Showing 45 items
matching public%20landscaping, themes: 'built environment','creative life','family histories','kelly country','service and sacrifice'
-
 Danielle Whitfield
Danielle WhitfieldGetting it Right
... There is a great deal of effort that goes into preparing a museum garment for display which the public never sees. This is especially true for historical items. Most obviously, there is the core work that our textile conservators do examining ...There is a great deal of effort that goes into preparing a museum garment for display which the public never sees. This is especially true for historical items.
Most obviously, there is the core work that our textile conservators do examining and treating works so that they are safe to exhibit. Equally vital is the task of creating the appropriate underpinnings and padded supports which ensure a garment has a historically accurate silhouette, and that the fragile fabrics are supported during display.
During the nineteenth century a lot went on beneath women’s gowns. Victorian fashion relied on a variety of contrivances to generate form; corsets compressed the waist, petticoats, crinolines and later cage-crinolines made skirts wider and fuller, while bustles produced a cantilevered behind. Working in tandem with the garment, these structures performed both functional and aesthetic roles.
-

State Film Centre
... Designed to collect and maintain a film library for general public consumption, the State Film Centre was established in 1946. It became a leading cultural institution for not only the archiving of Australian and international cinematic works ...Designed to collect and maintain a film library for general public consumption, the State Film Centre was established in 1946.
It became a leading cultural institution for not only the archiving of Australian and international cinematic works but in supporting the Victorian production industry, providing regional lending services and broadening audience reach through the use of mobile projection units.
With technological change, the Centre adapted to new media platforms and broadened its collections focus to include emerging filmmakers and student works. It evolved from a collection-based institution to a hub for screening and advocacy and increased its role as an invaluable education resource.
Into the 1990s work commenced on plans to establish the Australian Centre for the Moving Image as part of the Federation Square project and on January 1, 2002, the Australian Centre for the Moving Image was officially established by the Film Act 2001 (Victoria).
-

Digital Storytelling
... ) is Australia’s premier engine for screen and digital culture industries and assists in the creation and recording of hundreds of stories by individuals, community groups and organisations through its respected Digital Storytelling program, and ensures public ...Digital Storytelling is a powerful form of media expression that enables individuals and communities to reclaim their personal cultures and stories while exploring their artistic creativity.
The Australian Centre for the Moving Image (ACMI) is Australia’s premier engine for screen and digital culture industries and assists in the creation and recording of hundreds of stories by individuals, community groups and organisations through its respected Digital Storytelling program, and ensures public access to the stories through exhibition.
Recording these stories has ensured many vital individual and community memories are preserved. The digital stories provide a personal voice that gives 'life' to issues that are often hard to personalise.
The ACMI Digital Storytelling program reflects its philosophy of drawing people closer to the moving image in all its forms and to foster interaction, understanding and a personal connection.
For more information on ACMI’s Digital Storytelling program, visit: Collections digital storytelling
-

Sound in Space
... of public and ecclesiastical constructions from the first 100 years of the city’s history, as well as industrial and more recent buildings. Exploring and exploiting ‘non-customized’ spaces for musical performance is an important part of celebrating...Music always interacts with the architecture in which it is heard. Melbourne has some wonderful acoustic environments. Often, these spaces were built for other purposes – for example the splendid public and ecclesiastical buildings from the first ...Music always interacts with the architecture in which it is heard.
Melbourne has some wonderful acoustic environments. Often, these spaces were built for other purposes – for example the splendid public and ecclesiastical buildings from the first 100 years of the city’s history, and more recent industrial constructions.
Exploiting ‘non-customized’ spaces for musical performance celebrates and explores our architectural heritage.
For 30 years, the concerts of Astra Chamber Music Society have ranged around Melbourne’s architectural environment. Each concert has had a site-specific design that takes advantage of the marvellous visual qualities, spatial possibilities, and acoustic personality of each building.
The music, in turn, contributes a new quality to the perception of the buildings, now experienced by audiences as a sounding space - an area where cultural issues from music’s history are traversed, and new ideas in Australian composition are explored.
In this story take a tour of some of Melbourne’s intimate, hidden spaces and listen to the music that has filled their walls.
For further information about Astra Chamber Music Society click here.
-

Memories from a Soldier Settlement
... to store wartime artefacts donated by local families. By 1997 the collection had grown so much that the museum developed and started opening to the public. The collection continues to grow and holds artefacts from the Boer War, WW1, WW2, Vietnam and East ...At the close of the First World War, Australia began an ambitious and controversial soldier settlement scheme, allocating small parcels of potential farming land to returned soldiers.
33,000 acres were set aside in Red Cliffs, and in 1920, the returnees started clearing the Mallee Scrub, making Red Cliffs the largest Irrigated Soldiers' Settlement in Australia.
The Red Cliffs Military Museum, part of the Red Cliffs-Irymple RSL Sub-Branch, began around 1995, when a small billiard room was used to store wartime artefacts donated by local families. By 1997 the collection had grown so much that the museum developed and started opening to the public.
The collection continues to grow and holds artefacts from the Boer War, WW1, WW2, Vietnam and East Timor, and includes diaries, albums, arms, documents and uniforms, scale models and trench art.
A range of these artefacts, and interviews with soldiers and their families, telling of life in and between the First and Second World Wars, are presented here.
-
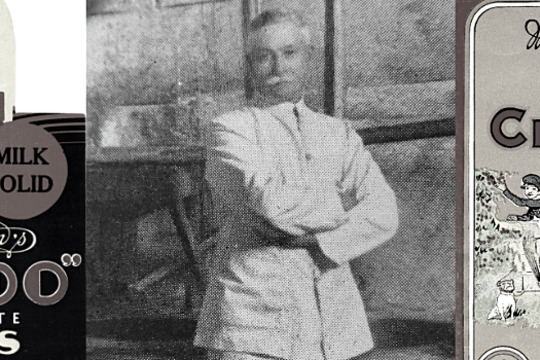 History Teachers' Association of Victoria / Royal Historical Society of Victoria
History Teachers' Association of Victoria / Royal Historical Society of VictoriaMacRobertson's Confectionery Factory
... While MacRobertson is no longer a household name, there are many places in Melbourne that preserve his legacy due to his generous and wide-ranging contributions to organisations, events and public buildings. In 1934 he was described by the Courier... Gold chocolate. Originally, Freddo Frog was supposed to be a chocolate mouse, but an employee called Harry Melbourne convinced Mac that women and children were afraid of mice, and that the public would be more receptive to a frog. The character ...MacRobertson Steam Confectionery Works was a confectionery company founded in 1880 by Macpherson Robertson and operated by his family in Fitzroy, Melbourne until 1967 when it was sold to Cadbury.
This story accompanies the 'Nail Can to Knighthood: the life of Sir Macpherson Robertson KBE' exhibition which took place at the Royal Historical Society of Victoria in 2015.
-
 Rural City of Wangaratta / State Library Victoria
Rural City of Wangaratta / State Library VictoriaThe Last Stand of the Kelly Gang: Sites in Glenrowan
... During the drawn out siege at Glenrowan a number of journalists, photographers and artists as well as members of the public gathered and watched the drama unfold. These photographs were taken on the day , Monday June 28th 1880. The view from...Ned Kelly, born in June 1855 at Beveridge, north-east of Melbourne, Northern Victoria, came to public attention as a bushranger in the late 1870s. He was hanged at the Melbourne Gaol, November 11th, 1880. Kelly is perhaps Australia’s best known folk ...Ned Kelly, born in June 1855 at Beveridge, north-east of Melbourne, Northern Victoria, came to public attention as a bushranger in the late 1870s.
He was hanged at the Melbourne Gaol, November 11th, 1880. Kelly is perhaps Australia’s best known folk hero, not least of all because of the iconic armour donned by his gang in what became known as the Siege at Glenrowan (or The Last Stand), the event that led to Ned Kelly’s capture and subsequent execution.
The siege at Glenrowan on Monday, June 28th, 1880, was the result of a plan by the Kelly Gang to derail a Police Special Train carrying Indigenous trackers (the Gang's primary targets), into a deep gully adjacent to the railway line. The plan was put into effect on Saturday, June 26 with the murder [near Beechworth] of Aaron Sherritt, a police informant, the idea being to draw the Police Special Train through the township of Glenrowan, an area the local Kellys knew intimately. After the Glenrowan Affair, the Kelly Gang planned to ride on to Benalla, blow up the undermanned police station and rob some banks.
However, Ned miscalculated, thinking the train would come from Benalla not Melbourne. Instead of the 12 hours he thought it would take for a police contingent to be organized and sent on its way from Benalla, the train took 31 hours to reach Glenrowan. This resulted in a protracted and uncertain wait, leading to the long period of containment of more than 60 hostages in the Ann Jones Inn. It also resulted in a seriously sleep deprived Kelly Gang and allowed for the intervention of Thomas Curnow, a hostage who convinced Ned that he needed to take his sick wife home, enabling him to get away and warn the Police Special train of the danger.
Eventually, in the early morning darkness of Monday, June 28th, the Police Special train slowly pulled into Glenrowan Railway Station, and the police contingent on board disembarked. The siege of the Glenrowan Inn began, terminating with its destruction by fire in the mid afternoon, and the deaths of Joe Byrne, Dan Kelly and Steve Hart. Earlier, shortly after daylight on the 29th, Ned was captured about 100 metres north east of the Inn.
Glenrowan is situated on the Hume Freeway, 16 kms south of Wangaratta. The siege precinct and Siege Street have State and National Heritage listing. The town centre, bounded by Church, Gladstone, Byrne and Beaconsfield parade, including the Railway Reserve and Ann Jones’ Inn siege site, have State and National listing.
-
 Hamilton Gallery / Public Galleries Association of Victoria
Hamilton Gallery / Public Galleries Association of VictoriaFrom Watercolours to Decorative Arts
Bequests have been critical to Victoria’s regional galleries, with the wealth generated from farming and the discovery of gold in leading to the establishment and the continuous expansion from colonial times through to today.
Hamilton Art Gallery was established through a bequest from a local grazier, Herbert Buchanan Shaw. The Shaw Bequest consisted of paintings and prints, European silver and glass as well as English, Chinese and Japanese ceramics dating from the 18th century.
Ten years after it was established, Hamilton Art Gallery acquired a group of watercolours by 18th century painter Paul Sandby through a grant from the state government. An upper floor was added to the gallery to accommodate these works.
The collection has continued to grow through gifts, grants and bequests. The original bequest of 870 items has expanded to 8,500 items, making Hamilton Art Gallery one of the largest and most diverse regional gallery collections in Australia, spanning watercolours to decorative arts.
Today, the gallery is divided into six spaces – upstairs you will find the Sandby collection, Asian art, the Print room and Australian art, while on the ground floor you will discover the Shaw Gallery of decorative arts and the Ashworth Gallery for travelling exhibitions.
Featured here is a selection of works from the gallery’s collection – from watercolours by Paul Sandy to world class examples of decorative arts together with work by Australian artists dating from the 19th century to contemporary times. Watch a video to learn about the initial Shaw Bequest and experience the richness and diversity of Hamilton Art Gallery’s collection acquired through the generosity of benefactors and governments over the past fifty years.
-
 State Library Victoria / Public Records Office Victoria
State Library Victoria / Public Records Office VictoriaNed Kelly
Ned Kelly, the most famous of our 'Wild Colonial Boys', was born in 1855.
He was raised in harsh poverty in Northern Victoria, and became an expert bushman; by his teens he had developed a reputation as a bushranger. Kelly and his 'gang' were proclaimed outlaws when they killed three policemen, accounts of which differ.
So began the prolonged hunt, which ended with Kelly's capture in Glenrowan, in iconic home-made armour made from plough parts. Ned Kelly was executed in 1880, hanged in the Melbourne Goal by order of Sir Redmond Barry. Barry was instrumental in the foundation of the State Library of Victoria where, perhaps ironically, Kelly's "manifesto", the Jerilderie letter and the armour are held.
Kelly's Irish heritage, his contempt for and success in humilating the authorities, his harsh and some say unfair treatment, his bad luck and his daring and notoriety have ensured Kelly's place as folk hero.
View videos and other Kelly artefacts from the State Library of Victoria Ergo site:
Capture of the Kelly Gang
Ned Kelly's Armour
The Life of Ellen Kelly, Ned Kelly's mother
The Jerilderie Letter
Ned Kelly's death mask
-

Ballarat Underground
... of the people seeking to commemorate them through research and family history, enabling an ongoing legacy through contributions to the public record. ...The story of Ballarat is tied to the story of mining, with hundreds of thousands of people flocking there in the 1850s to seek their fortune. The few lucky ones became wealthy, but most were faced with the harsh reality of needing a regular income. The Ballarat School of Mines was established in 1870 to train men in all aspects of mining.
When the First World War was declared in 1914, thousands of Ballarat men enlisted. Many of these men were miners who had trained at the Ballarat School of Mines and worked in the town’s mining industries. Their skills were recognised, and tunnelling companies were created to utilise them in strategic and secretive ways. Underground (literally) campaigns were designed where the men tunnelled underneath enemy lines to lay explosives. The intention: to cause significant destruction from below. It was dangerous and cramped work, not for the faint hearted.
One hundred years on, local collecting organisation Victorian Interpretive Projects, in conjunction with Ballarat Ranges Military Museum, is asking local residents and relatives of former Ballarat miners to share their photographs, objects and stories.
This is the story of the miners who left Ballarat to fight in the First World War. It is also the story of the people seeking to commemorate them through research and family history, enabling an ongoing legacy through contributions to the public record.
-
 Belinda Ensor
Belinda EnsorAt the Going Down of the Sun
... One hundred years on, evidence of the impact of the First World War can be plainly seen across Victoria. Built heritage including cenotaphs, statues, plaques and obelisks are peppered across the state’s public spaces, each dedicated ...One hundred years on, evidence of the impact of the First World War can be plainly seen across Victoria.
Built heritage including cenotaphs, statues, plaques and obelisks are peppered across the state’s public spaces, each dedicated to the commemoration of the war service of the thousands of Victorians who served between 1914 and 1918.
Many of these men and women died in active service and were buried overseas, so locally built monuments served as important places to mourn and remember them. They were places for private and collective mourning, commemoration and remembrance.
These memorials were truly local, often built through community fundraising and supported by communities who shared a sense of loss. Most are inscribed with the names of those who died from the region, while others list the names of all those who served.
Across Victoria, cenotaphs and built memorials remain central to ANZAC Day services, but the way we commemorate has changed with each generation and so has the way we remember and mourn the servicemen of the First World War. Photographic and material culture collections from across the state, catalogued here on Victorian Collections, capture some of the tangible and intangible heritage associated with the shifting ways we commemorate the First World War. They provide meaningful insight in to our society and how we make sense of war and loss.
-

Melbourne and Smellbourne
... , but there was still no sewerage system. An appalling stench wafted from the many cesspits and open drains. 'Nightsoil' (as human waste was politely referred to) polluted the streets and ran into the Yarra. Nightsoil collectors frequently dumped their loads on public ...Over the last 150 years Victoria has experienced a number of landmark capital works and landscaping projects in response to its changing economic, environmental and cultural relationship to water. The sewerage system that we take for granted today had to be built from scratch.
For all the grandeur that was 'Marvellous Melbourne' in the 1880s, the city was nicknamed 'Smellbourne', and for good reason. The building of Yan Yean Reservoir in the 1850s had ensured the availability of fresh water, but there was still no sewerage system.
An appalling stench wafted from the many cesspits and open drains. 'Nightsoil' (as human waste was politely referred to) polluted the streets and ran into the Yarra. Nightsoil collectors frequently dumped their loads on public roads. Ignorance and neglect of the hygienic disposal of human waste had devastating results at this time when hundreds died in a savage outbreak of typhoid.
Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works
In 1891 the Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) was created. It immediately began plans to build an underground drainage system linked to a pumping station at Spotswood, located on the western banks of the mouth of the Yarra River. The sewage flowed by gravity to Spotswood, where it was then pumped to the Werribee Treatment Farm.
Spotswood Pumping Station
Spotswood Pumping Station built to pump Melbourne's sewage to Werribee, was finished in 1897. At the pumping station, steam engines (later replaced by electrical ones) worked to pump the sewage up a rising main to join the major sewer outfall at the head of the pumping mains near Millers Road at Brooklyn. The outfall sewer then carried the sewage to the Werribee Treatment Farm where it was purified and discharged into the sea.
Werribee Farm
Werribee was the perfect site for the MMBW's new sewage farm. The farm was the Board's most important project, and one of the largest public works undertaken in Australia in the nineteenth century.
Land at Werribee was cheaper than at Mordialloc - the other site considered. Rainfall was low compared with the rest of Melbourne, which meant the land would adapt well to irrigation. Werribee was also 9 miles (14.4 KM) away from the nearest boundary of the metropolitan district (Williamstown), and 24 miles (38.6 KM) away from the influential and well-to-do suburb of Brighton. The Chirnside family sold 8,857 acres (3.2 hectares) to the Board for 17 pounds per acre.
The Earl of Hopetoun, Governor of Victoria, turned the first sod of earth in a ceremony on May 1892, which marked the beginning of the building of the outfall sewer near Werribee.
Connection!
On 5 February 1898, a ceremony marked the official connection of Melbourne to the new sewerage system. Guests - politicians, board members, city councillors and federal delegates - boarded a steamer to watch the Governor, Lord Brassey, raise the penstock (the partition between the smaller and larger sewers) at the Australian Wharf. They then visited the pumping station at Spotswood and the sewage farm at Werribee. Horses and carts conveyed the 180 guests around the farm.
After lunch and toasts, many of which looked forward to the future of a federated Australia, MMBW Chairman Mr Fitzgibbon proudly declared it "was not a question of how much the scheme was going to cost, but how much it was going to save in the lives of the citizens." Before the work was completed he hoped to see those puny punsters and petty wits who spoke of Melbourne as Marvellous Smellbourne constrained to speak of her as one of the sweetest and healthiest cities of the world.
-

The Palais Theatre
... in 1913, over 800 locals attended a public meeting to protest it being given a license. They voiced fears that it would lower the tone of St Kilda, “have a demoralising effect on young people", and be "common with a big C”. The battle was won ...It’s impossible for Melburnians to think about the St Kilda Esplanade without visualising the Palais Theatre standing majestically against Port Phillip Bay. Its grand Art Deco façade is as iconic to St Kilda as the Pavilion on the nearby pier, Acland Street or the theatre’s "just for fun" neighbour, Luna Park.
It’s surprising to discover, then, that the Palais wasn’t always regarded with such affection. When the original building – a dance hall called the Palais de Danse – was being constructed in 1913, over 800 locals attended a public meeting to protest it being given a license. They voiced fears that it would lower the tone of St Kilda, “have a demoralising effect on young people", and be "common with a big C”. The battle was won by the building owners, the three Phillips brothers (American immigrants who also built Luna Park), and an entertainment venue has stood on the site ever since.
The Palais Theatre is a magical place for Melburnians. It’s where generations of us have danced cheek to cheek, watched movies in the darkness, screamed lustily at the Rolling Stones, thrown roses at the feet of Margot Fonteyn and Rudolph Nureyev, and given standing ovations to Dame Joan Hammond’s awe-inspiring soprano. Your grandparents probably had their first date there. Ask them about the Palais and watch them smile.
The theatre is underwent restoration in 2016-17, which preserved the heritage value of the site and ensured the Palais remains a live performance venue and cultural icon in St Kilda for many generations to come. The restoration was funded by the State Government of Victoria and the City of Port Phillip.
-
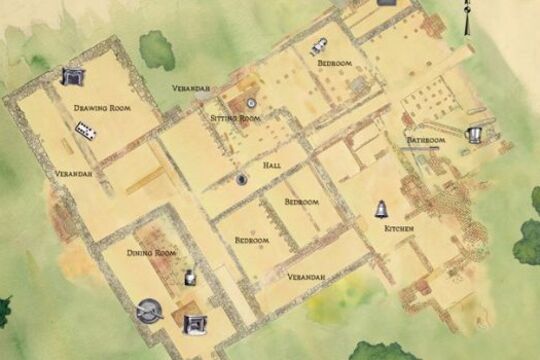
Viewbank: Unearthing a Colonial Homestead
... the area. By then, the house had fallen into disrepair and locals believed that it was haunted. For most of the 20th century, cattle grazed over the ruins and knowledge of the former grand homestead slipped from public knowledge until archaeologists ...Viewbank Homestead was one of the first grand homesteads built on the outskirts of Melbourne. Built around 1840, Viewbank was located near the junction of the Yarra and Plenty Rivers in Heidelberg.
The homestead was built in two phases. Originally a four room house, it was renovated and expanded in the 1850s and 1860s after it was acquired by wealthy squatter Dr Robert Martin.
Viewbank was destroyed by a professional demolition team in the early 1920s, long after the Martin family moved away from the area. By then, the house had fallen into disrepair and locals believed that it was haunted. For most of the 20th century, cattle grazed over the ruins and knowledge of the former grand homestead slipped from public knowledge until archaeologists returned to the site to unlock its secrets.
Between 1996 and 1999, Heritage Victoria conducted three excavations at the site with help from archaeologists from Melbourne, La Trobe and Flinders Universities, and more than 140 archaeology students and community members.
The archaeologists uncovered the stone foundations of the house and remnants of hand-made brick walls, fireplaces and other features. A range of artefacts were found during the excavation including children’s toys, coins, gaming tokens, thimbles and pins. A network of servant’s bells, fragments of marble fireplaces, and pieces of richly decorated plaster cornices reflect the affluence of the Martin family.
This story is made up of audio interviews with an archaeologist, an historian and a conservator. They discuss the Viewbank excavation, describe the artefacts found there and explain the process of their conservation at the Heritage Victoria conservation laboratory.
The Viewbank Homestead is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register. For more information on the Viewbank or other heritage sites visit The Victorian Heritage Database.
-

Rebuilding the school at Villers-Bretonneux, Victoria College
... than the population) for the first dawn Anzac Day service on the Somme. The Villers-Bretonneux School Photograph Collection housed at Public Record Office Victoria is significant because it reflects Victoria's particular connection with Villers ...The Villers-Bretonneux School Photograph Collection features items of various formats that document the role of the Victorian Department of Education and the school children of Victoria in the rebuilding of the school at Villers-Bretonneux, France after its destruction in 1918 during World War I.
Re-named 'Victoria College', the Ecole de Garcons (Boys School) in Villers-Bretonneux was destroyed along with much of the town on the 25 April 1918 when the Australian 13th and 15th Brigades under Brigadier-General Glasgow and Brigadier-General Elliot respectively recaptured it from the Germans in a battle in which over 1,200 Australian soldiers were killed.
The school was rebuilt with donations from Australia. School children and their teachers helped the effort by asking for pennies - in what became known as the Penny Drive - while the Victorian Department of Education contributed 12,000 pounds to the War Relief Fund. The school was appropriately renamed 'Victoria'. The inauguration of the new school occurred on ANZAC Day in 1927. “N’oublions jamais l’Australie“ (Never forget Australia) is inscribed in the school hall. Wood carvings on the pillars in the hall depict Australian flora and fauna.
Almost 180,000 Australian troops served on the Western Front, from Belgium through northern France, during World War 1. Around 52,000 of them died, and around 11,000 were never accounted for; their names are recorded at the memorial at Villers-Bretonneux. In 1975 the Franco-Australian Museum was opened in the Ecole Victoria. Based largely on papers, uniforms and other mementos donated by Australians, the museum is supported by entry fees and a E15 ($27.50) annual subscription paid by 50 locals. In the same year the town hosted close to 5000 visitors (more than the population) for the first dawn Anzac Day service on the Somme.
The Villers-Bretonneux School Photograph Collection housed at Public Record Office Victoria is significant because it reflects Victoria's particular connection with Villers-Bretonneux and evokes the enduring gratitude and friendship between Australia and France.
-
 Elizabeth Downes
Elizabeth DownesTallangatta: The town that moved
... hotels, 4 petrol stations, numerous shops and businesses, 4 churches, more than 900 residents and all the usual public amenities of a country town were relocated 8 kilometres west of the old site. The original location was then flooded under 6 feet ...Every now and then, when the Hume Dam is at a low ebb, the ghostly remains of old Tallangatta, in northern Victoria, can be seen above the water. Now located 39 kilometres east of Wodonga, Tallangatta is known as 'the town that moved'.
In 1956, 2 hotels, 4 petrol stations, numerous shops and businesses, 4 churches, more than 900 residents and all the usual public amenities of a country town were relocated 8 kilometres west of the old site. The original location was then flooded under 6 feet of water after the Hume Dam was expanded.
During 1954 the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission took more than 180 photos in and around the town, documenting houses, businesses and facilities before they were moved. Other images capture the remarkable feat of transporting the buildings to the new site, such as a weatherboard house being carefully towed toward a narrow bridge. Many photos give a vivid picture of the commercial centre of a small country town in the mid-1950s. Advertising signs promote Sennitts Icecream and The Argus newspaper, cluttered shops are packed to the gunnels with equipment and staples for small town life before large chain stores, supermarkets and cars changed country towns forever.
The shops and houses are distributed along straight Towong Street. Cars were scarce and bicycles were an important form of transport in the wide and mostly empty streets. Men and women in the 2 hotels were still segregated in the ladies lounge and main bar; and the hotel’s kitchen equipment was basic. The town offered butchers, barbers, and hairdressers, while the garages, plumbers, and hardware stores served both town and farming needs.
The Tallangatta photographs are part of The Rural Water Corporation Collection of more than 50,000 photographs held at The State Library of Victoria. This collection covers a range of water management projects and activities during the first half of the 20th century.
