Showing 37 items matching "net making"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Netting Shuttle, Early-to-mid 20th century
... net making.... The set of netting shuttles is an example of net-making tools used ...Maritime trades included making and mending nets. Netcraft skills have been taught and applied for centuries and are ongoing. Shuttles, or net needles, are used in the netting process, along with twine or cord, and a sharp knife or scissors. The twine is wound onto the shuttle and dispensed as the shuttle knots and weaves the cord to make the net. These shuttles are lightweight, compact and portable too. Nets were used on sailing ships for the crew's safety, often saving the sailor's lives in stormy seas Examples are the ship mast nets or shrouds that are wide at the base on the deck and taper to a point at the top of the mast, and railing nets that encircle the rails around the deck and prevent people and objects from rolling or falling into the sea. The shuttles were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) and Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, until 1969. Nets were an essential part of the life-saving safety equipment on sailing vessels. The set of netting shuttles is an example of net-making tools used in the 18th to 20th centuries and continues into modern times to create and repair safety equipment. The shuttles are part of the W.R. Angus Collection, which is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. Shuttles, set of three; wooden slats, one end pointed, the other a concave shape. The centre is cut-out, leaving a straight tab in the centre lengthwise. The set is part of the W.R. Angus Collection. warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, net making, net mending, net shuttle, net making tool, maritime trade, darning, shuttle, tool, 20th century, w.r. angus, weaving, netting shuttle, net craft, net needles, safety nets, safety equipment -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Spliceing Tool
... net making... netting net making sailmaker's tool Splicing tool; a spike on one ...This splicing tool is handmade on a forge. It is used for splicing in fibre and wire rope work to form a semi-permanent joint between two ropes, or parts of the same rope or steel cable. The rope is partly untwisted and then the strands are interwoven. Splices can be used to form a stopper at the end of a line, to form a loop or an eye in a rope, or to join two ropes together. Splices are preferred to knotted rope; a knot typically can reduce the strength by 20–40%, but a splice is capable of attaining a rope's full strength. This homemade, handmade splicer is an example of a tool used to splice a cable or rope, a craft that was in much need onboard a sailing ship. Splicing tool; a spike on one end and a flat blade on the other, with goose-neck centre for leverage. Handmade.warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, splicing tool, rope work, rope strands, knot making, netting, net making, sailmaker's tool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Tatting craft book, Paragon Art Needlecraft Pty Ltd, Tatting Designs, circa 1940's
... of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting.... Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". It looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. Paragon knitting, crochet and tatting books have been distributed throughout Australia since the 1930's, originally by "Paragon Art Needlework Pty Ltd" of Sydney, N.S.W. From 1946 these books were designed and printed in Australia from patterns provided by British and Australian thread companies. Consequently these patterns may also appear in similar British and American publications. Paragon Book No. 104 is an instruction book designed for the "beginner" whilst Paragon book No. 105 is designed for the more experienced tatter. The layout of these books was typical of the 1940s period when paper was in short supply. Most of the pattern books were approximately 18 cms wide by 24 cms high and some were smaller at about 13cm by 21 cms. The type used was small (about four lines of text per centimetre) which was difficult to read. This item is an excellent example of a needle work pattern book available to women in the 1940's in Australia.A soft covered, 16 page instruction book titled "Tatting Designs". It has black and white photographs and detailed patterns for tatted doilies, a tray mat, a chairback and arm rests, a cheval set, a luncheon set, collars and edgings for an underskirt, gloves and handkerchief. It is published by Paragon Art Needlecraft of Sydney.Front cover - "Paragon's No 105" "PRICE 1/3" "Tatting Designs" "Household Linens * Personal Wear" Plus a stylized drawing of a deerflagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, tatting book, tatting patterns, craft, handiwork, handcraft, needlework, shuttle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Tatting craft book, Paragon Art Needlecraft Pty Ltd, Learn to Tat, circa 1940's
... of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting.... Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". It looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. Paragon knitting, crochet and tatting books have been distributed throughout Australia since the 1930's, originally by "Paragon Art Needlework Pty Ltd" of Sydney, N.S.W. From 1946 these books were designed and printed in Australia from patterns provided by British and Australian thread companies. Consequently these patterns may also appear in similar British and American publications. Paragon Book No. 104 is an instruction book designed for the "beginner" whilst Paragon book No. 105 is designed for the more experienced tatter. The layout of these books was typical of the 1940s period when paper was in short supply. Most of the pattern books were approximately 18 cms wide by 24 cms high and some were smaller at about 13cm by 21 cms. The type used was small (about four lines of text per centimetre) which was difficult to read.This item is an excellent example of a needle work pattern book available to women in the 1940's in Australia.A soft covered 16 page instruction book with black and white photographs and detailed instructions explaining how to tat and eight tatting projects including how to make a collar and handkerchief edgings, published by Paragon Art Needlecraft of Sydney.Front cover - "PARAGON BOOK NO. 104" "PRICE 1/3" "Learn to/ TAT' Back Cover - "36/D5 E/A DO2" - handwritten in pencil flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, tatting, tatting pattern book, tatting instructions, handicraft, needlework, shuttle, tatting shuttle, paragon needlecraft, paragon craft book -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
... of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting.... Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, Ivoryflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
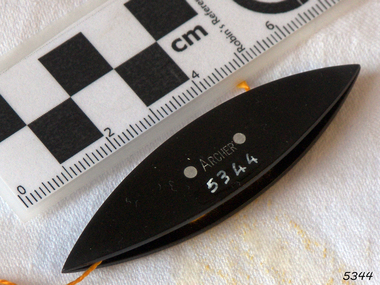 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
... of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting.... Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, Black plastic, "ARCHER" inscribed. "ARCHER" inscribed.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
... of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting.... Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, tortoise-shellflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
... of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting.... Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, ivory, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTatting Shuttle
... of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting.... Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic. The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound. The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace.Tatting Shuttle, black plastic flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tatting shuttle, handcraft, needlework -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Tatting Shuttle, Aero Needles Group Ltd, Mid to late 20th century
... of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting.... Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots.The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century.Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doylies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. A shuttle is a small tool that looks like a small boat "sailing" in and out of the thread. Tatting is called "schiffchenarbeit" in German, which means "the work of a little boat". There are two popular types of shuttles. The first has closed ends and a removable bobbin where the thread is wound around - often made from metal or plastic (as is item 8535.1). The second type has a post in the center where the thread is wound (e.g. item 8535.2). The ends of this bobbin are open but snug. Because it is constructed in two pieces, it can be made from materials like bone, ivory or mother of pearl. Shuttles hold a larger amount of thread (as compared with needles) which means fewer ends to weave in. Fishermen in the past are thought to have used large shuttles to weave cord into certain knots whilst making their fishing nets. Their methods were copied by weavers, who innovated by using threads and smaller shuttles to make lace. One type of tatting shuttle produced by "Aero" from the 1930's to the late 1960's was an anodized grey coated aluminium shuttle with a sharp pick at one end. In the 1970's it was superseded by the grey plastic "Aero" which has a removeable bobbin which you can put on the end of the shuttle to make thread winding easier and an embedded crochet hook for joining picots. The "Aero" company developed in Redditch, England - a town renowned as a centre for manufacturing needles. Firms run by Henry Milward and Abel Morrall were based in Redditch and by the 18th century Redditch was manufacturing one million sewing needles per year. Abel Morrall Ltd launched the "Aero" brand in 1936 and greatly expanded the firm's product line to include tatting shuttles and knitting needles. The classic plastic "Aero" tatting shuttle was manufactured in England from the early 1970's until the 1990's. These items are significant as examples of easily accessible handiwork tools that enabled women in the 1930s -1960s to be able to decorate and personalize their household linen and clothing.Shuttle no. 8535.1 is a beige, boat shaped plastic shuttle with enclosed ends, small round central indentations on both sides and an enclosed black removeable bobbin. The shuttle has a grooved point at one end to hold a bobbin and a small metal crochet hook at the other end. Shuttle no. 8535.2 is a beige, boat shaped metal shuttle with pointed ends that are open but snug, small round central indentations and two smaller circular markings (on both sides) and two internal posts with cream thread wound around.Shuttle no. 8535.1 - "AERO" / "ENGLAND" Shuttle no. 8535.2 - "AERO' / "ENGLAND" "39c" (written in ball point pen)flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, tatting shuttle, aero company, handwork, handwork tool, craft, handcraft, needlework, tatting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Craft book, Norma Benporath, Tatting, circa 1940's
... of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting.... Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques ...Tatting is a form of knotted lace making using thread and a small shuttle. Twisted threads are tied around or through small, pointed shuttles that can be made of bone, mother of pearl, tortoise shell, steel or plastic. This produces a stable, strong lace using simple knots of two half hitches to make rings and chains embellished with picots. The origins of tatting are not clear but early versions of decorative knotting were used by the Egyptians on their ceremonial dress. Tatting also has elements of fishermen's net making techniques and the decorative knotting that was practiced by aristocratic women from the 15th century. Tatting, as we know it today, emerged in the first half of the 19th century. The new availability of mercerised thread from 1835 encouraged a burgeoning of lace crafts of all sorts. It was known in Italy as "occhi" and in France as "la frivolite". Tatting looks fragile but is both strong and durable. An article in a column named "Wives and Daughters" published in the Star newspaper in May 1910 describes the durability of tatting lace - "there is edging and insertion still in existence that have outworn two sets of pillow slips." In the 19th century and well into the 20th century, tatting was used like crochet and knitted lace for decorative edgings, collars, doilies, tray cloths etc. At first, different tatting patterns were passed along by word of mouth from person to person, however in time, patterns regularly appeared in newspapers and magazines well into the 1950's. This book has photographs and detailed instructions for a wide range of tatted edgings and insertions suitable for household linens such as towels, doilies and tablecloths as well as patterns for whole mats. Stanley E. Mullen (a businessman) developed Semco Pty Ltd which began as a Melbourne based importation company in 1907. The first three letters of Semco's name were his initials. In 1915 it began manufacturing women's apparel, whitework and transfer patterns. In 1924 the company moved to Black Rock, Victoria and continued to produce an extensive range of needlework patterns and handcraft instruction booklets, threads etc. up until the late 1970's. Semco had a staff that included many young women. It was noted by E.J. Trait (editor of the local newspaper "Standard News") that the firm provided them with good working conditions and the correct rate of pay for women in a time of war - the starting rate for 15 year olds, mainly girls at Semco was 25 shillings per week. During World War 2, Manpower Regulations could be used to coerce workers to move into jobs that supported the war effort, but Trait argued that being employed at Semco could make this unlikely as the firm made some goods essential for the war effort. He even suggested that women be encouraged to produce needlework items (and play a part in the war effort) by sending them as presents, to the troops up north. He also heaped praise on the Semco workplace - noting that no Saturday work was the norm, allowing employees to shop and have "hair-do's" before enjoying a relaxing weekend! Semco also had a female cricket side in the women's Saturday association. After the war the firm stayed in production until the early 1990's when it was taken over by Coates-Paton Pty Ltd. Norma Benporath (1900 - 1998) was an expert in tatting techniques and taught and published extensively on the subject. She was born in New Zealand with impaired sight but cataract surgery restored 50% vision to one eye. She was inspired to learn tatting whilst watching her aunt tat and being told that tatting did not require as much sharp vision as embroidery. She quickly learnt to design her own patterns and published over 1000 tatted lace patterns between 1929 and 1952. She became a regular contributor to magazines (such as Home Beautiful) and newspapers across Australia. Her designs were also published in New Zealand, South Africa as well as the U.K. and U.S.A. When Semco, a thread manufacturer, noticed a rise in the sale of fine crochet threads, they realized they had an untapped market to explore. Norma designed a collection of tatting patterns for Semco that were used to help promote their threads. Norma also worked with Semco to produce a line of threads and shuttles specifically suited to tatting. In 1997, Norma was inducted into the "Order of Australia" for "Service to the craft of tatting as a designer and through the international publication of her patterns".This item is an excellent example of the needle work being enjoyed by women in the 1940's in Australia and the skills of the Australian designer, Norma Benporath. It is also an example of the trend that emerged for craft companies such as Semco to publish pattern books in order to advertise their own materials.A 32 page soft cover instruction book with green front and back covers showing two tatted doily designs. The book includes black and white photographs and written patterns by Norma Benporath.Front cover - "TATTING" "For / EXPERTS/ and / BEGINNERS" "By/Semco" "SEMCO INSTRUCTION BOOK" "No. 16" "WITH ILLUSTRATIONS AND INSTRUCTIONS" "9" Back cover - "FOR INSTRUCTIONS FOR WORKING SEE PAGE 22" "Published by Semco Pty. Ltd." "BLACK ROCK, 29, VIC"flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, tatting, tatting instruction book, tatting patterns, tatting shuttle, semco, semco pty ltd, norma benporath, needlework, handcrafts, household linen, craftwork -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Net Floats, 20th century
... as diamonds." A method for making cork net floats mentioned... as diamonds." A method for making cork net floats mentioned ...These net floats are handmade from lightweight cork wood and are used for suspending fishing nets in the water. Newspaper articles dated from 1848 to 1916 mention net fishing in Warrnambool's Hopkins and Merri rivers and Lady Bay. The Melbourne Argus dated January 11, 1848, published a quote from Captain Theobald of the vessels ELLEN and ELIZABETH, made on his first visit to Warrnambool "“…Fish are very plentiful here; on Christmas day a net was thrown into the Hopkins, and, after two or three draws, a boat load of beautiful fish was obtained…” The Argus, Melbourne, Sat. 29 May 1858, forwarded from The Examiner newspaper; "Extraordinary Fish. We have been presented with a very singular fish, caught by Mr. Meek in the Hopkins [Hopkins River, Warrnambool] last week. It is about three inches long, with a slate-coloured body, and a beautiful wing on each side. It was caught with other fish at night, in a net, and its eyes shone as bright as diamonds." A method for making cork net floats mentioned, in a 15th-century book, advised cutting the corks and then burning a hole through the centre of each one with a hot iron. The prepared corks were then joined together with a horsehair line. The cork's size and the line's thickness depended on the net's weight.The net floats are an example of fishing equipment used for many centuries and still in use today. In Warrnambool net fishing was a common practice from 1848 and became a livelihood for many fishermen. Net floats; cylindrical blocks of 16 corks threaded onto string with a hook-holding device at the end. warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, net floats, cork net floats, fishing, fisheries, fishing equipment, handmade, net fishing, fisheries act, andrew ferrier, william flett, warrnambool breakwater, merri river, hopkins river, captain theobald, ellen, elizabeth -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Net Floats, 20th century
... as diamonds." A method for making cork net floats mentioned... as diamonds." A method for making cork net floats mentioned ...These net floats are handmade from lightweight cork wood and are used for suspending fishing nets in the water. Newspaper articles dated from 1848 to 1916 mention net fishing in Warrnambool's Hopkins and Merri rivers and Lady Bay. The Melbourne Argus dated January 11, 1848, published a quote from Captain Theobald of the vessels ELLEN and ELIZABETH, made on his first visit to Warrnambool "“…Fish are very plentiful here; on Christmas day a net was thrown into the Hopkins, and, after two or three draws, a boat load of beautiful fish was obtained…” The Argus, Melbourne, Sat. 29 May 1858, forwarded from The Examiner newspaper; "Extraordinary Fish. We have been presented with a very singular fish, caught by Mr. Meek in the Hopkins [Hopkins River, Warrnambool] last week. It is about three inches long, with a slate-coloured body, and a beautiful wing on each side. It was caught with other fish at night, in a net, and its eyes shone as bright as diamonds." A method for making cork net floats mentioned, in a 15th-century book, advised cutting the corks and then burning a hole through the centre of each one with a hot iron. The prepared corks were then joined together with a horsehair line. The cork's size and the line's thickness depended on the net's weight.The net floats are an example of fishing equipment used for many centuries and still in use today. In Warrnambool net fishing was a common practice from 1848 and became a livelihood for many fishermen.Net floats; cylindrical blocks of 18 corks of various sizes threaded onto string.warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, net floats, cork net floats, fishing, fisheries, fishing equipment, handmade, net fishing, fisheries act, andrew ferrier, william flett, warrnambool breakwater, merri river, hopkins river, captain theobald, ellen, elizabeth -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Net Floats
... as diamonds." A method for making cork net floats mentioned... as diamonds." A method for making cork net floats mentioned ...These net floats are handmade from lightweight cork wood and are used for suspending fishing nets in the water. Newspaper articles dated from 1848 to 1916 mention net fishing in Warrnambool's Hopkins and Merri rivers and Lady Bay. The Melbourne Argus dated January 11, 1848, published a quote from Captain Theobald of the vessels ELLEN and ELIZABETH, made on his first visit to Warrnambool "“…Fish are very plentiful here; on Christmas day a net was thrown into the Hopkins, and, after two or three draws, a boat load of beautiful fish was obtained…” The Argus, Melbourne, Sat. 29 May 1858, forwarded from The Examiner newspaper; "Extraordinary Fish. We have been presented with a very singular fish, caught by Mr. Meek in the Hopkins [Hopkins River, Warrnambool] last week. It is about three inches long, with a slate-coloured body, and a beautiful wing on each side. It was caught with other fish at night, in a net, and its eyes shone as bright as diamonds." A method for making cork net floats mentioned, in a 15th-century book, advised cutting the corks and then burning a hole through the centre of each one with a hot iron. The prepared corks were then joined together with a horsehair line. The cork's size and the line's thickness depended on the net's weight.The net floats are an example of fishing equipment used for many centuries and still in use today. In Warrnambool net fishing was a common practice from 1848 and became a livelihood for many fishermen.Cork net floats; lengths of 15 various sized cylindrical blocks of cork threaded onto string. warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, net floats, cork net floats, fishing, fisheries, fishing equipment, handmade, net fishing, fisheries act, andrew ferrier, william flett, warrnambool breakwater, merri river, hopkins river, captain theobald, ellen, elizabeth -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Net Floats, 20th century
... as diamonds." A method for making cork net floats mentioned... as diamonds." A method for making cork net floats mentioned ...These net floats are handmade from lightweight cork wood and are used for suspending fishing nets in the water. Newspaper articles dated from 1848 to 1916 mention net fishing in Warrnambool's Hopkins and Merri rivers and Lady Bay. The Melbourne Argus dated January 11, 1848, published a quote from Captain Theobald of the vessels ELLEN and ELIZABETH, made on his first visit to Warrnambool "“…Fish are very plentiful here; on Christmas day a net was thrown into the Hopkins, and, after two or three draws, a boat load of beautiful fish was obtained…” The Argus, Melbourne, Sat. 29 May 1858, forwarded from The Examiner newspaper; "Extraordinary Fish. We have been presented with a very singular fish, caught by Mr. Meek in the Hopkins [Hopkins River, Warrnambool] last week. It is about three inches long, with a slate-coloured body, and a beautiful wing on each side. It was caught with other fish at night, in a net, and its eyes shone as bright as diamonds." A method for making cork net floats mentioned, in a 15th-century book, advised cutting the corks and then burning a hole through the centre of each one with a hot iron. The prepared corks were then joined together with a horsehair line. The cork's size and the line's thickness depended on the net's weight.The net floats are an example of fishing equipment used for many centuries and still in use today. In Warrnambool net fishing was a common practice from 1848 and became a livelihood for many fishermen.Cork net floats; a set of two cylindrical blocks of varying sizes threaded onto strings.warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, net floats, cork net floats, fishing, fisheries, fishing equipment, handmade, net fishing, fisheries act, andrew ferrier, william flett, warrnambool breakwater, merri river, hopkins river, captain theobald, ellen, elizabeth -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPostcard - Photograph, Nucolorvue Productions Pty Ltd, greetings from Diamond Creek, n.d
Diamond Creek Bini Shell Community venue Built in 1979 in Diamond Creek opposite the hotel using a construction method invented by Dante Bini. A net of flexible steel rods were laid on the building’s circular base, on the top of a fabric bladder. Concrete was poured onto the mesh and a sealed cover laid over the concrete making a sandwich of cover, bladder and mesh. Compressed air was pumped into the bladder and the sandwich slowly began to rise and become a massive self-supporting dome. The inflation of the dome attracted crowds of onlookers many from various technical schools, VIPs and the famous football doctor, Donald Cordner. An opening night dinner was held to celebrate the construction and the Diamond Creek Bini Shell was used as a community venue for over ten years including for the Town Fair. The Shell was closed for safety reasons after a Bini Shell in another State had chunks of concrete fall off the dome due to a construction fault. At the Diamond Creek Town Fair in 1991 the demolition of the Bini Shell was an item on the Town Fair’s program. Information: Kevin Patterson, Nillumbik Historical Societybini shell, diamond creek community centre, nu-color-vue, postcard -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Manufactured Glass, jar of Mustard Ointment 'Rawleigh's;, mid 20thC
WT Rawleigh (1870-1952) Freeport USA began in 1889 the direct selling method to sell his products, travelling around on horse and cart in the early days from house to house selling his medicines and other lines. Rawleigh's wide range of products includes: Medicinal, Nutritional, Gourmet, Homecare, Personal Care, Animal & Plant Care Since 1889, millions of families around the world have learned to rely upon and keep Rawleigh's reliable medicines and other products on hand ready for emergencies to relieve sickness, pains, injuries and for their daily needs. By 1920, young Rawleigh had built the biggest manufacturing organisation in the world. Mr Floyd George Rawleigh who was the son of David Rawleigh, W.T.Rawleigh's brother, came to Australia, with Mr Jackson, in 1931 and set up the Rawleighs Company Business . Generations of Australians, Canadians and Americans grew up waiting for The Rawleigh Man to arrive at their front door with his sample case of goodies to add spice to their life and to heal their ailments. In World War II, most Australian soldiers posted overseas carried a tin of Rawleigh Antiseptic Salve in their kits to treat wounds and ward off infection The Rawleigh Man brought to family front doors the best materials money could buy from around the world: spices from Sumatra, Java, China, India, Africa, the West Indies; black pepper from the island of Ponapai; lemon and orange oils from California and Sicily and Vanilla from Madagascar and Java; high grade coffee beans from the Andes. Most of the herbs, roots, barks and buds used in making cough medicines and tonics came from Europe, India, Ceylon, China, North America, the West Indies, Jamaica, Honduras and Asia. From Japan came camphor and menthol for making medicines. From Tavenui, the Garden Island of Fiji, came the food grade coconut oil for Rawleigh's gold medal winning Coconut Oil Soap. Rawleigh products are still only available from Rawleigh men and women who carry on the time-honoured tradition of the Rawleigh company to give individuals a go at developing their own business supplying products to people in their homes. Only now they are also doing it in cyberspace. A clear glass jar with a metal screw lid containing Mustard Ointment made by W.T. Rawleigh Co. Ltd. .Melbourne Lid ; Rawleigh’s Front ; Rawleigh’s / Net WT. / 1 ½ oz / COMPOUND / MUSTARD OINTMENT / WILL NOT BLISTER /preferable to Mustard Plaster / MNUFACTURED BY / The W, T. Rawleigh Co Ltd / MELBOURNE. / Left side ; DIRECTIONS …….. , / Right side ; Useful pharmacy, medicines, mustard ointment, w.t. rawleigh company ltd., hospitals, nursing, containers, moorabbin, bentleigh, cheltenham, melbourne, respiratory diseases -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBook - Country Women's Association of Victoria, Glove-Making at Home by Frances Staite, 1927
The Tawonga branch of the C.W.A. commenced on the 7th Feb. 1946 and often combined activities with the other branches in the Kiewa Valley. The C.W.A. aimed to improve health, welfare and education for women and children in the country. Doing craft helped the women achieve these aims as they would get together and learn from each other. Women living in Tawonga were mostly on farms and, in 1946, when the branch commenced would have been feeling more remote with WW11 having an effect on available workers and the well being of the women and children.Hard covered book with a yellow and black sleeve. The sleeve has a picture of a lady sitting on a lounge chair under a lamp admiring her glove. Inserted in the book is a page with further instructions on glove making. The book is bound and has 90 pages. The first and last 3 pages consist of advertising.Cover page "Country Womens' Association / of Victoria" stamp with purple ink Title: Clove-Making / At Home / by Frances Staite / Sir Isaac Pitman & Sons, Ltd 5/- net.tawonga. cwa. gloves. craft. country women's association of victoria -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTextile - Twine, 20th century
... their skills for other work such as net making. Warrnambool Shipwreck ...Sailmaker's twine is usually stored on a reel. It is wax coated and ready to use. The twine is made from strands of fibres that are plied together. The wax waterproofs the twine and smooths out the fine hairs of the fibres, making it easier to work with. The waxed twine helps prevent the ends of the rope work from fraying. Sailmakers use twine and needles to sew sails and many other canvas items such as bags and covers. Special tools, equipment, benches and seats are needed to work with the large heavy and thick pieces of canvas. Sometimes the sailmaker with have special-purpose tools made for his unique work. The place of work on shore is often called a sailmaker's loft. However, sailmakers also work on the job, on sailing ships and boats. This twine is an example imperative equipment for sailmakers. Sailmaking was an essential trade in the shipping industry of the 17th to 19th and early 20th centuries. Sailmakers were often part of a ship's crew, making repairs as needed and using their skills for other work such as net making.Twine; reel of brown waxed sailmaker's twine.warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, twine, waxed twine, sailmaker's twine, sailmaker's equipment, sailmaking, canvas work -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Demolishing the Bini Shell at Diamond Creek, 1991, 1991
In 1978 Diamond Valley Shire recognised the need for a new public hall in Diamond Creek. Council considered the Bini shell form of construction which was in operation overseas and in use in New South Wales as libraries, gymnasiums, sports centres and multi-purpose centres. The Council gave the go-ahead. A site was chosen opposite the Hotel and close to the railway line. One day in - the following year, in 1979, activity stood still in Diamond Creek as school children and other excited spectators watched the one-hour inflation of the Bini Shell. This unusual method of construction was invented by Italian industrial designer and architect Dante Bini. The construction pneumatically raises a level of reinforced concrete from ground level which has not been set, using an internal balloon. The inner membrane inflates and compresses the mesh and concrete against the outer membrane. A net of flexible steel rods was laid on the building’s circular base, on the top of a fabric bladder. 300 tonnes of reinforced concrete were poured onto the mesh and a sealed cover laid over the concrete making a sandwich of cover, bladder and mesh. Compressed air was pumped into the bladder and the sandwich slowly began to rise and become a massive self-supporting dome. After inflation and removal of the outer membrane workmen filled in any holes. It was some days before pneumatic drills pecked out the first opening. The ceiling of the concrete dome was lined with fluffy insulating material. The dome was 36 metres in diameter at the base and 12 metres high in the centre with a usable floor space of 670 square metres. An opening night dinner was held to celebrate the new facility on March 12, 1980. Shire President Ron Pata made a speech and unveiled a plaque. It was the first public building in Victoria to be erected using the Bini Shell design method of construction The facility could cater for up to 400 people and in 1980 a fee for use was $100 for up to 200 people, $150 for up to 300 people and $200 for up to 400 people. For the next ten years or so, locals attended the hall for marital arts classes, basketball and netball games and school discoes and various other activities. After pieces of concrete fell off a Bini shell interstate due to a construction fault, the Council closed the centre. Demotion took place during the Diamond Creek Town Fair in 1991, as part of the annual Town Fair’s program. Research by L.P. Jan 2022This was the first public building in Victoria to be erected using the Bini Shell design method of construction.Colour photograph1991, diamond creek, bini shell, demolition, oval -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Fred Mitchell, Bini Shell at Diamond Creek, 1983, 1983
In 1978 Diamond Valley Shire recognised the need for a new public hall in Diamond Creek. Council considered the Bini shell form of construction which was in operation overseas and in use in New South Wales as libraries, gymnasiums, sports centres and multi-purpose centres. The Council gave the go-ahead. A site was chosen opposite the Hotel and close to the railway line. One day in - the following year, in 1979, activity stood still in Diamond Creek as school children and other excited spectators watched the one-hour inflation of the Bini Shell. This unusual method of construction was invented by Italian industrial designer and architect Dante Bini. The construction pneumatically raises a level of reinforced concrete from ground level which has not been set, using an internal balloon. The inner membrane inflates and compresses the mesh and concrete against the outer membrane. A net of flexible steel rods was laid on the building’s circular base, on the top of a fabric bladder. 300 tonnes of reinforced concrete were poured onto the mesh and a sealed cover laid over the concrete making a sandwich of cover, bladder and mesh. Compressed air was pumped into the bladder and the sandwich slowly began to rise and become a massive self-supporting dome. After inflation and removal of the outer membrane workmen filled in any holes. It was some days before pneumatic drills pecked out the first opening. The ceiling of the concrete dome was lined with fluffy insulating material. The dome was 36 metres in diameter at the base and 12 metres high in the centre with a usable floor space of 670 square metres. An opening night dinner was held to celebrate the new facility on March 12, 1980. Shire President Ron Pata made a speech and unveiled a plaque. It was the first public building in Victoria to be erected using the Bini Shell design method of construction The facility could cater for up to 400 people and in 1980 a fee for use was $100 for up to 200 people, $150 for up to 300 people and $200 for up to 400 people. For the next ten years or so, locals attended the hall for marital arts classes, basketball and netball games and school discoes and various other activities. After pieces of concrete fell off a Bini shell interstate due to a construction fault, the Council closed the centre. Demotion took place during the Diamond Creek Town Fair in 1991, as part of the annual Town Fair’s program. Research by LP January 2022This was the first public building in Victoria to be erected using the Bini Shell design method of construction.Digital copy of colour photographfred mitchell collection, 1983, bini shell, diamond creek -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Black and White, Frank Wright, Laura Wright, 1924, 2/1/1924
Laura Wright was the sister of Frank Wright who was a renown resident of Smeaton, where they was born. They lived at Laura Villa, and attended Smeaton State School with their siblings. Their father William was a gold miner and their mother's name was Sarah. Their family won many singing and instrumental awards. Frank was tutored by Percy Code and was awarded a gold medal for the highest marks in the ALCM examinations in the British Colonies at the age of seventeen years. He became the Australian Open Cornet Champion by the age of eighteen. A year later, Frank conducted the City of Ballarat Band, and later the Ballarat Soldiers’ Memorial Band. He formed the Frank Wright Frisco Band and Frank Wright and his Coliseum Orchestra. These bands won many South Street awards, and Frank as conductor won many awards in the Australian Band Championship contest. In 1933 Frank Wright sailed to England to conduct the famous St Hilda’s Band and was later appointed Musical Director of the London County Council, where he organized many amazing concerts in parks, in and around the London district. He was made Professor of Brass and Military Band Scoring and conducted at the Guildhall of Music and Drama. Frank was often invited to adjudicate Brass Band Championships around Europe, in Australia, including South Street and in New Zealand. The Frank Wright Medal at the Royal South Street competition is awarded to an individual recognized as making an outstanding contribution to brass music in Australia. Laura married Mr W.M. Ritchie and lived in BallaratBlack and white photograph of a woman standing beside a net curtained window. The sunlight illuminates the face and torso. There is a marked contrast between the light and the darkened room. The woman is Laura WrightWritten in pen on the back - Laura Wright, 2/1/24, F.W.laura wright, frank wright, cornet, conductor -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTextile - Jug Cover, ca 1910
The jug cover was made by diagonally overlapping two squares of net fabric and stitching them together. The beads on the cover are used to weigh the cover down and keep it on the jug. In the Words of donor, Betty Stone, … “These crocheted and embroidered articles cover a period of three generations- ie. Sarah (nee Chamberlain) Lees, Ann (nee Lees) Dale, and Daisy Elvena (nee Dale) Welsh. All three were accomplished needlewomen; also, both Sarah Lees (born 1844) and her daughter, Ann (b 1865) crocheted a wide variety of articles for use in their homes. A few examples of these items have survived the years.” It was a tradition for brides to have a 'glory box' containing linen and embroidered articles to take to their new home. Many of the items were made by Daisy, a skilled dressmaker. Daisy began her apprenticeship at two shillings and sixpence per week at Miss A. E. Emery's dressmaking establishment at 150-152 Liebig Street, Warrnambool. Considered to be the leading house of fashion in Warrnambool, Miss Emery employed about eight young women who worked long hours to sew elaborate gowns for clients, including wives of graziers who would attend the race carnivals and social functions in Warrnambool. (NOTE: For additional information please refer to my book Pioneer and Places- A History of Three Warrnambool Pioneering Families ie. Chamberlain, Dale and Lees families)This item is associated with the Warrnambool pioneer families of Chamberlain, Dale and Lees. These families are listed in the Pioneers' Register for Warrnambool Township and Shire, 1835-1900, published by A.I.G.S. Warrnambool Branch. The item is significant for its association with a ‘glory box’ or hope chest, a tradition of single ladies making and collecting a range of linen and other domestic items in preparation for their future marriage. The item is a fine example of early 20th-century needlework and handmade domestic items.Jug cover; net fabric eight-point star shape, with white crocheted edges and red, white and green beads on each point. Part of the Chamberlain Dale Lees Collection.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, chamberlain family, dale family, lees family, betty stone, warrnambool pioneer, warrnambool genealogy, wangoom, chamberlain dale lees collection, glory box, handmade, craft, manchester, linen, haberdashery, needlework, crochet, miss a.e. emery dressmaker, jug cover, beaded cover, beaded jug cover -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTextile - Jug Cover, ca 1910
The jug cover was made by overlapping two squares of net fabric and joining them together. The beads on the cover’s border are used to weigh the cover down and keep it on the jug. In the Words of donor, Betty Stone, … “These crocheted and embroidered articles cover a period of three generations- ie. Sarah (nee Chamberlain) Lees, Ann (nee Lees) Dale, and Daisy Elvena (nee Dale) Welsh. All three were accomplished needlewomen; also, both Sarah Lees (born 1844) and her daughter, Ann (b 1865) crocheted a wide variety of articles for use in their homes. A few examples of these items have survived the years.” It was a tradition for brides to have a 'glory box' containing linen and embroidered articles to take to their new home. Many of the items were made by Daisy, a skilled dressmaker. Daisy began her apprenticeship at two shillings and sixpence per week at Miss A. E. Emery's dressmaking establishment at 150-152 Liebig Street, Warrnambool. Considered to be the leading house of fashion in Warrnambool, Miss Emery employed about eight young women who worked long hours to sew elaborate gowns for clients, including wives of graziers who would attend the race carnivals and social functions in Warrnambool. (NOTE: For additional information please refer to my book Pioneer and Places- A History of Three Warrnambool Pioneering Families ie. Chamberlain, Dale and Lees families)This item is associated with the Warrnambool pioneer families of Chamberlain, Dale and Lees. These families are listed in the Pioneers' Register for Warrnambool Township and Shire, 1835-1900, published by A.I.G.S. Warrnambool Branch. The item is significant for its association with a ‘glory box’ or hope chest’, a tradition of single ladies making and collecting a range of linen and other domestic items in preparation for their future marriage. The item is a fine example of early 20th-century needlework and handmade domestic items.Jug cover, square shape, net fabric with blue beads along the crocheted edge. Part of the Chamberlain Dale Lees Collection.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, chamberlain family, dale family, lees family, betty stone, warrnambool pioneer, warrnambool genealogy, wangoom, chamberlain dale lees collection, glory box, handmade, craft, manchester, linen, haberdashery, needlework, crochet, jug cover -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - black and white, Frank Wright Playing Tennis, 10/1928
Frank Wright was a renown resident of Smeaton, where he was born. He lived at Laura Villa, and attended Smeaton State School. His father William was a gold miner and his mother's name was Sarah. Their family won many singing and instrumental awards. Frank was tutored by Percy Code and was awarded a gold medal for the highest marks in the ALCM examinations in the British Colonies at the age of seventeen years. He became the Australian Open Cornet Champion by the age of eighteen. A year later, Frank conducted the City of Ballarat Band, and later the Ballarat Soldiers’ Memorial Band. He formed the Frank Wright Frisco Band and Frank Wright and his Coliseum Orchestra. These bands won many South Street awards, and Frank as conductor won many awards in the Australian Band Championship contest. In 1933 Frank Wright sailed to England to conduct the famous St Hilda’s Band and was later appointed Musical Director of the London County Council, where he organized many amazing concerts in parks, in and around the London district. He was made Professor of Brass and Military Band Scoring and conducted at the Guildhall of Music and Drama. Frank was often invited to adjudicate Brass Band Championships around Europe, in Australia, including South Street and in New Zealand. The Frank Wright Medal at the Royal South Street competition is awarded to an individual recognized as making an outstanding contribution to brass music in Australia.1). Black and white photograph of a man dressed in light coloured trousers and a white short sleeve shirt, serving a tennis ball. Situated on a tennis court with buildings in the background. The man is Frank Wright. 2). Black and white photograph of a young man dressed in tennis whites and a jacket, holding a tennis racquet and leaning against the net on a tennis court. In the background is a hedge topped timber fence with the roof of a house behind. The man is perhaps Frank Wright or a friend.frank wright, conductor, tennis, tennis racquet -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Clothing - Clothing, baby's lace bonnet, c1900
This baby’s bonnet is an example of the lace making and dressmaking skills of the early settler women in the Shire of Moorabbin A hand made lace and net lined baby's bonnetdressmaking, lacework, craftwork, lace, mooabbin, bentleigh, cheltenham, early settlers, pioneers, market gardeners -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)McKenzie's Excelsior Baking Powder
Tin printed in gold and blue text and with a white lid.FRONT: Phosphate Aerator - McKenzie's Excelsior - Baking Powder - 4 ozs. Net - Clifford, Love McKenzie Pty. Ltd. DIRECTIONS FOR USE - McKenzie's "EXCELSIOR" Baking Powder is produced under careful laboratory control to ensure reliable results. It may, for this reason, be used with complete confidence in all climates. Use this Making Powder as required by your Recipe. The great advantage, however, of using Baking Powder and Plain Flour instead of Self-Raising Flour, is that you can vary the amount of rising if you wish to do so. To make your own Self-Raising Flour, thoroughly mix together 1-ozs (two level dessertspoons) of "EXCELSIOR" Baking Powder and 1-lb. (flour and a half cups) of Plain Flour, and sift several times through your fFour Sifter. USE A DRY SPOON - KEEP THE TIN CLOSED - Clifford Love McKenzie Pty. Ltd. Australia -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumBottle of preserver, Douglas Packing Company Ltd, 1927
Small brown glass bottle with aluminium lid and damaged paper label depicting jars and fruit in black and yellow.Certo For Making Jams & Jellies concentrated fruit pectin. 8 oz net. Douglas Packing Company Ltd Coburg. -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumDomestic object - LACE MAKER
Includes; .1 Lace Maker .2 3 x samples of lace .3.Bill of Sale dated 7 March 1916 payment received with thanks C.H Coombe .4 Price list of Torchon Lace Co.229 Collins Street, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia .5The Torchon Lace Making Booklet, 12th edition, copyright 1904 .6 Letter (undated) offering The complete lacemaking outfit .7 Document with customer reviews .8 Booklet "The Torchon Lace Maker (illustrated) Copy right 1904 All rights Reserved .9 30 x cardboard lace making patterns No. 20 Torchon Edging, Diamond Point Edging, Net Ground, 2 x Round Point Edging, Edging No. 11, Diamond Antique Edging, Jewel Insertion, Smyrna Edging, Rose Ground, Edging No. 24, Insertion No. 22, No.5 Twisted Hole Ground with "Spider". Spider insertion, Copenhagen Lace, Plain Hole Ground, Ornamental Ground Pin Check, Block Lace, Spider Lace, No. 18 Medici Lace, ZigZag Lace, Wide Antique Lace, Diamond Antique Edging, Block Lace, Jewel Insertion, Edging No. 24, Spider Lace, Zig-Zag Lace, Medici Lace, No. 21 Maltese Lace. .10 .35 x bobbins (8 with cotton) .11 2 x cream coloured lace doyleys with square linen damask machine sewn into the centre of the doyley. .12 Large wooden cotton reel with cream coloured lacemaking thread .1 White sticker, "63" printed in black placed on Lace Maker .12 Eagley imprinted into one end of the reellace making machine, christina mckenzie lawrence -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumTextile - Cook Well Self Raising Flour Bag
These domestic kitchen bags were donated to the National Wool Museum by Lila Gore. Lila donated Children’s Clothing (RGE 8324) to the museum in 2022 and at her time of donating, inquired as to whether the museum would also be interested in these bags she had been collecting. Lila said there was no reason as to why she was saving the bags, other than she liked the art works and thought they were too good to end up in landfill. She had thought perhaps she would make something out of the bags, or perhaps give the bags to a friend to make something. When Lila was donating the Children’s Clothing to the museum, she thought that the National Wool Museum would be the perfect home for the bags. Domestic kitchen bags such as these date from the late 19th century through the mid-20th century. They were used at home, usually by women, containing household items which would not spoil, such as flour, sugar, animal feed, seeds, and other commodities. In modern times a trip to the supermarket is a daily chore, in the past however, these trips happened far less often, with big sacks such as these a large reason why. In the rural US and Canada, Feed sack dresses and Flour sack dresses, were an iconic part of rural life from the 1920s through the Great Depression, World War II, and post-World War II years. Australia also reused these sacks, typically for making wagga style blankets, but re-use for clothing was not unusual.Calico bag with yellow and blue graphic text on front.Front: COOK-WELL \ SELF- \ RAISING \ FLOUR \ PREPARED WITH \ PHOSHATE AERATOR \ HENRY BERRY & Co (A/S??Ltd) \ 568 580 COLLINS STREET \ MELBOURNE \ NET 7 LBSwagga, flour, oats, bag, calico, lila, gore, depression, war, kitchen
