Showing 9 items matching "soil samples"
-
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPhotograph - Black and white print, Information Branch Victorian Department of Agriculture, Student Taking Soil Samples, c. 1969
... Student Taking Soil Samples...soil samples...Black and white photograph. Student taking soil samples...students soil samples orchard publicity On reverse ...Black and white photograph. Student taking soil samples In the Orchard in Spring.On reverse, "Photograph by Information Branch Victoria Department Of Agriculture Ref. No. D1101.D."students, soil samples, orchard, publicity -
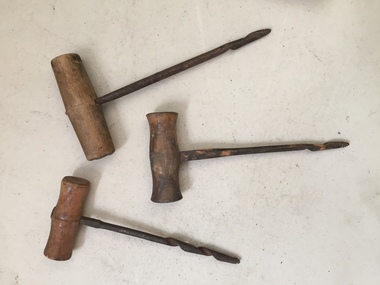 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyTools - Hand Augers - small x3
... for digging more shallow holes eg. gathering soil samples and making.... Used for digging more shallow holes eg. gathering soil samples ...Used by turning the auger around to create a round hole.Used by residents of the Kiewa ValleySmall steel hand auger tools with a wooden handle. Used for digging more shallow holes eg. gathering soil samples and making post holes -
 Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of Melbourne
Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of MelbourneDocument, 1907-1944
... of Eucalyptus; Fruits of other genera; Seeds; Soil samples; A.P.M...; Fruits of Eucalyptus; Fruits of other genera; Seeds; Soil samples ...This is a Catalogue of VSF Museum specimens. Timber Specimens (cont), Coniferous cones, fruit & seed; Fruits of Eucalyptus; Fruits of other genera; Seeds; Soil samples; A.P.M. samples.Catalogue -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPhotograph - Black and white print, Soil Testing, c. 1960
... possibly soil sampling. Possibly c.1960 when students spent some... (? Kidman). Activity possibly soil sampling. Possibly c.1960 when ...Note by T.H. Kneen 3 June 1992, "I think the gentleman with the hat is a member of HRS Tatura Staff (? Kidman). Activity possibly soil sampling. Possibly c.1960 when students spent some time at the Station."Black and white photograph. Man kneeling on the ground writing on paper while a student watches holding an implement?.staff, soil sampling, tatura, horticultural research station tatura, student sojourn, mr kidman, soil testing -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumGeological specimen - Montmorillonite
Montmorillonite is a type of clay composed of aluminium silicate that forms very small particles that are not well-bonded to one another. This is why it is so soft. When in the presence of water, all types of clay swell. Montmorillonite swells even more than most types of clay, which is why it is often chosen over other types of clay in its practical uses. Montmorillonite has many different practical uses, including in the mining industry, as a soil additive, as a sealant, as a desiccant to draw water out of the air, to clean ponds, to make kitty litter and in cosmetics. Montmorillonite is a common mineral and, despite being named after Montmorillon, France, can be found all over the world, including many deposits in Australia. It is not known where this particular specimen originates from. Montmorillonite is an economically and socially significant material with a wide variety of uses. Having samples of common and important minerals allows collections, like the Burke Museum, to have a more complete view of the land on which they are located, and therefore a more complete view of heritage. This specimen is part of a larger collection of geological and mineral specimens collected from around Australia (and some parts of the world) and donated to the Burke Museum between 1868-1880. A large percentage of these specimens were collected in Victoria as part of the Geological Survey of Victoria that begun in 1852 (in response to the Gold Rush) to study and map the geology of Victoria. Collecting geological specimens was an important part of mapping and understanding the scientific makeup of the earth. Many of these specimens were sent to research and collecting organisations across Australia, including the Burke Museum, to educate and encourage further study.A solid tennis-ball sized chunk of aluminium silicate clay. It is primarily white, accented with orange and brown.burke museum, beechworth, geological, geological specimen, clay, montmorillonite -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyDrill Bit Diamond, circa mid to late 1900's
This hollow core bit has hard cutting inserts for drilling into rock. It was used to drill and recover 50mm diameter (most common size) rock cores. The rock cores were assessed by geologists and engineers to provide information for design of structures such as tunnels, dams and underground power stations (eg. McKay Creek Power Station, West Kiewa Power Station). This type of bit was also used where damage to the surrounding rock had to be minimised. The Diamond Drill Bit,used in the early 1900's, when it was primarily used as a method of sampling rock for ore deposits and oil exploration resulting in a "coring" of rock. The use of "coring" to obtained samples for the SEC Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme(1920's onward) was to analyse the core to obtain temperature and rainfall patterns shown by the levels of layered solidified soil(rock). This diamond drill would have been used in the early 1900's to provide a sub strata map of temperature and water patterns (over an long period of time). This was a pre requisite to any decisions about the viability of the region to provide the water needed for a successful hydro electricity scheme.This diamond drill for core sampling was at the forefront of the analysis whether to construct a hydro electrical facility in the Kiewa Valley and the adjoining alpine region. The rock core samples produced were assessed by geologists and structural engineers. It was only after extensive core drilling covering the region that solid scientific evidence could be provided to start the "SEC Vic Hydro Electricity Scheme" within its current boundaries.This "diamond" drill bit has eight "teeth" at its cutting edge. The drill creates an 55mm hole in extremely hard rock material to obtain 50mm core samples.. Three quarters down the shank it has thread screw channels to attach the bit to the drill pipe. The coring pipe attaches via screwing it onto this bit. Core samples are the main objective of this tool.alternate energy supplies, alpine feasibility studies temperature, rainfall, sec, kiewa hydro electric scheme, electricity -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Lindsey Arkley, The hated protector : the story of Charles Wightman Sievwright, protector of Aborigines 1839-42, 2000
"The hated Protector" tells for the first time the real story behind the extraordinary experiences of Charles Sievwright, Assistant Aboriginal Protector from 1839-42 in what was then part of the British colony of New South Wales, but is now the Western District of the Australian state of Victoria. Sievwright, an Edinburgh-born former British army officer, lived in the bush with his young family as he tried to save the Aborigines of the District from extinction. In doing so, he would isolate himself from the rest of his fellow whites. The hated Protector tells of this process. The book should appeal to anyone interested in British colonial and Australian history, particularly in the years of first contact between British settlers and the Aborigines. More broadly, it should also appeal to anyone interested a story of one man's battle against overwhelming odds, where the price of failure was numerous deaths. It is a story of hatred, prejudice, courage, determination, and hope. In telling Sievwright's story, Lindsey Arkley draws largely on original archival material, including official reports, journals and letters, found in Melbourne, Sydney, Hobart, Edinburgh and London. Most has never before been published. The archival material is supplemented by contemporary newspaper accounts, and some oral history. Full notes are given to all sources, and the book is indexed and lavishly illustrated with drawings by Joan Bognuda, as well as about 80 paintings and samples of documents. Contents: 1. In the bush 2. "Equal and indiscriminate justice" 3. "A few doses of lead" 4. "A curse to the land" 5. "The most unpopular man" 6. Retaliation 7. A hostage debate 8. Hallucinations 9. A mass escape 10. Possessors of the soil 11. Move to Keilambete 12. Bureaucratic 13. "A hideous pandemonium" 14. Divine visitations 15. Pay backs 16. Explanations 17. A squatter on trial 18. Claptrap and deceit 19. The black cap - 20. To Mt Rouse 21. "The impending evil" 22. In the balance 23. An arrest at Mt Rouse 24. A fair moral name 25. Roger's trial 16. Intensified evidence 27. A declaration of war 28. Mr Cold Morning 29. Holding ranks 30. To rags 31. Fightback 32. Return to London 33. The inquiry 34. Judgement 35. And what remains.maps, document reproductions, b&w photographs, colour photographs, b&w illustrationscharles wightman sievwright, racial policies, british colonial history, race relations, victorian history -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumTextile - Diaper Set, Kathryn Knitwear, c.1960
Kathryn Knitwear, founded by Robert Blake, manufactured high quality children’s knitwear in Melbourne from the 1940s – 1980s. Robert Blake began manufacturing children’s knitwear in his bedroom in Strathmore using a hand powered machine in the late 1940s. The operation moved to Ascot Vale and Essendon, before eventually establishing a factory in Moonee Ponds in the early 1950s. The business continued to expand, necessitating a move to a new factory in Broadmeadows. By 1962, the Broadmeadows factory was producing an average of 20,000 garments per month, which increased to 24,000 by 1964. Robert Blake’s Son, Brendan recalls that “The Kathryn brand was famous around Australia, anywhere children needed to keep warm and dress smartly. It also won a number of wool fashion awards”, including the 1969 Wool Awards, which was held by the Australian Wool Bureau and published in Women’s Weekly. The Kathryn range was designed for durability, comfort and care, without sacrificing style. They used patterning techniques that increase stretchiness, comfort and fit, as well as integrating decorative elements into the fabric to prevent them from being bulky, uncomfortable or tight. Making longevity of style a priority, Brendan Blake remembers that “there was one particular garment that was in the range for at least thirty years”. He also recalls “In the past, when women have found out that I was associated with Kathryn Knitwear, they would often relate to me the story of a garment they had purchased or received as a gift and, when their child had grown out of it, they would hand it on to another child. Several ladies have told me of purchasing garments for their daughters’ glory box, or saving a particular garment after their daughter had grown out of it. Brendan Blake: “At the peak of their operation they employed approximately two hundred people, mainly women and girls. A family would often seek to send their daughter to work in this company because they knew they would be looked after and safe. One lady wrote to me telling me that working at the Moonee Ponds Factory prior to getting married was the happiest time of her life.” In 1963, workers at the Kathryn factory earned £13 per week, which was 8 shillings and 8 pence higher than the minimum weekly wage for female workers in the textile manufacturing industry (£12 11s 4d). By 1970, the Kathryn Knitwear brand expanded from children’s knitwear into womenswear under the brand name ‘Lady Kathryn’, and for boys and men under ‘Robert Blake’. Continuing to diversify their distribution, they also began exporting ‘Kathryn’ garments to New Zealand, the Pacific Islands, and Japan. ‘Kathryn Knitwear’ was well-known for their early adoption of modern materials and techniques that had broad appeal to their customer base. This is shown in their early use of the acrylic fibre ‘Orlon’ in the 50s and 60s and ‘Superwash’ wool in the 1970s. Many of Kathryn Knitwear’s styles, particularly those that were long running staples of the brand, were available in both wool and Orlon to suit the consumer’s preference. Cotton is a common material for knitwear worn in the warmer months, as it is very breathable and absorbs moisture easily. While we mostly associate knitwear with keeping us warm in the cold, the market for Australian knitwear would be very limited without options to wear all year round. The decoration on this garment was embroidered by hand by a skilled worker at the Kathryn Knitwear factory. Far from the humble origins of one man in his bedroom with a hand-cranked machine; at its closure in 1980, the Broadmeadows factory of ‘Kathryn’ housed more than 100 machines, including 53 sewing machines and 45 knitting machines. Robert Blake was “a passionate advocate for wool and Australian Made” throughout his whole life. A strong thread that ties through the lifespan of Robert Blake and Kathryn Knitwear is a balance between adopting new innovations without sacrificing the core values of durability, comfort, care and style that had made the brand so well known. Their legacy forms an integral part of both Australian social and manufacturing history.White diaper set. Short sleeved white top with two inverted box pleats along whole length, stitched at shoulder and mid chest. Embroidered in half cross stitch with two blue dogs on front. Closes in centre back with three plastic pearlescent buttons. White baby diaper shorts with ribbing at waist and leg holes .3 is a sample tag with manufacturing information, including price, size and colours available .4 is a swing tag with manufacturer care instructions.1 [label at back neck of top] Kathryn Reg’d / All Cotton / 18 .3 [sample label] [Obverse] STYLE: 314. Diaper Sat [sic] – Emb top. Combed Cotton. SIZE: 18” PRICE: 26/- COLOR: BLUE. LEMON. WHITE. [reverse] KATHRYN Garments are •PRE-SHRUNK •STANDARD MEASUREMENTS •FIT EXACTLY •LAUNDER PERFECTLY Designed and Manufactured by ROBERT BLAKE, MELBOURNE .4 [retail label] [obverse] Kathryn PRE-SHRUNK KNITWEAR Style: 314 [handwritten] DESIGNED & MANUFACTURED BY Robert Blake MELBOURNE [reverse] IMPORTANT. Special care should be taken with white and pastel shades. Rinse thoroughly. Do NOT dry in sunlight. WASHING INSTRUCTIONS 1.Wash frequently to AVOID HEAVY SOILING 2.Wash garment BY HAND, in lukewarm Velvet Soap suds. ON NO ACCOUNT RUB SOAP ON GARMENT. 3.Squeeze suds gently through garment but DO NOT RUB. Rubbing will cause garment to thicken. 4.RINSE AT LEAST TWICE IN CLEAN WATER TO REMOVE ALL SOAP. 5.To dry, roll garment in a towel to remove excess moisture, turn garment inside out and pull it lengthwise, then safety-pin to line through shoulder tape. 6.To keep Brushed Wool garments like new brush frequently with nylon brush.children's knitwear, children's clothing, knitwear, clothing, manufacturing, fashion textile production, embroidery, embroiderer, hand embroidery, dog embroidery, animal embroidery, animal motif, dog motif, dog, animal, baby clothes, baby knitwear, baby clothing -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPrototype fuel moisture meter
Bushfire behaviour is influenced by many things including temperature, relative humidity, forest type, fuel quantity and fuel dryness, topography and even slope. Wind has a dominant effect on the Rate of Spread (ROS), and also bushfire size, shape and direction. Fuel arrangement is as important as fuel quantity (tonnes/ha). Fibrous and ribbon bark, together with elevated and near-surface scrub fuels act as ladders which lead flames into the tree canopy. But the availability of fuel to burn depends largely on its moisture content. When it exceeds 20-25% not much will burn, whereas 12-15% is generally ideal for fuel reduction burning, but if the moisture content drops as low as 7-10% virtually everything will ignite, and fire behaviour becomes extreme. During the afternoon of the Ash Wednesday bushfires on 16 February 1983 fuel moisture contents were recorded at Stawell as low as 2.7%. Fine fuels like leaves and bark can rapidly absorb moisture after a shower of rain, or from the air when the Relative Humidity (RH) is high, and the temperature is low. Conversely, they can also dry out very quickly. So even though the overall fuel quantity in the forest doesn’t change, the fine fuel availability can increase rapidly from zero after rain to many tonnes per hectare as the fuel dries out. This can happen over a few hours on hot and windy days. Heavy fuels like logs on the ground take longer to dry out. Since the 1930s foresters, firefighters and researchers have been working to develop quick and reliable techniques for measuring fuel moisture content. One of the most accurate methods is slowly drying a sample of fuel in a conventional oven for 24-48 hours to remove all the moisture and measuring the weight difference, but this takes time and is not practical in the field when rapid measurements are needed. But oven drying is often used as a benchmark to compare other methods. Microwave ovens are faster but can cause uneven drying and even char the fuel. They are also not very practical for use in the field. Some mathematical models rely on weather records such as rainfall, wind speed, evaporation, cloud cover, shading, relative humidity, slope, aspect and season of the year to predict soil and fuel moisture. The Keetch-Byram Drought Index of soil dryness is the most common. But complex fuels with leaves, twigs, grass etc make the predictive models often inadequate for fine fuels. The most common technique in Victorian forests until recently was the trusty Speedy Moisture Meter. Originally developed in England during the 1920s for measuring moisture in wheat and other grains it was adapted for Australian forest fuels in the 1950s (I think). Fuel was first ground using a Spong mincer, often attached to the bullbar of a vehicle, and a small sample placed into the Speedy together with a measure of calcium carbide and then sealed. A chemical reaction created gas pressure which was read on the external dial. There were important techniques with cleaning, mincing and using the chemicals with the Speedy to give reliable readings, but it was quick, inexpensive, robust, portable and practical in the field. It was used routinely before igniting a fuel reduction burn or measuring fuel moisture differentials on slash burns. But in about 1996, Karen Chatto and Kevin Tolhurst from the Department’s Creswick Research Station developed the Wiltronics Fuel Moisture meter which measured electrical resistance. Wiltronics is an Australian owned company operating from Ballarat. The final result was a kit that was portable, accurate and could reliably measure fuel moisture contents between 3% and 200%. Although expensive, it is now widely used by fire agencies around the world which has virtually relegated the Speedy to the back cupboard.Prototype Fuel moisture meterT-H Fine Fuel Meterforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement
