Showing 74 items matching "mines sea mines"
-
 Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub Branch
Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub BranchWorld War 2 Era Contact Sea Mine
... World War 2 Era Contact Sea Mine...mines sea mines...These mines were tethered to the sea bed and were detonated... These mines were tethered to the sea bed and were detonated when ...These mines were tethered to the sea bed and were detonated when a ship came into contact with the "Horns" that protruded from the mines exterior surface (removed in this example although the fixing points are clearly visible.) The mines were usually laid by ships or submarines in "Fields" across harbour entrances or in busy shipping lanes. They were tethered so that they floated several feet below the water. This type of mine carried enough exlposive to sink even the largest of ships. Floating mines typically have a mass of around 200 kg,including 80 kg of explosives e.g. TNT, Minol or Amatol.mines sea mines -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumWeapon - SEA MINE, MARK XV11, 1939 - 45
... SEA MINE, MARK XV11...sea mine... bdrslinc sea mine Refer .1) plaque. .1) Plaque on black metal stand ...This mine is situated in the gardens of the Bendigo District RSL Sub Branch Inc Havilah Road Bendigo. Refer photo .1) re details of manufacture and its history/use..1) Plaque on black metal stand with white text with details re the mine. 2) Mine slightly oval shape, black with a white band, the top has a bolted on section as a lid, there are multiple "horns" attached around the mine.Refer .1) plaque.brsl, smirsl, bdrslinc, sea mine -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, 13-09-1947
... sea mine patrol... Bass Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance ...This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947.The photographer has captured the crew in a lifeboat surrounded by sea. The lifeboat is approaching the HMAS Swan II. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in May 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of rescue of crew from H.M.A.S. Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. Men in life boat surrounded by water. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at that time. flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, lifeboat, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Ship's Bell, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool 1941, 1948
... sea mine patrol... Bass Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance ...This photograph was taken at the wreck site of the HMAS Warrnambool J202, wrecked on September 13th 1947. The bell was recovered in 1948 by the Royal Australian Navy. The ship's bell has been of great importance to a ship for hundreds of years. The bell is used for the timing of ships watches, for emergencies and many other purposes. It is also a prized possession when a ship is wrecked or broken up, as lasting memorial of the ship's existence. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941 and was. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of ship bell from shipwreck of HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The black and white photograph of the bell shows its inverted 'U' shaped fitting on top and inscribed letters around it. The flared base of the bell has concentric rings as decoration. In photograph, inscription on bell "- ARNAMB-" [WARRNAMBOOL]flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, hmas warrnambool ship’s bell, ship’s bell, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
... sea mine patrol... Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance Navy ...This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the ship as it sinks at sea. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the sinking of the ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. This black and white photograph showing the vessel at sea is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
... sea mine patrol... Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance Navy ...This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the ship as it sinks at sea. The photograph is taken from a nearby vessel, likely to be the HMAS Swan II, which took the survivors onboard. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the sinking of the ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. Figures onboard a vessel are looking towards figures on the sinking vessel. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool J202, 13-09-1947
... sea mine patrol... Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance Navy ...This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the ship as it sinks at sea. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the starboard side of the sinking ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool J202, 13-09-1947
... sea mine patrol... Bass Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance ...This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the sinking ship with the crew still onboard. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941 . The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the sinking ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. Figures can be seen onboard the damaged vessel. The number of the ship-type is clearly visible on this starboard profile of the ship. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.Text on side of ship "J202"flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
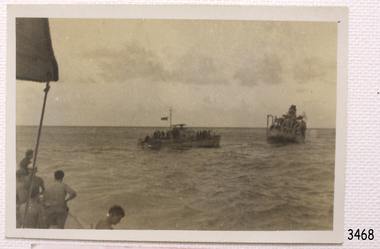 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool J202, 13-09-947
... sea mine patrol... Bass Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance ...This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the rescue boat approaching the sinking ship with the crew onboard. There small boat has several figures onboard. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of rescue of the crew from shipwreck HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. Figures onboard a larger vessel look across at rescue vessel heading towards the sinking ship. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool J202, 13-09-1947
... sea mine patrol... Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance Navy ...This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the ship as it sinks at sea. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the sinking ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The image shows the damaged ship tilting down on the starboard side. The ship-type number is still mostly visible. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool J202, 13-09-1947
... sea mine patrol... Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance Navy ...This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the ship as it sinks at sea, with, it seems, crew still on board.. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the sinking ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The image shows the ship leaning at an angle towards the sea. There appears to be figures near the bow. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool J202, 13-09-1947
... sea mine patrol... Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance Navy ...This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the ship as it sinks at sea. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the sinking ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The image shows the ship tilting towards port side and the bow dipping. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
... sea mine patrol... Bass Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance ...This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the crew being rescued, transferring from one vessel to another, which is likely to be the HMAS Swan II. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the rescue of the crew from shipwreck HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. Survivors are helped from one vessel to another by seamen. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
... sea mine patrol... Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance Navy ...This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the crew being rescued. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney, 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the rescue of the crew from shipwreck HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The image shows injured men being assisted onboard a vessel at sea. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
... sea mine patrol... Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance Navy ...This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the crew being rescued. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the rescue of the crew from shipwreck HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. Image shows men in a lifeboat beside men in a ship, at sea. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), 13-09-1947
... sea mine patrol... Bass Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance ...This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. The photographer has captured the crew being rescued, transferring from a lifeboat to the ship. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the rescue of the crew from shipwreck HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The image shows men being taken onboard a ship from a small boat. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Shipwreck rescue, Royal Australian Navy (RAN), HMAS Warrnambool J202, 13-09-1947
... sea mine patrol... Bass Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance ...This photograph was taken at the scene of the wreck of the HMAS Warrnambool J202 on September 13th 1947. Figures can be seen on deck. The photographer has captured the ship as it sinks at sea. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the sinking ship HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947. The image shows the damaged and listing ship in the sea with figures on deck. This black and white photograph is one of a series of photographs taken at the time. "HMAS Warrnambool being sunk by mine", "sunk in Queensland waters 13 September 1947"flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, minesweeper -
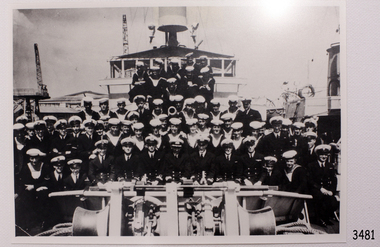 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Ship's crew, HMAS Warrnambool J202, Between 1941-1947
... sea mine patrol... patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance Navy divers ...This formal photograph shows the crew of the HMAS Warrnambool standing in rows on the deck of the ship while it is in port. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWII Photograph of the crew of HMAS Warrnambool (I). This black and white image shows the crew formally standing in rows on the bow of the ship, which is docked. Inscription on back. (PRIVATE details, see Notes)flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, minesweeper -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Ship's crew, HMAS Warrnambool J202, 1941
... sea mine patrol... Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance Navy ...This photograph shows the crew of the first HMAS Warrnambool (J202) marching east along Timor Street in Warrnambool, just opposite the Post Office on the corner of Gillies Street. People are watching the parade from the footpath and two boys, dressed in their ‘best’ clothes, are marching alongside the crew. The HMAS Warrnambool was one of 60 Bathurst class corvette vessels built during World War II for the Royal Australian Navy (RAN) as armed minesweepers. The namesake of the City of Warrnambool, Victoria, was launched in Sydney in 1941. The HMAS Warrnambool began service with patrols off Bass Strait in 1941. In December the ship docked in the Warrnambool harbour at Lady Bay. The crew came ashore and performed a march for the city. The Mayor, Cr. John R Astbury presented them with a plaque of the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms and the Warrnambool Patriotic Fund gave them a gift of 110 books for the crew’s library. The Warrnambool served in Darwin during the time it was bombed, it was involved in several rescues and carried troops to New Guinea, it carried out escort and patrol duties on Australia's east coast, then at Fremantle and back to Darwin. The ship was at Timor when the Japanese surrendered in 1945. It performed mine clearance work around the Solomon Islands and New Guinea after the war. In 1947 the HMAS Warrnambool was at the Great Barrier Reef, off the Queensland coast, to clear the defensive British mines previously laid to protect Australia’s boarders. The ship hit a mine near Cockburn Reef, exploded and sank shortly afterwards. One of the 70 or so men on board was killed and three died later. The rescued men were transferred by boats to the nearby HMAS Swan II, which took the survivors to Cairns. The four deceased were Victorian seamen. In May 1948 the Royal Australian Navy divers recovered a number of items from the wreck, including the ship’s bell and the City of Warrnambool plaque. In 1949 the RAN returned the plaque to the Warrnambool City Council, and donated the ship’s bell to the Australian War Memorial. Further objects were recovered in 1972-75 by Southern Cross Diving and Salvage. A memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool on September 13, 1995 in honour of all who served on HMAS Warrnambool. NOTE: (1)- HMAS Warrnambool II (FCPB204 was built in 1980 in Cairns, with a compliment of 22 personnel. It was decommissioned in 2005. (2)- SS Warrnambool, a steam and sail ship, was built in 1892 in London and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.]This photograph is significant for its association with the lifesaving rescue of the crew and the sinking Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWIIPhotograph of the crew of HMAS Warrnambool J202. This black and white image shows the crew marching east along Timor Street in Warrnambool. People are watching from the footpath and two formally dressed boys are marching alongside the sailors. Inscription on the reverse.(PRIVATE details - See Notes)flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, dedicatory plaque, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, marching, parade, timor street warrnambool, minesweeper -
 Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.
Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.Sketch, 1890
... The Cape Paterson shaft at Kilcunda Mine. A landscape... Mine. A landscape - sea and cliffs in the background. A small ...The Cape Paterson shaft at Kilcunda Mine. A landscape - sea and cliffs in the background. A small shed with chimney beside poppet head. Track winding down to three miners. Wooden sheds, all with chimneys. In Foreground a picket fence on cliff on right of picture. A small tree stump on left.The Kilcunda MineCape Paterson Shaft - Kilcundalocal history, photography, photographs, slides, film, kilcunda mine, black & white, pen and ink sketch, miss elms san remo, james stirling -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomMedal, Naval General Service Medal 1915-62
The Naval General Service Medal (NGSM) was instituted in 1915 for service in minor Naval war-like operations. As is the case with other ‘general service' medals the NGSM is always issued with a clasp denoting the area of operations. Subsequent service is recognised by the award of further clasps to be worn on the original medal. Members mentioned in despatches for operations recognised by the NGSM 1915-1962 after 11 Aug 1920 were approved to wear a bronze oak leaf on the medal ribbon. Clasps There have been sixteen clasps issued for the NGSM 1915-1962. These are: Persian Gulf 1909-1914 Iraq 1919-1920 NW Persia 1919-1920 NW Persia 1920 Palestine 1936-1939 SE Asia 1945-46 Minesweeping 1945-51 Palestine 1945-48 Bomb and Mine Clearance 1945-53 Malaya Yangtze 1949 Bomb and Mine Clearance, Mediterranean Cyprus Near East Arabian Peninsula Brunei Medal The NGSM 1915-62 is cupro-nickel medal with the obverse having the effigy of the reigning sovereign at time of issue. The reverse bears an image of ‘Britannia' in a chariot pulled by two sea-horses. The NGSM 1915-62 ribbon has a wide white central stripe, flanked by two red pin-stripes, further flanked by two white stripes, which in turn are flanked by two red outer stripes.naval general service medal -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Diary of R.W. Richards, c1960
Dick Richards was a member of the Shackleton Trans Antarctic Expedition Ross Sea Shore Party. He later became Principal of the Ballarat School of Mines. The text for this book was typed by Ballarat School of Mines librarian Heather Durant, who remembered that at times it was difficult to read the writing due to whale blubber oil from the lamps on the paper. Heather was told that Dick Richards only started keeping the diary when ther became a chance the Ross Sea Shore Party may not survive. Heather remembered Dick Richards affectionately - he always carried a pipe and called her 'girlie'.Blue hard covered book of 14 pages. It is the verbatim copy of the diary kept by Dick Richards from 23 February 1916 to 19 March 1918, during the Shackleton trans-antarctic Expedition 1914-17.Bookplate inside cover - "Ex Libris School of Mines and industries. Presented by Mr R.W. Richards"ballarat school of mines, dick richards, r.w. richards, antarctica, shackleton, heather durant, diary, bookplate, ballarat school of mines bookplate, scott's hut, richard w. richards -
![Photograph - Photo, [Dick Richards with Antarctic Memorabilia], 1982 (exact)](/media/collectors/4f729f6797f83e0308601707/items/4f72a5c497f83e03086027e0/item-media/589d0be9d0cdf4227c92feee/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photo, [Dick Richards with Antarctic Memorabilia], 1982 (exact)
Dick Richards was a member of the Shackleton Antartic Expedition and was marooned on the Ross Sea shelf. He was also a former principal of the Ballarat School of Mines.Framed colour photographic portrait of Richard W. Richards, in a gold aluminium frame with cream mount. The image includes Dick Richards holding a pipe, the book 'The Ross Sea Shore Party', an opened tin of food, globe of the world, a fur lines coat, and papers on a desk. dick richards, r w richards, antarctic exploration, ross sea shore party, richard w richards, ballarat school, mines, antarctica, available -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph (black & white), Four Principals of the Ballarat School of Mines, June 1983
This photograph was taken at the presentation of a bust of Dick Richards to the Ballarat School of Mines. Dick Richards joined the Ballarat School of Mines (SMB) in 1914, and soon afterwards was granted leave to join an expedition to Antartica. In 1915 he sailed from Australia with the Antartic Exploraton Expedition, led by Sir Ernest Shackleton. Dick Richards was the physicist and sled manager for Shackleton's Ross Sea Party - with the task to meet Shackleton on the other side of the continent. When Shackleton planned his transcontinental crossing he decided to use supply depots as loads of supplies were too heavy to pull. The depots would enable Shackleton's party to carry just enough to reach the Pole, relying on the depots which were to be left by the Aurora's crew every 60 miles, stowed in 2 sledge journeys in 1915 and 1916. Dick Richards spent 3 freezing years in Antarctica between 1914 and 1917. Travelling south with Sir Ernest Shackleton Richards' worst experience was when his ship Aurora, tethered offshore, was blown away in a gale leaving Richards marooned for two years with nine other men on the ice floe. The Ross Sea Party arrived in McMurdo Sound aboard the Aurora in January 1915. The going was tough on the sledging trips as the sledges were overloaded. Temperatures were as low as minus 68F. In June 1916 the party crossed on foot to Cape Evans, occupied Scott's Hut (from his Terra Nova Expedition, erected in January 1911) in May 1915, for two months. On 10 January 1917 Richards was hunting for seals when he saw a ship on the horizon. It was 'The Aurora'. Picking up the relieved survivors 'The Aurora' arrived in New Zealand on 9 February 1917 to a hero's welcome. Joyce, Wild, Hayward and Richards later won the Albert Medal for their heroic devotion to duty. Later an inlet on the Antartic continent was named after Richards. Dick Richards wrote the following years after the ordeal "To me no undertaking carried through to conclusion is for nothing. And so I don't think of our struggle as futile. It was something the human spirit accomplished." After returning to Australia Dick Richards resumed his work at SMB as Lecturer in Physics and Mathematics, and developed many pieces of experimental equipment. During World War Two he acted as a scientific adviser in the production of optical apparatus in Australia. In 1946 he was appointed Principal and twelve years later he retired after a total of 44 years service. Dick Richards has been honoured through the naming of a Ballarat School of Mines prize - The R.W. Richards Medal. This medal later became a University of Ballarat prize. It has been awarded annually since 1959 to the Bachelor of Applied Science graduate considered to have achieved the most outstanding academic performance of their course. The award was was introduced to commemerate the long years of service to tertiary education in Ballarat by Mr Richards. See http://guerin.ballarat.edu.au/aasp/is/library/collections/art_history/honour-roll/honourroll_Richards,Dick.shtmlBlack and white photograph featuring 4 men who had serves as Principal of the Ballarat School of Mines. Left to Right: E.J. (Jack) Barker, Peter Shiells, Richard W. Richards, Graham Beanland.ballarat school of mines, dick richards, antarctica, ernest shackleton -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph (black & white), Richard W. Richards, c1950
This photograph was taken at the presentation of a bust of Dick Richards to the Ballarat School of Mines. Dick Richards joined the Ballarat School of Mines (SMB) in 1914, and soon afterwards was granted leave to join an expedition to Antarctica. In 1915 he sailed from Australia with the Antartic Exploration Expedition, led by Sir Ernest Shackleton. Dick Richards was the physicist and sled manager for Shackleton's Ross Sea Party - with the task to meet Shackleton on the other side of the continent. When Shackleton planned his transcontinental crossing he decided to use supply depots as loads of supplies were too heavy to pull. The depots would enable Shackleton's party to carry just enough to reach the Pole, relying on the depots which were to be left by the Aurora's crew every 60 miles, stowed in 2 sledge journeys in 1915 and 1916. Dick Richards spent 3 freezing years in Antarctica between 1914 and 1917. Travelling south with Sir Ernest Shackleton Richards' worst experience was when his ship Aurora, tethered offshore, was blown away in a gale leaving Richards marooned for two years with nine other men on the ice floe. The Ross Sea Party arrived in McMurdo Sound aboard the Aurora in January 1915. The going was tough on the sledging trips as the sledges were overloaded. Temperatures were as low as minus 68F. In June 1916 the party crossed on foot to Cape Evans, occupied Scott's Hut (from his Terra Nova Expedition, erected in January 1911) in May 1915, for two months. On 10 January 1917 Richards was hunting for seals when he saw a ship on the horizon. It was 'The Aurora'. Picking up the relieved survivors 'The Aurora' arrived in New Zealand on 9 February 1917 to a hero's welcome. Joyce, Wild, Hayward and Richards later won the Albert Medal for their heroic devotion to duty. Later an inlet on the Antartic continent was named after Richards. Dick Richards wrote the following years after the ordeal "To me no undertaking carried through to conclusion is for nothing. And so I don't think of our struggle as futile. It was something the human spirit accomplished." After returning to Australia Dick Richards resumed his work at SMB as Lecturer in Physics and Mathematics, and developed many pieces of experimental equipment. During World War Two he acted as a scientific adviser in the production of optical apparatus in Australia. In 1946 he was appointed Principal and twelve years later he retired after a total of 44 years service. Dick Richards has been honoured through the naming of a Ballarat School of Mines prize - The R.W. Richards Medal. This medal later became a University of Ballarat prize. It has been awarded annually since 1959 to the Bachelor of Applied Science graduate considered to have achieved the most outstanding academic performance of their course. The award was was introduced to commemerate the long years of service to tertiary education in Ballarat by Mr Richards. See http://guerin.ballarat.edu.au/aasp/is/library/collections/art_history/honour-roll/honourroll_Richards,Dick.shtml Black and photo portrait of Richard W. (Dick) Richards, Principal of the Ballarat School of Mines. dick richards, r.w. richards, ballarat school of mines, antarctic explorer -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMedal - Numismatics, ANZAC Commemorative Medal for R.M. Serjeant, 1967
Robert M. Serjeant was the only son of Theo and Alice Serjeant, and grandson of famed mine manager Robert Malachy Serjeant (1829-1902). Robert Serjeant was a past student of the Ballarat School of Mines (SMB), and at the time of his World War One enlistment he had just finished an electrical course, and was working as a junior member of the SMB Department of Electricity. Robert Serjeant enlisted in December 1914. Corporal Serjeant (2138) of the 8th Battalion, died of wounds received in action at Gallipoli on 28 April 1915, aged 20. He was buried at sea and his name is listed at the Lone Pine Memorial. A brown paper parcel of Robert Serjeant's belongings was returned to his parents. It contained his discs, wrist-watch (damaged), notebook, hymn book and letters. [1] The Ballarat Courier reported: 'He was of quiet disposition, and a great student, devoting himself closely to his work.' Further information on R.M. Serjeant can be found at https://bih.federation.edu.au/index.php/Robert_M._Serjeant_Jnr The following statement on the ANZAC Commemorative Medallion and Badge was made by by Prime Minister Holt in 16 March 1967 when the Minister for Defence announced that it had been decided by the Australian Government, in consultation with the New Zealand Government, to issue a medallion and lapel badge to the veterans of the Gallipoli Campaign. "Last March, the Minister for Defence announced that it had been decided by the Australian Government, in consultation with the New Zealand Government, to issue a medallion and lapel badge to the veterans of the Gallipoli Campaign. I am glad to be able to announce that arrangements have now been completed for the production of the medallion and the badge. The Minister for the Army will be arranging distribution to those wishing to receive them as soon as possible. The Government hopes that production of the medallion and lapel badge will be sufficiently advanced to permit at least some of them to be distributed by ANZAC Day. The medallion (with the name of the recipient inscribed) will be issued to the surviving members of the Australian Defence Force who served on the Gallipoli Peninsula, or in direct support of the operations from close off-shore, at any time during the period from the first ANZAC Day in April, 1915 to the date of final evacuation in January, 1916. Next of kin or other entitled persons will be entitled to receive the medallion on behalf of their relatives, if the relative died on active service or has since died. For surviving members, a lapel badge will also be available for wearing. This will be a replica of the obverse (or front) of the medallion and will be about 1 inch high and 2/3 inch wide - the same size as the RSL badge. The medallion is the work of Mr. Raymond Ewers, the well-known Australian artist, based on a suggestion by Mr. Eric Garrett, a staff artist with the Department of the Army. It has been endorsed by both the Government of New Zealand and ourselves. It will be approximately 3 inches high and 2 inches wide. The obverse of the medallion depicts Simpson and his donkey carrying a wounded soldier to safety. It will be bordered on the lower half by a laurel wreath above the word ANZAC. The reverse (the back) shows a relief map of Australian and New Zealand superimposed by the Southern Cross. The lower half will be bordered by New Zealand fern leaves. The medallion will be cast in bronze and the lapel badge will be metal of a bronze colour. For the information of the honourable members I present also a brief statement setting out the conditions of eligibility which will apply to the medallion and badge and the manner in which those desiring to receive them should apply."(https://www.awm.gov.au/encyclopedia/anzac/medallion/doc.asp, accessed 26/02/2014) Conditions of eligibility. All members of the Australian Defence Force who served during the Gallipoli Campaign are entitled to receive the ANZAC Commemorative medallion. The campaign lasted from April 25, 1915 to January 8, 1916. The award will be made for service on the Gallipoli Peninsula and service in support of the operations in an area off-shore eastward of a line drawn from Yukyeri Point (lat 39 50' 40'' N long 26 9' 45'' E) through a point in lat 39 53' N long 26 0' E thence to Cape Gremea (lat 40 35' N long 26 6' E). The award will also be available to members of philanthropic organisations and the Press who were accredited to the AIF, and to Australian members of the crews of merchant ships or hospital ships which operated in direct support within the defined area. Note: The boundary line would run just off-shore from the land masses north and south of the Dardanelles, and is estimated to be within about 5 miles from the beach at ANZAC Cove. (https://www.awm.gov.au/encyclopedia/anzac/medallion/doc.asp, accessed 26/02/2014) This Item is significance because is was only issued to members of the Australian and New Zealand Defence Force who served at Gallipoli. This Medallion is significant because of its relationship to Robert M. Serjeant who died on 28 April 2015 at Gallipoli of wounds received in Action. Bronze commemorative medal in black presentation case showing Simpson and his donkey carrying a wounded soldier to safety. A crown is situated on top of the medal, and the word ANZAC beneath the medal. The opposite side depicts Australia, New Zealand and the Southern Cross Constellation. The lower half is bordered with New Zealand Fern leaves. The commemorative medal was presented to the family of Robert M. Serjeant. Gift of David Stevens, 2014.Engraved: "1238 R.M. Serjeant"serjeant, r.m. serjeant, robert m. sergeant, anzac, medal, numismatics -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Records of Meterological Data for Ballarat 1892-1897, 1892 - 1897
A summary of meteorological data appears in the Ballarat School of Mines Annual Report for 1887 (P.35, 50). The last such summary appears in the Ballarat School of Mines Calendar 1901-2 (p58), which contains the data for the year 1900. No references have been found re names and job duties/positions of data collectors. The data was recorded by J. Matsen and A. Kiedahl.A charcoal grey hard covered, 120 page ledger, with brown leather spine and corners. The ledger has 31 special column heading, with the observed data added by hand. The column headings are: (AM) Date, Barometer, Ther. of Bar., Wet Bulb., Dry Bulb, Maxim., Minim, Rainfall, Wind, Remarks and State of Weather (PM) Date, Barometer, Ther. of Bar., Wet Bulb., Dry Bulb, Maxim., Minim, Rainfall, Wind, Remarks and State of Weather.Gold lettering on spine "Meteorological Observations: and on a glued on leather patch "School of Mines Ballarat" also in gold lettering. Written on inside front page: "Elevation of barometer 1420ft above Sea Level. To reduce barometric readings to Sea Level When Thermometer stands at 40 add 1.606 (to barometer) 45 " 1.590 50 " 1.574 55 " 1.559 60 " 1.543 65 " 1.528 70 " 1.528 80 " 1.499 85 " 1.471 90 " 1.457 95 " 1.444 100 " 1.431 Lightly hand written in pencil on the next page: "J. Matsen Feb 1891 to Feb 1894 - 3 years A. Kildahl Feb 1894 - " A circle has been place around the hottest temperature for the month. ballarat school of mines, smb, meteorology, j. matsen, a. kiedahl, kiedahl, matsen, rain, weather, meteorological data -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, New York Post, The School of Mine Quarterly: A Journal of Applied Science, 1889-1809
The School of Mines Quarterly was a jpournal of Applied Science from Columbia College, New York City.The Index to the School of Mines Quarterlu Volumes X1-XX (1900) and 32 green covered journals school of mines, new york, columbia college, schools of mines, columbia school of mines, witwatersrand goldfield, inter-continental railway, mine ropes, harbor improvememnts on the pacific coast, glycerine and artificial butter industry, transit factors for teh columbia college observatory, tables for the reducation of transit observations, ancienct methods for dividing and recoording time in japan, assay of tin, john strong newberry, standards of linnear measure, comparison of costs of electric lighting, huanchaca mine bolivia, el callao gold mine venezuela, john magnus adams, ores in saxony, hartz and rhenish prussia, hofmann apparatus, adjustment of trangulation, determination of carbonic acid in white lead, lower coals in western clearfield county pennsylvania, old telegraph mine ningham canon utah, mechanical preparation of ores, modern waterworks construction, curdling of milk, french regenerative gas furnace, irrication canals, peruvian salt mine, collection of metallurgic dust and fume, permeability of iron and steel, assay of silver, explosion in a zinc fume condenser, teaching archtectural history, liquid air, between the mine and the smelter, ballistic galvonometer, assay of telluride ores, analytical chemistry, theory and design of the masonry arch, silver pick mine wilson colorado, telegraphy and telephoney, mineralogy, morse code, michigan mining practices, titaniferous magnetites, paradox of the pantheon, rocks from wyoming, witwatersrand goldfields, gaseous sun, alternating current distribution, engineering tests on direct current electrical machinery, thomas egleston, ore dressing, frederick morgan watson, camp bird gold mine and mills, magnetic properties of iron and steel, morphology of organic compounds, antimony, structure of the starch molecule, cerrillos hills new mexico, geology, rossie lead veins, practical electrochemistry, lines of graphic statics, anistic acid by the ozidation of anniseed oil, bromate method for antimony, john krom rees, trust company of america building, helion lamp, frederick arthur goetze, mine surveying, pine wood oils, malleable cast iron, electrolytic treatment of galena, turpentine and pine oils, bluestone, ashokan dam bluestone, road resistances, oxy-gas blowtorch, mine dumps, segregation of steel ingots, masonry dam formulas, putnam county magnetic belts, gases, continuity of education, hydraulic diagrams, standardistion of potassium permanganate, sewerage discharge into sea water, modern waterworks, true column formula, slags from lead furnaces, missouri river, tempreture of gases, rocks, architectural history, modern dome, oil machine, undulations in railway tracks, irrigation engineering, cleps-tachymeters, electrical engineering, new york shales, fan pump, sucrose, isaac newton, french school of anstronomers, electrolytic polarization, benjamin bowden lawrence, diamond drilling, new york ciy water front, engineering profession ethics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Speaking Tube, Morts Dock & Engineering Co. Ltd, circa 1941
... sea mine patrol... Bass Strait patrol sea mine patrol Mine sweeper Mine clearance ...This brass speaking tube or voice pipe was used by the crew to communicate within the ship. It was recovered from the wreck of the Royal Australian Navy vessel, HMAS Warrnambool in 1948. The HMAS Warrnambool J202 was commissioned by the Royal Australian Navy for use as a minesweeper during World War II. The Bathurst Class Corvette, fitted out with a range of armaments, was launched in Sydney 1941 and was. The ship began service in Bass Strait in 1941. At the end of the year it called into its namesake city, Warrnambool, where the crew paraded for the public marching eastwards along Timor Street. A gift of books for the ship’s personnel and a plaque bearing the City of Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms were presented to the ship. The ship was involved in evacuating a family of nine from the Dutch East Indies that was later successful in its challenge of Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act (White Australia Polity). The ship had many other appointments around Australia. On 13th September 1947 HMAS Warrnambool was leading a flotilla of minesweepers in northern Queensland’s coastal waters, clearing mines previously laid to defend Australia. The ship hit a mine, which exploded and very quickly sunk the ship. Boats from the nearby ships rescued most of the seamen although one was killed at the time. The survivors were taken by the HMAS Swan II to Darwin, and they went from there to hospitals in Brisbane and Sydney. Three of these men later died from their injuries. A number of items were recovered by Navy divers in 1948 including the ship’s bell and a plaque with Warrnambool’s Coat of Arms. In 1972-75 the wreck was sold and other items were salvaged. In 1995 a memorial plaque was erected in Warrnambool near the RSL. NOTE: The RAN built a second HMAS Warrnambool FCPB204, launched in 1981 and decommissioned in 2005. There was also a steam ship SS Warrnambool built in London 1892 and broken up in 1926. [A more detailed history can be found in our Collection Record 3477.] This speaking tube is an example of communication used in the mid-1900s on board a vessel. It is significant is significant for its association with Royal Australian Navy and its vessel, HMAS Warrnambool (J202). The HMAS Warrnambool played a nationally significant role in overturning Australia’s Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (colloquially known as the White Australia policy). The ship rescued, and brought to Australia, Samuel and Annie Jacob and their family after they evacuated Dutch East India. The family was threatened with deportation and made the first successful appeal to High Court regarding that Act. The HMAS Warrnambool has - Local significance for being the namesake of the City of Warrnambool - Local significance, having docked in Warrnambool Harbour - Local significance, the crew having paraded in Timor Street, Warrnambool - State significance for its first patrol being in Bass Strait. - National significance, being present in Timor at the Japanese surrender - National significance, shown by the significance of the ship’s bell being curated as Military Heritage and Technology at the Australian War Memorial. - National significance as part of Australia’s defence force history, being one of only four Bathurst class corvettes lost while in Australian service, the only Bathurst class corvette lost after World War II, the only RAN vessel to be sunk by a mine, and associated with the last four Navy deaths of WWIISpeaking tube or voice pipe, brass, conical shape, broken off at base. Wide end has a rolled edge. Recovered from HMAS Warrnambool, sunk on 13-09-1947.flagstaff hill, maritime village, maritime museum, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, mort's dock & engineering co ltd, h.m.a.s. warrnambool, hmas warrnambool, hmas warrnambool i, hmas warrnambool j202, hmas swan ii, j202, world war ii, bathurst class corvette, royal australian navy, ran, sydney built ship, bass strait patrol, sea mine patrol, mine sweeper, mine clearance, navy divers, great barrier reef, cockburn reef, southern cross diving and salvage, warrnambool city council, cr j r astbury, mayor j r astbury, warrnambool patriotic fund, seal, coat of arms, ship’s bell, hmas warrnambool 1941, shipwreck by sea mine 1947, sinking ship, sunk ship, sea rescue, life saving, lifesaving, speaking tube, voice pipe, communication on ship, marine technology, marine equipment, minesweeper -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument, Dick Richards Interview (Transcribed from ABC Radio National's Verbatim Programme, c1985, c1985
Richard W. Richards was Principal of the Ballarat School of Mines, and was a member of the Shackleton Antarctic Expedition. He was one of seven survivors of the Ross Sea Party who were stranded in Antarctical during Ernest Shackletyon's ill-fated 1914 expedition. Dick Richards died in 1985.Eight typed pagesdick richards, richard w. richards, ballarat school of mines, antarctica, michelle rayner, ernest shackleton, ross sea, mcmerdo sound, endurance, mount hope, beardmore glacier, cape evans, captain scott, ross sea party
