Showing 25 items
matching women, themes: 'aboriginal culture','gold rush','local stories','service and sacrifice'
-
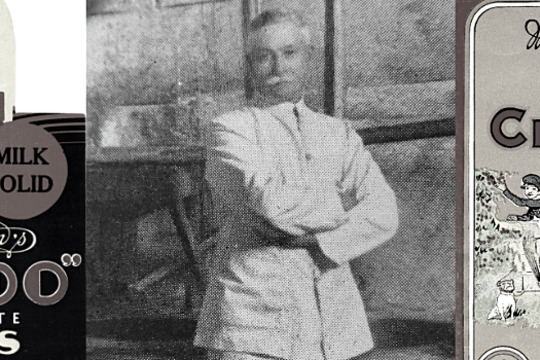 History Teachers' Association of Victoria / Royal Historical Society of Victoria
History Teachers' Association of Victoria / Royal Historical Society of VictoriaMacRobertson's Confectionery Factory
... be attached to any events or building created as a result of his donation, thus ensuring his own place in Melbourne’s social and economic history. In 1934, at a time where investment in women’s education was neither fashionable, nor promised good financial... Gold chocolate. Originally, Freddo Frog was supposed to be a chocolate mouse, but an employee called Harry Melbourne convinced Mac that women and children were afraid of mice, and that the public would be more receptive to a frog. The character ...MacRobertson Steam Confectionery Works was a confectionery company founded in 1880 by Macpherson Robertson and operated by his family in Fitzroy, Melbourne until 1967 when it was sold to Cadbury.
This story accompanies the 'Nail Can to Knighthood: the life of Sir Macpherson Robertson KBE' exhibition which took place at the Royal Historical Society of Victoria in 2015.
-
 Elizabeth Downes
Elizabeth DownesTallangatta: The town that moved
... straight Towong Street. Cars were scarce and bicycles were an important form of transport in the wide and mostly empty streets. Men and women in the 2 hotels were still segregated in the ladies lounge and main bar; and the hotel’s kitchen equipment ...Every now and then, when the Hume Dam is at a low ebb, the ghostly remains of old Tallangatta, in northern Victoria, can be seen above the water. Now located 39 kilometres east of Wodonga, Tallangatta is known as 'the town that moved'.
In 1956, 2 hotels, 4 petrol stations, numerous shops and businesses, 4 churches, more than 900 residents and all the usual public amenities of a country town were relocated 8 kilometres west of the old site. The original location was then flooded under 6 feet of water after the Hume Dam was expanded.
During 1954 the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission took more than 180 photos in and around the town, documenting houses, businesses and facilities before they were moved. Other images capture the remarkable feat of transporting the buildings to the new site, such as a weatherboard house being carefully towed toward a narrow bridge. Many photos give a vivid picture of the commercial centre of a small country town in the mid-1950s. Advertising signs promote Sennitts Icecream and The Argus newspaper, cluttered shops are packed to the gunnels with equipment and staples for small town life before large chain stores, supermarkets and cars changed country towns forever.
The shops and houses are distributed along straight Towong Street. Cars were scarce and bicycles were an important form of transport in the wide and mostly empty streets. Men and women in the 2 hotels were still segregated in the ladies lounge and main bar; and the hotel’s kitchen equipment was basic. The town offered butchers, barbers, and hairdressers, while the garages, plumbers, and hardware stores served both town and farming needs.
The Tallangatta photographs are part of The Rural Water Corporation Collection of more than 50,000 photographs held at The State Library of Victoria. This collection covers a range of water management projects and activities during the first half of the 20th century.
-

Possum Skin Cloaks
... sitePanel 5: Woman's circle and woman's business. These are the old women in ceremony with their message sticks and digging sticks. These pathways represent their journey into their sacred circle, and the woman's business is about connecting to Country.Panel ...CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images and voices of deceased persons, and images of places that could cause sorrow.
Continuing the practice of making and wearing possum skin cloaks has strengthened cultural identity and spiritual healing in Aboriginal communities across Victoria.Embodying 5,000 years of tradition, cultural knowledge and ritual, wearing a possum skin cloak can be an emotional experience. Standing on the barren escarpment of Thunder Point with a Djargurd Wurrong cloak around his shoulders, Elder Ivan Couzens felt an enormous sense of pride in what it means to be Aboriginal.
In this story, eight Victorian Elders are pictured on Country and at home in cloaks that they either made or wore at the 2006 Melbourne Commonwealth Games Opening Ceremony.
In a series of videos, the Elders talk about the significance of the cloaks in their lives, explain the meanings of some of the designs and motifs, and reflect on how the cloaks reinforce cultural identity and empower upcoming generations.
Uncle Ivan’s daughter, Vicki Couzens, worked with Lee Darroch, Treahna Hamm and Maree Clarke on the cloak project for the Games. In the essay, Vicki describes the importance of cloaks for spiritual healing in Aboriginal communities and in ceremony in mainstream society.
Traditionally, cloaks were made in South-eastern Australia (from northern NSW down to Tasmania and across to the southern areas of South Australia and West Australia), where there was a cool climate and abundance of possums. From the 1820s, when Indigenous people started living on missions, they were no longer able to hunt and were given blankets for warmth. The blankets, however, did not provide the same level of waterproof protection as the cloaks.
Due to the fragility of the cloaks, and because Aboriginal people were often buried with them, there are few original cloaks remaining. A Gunditjmara cloak from Lake Condah and a Yorta Yorta cloak from Maiden's Punt, Echuca, are held in Museum Victoria's collection. Reproductions of these cloaks are held at the National Museum of Australia.
A number of international institutions also hold original cloaks, including: the Smithsonian Institute (Washington DC), the Museum of Ethnology (Berlin), the British Museum (London) and the Luigi Pigorini National Museum of Prehistory and Ethnography (Rome).
Cloak-making workshops are held across Victoria, NSW and South Australia to facilitate spiritual healing and the continuation of this traditional practice.
-
 Wind & Sky Productions
Wind & Sky ProductionsMany Roads: Stories of the Chinese on the goldfields
... (possibly only up to 11) were women. Men generally outnumbered women on the Victorian goldfields, but the almost entire absence of Chinese women caused consternation and disapprobation amongst European miners and bureaucrats. However, Chinese society ...In the 1850s tens of thousands of Chinese people flocked to Victoria, joining people from nations around the world who came here chasing the lure of gold.
Fleeing violence, famine and poverty in their homeland Chinese goldseekers sought fortune for their families in the place they called ‘New Gold Mountain’. Chinese gold miners were discriminated against and often shunned by Europeans. Despite this they carved out lives in this strange new land.
The Chinese took many roads to the goldfields. They left markers, gardens, wells and place names, some which still remain in the landscape today. After a punitive tax was laid on ships to Victoria carrying Chinese passengers, ship captains dropped their passengers off in far away ports, leaving Chinese voyagers to walk the long way hundreds of kilometres overland to the goldfields. After 1857 the sea port of Robe in South Australia became the most popular landing point. It’s estimated 17,000 Chinese, mostly men, predominantly from Southern China, walked to Victoria from Robe following over 400kms of tracks.
At the peak migration point of the late 1850s the Chinese made up one in five of the male population in fabled gold mining towns of Victoria such as Ballarat, Bendigo, Castlemaine, Beechworth and Ararat. It was not just miners who took the perilous journey. Doctors, gardeners, artisans and business people voyaged here and contributed to Victoria’s economy, health and cultural life. As the nineteenth century wore on and successful miners and entrepreneurs returned home, the Chinese Victorian population dwindled. However some chose to settle here and Chinese culture, family life, ceremony and work ethic became a distinctive feature of many regional Victorian towns well into the twentieth century.
By the later twentieth century many of the Chinese relics, landscapes and legacy of the goldrush era were hidden or forgotten. Today we are beginning to unearth and celebrate the extent of the Chinese influence in the making of Victoria, which reaches farther back than many have realised.
-

Nyernila - Listen Continuously: Aboriginal Creation Stories of Victoria
... . The learning walk would take us from the very high mountain we lived beside, where the wide rolling water touches the land.When it was time to leave, the women gathered up all their belongings. On their hips and shoulders they carried grass baskets for food ...This story is based on the unique publication Nyernila – Listen Continuously: Aboriginal Creation Stories of Victoria.
The uniqueness is differentiated by two significant and distinguishing features. It is the first contemporary compilation of Victorian Aboriginal Creation Stories told by Victorian Aboriginal People, and it is the first to extensively use languages of origin to tell the stories.
‘Nyernila’ to listen continuously – a Wergaia/Wotjobaluk word recorded in the 20th century. To listen continuously. What is meant by this term. What meaning is being attempted to be communicated by the speaker to the recorder? What is implied in this term? What is the recorder trying to translate and communicate to the reader?
‘Nyernila’ means something along the lines of what is described in Miriam Rose Ungemerrs ‘dadirri’ – deep and respectful listening in quiet contemplation of Country and Old People. This is how our Old People, Elders and the Ancestors teach us and we invite the reader to take this with them as they journey into the spirit of Aboriginal Victoria through the reading of these stories.
Our stories are our Law. They are important learning and teaching for our People. They do not sit in isolation in a single telling. They are accompanied by song, dance and visual communications; in sand drawings, ceremonial objects and body adornment, rituals and performance. Our stories have come from ‘wanggatung waliyt’ – long, long ago – and remain ever-present through into the future.
You can browse the book online by clicking the items below, or you can download a PDF of the publication here.
nyernila
nye
ny like the ‘n’ in new
e like the ‘e’ in bed
rn
a special kind of ‘n’
i
i like the ‘i’ in pig
la
la
-

Seeing the Land from an Aboriginal Canoe
... a scene from station life in New South Wales in 1883. Aboriginal men are ready to guide two European women across the river on a canoe. The associated story acknowledges that the Aboriginal assistance is indispensable: “the ladies wish to cross the river ...This project explores the significant contribution Aboriginal people made in colonial times by guiding people and stock across the river systems of Victoria.
Before European colonisation Aboriginal people managed the place we now know as Victoria for millennia. Waterways were a big part of that management. Rivers and waterholes were part of the spiritual landscape, they were valuable sources of food and resources, and rivers were a useful way to travel. Skills such as swimming, fishing, canoe building and navigation were an important aspect of Aboriginal Victorian life.
European explorers and colonists arrived in Victoria from the 1830s onwards. The newcomers dispossessed the Aboriginal people of their land, moving swiftly to the best sites which tended to be close to water resources. At times it was a violent dispossession. There was resistance. There were massacres. People were forcibly moved from their traditional lands. This is well known. What is less well known is the ways Aboriginal people helped the newcomers understand and survive in their new environment. And Victoria’s river system was a significant part of that new environment.
To understand this world we need to cast ourselves back into the 19th century to a time before bridges and cars, where rivers were central to transport and movement of goods and people. All people who lived in this landscape needed water, but water was also dangerous. Rivers flooded. You could drown in them. And in that early period many Europeans did not know how to swim. So there was a real dilemma for the newcomers settling in Victoria – how to safely cross the rivers and use the rivers to transport stock and goods.
The newcomers benefited greatly from Aboriginal navigational skills and the Aboriginal bark canoe.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images of deceased persons and images of places that could cause sorrow.
-

Collingwood Technical School
... , tanneries, breweries, flour mills, and soap and candle works. It was a source of cheap labour [including] unskilled workers, unemployed craftsmen and increasing numbers of adolescents and women. The Collingwood Council encouraged the establishment ...For over 140 years, the site of the former Collingwood Technical School on Johnston Street, Melbourne, has played an integral role in the well being of the local community.
It has been a civic hub, including courthouse (1853), Council Chambers (1860) and the Collingwood Artisans’ School of Design (1871). The school opened in 1912 when its first principal, Matthew Richmond, rang a bell on the street to attract new students. Collingwood was a poor and industrial suburb, and as a trade school, young boys were offered the opportunity to gain industrial employment skills.
Throughout the twentieth century, Collingwood Technical School supported the local and broader community. From training schemes for ex-servicemen who were suffering from post traumatic stress following World War I (1914-1918), to extra classes during the Great Depression, and the development of chrome and electroplating for machine parts for the Australian Army and Air Force during World War II (1939-1945).
The precinct between Johnston, Perry and Wellington Streets has transformed over time, including expansion with new buildings and school departments, and the change in the demographic of students as Collingwood evolved from an industrial centre to eventual gentrification. And in 1984, New York street artist, Keith Haring (1958-1990), painted a large mural onsite.
Collingwood Technical College closed in 1987 when it amalgamated with the Preston TAFE (Technical and Further Education) campus. Education classes continued until 2005 and the site sat empty for more than a decade, before a section was redeveloped for Circus Oz in 2013.
The former school now has a new identity as Collingwood Arts Precinct, and is being developed into an independent space for small and medium creative organisations. The heritage buildings will house the next generation of thinkers and makers, and will become a permanent home to the arts in Collingwood. -
 Koorie Heritage Trust / NGV Australia / State Library Victoria
Koorie Heritage Trust / NGV Australia / State Library VictoriaKoorie Art and Artefacts
... Tribe: two sculptures with thirty eight pieces in each representing the men and the women of the thirty eight plus tribes of Victoria. Lee Darroch, Yorta Yorta/Mutti Mutti/Boonwurrung ...Koorie makers of art and artefacts draw upon rich and ancient cultural traditions. There are 38 Aboriginal Language Groups in Victoria, each with unique traditions and stories. These unique traditions include the use of geometric line or free flowing curving lines in designs.
This selection of artworks and objects has been chosen from artworks made across the range of pre-contact, mission era and contemporary times and reflects the richness and diverse voices of Koorie Communities. It showcases prehistoric stone tools, works by 19th century artists William Barak and Tommy McRae right through to artworks made in the last few years by leading and emerging Aboriginal artists in Victoria.
The majority of the items here have been selected from the extensive and significant collections at the Koorie Heritage Trust in Melbourne. The Trust’s collections are unique as they concentrate solely on the Aboriginal culture of south-eastern Australia (primarily Victoria). Over 100,000 items are held in trust for current and future generations of Koorie people and provide a tangible link, connecting Community to the past.
Within the vibrant Koorie Community, artists choose their own ways of expressing identity, cultural knowledge and inspiration. In a number of short films Uncle Wally Cooper, Aunty Linda Turner and Aunty Connie Hart practice a range of traditional techniques and skills. These short documentaries show the strength of Koorie culture today and the connection with past traditions experienced by contemporary Koorie artists.
Taungurung artist Mick Harding draws upon knowledge from his Country about deberer, the bogong moth: "The long zigzag lines represent the wind currents that deberer fly on and the gentle wavy lines inside deberer demonstrate their ability to use those winds to fly hundreds of kilometres to our country every year."
Koorie artists today also draw inspiration from the complex and changing society we are all part of. Commenting on his artwork End of Innocence, Wiradjuri/Ngarigo artist Peter Waples-Crowe explains: "I went on a trip to Asia early in the year and as I wandered around Thailand and Hong Kong I started to think about Aboriginality in a global perspective. This series of works are a response to feeling overwhelmed by globalisation, consumerism and celebrity."
Koorie culture is strong, alive and continues to grow.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images and voices of deceased persons, and images of places that could cause sorrow.
-

A Sensory Experience
... of young hearing people. On the edge of reaching out into the world, young men and women talk about the much the same things. And often there was a lot to laugh about. And with these deaf people I had met, that was an astonishing difference. It was quite ...The mainstream understanding of deaf and blind people has shifted over time. When once it was thought that blind people should be taken care of and sheltered, or deaf people taught to hear and speak, a deeper awareness of distinct culture and experience has emerged.
'A Sensory Experience' explores the world through the eyes and ears of the deaf and blind communities in Victoria and seeks to demystify some of the stereotypes and preconceptions that survive to this day.
The four films that make up part of this story highlight Victoria’s Deaf and blind communities within an historical framework, fostering new insights and provoking thought about the way we understand these communities today. Each film is an open invitation to share the experience of the world from another perspective.
The accompanying images complement the films, giving further understanding to the rich history held within the two groups. In addition, two contemporary essays by prominent writers offer the unique opportunity to share their lived experiences. Finally, the story contains an education kit for secondary students, which allows for a deeper study and understanding.
