Showing 13 items matching "seamer foot"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
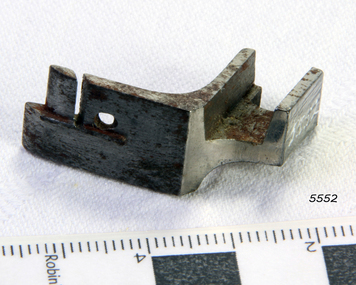
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Seamer Foot, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
... Seamer Foot...seamer foot...Seamer foot; feller single seamer for a Wertheim sewing... Sewing Machines sewing machine foot seamer foot domestic machines ...This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Seamer foot; feller single seamer for a Wertheim sewing machine. Made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, seamer foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Braider foot, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
... seamer foot... Sewing Machines sewing machine foot seamer foot domestic machines ...This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin.The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim.Wertheim braider; an accessory for a Wertheim sewing machine. Made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, seamer foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Sewing Machine Foot, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
... seamer foot... Sewing Machines sewing machine foot seamer foot domestic machines ...This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Foot accessory, metal, for a Wertheim sewing machine. Made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, seamer foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Binder, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
... seamer foot... Sewing Machines sewing machine foot seamer foot domestic machines ...This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin.The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Adjustable binder for a Wertheim sewing machine. Made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, seamer foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion, binder -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Tool Part, Joseph Wertheim, ca. 1891
... seamer foot... Sewing Machines sewing machine foot seamer foot domestic machines ...This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Tool part for a Wertheim sewing machine. Made by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, sewing machine foot, seamer foot, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Clothing - Stockings, 1940s
... and top and back and foot seams. Nylon legs. Red cross stitch... with lisle feet and top and back and foot seams. Nylon legs. Red ...A pair of medium-tan Service Stockings with lisle feet and top and back and foot seams. Nylon legs. Red cross stitch line at top.Wonderfoot foot comfort series service weight nylon and lisle. Prestige 9-1/2costume accessories, female, costume, female underwear -
 Victorian Interpretive Projects Inc.
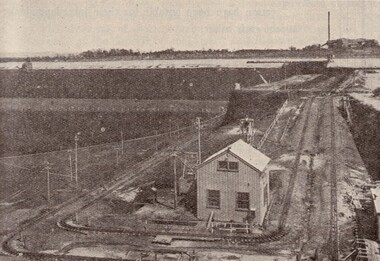
Victorian Interpretive Projects Inc.Image, Yallourn, 1934
... down another 90 feet to the bottom of the 180 foot seam.... of the 180 foot seam. Yallourn, 1934 Image ...The coal from this open-cut mine is used to generate electricity for the State of Victoria. in 1934 two thousand miles of high tension transmission lines conveyed energy from a system of inter-linked power stations to the whole Melbourne metropolitan area, as well as to nearly 170 rural centres. Black and white image of the western end of the Yallourn open-cut in 1934. the bucket dredge on surface is reaching down 90 feet, on which level there is another similar dredge going down another 90 feet to the bottom of the 180 foot seam.yallourn, electricty, power, coal, open-cut, dredge -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLeisure object - Toy Soldier, circa 1878
The toy soldier is a relic from the shipwreck of the LOCH ARD in 1878. It has a companion piece in the Flagstaff Hill collection. The toy soldier is unpainted, but the style of uniform, and the weapons carried (a musket and a basket-handled cutlass), indicate it is a representation of the Napoleonic Wars period from the beginning of the nineteenth century. Mass-produced toy soldiers made of cast metal (lead or tin) became popular during the 1800s. Heyde of Germany manufactured silhouette-shaped flat toy soldiers early in the century. Mignot of France released three-dimensional solid figures and later around 1893 W. Britain, a toy company became known for its die-cast lead toy soldiers. These innovations were designed to make sets of toy soldiers more affordable for middle and lower-class children, extending the market beyond the intricately made and hand-crafted replicas that were the preserve of the rich in the eighteenth century. Wooden military figures, specially carved and unpainted ones, were therefore not particularly common at the time when the Loch Ard foundered on Victoria’s southwest coast. Mignot was the first to sell unpainted soldiers, leaving their customers to fill in the colours according to their own patriotic preferences. It is, therefore, possible the two figures in the Flagstaff Hill collection were part of a new set intended for sale, rather than part of a passenger’s existing collection. Loch Ard History: The Loch Ard got its name from ”Loch Ard” a loch that lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic. The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curle & Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold their position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as Lochard Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the Lochard tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of Lochard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up into Lochard Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck, it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artifact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register.The toy soldier represents a 19th-century child's interest in military history. The item is one of two toy soldiers recovered from the Loch Ard in Flagstaff Hill's collection. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulations of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck of which the subject items are a small part. The collections of objects give us a snapshot of how we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history, allowing us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes. Through is associated with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.An unpainted, cream-coloured toy soldier, recovered from the Loch Ard. The figure wears a Napoleonic Wars-era uniform, a plumed helmet, a short jacket with tails, bib-front trousers with button closure, straps crossed at the front and back, and epaulettes. The figure is in marching posture with one foot extended forward, and is bearing a musket at the slope-arms position, with a sabre or cutlass slung behind. It is unable to stand on its own. There are reddish-brown and orange-brown stains on the head and body. The body has seams along both sides that are uneven at the lower leg. There is a hole in the back and the inside is hollow. The material has a rough texture.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch ard, toy soldier, napoleonic uniforms, military toy, moulded soldier -
 Blacksmith's Cottage and Forge
Blacksmith's Cottage and ForgeStockings-box
Bacchus Marsh had a prestige Hosiery Factory for a short time approximately 1945/1950. Not known where this pair were made but possibly bought at Shepards shop (written on box).An example of local history, factory and shop.Cream cardboard box containing one pair of used nylon stockings, light brown with a seam on back. One stocking has a ladder and is mended with nail varnish. Re-inforced foot.Side of box-T5 Denier nylons "enchantment 10" Top of box-"Prestige- Parallels" Ultra Sheer Nylons/ Shepards Bacchus Marsh WA/Abox, stockings, prestige, shepards, nylons -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Clothing - PAIR OF SPATS, 1900-1920
Gentleman's brown suede fabric spats, bound at seams and lower edge in .75 cm leather strips. Four one cm, diameter plastic buttons at outer ankle, with four stitched buttonholes. Centre front seam is lined with a leather strip, opening edges lined with cotton tape, and finely machine stitched. A two cm wide and 16.5 cm long strap passes under the instep, and fastens with a metal buckle on the outside of the foot, leather -tapered 2.5 cm to 1.5 cm.H.E.Randall Ltd (written on fine leather label, six cm long on inside of spat. Lettering in gold. ( An English Company).costume, male footwear, spats -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayEquipment - Victorian Railways Carriage Foot Warmer
During prestige, long distance train journeys some carriages had air-conditioning, and the majority of passengers had to brave unheated carriages. To offer some comfort during the winter months, the non-air-conditioned carriages were provided with footwarmers. These were metal containers roughly 100 mm thick and 300 mm wide, and about 750 mm long, which were filled with salt crystals (concentrated crystalline hydrated sodium acetate). The footwarmers were covered by sleeves of thick canvas, and two footwarmers were usually placed in each compartment of non-air-conditioned carriages. To activate the chemicals, the footwarmers were heated almost to boiling point. This was done by removing the canvas sleeves and placing the footwarmers in a large bath of very hot water. After they had been heated, they were removed from the bath and the sleeves refitted. They were then ready to be placed in the carriages. The McLaren patent foot warmer was used on railways in New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria and South Australia as well as South Africa and New Zealand. It was during the 1901 royal visit by the Duke and Duchess of Cornwall that these foot warmers were first used in New Zealand in the royal carriage. Before railway carriage heating was introduced, McLaren patent foot warmers were placed on the floor of New South Wales government railway carriages from 1891 to provide a little passenger comfort. The rectangular steel container worked a bit like a hot water bottle but instead of water contained six and a half kilograms of loosely-packed salt crystals, (concentrated crystalline hydrated sodium acetate). This was permanently sealed inside the container with a soldered cap. After the foot warmer was heated in vat of boiling water for about one and a quarter hours the crystals became a hot liquid. (The melting point for sodium acetate is 58 degrees). There was a whole infrastructure of special furnaces set up at stations for the daily heating of foot warmers. By 1914 the Victorian railways had 4,000 foot warmers in service and by 1935 there were 33 furnaces at principal stations to heat them. After about 10 hours the container was picked up by the handle and given a good vertical shake which helped the cooled liquid reform into a solid mass of hot crystals. Staff or sometimes passengers shook them en route when the foot warmers began to get cold. However, as they were heavy this was only possible by fit and agile passengers. At the end of the journey the containers were boiled again for reuse on the next trip. Sodium acetate railway foot warmers were introduced in Victoria in 1889, Adelaide to Melbourne express in 1899. "Shaking up" on this service took place at Murray Bridge and Stawell on the tip to Melbourne and at Ballarat and Serviceton on the trip to Adelaide. The use of foot warmers began to decline in New South Wales from the 1930s with the first trial of carriage air-conditioning in 1936, steam heating from 1948 ad LP gas heating from 1961. By the early 1960s the main services using foot warmers were the overnight mail trains. info from : http://www.powerhousemuseum.com/collection/database/?irn=67564#ixzz4UBNzVf6t Under Creative Commons License: Attribution Non-Commercial There was a whole infrastructure set up at stations for the daily heating of foot warmers in special furnaces. In Victoria alone in 1935 there were 33 heating works.Historic - Victorian Railways - Carriage Heater - Foot warmerA rectangular-shaped stainless steel casing with a welded seam down the back and welded ends. There is a handle at one end for carrying and shaking. Inside the foot warmer are two baffle plates and three trays to contain the sodium acetate. There was a cast-iron ball in each internal compartment. puffing billy, victorian railways, carriage haeter, foot warmer, passenger comfort, station furnace, railway ephemera, early heating methods -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Clothing - Stockings, 1940s
A pair of Service Brown stocking with reinforced foot and top in lisle and leg of nylon with back seams.H Loyalty Service Weight Nylons by Holeproof 9-1/2costume, female, female underwear -
 8th/13th Victorian Mounted Rifles Regimental Collection
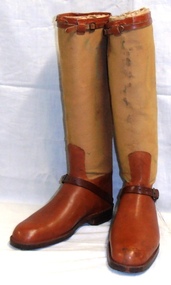
8th/13th Victorian Mounted Rifles Regimental Collectionboots, 1930 circa
Officer's stable boot worn by Brigadier Geoffrey Austin Street MC who served in WWI at Gallipoli and on the Western Front. Following the war he was placed on the Reserve of Officers. He returned to military service in 1931 as Squadron Commander in the 4th Light Horse. He was promoted to the command of the regiment after l8 months' service, and finally to the command of the Third Cavalry Brigade which included the 8th Light Horse Regiment. Brigadier Street had entered Federal Parliament in 1934 and in November 1938 was seconded from military duties to serve as Minister for Defence in the Lyons Government . He was serving in this capacity in the Menzies government when he was killed in an air crash near Canberra on 13 August 1940.Representative example of officer's stable boots from the 'between the wars' period. Well preserved example of the boot makers art, complete and in good condition. Owned by well known Australian soldier and politician tragically killed at commencement of Second World War.Leather and canvas boots with leather boot and canvas upper calf legging. Leather strap at instep and leather stiffened back seam to canvas section; Leather edging at top of canvas upper legging together with adjustable strap. Foot of boot is stabilised by a metal 'Dasco' insert. On metal heal protector "704603"boot, street geoffrey a brigadier
