Melbourne and Smellbourne
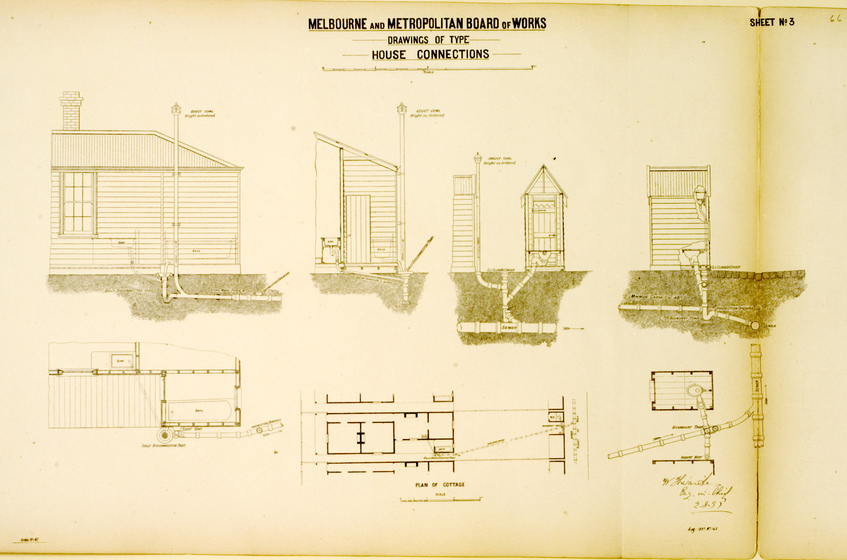
Over the last 150 years Victoria has experienced a number of landmark capital works and landscaping projects in response to its changing economic, environmental and cultural relationship to water. The sewerage system that we take for granted today had to be built from scratch.
For all the grandeur that was 'Marvellous Melbourne' in the 1880s, the city was nicknamed 'Smellbourne', and for good reason. The building of Yan Yean Reservoir in the 1850s had ensured the availability of fresh water, but there was still no sewerage system.
An appalling stench wafted from the many cesspits and open drains. 'Nightsoil' (as human waste was politely referred to) polluted the streets and ran into the Yarra. Nightsoil collectors frequently dumped their loads on public roads. Ignorance and neglect of the hygienic disposal of human waste had devastating results at this time when hundreds died in a savage outbreak of typhoid.
Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works
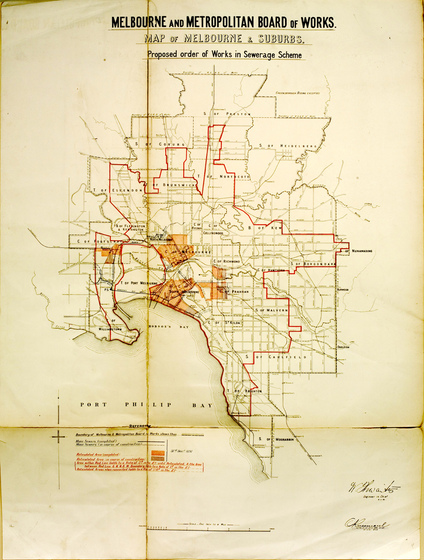
In 1891 the Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) was created. It immediately began plans to build an underground drainage system linked to a pumping station at Spotswood, located on the western banks of the mouth of the Yarra River. The sewage flowed by gravity to Spotswood, where it was then pumped to the Werribee Treatment Farm.
Spotswood Pumping Station
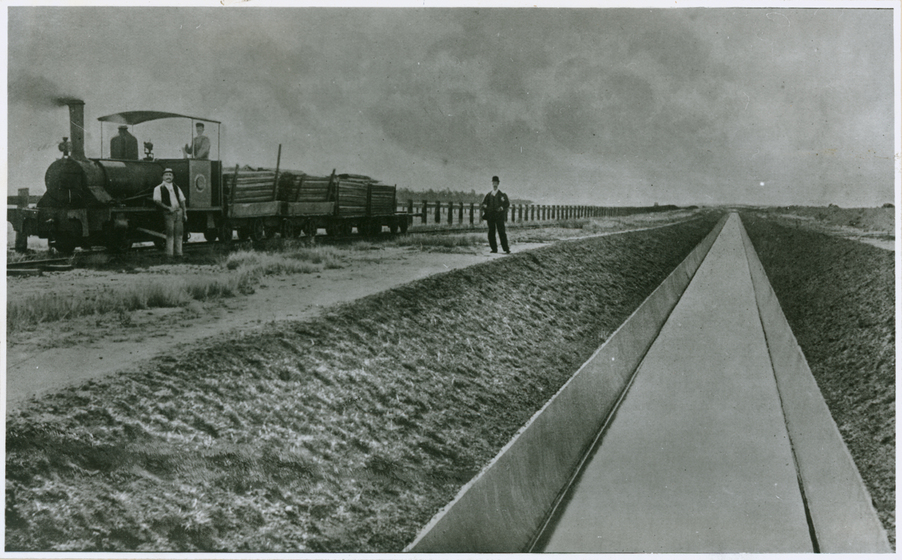
Spotswood Pumping Station built to pump Melbourne's sewage to Werribee, was finished in 1897. At the pumping station, steam engines (later replaced by electrical ones) worked to pump the sewage up a rising main to join the major sewer outfall at the head of the pumping mains near Millers Road at Brooklyn. The outfall sewer then carried the sewage to the Werribee Treatment Farm where it was purified and discharged into the sea.
Werribee Farm
Werribee was the perfect site for the MMBW's new sewage farm. The farm was the Board's most important project, and one of the largest public works undertaken in Australia in the nineteenth century.
Land at Werribee was cheaper than at Mordialloc - the other site considered. Rainfall was low compared with the rest of Melbourne, which meant the land would adapt well to irrigation. Werribee was also 9 miles (14.4 KM) away from the nearest boundary of the metropolitan district (Williamstown), and 24 miles (38.6 KM) away from the influential and well-to-do suburb of Brighton. The Chirnside family sold 8,857 acres (3.2 hectares) to the Board for 17 pounds per acre.
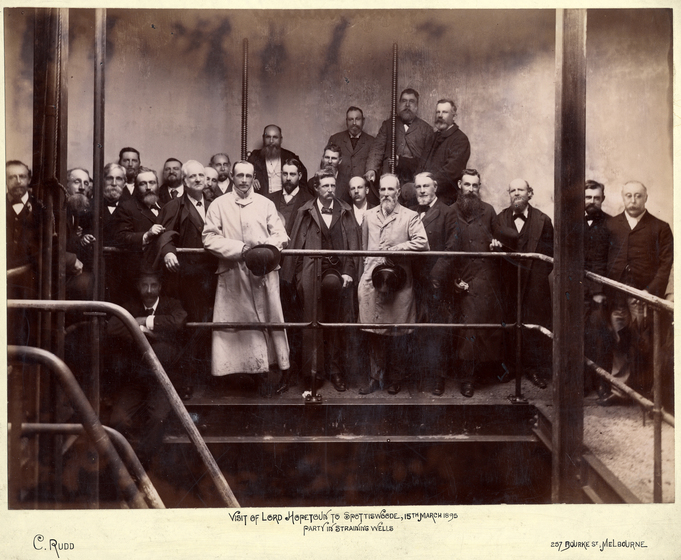
The Earl of Hopetoun, Governor of Victoria, turned the first sod of earth in a ceremony on May 1892, which marked the beginning of the building of the outfall sewer near Werribee.
Connection!
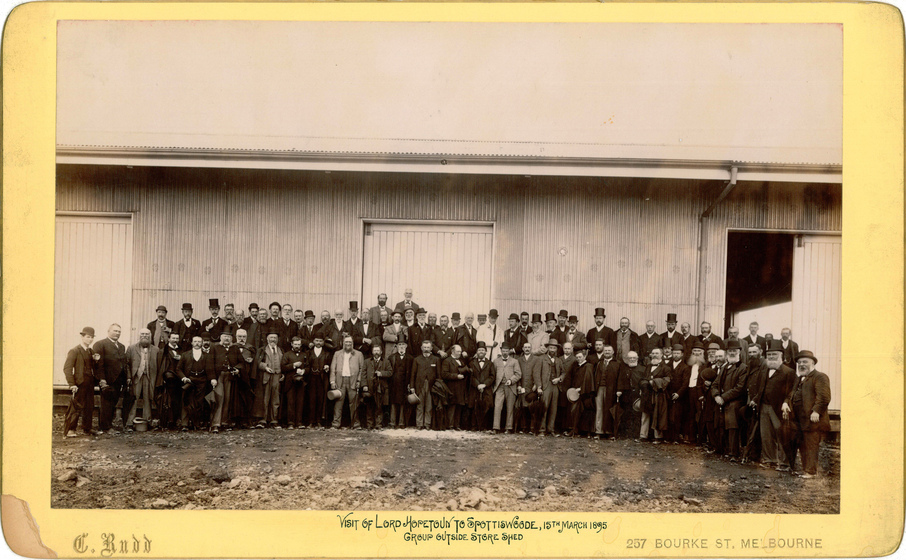
On 5 February 1898, a ceremony marked the official connection of Melbourne to the new sewerage system. Guests - politicians, board members, city councillors and federal delegates - boarded a steamer to watch the Governor, Lord Brassey, raise the penstock (the partition between the smaller and larger sewers) at the Australian Wharf. They then visited the pumping station at Spotswood and the sewage farm at Werribee. Horses and carts conveyed the 180 guests around the farm.
After lunch and toasts, many of which looked forward to the future of a federated Australia, MMBW Chairman Mr Fitzgibbon proudly declared it "was not a question of how much the scheme was going to cost, but how much it was going to save in the lives of the citizens." Before the work was completed he hoped to see those puny punsters and petty wits who spoke of Melbourne as Marvellous Smellbourne constrained to speak of her as one of the sweetest and healthiest cities of the world.