Showing 27 items
matching Yarra%20Ranges%20Regional%20Museum, themes: 'a diverse state','aboriginal culture','creative life','family histories'
-

Wangaratta, Textile Town
... brother lived, and then onto Australia. He opened a studio in South Yarra, Melbourne, which later moved to Collins Street. His work was hugely influential, especially his industrial photography with its socialist/heroic use of workers and theatrically lit ...It is 1919, the end of First World War, and a group of Wangaratta businessmen come together with a big idea: to build a woollen mill to create jobs, keep people in the town, draw workers and families from afar, and make the town prosper.
They start a share float and one of the men, William Callander, comes up with a bold plan to promote the project. His two daughters Alma and Lena take to the skies in an open biplane, seated on kerosene tins, to scatter leaflets across the region. The Wangaratta Woollen Mills is born, and soon becomes the largest mainland woollen mill in the nation.
It was the success of its textile industry that took Wangaratta from small country town to major rural city. But Wangaratta’s story as a textile town also reflects the making of modern Australia. It traces the path of post-war migration and the accompanying growth of Australia’s economy.
Following the Second World War Australia's prosperity began to boom and thousands of Europeans settled here. It was in this atmosphere, in 1946, that a Canadian company, Bruck Textiles, comes to Wangaratta and creates a population explosion, employing thousands of workers from places as diverse as Poland, Italy, Holland and Wangaratta itself.
Some of these workers' stories are presented here, as well as interviews with employees of Australian Country Spinners (formerly Wangaratta Woollen Mills). Photographs of the factories are also presented, along with moving image postcards of the industrial processes.
-
 Kate Luciano
Kate LucianoSchool Days: Education in Victoria
... One of the earliest Aboriginal schools in Victoria was established in 1846 near the Yarra Aboriginal Protectorate Station, on land between the Merri Creek and the Yarra River. This early Aboriginal school was supported by the local tribe ...The exhibition, School Days, developed by Public Record Office Victoria and launched at Old Treasury Building in March 2015, is a history of more than 150 years of schooling in Victoria.
It is a history of the 1872 Education Act - the most significant education reform in Victoria, and a world first! It is a history of early schooling, migrant schooling, Aboriginal schools, women in education, rural education and, of course, education during war time (1914-1918).
This online exhibition is based on the physical exhibition School Days originally displayed at Old Treasury Building, 20 Spring Street, Melbourne, www.oldtreasurybuilding.org.au and curated by Kate Luciano in collaboration with Public Record Office Victoria.
-

Women on Farms
... Icon selected to represent the Healesville Gathering. "The object represented the large number of horses in the Yarra Valley. A majority of the committee also owned horses. It was Kay Thomas who first wanted to host a gathering in the Yarra ...In 1990, a group of rural and farming women met in Warragul for what was to be the inaugural Women on Farms Gathering.
A group of local women had developed the idea while involved in a Women on Farms Skill Course. It was to prove inspirational, and the gatherings have been held annually ever since, throughout regional Victoria.
The Women on Farms Gathering provides a unique opportunity for women to network, increase their skills base in farming and business practices, share their stories and experience a wonderful sense of support, particularly crucial due to the shocking rural crises of the last decade. Importantly, the gatherings help promote and establish the notion of rural women as farmers, business women and community leaders.
The relationship between Museums Victoria and the Women on Farms Gathering is a model of museums working with living history.
-
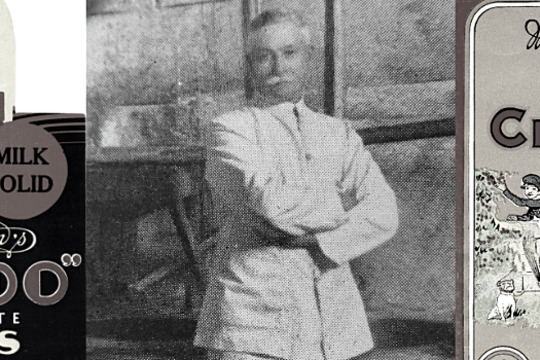 History Teachers' Association of Victoria / Royal Historical Society of Victoria
History Teachers' Association of Victoria / Royal Historical Society of VictoriaMacRobertson's Confectionery Factory
... the Shrine of Remembrance, building the MacRobertson Bridge over the Yarra River and the construction of a new building for the National Herbarium. One of MacRobertson’s most unusual bequests was of 10,000 pounds to Mawson’s 1929 Antarctica Expedition. His ...MacRobertson Steam Confectionery Works was a confectionery company founded in 1880 by Macpherson Robertson and operated by his family in Fitzroy, Melbourne until 1967 when it was sold to Cadbury.
This story accompanies the 'Nail Can to Knighthood: the life of Sir Macpherson Robertson KBE' exhibition which took place at the Royal Historical Society of Victoria in 2015.
-

Speed, Style, Spirit: The Rob Roy Hillclimb
... . It is only 28 miles from Melbourne on the main Yarra Glen road through Eltham and Kangaroo Grounds. The other route is through Panton Hills to Smiths Gully, thence to Yarra Glen road. It is ideally situated for picnicking, even for those not interested ..."We have at last discovered a venue for a hillclimb par excellence. I cannot tell you about it in this issue but .... This I can promise you; that when the news is released, hillclimb enthusiasts will set to work on their cars with great zest".
The Car, October issue, 1935
In 1935, members of the Light Car Club of Australia inspected a property in Christmas Hills, some thirty kilometres north-east of Melbourne, known as Clinton's Pleasure Grounds, a picnicking venue which included the Rob Roy Shetland Pony Stud, a swimming hole, tennis courts, a cricket and football field, tea room and dance hall.
Their mission was to establish a Hillclimbing venue. Hillclimbing, a speed event in which drivers compete, one at a time, on an uphill course against the clock, is one of motorsport’s oldest events; the first was held at La Turbie near Nice, France, in 1897.
Opening on February 1, 1937, the Rob Roy Hillclimb was the first purpose-built Hillclimb in Australia. Cut out of the bush, it included an uphill half-mile, graded dirt road, a judges box and telephone boxes at the start and finish. In 1939, the track was sealed and became one of only three bitumen-surfaced purpose-built hillclimbs in the world, the other two being the Shelsley Walsh and Prescott courses in the UK.
The Rob Roy Hillclimb has a special place in Australia’s motoring history, with eight record holders going on to become Australian Grand Prix winners and one – Jack Brabham – a triple F1 World Champion. The roll call of other drivers who displayed their skills at the Rob Roy includes Harry Firth, Stan Jones, Lex Davison, Bill Patterson, Doug Whiteford, Peter Whitehead, Reg Hunt, Diana Davison Gaze, Tony Gaze and Len Lukey.
The Rob Roy Hillclimb was more than a racing event, it was a culture. Connected to Formula One racing, celebrities, champion drivers, patrons, collectors, and prestige and iconic cars, the Rob Roy had an aura of glamour, and club meets were social occasions, with drivers adhering to collar and tie dress codes and picnickers fashionably attired.
Nevertheless the cars were central. Over the years Bugattis, Jaguars, MGs, Falkenbergs, Oldses and Altas have competed with Australian makes such as Holdens, Fords and Elfins, from road cars to specialist cars. Many Australian cars started or developed their racing history at Rob Roy, including the Chamberlain, Maybach, BWA, Wyliecar, Klienig Special, the Walton JAP, and numerous other Australian Specials.
The Specials were modified and home-built cars. Hillclimbs make particular demands – lightweight cars with loads of torque are ideal – and so engines were upgraded, bodies stripped, cars were made up of the most suitable parts or whatever one had access to. The Specials were evidence of the culture of creativity and passion that surrounded the Hillclimb. Many cars, some pre-war, and modified constantly over time, have passed from driver to driver along with their history, to compete to this day.
In 1962, bushfires ravaged the Rob Roy, and it lay unused for another 30 years until the MG Car Club of Victoria secured a lease on the property and faithfully restored the track to host a bustling schedule of Hillclimb events. Since 1993, the Rob Roy Hillclimb culture – the drivers, the cars, the inventive mechanics and the enthralled daytrippers – thrives in the Christmas Hills.
Sources: Leon Sims, A history of Rob Roy Hillclimb - 1937 to 1961 - The Hill, The Drivers, The Cars. And, the MG Car Club of Victoria
-
 Lucinda Horrocks
Lucinda HorrocksThe Missing
... Born in 1891, Vera grew up with her two older sisters Stella and Ivy in the two-storey house ‘Llanarth’, South Yarra. ...When WW1 brought Australians face to face with mass death, a Red Cross Information Bureau and post-war graves workers laboured to help families grieve for the missing.
The unprecedented death toll of the First World War generated a burden of grief. Particularly disturbing was the vast number of dead who were “missing” - their bodies never found.
This film and series of photo essays explores two unsung humanitarian responses to the crisis of the missing of World War 1 – the Red Cross Wounded and Missing Enquiry Bureau and the post-war work of the Australian Graves Detachment and Graves Services. It tells of a remarkable group of men and women, ordinary people in extraordinary circumstances, who laboured to provide comfort and connection to grieving families in distant Australia.
-
 Brian Allison
Brian AllisonJohn Harry Grainger
... a thriving private practice in Adelaide. Less than 18 months later in 1878 he resigned his government position to pursue private commissions. In 1880, while Grainger was still living in Adelaide, he won the competition to design Princes Bridge over the Yarra ...Architect and Civil Engineer
John Harry Grainger was a creative figure, largely overlooked by history. He receives a brief mention in the much-examined life story of his famous son, the composer and pianist Percy Grainger, where he is depicted as a proud but ineffectual father.
Grainger's prolific output as an architect and his extraordinary talents for bridge building have not yet received due recognition.
The material presented here is sourced from the Grainger Museum Collection at the University of Melbourne. Additional material is held in the Public Record Office of Victoria and in the State Library of Victoria collections.
-

Out of the Closets, Into the Streets
... Later the dances were held at the Melburnian Receptions rooms at the Block Arcade in the centre of Melbourne. The dances were quite different from the other social events of the time, venues such as Maisie’s (Her Majesty’s) in South Yarra, which ...This project documents the very beginning of the Gay Liberation Movement in Melbourne.
Through the manifestos, photographs, flyers and recollections of those who were part of the movement, this digital story explores the ways in which gay people found their voice in Melbourne, and refused to pass for straight anymore.
Gay Liberation had both local and imported roots. Internationally the New York City Stonewall riots in 1969 sparked off a new phase of radical gay politics, drawing on the momentum of activist organisations and protests across America throughout the 1960s, but locally few people took immediate notice, though fledgling advancements in homosexual law reform had developed within the civil liberties movement.
In Melbourne, the short-lived Daughters of Bilitis (later Australasian Lesbian Movement) arrived quietly on the scene in January 1970, gaining media coverage but limited influence. The real start to the Australian gay movement occurred in September 1970 with the formation of the Campaign Against Moral Persecution, or CAMP, in Sydney. Within two years there were CAMP branches in most Australian capital cities, with the Melbourne branch established in January 1971, soon renamed Society Five. However, despite the success of these organisations in counselling and socialising and later law reform, the relatively closeted nature of Society Five was never radical enough for some activists.
Gay Liberation arrived in Australia first in Sydney in 1971 and soon after in Melbourne and other states. By 1972 small Gay Liberation groups were springing up around the country. The differences between Gay Liberation and Society Five were in practice small, but those in Gay Liberation prided themselves on their commitment to bringing about radical social change.
Influenced by the counter-cultural movements and radical political movements of the 1970s, the politics of gay liberation became an all-encompassing liberation, an ‘embodied politics’ that saw liberation in all aspects of one’s life, from households to classrooms, sexual relations to workplaces, clothing to protests. Young gay people had found their voice, and group members organised the demonstrations, marches and public events illustrated in this story.
This Digital Story draws on material produced for the Australian Lesbian and Gay Archives (now Australian Queer Archives) exhibition Out of the Closets, Into the Streets: Histories of Melbourne Gay Liberation, curated and written by Nick Henderson, drawing on the original research of Graham Willett. A complementary documentary film, additional interviews, and written curatorial and audio content was produced by documentary film makers Wind & Sky Productions.
-
 Jary Nemo and Lucinda Horrocks
Jary Nemo and Lucinda HorrocksCollections & Climate Change
... , and there is a lot of the type of grass it likes to eat nearby. It is most commonly found in alpine heathlands and grasslands in the open areas between the snow line and thicker shrubs. It lives in places like the Otway Ranges, Wilson’s Promontory, the Yarra Ranges ...The world is changing. Change is a natural part of the Earth’s cycle and of the things that live on it, but what we are seeing now is both like and unlike the shifts we have seen before.
Anthropogenic change, meaning change created by humans, is having an impact on a global scale. In particular, human activity has altered the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere, causing the world’s climate to change.
Already in the state of Victoria we are seeing evidence of this change around us. In the natural world, coastal waters are warming and bringing tropical marine species to our bays. Desert animals are migrating to Victoria. Alpine winters are changing, potentially putting plants and animals at risk of starvation and pushing species closer to the margins. In the world of humans, island and coastal dwellers deal with the tangible and intangible impacts of loss as sea levels rise, bush dwellers live with an increased risk of life-threatening fires, farmers cope with the new normal of longer droughts, and we all face extreme weather events and the impacts of social and economic change.
This Collections and Climate Change digital story explores how Victoria’s scientific and cultural collections help us understand climate change. It focuses on three Victorian institutions - Museums Victoria, the Royal Botanic Gardens Victoria and Parks Victoria. It looks at how the information gathered and maintained by a dedicated community of researchers, curators, scientists, specialists and volunteers can help us understand and prepare for a hotter, drier, more inundated world.
The story is made up of a short documentary film and twenty-one examples highlighting how botanical records, geological and biological specimens and living flora and fauna provide a crucial resource for scientists striving to map continuity, variability and change in the natural world. And it helps us rethink the significance of some of Victoria’s cultural collections in the face of a changing climate.
-

Sound in Space
... Melbourne’s science museum on the Yarra at Spotswood combines the French chateau style of the 19th-century pumping station with a modern circular building – an environment for a program combining traditional choral sound with live sound processing ...Music always interacts with the architecture in which it is heard.
Melbourne has some wonderful acoustic environments. Often, these spaces were built for other purposes – for example the splendid public and ecclesiastical buildings from the first 100 years of the city’s history, and more recent industrial constructions.
Exploiting ‘non-customized’ spaces for musical performance celebrates and explores our architectural heritage.
For 30 years, the concerts of Astra Chamber Music Society have ranged around Melbourne’s architectural environment. Each concert has had a site-specific design that takes advantage of the marvellous visual qualities, spatial possibilities, and acoustic personality of each building.
The music, in turn, contributes a new quality to the perception of the buildings, now experienced by audiences as a sounding space - an area where cultural issues from music’s history are traversed, and new ideas in Australian composition are explored.
In this story take a tour of some of Melbourne’s intimate, hidden spaces and listen to the music that has filled their walls.
For further information about Astra Chamber Music Society click here.
-

Collingwood Technical School
... for the next generation of creative industries. From Smith Street [1], the land slopes eastwards down to Wellington Street, where it levels out towards the Yarra River. Known in the nineteenth century as the ‘Flat’, the area was a natural marsh, prone ...For over 140 years, the site of the former Collingwood Technical School on Johnston Street, Melbourne, has played an integral role in the well being of the local community.
It has been a civic hub, including courthouse (1853), Council Chambers (1860) and the Collingwood Artisans’ School of Design (1871). The school opened in 1912 when its first principal, Matthew Richmond, rang a bell on the street to attract new students. Collingwood was a poor and industrial suburb, and as a trade school, young boys were offered the opportunity to gain industrial employment skills.
Throughout the twentieth century, Collingwood Technical School supported the local and broader community. From training schemes for ex-servicemen who were suffering from post traumatic stress following World War I (1914-1918), to extra classes during the Great Depression, and the development of chrome and electroplating for machine parts for the Australian Army and Air Force during World War II (1939-1945).
The precinct between Johnston, Perry and Wellington Streets has transformed over time, including expansion with new buildings and school departments, and the change in the demographic of students as Collingwood evolved from an industrial centre to eventual gentrification. And in 1984, New York street artist, Keith Haring (1958-1990), painted a large mural onsite.
Collingwood Technical College closed in 1987 when it amalgamated with the Preston TAFE (Technical and Further Education) campus. Education classes continued until 2005 and the site sat empty for more than a decade, before a section was redeveloped for Circus Oz in 2013.
The former school now has a new identity as Collingwood Arts Precinct, and is being developed into an independent space for small and medium creative organisations. The heritage buildings will house the next generation of thinkers and makers, and will become a permanent home to the arts in Collingwood.
