird island, loch ard survivor, loch ard hero, coleman jacobs, the young hero schottische, photograph of tom pearce, glenample homestead -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Knife, Made on or before September 1891
... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200 m high cliffs... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200 m high cliffs ...This sheath knife belonging originally to German seaman Julius Gebauhr and an artifact associated with the story of the survivors of the wreck of Fiji. A three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a varied cargo consisting of cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, various spirits, sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos and other musical instruments. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in a squally and boisterous south-west wind, the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers' calculation of his position. At about 2:30 am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed Fiji struck rock only 274 meters from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Efforts were made to lower boats but all capsized or became swamped two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after the line broke. The other, 17-year-old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt without a line, which he had cut loose with his sheath-knife when it becomes tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the cliffs in search of help. At about 10 am on Sunday a party of land selectors including F. J. Stanmore, Leslie Dickson found Gebauer. They were on their travels back from Princetown towards Moonlight Head. Gebauer was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in a singlet, socks, belt and his sheath-knife. His rescues gave him food and brandy and some clothing and gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stanmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and was set up on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line the light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, as many as five at a time, however, some were washed off. Only 14 of the 24 men who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. The wreck of Fiji has smashed apart within 20 minutes of the last man being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6 m of water. Of the 26 men on Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach. They were buried on the clifftop above the wreck. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship and his Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe who had dragged the captain out of the surf with his silver cased pocket watch, the only possession that he had left, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother in law Gilbert Hulands as payment of a debt. Since that time it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stanmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle has a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200 m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are china miniature animals, limbs from small china dolls, rubber balls, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with this sheath knife and Captain Vickers’ pocket watch. Flagstaff Hill’s collection from the wreck of the Fiji and Julius Gebauhr knife is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the vessel, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S 259). The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th-century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo still evident. Also the story of the heroic attempt by many to save the crew of the Fiji. The knife also represents an aspect of shipping history and fits in well with Victoria's framework of historical themes of living with natural processes as items such as these contribute to a better understanding of Victoria’s cultural history.Knife, metal with black wooden handle. Handle is riveted to knife in 3 places, with shaft of knife between the 2 parts of the handle. The handle also has a carved ring around the end, possibly for attaching a wrist strap. Knife blade is pointed in the centre of the tip and is rusty. The knife has a rectangular metal plaque on handle with inscription. The hand crafted dark brown, soft leather sheath is shaped to fit the knife and joined at the back with cross stitching. The sheath also has a leather belt strap that has come away from the sheath at one end.Metal plaque “FROM JULIUS GEBAUHR/”FIJI” /TO F.J.S.” (F J Standmore recipient)1891, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, knife, fiji, pocket watch, moonlight head, gebauhr, stansmore, wreck bay, sheath knife -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSouvenir - Rope Sample, before September 1891
... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs ...The rope was part of the distress rocket used during the time that the sailing ship Fiji was in distress, before it became a wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and distress rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Cartland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryan's Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to River nook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the last man being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to River nook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967.This rope is part of the collection of artefacts from the wreck of the Fiji. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes).Rope, plaited, brown in colour, cut straight at one end, and the other end is separated into 3 pieces, from distress rockets used during the wreck of the sailing ship Fiji. Rope was in envelope printed with an address, and a description, and there was a display card with further details on it. Printed on the envelope: "Shire of Hampden / PO Box 84, Camperdown 3260" Hand written "rope of wreck of Fiji / 7cm / Mr Wm "Boyce" Display card with rope includes words "Piece of Rope from the Fiji distress rockets and was donated to Flagstaff Hill by a private donor in 1989"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, rope, the fiji, william boyce, distress signal, rocket rescue, life saving equipment -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph, C. 1891
... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs ...Photograph shows the ship FIJI where she met her demise, in Wreck Bay, on the shipwreck coast of South West Victoria. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are china miniature animals, limbs from small china dolls, rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Black and White Photograph of the ship "Fiji" taken from Wreck Creek. warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, pocket watch, fob watch fiji, william vickers, william robe, bill robe, gebauhr, stansmore, carmody, wreck bay, moonlight head, fiji shipwreck 1891, port campbell rocket crew, wreck bay victoria -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDog, 19th century
... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs ...This toy dog was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife.Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history.China toy dog salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. This moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and is tan in colour. The dog is solid with a pitted surface1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTextile - Rope Sample, After September 1891
... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs ...The light line or rope used to construct this Turk’s Head knot was part of the line line-throwing apparatus used by the Rocket Rescue Crew. In normal operation a rocket carrying the line was fired over a ship, fastened to the ship, then hauled by the crew to pull a heavier rope from shore, which would have a canvas ‘breaches buoy’ attached to it. A tripod or triangle would be used to keep it free from breakers and rocks. One by one the crew on the wreck would sit in the buoy and be hauled safely back to shore. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the last man being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967.This rope is part of the collection of artefacts from the wreck of the Fiji. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Rope salvaged from the distress rocket rope line used in the rescue of the crew of the sailing ship “Fiji”. The light-weight brown rope has been crafted into a decorative 'Monkey fist' or 'Turk’s head' knot using three interwoven strands. 1891, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, rope, moonlight head, wreck bay, distress rocket, line, light line, rocket rescue apparatus, rocket equipment, rocket line -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCandlestick holder, Made on or before 1891
... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs ...This candlestick holder is one of the artefacts salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the last man being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are china miniature animals, limbs from small china dolls, rubber balls, a glass bottle and a sample of rope from the distress rocket. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife.This candlestick holder is Artefact Reg No Fiji/2, part of the Fiji collection. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Candlestick holder or Chamber Candle. Made of china, off white in colour with crazed glazing. The round concave dish has the base of a round candle holder in centre (remainder of holder has been broken off). The base of a circular china finger ring is attached to both the rim and the dish, about ¾ of the way towards the centre - the top 2/3rds of the finger ring is broken off. A conical thimble-like spike, placed about a quarter of the way around from the finger ring, is intact. This spike was probably used to hold a candle snuffer of similar but larger size and shape. The candlestick holder was recovered from the wreck of the Fiji.1891, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, fiji, pocket watch, moonlight head, candlestick holder, candle holder, chamber candle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDoll's leg, Bisque dolls were being made from the 1860’s
... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs ...This doll’s leg was part of the cargo from the Fiji and was part of the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife.Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Doll’s leg salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. This moulded leg, made of bisque (sometimes described as china or porcelain) is for a small doll. The leg is solid rather than jointed, and goes from the lower thigh down to the foot, which has a shoe-shaped heel. The white coloured leg is finished with glazed paint and the shoe of the foot is painted black. The leg is discoloured in places with a tan colour. There is a groove around the top of the leg, which would enable the leg to be attached to the cloth body of a doll.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, doll, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, dolls limb, dolls leg, toys, doll's leg, doll's limb -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDoll's arm, Bisque dolls were being made from the 1860’s
... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs ...This doll’s arm was part of the cargo from the Fiji and was part of the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Doll’s arm salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. This moulded arm, made of bisque (sometimes described as china or porcelain) is for a small doll. Its hand has the fingers touching each other with the thumb tucked into the palm. The white coloured arm is finished with glazed paint. The arm is discoloured in places with a tan colour. The arm is solid rather than jointed and goes from hand to upper arm. There is a groove around the top of the arm, which would enable the arm to be attached to the cloth body of a doll.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, doll, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, doll's arm, doll's limb -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDoll's leg, Bisque dolls were being made from the 1860’s
... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs ...This doll’s leg was part of the cargo from the Fiji and was part of the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Doll’s leg salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. This moulded, shapely leg, made of bisque (sometimes described as china or porcelain) and tan in colour, is for a small doll. It has a shoe shaped foot complete with heel. The leg would have probably been finished with paint and the shoe would also be painted on. However this leg has no paint remaining. The leg is solid rather than jointed and goes from foot to lower thigh. Around the top edge of the thigh is a groove, which would enable the leg to be attached to the cloth body of a doll.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, doll, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, dolls limb, dolls leg, toys, doll's limb, doll's leg -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSlate pencil, Made on or before May 1891
... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs ...Slate pencils were made from a rod of soft slate material and used for writing on thin slate boards. The slate boards were approximately 9cm x 12cm used in schools for writing practice in place of pencil and paper, which were more expensive and less durable. They could be used then easily erased for re-use. In work places, slate boards were sometimes bound into slate books The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are china miniature animals, limbs from small china dolls, rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Remnants of a black slate pencil salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. Pencil has no casing and is in three pieces. One piece is broken laterally and has a rounded end. The other two pieces have a longitudinal break and fit together. (The nature of the break indicates a material of natural formation, for example sedimentary rock such as slate.) flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, slate pencil, pencil, slate board, writing, stationery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLeisure object - Monkey, ca. 1891
... headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west... headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west ...This toy monkey was part of the cargo from Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool-based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation of Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous southwest winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30 am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17-year-old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut loose with his sheath knife when it became tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach and then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10 am on Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in a singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath knife, ready for all emergencies. At first, they were concerned about his wild and shaggy-looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 remaining on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29-year-old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26-year-old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of Fiji smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Master's Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism of the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue were in half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. The essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers' homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the lootings, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand-crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, and limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, a sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Toy white China monkey in a seated pose. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and is creamy sand colour with a rust-coloured mark on its face. The surface is slightly pitted. It was salvaged from the wreck of the ship FIJI. 1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, monkey -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMonkey, 19th Century
... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs ...This toy monkey was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. This toy monkey is classified as Fiji 5 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Ceramic toy monkey salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The monkey is in a seated pose with its arms around its knees. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and the material is an orange colour. The surface is slightly pitted.ceramic, china, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, bisque, toys, miniature animals, monkey, ornament -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMonkey, 19th century
... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs ...This toy monkey was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. This toy monkey is classified as Fiji 5 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. China toy monkey salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The monkey is in a seated pose with its arms around its knees. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and the material is an pinkish brown colour with darker orange in its lap. The surface is worn and slightly pitted.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, monkey -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageRabbit, 19th century
... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs ...This toy rabbit was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife This toy rabbit is classified as Fiji 4 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. China toy rabbit salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The rabbit is in a lying pose. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and the material is an orange-sandy colour with darker orange markings. The surface is slightly pitted.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, rabbit -
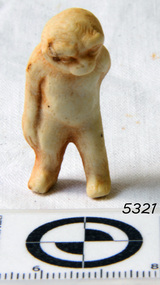 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageGorilla, 19th century
... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs... inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs ...This toy gorilla was part of the cargo from the Fiji and amongst the articles salvaged from the wreck. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are bisque (or china) toys, (including miniature animals, limbs from small bisque dolls), rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife This toy gorilla is classified as Fiji 7 on the SWR Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. China toy gorilla salvaged from the wreck of the Fiji. The gorilla is in a standing pose. This solid, moulded toy is made of bisque (sometimes described as bisque or porcelain) and the material is pale creamy colour with a slightly pitted surface.1891, china, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, porcelain, moonlight head, wreck bay, cargo, bisque, toys, miniature animals, gorilla
