Showing 110 items
matching themes: 'built environment','family histories','gold rush','immigrants and emigrants','kelly country','land and ecology'
-

Hubcaps to Creative Hubs
The project aims to tell the stories of Geelong’s industrial sites undergoing transformation, pointing to a new creative and maker culture that connects the past with the present.
The Returned Soldier & Sailors Woollen and Worsted Mills in Rutland Street Newtown, the Federal Woollen Mills in North Geelong and the Old Paper Mills in Fyansford are all in the process of becoming new creative spaces.
Part One explores how a once-overlooked industrial site the Returned Soldiers and Serviceman’s Mills (RS&S) has become the hub for a remarkable network of artists and creative makers...and if you listen closely, you might hear sounds of the past reverberating in the building’s walls.
Part Two tells the story of the recent reinvention of the Federal Woollen Mills into a tech and creative start-up hub which marks Geelong’s 21st century pivot from industrial decline to rising creative city.
Part Three explores the Fyansford Paper Mills’ salvage and restoration, a remarkable process of “creative conservation”, working with the buildings’ industrial patina and fine-grained details. The mill now hosts a creative community that draws uniquely from the large spaces and mazy corners, with secrets waiting to be unearthed.
Watch the trailer for a quick taste of the project or enjoy the full three part documentary to learn about the transformation of these places. You can also read about how these films were supported by community grants and the people and businesses of Geelong.
‘Hubcaps to Creative Hubs’ is a creative research project by Dr Fiona Gray from Deakin University, Dr Cristina Garduño Freeman from the Australian Centre for Architectural History and Cultural Heritage at the University of Melbourne, in collaboration with industry partners Jennifer Cromarty and Helen Kostiuk of Creative Geelong Inc. The films have been made by documentary producer Nicholas Searle.
-
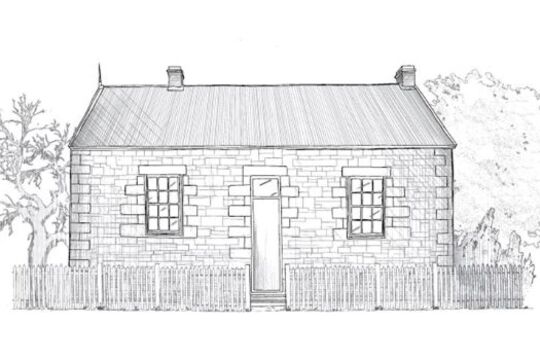
What House Is That?
More than just bricks and mortar, our homes are prisms, reflecting the society of the time they were built. Through them, we can understand the changing context of social, economic and architectural history, and the values and assumptions of the people who built and lived in them.
What house is that? is an exploration of the social and architectural history of Victoria’s housing styles. From our earliest Victorian cottages through to the light filled, open plan houses of the Modern era, we look at the houses Victorians call home.
The nine images and text give an overview of each of the main housing styles of Victoria’s history from the 1840s onwards. The 15 videos feature interviews with architects, historians and residents and explore the styles in more detail. This collection of images, text and videos comes from an interactive website created by Heritage Victoria.
-

Melbourne's Homes
These house plans from the late 19th and early 20th Centuries, give us an indication of how those with the means to build larger houses lived.
Servant's quarters, groom's rooms, sculleries, stables, parlours and children's areas give us clues to social attitudes, relationships to children and employees, social mores and living conditions.
-

Ash Wednesday 30
On 16 February 1983 the Ash Wednesday bushfires burned approximately 210,000 hectares of land, 2,080 homes were destroyed and 75 people, including 47 Victorians, lost their lives.
Among the 47 Victorians killed were volunteer Country Fire Authority (CFA) firefighters from Panton Hill, Nar Nar Goon, Narre Warren and Wallacedale brigades.
Many businesses, stores, equipment, machinery, stock and other assets were lost. The total cost of the property damage in Victoria was estimated to be over $200 million.
These web pages were created to commemorate the 30th anniversary of the Ash Wednesday Bushfires in 2013.
The Victorian Government invited people to share their stories of recovery, healing and hope as a tribute to those who experienced a natural disaster, and as an inspiration to all Victorians.
A collection of selected stories and short films have now been published here.
-

Eureka Stories
What is Eureka and what happened there?
In the early hours of 3 December 1854 a force of police and other troops charged a reinforced camp constructed by miners on the Eureka gold diggings. About 150 diggers were inside the stockade at the time of the attack. In the fighting, 4 soldiers and about 30 other people were killed, and another 120 people taken prisoner. Thirteen people from the stockade were charged with treason – these men were either tried and found not guilty, or charges against them were dropped.
Many people think of the Eureka Stockade as a battle between the diggers (rebellious Irish fighting for democracy) and the police and colonial militia (the forces of the British Crown in the Colony). It’s nice to have a single story to make sense of everything. Eureka, however, is not a single simple narrative. Several stories intertwine and involve many of the same people and places. Let’s look at some of them.
The Hated Gold Licences
In 1854, people mining for gold around Victoria had to pay a monthly fee of 30 shillings for the right to mine, regardless of how much gold they found. Someone who had been looking for gold unsuccessfully for months still had to pay the same fee as someone who was pulling out gold by the pound. Diggers argued that it was an unfair tax, imposed on them without their consent, as they did not have the right to vote. (After the Goldfields Royal Commission the licensing fee was changed to a tax on gold when it was being exported.)
Not only did the diggers resent the licence fee, they were angry at the way the goldfields police went about checking that miners had licences. Diggers claimed that police were beating people up or chaining them to trees if they could not produce a licence, and undertaking unnecessary inspections on people they didn’t like. Resentment of the licence fee and the conduct of police in their “licence hunts” was expressed across the Victorian goldfields.
The Unfair Treatment of Diggers by the Police and Justice System
People around the Victorian goldfields were also unhappy with the lack of thoroughness with which police had investigated a number of goldfields crimes. They were concerned about what they thought was the unfair and secretive way people were charged and convicted of crimes. There were claims by people living on the goldfields that it was necessary to bribe police and government officials in order to do business and stay safe. As the goldfields populations increased, tensions between the goldfields communities and police and other government officials rose.
In Ballarat a series of events (a murder, an arrest and a hotel burning) in late 1854 involving police and Ballarat locals led to the arrests of three men for burning down the Eureka Hotel. These arrests caused enormous disquiet in the area, adding weight to calls by the Ballarat Reform League and other organisations around the goldfields for a fundamental change to the system of government in the Colony – the next element in our Eureka story.
Demands for a Democratic Political System
Since the early 1850s people had been calling for the government to abandon the gold licensing system, remove the gold commissioners, and provide the Colony with a better policing and justice system. Despite an investigation by the Victorian parliament into the goldfields in 1853 (a Legislative Council Select Committee) the government did not make significant changes. By November 1854 an organisation called the Ballarat Reform League had formed in response to official inaction and had written a Charter of democratic rights. They organised a "monster meeting" in Ballarat on 11 November 1854, to have it accepted, and met with Governor Hotham on 27 November 1854, to demand his acceptance of the Charter, and the release of the three prisoners charged with burning down the Eureka Hotel.
Population Explosion
The people calling for these changes to taxes, justice and political participation came from many different parts of the world, such as the United States, Canada, England, Ireland, Scotland, Italy, Germany. This corner of South-Eastern Australia was rapidly changing as thousands and thousands of people arrived to search for gold. Many of these people were educated and from middle-class or merchant backgrounds. The domination of squatters running sheep on large land holdings was being challenged by dense populations of people in goldrush regions generating enormous wealth in the colony, and a desire from these recent arrivals to take up land, and have a say in the making of laws.
We have looked at some parts of the Eureka story; at what unfolded around the colony as a result of this mix of people, events and system of government. There are many other stories about Eureka. To find out more, you can explore the stories through original documents at Eureka on Trial.
-
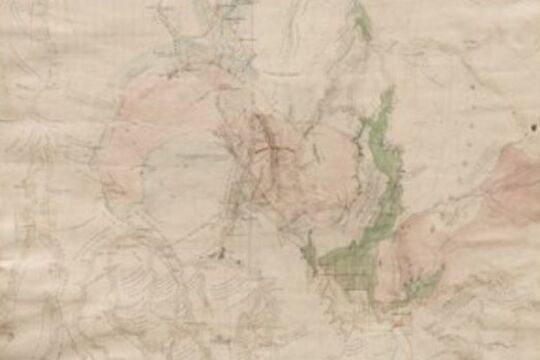
Mapping Great Change
This series of films and stories is centred on a beautiful and complex map with the ungainly name: Plan of the General Survey from the Town of Malmsbury to the Porcupine Inn, from the sources of Forest Creek to Golden Point, shewing the Alexandrian Range, also Sawpit Gully, Bendigo and Bullock Creeks.
In many ways, the map is a mirror of our times: the map is a record of the 'critical years' between 1835 and 1852 in which the dispossession of Aboriginal people of Victoria was allowed to occur; we contemporary people are in the "critical decade" for making the changes necessary to avoid catastrophic climate change.
If we fail to act effectively in this decade, it will be as loaded with moral and practical consequences for coming generations as the moral and policy failures of our colonial ancestors was for the Traditional Owners of the land.
-

Nyabana Riek
Nyabana Riek left Nasir, southern Sudan, to escape civil war when she was only 9 years old.
With her older sister Mary, she travelled to a refugee camp in Itang, Ethiopia in 1986. But after years in various camps, the sisters made a dangerous trek at night across the mountains between Ethiopia and Kenya. The 12-hour journey was steep, sharp rocks tore their shoes and soldiers patrolled both sides of the border. They managed to cross the border into Kenya and then spent 3 years in a Kenyan refugee camp.
Finally, in 1995, Nyabana reached Australia. When she arrived, Melbourne's Sudanese community was small; she was the first teenager from the Nuer language group and spoke little English. But things are different now - more family members have come to Melbourne, Nyabana completed a Bachelor of Business Management, and the Sudanese community and support networks are growing.
-
 Carissa Goudey
Carissa GoudeyMaking & Using Transport on the Goldfields
During the nineteenth century, horse-drawn vehicles were an essential part of life in rural Victoria.
In Ballarat, local coachbuilding firms assisted with the town’s growth in more ways than providing passage to the diggings. Horse-drawn vehicles were vital for the delivery of goods, responding to emergencies and often symbolised one’s social standing.
The Gold Rush ushered in a period of incredible growth for colonial Victoria. Ballarat’s escalating population and burgeoning industries highlighted the need for horse-drawn transport – not only for getting to the diggings, but also for delivering goods and building material, responding to emergencies and performing significant social rituals.
In the early nineteenth century, the goldfields were dominated by vehicles either imported from England or English-style vehicles built locally. Coaches, carriages and carts were typically constructed part-by-part, one at a time. As a result, each vehicle was highly unique.
By the mid-1850s, the American coachbuilding tradition had arrived on the goldfields. The American method, which had been developing since the 1840s, relied on mass-produced, ready-made components. In comparison to English designs, American coaches were known to be more reliable for goldfields travel; they were primed for long-distance journeys on rough terrain and were less likely to tip over.
As the nineteenth century progressed, a plethora of English, American and European vehicles populated Ballarat – both locally made and imported. The abundance of coaches, carriages and carts – and their value to the Ballarat community – can be seen in photographs and objects catalogued here on Victorian Collections.
-

1956 Flood
In 1956, a monster flood overwhelmed the banks of the Murray and Darling Rivers, producing floodwaters in surrounding towns and rural areas that reached over 30 feet above normal levels.
The Murray Darling Environmental Foundation's 1956 Flood video features historical footage - including photographs and wonderful super8 film from personal collections - that document the rise and flow of the waters, and the monumental effort mobilised to tackle them.
It is presented here in 3 extracts.
The full video is over 25 minutes long, and copies can be obtained from:
Emma Bradbury, Murray Darling Association, Post Office Box 1268, Echuca 3564
Email: [email protected]
-
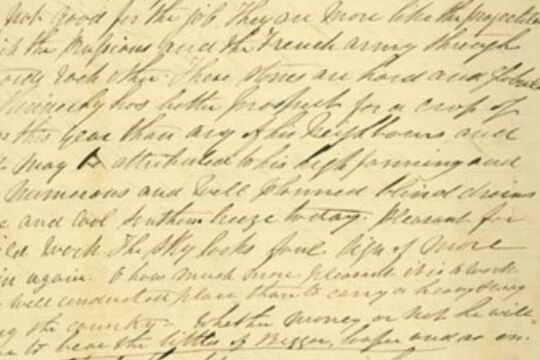
The Welsh Swagman
Joseph Jenkins was a Welsh itinerant labourer in late 1800s Victoria.
Exceptional for a labourer at the time, Jenkins had a high level of literacy and kept detailed daily diaries for over 25 years, resulting in one of the most comprehensive accounts of early Victorian working life.
Itinerant labourers of the 1800s, or 'swagmen', have become mythologised in Australian cultural memory, and so these diaries provide a wonderful source of information about the life of a 'swagman'. They also provide a record of the properties and districts Jenkins travelled to, particularly around the Castlemaine and Maldon area.
The diaries were only discovered 70 years after Jenkins' death, in an attic, and were in the possession of Jenkins’s descendants in Wales until recently, when they were acquired by the State Library of Victoria in 1997.
-
 Lauren McAlary
Lauren McAlaryCollecting Fire: A new kind of practice
The fires of February 2009 left an indelible mark on the histories of Victoria’s community collecting organisations; whether through blackened ash markings or by the absence of once cherished objects and ephemera.
This exploration of Victoria’s collecting response to the Black Saturday bushfires is inspired by Liza Dale‐Hallett, Rebecca Carland and Peg Fraser’s reflections on the Victorian Bushfires Collection project, in 'Sites of Trauma: Contemporary Collecting and Natural Disaster'.
-
 Paige Gleeson
Paige GleesonMaking Do on ‘the Susso’: The material culture of the Great Depression
There are currently 5.25 trillion pieces of plastic in our oceans. The demands on renewable sources like timber, clean water and soil are so great they are now being used at almost twice the rate that the earth can replenish them. Finite resources like fossil fuel are consumed at an alarming rate, changing the earth’s climate and pushing animal species to the brink of extinction. Current patterns of consumption are exceeding the capacity of the earth’s ability to provide into the future.
All over the world, environmental movements concerned with sustainability have sprung up in response. Conscious consumers are advocating for their right to repair their own electronic devices, fighting a culture of planned obsolesce and disposability. Others are championing the repair, reuse and recycling of clothing and household goods to extend their lives. Reducing waste in the kitchen and promoting food options with lower environmental impact has become increasingly popular.
Climate change may be a uniquely twenty-first century challenge, but sustainability has a history. In 2021 many people are making a conscious choice to embrace anti-consumerism, but during the Great Depression of the 1930s it was necessity that drove a philosophy of mend and make do.
In 1929 stock markets crashed and sent economies around the western world into free fall, triggering the Great Depression. Australia’s economic dependence on wool and wheat exports meant that it was one of the worst affected countries in the world. The impact of the Depression on the everyday lives of Australians was immense. Not everyone was effected with the same severity, but few escaped the poverty and austerity of the years 1929-1933 unscathed.At the height of the Depression in 1932 Australia had an unemployment rate of 29%, and thousands of desperate people around the country queued for the dole. Aboriginal Australians were not eligible for the dole, and had to rely solely on government issued rations.
-

Early Photographs - Gold
These images are part of the first photographic series of Australian scenes presented for sale to the public. Produced by the studio of Antoine Fauchery and Richard Daintree in 1858, these photograph are from a series of 53 collectively known as the Fauchery-Daintree Album.
Using the latest collodion wet-plate process, Fauchery and Daintree produced their collection of albumen silver prints at a time when the sales of photographs were flourishing.
Antoine Fauchery and Richard Daintree produced iconic images of both early gold diggers and the landscapes scarred by the exploding search for gold, which attracted miners from all over the world and created the boom that made Melbourne the fastest growing metropolis of the time.
Antoine Fauchery and Richard Daintree were both migrants who tried their luck on the goldfields – Daintree coming out from England in 1853, Fauchery from France in 1852.
Unsuccessful on the goldfields, in 1857 they combined forces to produce a series of photographs titled Sun Pictures of Victoria, capturing important early images of the goldfields, Melbourne Streets, landscapes and portraits of Indigenous Victorians. Using the new collodion wet-plate process, they created albumen silver prints of a rare quality for the time.
Further information on Antoine Fauchery's time in Melbourne can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site.
-
 Elizabeth Downes
Elizabeth DownesThe Unsuspected Slums
Campaigner Frederick Oswald Barnett recorded the poverty facing many in the Melbourne slums of the 1930s.
“All the houses face back-yards…The woman living in the first house…was so desperately poor that she resolved to save the maternity bonus, and so, with her last baby had neither anaesthetic nor doctor.”
So observed campaigner Frederick Oswald Barnett of the poverty facing many in the Melbourne slums of the 1930s. After touring these slums with Barnett, it’s said the Victorian Premier, Albert Dunstan, couldn’t sleep for days.
In 1936 Dunstan established the Slum Abolition Board, and Barnett became vice-chairman of the newly established Housing Commission of Victoria in 1938.
A Methodist and accountant, Barnett became determined to improve the situation for the poor, sick, elderly and unemployed after encountering a slum in the 1920s. He was an astute crusader who coordinated letter writing campaigns and lectured throughout Victoria using many of his own poignant and arresting photographs of the cramped and unsanitary housing conditions.
-

Nyernila - Listen Continuously: Aboriginal Creation Stories of Victoria
This story is based on the unique publication Nyernila – Listen Continuously: Aboriginal Creation Stories of Victoria.
The uniqueness is differentiated by two significant and distinguishing features. It is the first contemporary compilation of Victorian Aboriginal Creation Stories told by Victorian Aboriginal People, and it is the first to extensively use languages of origin to tell the stories.
‘Nyernila’ to listen continuously – a Wergaia/Wotjobaluk word recorded in the 20th century. To listen continuously. What is meant by this term. What meaning is being attempted to be communicated by the speaker to the recorder? What is implied in this term? What is the recorder trying to translate and communicate to the reader?
‘Nyernila’ means something along the lines of what is described in Miriam Rose Ungemerrs ‘dadirri’ – deep and respectful listening in quiet contemplation of Country and Old People. This is how our Old People, Elders and the Ancestors teach us and we invite the reader to take this with them as they journey into the spirit of Aboriginal Victoria through the reading of these stories.
Our stories are our Law. They are important learning and teaching for our People. They do not sit in isolation in a single telling. They are accompanied by song, dance and visual communications; in sand drawings, ceremonial objects and body adornment, rituals and performance. Our stories have come from ‘wanggatung waliyt’ – long, long ago – and remain ever-present through into the future.
You can browse the book online by clicking the items below, or you can download a PDF of the publication here.
nyernila
nye
ny like the ‘n’ in new
e like the ‘e’ in bed
rn
a special kind of ‘n’
i
i like the ‘i’ in pig
la
la
-

Drought Stories
“The social impact it has is huge, but the footy club survives," says Charlie Gillingham, mixed farmer from Murrabit.
In this story the community talks about drought: its social impact, resilience, changes to farming practises, changing weather patterns and water trading.
The median annual rainfall of the Wimmera and northern plains of Victoria is 420mm. But this median does not convey the deluges that sometimes double the figure, or the dry spells that can halve it. Like semi-arid places elsewhere, the climate cycle of this region is variable.
Aboriginal people have had thousands of years to adapt to the fluctuations, whilst recent settlers are still learning.
The introduction of the Land Act of 1869 accompanied by the high rainfall La Niña years of the early 1870s brought selectors to northern Victoria and the Wimmera. A series of dry years in the 1880s initiated storage and channel projects to assist them to stay.
Irrigation was introduced in 1886 to settle the northern plains and was expanded under closer settlement legislation. The drought years from 1895 to 1902 came to be known as the Federation Drought. Water supplies dried up completely in the El Niño years of 1914 and 1915 and people took the opportunity to picnic in the empty bed of the River Murray.
Drought hit again during World War Two, and then in the period 1965-8. The drought of 1982-3 was short but devastating. Our most recent drought, lasting more than a decade, broke late in 2010 with extensive flooding.
Policy responses have changed over the years and with the recent onset of human induced climate change, continual adaptation will be required.
In 2009, the History Council of Victoria captured resident’s experiences in the project titled Drought Stories: a spoken and visual history of the current drought in Victoria. There were two aims to the project: to create a historic record of the experience, and to strengthen community capacity in rural and regional areas through telling and listening to local stories.
Two types of collections were produced: Drought Stories Local Collections, held by historical societies, and the Drought Stories Central Archive, a selection of interviews held by the State Library of Victoria.
The History Council of Victoria believes that the project material provides a rich resource to assist researchers understand Australian society at a crucial and revealing stage of adjustment to the Australian environment.
Legislation and other land records are held at the Public Record Office Victoria.
