Showing 60 items matching "steel barque"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Vessel "Strathgryfe", late 19th or early 20th century
... steel barque... masted steel barque built in 1890 by "Russell and Company", Port... masted steel barque built in 1890 by "Russell and Company", Port ...This photograph was one of ten photographs donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village by Fred Trewartha. Frederick John Fox Trewartha (Fred) was a well-known Warrnambool businessman. He was born in Beeac near Geelong in 1920 and came to Warrnambool with his family as a very young child. He was apprenticed to his father John, as a saddler and later opened his own shop on Raglan Parade. He then moved into working with tarpaulins and canvases for the trucking industry. Fred was keenly interested in photography (and was a member of the Warrnambool Cine Club), yachting and boat building. He kept his yacht moored at Port Fairy for many years and participated in sailing events locally and interstate. He also built boats with his sons. He had the opportunity to meet many older sailors and it's thought this photo (and others in the set) may have been given to him by one of these men. Fred Trewartha died in 2016 in Warrnambool. The "Strathgryfe" was a four masted steel barque built in 1890 by "Russell and Company", Port Glasgow and was owned by Duncan McGillivray (The Strathgryfe Ship Company Limited), Greenock. It arrived in Melbourne in December 1891 from New York. Between 1891 and 1910 it carried merchandise in and out of Australia to ports around the world - Melbourne to London (1892), Newcastle to San Francisco (1894), Capetown to Newcastle (1894), New York to Shanghai (1897), New York to Melbourne (1898), Frederickstadt to Melbourne (1899), Liverpool to Sydney (1900), San Francisco to Brisbane (1903), Newcastle to Pisagna, Chile (1905) and Rotterdam to Melbourne (1910). It carried breadstuffs from San Francisco, coal from Newcastle, wool from Sydney, saltpetre from Hamburg and wheat from Brisbane and Melbourne as well as a variety of general merchandise. In 1898, whilst on route between New York and Melbourne, it came across the Captain and crew of the missing barque "Glen Huntley" which had been reported as "lost" several months earlier. They had been marooned at Tristan D'Acunha (a remote group of volcanic islands in the South Atlantic ocean). Captain McIntyre, of the Strathgryfe, offered to bring Captain Shaw (of the Glen Huntly) on to Melbourne with them but the "old mariner" decided to stay on with his crew till arrangements could be made for rescuing the whole of them. In 1899, when in Melbourne, seven of its crew refused to go to sea in it due to its unsafe conditions. They said the vessel was unseaworthy and that the rigging was unsafe and the lifeboats, not watertight. The Captain (Donald McIntyre) denied the allegations and produced a marine surveyor's certificate as evidence of the condition of the vessel. The men were sentenced to three weeks imprisonment. In 1901 there was a fire on board the Strathgryfe just after it left Sydney for London which resulted in many bales of wool being destroyed. In 1902 it was beached at Shellback island (near Wilson's promontory) for several weeks and had to be considerably dismantled in order to lighten its load enough to allow tugs to pull it back into deep water. In 1910 it was sold to a German firm and renamed "Margretha". It continued to operate in Australian ports until 1914 when it left Sydney for the English Channel with 42,438 bags of wheat. However owing to W.W.1 breaking out, it made for the port of St Michael's where it remained for twenty-one months. Later it was seized by the Portuguese Government and renamed "Graciosa" and was leased back to the English Government. It was sunk by two German submarines in 1918.This photograph is significant as a record of the world wide mercantile trade Australia was engaged in at the end of the nineteenth century and beginning of the twentieth century.Black and white photograph of a four masted barque moored at a dock. The rigging and two lifeboats are clearly visible. Three large timber logs are in the foreground. On the back of the photograph, the donor's name and telephone number have been written in black ballpoint pen and the name of the ship has been handwritten (incorrectly) in pencil in cursive script.Back of Photo - donor's name and telephone number "Strarthgryfe" [Strathgryfe] / "late" / "Margurita" [Margretha]flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, strathgryfe, barque, steel barque, margretha, graciosa, frederick trewartha, mercantile trade, russell and company, merchandise, cargo ship, glen huntly, w. w. 1 -
 Seaworks Maritime Museum
Seaworks Maritime MuseumModel ship, The model was built by the ship's carpenter on board the Archibald Russell, Archibald Russell, 1905
... Hardie & Sons. Steel barque built by Scott Shipbuilding... at Greenock in 1905 for John Hardie & Sons. Steel barque built ...ARCHIBALD RUSSELL (1905-1949) Until 1922 completed numerous cargo voyages to Sydney, Newcastle, Fremantle, Geelong, and especially Melbourne. In 1923 she was bought by Gustaf Erikson, the famous Finnish ship-owner, and carried timber to Melbourne in 1926, 1927 and 1928, and carried grain from Geelong in 1927 and Williamstown in 1929 - and that was the year she won the Grain Race (93 days). She then carried grain from South Australia until the war and was then was taken over by the British and used as a food storehouse through the war. She was broken up in 1949 on Tyneside. An example of end-era sailing ship trade with Australia. Reference: http://www.bruzelius.info/Nautica/Ships/Fourmast_ships/Archibald_Russell%281905%29.html She was launched at Greenock in 1905 for John Hardie & Sons.Has significant links with Australian and Victorian commerce. An example of end of era sailing ship trade with Australia. A detailed static model with carved and laminated hull painted in white and maroon, the varnished deck with detailed fittings and rigging, raised on wooden base with simulated waves. Model of 4-masted barque launched at Greenock in 1905 for John Hardie & Sons. Steel barque built by Scott Shipbuilding and Engineering Co., Greenock, at a cost of £20.750. Her dimensions were: 291'3 × 42'9 × 24'0 (88.77 x 13.03 x 7.32m) and tonnage: 2354 GRT, 2048 NRT and 3950 DWT. Equipped with two 120' long bilgekeels. Rigged with royal sails over double top-gallant sails. "Archibald Russell" painted on ship -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers Victoriaphotograph, 5 mast barque (France) wrecked on the Caledonian coast on the 12th of July 1922, 12 July 1922
... as a five-masted steel-hulled barque. and belonging... rigged as a five-masted steel-hulled barque. and belonging ..."France II" was an extremely large tall ship, square rigged as a five-masted steel-hulled barque. and belonging to the "Compagnie française de marine et de commerce" was a totally wrecked in a coral reef of Ouano on the coast of New Caledonia in the night between 11 and 12 July 1922. The France II was the second largest commercial merchant sailing ship ever built (hull length:142,2m).Black and white photograph mounted on grey cardboard depicting a sailing shipHandwritten in black ink at bottom on mount: "5 mast barque (France) wrecked on the Caledonian coast / on the 12th of July 1922"shipwreck, france, barque, new caledonia, ships, crews and ships, barque france, 1922 -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaPhotograph, Peckham Photographic Studios, Geo Beachcroft, Capt Dahlström and 2nd mate of the C.B. Pedersen, c. 1935
... in 1938. Built in 1891 the C.B Pedersen, a four-masted steel... in 1938. Built in 1891 the C.B Pedersen, a four-masted steel ...In the Sydney Morning Herald, Tuesday 27 April 1937, page 12: "The C. B. Pedersen was built in 1891. It has visited Australia several times, the most recent occasion having been in 1935, when It was anchored in Port Phillip Bay, Victoria, for several weeks, awaiting a suitable cargo. At length the master, (Captain Hjalmar Dahlström) announced that, as no cargo could be obtained he would be prepared to carry passengers in a voyage to Gothenburg, via Torres Strait. Eight persons, including three women and a small boy were accepted as passengers, and signed on as members of the crew at salaries of 1/ a month". Artist Violet Teague was one of the passengers. She painted during the voyage and exhibited her work in 1938. Built in 1891 the C.B Pedersen, a four-masted steel barque (2142 tons) was used as a training Barque. The ship foundered in April 1937, the crew was saved. Several photographs of the C.B. Pedersen taken by the same studio are held at the State Library of Victoria.see links aboveBlack and white photograph depicting two sailors in attire on the deck of a ship.verso in Black ink; Photographic studio stampcrew, c.b pedersen, captain hjalmar dahlström, violet teague, windjammer -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaPhotograph, circa 1935
... the C.B Pedersen, a four-masted steel barque (2142 tons) was used... in 1938. Built in 1891 the C.B Pedersen, a four-masted steel ...In 1935, the CB Pedersen arrived on the 13th of April after 198 days at sea. The ship left on the 18th June (date written on the photograph) after two months in Melbourne. Captain Dalhstrom had been its skipper for 13 years. In the Sydney Morning Herald, Tuesday 27 April 1937, page 12: "The C. B. Pedersen was built in 1891. It has visited Australia several times, the most recent occasion having been in 1935, when It was anchored in Port Phillip Bay, Victoria, for several weeks, awaiting a suitable cargo. At length the master, (Captain Hjalmar Dahlström) announced that, as no cargo could be obtained he would be prepared to carry passengers in a voyage to Gothenburg, via Torres Strait. Eight persons, including three women and a small boy were accepted as passengers, and signed on as members of the crew at salaries of 1/ a month". Artist Violet Teague was one of the passengers. She painted during the voyage and exhibited her work in 1938. Built in 1891 the C.B Pedersen, a four-masted steel barque (2142 tons) was used as a training Barque. The ship foundered in April 1937, the crew was saved.The C.B. Pedersen was one of the last windjammers sailing in the 1930s with the Herzogin Cecilie and the Grace Harwar. Black and white photographLower right corner front in black ink: H. Dahlström / June 13th 1935 / On board the CBP / in Hobson's Bayc.b. pedersen, captain hjalmar dahlström, violet teague, windjammer, sweden -
![Photograph - Photograph, Black and white, Peckham Photographic Studios, Geo Beachcroft, Hanging on up aloft [the] C.B. Pedersen, c. 1935](/media/collectors/4f729f5897f83e0308601603/items/4f72bbce97f83e03086061e1/item-media/581a839ad0cdd11ed4ac0ec3/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaPhotograph - Photograph, Black and white, Peckham Photographic Studios, Geo Beachcroft, Hanging on up aloft [the] C.B. Pedersen, c. 1935
... the C.B Pedersen, a four-masted steel barque (2142 tons) was used... the C.B Pedersen, a four-masted steel barque (2142 tons) was used ...Snapshot in time of tall ship and the relaxed clambering about the rigging by sailors. The C.B. Pedersen is also referred to as a Training Ship for Swedish seamen and cadets. A reference in Annual reports and in Jottings from our log notes that classes in Swedish amongst other languages were offered by the LHLG to members and some of the earliest photographs note Swedish sailors relaxing. The first officer and captain of the C.B. Pedersen are depicted in photograph (0706) on permanent display. In the Sydney Morning Herald, Tuesday 27 April 1937, page 12: "The C. B. Pedersen was built in 1891. It has visited Australia several times, the most recent occasion having been in 1935, when It was anchored in Port Phillip Bay, Victoria, for several weeks, awaiting a suitable cargo. At length the master, (Captain Hjalmar Dahlström) announced that, as no cargo could be obtained he would be prepared to carry passengers in a voyage to Gothenburg, via Torres Strait. Eight persons, including three women and a small boy were accepted as passengers, and signed on as members of the crew at salaries of 1/ a month". Artist Violet Teague was one of the passengers. She painted during the voyage and exhibited her work in 1938. Built in 1891 the C.B Pedersen, a four-masted steel barque (2142 tons) was used as a training Barque. The ship foundered in April 1937, the crew was saved. Several other photographs of the C.B. Pedersen taken by the same studio are held at the State Library of Victoria.Training of seamen has always been of of keen interest to the Mission to Seamen and many cadets have been welcomed over the 20th Century when widespread training was undertaken by a number of seafaring nations. Black and white photograph of 9 men hanging from ropes in the rigging. One man is upside down, another is holding his hat out. The mast is off to the right-hand side of the photograph and there are several ropes and chains.On the back of the photograph in the top left-hand corner is an ink stamp with the text "Peckham Photographic Studios/Geo Beachcroft/Propr./21 Charlotte St./Richmond/Victoria, Australia". In black pen is the text "Hanging on up aloft/C.B.Pedersen".richmond, chains, rope, seafarers, rigging, peckham photographic studios, geo beachcroft propr, cb pedersen, tall ships, captain hjalmar dahlström, windjammer -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePainting - Watercolour painting, Beni Carr Glyn Burnett, Magdalene Vinnen, 1933
... . It was a 4 masted steel barque, built in 1921 in Kiel, Germany.... It was a 4 masted steel barque, built in 1921 in Kiel, Germany ...Beni Carr Glyn Burnett (also known as B. C. G. Burnett or Beni Burnett) was born in 1889 to missionary parents in Mongolia. When he was 15 years old he began training as an architect with a firm in Shanghai. He worked in Singapore, Japan and China before moving to Australia around 1933. In 1937 he was appointed as the Commonwealth principal architect in the Northern Territory. He went on to design a series of houses for senior public servants and military personnel which became very popular as they were specifically designed for the tropics - incorporating louvres, high ceilings and good ventilation. When Darwin was bombed in February 1942, he was evacuated to Alice Springs where he continued to work as an architect. He also became a Magistrate and Coroner in Alice Springs. In later life he was well known for sketching clientele in public bars. He died in 1955. Beni Burnett was living in Sydney in 1933 when he produced these three artworks. There were several photography firms operating in Sydney at this time who specialised in photographing ships and the shipping trade (e.g. Samuel J. Hood and William James Hall) and whose photographs were used by artists to produce ship portraits. Both of these photographers took photographs of the two ships in B. C. G. Burnett's watercolours. The "Magdalene Vinnen" was photographed by Samuel J Hood in a series of photos taken in March 1933. It was a 4 masted steel barque, built in 1921 in Kiel, Germany and for almost 80 years was the largest traditional sailing ship in operation. She was used extensively as a cargo ship. She sailed into Sydney Harbour on 27th Feb 1933, loaded with almost 16,000 bales of wool destined for Falmouth, England. In March 1933 (whilst in Sydney) the German Republic flag (on orders from Adolph Hitler) was lowered and replaced with the old monarchist flag which was then to be the official flag and beside it the Nazi flag was to be flown on all ceremonial occasions. It visited Australia again in 1935 with its cargo being wheat from Port Broughton, S. A. In 1936 it was renamed "Kommodore Johnsen" and in 1945 (after WW2) the ship was awarded to the Soviet Union as war compensation and renamed "STS Sedov". This painting (one of a set of 3 small artworks) is significant as an example of shipping (particularly the use of sailing ships) that were still being used as late as the 1930's in Australia. It is also important because its creator (B. C. G. Burnett) went on to become a well-known public figure in the Northern Territory in the late 1930's due to his innovative approach to designing homes for the tropical climate. A watercolour painting of a sailing ship called "Magdalene Vinnen". It shows a 4 masted barque with a blue and red steel hull in full sail heading towards the viewer. The painter's name (B. C. G. Burnett) and date (1933) are written on the bottom left-hand corner of the painting. The location and name of the ship is written in ink on the back of the painting.front - "B. C. G. BURNETT. 1933 back - "off Sydney" / "Magdalene Vinnen"flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, sailing ships, ships, barque, magdalene vinnen, beni carr glyn burnett, b. c. g. burnett, beni burnett, painting, watercolour painting, sketch, sydney harbour, architect, darwin, burnett house, photography, samuel j. hood, william james hall, sedov, kommodore johnsen -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Toolbox
... , Marjorie Craig, Louisa Craig and Joseph Craig. The steel barque..., Marjorie Craig, Louisa Craig and Joseph Craig. The steel barque ...This toolbox was originally part of the equipment on the barque Marjorie Craig, which brought New Zealand timber into Warrnambool from about 1908 to 1912 for the local merchants P J McGennan & Co. The toolbox was donated by a member of a local family connected with the La Bella rescue in 1905. The toolbox has carvings and markings that make it unique and connect it to the Marjorie Craig. The Craig Line of sailing ships was from Auckland, New Zealand, and traded in timber and some coal from New Zealand ports to Australia, including Sydney, Adelaide, Melbourne and Warrnambool. They returned with produce from Australia as ballast. In 1912 the Craig fleet included the Ihumata, Inga, Jessie Craig, Marjorie Craig, Louisa Craig and Joseph Craig. The steel barque Marjorie Craig, 500 ton, was built in 1891 as the 'Hirotha', in Ardrossan, Scotland for Norwegian owners. The ship was sold to Auckland’s Donald Ross and others in 1900, then in 1905 it was sold, registered by J.J. Craig in Auckland, New Zealand and renamed Marjorie Craig. Marjorie Craig’s commanders included Master R A Campbell in 1907, J MacFarlane in 1909 and Master R.G. Holmes in 1913. From February 1908, the Marjorie Craig was regularly seen in the Port of Warrnambool with loads of timber for merchants P J McGennan & Co. In February 1912 Marjorie Craig delivered white pine for P J McGennan & Co. In April of the same year, she brought 500,000 feet of timber for McGennan & Co and again in May 1912. On May 12 1912 Marjorie left the Port of Warrnambool with 500 tons of flour for New Zealand; it seems that this was her last time at Warrnambool. Prior to 1908, the vessel Speculant brought in timber from New Zealand for the McGennan firm. The Marjorie Craig had a strong reputation for being a ‘Fast Flyer’, breaking the sailing records for voyages between New Zealand and Australia. It was reported that she made passages with a speed equal to steamboats on several occasions. One of her records was from Warrnambool to Hokianga, NZ in eight-and-a-half days. The ship broke the record in October 1913 for the time from Adelaide to Auckland, sailing in 28 days, even with a damaged ship, and the owner presented Captain Holmes with a gold watch and chain. By the end of December 1913, the Craig Line’s last two surviving sailing ships, Marjorie Craig and Jessie Craig, had been purchased by Huddart, Parker & Co. Ltd. to work as coal hulks, one in Melbourne and one in Hobart.The toolbox is significant for being created for use in 1905 when the steel barque Marjorie Craig was purchased by J J Craig and given that name. The carved ships’ images and related inscriptions within the toolbox support the origin of the toolbox. The toolbox is significant for its association with the well-known Marjorie Craig, a frequent visitor to the Port of Warrnambool 1908 to 1912, a supplier of New Zealand timber for the local firm P J McGennan & Co, and one of the fastest inter-colonial sailing ships that broke numerous records for its speed including the fastest sailing from Warrnambool to Hokianga. Wooden toolbox from the ship Marjorie Craig. Wooden box, stained brown, decorative metal handles on sides, dovetailed joints, lid with metal and leather strap hinge, tapered feet and metal keyhole at front. Inscriptions are inside the box. Box contains newspaper clippings relating to sailing and maritime topics. A handwritten tag is attached to the box. Handwritten tag: "SAILING SHIP / MARJORIE CRAIG, EARLY 1900's / TOOL BOX / PORT OF W'BOOL”. Inside the lid is a carved silhouette of a 3-masted sailing ship with pink chalk lettering "M C" and "1912". Inside the front panel is "MARJORIE CRAIG". Inside the left panel is stamped a black oval with lettering inside.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, port of warrnambool, marjorie craig, flour export - warrnambool, toolbox, steel barpue, p j mcgennan & co, craig line, craig fleet, 1891, hirotha, donald ross, j.j. craig, r a campbell, j macfarlane, r.g. holmes -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMachine - Pulley, Ca 1889
... ”. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee... and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander ...Wooden pulley wheel section from the wreck “Newfield”. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt, the main export product of Sharpness. At about 9pm on 28th August 1892, in heavy weather, Captain Scott sighted, between heavy squalls, the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria but, due to a navigational error (the ship’s chronometers were wrong), he assumed it to be the Cape Wickham light on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered his course to the north, expecting to enter Bass Strait. The ship was now heading straight for the south west Victorian coast and at about 1:30am ran aground on a reef about 100 yards from shore and one mile east of Curdie’s Inlet, Peterborough. The ship struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with 6 feet of water in the holds. Rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The Port Campbell rocket crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. A local man, Peter Carmody, volunteered to swim one mile to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. According to Jack Loney ‘… when the drama was over . . the Newfield was deserted except for the Captain’s dog and two pigs.’ Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum has several artefacts that have been salvaged from the wreck. See also other items in the Flagstaff Hill Newfield Collection.The report from SHP documented the following in regards to the Newfield collection: Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, because of its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register. The collection is significant because of its relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as it is the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 (Living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck. The Newfield collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criteria A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history Criteria B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criteria C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history This item is an oval-shaped brown and orange wooden shell from a ship’s pulley. The original wooden material is now petrified but the lighter coloured concentric rings of the wood's grain are still visible. A metal sheave or drum is fitted into the centre hole and some of the edge of its sheave’s collar has corroded and broken away. The collar has three holes of equal size that are evenly spaced around it. The bearing ring is now detached but still connected to the pulley with a string on which a label is attached. Most of the six cylindrical metal roller bearings are sand encrusted but some are still visible. Recovered from the wreck of the ship NEWFIELD.The pulley has a string through it that attaches it to the bearing. The label on the string bears the handwritten words “PULLEY WHEEL / NEWFIELD / PETER ROLAND”.block, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, peter carmody, carmody, newfield, shipwreck, pulley, wheel, pulley block, sheave, drum, peterborough, south west victoria, rocket, rocket crew, shipwreck artefact, flagstaff hil maritime museum -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph, post 1889
... The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee... and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander ...The photograph shows the three-masted iron and steel bark "Newfield" sailing in open seas. It event would have been between 1889-1892 during the ship's working life. ABOUT THE NEWFIELD The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt, the main export product of Sharpness. At about 9pm on 28th August 1892, in heavy weather, Captain Scott sighted, between heavy squalls, the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria but, due to a navigational error (the ship’s chronometers were wrong), he assumed it to be the Cape Wickham light on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered his course to the north, expecting to enter Bass Strait. The ship was now heading straight for the south west Victorian coast and at about 1:30am ran aground on a reef about 100 yards from shore and one mile east of Curdie’s Inlet, Peterborough. The ship struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with 6 feet of water in the holds. Rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The Port Campbell rocket crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. A local man, Peter Carmody, volunteered to swim one mile to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. One of the men, apprentice William McLeod, was rescued by local woman Margaret E. MacKenzie. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. According to Jack Loney ‘… when the drama was over . . the Newfield was deserted except for the Captain’s dog and two pigs.’ Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum has several artefacts that have been salvaged from the wreck. The report from SHP documented the following in regards to the Newfield collection: Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, because of its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register. The collection is significant because of its relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as it is the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 (Living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck. Black and white photograph of the three-masted sailing ship “Newfield” in the open sea, sails unfurled. The ship was built in 1859 by Alexander Stephen and Sons Limited of Dundee, Scotland. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, barque newfield, photograph, 1880s sailing ship -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Saw, 1905-1913
... , Marjorie Craig, Louisa Craig and Joseph Craig. The steel barque..., Marjorie Craig, Louisa Craig and Joseph Craig. The steel barque ...This crosscut saw was originally part of the equipment on the barque Marjorie Craig, which brought New Zealand timber into Warrnambool from about 1908 to 1912 for the local merchants P J McGennan & Co. The toolbox was donated by a member of a local family connected with the La Bella rescue in 1905. The toolbox has carvings and markings that make it unique and connect it to the Marjorie Craig. The Craig Line of sailing ships was from Auckland, New Zealand, and traded in timber and some coal from New Zealand ports to Australia, including Sydney, Adelaide, Melbourne and Warrnambool. They returned with produce from Australia as ballast. In 1912 the Craig fleet included the Ihumata, Inga, Jessie Craig, Marjorie Craig, Louisa Craig and Joseph Craig. The steel barque Marjorie Craig, 500 ton, was built in 1891 as the 'Hirotha', in Ardrossan, Scotland for Norwegian owners. The ship was sold to Auckland’s Donald Ross and others in 1900, then in 1905 it was sold, registered by J.J. Craig in Auckland, New Zealand and renamed Marjorie Craig. Marjorie Craig’s commanders included Master R A Campbell in 1907, J MacFarlane in 1909 and Master R.G. Holmes in 1913. From February 1908, the Marjorie Craig was regularly seen in the Port of Warrnambool with loads of timber for merchants P J McGennan & Co. In February 1912 Marjorie Craig delivered white pine for P J McGennan & Co. In April of the same year, she brought 500,000 feet of timber for McGennan & Co and again in May 1912. On May 12 1912 Marjorie left the Port of Warrnambool with 500 tons of flour for New Zealand; it seems that this was her last time at Warrnambool. Prior to 1908, the vessel Speculant brought in timber from New Zealand for the McGennan firm. The Marjorie Craig had a strong reputation for being a ‘Fast Flyer’, breaking the sailing records for voyages between New Zealand and Australia. It was reported that she made passages with a speed equal to steamboats on several occasions. One of her records was from Warrnambool to Hokianga, NZ in eight-and-a-half days. The ship broke the record in October 1913 for the time from Adelaide to Auckland, sailing in 28 days, even with a damaged ship, and the owner presented Captain Holmes with a gold watch and chain. By the end of December 1913, the Craig Line’s last two surviving sailing ships, Marjorie Craig and Jessie Craig, had been purchased by Huddart, Parker & Co. Ltd. to work as coal hulks, one in Melbourne and one in Hobart.The saw is significant for being created for use in 1905 when the steel barque Marjorie Craig was purchased by J J Craig and given that name. The saw would be part of the sip's equipment and could have been used for the timber carried as cargo on the Marjorie Craig. The saw is significant for its association with the well-known Marjorie Craig, a frequent visitor to the Port of Warrnambool 1908 to 1912, a supplier of New Zealand timber for the local firm P J McGennan & Co, and one of the fastest inter-colonial sailing ships that broke numerous records for its speed including the fastest sailing from Warrnambool to Hokianga. Crosscut saw; blade attached to wooden handles by wingnut each end. The saw has 63 teeth. Also has a tag attached with an inscription. The saw was ship's equipment on the barque, Marjorie Craig.Handwritten on tab: "From sailing ship Marjorie Craig early 1900 Port of Warrnambool"flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shiopwreck coast, woodworking tool, crosscut saw, shipwright tool, saw, marine trade, carpenter, marjorie craig, j j craig, craig line, 1905-1912 -
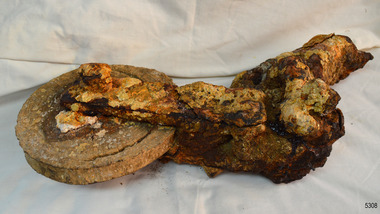 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Block, Alexander Stephen and Sons, 1869
... . The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee... of the vessel. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque ...These remains of a block, shackle and wire are from the sailing ship Newfield. This would have been one of the hundreds of blocks and shackles used in the rigging of the vessel. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1869 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt. On the night of 28 August 1892, the Captain mistook the Cape Otway light for that of Cape Wickham (King Island) and altered tack to the north and east putting the vessel on a collision course with the Victorian coast. At around 3:40 am the Newfield struck rocks about 100 yards from shore, and 5 feet of water filled the holds immediately. The captain gave orders to lower the boats which caused a disorganised scramble for safety among the crew. The starboard lifeboat was cleared for lowering with two seamen and two apprentices in her, but almost as soon as she touched the water she was smashed to bits against the side of the vessel, and only one of the four reached safety ashore, able seaman McLeod. The rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The rescue was a difficult operation. The Port Campbell Rocket Crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. Peter Carmody, a local man, volunteered to swim about one mile offshore to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. He was assisted by James McKenzie and Gerard Irvine. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one-man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. For his heroic efforts, Peter Carmody was awarded the Bramley-Moore medal by the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society for Saving Life at sea on January 21st 1893. The medal and a letter of congratulations were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum by Peter Carmody's granddaughter Norma Bracken and her son Stuart Bracken on 25th May 2006. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is additionally significant because of the medal awarded to a local man Peter Carmody. The Newfield collection historically also represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history and its association with the shipwreck.This is what remains of a block, shackle and wire from the wreck of the sailing ship “Newfield”. The object is heavily encrusted. The exterior (cheeks) of the block is missing. The disc of the block has a channel part way around its face, about 2 cm from the edge. Two long, narrow plates are joined onto the centre of the disc’s face with a bolt through the centre. The other ends of the two plates join onto the elbow of the shackle. The elbow of the shackle is also joined onto a rod. At the other end of the rod can be seen the ends of thick wire strands.block, 1893, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, peter carmody, newfield, 1892, port campbell, shipwreck, ship, victorian shipwrecks, barque, ship wreck, peterborough, sailing ship, 29 august 1892, block and shackle, curdies river, bramley-moore medal -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Porthole, Alexander Stephen and Sons, 1869
... and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1869 by Alexander... was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland ...This large brass porthole is from the sailing ship Newfield this would have been one of the many port holes in the vessel used for light and ventilation. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1869 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt. On the night of 28 August 1892, the Captain mistook the Cape Otway light for that of Cape Wickham (King Island) and altered tack to the north and east putting the vessel on a collision course with the Victorian coast. At around 3:40 am the Newfield struck rocks about 100 yards from shore, and 5 feet of water filled the holds immediately. The captain gave orders to lower the boats which caused a disorganised scramble for safety among the crew. The starboard lifeboat was cleared for lowering with two seamen and two apprentices in her, but almost as soon as she touched the water she was smashed to bits against the side of the vessel, and only one of the four reached safety ashore, able seaman McLeod. The rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The rescue was a difficult operation. The Port Campbell Rocket Crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. Peter Carmody, a local man, volunteered to swim about one mile offshore to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. He was assisted by James McKenzie and Gerard Irvine. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one-man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. For his heroic efforts, Peter Carmody was awarded the Bramley-Moore medal by the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society for Saving Life at sea on January 21st 1893. The medal and a letter of congratulations were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum by Peter Carmody's granddaughter Norma Bracken and her son Stuart Bracken on 25th May 2006. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is additionally significant because of the medal awarded to a local man Peter Carmody. The Newfield collection historically also represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history and its association with the shipwreck.Heavily encrusted large brass porthole, complete with glass intact object is a circular, thick glass window surrounded by a round brass frame and attached to a round brass porthole frame with 9 bolt holes. This porthole was recovered from the wreck of the NEWFIELD.Nonewarrnambool, peter carmody, newfield, port campbell, shipwreck, nineteenth century, ship, victorian shipwrecks, peterborough, peter ronald, dog screw, newfield porthole, bramley-moore medal, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck artefact, ship fitting, ship window -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Skylight frame, Alexander Stephen and Sons, 1869
... was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland.... The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee ...This skylight frame would have been fitted on the Newfield’s poop deck (or raised deck that forms the roof of a cabin at the aft or rear of the ship). It would have covered and protected a glass pane that allowed light to enter the area below desk. The glass pane from the skylight is missing. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1869 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt. On the night of 28 August 1892, the Captain mistook the Cape Otway light for that of Cape Wickham (King Island) and altered tack to the north and east putting the vessel on a collision course with the Victorian coast. At around 3:40 am the Newfield struck rocks about 100 yards from shore, and 5 feet of water filled the holds immediately. The captain gave orders to lower the boats which caused a disorganised scramble for safety among the crew. The starboard lifeboat was cleared for lowering with two seamen and two apprentices in her, but almost as soon as she touched the water she was smashed to bits against the side of the vessel, and only one of the four reached safety ashore, able seaman McLeod. The rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The rescue was a difficult operation. The Port Campbell Rocket Crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. Peter Carmody, a local man, volunteered to swim about one mile offshore to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. He was assisted by James McKenzie and Gerard Irvine. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one-man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. For his heroic efforts, Peter Carmody was awarded the Bramley-Moore medal by the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society for Saving Life at sea on January 21st 1893. The medal and a letter of congratulations were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum by Peter Carmody's granddaughter Norma Bracken and her son Stuart Bracken on 25th May 2006. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is additionally significant because of the medal awarded to a local man Peter Carmody. The Newfield collection historically also represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history and its association with the shipwreck.Skylight, frame only. The heavily encrusted brass framework has eight bolts around the long side, and four metal bars forming two ‘v’ shapes across the centre. The frame is, slightly concave towards the inner side. The shorter ends of the frame each have a ‘U’ shaped bracket attached in the centre. The shorter ends are wider on one end and taper towards the other end to about a quarter of the thickness. The frame was recovered from the wreck of the NEWFIELD.Noneflagstaff hill maritime museum, newfield ship wreck, alexander stephen & sons, brownells & co, captain george scott, great ocean road ship wreck, peter carmody, bramley-moore medal, liverpool shipwreck and humane society, skylight cover, skylight frame, ship fitting, light cover, newfield -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageHandle, c. 1859
... THE "NEWFIELD" The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque... and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander ...This brass handle was found on Sea Elephant Bay beach in King Island, Tasmania, in 1913. The donor identified it as being from the wreck of the Newfield. It would could have been part of the fittings or amongst the cargo on the ship. ABOUT THE "NEWFIELD" The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt, the main export product of Sharpness. At about 9pm on 28th August 1892, in heavy weather, Captain Scott sighted, between heavy squalls, the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria but, due to a navigational error (the ship’s chronometers were wrong), he assumed it to be the Cape Wickham light on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered his course to the north, expecting to enter Bass Strait. The ship was now heading straight for the south west Victorian coast and at about 1:30am ran aground on a reef about 100 yards from shore and one mile east of Curdie’s Inlet, Peterborough. The ship struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with 6 feet of water in the holds. Rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The Port Campbell rocket crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. A local man, Peter Carmody, volunteered to swim one mile to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. One of the men, apprentice William McLeod, was rescued by local woman Margaret E. MacKenzie. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. According to Jack Loney ‘… when the drama was over . . the Newfield was deserted except for the Captain’s dog and two pigs.’ Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum has several artefacts that have been salvaged from the wreck. A report from SHP documented the following in regards to the Newfield collection: Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is of historical and archaeological significance at a State level, because of its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register. The collection is significant because of its relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as it is the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 (Living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the shipwreck. The Newfield collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criteria A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history Criteria B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criteria C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history Ornate brass handle, round plates each end, each with 4 round fixing holes. Found washed up on Sea Elephant Bay beach, King Island 1913, identified by donor as being from the wreck of the Newfield.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, barque newfield, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, ornate handle, sailing ship fitting, sea elephant bay, king island -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBearing cap, (estimated); Before The Newfield completion in 1889
... . The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee... it to the flue. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque ...This bearing cap is thought to be from a donkey winch engine, (or steam donkey, or donkey winch), which is a small secondary steam engine with a cylindrical shaped boiler. In 19th century merchant sailing a steam donkey was often used in marine applications such as to help raise and lower larger sails, load and unload cargo or to power pumps. The bearing cap could have been used on the donkey engine to hold the rod of the winch gear wheel in place, or bolted to another bearing cap around the neck on the top of the boiler’s cylinder, connecting it to the flue. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt, the main export product of Sharpness. At about 9pm on 28th August 1892, in heavy weather, Captain Scott sighted, between heavy squalls, the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria but, due to a navigational error (the ship’s chronometers were wrong), he assumed it to be the Cape Wickham light on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered his course to the north, expecting to enter Bass Strait. The ship was now heading straight for the south west Victorian coast. At about 1:30am the Newfield ran aground on a reef about 100 yards from shore and one mile east of Curdie’s Inlet, Peterborough. The ship struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with 6 feet of water in the holds. Rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The rescue was a difficult operation. The Port Campbell Rocket Crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. Peter Carmody, a local man, volunteered to swim about one mile off shore to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. He was assisted by James McKenzie and Gerard Irvine. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. According to Jack Loney ‘… when the drama was over . . the Newfield was deserted except for the Captain’s dog and two pigs.’ Peter Carmody was awarded the Bramley-Moore medal by the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society for Saving Life at Ssea, which he received by mail on January 21st 1893. The medal and a letter of congratulations were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum by Peter Carmody’s grand-daughter Norma Bracken and her son Stuart Bracken on 25th May 2006. The Bearing Cap joins other items in the Newfield collection.Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its association with the shipwreck.Brass bearing cap from the wreck of the sailing ship “Newfield” is possibly from a donkey winch engine. The half-circle shaped cuff with a rectangular brass block attached to the outside of each end of the half-circle. Both blocks have a round hole in their centre and are approximately the same depth and width as the cuff. Midway around the half-circle cuff is another brass block that is about twice the depth of the cuff. It appears to have been a circular shape that has been modified to match the width of the collar, having had the sides of the circle cut off to leave straights edge parallel to the edges of the cuff. In the centre of this block is another hole, and there appears to be the head of a bolt inside this hole. The bearing cap is lightly encrusted.1893, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, warrnambool, newfield, 1892, 28 august 1892, port campbell, shipwreck, nineteenth century, ship, curdie s river, victorian shipwrecks, barque, ship wreck, 29 august 1892, 19th century, bearing cap, donkey engine, donkey winch, steam donkey -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAward - Medal, ca. 1872
... shipwreck. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque... shipwreck. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque ...This medal is the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society’s “Bramley-Moore medal for saving life at sea 1872”. The Society was formed in 1839. In 1872 Mr John Bramley-Moore donated £500 on condition that the medal have the specific inscription above on its reverse. The Bramley Morre medal was first awarded in 1874 and records show that since that time only one gold medal has been awarded, twenty-two silver medals and seventeen bronze medals, the last being in 1945. This Bromley-Moore medal was awarded to Peter Carmody for his bravery in saving lives on the Newfield shipwreck. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt, the main export product of Sharpness. At about 9pm on 28th August 1892, in heavy weather, Captain Scott sighted, between heavy squalls, the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria but, due to a navigational error (the ship’s chronometers were wrong), he assumed it to be the Cape Wickham light on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered his course to the north, expecting to enter Bass Strait. The ship was now heading straight for the south west Victorian coast. At about 1:30am the Newfield ran aground on a reef about 100 yards from shore and one mile east of Curdie’s Inlet, Peterborough. The ship struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with 6 feet of water in the holds. Rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The rescue was a difficult operation. The Port Campbell Rocket Crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. Peter Carmody, a local man, volunteered to swim about one mile off shore to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. He was assisted by James McKenzie and Gerard Irvine. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. According to Jack Loney ‘… when the drama was over . . the Newfield was deserted except for the Captain’s dog and two pigs.’ Peter Carmody was awarded the Bramley-Moore medal by the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society for Saving Life at Ssea, which he received by mail on January 21st 1893. The medal and a letter of congratulations were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum by Peter Carmody’s grand-daughter Norma Bracken and her son Stuart Bracken on 25th May 2006. The Medal and Letter of Congratulations join other items in the Newfield collection.The Carmody Medal recognises the bravery of Peter Carmody in risking his life to rescue crew members of the Barque Newfield when it was wrecked near Curdies Inlet in August 1892. The ‘Bramley-Moore medal for saving life at sea, 1872’ was presented by the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society. The medal and accompanying letter have local and international historic significance as they demonstrate both the difficulties associated with navigation and the dangers of shipping along the South West Coast of Victoria in the 19th century and the medal’s association with the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society and John Bramley-Moore, who provided £500 to found the Bramley-Moore medal. The medal is socially significant. It emphasises the importance of Peter Carmody in rescuing victims of shipwrecks with little thought for his own safety. The medal reminds us of the importance of local people to Victoria’s maritime history. The Carmody Medal and Humane Society letter were in the Carmody family until they were presented to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, by the grand-daughter and great-grandson of Peter Carmody, on the 25th May 2006. The medal is significant for its complete provenance recorded in the donation documentation. The medal is in very good condition and relatively rare with only 22 silver medals awarded between 1874 and 1945. The Carmody Medal and letter add a human element to the story of the shipwrecks. They give life and significance to the Newfield, its victims and its artefacts. Bramley-Moore medal from the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society, awarded to Peter Carmody. The round,silver medal is attached to a looped blue ribbon by a decorative, swivelling silver connector. The top of the ribbon has a silver pin bar threaded through it. The obverse of the medal has a design of a man kneeling on a floating part of a wreck. He is rescuing a child from the sea. There is a manned boat in the distance rescuing someone from the sea. In the far background there is a sailing ship. The top third of the medal has an inscription around it. The reverse shows a long-legged hen cormorant with extended wings holding an olive branch in its beak. The bird is surrounded by a wreath of oak leaves made from two branches. There is an inscription between the design and the rim that goes all the way around the circumference. There is a name engraved around the edge of the medal. The medal in embedded in a purple velvet panel that rests inside a brown, leather-covered case. The lid of the case has a gold embossed emblem in the cemtre. Both the lid and base have a rectangular gold border. The lid is attached to the base with two brass hinges. The base has a brass push-button catch. The box is lined with padded cream silk. The lining inside the lid has a gold emblem in the centre.The obverse has the words "LORD, SAVE US, WE PERISH". The reverse has the words "BRAMLEY-MOORE MEDAL FOR SAVING LIFE AT SEA" and "1872". Around the edge of the medal are the words "PETER CARMODY, FOR HAVING BEEN MAINLY INSTRUMENTAL IN RESCUING THE CREW OF THE BARQUE NEWFIELD, AUG 29 1892" The pin bar has the words “LIVERPOOL SHIPWRECK & HUMANE SOCIETY” written across it. The gold embossed emblem on the lid of the box has the words in the centre "SHIPWRECK AND …. …. ….FOUNDED 1839" The gold emblem on the cream silk lining has the words “BY APPOINTMENT ELKINGTON & CO” printed on it.medal, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, peter, peter carmody, carmody, bramley moore, newfield, liverpool shipwreck and humane society, 1892, 28 august 1892, august 1892, port campbell, bravery, shipwreck, rescue, nineteenth century, ship, curdie s river, victorian shipwrecks, barque, stuart bracken, norma bracken, gerard irvine, james mckenzie -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePainting - Paintings - set of three, Beni Carr Glyn Burnett, 1933
... . It was a 4 masted steel barque, built in 1921 in Kiel, Germany.... It was a 4 masted steel barque, built in 1921 in Kiel, Germany ...Beni Carr Glyn Burnett (also known as B. C. G. Burnett or Beni Burnett) was born in 1889 to missionary parents in Mongolia. When he was 15 years old he began training as an architect with a firm in Shanghai. He worked in Singapore, Japan and China before moving to Australia around 1933. In 1937 he was appointed as the Commonwealth principal architect in the Northern Territory. He went on to design a series of houses for senior public servants and military personnel which became very popular as they were specifically designed for the tropics - incorporating louvres, high ceilings and good ventilation. When Darwin was bombed in February 1942, he was evacuated to Alice Springs where he continued to work as an architect. He also became a Magistrate and Coroner in Alice Springs. In later life he was well known for sketching clientele in public bars. He died in 1955. Beni Burnett was living in Sydney in 1933 when he produced these three artworks. There were several photography firms operating in Sydney at this time who specialised in photographing ships and the shipping trade (e.g. Samuel J. Hood and William James Hall) and whose photographs were used by artists to produce ship portraits. Both of these photographers took photographs of the two ships in B. C. G. Burnett's watercolours. The "Magdalene Vinnen" was photographed by Samuel J Hood in a series of photos taken in March 1933. It was a 4 masted steel barque, built in 1921 in Kiel, Germany and for almost 80 years was the largest traditional sailing ship in operation. It was used extensively as a cargo ship. It sailed into Sydney Harbour on 27th Feb 1933, loaded with almost 16,000 bales of wool destined for Falmouth, England. In March 1933 (whilst in Sydney) the German Republic flag (on orders from Adolph Hitler) was lowered and replaced with the old monarchist flag which was then to be the official flag and beside it the Nazi flag was to be flown on all ceremonial occasions. It visited Australia again in 1935 with its cargo being wheat from Port Broughton, S. A. In 1936 it was renamed "Kommodore Johnsen" and in 1945 (after WW2) the ship was awarded to the Soviet Union as war compensation and renamed "STS Sedov". The "Winterhude" (originally called "Mabel Rickmers) was a three masted Finnish barque built in 1898 by Rickers - Werft Bremerhaven for use on the East India rice trade and later the South American nitrate trade. After WW1 it came under French control as war compensation. It was also sold several times and at one stage was called "Selma Hemsoth" but in 1925 it was bought by Gustaf Erikson who restored the name "Winterhude" and the vessel became a regular transport in the Australian wheat trade. In 1944 it was sold to the German navy before being taken over by the British at the end of WW2. It was photographed in Sydney by William James Hall in 1931 on its way to Port Lincoln, South Australia to load wheat for Europe. The third ship depicted by B. C. G. Burnett is a pen and wash sketch labelled "The White Ship" and exactly matches a photograph pasted into his personal scrapbook which is in the "Library and Archives N. T.". The name of the ship is unknown and B. C. G. Burnett may have taken some artistic licence with the colouring as in the original photograph, the ship had a dark hull.This set of three small artworks is significant as examples of shipping (particularly the use of sailing ships) that were still being used as late as the 1930's in Australia. They are also important because their creator (B. C. G. Burnett) went on to become a well-known public figure in the Northern Territory in the late 1930's due to his innovative approach to designing homes for the tropical climate.A set of three artworks by B. C. G. Burnett of sailing ships in Sydney Harbour. They are all on rectangular watercolour paper with small diagonal edges at each corner. Painting 1 is a watercolour painting of a sailing ship called "Magdalene Vinnen". It shows a 4 masted barque with a blue and red steel hull in full sail heading towards the viewer. The painter's name (B. C. G. Burnett) and date (1933) are written on the bottom left-hand corner of the painting. Painting 2 is a watercolour painting of a sailing ship called "Winterhude". It shows a 3-masted barque with a blue and red steel hull in full sail heading away from the viewer. A small figure can be seen at the wheel at the rear of the ship. The painter's name (B. C. G. Burnett) and date (1933) are written on the bottom left-hand corner of the painting. Sketch 3 is an ink sketch of an unknown sailing ship moored to a dock. There are several small boats tied up near the sailing ship and a large steel freighter can be seen in the background. There is a faint wash of colour on parts of the sketch - the bottom of the ship, the masts and booms and the water at the end of the pier. The title (The White Ship) and the artist's name (B. C. G. Burnett) are written in ink in the top left corner. 1 (front) - "B. C. G. BURNETT. 1933 2 (front) - "B. C. G. BURNETT. 1933" 3 (front) - "THE WHITE SHIP / B. C. G. BURNETT"flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, sailing ships, ships, barque, magdalene vinnen, winterhude, beni carr glyn burnett, b. c. g. burnett, beni burnett, painting, watercolour painting, sketch, ink sketch, sydney harbour, architect, darwin, burnett house, photography, samuel j. hood, william james hall, sedov, kommodore johnsen, mabel rickmers -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Pill bottle, from mid-19th century to 1902
... -1902 - The Inverlochy was a steel sailing barque built...-1902 - The Inverlochy was a steel sailing barque built ...This small handmade bottle possibly dates from the mid-1840s. It may have been used as a traveller's ink bottle, due to its wide mouth. It was recovered from the wreck of the Inverlochy and is part of the John Chance collection. Small glass ink bottles similar to this one were handmade, blown into a cup shaped mould, and sharply broken off from the blow-pipe at the neck and sealed with a cork or wax. The mouth of this bottle appears to have been added after it was blown. INVERLOCHY 1895-1902 - The Inverlochy was a steel sailing barque built in Scotland in 1895 for international trade. In 1902 the Inverlochy left Liverpool under the command of Captain E.R. Kendrick. There were 21 officers and crew and the captain’s wife Mrs Kendrick, on board, bound for Australia with cargo that included tools, chemicals, liquor (beer, whisky, stout, rum, and brandy), steel, iron, wire netting, hoop iron, tinplate and pig iron), and steel wire for the Melbourne Tramway Company, tiles, soap, soft goods and earthenware. On December 18 almost at their destination, the Inverlochy ran aground on Ingoldsby Reef at Point Addis, near Anglesea. The crew and passengers left the ship via lifeboat and landed at Thompson’s Creek, then walked about 20 kilometres to Barwon Heads. Salvagers were interested in the 10 miles of cable in the hold. Mrs Kendrick’s ‘high grade’ bicycle was amongst the items salvaged but she lost her jewellery and two pianos. By February 1903 the ship had broken up and objects such as bottles and casks of liquor were washed ashore. Bad weather shook the wreck in June 1903, causing the ship’s spars and figurehead to be washed ashore. This handmade bottle is historically significant for its association with being made and used during the mid-to-late 19th century. This handmade glass bottle is significant for its connection with the John Chance Collection, which is historically significant as an example of artefacts from wrecks that had been lost in the coastal waters of Victoria from thirty to over one hundred years before John Chance and others discovered them. These artefacts are a sample of goods carried as cargo or personal possessions, and of ship hardware of that era. The bottle is significant through its connection with the barque, Inverlochy, The Inverlochy is significant for its cargo, which is a snapshot of the array of goods imported into Australia at the turn of the 19th century, including cable for the Melbourne Tramway Company. The Inverlochy is historically significant and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Database, VHR S338. The wreck of the Inverlochy is important as an accessible dive site that shows the remains of a large international trading vessel and its contents. It is valuable for an insight into Victorian era of shipping and maritime history.Bottle, clear glass, handmade, mould-blown. Small pill bottle has round mouth and neck, straight sides, rectangular base, no seams, shiny surface. Thickness of glass varies. Mouth is lop-sided and lip varies in width. Inscription of logo on both wide sides. Inscription embossed on sides [tear drop] logo. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, john chance, inverlochy, scotland, captain e.r. kendrick, melbourne tramway company, tramway cable, ingoldsby reef, point addis, anglesea, thompson’s creek, barwon heads, victorian, antique, handmade, mould blown, small glass bottle, rectangular glass bottle, pill bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAward - Document, 21/1/1893
... was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland... was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland ...The name on the letterhead, “Canning Pierhead North” is the name of the Liverpool Pilot Authority, which was situated in 1883 at Cannon Pier on the River Mersey where ships entered to travel to Liverpool. The logo on the letterhead belongs to the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society. The letter is addressed to “Mr Peter Carmody, Port Campbell, south coast of Australia”, and reads as follows: “January 21st 1893, Dear Sir, I have the pleasure to forward to you by post herewith a Silver Medal and a Certificate of Thanks, voted to you by the Committee of the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society for your courage and humanity in going out into the surf to rescue the survivors of the crew of the barque “Newfield” which vessel was wrecked near Port Campbell on the 29th of August last. Be kind enough to send a few lines acknowledging receipt of the testimonials. I am Dear Sir, Yours Faithfully, Robert P. J. Simpson, Secretary.” The medal accompanying the letter is the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society’s “Bramley-Moore medal for saving life at sea 1872”. The Society was formed in 1839. In 1872 Mr John Bramley-Moore donated £500 on condition that the medal have the specific inscription above on its reverse. The Bramley Morre medal was first awarded in 1874 and records show that since that time only one gold medal has been awarded, twenty-two silver medals and seventeen bronze medals, the last being in 1945. This Bromley-Moore medal was awarded to Peter Carmody for his bravery in saving lives on the Newfield shipwreck. The Newfield was a three-masted iron and steel barque, built in Dundee, Scotland, in 1889 by Alexander Stephen and Sons. It was owned by the Newfield Ship Company in 1890 and later that year It was registered in Liverpool to owners Brownells and Co. The Newfield left Sharpness, Scotland, on 28th May 1892 with a crew of 25 under the command of Captain George Scott and on 1st June left Liverpool. She was bound for Brisbane, Australia, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt, the main export product of Sharpness. At about 9pm on 28th August 1892, in heavy weather, Captain Scott sighted, between heavy squalls, the Cape Otway light on the mainland of Victoria but, due to a navigational error (the ship’s chronometers were wrong), he assumed it to be the Cape Wickham light on King Island, some 40 miles south. He altered his course to the north, expecting to enter Bass Strait. The ship was now heading straight for the south west Victorian coast. At about 1:30am the Newfield ran aground on a reef about 100 yards from shore and one mile east of Curdie’s Inlet, Peterborough. The ship struck heavily three times before grounding on an inner shoal with 6 feet of water in the holds. Rough sea made the job of launching lifeboats very difficult. The first two lifeboats launched by the crew were smashed against the side of the ship and some men were crushed or swept away. The third lifeboat brought eight men to shore. It capsized when the crew tried to return it to the ship for further rescue The rescue was a difficult operation. The Port Campbell Rocket Crew arrived and fired four rocket lines, none of which connected with the ship. Peter Carmody, a local man, volunteered to swim about one mile off shore to the ship with a line to guide the fourth and final lifeboat safely to shore. He was assisted by James McKenzie and Gerard Irvine. Seventeen men survived the shipwreck but the captain and eight of his crew perished. The Newfield remained upright on the reef with sails set for a considerable time as the wind slowly ripped the canvas to shreds and the sea battered the hull to pieces. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one man style of navigation" and that the Captain had not heeded the advice of his crew. According to Jack Loney ‘… when the drama was over . . the Newfield was deserted except for the Captain’s dog and two pigs.’ Peter Carmody was awarded the Bramley-Moore medal by the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society for Saving Life at Ssea, which he received by mail on January 21st 1893. The medal and letter of congratulations were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum by Peter Carmody’s grand-daughter Norma Bracken and her son Stuart Bracken on 25th May 2006. The Medal and Letter of Congratulations join other items in the Newfield collectionlFlagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from the Newfield is significant for its association with the shipwreck Newfield, which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Registry. The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects. The Newfield collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of an international cargo ship. The Newfield collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its association with the shipwreck. The Letter accompanying the Medal for Bravery awarded to Peter Carmody is significant because the attempt to save lives is associated with the shipwreck Newfield.A copy of a letter from the Liverpool Shipwreck and Humane Society to Peter Carmody in reference to the bravery of Peter Carmody over the wreck of the "Newfield". The letter is divided into 2 columns and is written in longhand using black ink on both columns. There is a letterhead in the centre of the left hand page and a round logo printed or stamped on the top of left of the left hand page. The centre of the logo shows a design of a man kneeling on a floating part of a wreck. He is rescuing a child from the sea. On the top of the circle of the logo a design shows a long-legged hen cormorant with extended wings holding an olive branch in its beak. There is also the name of a city printed onto the page under the letterhead. The letter has been folded into half along its long side, then in half again along its long side then into thirds. The letter is dated January 21st 1893. “CANNING, PIERHEAD, NORTH” and “LIVERPOOL” are printed on the top left hand page. The logo “LIVERPOOL SHIPWRECK AND HUMANE SOCIETY” is printed or embossed on the paper.28 august 1892, bramley moore, carmody, certificate of thanks, curdie's river, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, gerard irvine, james mckenzie, liverpool shipwreck and humane society, maritime museum, medal, newfield, nineteenth century, norma bracken, peter carmody, port campbell, rescue, robert simpson,, shipwreck, ship wreck, stuart bracken, victorian shipwrecks -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle, from mid-19th century to 1902
... . INVERLOCHY 1895-1902 - The Inverlochy was a steel sailing barque... to their low cost. INVERLOCHY 1895-1902 - The Inverlochy was a steel ...This ink bottle is ‘boat’ shaped, which was a common design from the mid-1840s. It was crudely made; maybe it was rejected as a practice bottle or perhaps heat or pressure has distorted it. The bottle was recovered from the wreck of the Inverlochy and is part of the John Chance collection. Ink in the 1700s ink could be purchased in powdered or block form from apothecary shops, to be mixed with water as needed. Then in the mid-1800s chemists began selling ink in liquid form, in small, inexpensive and often attractive bottles. The small glass ink bottles were handmade, blown into a cup shaped mould, and sharply broken off from the blow-pipe at the neck, referred to as the English-made ‘burst-off’ finish. The neck was then filed, filled with liquid ink and sealed with a cork or wax. It was a quick, affordable container and made pen and ink writing available to the public. The name ‘penny ink’ bottles was a common title due to their low cost. INVERLOCHY 1895-1902 - The Inverlochy was a steel sailing barque built in Scotland in 1895 for international trade. In 1902 the Inverlochy left Liverpool under the command of Captain E.R. Kendrick. There were 21 officers and crew and the captain’s wife Mrs Kendrick, on board, bound for Australia with cargo that included tools, chemicals, liquor (beer, whisky, stout, rum, and brandy), steel, iron, wire netting, hoop iron, tinplate and pig iron), and steel wire for the Melbourne Tramway Company, tiles, soap, soft goods and earthenware. On December 18 almost at their destination, the Inverlochy ran aground on Ingoldsby Reef at Point Addis, near Anglesea. The crew and passengers left the ship via lifeboat and landed at Thompson’s Creek, then walked about 20 kilometres to Barwon Heads. Salvagers were interested in the 10 miles of cable in the hold. Mrs Kendrick’s ‘high grade’ bicycle was amongst the items salvaged but she lost her jewellery and two pianos. By February 1903 the ship had broken up and objects such as bottles and casks of liquor were washed ashore. Bad weather shook the wreck in June 1903, causing the ship’s spars and figurehead to be washed ashore. This boat shaped handmade ink bottle is historically significant for its association with communications and record keeping in the mid-to-late 19th century. The bottle is socially significant as an example of making a useful product affordable to every day people. This handmade glass ink bottle is significant for its connection with the John Chance Collection, which is historically significant as an example of artefacts from wrecks that had been lost in the coastal waters of Victoria from thirty to over one hundred years before John Chance and others discovered them. These artefacts are a sample of goods carried as cargo or personal possessions, and of ship hardware of that era. The ink bottle is significant through its connection with the barque, Inverlochy, The Inverlochy is significant for its cargo, which is a snapshot of the array of goods imported into Australia at the turn of the 19th century, including cable for the Melbourne Tramway Company. The Inverlochy is historically significant and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Database, VHR S338. The wreck of the Inverlochy is important as an accessible dive site that shows the remains of a large international trading vessel and its contents. It is valuable for an insight into Victorian era of shipping and maritime history.Ink bottle, thick clear glass, rectangular base with small round mouth, long sides have have a U shaped groove along the shoulders (used for resting pen handles). The outside surface has a white clay-type reside over it. Bottle is very bent and distorted. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, john chance, inverlochy, scotland, captain e.r. kendrick, melbourne tramway company, tramway cable, ingoldsby reef, point addis, anglesea, thompson’s creek, barwon heads, boat ink bottle, cottage ink, penny ink, glass ink bottle, pen rest, writing accessory, victorian, antique, ink well, sheer lip, distorted body, handmade, mould blown, statoionery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMachine - Steering Gear, 1889
... ): - The Newfield was an iron and steel sailing barque of 1306 tons, built...): - The Newfield was an iron and steel sailing barque of 1306 tons, built ...Steering Gear Operation: All steering was done from the stern of the ship and a steering mechanism was used to connect the rudder to the ship's wheel, often housed in a box-like construction behind the helm. The rudder was, in turn, mounted on a pintle or stern-post held in place by gudgeon's (sockets). The steering was activated with lines attached to the blocks on the two threads (half left hand, half right hand) of the steering gear. As the helmsman turned the helm in the direction in which he wished the ship to travel, the central screw of the steering gear, which was attached to the back of the helm, turned horizontally. This caused the rods on either side of the gear to move backwards or forwards at the same time, which then turned the pintle and rudder to port or starboard. A brief history of the Newfield (1889-1892): - The Newfield was an iron and steel sailing barque of 1306 tons, built in 1889 by Alexander Stephen & Sons Dundee (Yard No 89) for Brownelles & Co., Liverpool. The Newfield was on a voyage from Sharpness to Brisbane on 29 August 1892, with a cargo of 1850 tons of fine rock salt. The Cape Otway light had been sighted in squally, bumpy weather, but the captain was under the impression it was the King Island light. The ship’s chronometers were wrong, and orders were given to tack the ship away from the light, which headed it straight for the cliffs of the Victorian coast. The vessel struck rocks about 100 yards from shore, and five feet of water immediately filled the holds. The captain gave orders to lower the boats which caused a disorganised scramble for safety among the crew. The panic resulted in the deaths of nine men, including the captain when they drowned after the boats capsized in heavy seas. The seventeen men who regained the ship decided to wait until daylight and rowed to Peterborough in the ship’s jolly boat and gig after locals had failed to secure a rocket apparatus line to the ship. The Marine Board inquiry found the wreck was caused by a "one-man style of navigation" and that the captain had not heeded the advice of his crew.The Newfield wreck and its collection of recovered items are heritage listed and are regarded as historically significant. They represent aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and their potential for us today to interpret the maritime history and social themes of the time. The assemblage of various Newfield artefacts held in the Flagstaff Hill Museum is not only significant for its association with the shipwreck but helps archaeologists when examining the relationship between the objects to better understand our colonial marine past.Ship’s steering gear, cast iron, consists of a long round metal rod into which gears have been machined. The thread of the gear from one end to almost the centre winds in a left hand direction while the thread of the gear from the other end to almost the centre winds in the right hand direction. Each end of the rod has a metal coupler attached and two narrower round rods are also attached to the coupling, one each side of the gear rod, the same length as it and parallel to it. Two more ‘S’ shaped couplers are joined to the gear rod. Each of these have an opening through which the gear rod is threaded and can move along. There is another opening in these couplers through which one of the narrower rods is threaded. The other end of this coupler has half length metal rod attached to it by a bolt through the ring at the end of the rod. One end of the steering gear still has the brass hub of the ship’s wheel solidly attached. The hub no longer has its wooden spokes but the ten holes for the spokes can be easily recognised.Noneflagstaff hill, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, peter carmody, carmody, newfield, shipwreck, peterborough, south west victoria, rocket, rocket crew, shipwreck artefact, flagstaff hil maritime museum, steering, steering gear, screw steering gear, sailing ship -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Glass Bottle, mid-19th century to 1902
... . THE INVERLOCHY (1895-1902) - The Inverlochy was a steel sailing barque.... THE INVERLOCHY (1895-1902) - The Inverlochy was a steel sailing barque ...This handmade glass bottle was recovered from the wreck of the 1895-1902 ship Inverlochy and is part of the John Chance Collection. The bottle has side seams that extend from base to mouth, indicating that it would have been made in a mould. The parallel, diagonal lines are likely to have been made by the molten glass being mouth-blown into the mould. The mould would have also had the pattern for the embossed numbers in the base. The seamless applied mouth would have been added after the bottle was removed from the two-piece mould. The even neck of the bottle would have probably been sealed with a cork or glass stopper. Bottles similar to this one were used for medical (apothecary) and cosmetic purposes. Bottles with these features date from around the late 19th to early 20th century. Bottles began to have embossed numbers on the bases from the late 19th century and the practice continues into modern times. The numbers may represent the date of manufacture i.e. “4188” may be 4th January 1888. It may instead be the date of the patent or design pattern number. This bottle may have been made around 1888 and the latest it could have been made was 1902, the year of the wreck of the Inverlochy. THE INVERLOCHY (1895-1902) - The Inverlochy was a steel sailing barque built in Scotland in 1895 for international trade. In 1902 the Inverlochy left Liverpool under the command of Captain E.R. Kendrick. There were 21 officers and crew and the captain’s wife Mrs Kendrick, on board, bound for Australia with cargo that included tools, chemicals, liquor (beer, whisky, stout, rum, and brandy), steel, iron, wire netting, hoop iron, tinplate and pig iron), and steel wire for the Melbourne Tramway Company, tiles, soap, soft goods and earthenware. On December 18 almost at their destination, the Inverlochy ran aground on Ingoldsby Reef at Point Addis, near Anglesea. The crew and passengers left the ship via lifeboat and landed at Thompson’s Creek, then walked about 20 kilometres to Barwon Heads. Salvagers were interested in the 10 miles of cable in the hold. Mrs Kendrick’s ‘high grade’ bicycle was amongst the items salvaged but she lost her jewellery and two pianos. By February 1903 the ship had broken up and objects such as bottles and casks of liquor were washed ashore. Bad weather shook the wreck in June 1903, causing the ship’s spars and figurehead to be washed ashore. This glass bottle is historically significant as it represents methods of storage and manufacture that were used from the 19th century and into the early-20th century, before machine made bottles were becoming common. The shape and size of the bottle are similar to bottles used for medical and cosmetic purposes in that period. The glass bottle also has significant as it was recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Inverlochy in the late 1960s to early 1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. This glass bottle is significant because of its historical connection to the barque Inverlochy, which is an example of a commercial international steel sailing barque and is listed on the Victorian Heritage Database VHR S338. The Inverlochy is significant for its cargo, which is a snapshot of the kind of goods imported into Australia at the turn of the 19th century, including cable for the Melbourne Tramway Company. The wreck of the Inverlochy is important as an accessible dive site that shows the remains of a large international trading vessel and its contents. It is valuable for an insight into Victorian era of shipping and maritime history. Bottle; clear glass, round, handmade. Narrow lip is flat across top and on side edge, neck is straight, about a third of the bottle’s height. The shoulder is rounded, and the body has straight sides with two side seams from below the lip to the base, which is shallow. Outer glass surface is rough, inner surface has areas of dried, light coloured substance. The body has several diagonal parallel lines and areas with opalescent shine. Base has embossed inscription. Embossed inscription on base "4188".flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, john chance, inverlochy, scotland, captain e.r. kendrick, melbourne tramway company, ingoldsby reef, handmade, glass bottle, apothecary, cosmetic, mould blown, vintage, two-piece bould, point addis, medicine -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Glass Bottle, mid-19th century to 1902
... -1902) - The Inverlochy was a steel sailing barque built...-1902) - The Inverlochy was a steel sailing barque built ...This handmade glass bottle was recovered from the wreck of the 1895-1902 ship Inverlochy and is part of the John Chance Collection. The bottle has side seams that extend from base to mouth, indicating that it would have been made in a mould. The parallel, diagonal lines are likely to have been made by the molten glass being mouth-blown into the mould. The mould would have also had the pattern for the embossed numbers in the base. The seamless applied mouth would have been added after the bottle was removed from the two-piece mould. The even neck of the bottle would have probably been sealed with a cork or glass stopper. Bottles similar to this one were used for medical (apothecary) and cosmetic purposes. Bottles with these features date from around the late 19th to early 20th century. Bottles began to have embossed numbers on the bases from the late 19th century and the practice continues into modern times. The numbers may represent the date of manufacture i.e. “463” may be April 1863. It may instead be the date of the patent or design pattern number. This bottle may have been made around 1863 and the latest it could have been made was 1902, the year of the wreck of the Inverlochy. THE INVERLOCHY (1895-1902) - The Inverlochy was a steel sailing barque built in Scotland in 1895 for international trade. In 1902 the Inverlochy left Liverpool under the command of Captain E.R. Kendrick. There were 21 officers and crew and the captain’s wife Mrs Kendrick, on board, bound for Australia with cargo that included tools, chemicals, liquor (beer, whisky, stout, rum, and brandy), steel, iron, wire netting, hoop iron, tinplate and pig iron), and steel wire for the Melbourne Tramway Company, tiles, soap, soft goods and earthenware. On December 18 almost at their destination, the Inverlochy ran aground on Ingoldsby Reef at Point Addis, near Anglesea. The crew and passengers left the ship via lifeboat and landed at Thompson’s Creek, then walked about 20 kilometres to Barwon Heads. Salvagers were interested in the 10 miles of cable in the hold. Mrs Kendrick’s ‘high grade’ bicycle was amongst the items salvaged but she lost her jewellery and two pianos. By February 1903 the ship had broken up and objects such as bottles and casks of liquor were washed ashore. Bad weather shook the wreck in June 1903, causing the ship’s spars and figurehead to be washed ashore. This glass bottle is historically significant as it represents methods of storage and manufacture that were used from the 19th century and into the early-20th century, before machine made bottles were becoming common. The shape and size of the bottle are similar to bottles used for medical and cosmetic purposes in that period. The glass bottle also has significant as it was recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Inverlochy in the late 1960s to early 1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. This glass bottle is significant because of its historical connection to the barque Inverlochy, which is an example of a commercial international steel sailing barque and is listed on the Victorian Heritage Database VHR S338. The Inverlochy is significant for its cargo, which is a snapshot of the kind of goods imported into Australia at the turn of the 19th century, including cable for the Melbourne Tramway Company. The wreck of the Inverlochy is important as an accessible dive site that shows the remains of a large international trading vessel and its contents. It is valuable for an insight into Victorian era of shipping and maritime history. Bottle; clear glass with opalescent shine in places, round, handmade. Narrow lip is flat across top and on side edge, neck is straight, about a third of the bottle’s height. The shoulder is rounded, and the body has straight sides with two pronounced side seams from below the lip to the base, which is shallow. Outer glass surface is smooth, inner surface has areas of dried, light coloured substance. Base has embossed inscription. Embossed "463" and logo symbol [trident]flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, john chance, inverlochy, scotland, captain e.r. kendrick, melbourne tramway company, ingoldsby reef, handmade, glass bottle, apothecary, cosmetic, mould blown, vintage, two-piece bould, point addis, medicine -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle, 1890s to 1902
... - The Inverlochy was a steel sailing barque built in Scotland in 1895... calligraphy. INVERLOCHY 1895-1902 - The Inverlochy was a steel ...This design of ink bottle or ink well was commonly referred to as a ‘penny ink well’ because it was very inexpensive to produce. It is also known as a dwarf ink bottle. It was recovered from the wreck of the 1895-1902 ship Inverlochy and is part of the John Chance Collection. Pen and ink has been in use for hand writing from about the seventh century up until the mid-20th century. Up until around the mid-19th century a quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used. In the 1850s the steel point pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. In the 1880s a successful portable fountain pen was designed, giving a smooth flowing ink and ease of use. Ink wells, used with steel nib dip pens, were commonly used up until the mid-20th century. The pens only held a small amount of ink so users had to frequently dip the nib of the pen into an ink well for more ink. Hand writing with pen and ink left wet writing on the paper, so blotting paper was carefully used to absorb the excess ink and prevent smudging. Ink could be purchased, ready to use, or in the powdered form, which needed to be mixed with water. After the invention of fountain pens, which had a reservoir of ink, and then ballpoint pens, which also had ink that flowed freely, the dip pen was slowly replaced. However, artisans continue to use nib pens to create beautiful calligraphy. INVERLOCHY 1895-1902 - The Inverlochy was a steel sailing barque built in Scotland in 1895 for international trade. In 1902 the Inverlochy left Liverpool under the command of Captain E.R. Kendrick. There were 21 officers and crew and the captain’s wife Mrs Kendrick, on board, bound for Australia with cargo that included tools, chemicals, liquor (beer, whisky, stout, rum, and brandy), steel, iron, wire netting, hoop iron, tinplate and pig iron), and steel wire for the Melbourne Tramway Company, tiles, soap, soft goods and earthenware. On December 18 almost at their destination, the Inverlochy ran aground on Ingoldsby Reef at Point Addis, near Anglesea. The crew and passengers left the ship via lifeboat and landed at Thompson’s Creek, then walked about 20 kilometres to Barwon Heads. Salvagers were interested in the 10 miles of cable in the hold. Mrs Kendrick’s ‘high grade’ bicycle was amongst the items salvaged but she lost her jewellery and two pianos. By February 1903 the ship had broken up and objects such as bottles and casks of liquor were washed ashore. Bad weather shook the wreck in June 1903, causing the ship’s spars and figurehead to be washed ashore. This ink bottle is historically significant as it represents methods of hand written communication that were still common up until the mid-20th century, when fountain pens and ballpoint pens took over in popularity and convenience. The Ink bottle also has significant as it was recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Inverlochy in the late 1960s to early 1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. This Ink bottle is significant because of its historical connection to the barque Inverlochy, which is an example of a commercial international steel sailing barque and is listed on the Victorian Heritage Database VHR S338. The Inverlochy is significant for its cargo, which is a snapshot of the kind of goods imported into Australia at the turn of the 19th century, including cable for the Melbourne Tramway Company. The wreck of the Inverlochy is important as an accessible dive site that shows the remains of a large international trading vessel and its contents. It is valuable for an insight into Victorian era of shipping and maritime history.Ink bottle or ink well; cylindrical shaped, salt-glazed, mid-brown ceramic bottle. It has a small round mouth, rounded lip that extend past the short neck, wide shoulders, straight sides, flat bottom. Handmade. Also called a Penny Ink Well.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, john chance, inverlochy, scotland, captain e.r. kendrick, melbourne tramway company, tramway cable, ingoldsby reef, point addis, anglesea, thompson’s creek, barwon heads, ink bottle, writing equipment, writing accessory, office equipment, stationery, domestic, stoneware, clay, ceramic, pottery, ink well, inkwell, penny ink well, nib pen, dip pen, ink, hand writing, record keeping, household, business, vintage, blotting paper, dwarf ink -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle, 1890s to 1902
... was a steel sailing barque built in Scotland in 1895 for international... calligraphy. INVERLOCHY 1895-1902 - The Inverlochy was a steel ...This design of ink bottle or ink well was commonly referred to as a ‘penny ink well’ because it was very inexpensive to produce. It is also known as a dwarf bottle. It was recovered from the wreck of the 1895-1902 ship Inverlochy and is part of the John Chance Collection. Pen and ink has been in use for hand writing from about the seventh century up until the mid-20th century. Up until around the mid-19th century a quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used. In the 1850s the steel point pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. In the 1880s a successful portable fountain pen was designed, giving a smooth flowing ink and ease of use. Ink wells, used with steel nib dip pens, were commonly used up until the mid-20th century. The pens only held a small amount of ink so users had to frequently dip the nib of the pen into an ink well for more ink. Hand writing with pen and ink left wet writing on the paper, so blotting paper was carefully used to absorb the excess ink and prevent smudging. Ink could be purchased, ready to use, or in the powdered form, which needed to be mixed with water. After the invention of fountain pens, which had a reservoir of ink, and then ballpoint pens, which also had ink that flowed freely, the dip pen was slowly replaced. However, artisans continue to use nib pens to create beautiful calligraphy. INVERLOCHY 1895-1902 - The Inverlochy was a steel sailing barque built in Scotland in 1895 for international trade. In 1902 the Inverlochy left Liverpool under the command of Captain E.R. Kendrick. There were 21 officers and crew and the captain’s wife Mrs Kendrick, on board, bound for Australia with cargo that included tools, chemicals, liquor (beer, whisky, stout, rum, and brandy), steel, iron, wire netting, hoop iron, tinplate and pig iron), and steel wire for the Melbourne Tramway Company, tiles, soap, soft goods and earthenware. On December 18 almost at their destination, the Inverlochy ran aground on Ingoldsby Reef at Point Addis, near Anglesea. The crew and passengers left the ship via lifeboat and landed at Thompson’s Creek, then walked about 20 kilometres to Barwon Heads. Salvagers were interested in the 10 miles of cable in the hold. Mrs Kendrick’s ‘high grade’ bicycle was amongst the items salvaged but she lost her jewellery and two pianos. By February 1903 the ship had broken up and objects such as bottles and casks of liquor were washed ashore. Bad weather shook the wreck in June 1903, causing the ship’s spars and figurehead to be washed ashore. This ink bottle is historically significant as it represents methods of hand written communication that were still common up until the mid-20th century, when fountain pens and ballpoint pens took over in popularity and convenience. The Ink bottle also has significant as it was recovered by John Chance, a diver from the wreck of the Inverlochy in the late 1960s to early 1970s. Items that come from several wrecks along Victoria's coast have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. This Ink bottle is significant because of its historical connection to the barque Inverlochy, which is an example of a commercial international steel sailing barque and is listed on the Victorian Heritage Database VHR S338. The Inverlochy is significant for its cargo, which is a snapshot of the kind of goods imported into Australia at the turn of the 19th century, including cable for the Melbourne Tramway Company. The wreck of the Inverlochy is important as an accessible dive site that shows the remains of a large international trading vessel and its contents. It is valuable for an insight into Victorian era of shipping and maritime history. Ink bottle, glazed, prange-brown ceramic cylinder, ring of clay on top for lip, narrow mouth, very short neck on wide shoulder that reaches out to edge of of straight-sided body, flat base. On the shoulder, close to the neck, are concentric lines in the clay. There are dark areas around the lip and mouth opening. The clay appears to have a fold line on its body. The material has flecks of darker material in it. Sediment around shoulder. Handmade. Also called a Penny Ink Well.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, john chance, inverlochy, scotland, captain e.r. kendrick, melbourne tramway company, tramway cable, ingoldsby reef, point addis, anglesea, thompson’s creek, barwon heads, ink bottle, writing equipment, writing accessory, office equipment, stationery, domestic, stoneware, clay, ceramic, pottery, ink well, inkwell, penny ink well, nib pen, dip pen, ink, hand writing, record keeping, household, business, vintage, blotting paper, dwarf ink -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph, C. 1915 - 09/07/1917
... steel barque built in 1894 by Robert Duncan & Co. Limited... INVERNESS-SHIRE was a four masted steel barque built in 1894 ...This black and white photograph of the tugboat NYORA towing the steam ship INVERNESS-SHIRE was taken between 1915, when the INVERNESS-SHIRE was dis-masted, and 9the July 1917, when NYORA tragically sank. The sailing ship INVERNESS-SHIRE was a four masted steel barque built in 1894 by Robert Duncan & Co. Limited, Glasgow, U.K. (The supervising engineer during the building was William Cumming. He accompanied every ship he’d built on their maiden voyages from UK to Melbourne.) In 1916 she was purchased by A/S Christiansand (Sven O. Stray), Kristiansand, Norway and renamed SVARTSKOG. In October 1920 she disappeared at sea, carrying a cargo of coal, and all hands were lost. The steam powered NYORA was a powerful tugboat and a salvage vessel built by J.P. Rennoldson & Sons Ltd, South Shields, Tyne and Wear, UK. She was originally launched with the name NEPEAN in May 1909, then as NYORA in August 1909 and registered in Melbourne in November 1909 by owners Huddart Parker Pty Ltd. She was made of steel, had triple-compounded steam engines, and her dimensions were 306 ton, 135.0 x 25.1 x 13.6ft. The Melbourne tug NYORA was known as “one of the best known tugs in Victoria, and carried the latest appliances for firefighting and salvage purposes.” She serviced the Port of Melbourne for most of her career. In July 1917 NYORA was towing the American schooner ASTORIA from Port Pirie to Sydney, because ASTORIA’s engines had broken down; she had been delivering a large cargo of timber. On July 9th the vessels were two days out from Port Pirie. At 10:30am NYORA foundered after casting off at Cape Jaffa, 50 miles south of Kingston, South Australia, and sank. Only 2 of the 16 crew survived; NYORA’s Master, Captain W.M. McBain (William Murray) and helmsman, able seaman Gordon Lansley. They were rescued by the two Cape Jaffa light keepers, Jamieson & Clark, who launched the rescue from the Cape Jaffa lighthouse on Margaret Brock Reef. Both men were brought to the lighthouse keeper’s cottage where they recuperated after their long exposure to the rough. (The Queenscliff Sentinal of 14th July 1917 noted that both saved men originated from the same district; Gordon Lansley was from Queenscliff and Captain McBain formerly from Point Lonsdale.) The ASTORIA was “in a very dangerous position ten miles west of the Margaret Brock reef near the Cape Jaffa lighthouse, setting towards the land.” Captain Solly from Beachport later said “Owing to the position … the ship was very fortunate in making Guichen Bay in safety, as she did” (Guichen Bay is south of Robe). Captain Bull, manager of Huddart Packer Pty Ltd, NYORA’s owner, was unable to see any reason for the foundering, as the NYORA was well known for its seaworthiness. At a hearing later on, the Marine Board could blame on no-one either, but found that the ship had been swamped by heavy seas, and had listed to one side when a load of 40 tons of coal in sacks on her deck shifted. The tow line to the ASTORIA was cut to try and save the tug but a huge wave swamped her, crashed open the engine room door and flooded the compartment. It was impossible to launch the lifeboats due to the listing of the sea and NYORA sank within 15 minutes. There was some criticism of the length of time it took Captain Solly and the lifeboat crew to get from Beachport to Cape Jaffa to help with the rescue. However, they had great difficulty in the very strong seas, taking 9 hours just to reach Robe, which was only 32 miles away. There they filled the tanks with ample benzene for the task ahead (impossible to do at sea at the time), took in food and brought on board the Robe Harbour Master, Mr Sneath. The Harbour Master was then able to safely pilot the lifeboat to Cape Jaffa in the smoother coastal waters, saving very much time, but by the time they arrived at Cape Jaffa the 2 survivors had already been taken to the lighthouse on the mainland. There was also a question as to the chances of the ship ASTORIA lowering a lifeboat to help with the disaster. Captain Solly explained that it would have been impossible without sacrificing the lives of the lifeboat crew , due to the great height of the ship out of the water and the roughness of the sea. Captain Svenson, of the ASTORIA, said himself “We are ourselves in a helpless position” and “"Cannot see anything of lifeboats”. One of the 14 lost crew of the NYORA was Hugh Edwards, whose body was not recovered. The descendants of Captain William McBain have continued the seafaring heritage. His son was also a tugboat captain (Captain Norman Clive McBain), working mostly from Reid Street Pier, Williamstown, who would often take his own grandson out to sea to spend time with him on his tugboat. Now that grandson has built a tugboat in memory of his heritage and spends time in it with his own grandson. The Cape Jaffa original lighthouse has been dismantled and moved to Kingston and is now a Lighthouse Museum. The attached photographs of Margaret Brock Reef, and the Cape Jaffa Lighthourse keeper's cottage (now in ruins) is courtesy of Capt. William McBain's great grandson, who visited the area in 2015. There is a model of the NYORA in Museum Victoria, donated by Huddart Packer & Co Ltd. in 1937. This photograph is significant for its association with the tugboat NYORA, that is part of the seafaring history of the Port of Melbourne and associated Victorian ports. Black and White photograph of the tugboat NYORA and steam ship INVERNESS-SHIRE. C. 1915-1917.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, historic maritime photograph, lighthouses, shipwrecks, steamships, j.p. rennoldson & sons ltd, huddart parker pty ltd, nepean, nyora, inverness-shire, astoria, captain w.m. mcbain, william cummings supervising engineer, cape jaffa lighthouse, beachport lifeboat, captain solly, captain svenson, margaret brock reef -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Fob watch, 1882
... and that of the crew on September 6th 1891 when the steel barque Fiji had... and that of the crew on September 6th 1891 when the steel barque Fiji had ...The watch was given to William James Robe by the captain of the barque Fiji as a token for helping to save his life and that of the crew on September 6th 1891 when the steel barque Fiji had foundered off “wreck beach" near Moonlight Head Warrnambool during a voyage from Hamburg to Melbourne. William or Bill as he was called was the one who had hauled out the last man, the captain, after he had become tangled in the kelp. William along with many other onlookers on the beach at the time had taken it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers along with William James Robe, included Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. Years later Bill passed the watch on to his brother-in-law Gilbert Hulands as payment of a debt. The grandson of Gilbert Hulands, John Hulands, has donated this watch to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum. The Fiji Wreck: The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south-west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers' calculation of his position. At about 2:30 am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed Fiji struck rock only 274 metres from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17-year-old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut loose with his sheath-knife when it becomes tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the cliffs in search of help. At about 10 am on Sunday a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stanmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. They found Gebauhr lying in scrub and a poor state, bleeding and scantly dressed and with a sheath-knife. At first, they were concerned about his appearance and gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after Gebauhr threw his knife away realising he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. One of the rescuers Arthur Wilkinson, a 29-year-old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship's crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken who was attempting to swim to shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck, a line was thrown to them. It was thought that Wilkinson had struck his head on the anchor during the rescue and had remained unconscious, the carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson died and his body was washed up the next day. The wreck of Fiji smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it finally settling in 6m of water. Of the 26 men on Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach. They were buried on the clifftop above the wreck. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship and his is Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was 'detained' for 14 days. The essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck "Fiji tobacco" was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (S 259). The collection also represents key aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its items offer the potential to interpret maritime historical events and social history of the time. Along with the potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history.Sterling silver fob watch Fusee movement face has a white background with black Roman numerals on it. The minute hand is gold coloured with a leaf shape. Seconds dial is inset at position 6, with Arabic numerals around it. Watch has machine engraving flower pattern front and back. The spherical winder has a number and a symbol on the upper face and a hole through the centre, the ring for the chain is missing. Back of a the watch opens to reveal a concave cover with a winding hole, which has a border of overlapping crescent-shapes. Inside cover a diamond with initials “JR”(John Rotherham) inside, a date letter “G” (1882) with a Lion Passant (Sterling Silver) also 3 numbers “8 1 9“embossed beside each other. The clock face has “Rotherhams / London” printed on it. The winder is also marked with a maker and sterling silver mark. “Y” and numbers “688” “3 CI A” “3309” “819” “555 A” and other numbers including a set engraved around the edge possibly jewelers marks who did repairs or maintenance on the item over the years.1891, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, fiji, pocket watch, william vickers, william robe, bill robe, fiji watch -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph
Black and White Photograph of a large Photograph of the barque Brilliant, Inscription on back read world's fastest oil - clipper. Steel 4 master .3765 tons 353feet long. SH 046 Ships A - B.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, photograph, brilliant, barque brilliant -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph, C. 1891
Photograph shows the ship FIJI where she met her demise, in Wreck Bay, on the shipwreck coast of South West Victoria. The three-masted iron barque Fiji had been built in Belfast, Ireland, in 1875 by Harland and Wolfe for a Liverpool based shipping company. The ship departed Hamburg on 22nd May 1891 bound for Melbourne, under the command of Captain William Vickers with a crew of 25. The ship’s manifest shows that she was loaded with a cargo of 260 cases of dynamite, pig iron, steel goods, spirits (whisky, schnapps, gin, brandy), sailcloth, tobacco, coiled fencing wire, concrete, 400 German pianos (Sweet Hapsburg), concertinas and other musical instruments, artists supplies including brushes, porcelain, furniture, china, and general cargo including candles. There were also toys in anticipation for Christmas, including wooden rocking horses, miniature ships, dolls with china limbs and rubber balls. On September 5th, one hundred days out from Hamburg in squally and boisterous south west winds the Cape Otway light was sighted on a bearing differing from Captain Vickers’ calculation of his position. At about 2:30am, Sunday 6th September 1891 land was reported 4-5 miles off the port bow. The captain tried to put the ship on the other tack, but she would not respond. He then tried to turn her the other way but just as the manoeuvre was being completed the Fiji struck rock only 300 yards (274 metres) from shore. The place is known as Wreck Bay, Moonlight Head. Blue lights were burned and rockets fired whilst an effort was made to lower boats but all capsized or swamped and smashed to pieces. Two of the younger crewmen volunteered to swim for the shore, taking a line. One, a Russian named Daniel Carkland, drowned after he was swept away when the line broke. The other, 17 year old able seaman Julius Gebauhr, a German, reached shore safely on his second attempt but without the line, which he had cut lose with his sheath-knife when it become tangled in kelp. He rested on the beach a while then climbed the steep cliffs in search of help. At about 10am on the Sunday morning a party of land selectors - including F. J. Stansmore, Leslie Dickson (or Dixon) and Mott - found Gebauhr. They were near Ryans Den, on their travels on horseback from Princetown towards Moonlight Head, and about 5km from the wreck. Gebauhr was lying in the scrub in a poor state, bleeding and dressed only in singlet, socks and a belt with his sheath-knife, ready for all emergencies. At first they were concerned about his wild and shaggy looking state and what seemed to be gibberish speech, taking him to be an escaped lunatic. They were reassured after he threw his knife away and realised that he was speaking half-English, half-German. They gave him food and brandy and some clothing and were then able to gain information about the wreck. Some of the men took him to Rivernook, a nearby guest house owned by John Evans, where he was cared for. Stansmore and Dickson rode off to try and summon help. Others went down to the site of the wreck. Messages for rescuing the rest of the crew were sent both to Port Campbell for the rocket rescue crew and to Warrnambool for the lifeboat. The S.S. Casino sailed from Portland towards the scene. After travelling the 25 miles to the scene, half of the Port Campbell rocket crew and equipment arrived and set up the rocket tripod on the beach below the cliffs. By this time the crew of the Fiji had been clinging to the jib-boom for almost 15 hours, calling frantically for help. Mr Tregear from the Rocket Crew fired the line. The light line broke and the rocket was carried away. A second line was successfully fired across the ship and made fast. The anxious sailors then attempted to come ashore along the line but, with as many as five at a time, the line sagged considerably and some were washed off. Others, nearly exhausted, had to then make their way through masses of seaweed and were often smothered by waves. Only 14 of the 24 who had remained on the ship made it to shore. Many onlookers on the beach took it in turns to go into the surf and drag half-drowned seamen to safety. These rescuers included Bill (William James) Robe, Edwin Vinge, Hugh Cameron, Fenelon Mott, Arthur Wilkinson and Peter Carmody. (Peter Carmody was also involved in the rescue of men from the Newfield.) Arthur Wilkinson, a 29 year old land selector, swam out to the aid of one of the ship’s crewmen, a carpenter named John Plunken. Plunken was attempting to swim from the Fiji to the shore. Two or three times both men almost reached the shore but were washed back to the wreck. A line was thrown to them and they were both hauled aboard. It was thought that Wilkinson struck his head on the anchor before s they were brought up. He remained unconscious. The carpenter survived this ordeal but Wilkinson later died and his body was washed up the next day. It was 26 year old Bill Robe who hauled out the last man, the captain, who had become tangled in the kelp. The wreck of the Fiji was smashed apart within 20 minutes of the captain being brought ashore, and it settled in about 6m of water. Of the 26 men on the Fiji, 11 in total lost their lives. The remains of 7 bodies were washed onto the beach and their coffins were made from timbers from the wrecked Fiji. They were buried on the cliff top above the wreck. The survivors were warmed by fires on the beach then taken to Rivernook and cared for over the next few days. Funds were raised by local communities soon after the wreck in aid of the sufferers of the Fiji disaster. Captain Vickers was severely reprimanded for his mishandling of the ship. His Masters Certificate was suspended for 12 months. At the time there was also a great deal of public criticism at the slow and disorganised rescue attempt to save those on board. The important canvas ‘breech buoy’ or ‘bucket chair’ and the heavy line from the Rocket Rescue was in the half of the rocket outfit that didn’t make it in time for the rescue: they had been delayed at the Gellibrand River ferry. Communications to Warrnambool were down so the call for help didn’t get through on time and the two or three boats that had been notified of the wreck failed to reach it in time. Much looting occurred of the cargo that washed up on the shore, with nearly every visitor leaving the beach with bulky pockets. One looter was caught with a small load of red and white rubber balls, which were duly confiscated and he was ‘detained’ for 14 days. Essence of peppermint mysteriously turned up in many settlers homes. Sailcloth was salvaged and used for horse rugs and tent flies. Soon after the wreck “Fiji tobacco” was being advertised around Victoria. A Customs officer, trying to prevent some of the looting, was assaulted by looters and thrown over a steep cliff. He managed to cling to a bush lower down until rescued. In 1894 some coiled fencing wire was salvaged from the wreck. Hundreds of coils are still strewn over the site of the wreck, encrusted and solidified. The hull is broken but the vessel’s iron ribs can be seen along with some of the cargo of concrete and pig iron. Captain Vickers presented Bill Robe with his silver-cased pocket watch, the only possession that he still had, as a token for having saved his life and the lives of some of the crew. (The pocket watch came with 2 winding keys, one to wind it and one to change the hands.) Years later Bill passed the watch to his brother-in-law Gib (Gilbert) Hulands as payment of a debt and it has been passed down the family to Gilbert Hulands’ grandson, John Hulands. Seaman Julius Gebauhr later gave his knife, in its hand crafted leather sheath, to F. J. Stansmore for caring for him when he came ashore. The knife handle had a personal inscription on it. A marble headstone on the 200m high cliffs overlooking Wreck Beach, west of Moonlight Head, paying tribute to the men who lost their lives when Fiji ran aground. The scene of the wreck is marked by the anchor from the Fiji, erected by Warrnambool skin divers in 1967. Amongst the artefacts salvaged from the Fiji are china miniature animals, limbs from small china dolls, rubber balls, a slate pencil, a glass bottle, sample of rope from the distress rocket and a candlestick holder. These items are now part of the Fiji collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum, along with Captain Vickers’ pocket watch and Julius Gebauhr’s sheath knife. Flagstaff Hill’s Fiji collection is of historical significance at a State level because of its association with the wreck Fiji, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register VHR S259. The Fiji is archaeologically significant as the wreck of a typical 19th century international sailing ship with cargo. It is educationally and recreationally significant as one of Victoria's most spectacular historic shipwreck dive sites with structural features and remains of the cargo evident. It also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The Fiji collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Black and White Photograph of the ship "Fiji" taken from Wreck Creek. warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, shipwrecked artefact, pocket watch, fob watch fiji, william vickers, william robe, bill robe, gebauhr, stansmore, carmody, wreck bay, moonlight head, fiji shipwreck 1891, port campbell rocket crew, wreck bay victoria
