Showing 13 items matching "troughton and simms"
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionScientific Instruments, Theodolite: Early 1900s, Early 1900s
... Troughton & Simms...Troughton & Simms ...Troughton & Simms - Londontheodolite, scientific instruments, troughton & simms, spirit levels, guages -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTheodolite, Troughton & Simms, Mid 19th Century
... Troughton & Simms ...The theodolite was sold by T. Gaunt & Co. of Melbourne, a manufacturer, importer and retailer of a wide variety of goods including jewellery, clocks and watches, navigational and measuring instruments, dinnerware, glassware and ornaments. Thomas Gaunt photograph was included in an album of security identity portraits of members of the Victorian Court, Centennial International Exhibition, Melbourne, 1888. (See further details below.) History for Troughton & Simms: Edward Troughton & William Simms established a scientific instrument making business in London in 1826. Edward Troughton (1756-1835) had previously had his own scientific instrument business, inherited from his father. His achievement's included a transit telescope for Greenwich Observatory (1816) and the precision surveying instruments for the Ordnance Survey of Britain, Ireland and India. William Simms (1793-1860) had trained as a goldsmith and began to gain work dividing circles on fine astronomical instruments. When William Simms died in 1860, the business was taken over by his son James and nephew William. Troughton & Simms shop in Fleet Street became the hub of the finest scientific instrument made in London, in a period in which there was an expanding demand for precision instruments, for astronomy, surveying and precision measurement. They made instruments for Greenwich Observatory, for imperial surveys and exploring expeditions. When fire destroyed the Houses of Parliament in 1834, the firm was commissioned to create new standard lengths, this required 10 years of testing against the remaining old measurements. Troughton and Simms made several of the main instruments for Melbourne Observatory, including an 18 inch azimuth used of the Geodetic Survey, portable transit instrument (circa 1850), zenith sector (1860), a 4.5 inch equatorial telescope (1862), an 8 inch equatorial telescope (1874) spectroscope (1877) and an 8 inch transit instrument in (1884). While the firm had an excellent reputation for quality the company exasperated many of its customers with delays of years in delivering some instruments. History for Thomas Gaunt: Thomas Ambrose Gaunt (1829 – 1890) was a jeweller, clock maker, and manufacturer of scientific instruments, whose head office and showroom were at 337–339 Bourke Street, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Thomas Gaunt established Melbourne's leading watchmaking, optical and jewellery business during the second half of the 19th century. Gaunt arrived in Melbourne in 1852, and by 1858 had established his own business at 14 Little Bourke Street. Around 1869 he moved to new premises in Bourke Street on the corner of Royal Arcade, Gaunt's shop quickly became a Melbourne institution. Gaunt proudly advertised that he was 'The only watch manufacturer in the Australian colonies'. While many watches and clocks may have had Gaunt's name on the dial, few would have been made locally. Gaunt did make some watches for exhibitions, and perhaps a few expensive watches for wealthy individuals. Gaunt's received a telegraph signal from Melbourne Observatory each day to correct his main clock and used this signal to rate and repair ship's chronometers and good quality watches. Thomas Gaunt also developed a department that focused on scientific instrumentation, making thermometers and barometers (from imported glass tubes), telescopes, surveying instruments and microscopes. Significance: With the rapid urban expansion, one of the most important needs of the new colony was to survey and map the landscape of the Australian Colony’s interior. Theodolites, such as this one, made by Troughton and Simms, who were significant scientific instrument makers of the 19th century were instrumental to the colony's surveyors and would have played an important part in their everyday work. This transit theodolite remains of national significance due to its pioneering role in Australian science and its association with Australia's earliest surveyors and astronomers. It is also significant for its association with nineteenth-century surveying instruments and instrument makers. Theodolite, Vernier repetition theodolite with enclosed horizontal circle (of about 130 mm diameter). Vertical circle exposed and somewhat corroded (diameter about 115 mm). Plate level 20" per division. Altitude bubble 20" per division. Horizontal and vertical circle intervals 20". Original (blue/grey) paint. Altitude bubble setting screw disabled. Tribrach allows movement of theodolite by 15 mm inside tribrach (for centering).Inscribed on the inner mounting plate,“Specially made in England for T Gaunt & Co Melbourne” and inscribed a little lower “Troughton & Simms London”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, theodolite, t. gaunt & co, troughton & simms, scientific instrument, measuring instrument, surveyor's instrument -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyclinometer rule, mid 19th -earl 20th century
... Troughton & Simms ...This clinometer, is a hand-held optical scientific instrument used in surveying to measure vertical angles. It is used to measure the angle of elevation from the ground in a right-angled triangle. It may have been used by a surveyor or a forester to measure the height of tall things where you couldn't possibly reach to the top of e.g. flag poles, buildings or trees.This item is an example of an early hand held measuring instrument.. Today the use of electronic sensors is an important component in the design and function of the clinometers.A rectangular wooden folding measuring instrument. the panels are brass framed. Inside is a brass semi-protractorgraduated 90-0-90' with index arm pointeran dwith a graduated edge in inches. Outside is a temperature conversion scale,Troughton & Simms, LONDONscientific-instrument measurement clinometer -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Sextant, Troughton & Simms, late 19th C. to 1922
... Troughton & Simms ...This sextant is very similar to a 1915 Sextant design. A sextant is an astronomical instrument used in measuring angular distances especially the altitudes of sun, moon and starts at sea determining latitude and longitude.This sextant is an example of a 19th-century marine instrument used for finding location at sea. It was made by London scientific instrument maker Troughton and Simms, which originated in 1826 and continued until 1922.Sextant and its fitted square wooden box. The handle of the sextant is carved with a cross-hatched pattern. Made by Troughton and Simms, London.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, sextant, navigational instrument, marine navigation, marine equipment, instrument, navigation, troughton and simms, london, scientific instrument -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesInstrument - Optical Dumpy Level, Troughton & Simms, Dumpy Level, Pre 1915
... Troughton & Simms ...Found in the Curator's CottageBrass Troughton & Simms, London optical dumpy level on compass base. Made for Kilpatrick & Co, Melbourne. See B91.126 for photograph of student using it Circa1968.Troughton & Sims LONDON Kilpatrick & Co Melbourne No. 702surveying equipment, students, landscaping, artifact -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societytheodolite, first half 20th century
... Cooke Troughton & Simms ...Theodolites have been used to measure horizontal and vertical angles by surveyors since the 1500s. A theodolite is a precision instrument for measuring angles in the horizontal and vertical planes. Theodolites are used mainly for surveying applications, and have been adapted for specialized purposes in fields like meteorology and rocket launch technology. Theodolites, such as this one, were instrumental to early surveyors, and would have played a significant part in their everyday work. The plumb bob was used to set the instrument exactly over a fixed survey marker.This theodolite was made by Troughton and Simms, who were significant scientific instrument makers of the 19th century and early 20th century. In 1782 John Troughton purchased Benjamin Cole's shop in Fleet Street, London enabling him to sell his own signed products. His instrument making business supported several dynasties of Troughtons before becoming Troughton and Simms and later still Cooke Troughton & Simms. This firm was one of the most well respected firms of instrument makers of the 1800s. A grey metal theodolite - probably made of brass. It has movable parts and there is a weight ( a plumb bob) attached with string.Cooke Troughton & Simms Yorke England V012318 Supplied by A. E. Parsons Melbournetheodolite scientific-instruments surveying -
 City of Greater Bendigo - Civic Collection
City of Greater Bendigo - Civic CollectionInstrument - Theodolite, Cooke, Troughton & Simms, c 1940
... Cooke, Troughton & Simms. ...Theodolites are a highly accurate instrument that measures angles between designated visible points in the horizontal and vertical planes. The theodolite has a long history, with the term first found in 1571 in a surveying textbook 'A geometric practice named Pantometria' by Leonard Digges. (source https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theodolite). Cooke Troughton & Simms began when John Troughton starting selling products in Fleet Street, London in 1782. He went into partnership with his brother Edward in 1807 who expanded the business considerably. William Simms, a former apprentice with the company was taken as a partner and then manager after Edward died in 1835 and the company became Troughton & Simms. By 1887 the company was able to produce all the parts necessary for their instruments and the company employed nearly 200 people and was one of the most well respected firms of instrument makers of the 1800's. James Simms, son of William who had inherited the company died in 1915 and the company was turned into a limited liability company by his two sons William and James. Things however were not so easy for the two sons and in 1922 the business was brought out by their rival T. Cooke & Sons becoming Cooke, Troughton & Simms. Theodolites are used by surveyors as part of their everyday work and although there is no specific information regarding the provenance of this particular one it is assumed it was used locally by the City of Bendigo and / or the Lands Department.A grey theodolite no 39161 made by Cooke, Thoughton & Simms. Various moving parts showing signs of extensive use particularly on the uprights on the main body and around knobs and dials where the paint is worn back to brass.Cooke, Thoughton & Simms Ltd / York. England / No 39161. Sticker; DPS - Asset No / (barcode) / 0010173city of greater bendigo administration item, lands and survey department bendigo -
 Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of Melbourne
Creswick Campus Historical Collection - University of MelbourneEquipment, Troughton and Simms of London, nd
... Troughton and Simms of London ...The Theodolite is in its original case for field work.Equipment -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumSteel protractor, 1915 (Approx)
8384.1 - Large steel protractor.- Troughton and simms, London. - G.H.G. -
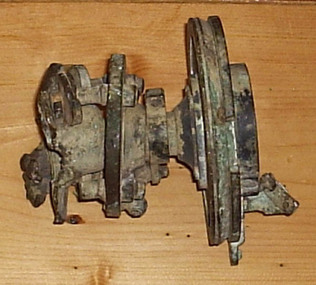 Stratford and District Historical Society
Stratford and District Historical SocietyTheodolite
This theodolite was used by `Mr Dawson' (presumably William Tennant Dawson c.1820-1873) who `surveyed much of the area around and beyond Stratford'. It was damaged by the fire which burnt the original Roseneath home in 1921, when the Macleods were in residence. (Mrs W.T. Dawson was a Macleod). One little boy aged 3 years was given the job of saving everything on the kitchen table when the fire started at breakfast time. The theodolite was possibly in use by Dawson when he laid out St Kilda Road.This theodoite consists of a bottom plate, which is damaged and has melted metal. This rises to a ball joint, on which is pivoted another plate on which were housed four screws, of which three remain, to adjust the level. Above this is another plate, with compass markings and melted glass."Troughton and Simm's/London" in fine engraving on upper plate.surveyors, instruments -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumInstrument - Accessory box for a No 6 Director Mk I
Possibly related to the range-finding equipment sent from England for dismantling during the 1940s so University of Melbourne Physics staff could develop their own equipment. Related to object 463.1Leather accessory box with shoulder strap and metal buckles. Flip open lid.Embossed in lid: 'CASE NO 6 DETECTOR MK 1 / COOKE, TROUGHTON & SIMMS, LTD / 9 / 22 / A.F.A' and broad arrow symbol.accessory box, no 6 director mk i, broad arrow, cooke troughton and simms ltd, wwii, mathematical instrument -
 The Ed Muirhead Physics Museum
The Ed Muirhead Physics MuseumInstrument - Artillery director (No 6 Mk II with tripod), c1924
Possibly related to the range-finding equipment sent from England for dismantling during the 1940s so University of Melbourne Physics staff could develop their own equipment. Related to object 463.2Green painted brass director mounted on a grey metal base plate. Secured to a wooden tripod with coated copper wire cord linking tripod legs.Theodolite body engraved with: the broad arrow on top, and on side with 'DIRECTOR No 6 MK II / COOKE TROUGHTON & SIMMS LTD / 1924 / No 1126'artillery instruments, wwii artillery, no 6 director mk ii, optical equipment, cooke troughton & simms -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumAdministrative record - Royal Australian Survey Corps - 1st, 2nd and 3rd Order Triangulation Precis, School of Military Survey, Balcombe, Circa 1948 - 1960
A School of Military Survey Precis, 8 x foolscap sized pages of typed text, stapled and two hole punched. The precis No 3 covers the Observation procedure to be used for 1st, 2nd and 3rd Order Triangulation using the Royal Australian Survey Corps standard Cooke, Troughton and Simms Tavistock or Wild T2. The geodetic model Tavistock with a 5.25" horizontal circle should be used for 1st Order Triangulation and maybe used for 2nd Order Triangulation if specially directed. The standard Tavistock with 3.5" horizontal circle or the Wild T2 should be used for 2nd and 3rd Order observations. The Precis discusses the types of errors, the source of errors and the best ways of managing them. In surveying, triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by measuring only angles to it from known points at either end of a fixed baseline by using trigonometry, rather than measuring distances to the point directly as in trilateration.A School of Military Survey Precis, 8 x foolscap sized pages of typed text, stapled and two hole punched.royal australian survey corps, rasvy, fortuna, army survey regiment, army svy regt, asr, school of military survey, sms, balcombe
